A New Baroreceptor Sensitivity-Restoring Ca-Channel Blocker Diminishes Age-Related Morning Blood Pressure Increase in Hypertensive Patients: Open-Label Monitoring of Azelnidipine Treatment for Hypertension in the Early Morning (At-HOME) Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline characteristics
| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.1 ± 11.7 | |
| 15–<65, n (%) | 1168 (45.9) | |
| 65–<75, n (%) | 806 (31.7) | |
| 75–, n (%) | 571 (22.4) | |
| Female (%) | 53.6 | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.3 ± 3.6 | |
| Regular alcohol drinking (almost every day), n (%) | 460 (18.1) | |
| Current smoking, n (%) | 371 (14.6) | |
| Clinic SBP, mmHg | 157.5 ± 18.7 | |
| Clinic DBP, mmHg | 88.9 ± 13.4 | |
| Clinic pulse rate, beats/min | 74.8 ± 10.9 | |
| Morning SBP, mmHg | 156.9 ± 16.1 | |
| Morning DBP, mmHg | 89.7 ± 11.7 | |
| Morning pulse rate, beats/min | 72.1 ± 10.2 | |
| Evening SBP, mmHg | 150.2 ± 17.6 | |
| Evening DBP, mmHg | 85.6 ± 12.2 | |
| Evening pulse rate, beats/min | 72.5 ± 9.6 | |
| Heart disease, n (%) | 305 (12.0) | |
| Cerebrovascular disease, n (%) | 178 (7.0) | |
| Renal disease, n (%) | 106 (4.2) | |
| Previous antihypertensive medication, n (%) | 1407 (55.3) | |
| Calcium channel blocker | 591 (23.2) | |
| Angiotensin receptor blocker | 936 (36.8) | |
| ACE inhibitor | 156 (6.1) | |
| Diuretic | 159 (6.2) | |
| Alpha-blocker | 93 (3.7) | |
| Beta-blocker | 189 (7.4) | |
| Other | 42 (1.6) | |
| Timing of morning BP measurement, n (%) | ||
| Before breakfast and AZ dosing | 2,209 (86.8) | |
| Other | 337 (13.2) | |
2.2. Time-course of home BP and home pulse rate

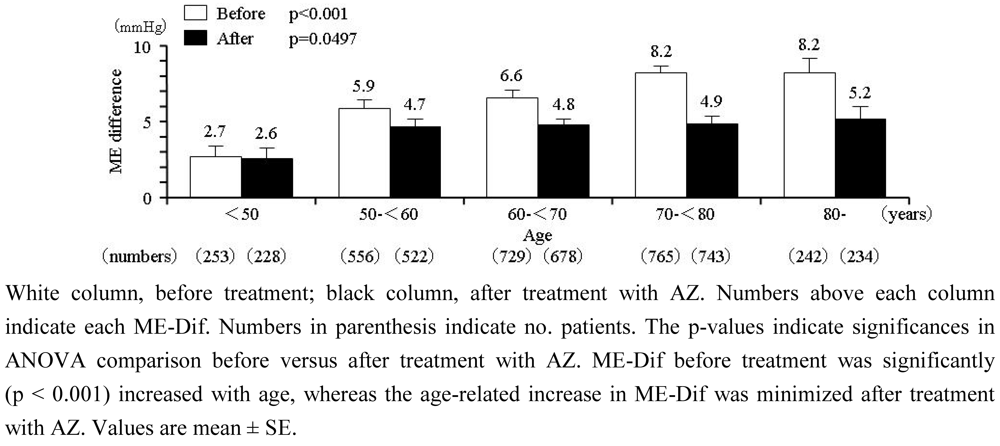
2.3. Time-course of ME-Ave and ME-Dif
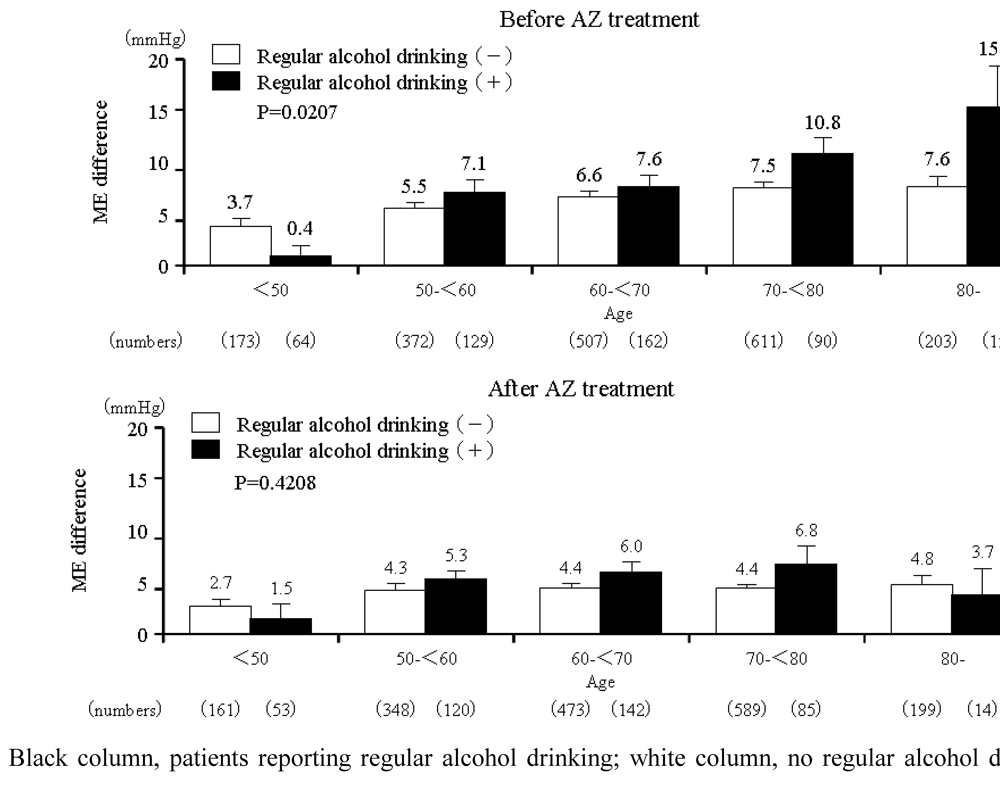
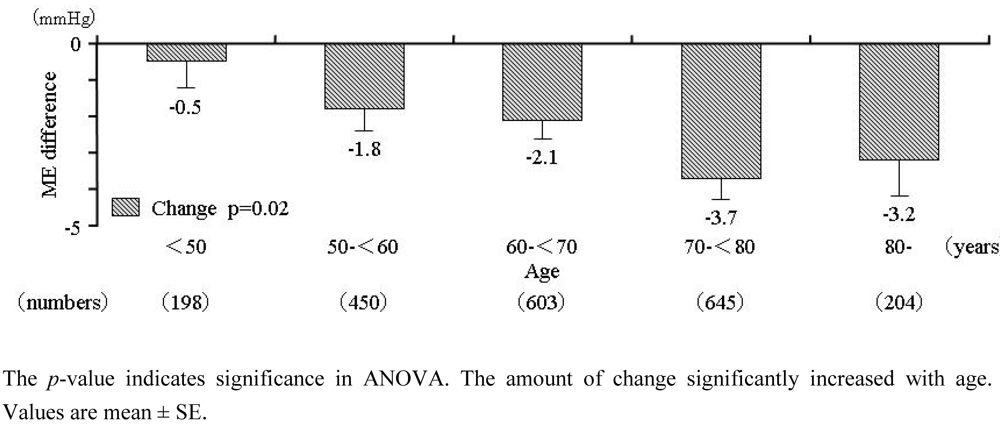
2.4. Relationship between ME-Dif and age
2.6. Safety
2.7. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Study design and participants
3.2. Drug administration
3.3. Blood pressure measurement
3.4. Alcohol drinking habits
3.5. Data analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Muller, J.E.; Tofler, G.H.; Stone, P.H. Circadian variation and triggers of onset of acute cardiovascular disease. Circulation 1989, 79, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohkubo, T.; Imai, Y.; Tsuji, I.; Nagai, K.; Kato, J.; Kikuchi, N.; Nishiyama, A.; Aihara, A.; Sekino, M.; Kikuya, M.; Ito, S.; Satoh, H.; Hisamichi, S. Home blood pressure measurement has a stronger predictive power for mortality than does screening blood pressure measurement: a population-based observation in Ohasama, Japan. J. Hypertens. 1998, 16, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kario, K.; Ishikawa, J.; Pickering, T.G.; Hoshide, S.; Eguchi, K.; Morinari, M.; Hoshide, Y.; Kuroda, T.; Shimada, K. Morning hypertension: the strongest independent risk factor for stroke in elderly hypertensive patients. Hypertens. Res. 2006, 29, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinaga, M.; Takata, J.; Okumiya, K.; Matsubayashi, K.; Ozawa, T.; Doi, Y. High morning home blood pressure is associated with a loss of functional independence in the community-dwelling elderly aged 75 years or older. Hypertens. Res. 2005, 28, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Gomi, T.; Shibuya, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Kosugi, T.; Oku, N.; Uetake, Y.; Kinugasa, S.; Furutera, R. Morning rise in blood pressure is a predictor of left ventricular hypertrophy in treated hypertensive patients. Hypertens. Res. 2004, 27, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Eguchi, K.; Shibasaki, S.; Shimizu, M.; Ishikawa, J.; Shimada, K.; Kario, K. Association between the morning–evening difference in home blood pressure and cardiac damage in untreated hypertensive patients . J. Hypertens. 2009, 27, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, J.; Kario, K.; Hoshide, S.; Eguchi, K.; Morinari, M.; Kaneda, R.; Umeda, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Kuroda, T.; Hojo, Y.; Shimada, K.; J-MORE Study Group. Determinants of exaggerated difference in morning and evening blood pressure measured by self-measured blood pressure monitoring in medicated hypertensive patients: Jichi Morning Hypertension Research (J-MORE) Study . Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribbin, B.; Pickering, T.G.; Sleight, P.; Petro, R. Effect of age and high blood pressure on baroreflex sensitivity in man. Circ. Res. 1971, 29, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.P.; Christou, D.D.; Jordan, J.; Seals, D.R. Baroreflex buffering is reduced with age in healthy men. Circulation 2003, 107, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramoto, K.; Ichikawa, S.; Hirai, A.; Kanada, S.; Nakachi, T.; Ogihara, T. Azelnidipine and amlodipine: a comparison of their pharmacokinetics and effect on ambulatory blood pressure. Hypertens. Res. 2003, 26, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Hashizume, T.; Tanigawa, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Nishio, H. A new Ca-antagonist, azelnidipine, reduced blood pressure during exercise without augmentation of sympathetic nervous system in essential hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1999, 33, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nada, T.; Nomura, M.; Koshiba, K.; Kawano, T.; Mikawa, J.; Ito, S. Clinical study with azelnidipine in patients with essential hypertension. Antiarteriosclerotic and cardiac hypertrophy-inhibitory effects and influence on autonomic nervous activity. Arzneimittelforschung 2007, 57, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Tomizawa, H.; Ishikawa, J.; Hoshide, S.; Fukuda, T.; Numao, T.; Shimada, K.; Kario, K. Effect of new calcium channel blocker, azelnidipine, and amulodipine on baroreflex sensitivity and ambulatory blood pressure. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2007, 49, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kario, K.; Sato, Y.; Shirayama, M.; Takahashi, M.; Shiosakai, K.; Hiramatsu, K.; Komiya, M.; Shimada, K. Inhibitory effects of azelnidipine (Calblock) tablet on early-morning hypertension (in Japanese). J. Clin. Ther. Med. 2008, 24, 1083–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Yagil, Y.; Lustig, A. Azelnidipine (CS-905), a novel dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker with gradual onset and prolonged duration of action. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 1995, 13, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, K.; Scott, L.J. Azelnidipine. Drugs 2003, 63, 2613–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Tochikubo, O.; Minamisawa, K.; Miyajima, E.; Ishii, M. Circadian variation of haemodynamics in patients with essential hypertension: comparison between early morning and evening. J. Hypertens. 1994, 12, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinenno, F.A.; Dietz, N.M.; Joyner, M.J. Aging and forearm postjunctional alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction in healthy men. Circulation 2002, 106, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.P.; Shapiro, L.F,; Keisling, G.A.; Jordan, J.; Shannon, J.R.; Quaife, R.A.; Seals, D.R. Altered autonomic support of arterial blood pressure with age in healthy men . Circulation 2001, 104, 2424–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochikubo, O.; Kawano, Y.; Miyajima, E.; Toshihiro, N.; Ishii, M. Circadian variation of hemodynamics and baroreflex functions in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 1997, 20, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y. Effects of alcohol consumption and restriction on home blood pressure in hypertensive patients: serial changes in the morning and evening records. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2002, 24, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grogan, J.R.; Kochar, M.S. Alcohol and hypertension. Arch. Fam. Med. 1994, 3, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panza, J.A.; Epstein, S.E.; Quyyumi, A.A. Circadian variation in vascular tone and its relation to alpha-sympathetic vasoconstrictor activity. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pickering, J.A.; Levenstein, M.; Walmsley, P. Nighttime dosing of doxazosin has peak effect on morning ambulatory blood pressure. Results of the HALT Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 1994, 7, 844–847. [Google Scholar]
- Kario, K.; Pickering, T.G.; Hoshide, S.; Eguchi, K.; Ishikawa, J.; Morinari, M.; Hoshide, Y.; Shimada, K. Morning blood pressure surge and hypertensive cerebrovascular disease: role of the alpha adrenergic sympathetic nervous system. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004, 17, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Gomi, T.; Shibuya, Y.; Shinozaki, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Matsuda, N. Add-on effect of bedtime dosing of the alpha(1)-adrenergic receptor antagonist doxazosin on morning hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy in patients undergoing long-term amlodipine monotherapy. Hypertens. Res. 2007, 30, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kario, K.; Shirayama, M.; Hiramatsu, K.; Shiosakai, K.; Sugiyama, M.; Shimada, K. A New Baroreceptor Sensitivity-Restoring Ca-Channel Blocker Diminishes Age-Related Morning Blood Pressure Increase in Hypertensive Patients: Open-Label Monitoring of Azelnidipine Treatment for Hypertension in the Early Morning (At-HOME) Study. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 225-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010225
Kario K, Shirayama M, Hiramatsu K, Shiosakai K, Sugiyama M, Shimada K. A New Baroreceptor Sensitivity-Restoring Ca-Channel Blocker Diminishes Age-Related Morning Blood Pressure Increase in Hypertensive Patients: Open-Label Monitoring of Azelnidipine Treatment for Hypertension in the Early Morning (At-HOME) Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(1):225-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010225
Chicago/Turabian StyleKario, Kazuomi, Masayuki Shirayama, Katsutoshi Hiramatsu, Kazuhito Shiosakai, Mitsunori Sugiyama, and Kazuyuki Shimada. 2010. "A New Baroreceptor Sensitivity-Restoring Ca-Channel Blocker Diminishes Age-Related Morning Blood Pressure Increase in Hypertensive Patients: Open-Label Monitoring of Azelnidipine Treatment for Hypertension in the Early Morning (At-HOME) Study" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 1: 225-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010225
APA StyleKario, K., Shirayama, M., Hiramatsu, K., Shiosakai, K., Sugiyama, M., & Shimada, K. (2010). A New Baroreceptor Sensitivity-Restoring Ca-Channel Blocker Diminishes Age-Related Morning Blood Pressure Increase in Hypertensive Patients: Open-Label Monitoring of Azelnidipine Treatment for Hypertension in the Early Morning (At-HOME) Study. Pharmaceuticals, 3(1), 225-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3010225