Deregulation of Interferon Signaling in Malignant Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
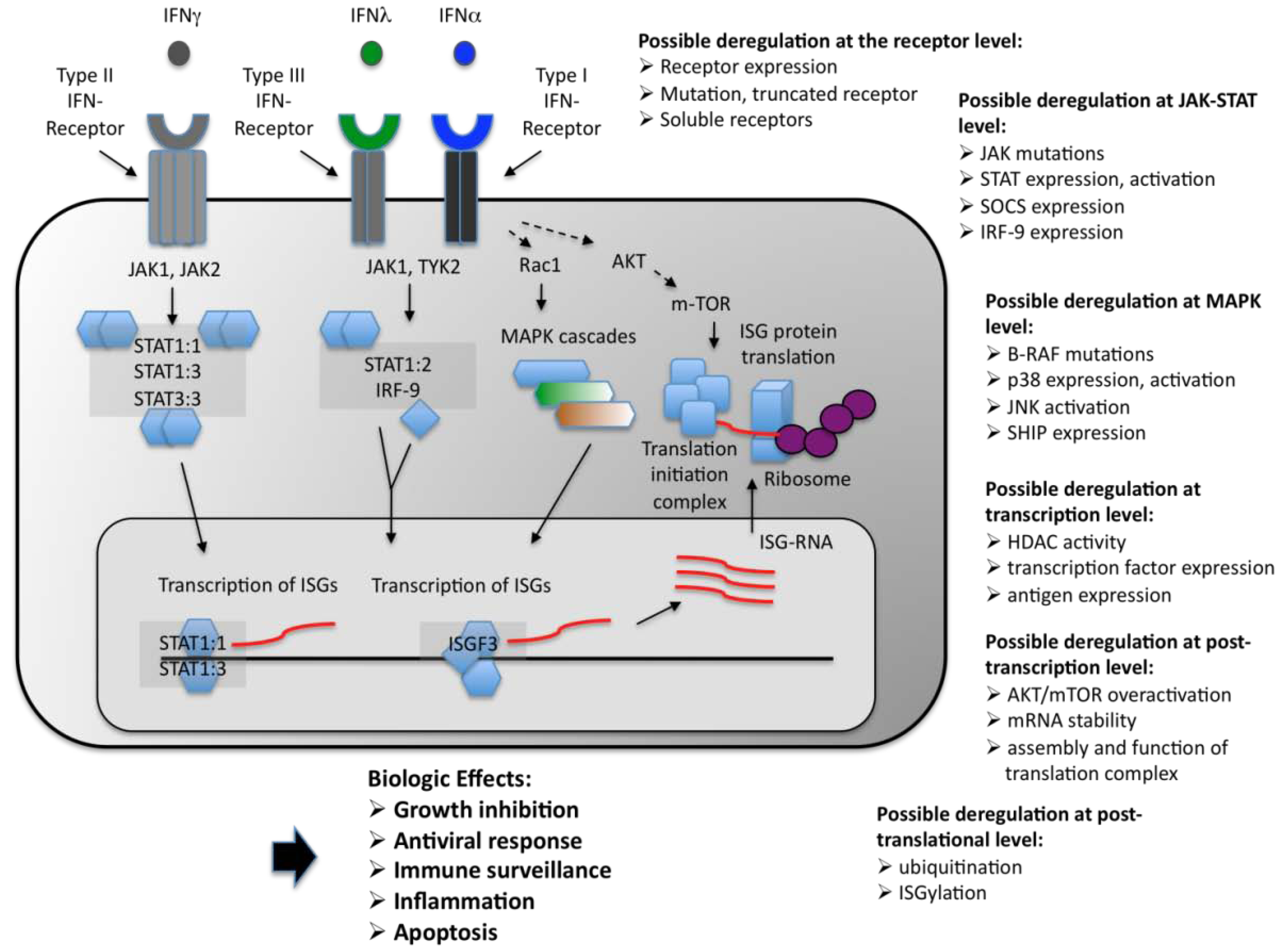
2. Classification of the IFNs
3. The IFN Receptors in Malignancies
4. The JAK-STAT Pathway
4.1. JAK kinases in Malignancies
4.2. STAT Proteins in Malignancies
5. Additional Regulatory Mechanisms and Concluding Remarks
References
- Isaacs, A.; Lindenmann, J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1957, 147, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pestka, S.; Langer, J.A.; Zoon, K.C.; Samuel, C.E. Interferons and their actions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 727–777. [Google Scholar]
- Pestka, S.; Krause, C.D.; Walter, M.R. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 202, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katze, M.G.; He, Y.; Gale, M. Viruses and interferon: a fight for supremacy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 675–687. [Google Scholar]
- Darnell, J.E.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Young, H.A.; Ortaldo, J. Cytokines as critical co-stimulatory molecules in modulating the immune response of natural killer cells. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Borden, E.C.; Sen, G.C.; Uze, G.; Silverman, R.H.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Foster, G.R.; Stark, G.R. Interferons at age 50: Past, current and future impact on biomedicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 975–990. [Google Scholar]
- Pestka, S. The interferons: 50 years after their discovery, there is much more to learn. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20047–20051. [Google Scholar]
- Platanias, L.C. Map kinase signaling pathways and hematologic malignancies. Blood 2003, 101, 4667–4679. [Google Scholar]
- Nusinzon, I.; Horvath, C.M. Interferon-stimulated transcription and innate antiviral immunity require deacetylase activity and histone deacetylase 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14742–14747. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, I.A.; Verma, A.; Grumbach, I.M.; Uddin, S.; Lekmine, F.; Ravandi, F.; Majchrzak, B.; Fujita, S.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. The p38 MAPK pathway mediates the growth inhibitory effects of interferon-alpha in BCR-ABL-expressing cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 28570–28577. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, S.; Platanias, L.C. Interferons: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2003, 15, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson, D.S.; Horvath, C.M. A road map for those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science 2002, 296, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, G.P.; Bruce, A.T.; Ikeda, H.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Cancer immunoediting: From immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 991–998. [Google Scholar]
- Shankaran, V.; Ikeda, H.; Bruce, A.T.; White, J.M.; Swanson, P.E.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature 2001, 410, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, D.H.; Shankaran, V.; Dighe, A.S.; Stockert, E.; Aguet, M.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Demonstration of an interferon gamma-dependent tumor surveillance system in immunocompetent mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7556–7561. [Google Scholar]
- Noser, J.A.; Mael, A.A.; Sakuma, R.; Ohmine, S.; Marcato, P.; Lee, P.W.; Ikeda, Y. The RAS/Raf1/MEK/ERK signaling pathway facilitates VSV-mediated oncolysis: Implication for the defective interferon response in cancer cells. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Sexl, V.; Kovacic, B.; Piekorz, R.; Moriggl, R.; Stoiber, D.; Hoffmeyer, A.; Liebminger, R.; Kudlacek, O.; Weisz, E.; Rothammer, K.; Ihle, J.N. Jak1 deficiency leads to enhanced Abelson-induced B-cell tumor formation. Blood 2003, 101, 4937–4943. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.M.; Tanaka, N.; Mitani, Y.; Oda, E.; Nozawa, H.; Chen, J.Z.; Yanai, H.; Negishi, H.; Choi, M.K.; Iwasaki, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Takaoka, A. Critical role for constitutive type I interferon signaling in the prevention of cellular transformation. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, S.; Witte, O.N. The BCR-ABL story: Bench to bedside and back. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 247–306. [Google Scholar]
- Cebo, C.; Voutsadakis, I.A.; Da Rocha, S.; Bourhis, J.H.; Jalil, A.; Azzarone, B.; Turhan, A.G.; Chelbi-Alix, M.; Chouaib, S.; Caignard, A. Altered IFNgamma signaling and preserved susceptibility to activated natural killer cell-mediated lysis of BCR/ABL targets. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2914–2920. [Google Scholar]
- Pansky, A.; Hildebrand, P.; Fasler-Kan, E.; Baselgia, L.; Ketterer, S.; Beglinger, C.; Heim, M.H. Defective Jak-STAT signal transduction pathway in melanoma cells resistant to growth inhibition by interferon-alpha. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 85, 720–725. [Google Scholar]
- Vainchenker, W.; Dusa, A.; Constantinescu, S.N. JAKs in pathology: Role of Janus kinases in hematopoietic malignancies and immunodeficiencies. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar]
- Critchley-Thorne, R.J.; Simons, D.L.; Yan, N.; Miyahira, A.K.; Dirbas, F.M.; Johnson, D.L.; Swetter, S.M.; Carlson, R.W.; Fisher, G.A.; Koong, A.; Holmes, S.; Lee, P.P. Impaired interferon signaling is a common immune defect in human cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9010–9015. [Google Scholar]
- Dellgren, C.; Gad, H.H.; Hamming, O.J.; Melchjorsen, J.; Hartmann, R. Human interferon-lambda3 is a potent member of the type III interferon family. Genes Immun. 2009, 10, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann, C.; Nagata, S.; Boll, W.; Fountoulakis, M.; Fujisawa, A.; Fujisawa, J.I.; Haynes, J.; Henco, K.; Mantei, N.; Ragg, H.; Schein, C.; Schmid, J.; Shaw, G.; Streuli, M.; Taira, H.; Todokoro, K.; Weidle, U. Structure and expression of human IFN-alpha genes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1982, 299, 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn, S. The regulation of beta-interferon gene expression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1990, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, M. Multiple interferon subtypes: The phenomenon and its relevance. J. Interferon Res. 1987, 7, 545–551. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski, A.; Harris, J.M. Improvements in protein PEGylation: Pegylated interferons for treatment of hepatitis C. J. Control Release 2001, 72, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Veronese, F.M.; Mero, A. The impact of PEGylation on biological therapies. BioDrugs 2008, 22, 315–329. [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea, J.J.; Gadina, M.; Schreiber, R.D. Cytokine signaling in 2002: New surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell 2002, 109, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- de Weerd, N.A.; Samarajiwa, S.A.; Hertzog, P.J. Type I interferon receptors: Biochemistry and biological functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20053–20057. [Google Scholar]
- Pestka, S.; Kotenko, S.V.; Muthukumaran, G.; Izotova, L.S.; Cook, J.R.; Garotta, G. The interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) receptor: A paradigm for the multichain cytokine receptor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997, 8, 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, E.A.; Aguet, M.; Schreiber, R.D. The IFN gamma receptor: A paradigm for cytokine receptor signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 563–591. [Google Scholar]
- Kotenko, S.V.; Gallagher, G.; Baurin, V.V.; Lewis-Antes, A.; Shen, M.; Shah, N.K.; Langer, J.A.; Sheikh, F.; Dickensheets, H.; Donnelly, R.P. IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, P.; Kindsvogel, W.; Xu, W.; Henderson, K.; Schlutsmeyer, S.; Whitmore, T.E.; Kuestner, R.; Garrigues, U.; Birks, C.; Roraback, J.; Ostrander, C.; Dong, D.; Shin, J.; Presnell, S.; Fox, B.; Haldeman, B.; Cooper, E.; Taft, D.; Gilbert, T.; Grant, F.J.; Tackett, M.; Krivan, W.; McKnight, G.; Clegg, C.; Foster, D.; Klucher, K.M. IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Onoguchi, K.; Yoneyama, M.; Takemura, A.; Akira, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Namiki, H.; Fujita, T. Viral infections activate types I and III interferon genes through a common mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7576–7581. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Hamming, O.J.; Ank, N.; Paludan, S.R.; Nielsen, A.L.; Hartmann, R. Type III interferon (IFN) induces a type I IFN-like response in a restricted subset of cells through signaling pathways involving both the Jak-STAT pathway and the mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7749–7758. [Google Scholar]
- Mizukoshi, E.; Kaneko, S.; Kaji, K.; Terasaki, S.; Matsushita, E.; Muraguchi, M.; Ohmoto, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Serum levels of soluble interferon Alfa/Beta receptor as an inhibitory factor of interferon in the patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 1999, 30, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Frodsham, A.J.; Zhang, L.; Dumpis, U.; Taib, N.A.; Best, S.; Durham, A.; Hennig, B.J.; Hellier, S.; Knapp, S.; Wright, M.; Chiaramonte, M.; Bell, J.I.; Graves, M.; Whittle, H.C.; Thomas, H.C.; Thursz, M.R.; Hill, A.V. Class II cytokine receptor gene cluster is a major locus for hepatitis B persistence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9148–9153. [Google Scholar]
- Leyva, L.; Fernandez, O.; Fedetz, M.; Blanco, E.; Fernandez, V.E.; Oliver, B.; Leon, A.; Pinto-Medel, M.J.; Mayorga, C.; Guerrero, M.; Luque, G.; Alcina, A.; Matesanz, F. IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 polymorphisms confer susceptibility to multiple sclerosis but not to interferon-beta treatment response. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 163, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, M.P.; Owczarek, C.M.; Trajanovska, S.; Liu, X.; Kola, I.; Hertzog, P.J. The soluble murine type I interferon receptor Ifnar-2 is present in serum, is independently regulated, and has both agonistic and antagonistic properties. Blood 2001, 97, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.G.; Tang, W.; Ravindranath, A.K.; Clark, W.A.; Croze, E.; Fuchs, S.Y. SCF(HOS) ubiquitin ligase mediates the ligand-induced down-regulation of the interferon-alpha receptor. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5480–5490. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, G.P.; Bruce, A.T.; Sheehan, K.C.; Shankaran, V.; Uppaluri, R.; Bui, J.D.; Diamond, M.S.; Koebel, C.M.; Arthur, C.; White, J.M.; Schreiber, R.D. A critical function for type I interferons in cancer immunoediting. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 722–729. [Google Scholar]
- Morell-Quadreny, L.; Fenollosa-Entrena, B.; Clar-Blanch, F.; Navarro-Fos, S.; Llombart-Bosch, A. Expression of type I interferon receptor in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 1999, 6, 639–642. [Google Scholar]
- Steelman, L.S.; Abrams, S.L.; Whelan, J.; Bertrand, F.E.; Ludwig, D.E.; Basecke, J.; Libra, M.; Stivala, F.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A.; Lunghi, P.; Bonati, A.; Martelli, A.M.; McCubrey, J.A. Contributions of the Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR and Jak/STAT pathways to leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 686–707. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Stark, G.R. Roles of unphosphorylated STATs in signaling. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Wei, L.; Murti, A.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Fan, M.; Yang, C.H.; Pfeffer, L.M. Non-conventional signal transduction by type 1 interferons: The NF-kappaB pathway. J. Cell Biochem. 2007, 102, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez, L.; Fellous, M.; Stark, G.R.; Pellegrini, S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell 1992, 70, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Hilkens, C.M.; Is'harc, H.; Lillemeier, B.F.; Strobl, B.; Bates, P.A.; Behrmann, I.; Kerr, I.M. A region encompassing the FERM domain of Jak1 is necessary for binding to the cytokine receptor gp130. FEBS Lett. 2001, 505, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Chen, M.; Cusack, N.A.; Kimmel, L.H.; Magnuson, K.S.; Boyd, J.G.; Lin, W.; Roberts, J.L.; Lengi, A.; Buckley, R.H.; Geahlen, R.L.; Candotti, F.; Gadina, M.; Changelian, P.S.; O'Shea, J.J. Unexpected effects of FERM domain mutations on catalytic activity of Jak3: Structural implication for Janus kinases. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 959–969. [Google Scholar]
- Karaghiosoff, M.; Neubauer, H.; Lassnig, C.; Kovarik, P.; Schindler, H.; Pircher, H.; McCoy, B.; Bogdan, C.; Decker, T.; Brem, G.; Pfeffer, K.; Muller, M. Partial impairment of cytokine responses in Tyk2-deficient mice. Immunity 2000, 13, 549–560. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda, K.; Kato, K.; Aoki, K.; Matsuda, T.; Miyamoto, A.; Shibamori, M.; Yamashita, M.; Numata, A.; Takase, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Shibata, S.; Asano, Y.; Gondo, H.; Sekiguchi, K.; Nakayama, K.; Nakayama, T.; Okamura, T.; Okamura, S.; Niho, Y. Tyk2 plays a restricted role in IFN alpha signaling, although it is required for IL-12-mediated T cell function. Immunity 2000, 13, 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, J.A.; Kawamura, M.; Kirken, R.A.; Chen, Y.Q.; Blake, T.B.; Shibuya, K.; Ortaldo, J.R.; McVicar, D.W.; O'Shea, J.J. Phosphorylation and activation of the Jak-3 Janus kinase in response to interleukin-2. Nature 1994, 370, 151–153. [Google Scholar]
- Nosaka, T.; van Deursen, J.M.; Tripp, R.A.; Thierfelder, W.E.; Witthuhn, B.A.; McMickle, A.P.; Doherty, P.C.; Grosveld, G.C.; Ihle, J.N. Defective lymphoid development in mice lacking Jak3. Science 1995, 270, 800–802. [Google Scholar]
- Witthuhn, B.A.; Silvennoinen, O.; Miura, O.; Lai, K.S.; Cwik, C.; Liu, E.T.; Ihle, J.N. Involvement of the Jak-3 Janus kinase in signalling by interleukins 2 and 4 in lymphoid and myeloid cells. Nature 1994, 370, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Lai, R.; Chirieac, L.R.; Li, C.; Thomazy, V.A.; Grammatikakis, I.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Zhang, W.; Fujio, Y.; Kunisada, K.; Hamilton, S.R.; Amin, H.M. Constitutive activation of JAK3/STAT3 in colon carcinoma tumors and cell lines: Inhibition of JAK3/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of colon carcinoma cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 969–980. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, E.G.; Kim, M.S.; Nam, H.K.; Min, C.K.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.J.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Somatic mutations of JAK1 and JAK3 in acute leukemias and solid cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, D.K.; Mercher, T.; Gu, T.L.; O'Hare, T.; Tyner, J.W.; Loriaux, M.; Goss, V.L.; Lee, K.A.; Eide, C.A.; Wong, M.J.; Stoffregen, E.P.; McGreevey, L.; Nardone, J.; Moore, S.A.; Crispino, J.; Boggon, T.J.; Heinrich, M.C.; Deininger, M.W.; Polakiewicz, R.D.; Gilliland, D.G.; Druker, B.J. Activating alleles of JAK3 in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Mitaksov, V.; Fremont, D.H.; Kasai, Y.; Molitoris, A.; Ries, R.E.; Miner, T.L.; McLellan, M.D.; DiPersio, J.F.; Link, D.C.; Payton, J.E.; Graubert, T.A.; Watson, M.; Shannon, W.; Heath, S.E.; Nagarajan, R.; Mardis, E.R.; Wilson, R.K.; Ley, T.J.; Tomasson, M.H. Identification of somatic JAK1 mutations in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 4809–4812. [Google Scholar]
- Flex, E.; Petrangeli, V.; Stella, L.; Chiaretti, S.; Hornakova, T.; Knoops, L.; Ariola, C.; Fodale, V.; Clappier, E.; Paoloni, F.; Martinelli, S.; Fragale, A.; Sanchez, M.; Tavolaro, S.; Messina, M.; Cazzaniga, G.; Camera, A.; Pizzolo, G.; Tornesello, A.; Vignetti, M.; Battistini, A.; Cave, H.; Gelb, B.D.; Renauld, J.C.; Biondi, A.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Foa, R.; Tartaglia, M. Somatically acquired JAK1 mutations in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 751–758. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; Kambhampati, S.; Parmar, S.; Platanias, L.C. Jak family of kinases in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 423–434. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, R.L.; Pardanani, A.; Tefferi, A.; Gilliland, D.G. Role of JAK2 in the pathogenesis and therapy of myeloproliferative disorders. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 673–683. [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, M.; Griffin, J.D. JAK2 gets histone H3 rolling. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 365–366. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, M.A.; Bannister, A.J.; Gottgens, B.; Foster, S.D.; Bartke, T.; Green, A.R.; Kouzarides, T. JAK2 phosphorylates histone H3Y41 and excludes HP1alpha from chromatin. Nature 2009, 461, 819–822. [Google Scholar]
- Cacalano, N.A.; Migone, T.S.; Bazan, F.; Hanson, E.P.; Chen, M.; Candotti, F.; O'Shea, J.J.; Johnston, J.A. Autosomal SCID caused by a point mutation in the N-terminus of Jak3: Mapping of the Jak3-receptor interaction domain. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, C.; Levy, D.E.; Decker, T. JAK-STAT signaling: From interferons to cytokines. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20059–20063. [Google Scholar]
- Brierley, M.M.; Fish, E.N. Stats: Multifaceted regulators of transcription. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005, 25, 733–744. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, S.; Sassano, A.; Deb, D.K.; Verma, A.; Majchrzak, B.; Rahman, A.; Malik, A.B.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. Protein kinase C-delta (PKC-delta ) is activated by type I interferons and mediates phosphorylation of Stat1 on serine 727. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14408–14416. [Google Scholar]
- Sekimoto, T.; Imamoto, N.; Nakajima, K.; Hirano, T.; Yoneda, Y. Extracellular signal-dependent nuclear import of Stat1 is mediated by nuclear pore-targeting complex formation with NPI-1, but not Rch1. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 7067–7077. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, K.M.; Banninger, G.; McDonald, C.; Reich, N.C. Regulated nuclear import of the STAT1 transcription factor by direct binding of importin-alpha. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, N.C.; Liu, L. Tracking STAT nuclear traffic. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 602–612. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, K.M.; McDonald, C.; Reich, N.C. Nuclear export signal located within theDNA-binding domain of the STAT1transcription factor. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6196–6206. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar]
- Benekli, M.; Baer, M.R.; Baumann, H.; Wetzler, M. Signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins in leukemias. Blood 2003, 101, 2940–2954. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, T.; Garcia, R.; Turkson, J.; Jove, R. STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2474–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E. Stats: Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerer, J.M.; Lesinski, G.B.; Radmacher, M.D.; Ruppert, A.; Carson, W.E. STAT1-dependent and STAT1-independent gene expression in murine immune cells following stimulation with interferon-alpha. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis, S.; Dargemont, C.; Fieschi, C.; Thomassin, N.; Rosenzweig, S.; Harris, J.; Holland, S.M.; Schreiber, R.D.; Casanova, J.L. Impairment of mycobacterial but not viral immunity by a germline human STAT1 mutation. Science 2001, 293, 300–303. [Google Scholar]
- Meraz, M.A.; White, J.M.; Sheehan, K.C.; Bach, E.A.; Rodig, S.J.; Dighe, A.S.; Kaplan, D.H.; Riley, J.K.; Greenlund, A.C.; Campbell, D.; Carver-Moore, K.; DuBois, R.N.; Clark, R.; Aguet, M.; Schreiber, R.D. Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell 1996, 84, 431–442. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.K.; Rao, D.T.; Gertner, R.; Gimeno, R.; Frey, A.B.; Levy, D.E. Distinct requirements for IFNs and STAT1 in NK cell function. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 3571–3577. [Google Scholar]
- Katsoulidis, E.; Li, Y.; Mears, H.; Platanias, L.C. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in interferon signal transduction. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005, 25, 749–756. [Google Scholar]
- Platanias, L.C. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and its role in interferon signaling. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 98, 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Platanias, L.C.; Fish, E.N. Signaling pathways activated by interferons. Exp. Hematol. 1999, 27, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; Platanias, L.C. Signaling via the interferon-alpha receptor in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2002, 43, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoulidis, E.; Sassano, A.; Majchrzak-Kita, B.; Carayol, N.; Yoon, P.; Jordan, A.; Druker, B.J.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. Suppression of interferon (IFN)-inducible genes and IFN-mediated functional responses in BCR-ABL-expressing cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 10793–10803. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, S.; Katsoulidis, E.; Verma, A.; Li, Y.; Sassano, A.; Lal, L.; Majchrzak, B.; Ravandi, F.; Tallman, M.S.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. Role of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in the generation of the effects of imatinib mesylate (STI571) in BCR-ABL-expressing cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25345–25352. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, S.; McLaughlin, J.; Cheng, D.; Witte, O.N. Cell context-specific effects of the BCR-ABL oncogene monitored in hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 2003, 101, 4088–4097. [Google Scholar]
- Tzoanopoulos, D.; Speletas, M.; Arvanitidis, K.; Veiopoulou, C.; Kyriaki, S.; Thyphronitis, G.; Sideras, P.; Kartalis, G.; Ritis, K. Low expression of interferon regulatory factor-1 and identification of novel exons skipping in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 119, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, J.B.; Hassel, B.A. The interferon regulated ubiquitin-like protein, ISG15, in tumorigenesis: Friend or foe? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Penninger, J.; Karin, M. Immunity by ubiquitylation: A reversible process of modification. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 941–952. [Google Scholar]
- Bektas, N.; Noetzel, E.; Veeck, J.; Press, M.F.; Kristiansen, G.; Naami, A.; Hartmann, A.; Dimmler, A.; Beckmann, M.W.; Knuchel, R.; Fasching, P.A.; Dahl, E. The ubiquitin-like molecule interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) is a potential prognostic marker in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, R58. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, K.; Hofstra, R.; Pilz, A.; van den Berg, A.; Terpstra, P.; Buys, C.H.; Carritt, B. A gene in the chromosomal region 3p21 with greatly reduced expression in lung cancer is similar to the gene for ubiquitin-activating enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6071–6075. [Google Scholar]
- Malakhova, O.A.; Yan, M.; Malakhov, M.P.; Yuan, Y.; Ritchie, K.J.; Kim, K.I.; Peterson, L.F.; Shuai, K.; Zhang, D.E. Protein ISGylation modulates the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Q.; Pestka, S.; Fisher, P.B. Cloning and characterization of human ubiquitin-processing protease-43 from terminally differentiated human melanoma cells using a rapid subtraction hybridization protocol RaSH. Gene 2001, 267, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Sassano, A.; Dolniak, B.; Joshi, S.; Majchrzak-Kita, B.; Baker, D.P.; Hay, N.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. Role of the Akt pathway in mRNA translation of interferon-stimulated genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4808–4813. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Katsoulidis, E.; Platanias, L.C. Akt and mRNA translation by interferons. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2112–2116. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, S.; Uddin, S.; Platanias, L.C. The PI3' kinase pathway in interferon signaling. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005, 25, 780–787. [Google Scholar]
- Redig, A.J.; Platanias, L.C. Protein kinase C signalling in leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2008, 49, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, W.S. Suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS) in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 410–416. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Katsoulidis, E.; Kaur, S.; Platanias, L.C. Deregulation of Interferon Signaling in Malignant Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 406-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3020406
Katsoulidis E, Kaur S, Platanias LC. Deregulation of Interferon Signaling in Malignant Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(2):406-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3020406
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatsoulidis, Efstratios, Surinder Kaur, and Leonidas C. Platanias. 2010. "Deregulation of Interferon Signaling in Malignant Cells" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 2: 406-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3020406
APA StyleKatsoulidis, E., Kaur, S., & Platanias, L. C. (2010). Deregulation of Interferon Signaling in Malignant Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 3(2), 406-418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3020406



