Dendritic Guanidines as Efficient Analogues of Cell Penetrating Peptides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Tat49-57 | RKKRRQRRR |
| Polyarginine | RRRRRRRRR |
| Decalysine | KKKKKKKKKK |
| Penetratin | RQIKIWFQNRRMKWKK |
| Transportan | GWTLNSAGYLLGKINLKALAALAKKIL |
| MPG | GALFLGFLGAAGSTMGAWSQPKKKRKV |
| Pep1 | KETWWETWWTEWSQPKKKRKV |
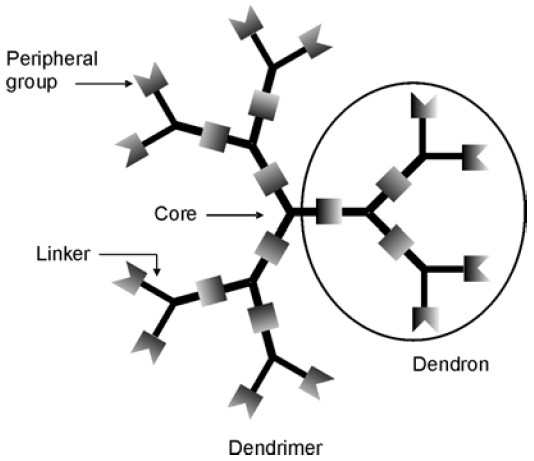
2. Dendrimers as Cell-Penetrating Agents
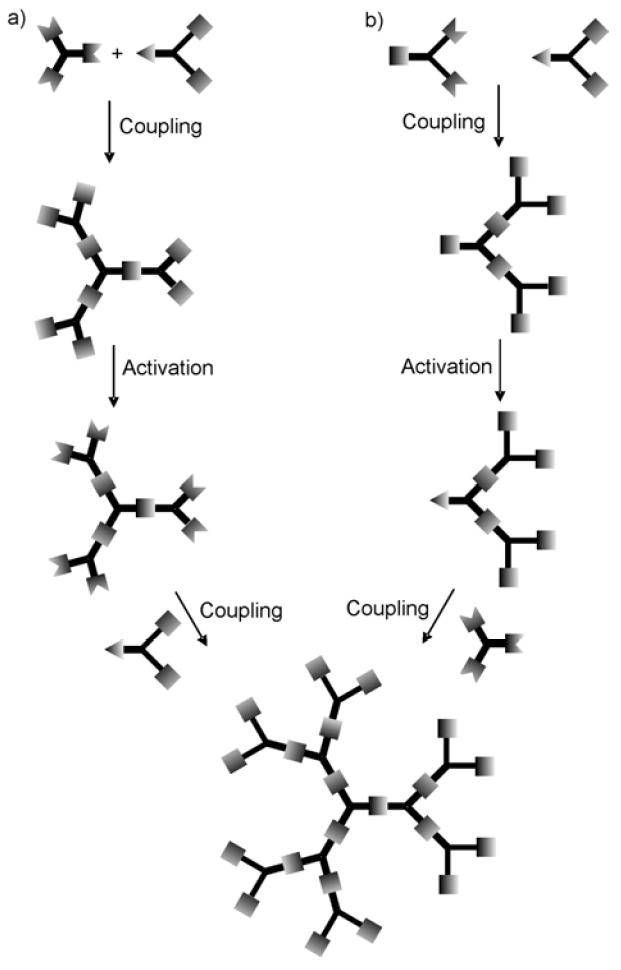
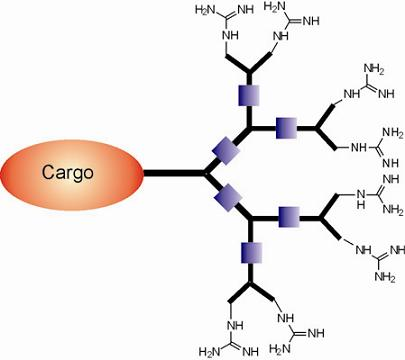
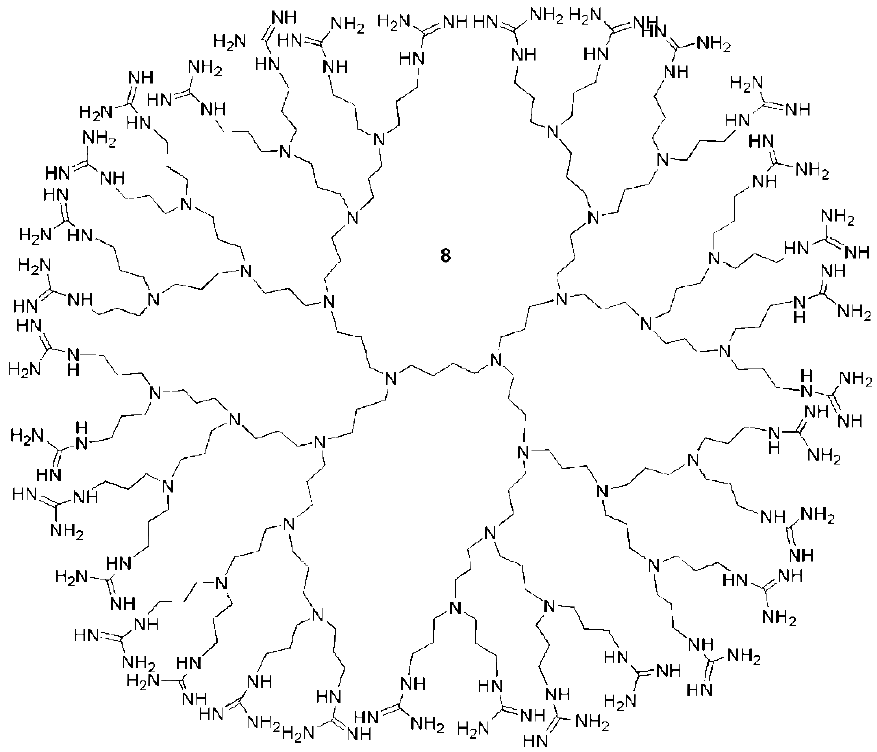
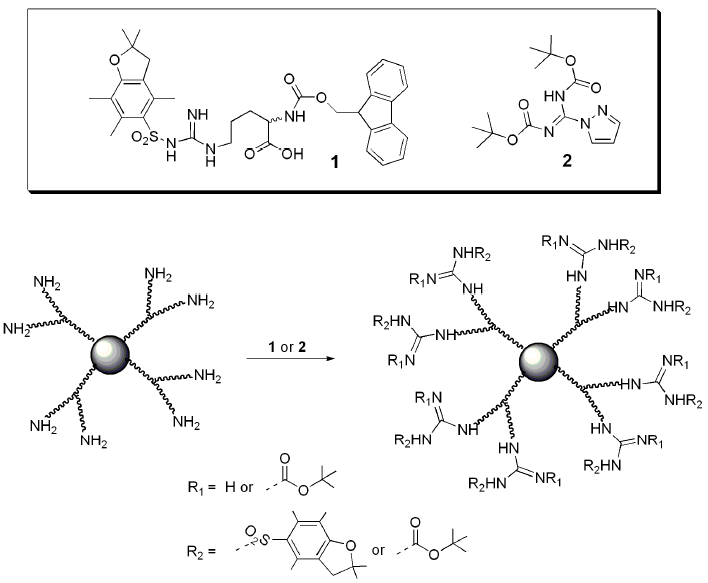
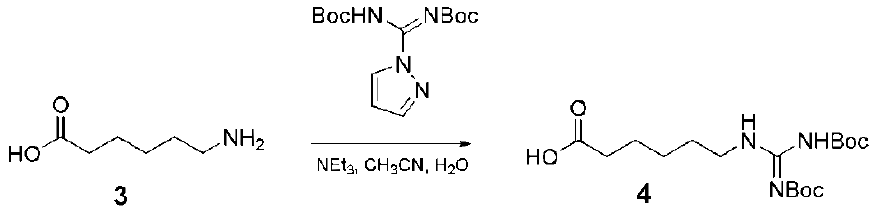
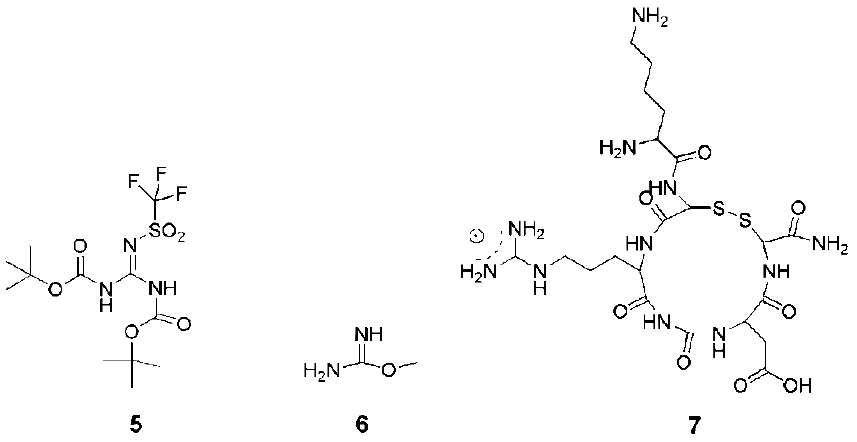
3. Syntheses of Guanidine Functionalized Dendrimers
4. Structures and Cellular Internalization of Guanidine Functionalized Dendrimers
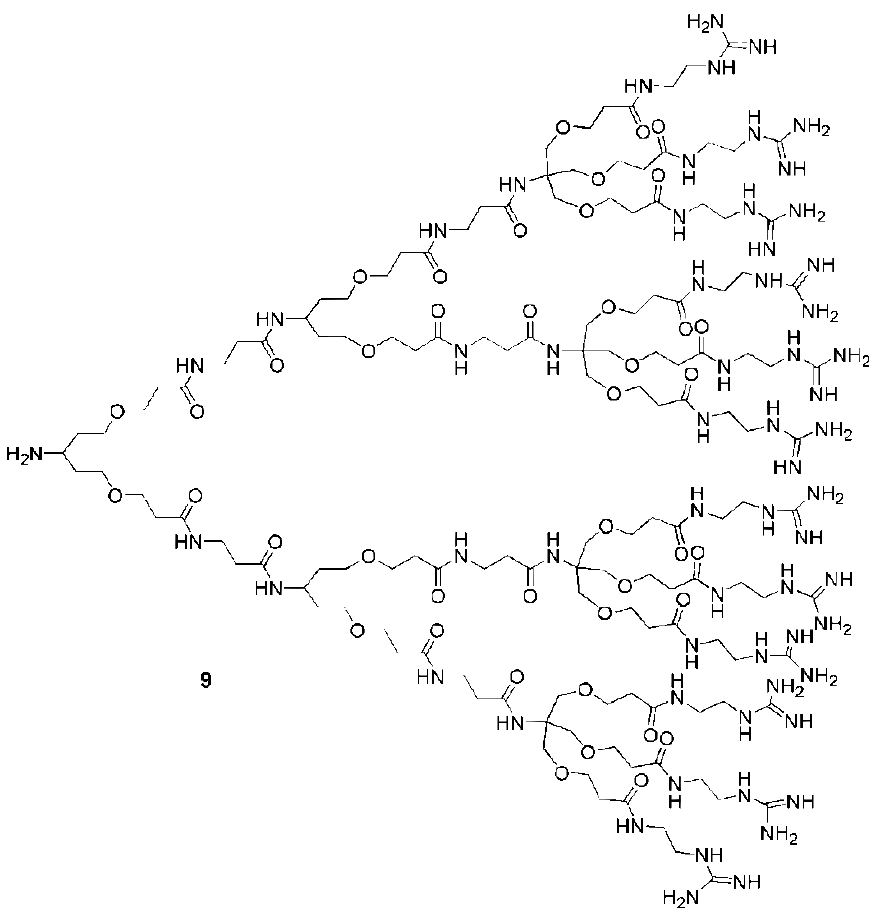
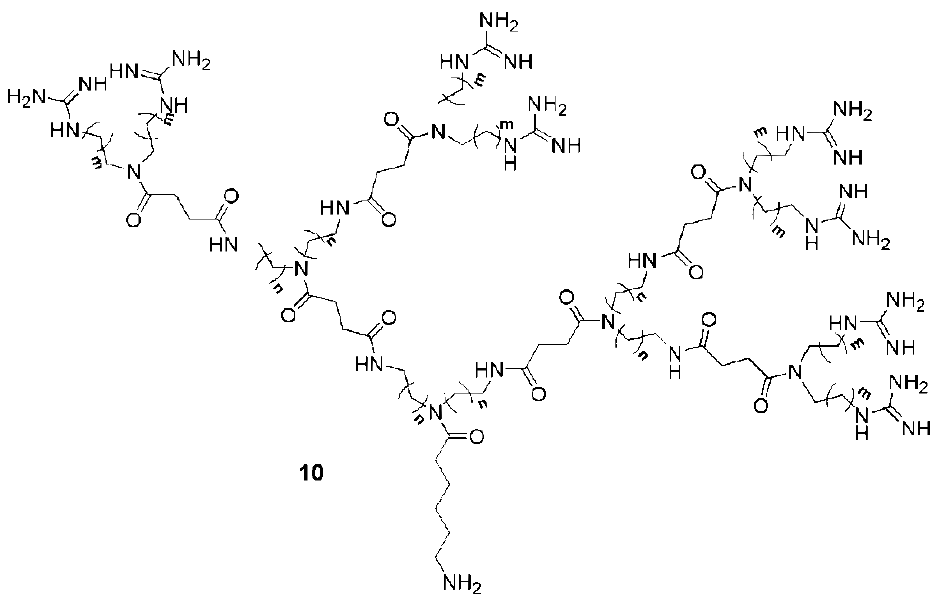
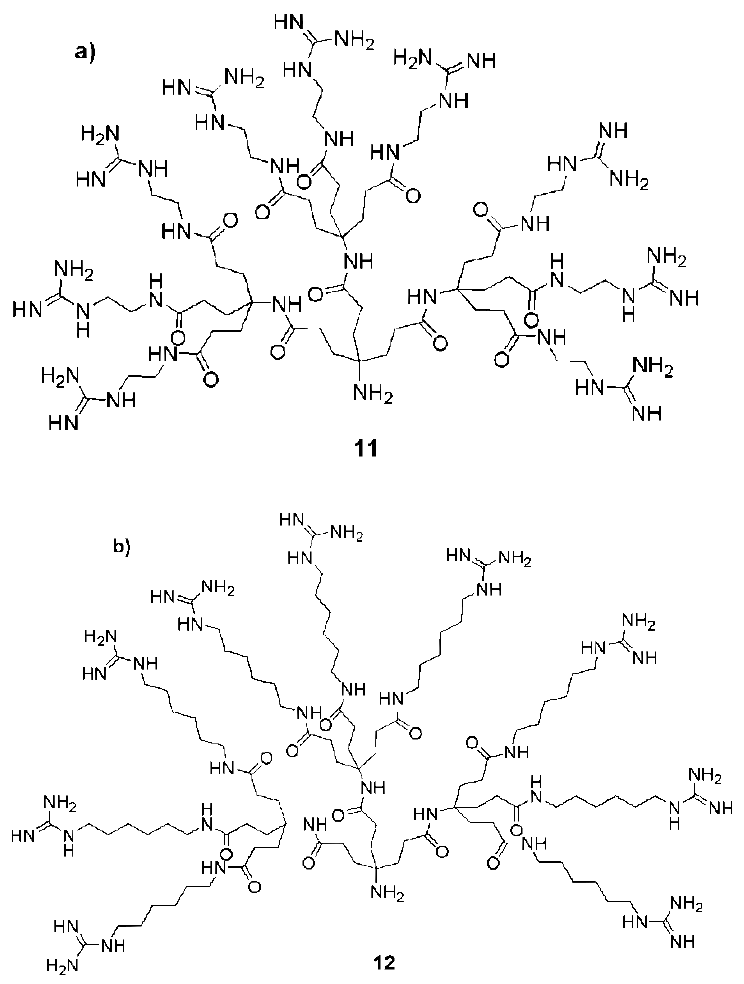
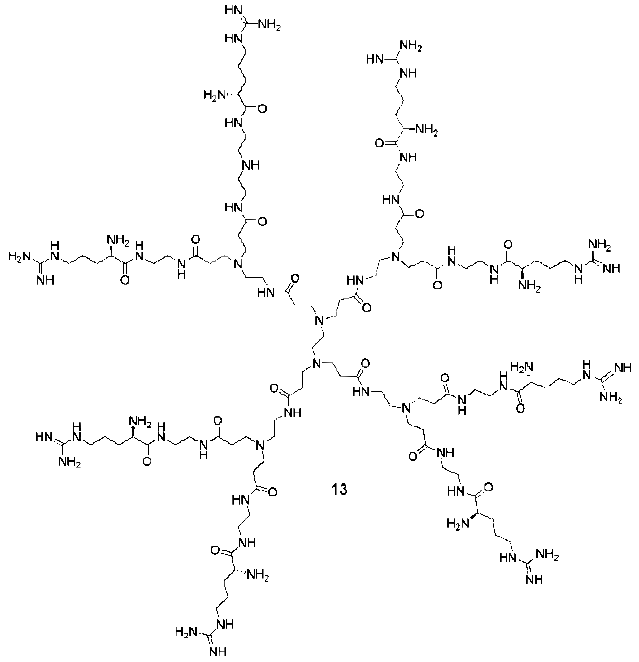
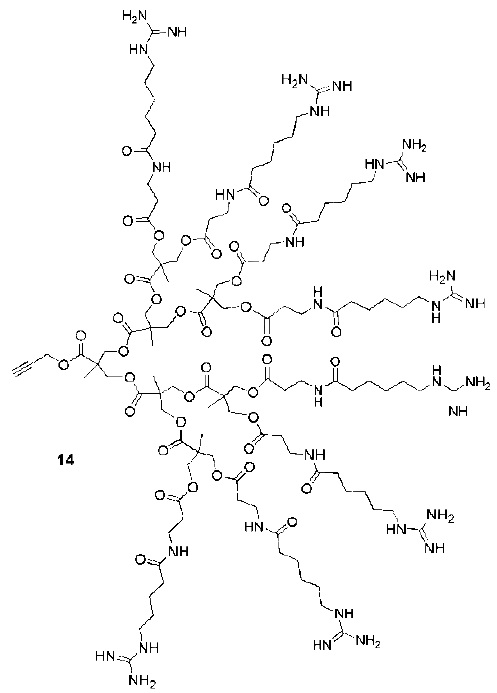
| Backbone | Guanidines | Cargo | Cell-line | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(propylene imine) | 0,6,12 | Betamethasone derivatives | Liposomes | [89] |
| Poly(propylene imine) | 4,8 | - | Liposomes | [90] |
| Poly(propylene imine) | 8,14 | FITC | Human lung carcinoma (A549) | [87] |
| Poly(propylene imine) | 16,32 | - | Liposomes | |
| Poly(propylene imine) | 0-32 | DNA | HEK293, COSY7 | [88] |
| Poly(propylene imine) | 8 | DNA | HeLa, 293 cells | [85] |
| Polyamide | 3,6,9,12 | GFP, FITC | HeLa S3 and Human cervical carcinoma | [26] |
| Polyamide | 9 | FITC | NIH-3T3 fibroblasts and HMEC | [95] |
| Polyamide | 9 | IgG-Antibodies | Hep-2 (RSV-GFP) | [97] |
| Polyamide | 9 | Polymer nanoparticles | NIH-3T3 fibroblasts | [96] |
| Polyamide (dendrigrafts) | 12 | FITC | Human lung carcinoma (A549) | [86] |
| Polyamide | 8 | FITC | Human lymphocyte (T cell line Jurkat) | [29] |
| PAMAM | 58 | DNA | 293, HepG2, Neuro2A, rat vascular smooth muscle cells | [80] |
| PAMAM | 58 | DNA,RNA | Primary cortical cells (Neurons, glial cells) | [79] |
| PAMAM | 16,32,64 | DNA,RNA | 293, HUVECs | [81] |
| PAMAM | 64 | DNA | HepG2, HeLa, SMCs, HUVECs | [82] |
| PAMAM | 31,59,60,116 | DNA | HeLa, 293, A549 | [83] |
| Polycarbonate | 8 | Oligonucleotides | mouse | [99] |
| Polycarbonate | 8 | Oligonucleotides | mouse | [98] |
| Polyester | 8 | Fe3O4 nanoparticles | GL261 mouse glioma | [94] |
5. Cellular Internalization Mechanism
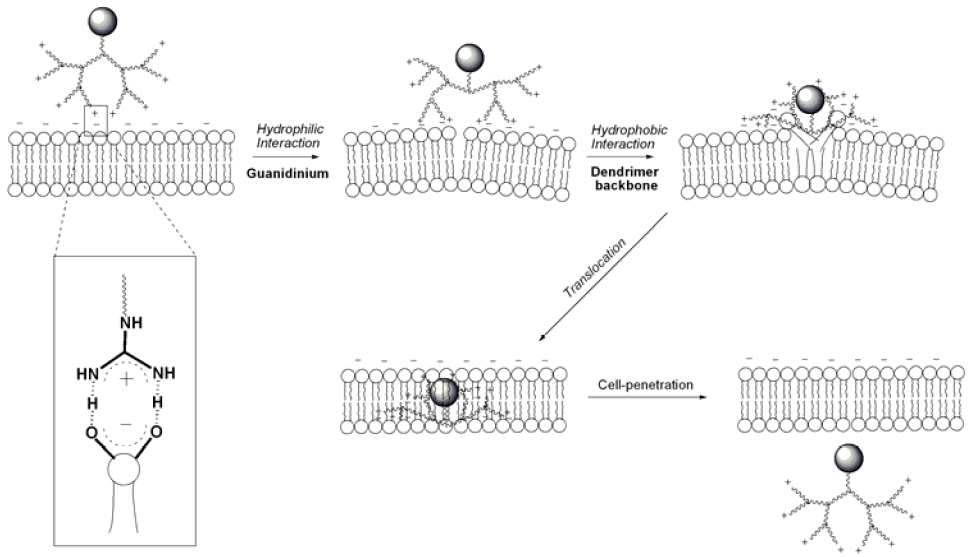
6. Toxicity of Guanidine Functionalized Dendrimers
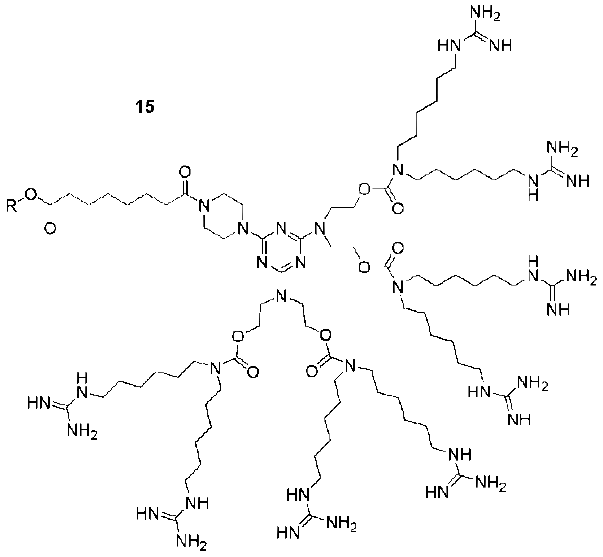
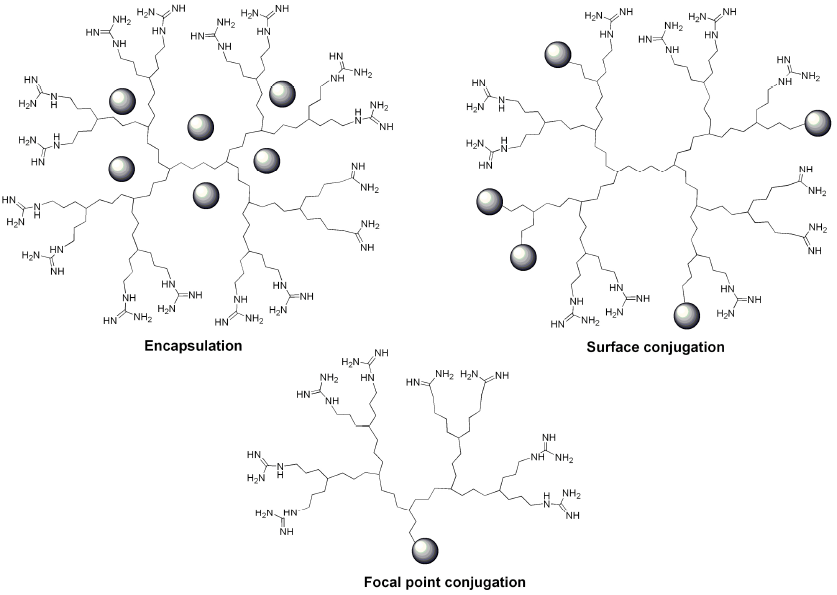
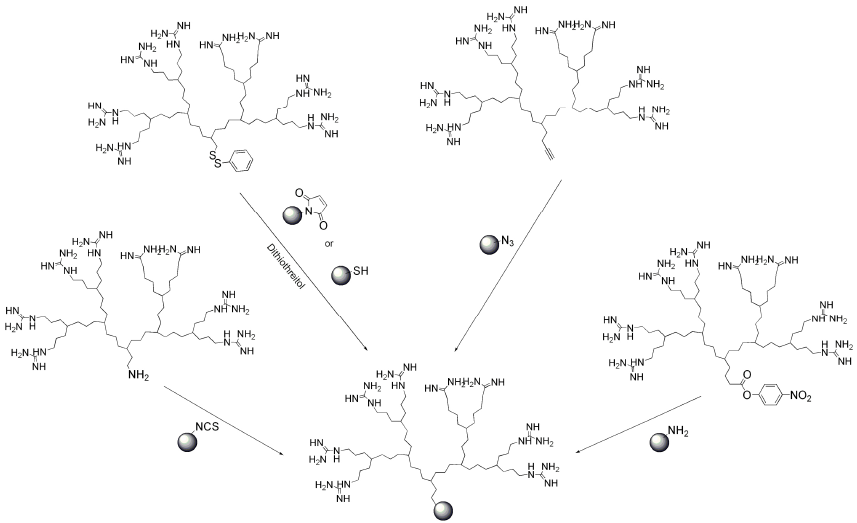
7. Conjugation of Guanidine Functionalized Dendrimers to Cargo
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Frankel, A.D.; Pabo, C.O. Cellular Uptake of the Tat Protein From Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Cell 1988, 55, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Joliot, A.H.; Triller, A.; Volovitch, M.; Pernelle, C.; Prochiantz, A. Alpha-2,8-Polysialic Acid is the Neuronal Surface Receptor of Antennapedia Homeobox Peptide. New Biol. 1991, 3, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derossi, D.; Joliot, A.H.; Chassaing, G.; Prochiantz, A. The Third Helix of the Antennapedia Homeodornain Translocates through Biological Membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10444–10450. [Google Scholar]
- Vives, E.; Brodin, P.; Lebleu, B. A Truncated HIV-1 Tat Protein Basic Domain Rapidly Translocates through the Plasma Membrane and Accumulates in the Cell Nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16010–16017. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.C.; Vidal, P.; Chaloin, L.; Heitz, F.; Divita, G. A New Peptide Vector for Efficient Delivery of Oligonucleotides into Mammalian Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 2730–2736. [Google Scholar]
- Pooga, M.; Hallbrink, M.; Zorko, M.; Langel, U. Cell Penetration by Transportan. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.C.; Deshayes, S.; Heitz, F.; Divita, G. Cell-penetrating Peptides: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Biol. Cell 2008, 100, 201–217. [Google Scholar]
- Oehlke, J.; Scheller, A.; Wiesner, B.; Krause, E.; Beyermann, M.; Klauschenz, E.; Melzig, M.; Bienert, M. Cellular Uptake of an Alpha-helical Amphipathic Model Peptide with the Potential to Deliver Polar Compounds into the Cell Interior Non-endocytically. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1414, 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Abes, S.; Moulton, H.M.; Clair, P.; Prevot, P.; Youngblood, D.S.; Wu, R.P.; Iversen, P.L.; Lebleu, B. Vectorization of Morpholino Oligomers by the (R-Ahx-R)4 Peptide Allows Efficient Splicing Correction in the Absence of Endosomolytic Agents. J. Control. Release 2006, 116, 304–313. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, G.D.; Arzumanov, A.; Abes, R.; Yin, H.; Wood, M.J.; Lebleu, B.; Gait, M.J. Improved Cell-penetrating Peptide-PNA Conjugates for Splicing Redirection in HeLa Cells and Exon Skipping in Mdx Mouse Muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 6418–6428. [Google Scholar]
- Mae, M.; El Andaloussi, S.; Lundin, P.; Oskolkov, N.; Johansson, H.J.; Guterstam, P.; Langel, U. A Stearylated CPP for Delivery of Splice Correcting Oligonucleotides Using a Non-covalent Co-incubation Strategy. J. Control. Release 2009, 134, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- De Coupade, C.; Fittipaldi, A.; Chagnas, V.; Michel, M.; Carlier, S.; Tasciott, E.; Darmon, A.; Ravel, D.; Kearsey, J.; Giacca, M.; Cailler, F. Novel Human-derived Cell-penetrating Peptides for Specific Subcellular Delivery of Therapeutic Biomolecules. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, D.J.; Kim, D.T.; Steinman, L.; Fathman, C.G.; Rothbard, J.B. Polyarginine Enters Cells More Efficiently Than Other Polycationic Homopolymers. J. Pept. Res. 2000, 56, 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Futaki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Ohashi, W.; Yagami, T.; Tanaka, S.; Ueda, K.; Sugiura, Y. Arginine-rich Peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 5836–5840. [Google Scholar]
- Futaki, S.; Nakase, I.; Tadokoro, A.; Takeuchi, T.; Jones, A.T. Arginine-rich Peptides and Their Internalization Mechanisms. Bio. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 784–787. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, B.; Seal, B.L.; Brophy, C.M.; Panitch, A. Design of a Bioactive Cell-penetrating Peptide: When a Transduction Domain Does More Than Transduce. J. Pept. Sci. 2009, 15, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.; Kretzschmar, I.; Volkmer, R.; Boisguerin, P. Comparison of Cellular Uptake Using 22 CPPs in 4 Different Cell Lines. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Said Hassane, F.; Saleh, A.F.; Abes, R.; Gait, M.J.; Lebleu, B. Cell Penetrating Peptides: Overview and Applications to the Delivery of Oligonucleotides. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 67, 715–726. [Google Scholar]
- Heitz, F.; Morris, M.C.; Divita, G. Twenty Years of Cell-penetrating Peptides: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Langel, U. Cell-penetrating Peptides: Processes and Applications.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, M.A. Peptide-Mediated Cell Delivery: Application in Protein Target Validation. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2002, 2, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, R.P.; Dalby, B. Protein Delivery Using VP22. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 20–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wender, P.A.; Galliher, W.C.; Goun, E.A.; Jones, L.R.; Pillow, T.H. The Design of Guanidinium-rich Transporters and Their Internalization Mechanisms. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2008, 60, 452–472. [Google Scholar]
- Wender, P.A.; Mitchell, D.J.; Pattabiraman, K.; Pelkey, E.T.; Steinman, L.; Rothbard, J.B. The Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Molecules that Enable or Enhance Cellular Uptake: Peptoid Molecular Transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13003–13008. [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard, J.B.; Kreider, E.; VanDeusen, C.L.; Wright, L.; Wylie, B.L.; Wender, P.A. Arginine-Rich Molecular Transporters for Drug Delivery: Role of Backbone Spacing in Cellular Uptake. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 3612–3618. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.; Harms, G.; Seong, C.M.; Choi, B.H.; Min, C.; Taulane, J.P.; Goodman, M. Dendritic Oligoguanidines as Intracellular Translocators. Biopolymers 2004, 76, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Futaki, S.; Nakase, I.; Suzuki, T.; Youjun, Y.; Sugiura, Y. Translocation of Branched-Chain Arginine Peptides through Cell Membranes: Flexibility in the Spatial Disposition of Positive Charges in Membrane-Permeable Peptides. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7925–7930. [Google Scholar]
- Pantos, A.; Tsogas, I.; Paleos, C.M. Guanidinium Group: A Versatile Moiety Inducing Transport and Multicompartmentalization in Complementary Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 811–823. [Google Scholar]
- Wender, P.A.; Kreider, E.; Pelkey, E.T.; Rothbard, J.; VanDeusen, C.L. Dendrimeric Molecular Transporters: Synthesis and Evaluation of Tunable Polyguanidino Dendrimers That Facilitate Cellular Uptake. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 4815–4818. [Google Scholar]
- Wender, P.A.; Rothbard, J.B.; Jessop, T.C.; Kreider, E.L.; Wylie, B.L. Oligocarbamate Molecular Transporters: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of a New Class of Transporters for Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13382–13383. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Huang, J.; Jiang, H.; Quan, J.; Cho, M.; Cho, C. Guanidinylated Poly(allyl amine) as a Gene Carrier. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 926–933. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, A. Thermodynamic Studies and Binding Mechanisms of Cell-penetrating Peptides with Lipids and Glycosaminoglycans. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2008, 60, 580–597. [Google Scholar]
- Goun, E.A.; Pillow, T.H.; Jones, L.R.; Rothbard, J.B.; Wender, P.A. Molecular Transporters: Synthesis of Oligoguanidinium Transporters and Their Application to Drug Delivery and Real-T ime Imaging. Chem. Bio. Chem. 2006, 7, 1497–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, L.R.; Rothbard, J.B.; Wender, P.A. Guanidinium Rich Peptide Transporters and Drug Delivery. Curr. Prot. Pept. Sci. 2003, 4, 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Wender, P.A.; Jessop, T.C.; Pattabiraman, K.; Pelkey, E.T.; VanDeusen, C.L. An Efficient, Scalable Synthesis of the Molecular Transporter Octaarginine Via a Segment Doubling Strategy. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3229–3232. [Google Scholar]
- Futaki, S.; Ohashi, W.; Suzuki, T.; Niwa, M.; Tanaka, S.; Ueda, K.; Harashima, H.; Sugiura, Y. Stearylated Arginine-Rich Peptides: A New Class of Transfection Systems. Bioconjug. Chem. 2001, 12, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potocky, T.B.; Menon, A.K.; Gellman, S.H. Effects of Conformational Stability and Geometry of Guanidinium Display on Cell Entry by Beta-Peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3686–3687. [Google Scholar]
- Rueping, M.; Mahajan, Y.; Sauer, M.; Seebach, D. Cellular Uptake Studies with Beta-Peptides. Chem. Bio. Chem. 2002, 3, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, S.H.; El-Sayed, M.E.H. Dendrimers as Carriers for Delivery of Chemotherapeutic Agents. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3141–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Tomalia, D.A. Birth of a New Macromolecular Architecture: Dendrimers as Quantized Building Blocks for Nanoscale Synthetic Polymer Chemistry. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 294–324. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, T. The Effect of Dendrimers on the Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Behaviors of Non-Covalently or Covalently Attached Drugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 2291–2297. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, R.C. Drug Carriers in Pharmaceutical Design: Promises and Progress. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 761–769. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Instability, Stabilization, and Formulation of Liquid Protein Pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 185, 129–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, A.; Falciani, C.; Bracci, L. Branched Peptides as therapeutics. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2008, 9, 468–477. [Google Scholar]
- Buhleier, E.; Wehner, W.; Vogtle, F. "Cascade"- and "Nonskid-Chain-like" Syntheses of Molecular Cavity Topologies. Synthesis 1978, 55, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Tomalia, D.A.; Baker, H.; Dewald, J.; Hall, M.G.K.; Martin, S.; Roek, J.; Ryder, J.; Smith, P. A New Class of Polymers : Starbust-Dendritic Macromolecules. Polym. J. 1985, 17, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Tomalia, D.A.; Naylor, A.M.; Goddard, W.A. Starburst Dendrimers: Molecular-Level Control of Size, Shape, Surface Chemistry, Topology, and Flexibility from Atoms to Macroscopic Matter. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1990, 29, 138–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frechet, J.M.J.; Tomalia, D. Dendrimers and Other Dentritic Polymers.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Newkome, G.R.; Moorefield, C.N.; Vogtle, F. Dendrimers and Dendrons: Concepts, Syntheses, Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Aulenta, F.; Hayes, W.; Rannard, S. Dendrimers: A New Class of Nanoscopic Containers and Delivery Devices. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 1741–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Caminade, A.; Laurent, R.; Majoral, J. Characterization of Dendrimers. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 2130–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, E.R.; Frechet, J.M.J. Dendrimers and Dendritic Polymers in Drug Delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Boas, U.; Heegaard, P.M.H. Dendrimers in Drug Research. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; MacKay, J.A.; Frechet, J.M.J.; Szoka, F.C. Designing Dendrimers for Biological Applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Hawker, C.J.; Frechet, J.M.J. Preparation of Polymers with Controlled Molecular Architecture. A New Convergent Approach to Dendritic Macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 7638–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, P.R.; Boyd, S.E.; Brown, C.L.; Jayaraman, N.; Nepogodiev, S.A.; Stoddart, J.F. A Convergent Synthesis of Carbohydrate-Containing Dendrimers. Chem. Eur. J. 1996, 2, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y.; Fan, M.; Tang, H.; Radosz, M. Facile Synthesis of Polyester Dendrimers from Sequential Click Coupling of Asymmetrical Monomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14795–14803. [Google Scholar]
- Sahota, H.; Lloyd, P.M.; Yeates, S.G.; Derrick, P.J.; Taylor, P.C.; Haddleton, D.M. Characterization of Aromatic Polyester Dendrimers by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1994, 2445–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Ihre, H.; De Jesus, O.L.P.; Frechet, J.M.J. Fast and Convenient Divergent Synthesis of Aliphatic Ester Dendrimers by Anhydride Coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5908–5917. [Google Scholar]
- Baytekin, B.; Werner, N.; Luppertz, F.; Engeser, M.; Bruggemannb, J.; Bitter, S.; Henkel, R.; Felder, T.; Schalley, C.A. How Useful is Mass Spectrometry for the Characterization of Dendrimers? “Fake Defects” in the ESI and MALDI Mass Spectra of Dendritic Compounds. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 249-250, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfand, R.; Tomalia, D.A. Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) Dendrimers: From Biomimicry to Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications. Drug Discov. Today 2001, 6, 427–436. [Google Scholar]
- de Bradander-van den Berg, E.M.M.; Meijer, E.W. Poly(propylenimine) Dendrimers: Large-Scale Synthesis via Heterogeneously Catalyzed Hydrogenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1993, 32, 1308–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kroll, D.J.; Griset, A.P.; Carnahan, M.A.; Wathier, M.; Oberlies, N.H.; Manikumar, G.; Wani, M.C.; Grinstaff, M.W. Dendrimer-Encapsulated Camptothecins: Increased Solubility, Cellular Uptake, and Cellular Retention Affords Enhanced Anticancer Activity In vitro. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11913–11921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grinstaff, M.W. Biodendrimers: New Polymeric Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering. Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 2838–2846. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, A.P.; Lam, S.S.; Frechet, J.M.J. Rapid, Efficient Synthesis of Heterobifunctional Biodegradable Dendrimers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6994–6995. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla De Jesus, O.L.; Ihre, H.R.; Gagne, L.; Frechet, J.M.J.; Szoka, F.C. Polyester Dendritic Systems for Drug Delivery Applications: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 13, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newkome, G.R.; Lin, X.; Weis, C.D. Polytryptophane Terminated Dendritic Macromolecules. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1991, 2, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, K.; Fukui, T.; Takagishi, T.; Sakurai, S.; Kojima, C. Preparation of Poly(ethylene glycol)-Modified Poly(amidoamine) Dendrimers with a Shell of Hydrophobic Amino Acid Residues and Their Function as a Nanocontainer. Polymer 2008, 49, 2832–2838. [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan, D.; Kurur, S. Synthesis of Totally Chiral, Multiple Armed, Poly Glu and Poly Asp Scaffoldings on Bifunctional Adamantane Core. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Zeng, F.; Zimmerman, S.C. Peptide Dendrimers from Natural Amino Acids. Chem. Eur. J. 1999, 5, 2133–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Kress, J.; Rosner, A.; Hirsch, A. Depsipeptide Dendrimers. Chem. Eur. J. 2000, 6, 247–257. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R. A Decade of Glycodendrimer Chemistry. Trend Glycosci. Glycotech. 2003, 15, 291–310. [Google Scholar]
- Röckendorf, N.; Lindhorst, T.K. Glycodendrimers. Top. Curr. Chem. 2001, 217, 202–238. [Google Scholar]
- Patri, A.K.; Majoros, I.J.; Baker, J.R. Dendritic Polymer Macromolecular Carriers for Drug Delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Frechet, J.M.J. Dendrimers and Supramolecular Chemistry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4782–4787. [Google Scholar]
- Carpino, L.A.; Han, G.Y. 9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl Amino-protecting Group. J. Org. Chem. 1972, 37, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar]
- Bernatowicz, M.S.; Wu, Y.; Matsueda, G.R. 1H-Pyrazole-1-carboxamidine Hydrochloride an Attractive Reagent for Guanylation of Amines and its Application to Peptide Synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 2497–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Kasai, S.; Nagasawa, H.; Shimamura, M.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H. Design and Synthesis of Antiangiogenic/Heparin-Binding Arginine Dendrimer Mimicking the Surface of Endostatin. Bio. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 951–954. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-B.; Choi, J.S.; Nam, K.; Lee, M.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, J.-K. Enhanced Transfection of Primary Cortical Cultures using Arginine-grafted PAMAM Dendrimer, PAMAM-Arg. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Nam, K.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Park, J. Enhanced Transfection Efficiency of PAMAM Dendrimer by Surface Modification with L-Arginine. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 445–456. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.Y.; Hahn, H.J.; Nam, K.; Choi, W.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, D.; Park, J.S. Evaluation of Generations 2, 3 and 4 Arginine Modified PAMAM Dendrimers for Gene Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.Y.; Nam, K.; Hahn, H.J.; Kim, B.H.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, J.S.; Park, J.-S. Biodegradable PAMAM ester for enhanced transfection efficiency with low cytotoxicity. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 665–673. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.-I.; Bai, C.Z.; Nam, K.; Park, J.-S. Comparison Between Arginine Conjugated PAMAM Dendrimers with Structural Diversity for Gene Delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Pisal, D.S.; Yellepeddi, V.K.; Kumar, A.; Kaushik, R.S.; Hildreth, M.B.; Guan, X.; Palakurthi, S. Permeability of Surface-Modified Polyamidoamine (PAMAM) Dendrimers Across Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 350, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Baek, J.; Bai, C.Z.; Park, J.S. Arginine-conjugated Polypropylenimine Dendrimer as a Non-toxic and Efficient Gene Delivery Carrier. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2061–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Tsogas, I.; Theodossis, T.; Sideratou, Z.; Paleos, C.M.; Collet, H.; Rossi, J.C.; Romestand, B.; Commeyras, A. Interaction and Transport of Poly(L-lysine) Dendrigrafts through Liposomal and Cellular Membranes: The Role of Generation and Surface Functionalization. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3263–3270. [Google Scholar]
- Tsogas, I.; Sideratou, Z.; Tsiourvas, D.; Theodossiou, T.A.; Paleos, C.M. Interactive Transport of Guanidinylated Poly(propylene imine)-Based Dendrimers through Liposomal and Cellular Membranes. Chem. Bio. Chem. 2007, 8, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar]
- Tziveleka, L.; Psarra, A.G.; Tsiourvas, D.; Paleos, C.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Guanidinylated Poly(propylene imine) Dendrimers as Gene Transfection Agents. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Pantos, A.; Tsiourvas, D.; Nounesis, G.; Paleos, C.M. Interaction of Functional Dendrimers with Multilamellar Liposomes: Design of a Model System for Studying Drug Delivery. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7483–7490. [Google Scholar]
- Sideratou, Z.; Foundis, J.; Tsiourvas, D.; Nezis, I.P.; Papadimas, G.; Paleos, C.M. A Novel Dendrimeric “Glue” for Adhesion of Phosphatidyl Choline-Based Liposomes. Langmuir 2002, 18, 5036–5039. [Google Scholar]
- Cordes, H.; Boas, U.; Olsen, P.; Heegaard, P.M.H. Guanidino- and Urea-Modified Dendrimers as Potent Solubilizers of Misfolded Prion Protein Aggregates under Non-cytotoxic Conditions. Dependence on Dendrimer Generation and Surface Charge. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3578–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Neerman, M.F.; Parrish, A.R.; Simanek, E.E. Cytotoxicity, Hemolysis, and Acute in Vivo Toxicity of Dendrimers Based on Melamine, Candidate Vehicles for Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10044–10048. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okuro, K.; Kinbara, K.; Tsumoto, K.; Ishii, N.; Aida, T. Molecular Glues Carrying Multiple Guanidinium Ion Pendants via an Oligoether Spacer: Stabilization of Microtubules against Depolymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1626–1627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.L.; Bernas, L.M.; Rutt, B.K.; Foster, P.J.; Gillies, E.R. Enhanced Cell Uptake of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Functionalized with Dendritic Guanidines. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Voss, B.; Kumar, D.; Hamm, H.E.; Harth, E. Dendritic Molecular Transporters Provide Control of Delivery to Intracellular Compartments. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 403–409. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, S.K.; Harth, E. Molecular Dendritic Transporter Nanoparticle Vectors Provide Efficient Intracellular Delivery of Peptides. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 402–410. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, S.K.; Ikizler, M.R.; Wallen, C.; Wright, P.F.; Harth, E. Effective Delivery of IgG-antibodies Into Infected Cells via Dendritic Molecular Transporter Conjugate IgGMTw. Mol. BioSyst. 2008, 4, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Morcos, P.A.; Doran, T.J.; Lu, P.; Lu, Q.L. Octa-guanidine Morpholino Restores Dystrophin Expression in Cardiac and Skeletal Muscles and Ameliorates Pathology in Dystrophic mdx Mice. Mol. Therapy 2009, 17, 864–871. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Morcos, P.A. Design and Synthesis of Dendritic Molecular Transporter that Achieves Efficient in Vivo Delivery of Morpholino Antisense Oligo. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, A.; Rossin, R.; Shokeen, M.; Hagooly, A.; Ananth, A.; Capoccia, B.; Guillaudeu, S.; Abendschein, D.; Anderson, C.J.; Welch, M.J.; Frechet, J.M.J. Biodegradable Dendritic Positron-emitting Nanoprobes for the Noninvasive Imaging of Angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Lesniak, W.G.; Kariapper, M.S.T.; Nair, B.M.; Tan, W.; Hutson, A.; Balogh, L.P.; Khan, M.K. Synthesis and Characterization of PAMAM Dendrimer-Based Multifunctional Nanodevices for Targeting rvâ3 Integrins. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Boswell, C.A.; Eck, P.K.; Regino, C.A.S.; Bernardo, M.; Wong, K.J.; Milenic, D.E.; Choyke, P.L.; Brechbiel, M.W. Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Evaluation of Integrinαvβ3-Targeted PAMAM Dendrimers. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammen, M.; Choi, S.; Whitesides, G.M. Polyvalent Interactions in Biological Systems: Implications for Design and Use of Multivalent Ligands and Inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2754–2794. [Google Scholar]
- Kitov, P.I.; Bundle, D.R. On the Nature of the Multivalency Effect: A Thermodynamic Model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 16271–16284. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, G.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Dowdy, S.F.; Cheng, G. Excision of Selectable Genes from Transgenic Goat Cells by a Protein Transducible TAT-Cre Recombinase. Gene 2008, 419, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gitton, Y.; Tibaldi, L.; Dupont, E.; Levi, G.; Joliot, A. Efficient CPP-mediated Cre Protein Delivery to Developing and Adult CNS Tissues. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard, J.B.; Jessop, T.C.; Lewis, R.S.; Murray, B.A.; Wender, P.A. Role of Membrane Potential and Hydrogen Bonding in the Mechanism of Translocation of Guanidinium-rich Peptides into Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9506–9507. [Google Scholar]
- Onda, M.; Yoshihara, K.; Koyano, H.; Ariga, K.; Kunitake, T. Molecular Recognition of Nucleotides by the Guanidinium Unit at the Surface of Aqueous Micelles and Bilayers. A Comparison of Microscopic and Macroscopic Interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8524–8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, A.M.; Casey, D.; Law, R.V.; Gee, A.; Templer, R.H.; Ces, O. Drug Interactions with Lipid Membranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar]
- Drin, G.; Cottin, S.; Blanc, E.; Rees, A.R.; Temsamani, J. Studies on the Internalization Mechanism of Cationic Cell-penetrating Peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31192–31201. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, J.P.; Melikov, K.; Vives, E.; Ramos, C.; Verbeure, B.; Gait, M.J.; Chernomordik, L.V.; Lebleu, B. Cell-penetrating Peptides. A Reevaluation of the Mechanism of Cellular Uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maiolo, J.R.; Ferrer, M.; Ottinger, E.A. Effects of Cargo Molecules on the Cellular Uptake of Arginine-rich Cell-penetrating Peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1712, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Futaki, S.; Niwa, M.; Tanaka, S.; Ueda, K.; Sugiura, Y. Possible Existence of Common Internalization Mechanisms among Arginine-rich Peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2437–2443. [Google Scholar]
- Pouny, Y.; Rapaport, D.; Mor, A.; Nicolas, P.; Shai, Y. Interaction of Antimicrobial Dermaseptin and its Fluorescently Labeled Analogues with Phospholipids Membranes. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 12416–12423. [Google Scholar]
- Nakase, I.; Takeuchi, T.; Tanaka, G.; Futaki, S. Methodological and Cellular Aspects That Govern the Internalization Mechanisms of Arginine-rich Cell-penetrating Peptides. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 598–607. [Google Scholar]
- Theodossiou, T.A.; Pantos, A.; Tsogas, I.; Paleos, C.M. Guanidinylated Dendritic Molecular Transporters: Prospective Drug Delivery Systems and Application in Cell Transfection. Chem. Med. Chem 2008, 3, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard, J.B.; Jessop, T.C.; Wender, P.A. Adaptive Translocation: The Role of Hydrogen Bonding and Membrane Potential in the Uptake of Guanidinium-rich Transporters into Cells. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 495–504. [Google Scholar]
- Tsogas, I.; Tsiourvas, D.; Nounesis, G.; Paleos, C.M. Modeling Cell Membrane Transport: Interaction of Guanidinylated Poly(propylene imine) Dendrimers with a Liposomal Membrane Consisting of Phosphate-based Lipids. Langmuir 2006, 22, 11322–11328. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, K.L.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Tabrizian, M. Cell Line-dependent Internalization Pathways and Intracellular Trafficking Determine Transfection Efficiency of Nanoparticle Vectors. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 676–687. [Google Scholar]
- Godbey, W.T.; Wu, K.K.; Mikos, A.G. Poly(ethylenimine)-mediated Gene Delivery Affects Endothelial Cell Function and Viability. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 471–480. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, E.S.; Aguilera, T.A.; Jiang, T.; Ellies, L.G.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Wong, E.H.; Gross, L.A.; Tsien, R.Y. In vivo Characterization of Activatable Cell Penetrating Peptides for Targeting Protease Activity in Cancer. Integr. Biol. (Camb). 2009, 5, 382–393. [Google Scholar]
- Vives, E. Present and Future of Cell-Penetrating Peptide Mediated Delivery Systems: "Is the Trojan Horse too Wild to go only to Troy?". J. Control. Release 2005, 109, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, G.P.; Bähr, M. Synthesis of Cell-Penetrating Peptides and their Application in Neurobiology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 399, 181–198. [Google Scholar]
- Scheller, A.; Oehlke, J.; Wiesner, B.; Dathe, M.; Krause, E.; Beyermann, M.; Melzig, M.; Bienert, M. Structural Requirements for Cellular Uptake of Alpha-helical Amphipathic Peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 1999, 5, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hallbrink, M.; Floren, A.; Elmquist, A.; Pooga, M.; Bartfai, T.; Langel, U. Cargo Delivery Kinetics of Cell-Penetrating Peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1515, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- El-Andaloussi, S.; Järver, P.; Johansson, H.J.; Langel, U. Cargo-Dependent Cytotoxicity and Delivery Efficacy of Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Comparative Study. Biochem. J. 2007, 407, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Bonavia, R.; Bajetto, A.; Barbero, S.; Albini, A.; Noonan, D.M.; Schettini, G. HIV-1 Tat causes Apoptotic Death and Calcium Homeostasis Alterations in Rat Neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, A.; Psooy, K.; Martin, C.; Knudsen, B.; Magnuson, D.S.; Haughey, N.; Geiger, J.D. Identification of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat epitope that is neuroexcitatory and neurotoxic. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Benjouad, A.; Mabrouk, K.; Moulard, M.; Gluckman, J.C.; Rochat, H.; Van Rietschoten, J.; Sabatier, J.M. Cytotoxic Effect on Lymphocytes of Tat from Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1). Fed. Eur. Biochem. Soc. Lett. 1993, 319, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Lohr, M.; Jezequel, S.; Davis, D.; Shaikh, S.; Selwood, D.; Zachary, I. Cysteine-Rich and Basic Domain HIV-1 Tat Peptides Inhibit Angiogenesis and Induce Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 283, 469–479. [Google Scholar]
- Trehin, R.; Merkle, H.P. Chances and Pitfalls of Cell Penetrating Peptides for Cellular Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Tomalia, D.A.; Reyna, L.A.; Svenson, S. Dendrimers as Multi-Purpose Nanodevices for Oncology Drug Delivery and Diagnostic Imaging. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjwade, B.K.; Bechra, H.M.; Derkar, D.K.; Manvi, F.V.; Nanjwade, V.K. Dendrimers: Emerging Polymers for Drug-Delivery Systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; Gillies, E.R.; Fox, M.E.; Guillaudeu, S.J.; Fréchet, J.M.; Dy, E.E.; Szoka, F.C. A Single Dose of Doxorubicin-Functionalized Bow-tie Dendrimer Cures Mice Bearing C-26 Colon Carcinomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16649–16654. [Google Scholar]
- Majoros, I.J.; Williams, C.R.; Becker, A.; Baker, J.R. Methotrexate Delivery via Folate Targeted Dendrimer-based Nanotherapeutic Platform. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 1, 502–510. [Google Scholar]
- Halford, B. Dendrimers Branch Out. Chem. Eng. News 2005, 83, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Leroueil, P.R.; Hong, S.; Mecke, A.; Baker, J.R.; Orr, B.G.; Banaszak-Holl, M.M. Nanoparticle Interaction with Biological Membranes: Does Nanotechnology Present a Janus Face? Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroueil, P.R.; Berry, S.A.; Duthie, K.; Han, G.; Rotello, V.M.; McNerny, D.Q.; Baker, J.R.; Orr, B.G.; Banaszak Holl, M.M. Wide Varieties of Cationic Nanoparticles Induce Defects in Supported Lipid Bilayers. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 420–424. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, D.; Li, Y.; Ahlemeyer, B.; Krieglstein, J.; Kissel, T. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing of Polycations: Influence of Polymer Structure on Cell Viability and Hemolysis. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Bielinska, A.U.; Mecke, A.; Keszler, B.; Beals, J.L.; Shi, X.; Balogh, L.; Orr, B.G.; Baker, J.R.; Banaszak-Holl, M.M. Synthetic and Natural Polycationic Polymer Nanoparticles Interact Selectively with Fluid-Phase Domains of DMPC Lipid Bilayers. Bioconjug. Chem. 2004, 15, 774–782. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Leroueil, P.R.; Janus, E.K.; Peters, J.L.; Kober, M.M.; Islam, M.T.; Orr, B.G.; Baker, J.R.; Banaszak Holl, M.M. Interaction of Polycationic Polymers with Supported Lipid Bilayers and Cells: Nanoscale Hole Formation and Enhanced Membrane Permeability. Bioconjug. Chem. 2006, 17, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, N.; Wiwattanapatapee, R.; Klopsch, R.; Lorenz, K.; Frey, H.; Weener, J.W.; Meijer, E.W.; Paulus, W.; Duncan, R. Dendrimers: Relationship Between Structure and Biocompatibility in Vitro, and Preliminary Studies on the Biodistribution of 125I-Labelled PAMAM Dendrimers in Vivo. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, J.P. Synthetic Gene-transfer Vectors. Acc. Chem. Res. 1993, 26, 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Akinc, A.; Thomas, M.; Klibanov, A.M.; Langer, R.J. Exploring Polyethylenimine-mediated DNA Transfection and the Proton Sponge Hypothesis. Gene Med. 2005, 7, 657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Sonawane, N.D.; Szoka, F.C.; Verkman, A.S. Chloride Accumulation and Swelling in Endosomes Enhances DNA Transfer by Polyamine-DNA Polyplexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44826–44831. [Google Scholar]
- Kichler, A.; Leborgne, C.; Coeytaux, E.; Danos, O. Polyethylenimine-mediated Gene Delivery: A Mechanistic Study. J. Gene Med. 2001, 3, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Fawell, S.; Seery, J.; Daikh, Y.; Moore, C.; Chen, L.L.; Pepinsky, B.; Barsoum, J. Tat-mediated Delivery of Heterologous Proteins into Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 664–668. [Google Scholar]
- Wadia, J.S.; Dowdy, S.F. Tat Peptide-mediated Cellular Delivery: Back to Basics. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 559–577. [Google Scholar]
- Wadia, J.S.; Dowdy, S.F. Transmembrane Delivery of Protein and Peptide Drugs by TAT-mediated Transduction in the Treatment of Cancer. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 579–596. [Google Scholar]
- Fittipaldi, A.; Giacca, M. Transcellular Protein Transduction Using the Tat Protein of HIV-1. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 597–608. [Google Scholar]
- Hallbrink, M.; Floren, A.; Elmquist, A.; Pooga, M.; Bartfai, T.; Langel, U. Cargo Delivery Kinetics of Cell-penetrating Peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1515, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Corradin, S.; Ransijn, A.; Corradin, G.; Bouvier, J.; Delgado, M.B.; Fernandez-Carneado, J.; Mottram, J.C.; Vergeres, G.; Mauel, J. Novel Peptide Inhibitors of Leishmania gp63 Based on the Cleavage Site of MARCKS (Myristoylated Alanine-rich C Kinase Substrate)-Related Protein. Biochem. J. 2002, 367, 761–769. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, K.; Sundberg, C.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Mukhopadhyay, D. The 104-123 Amino Acid Sequence of the b-domain of von Hippel-Lindau Gene Product Is Sufficient to Inhibit Renal Tumor Growth and Invasion. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi, A.; Akuta, T.; Okuyama, H.; Senda, T.; Yokoi, H.; Inokuchi, H.; Fujita, S.; Hayakawa, T.; Takeda, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Nakanishi, M. Protein Transduction Domain of HIV-1 Tat Protein Promotes Efficient Delivery of DNA into Mammalian Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26204–26210. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, E.L.; Dowdy, S.F. Protein/peptide Transduction Domains: Potential to Deliver Large DNA Molecules into Cells. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu, B.; Moulton, H.M.; Abes, R.; Ivanova, G.D.; Abes, S.; Stein, D.A.; Iversen, P.L.; Arzumanov, A.A.; Gait, M.J. Cell Penetrating Peptide Conjugates of Steric Block Oligonucleotides. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2008, 60, 517–529. [Google Scholar]
- Abes, R.; Arzumanov, A.; Moulton, H.; Abes, S.; Ivanova, G.; Gait, M.J.; Iversen, P.; Lebleu, B. Arginine-rich Cell Penetrating Peptides: Design, Structure-activity, and Applications to Alter Pre-mRNA Splicing by Steric-block Oligonucleotides. J. Pept. Sci. 2008, 14, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhoen, S.; Laufer, S.D.; Restle, T. Recent Developments in Peptide-Based Nucleic Acid Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 1276–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Crombez, L.; Aldrian-Herrada, G.; Konate, K.; Nguyen, Q.; McMaster, G.K.; Brasseur, R.; Heitz, F.; Divita, G. A New Potent Secondary Amphipathic Cell-penetrating Peptide for siRNA Delivery into Mammalian Cells. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Abes, R.; Arzumanov, A.A.; Moulton, H.M.; Abes, S.; Ivanova, G.D.; Iversen, P.L.; Gait, M.J.; Lebleu, B. Cell-penetrating-peptide-based Delivery of Oligonucleotides: An Overview. Bio. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 775–779. [Google Scholar]
- Kersemans, V.; Kersemans, K.; Cornelissen, B. Cell Penetrating Peptides for In Vivo Molecular Imaging Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2415–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhorade, R.; Weissleder, R.; Nakakoshi, T.; Moore, A.; Tung, C.H. Macrocyclic Chelators with Paramagnetic Cations Are Internalized into Mammalian Cells via a HIV-Tat Derived Membrane Translocation Peptide. Bioconjug. Chem. 2000, 11, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyakov, V.; Sharma, V.; Dahlheimer, J.L.; Pica, C.M.; Luker, G.D.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Novel Tat-Peptide Chelates for Direct Transduction of Technetium-99m and Rhenium into Human Cells for Imaging and Radiotherapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2000, 11, 762–771. [Google Scholar]
- Torchilin, V.P. Tat Peptide-mediated Intracellular Delivery of Pharmaceutical Nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2008, 60, 548–558. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph, C.; Schillinger, U.; Ortiz, A.; Tabatt, K.; Plank, C.; Muller, R.H.; Rosenecker, J. Application of Novel Solid Lipid Nanoparticle (SLN)-Gene Vector Formulations Based on a Dimeric HIV-1 TAT-Peptide in Vitro and in Vivo. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.M.; Berry, C.C. Tat Peptide as an Efficient Molecule To Translocate Gold Nanoparticles into the Cell Nucleus. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Sethuraman, V.A.; Bae, Y.H. Tat Peptide-based Micelle System for Potential Active Targeting of Anti-cancer Agents to Acidic Solid Tumors. J. Control. Release 2007, 118, 216–224. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.; Su, W.; Pohmann, R.; Pfeuffer, J.; Sauer, M.G.; Ugurbil, K.; Engelmann, J. Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Peptide Nucleic Acid-Coupled MRI Contrast Agents: Evaluation of Cellular Delivery and Target Binding. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, Y.L.; Liu, J.J.; Hong, R.L. Translocation of Liposomes into Cancer Cells by Cell-Penetrating Peptides Penetratin and Tat: A Kinetic and Efficacy Study. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 62, 864–872. [Google Scholar]
- Torchilin, V.P.; Levchenko, T.S. TAT-Liposomes: A Novel Intracellular Drug Carrier. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2003, 4, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Torchilin, V.P.; Rammohan, R.; Weissig, V.; Levchenko, T.S. TAT peptide on the surface of liposomes affords their efficient intracellular delivery even at low temperature and in the presence of metabolic inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8786–8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschberg, T.A.; VanDeusen, C.L.; Rothbard, J.B.; Yang, M.; Wender, P.A. Arginine-Based Molecular Transporters: The Synthesis and Chemical Evaluation of Releasable Taxol-Transporter Conjugates. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 3459–3462. [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard, J.B.; Garlington, S.; Lin, Q.; Kirschberg, T.; Kreider, E.; McGrane, P.L.; Wender, P.A.; Khavari, P.A. Conjugation of Arginine Oligomers to Cyclosporin A Facilitates Topical Delivery and Inhibition of Inflammation. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.; Levchenko, T.S.; Torchilin, V.P. Intracellular Delivery of Large Molecules and Small Particles by Cell-penetrating Proteins and Peptides. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 637–651. [Google Scholar]
- Svenson, S. Dendrimers as Versatile Platform in Drug Delivery Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Bio. 2009, 71, 445. [Google Scholar]
- Samad, A.; Alam, I.; Saxena, K. Dendrimers : A Class of Polymers in the Nanotechnology for the Delivery of Active Pharmaceuticals. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2958–2969. [Google Scholar]
- D’Emanuele, A.; Attwood, D. Dendrimer-drug Interactions. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2005, 57, 2147–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jearawiriyapaisarn, N.; Moulton, H.M.; Buckley, B.; Roberts, J.; Sazani, P.; Fucharoen, S. Sustained Dystrophin Expression Induced by Peptide-Conjugated Morpholino Oligomers in the Muscles of mdx Mice. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonduelle, C.V.; Gillies, E.R. Dendritic Guanidines as Efficient Analogues of Cell Penetrating Peptides. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 636-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030636
Bonduelle CV, Gillies ER. Dendritic Guanidines as Efficient Analogues of Cell Penetrating Peptides. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(3):636-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030636
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonduelle, Colin V., and Elizabeth R. Gillies. 2010. "Dendritic Guanidines as Efficient Analogues of Cell Penetrating Peptides" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 3: 636-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030636
APA StyleBonduelle, C. V., & Gillies, E. R. (2010). Dendritic Guanidines as Efficient Analogues of Cell Penetrating Peptides. Pharmaceuticals, 3(3), 636-666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3030636