Development of Novel Proline- and Pipecolic Acid-Based Allosteric Inhibitors of Dengue and Zika Virus NS2B/NS3 Protease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
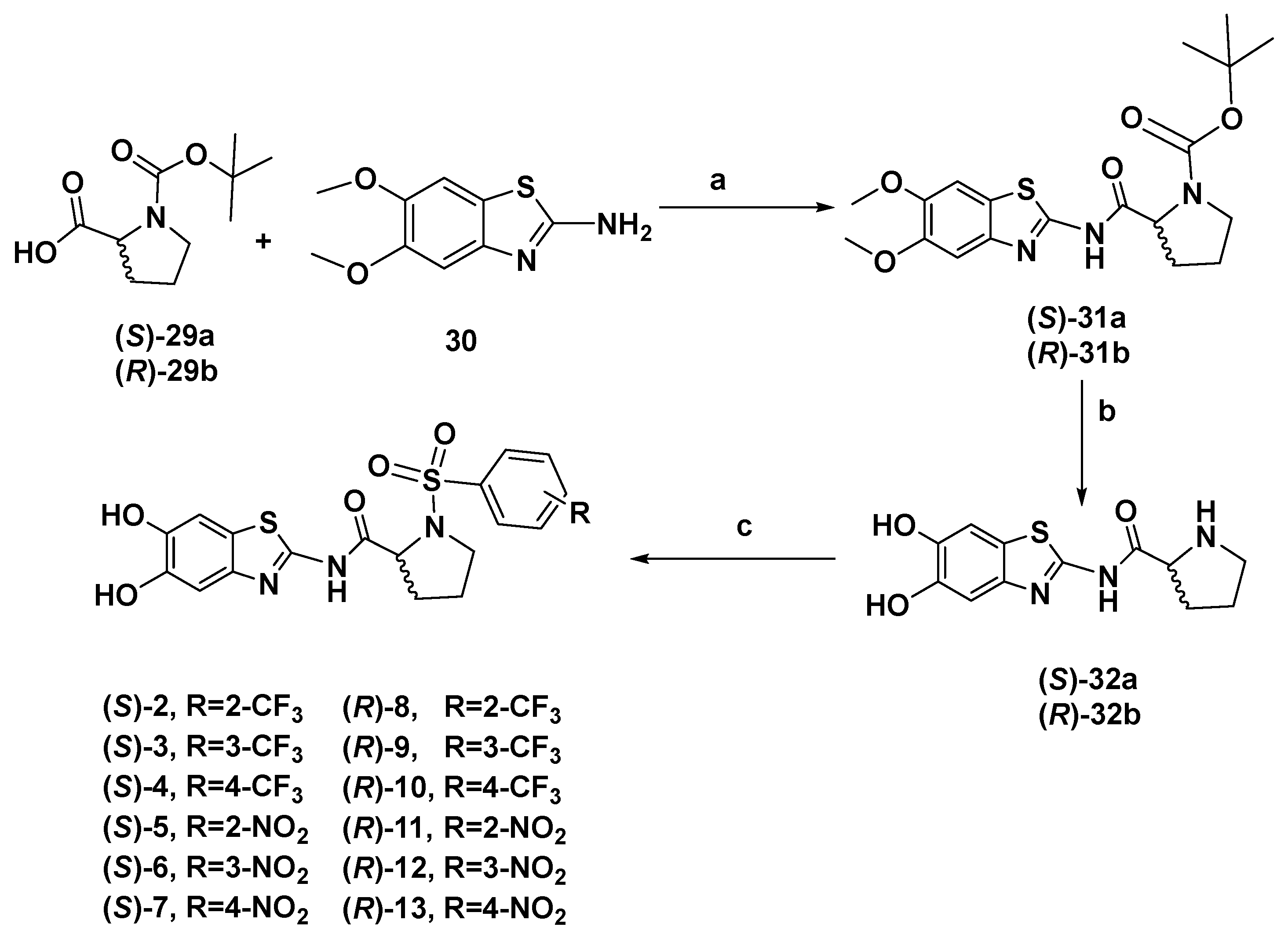
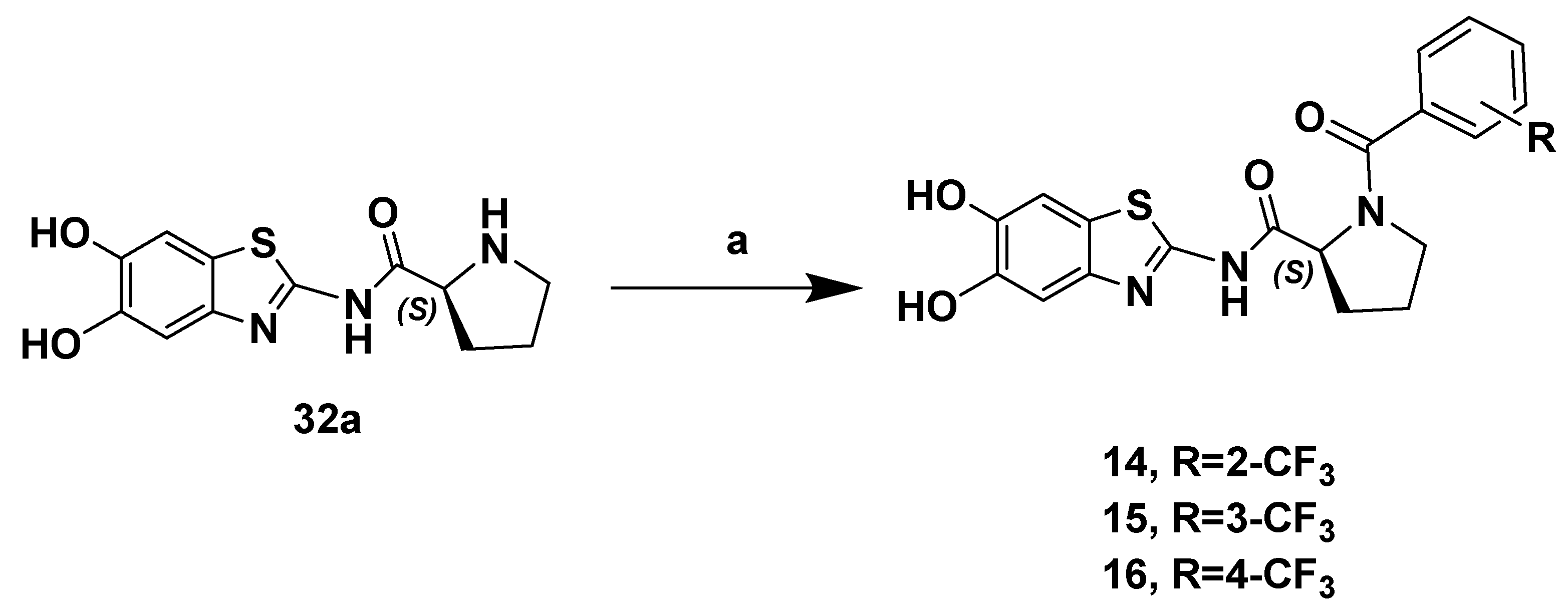
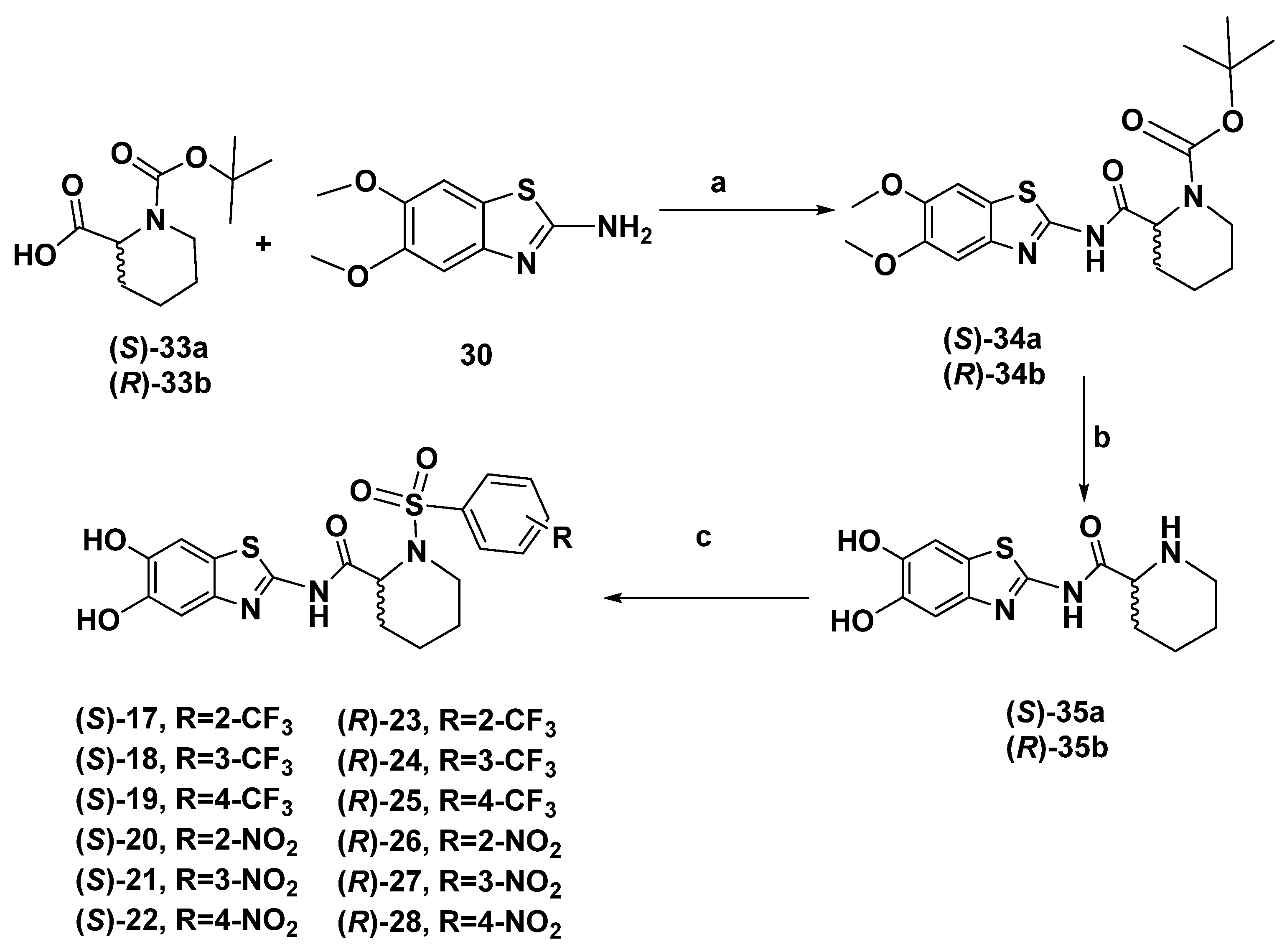
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Activity
2.3. Docking Studies and In Silico Investigation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Tert-butyl (S)-2-((5,6-Dimethoxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl) Carbamoyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (31a)
3.1.2. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (32a)
3.1.3. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((2-trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (2)
3.1.4. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((3-trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (3)
3.1.5. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (4)
3.1.6. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (5)
3.1.7. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (6)
3.1.8. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((4-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (7)
3.1.9. Tert-butyl (R)-2-((5,6-Dimethoxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (31b)
3.1.10. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (32b)
3.1.11. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((2-trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (8)
3.1.12. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((3-trifluoromethyl) phenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (9)
3.1.13. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (10)
3.1.14. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (11)
3.1.15. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (12)
3.1.16. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((4-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (13)
3.1.17. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (14)
3.1.18. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (15)
3.1.19. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-(4(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (16)
3.1.20. Tert-butyl (S)-2-((5,6-Dimethoxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl) Carbamoyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (34a)
3.1.21. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (35a)
3.1.22. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (17)
3.1.23. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (18)
3.1.24. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (19)
3.1.25. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (20)
3.1.26. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (21)
3.1.27. (S)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((4-nitrophenyl) sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (22)
3.1.28. Tert-butyl (R)-2-((5,6-Dimethoxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl) Carbamoyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (34b)
3.1.29. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (35b)
3.1.30. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (23)
3.1.31. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (24)
3.1.32. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (25)
3.1.33. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((2-nitrophenyl) sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (26)
3.1.34. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (27)
3.1.35. (R)-N-(5,6-Dihydroxybenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-1-((4-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide (28)
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. Protease Relative Inhibition Assay
3.2.2. Inhibitory Activity of Compounds Against Thrombin and Trypsin
3.2.3. Cell Culture
3.2.4. DENV2 Reporter Gene Assay (DENV2proHeLa)
3.2.5. Cytotoxicity
3.3. Molecular Modeling
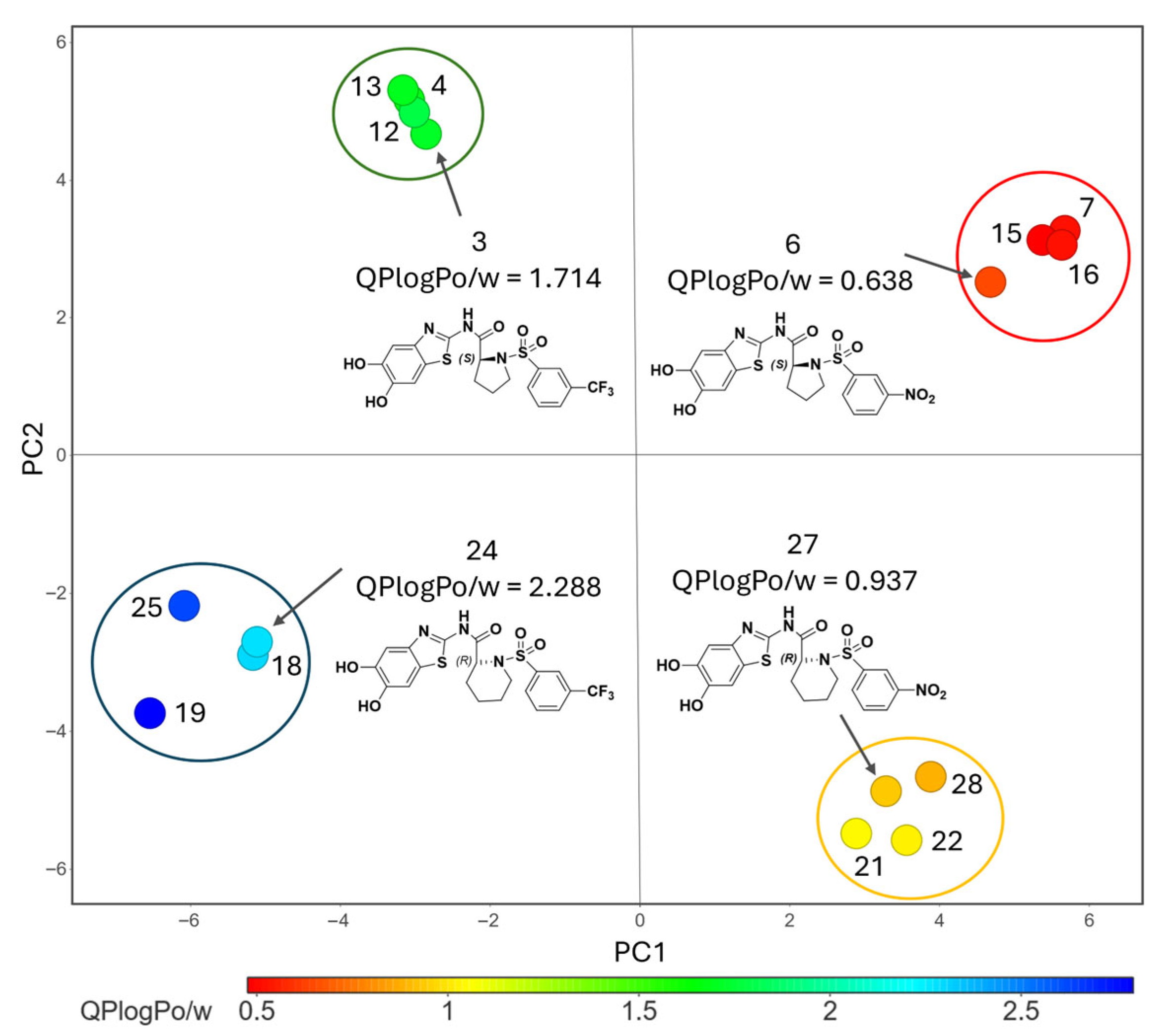
3.3.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
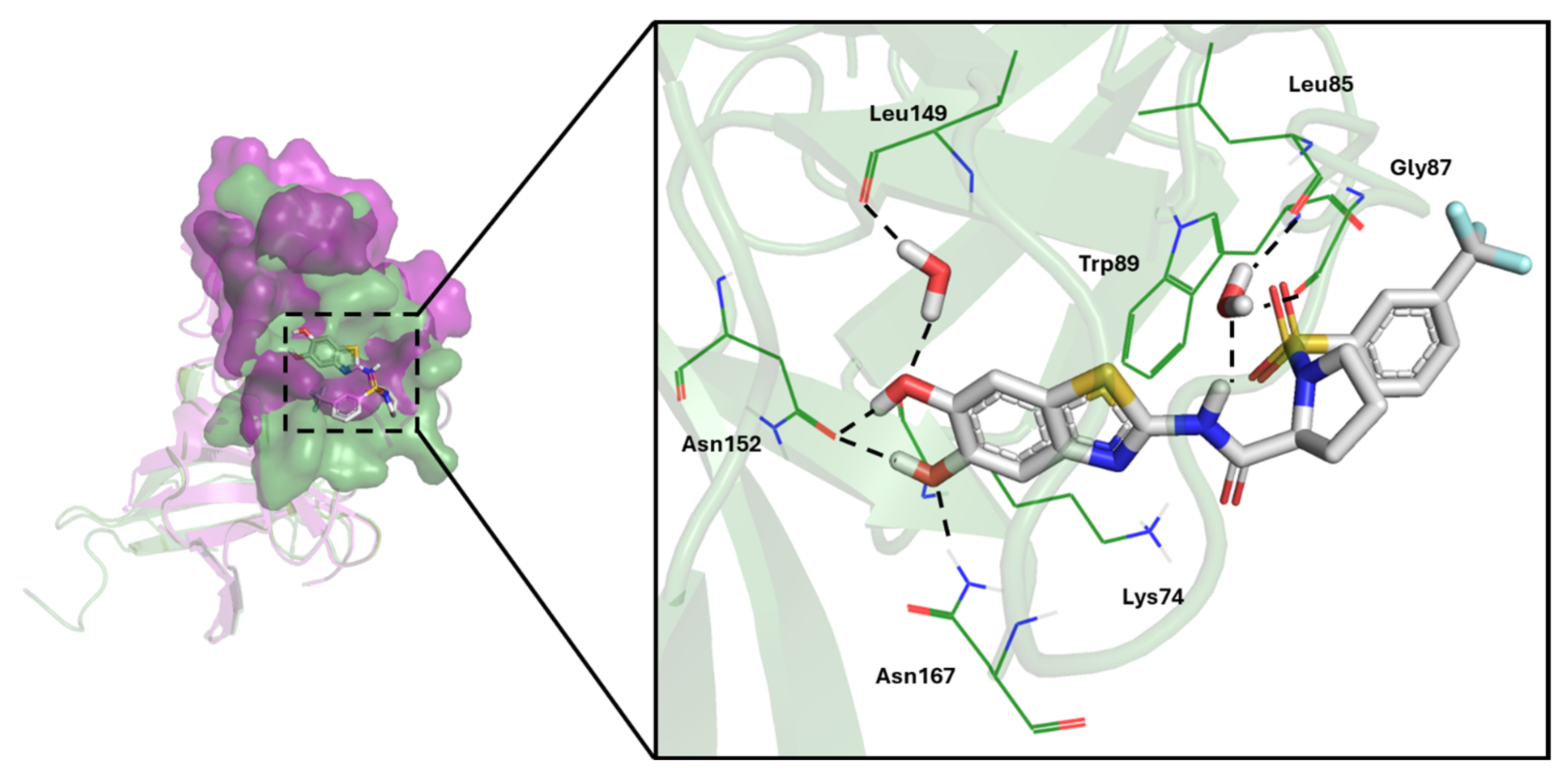
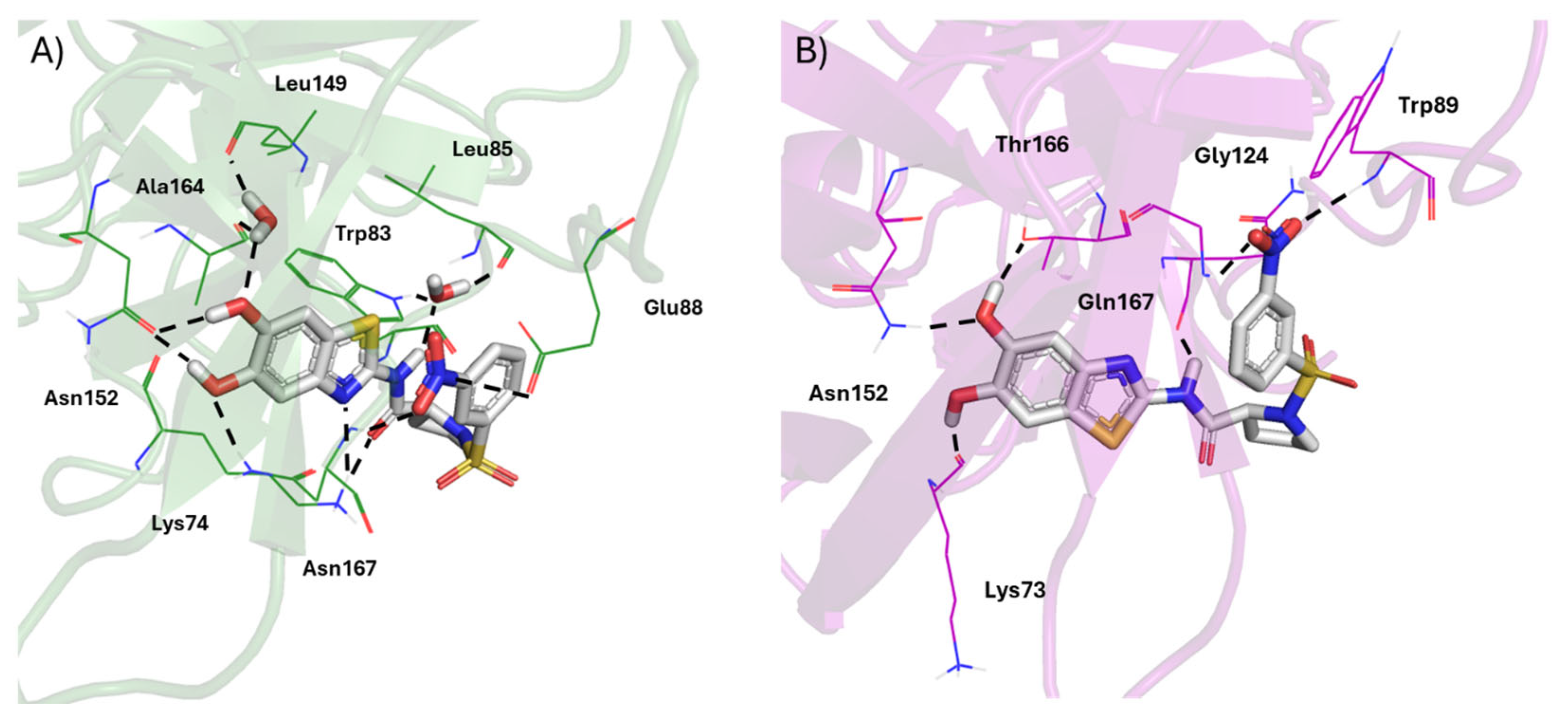
3.3.2. Cavity Detection
3.3.3. Docking Protocol Calibration
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEARO | South-East Asia Region |
| PAHO | Pan American Health Organization |
| WPRO | Western Pacific Region |
| EMRO | Eastern Mediterranean Region |
| EU | European Union |
| DENV | Dengue virus |
| ZIKV | Zika viruses |
| STING | stimulator of interferon genes |
| SAR | Structure–activity relationship |
| EWGs | electron-withdrawing groups |
References
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Dengue Monthly. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/dengue-monthly (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Dengue and Severe Dengue. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/dengue-and-severe-dengue (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Zika Virus. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/zika-virus (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.P.; Dao, T.H.; Tran, T.L.; Le, H.M.; Le, H.Q.; Le, N.T.; Pham, H.T.; Nguyen, H.T. Mechanical Transmission of Dengue Virus by Aedes aegypti May Influence Disease Transmission Dynamics during Outbreaks. EBioMedicine 2023, 94, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, G.S.; Bandeira, A.C.; Sardi, S.I. Zika Virus Outbreak, Bahia, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1885–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, D.; Gubler, D.J. Zika Virus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 487–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessey, M.; Fischer, M.; Staples, J.E. Zika Virus Spreads to New Areas—Region of the Americas, May 2015–January 2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazin, A.N.; Poretti, A.; Di Cavalcanti Souza Cruz, D.; Tenorio, M.; van der Linden, A.; Pena, L.J.; Brito, C.; Gil, L.H.V.; de Barros Miranda-Filho, D.; Marques, E.T.D.A.; et al. Computed Tomographic Findings in Microcephaly Associated with Zika Virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2193–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyenke, C.U.; Nnokam, B.A.; Esiere, R.K.; Nwalozie, R. Dengue Fever: Etiology, Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment. Asian J. Res. Infect. Dis. 2023, 14, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Lormeau, V.-M.; Blake, A.; Mons, S.; Lastère, S.; Roche, C.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Dub, T.; Baudouin, L.; Teissier, A.; Larre, P.; et al. Guillain-Barré Syndrome Outbreak Associated with Zika Virus Infection in French Polynesia: A Case-Control Study. Lancet 2016, 387, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder-Smith, A. TAK-003 Dengue Vaccine as a New Tool to Mitigate Dengue in Countries with a High Disease Burden. Lancet 2024, 12, e179–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, W.; Ma, H.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Dengue Virus Protease NS2B3 Cleaves cGAS, Antagonizing cGAS–STING Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1121889. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, S.; Maestre, A.M.; Pagni, S.; Patel, J.R.; Savage, T.; Gutman, D.; Maringer, K.; Bernal-Rubio, D.; Shabman, R.S.; Simon, V.; et al. DENV Inhibits Type I IFN Production in Infected Cells by Cleaving Human STING. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01960-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starvaggi, J.; Previti, S.; Zappalà, M.; Ettari, R. The Inhibition of NS2B/NS3 Protease: A New Therapeutic Opportunity to Treat Dengue and Zika Virus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zephyr, J.; Kurt Yilmaz, N.; Schiffer, C.A. Viral Proteases: Structure, Mechanism and Inhibition. Enzymes 2021, 50, 301–333. [Google Scholar]
- Phoo, W.W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, M.Y.; Loh, Y.R.; Tan, Y.B.; Ng, E.Y.; Lescar, J.; Kang, C.; Luo, D. Structure of the NS2B-NS3 Protease from Zika Virus after Self-Cleavage. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maus, M.; Den Boer, M.A.; Götz, R.; Klöckner, C.; Zhang, X.; Jansen, S.; Plevka, P.; Mulder, B.; Tompa, P.; Heck, A.J.R.; et al. A Competition smFRET Assay to Study Ligand-Induced Conformational Changes of the Dengue Virus Protease. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4526. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, S.; Braun, N.J.; Schmacke, L.C.; Murra, R.; Bender, D.; Hildt, E.; Heine, A.; Steinmetzer, T. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of New Macrocyclic Active Site-Directed Inhibitors of the Zika Virus NS2B-NS3 Protease. Arch. Pharm. 2024, 357, e2400250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Braun, N.J.; Schmacke, L.C.; Quek, J.P.; Murra, R.; Bender, D.; Hildt, E.; Luo, D.; Heine, A.; Steinmetzer, T. Structure-Based Optimization and Characterization of Macrocyclic Zika Virus NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 6555–6572. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, N.A.; Quek, J.P.; Schroeder, B.; Morewood, R.; Rademann, J.; Luo, D.; Nitsche, C. 2-Cyanoisonicotinamide Conjugation: A Facile Approach to Generate Potent Peptide Inhibitors of the Zika Virus Protease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, N.J.; Quek, J.P.; Huber, S.; Kouretova, J.; Rogge, D.; Lang-Henkel, H.; Cheong, E.Z.K.; Chew, B.L.A.; Heine, A.; Luo, D.; et al. Structure-Based Macrocyclization of Substrate Analogue NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors of Zika, West Nile and Dengue Viruses. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Z.; Shao, X.; Graf, D.; Wang, C.; Klein, C.D.; Wang, J.; Zhou, G.C. Identification of Fused Bicyclic Derivatives of Pyrrolidine and Imidazolidinone as Dengue Virus-2 NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, C.; Zhang, L.; Weigel, L.F.; Schilz, J.; Graf, D.; Bartenschlager, R.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Klein, C.D. Peptide-Boronic Acid Inhibitors of Flaviviral Proteases: Medicinal Chemistry and Structural Biology. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavina, L.; Bouma, M.J.; Gironés, D.; Feiters, M.C. Orthoflaviviral Inhibitors in Clinical Trials, Preclinical In Vivo Efficacy Targeting NS2B-NS3 and Cellular Antiviral Activity via Competitive Protease Inhibition. Molecules 2024, 29, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecher, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Koetzner, C.A.; Alifarag, A.; Jones, S.A.; Lin, Q.; Kramer, L.D.; Li, H. A Conformational Switch High-Throughput Screening Assay and Allosteric Inhibition of the Flavivirus NS2B-NS3 Protease. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millies, B.; von Hammerstein, F.; Gellert, A.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Barthels, F.; Goppel, U.; Immerheiser, M.; Elgner, F.; Jung, N.; Basic, M.; et al. Proline-Based Allosteric Inhibitors of Zika and Dengue Virus NS2B/NS3 Proteases. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 11359–11382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbel, P.; Schiering, N.; D’Arcy, A.; Renatus, M.; Kroemer, M.; Lim, S.P.; Yin, Z.; Keller, T.H.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Hommel, U.; et al. Structural Basis for the Activation of Flaviviral NS3 Proteases from Dengue and West Nile Virus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Loh, Y.R.; Phoo, W.W.; Hung, A.W.; Kang, C.; Luo, D. Crystal Structure of Unlinked NS2B-NS3 Protease from Zika Virus. Science 2016, 354, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnam, M.A.M.; Nitsche, C.; Vechi, S.M.; Klein, C.D. C-Terminal Residue Optimization and Fragment Merging: Discovery of a Potent Peptide-Hybrid Inhibitor of Dengue Protease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnam, M.A.M.; Graf, D.; Bartenschlager, R.; Zlotos, D.P.; Klein, C.D. Discovery of Nanomolar Dengue and West Nile Virus Protease Inhibitors Containing a 4-Benzyloxyphenylglycine Residue. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9354–9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Dutta, S.K.; Leuthold, M.M.; Reichert, L.; Kuhl, N.; Martina, B.; Klein, C.D. Antiviral Drug Discovery with an Optimized Biochemical Dengue Protease Assay: Improved Predictive Power for Antiviral Efficacy. Antivir. Res. 2024, 234, 106053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, N.; Graf, D.; Bock, J.; Behnam, M.A.M.; Leuthold, M.-M.; Klein, C.D. A New Class of Dengue and West Nile Virus Protease Inhibitors with Submicromolar Activity in Reporter Gene DENV-2 Protease and Viral Replication Assays. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8179–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabski, H.; Grabska, S.; Abagyan, R. Identifying Allosteric Small-Molecule Binding Sites of Inactive NS2B-NS3 Proteases of Pathogenic Flaviviridae. Viruses 2024, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carofiglio, F.; Tonnarini, G.; Malandrino, F.; Caligiuri, I.; Musumeci, D.; Dal Piaz, F.; Bellucci, M.C. Bcr-Abl Allosteric Inhibitors: Where We Are and Where We Are Going To. Molecules 2020, 25, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meewan, I.; Shiryaev, S.A.; Kattoula, J.; Huang, C.-T.; Lin, V.; Chuang, C.-H.; Terskikh, A.V.; Abagyan, R. Allosteric Inhibitors of Zika Virus NS2B–NS3 Protease Targeting Protease in “Super-Open” Conformation. Viruses 2023, 15, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, C.; Klein, C.D. Fluorimetric and HPLC-Based Dengue Virus Protease Assays Using a FRET Substrate. In Antiviral Methods and Protocols; Gong, E.Y., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 221–236. [Google Scholar]
- Di Chio, C.; Previti, S.; De Luca, F.; Bogacz, M.; Zimmer, C.; Wagner, A.; Schirmeister, T.; Zappalà, M.; Ettari, R. Drug Combination Studies of the Dipeptide Nitrile CD24 with Curcumin: A New Strategy to Synergistically Inhibit Rhodesain of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Hansen, G.; Nitsche, C.; Klein, C.D.; Zhang, L.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal Structure of Zika Virus NS2B-NS3 Protease in Complex with a Boronate Inhibitor. Science 2016, 353, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, C.; Schreier, V.N.; Behnam, M.A.M.; Kumar, A.; Bartenschlager, R.; Klein, C.D. Thiazolidinone–Peptide Hybrids as Dengue Virus Protease Inhibitors with Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8389–8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, N.; Leuthold, M.M.; Behnam, M.A.M.; Klein, C.D. Beyond Basicity: Discovery of Nonbasic DENV-2 Protease Inhibitors with Potent Activity in Cell Culture. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 4567–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2024-1: QikProp; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2025.
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An Open Source Program for Chemistry Aware Data Visualization and Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottin, M.; Caesar, L.K.; Brodsky, D.; Mesquita, N.C.M.R.; de Oliveira, K.Z.; Noske, G.D.; Sousa, B.K.P.; Ramos, P.R.P.S.; Jarmer, H.; Loh, B.; et al. Chalcones from Angelica keiskei (Ashitaba) Inhibit Key Zika Virus Replication Proteins. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 120, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2024-1: Protein Preparation Workflow; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC.; Impact, Schrödinger, LLC.; Prime, Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Schrödinger Release 2024-1: Force Fields; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a Chemical Language and Information System. 1. Introduction to Methodology and Encoding Rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2024-1: LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Schrödinger Release 2024-1: Glide; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Schrödinger Release 2024-1: IFD; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Schrödinger, LLC. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 3.0; Schrödinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024. Available online: https://pymol.org/2/ (accessed on 13 November 2025).
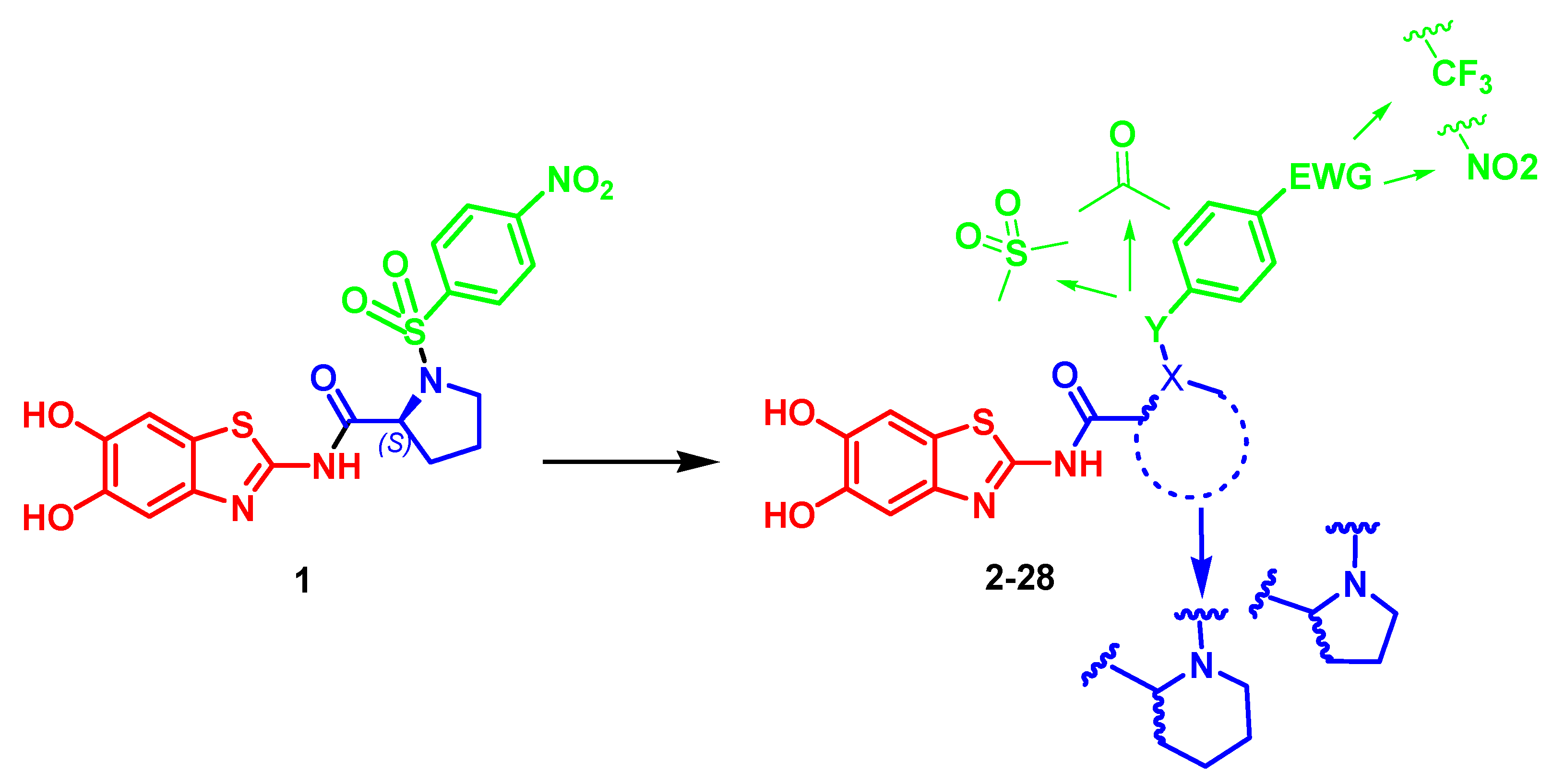
| COMP | n | Y | R | DENV | ZIKV | DENV2 proHeLa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % inhibition at 50 µM or IC50 µM | % inhibition at 50 µM or IC50 µM | % inhibition at 25 µM or EC50 µM | |||||
| MB-8 | 33.2% | 44.8% | - | ||||
| MB-53 | 89.0% | 82.3% | - | ||||
| 2 | (S) | 1 | SO2 | 2-CF3 | 5.1 ± 0.29 µM | 49.6% | 27.7% |
| 3 | (S) | 1 | SO2 | 3-CF3 | 5.0 ± 0.29 µM | 36.6% | 46.6% |
| 4 | (S) | 1 | SO2 | 4-CF3 | 5.6 ± 0.39µM | 35.4% | 19.5% |
| 5 | (S) | 1 | SO2 | 2-NO2 | 8.0 ± 0.52 µM | 8.8 ± 0.54 µM | 18.5% |
| 6 | (S) | 1 | SO2 | 3-NO2 | 6.4 ± 0.52 µM | 8.5 ± 0.23 µM | 23.5% |
| 7 | (S) | 1 | SO2 | 4-NO2 | 5.0 ± 0.37 µM | 4.6 ± 0.15 µM | 43.0% |
| 8 | (S) | 1 | CO | 2-CF3 | n.i. | n.i. | n.i. |
| 9 | (S) | 1 | CO | 3-CF3 | 55.9% | 56.5% | 42.2% |
| 10 | (S) | 1 | CO | 4-CF3 | 16.8% | 39.2% | 15.4% |
| 11 | (R) | 1 | SO2 | 2-CF3 | 40.0% | 64.8% | 48.9% |
| 12 | (R) | 1 | SO2 | 3-CF3 | 28.2% | 67.9% | 32.1% |
| 13 | (R) | 1 | SO2 | 4-CF3 | 35.0% | 38.8% | 33.9% |
| 14 | (R) | 1 | SO2 | 2-NO2 | 13.5% | 68.5% | 17.7% |
| 15 | (R) | 1 | SO2 | 3-NO2 | 16.9% | 54.6% | 26.9% |
| 16 | (R) | 1 | SO2 | 4-NO2 | 40.7% | 8.7 ± 0.4 µM | 51.3% |
| 17 | (S) | 2 | SO2 | 2-CF3 | 58.7% | 57.2% | 41.7% |
| 18 | (S) | 2 | SO2 | 3-CF3 | 55.9% | 42.2% | 12.8 ± 0.99 µM |
| 19 | (S) | 2 | SO2 | 4-CF3 | 51.3% | 18.3 ± 0.82 µM | 20.3 ± 1.5 µM |
| 20 | (S) | 2 | SO2 | 2-NO2 | 29.6% | 20.9 ± 0.87 µM | 31.4% |
| 21 | (S) | 2 | SO2 | 3-NO2 | n.i. | 13.8 ± 1.8 µM | 22.0 ± 1.5 µM |
| 22 | (S) | 2 | SO2 | 4-NO2 | 59.8% | 11.9 ± 0.32 µM | 13.4 ± 1.2 µM |
| 23 | (R) | 2 | SO2 | 2-CF3 | 41.8 ± 2.2 µM | 36.2% | 18.5% |
| 24 | (R) | 2 | SO2 | 3-CF3 | 30.8 ± 1.7 µM | 34.5% | 5.2 ± 0.43 µM |
| 25 | (R) | 2 | SO2 | 4-CF3 | 22.3 ± 1.4 µM | 48.4% | 38.0% |
| 26 | (R) | 2 | SO2 | 2-NO2 | 38.9 ± 4.0 µM | 12.1 ± 0.48 µM | 9.5% |
| 27 | (R) | 2 | SO2 | 3-NO2 | 35.0 ± 2.1 µM | 12.3 ± 0.35 µM | 5.1 ± 0.53 µM |
| 28 | (R) | 2 | SO2 | 4-NO2 | 27.0 ± 1.6 µM | 10.6 ± 0.30 µM | 9.0 ± 0.40 µM |
| BioGPS Pocket Residues | |
|---|---|
| Dengue NS2B/NS3 protease | NS3: Met49, Trp69, Lys73, Lys74, Leu76, Trp83, Leu85, Glu86, Gly87, Glu88, Trp89, Thr118, Asn119, Thr120, Gly121, Thr122, Ile123, Gly124, Val146, Val147, Gly148, Leu149, Asn152, Val154, Val155, Ala164, Ile165, Ala166, Asn167 |
| Zika NS2B/NS3 protease | NS2B: Asp75, Val76, Ala77, Leu78, Phe84, Ser85, Leu86, Val87NS3: Lys73, Gln74, Leu76, Ala87, Ala88, Trp89, Asp90, Gly91, Gly114, Ile115, Phe116, Lys117, Thr118, Lys119, Asp120, Gly121, Asp122, Ile123, Gly124, Ile147, Asn152, Ala164, Ile165, Thr166, Gln167, Gly168 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Starvaggi, J.; Di Chio, C.; Lang, J.; Belgiovine, V.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Previti, S.; Klein, C.; Nicolotti, O.; Di Maro, S.; Zappalà, M.; et al. Development of Novel Proline- and Pipecolic Acid-Based Allosteric Inhibitors of Dengue and Zika Virus NS2B/NS3 Protease. Pharmaceuticals 2026, 19, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19010024
Starvaggi J, Di Chio C, Lang J, Belgiovine V, Trisciuzzi D, Previti S, Klein C, Nicolotti O, Di Maro S, Zappalà M, et al. Development of Novel Proline- and Pipecolic Acid-Based Allosteric Inhibitors of Dengue and Zika Virus NS2B/NS3 Protease. Pharmaceuticals. 2026; 19(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleStarvaggi, Josè, Carla Di Chio, Johannes Lang, Valentina Belgiovine, Daniela Trisciuzzi, Santo Previti, Christian Klein, Orazio Nicolotti, Salvatore Di Maro, Maria Zappalà, and et al. 2026. "Development of Novel Proline- and Pipecolic Acid-Based Allosteric Inhibitors of Dengue and Zika Virus NS2B/NS3 Protease" Pharmaceuticals 19, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19010024
APA StyleStarvaggi, J., Di Chio, C., Lang, J., Belgiovine, V., Trisciuzzi, D., Previti, S., Klein, C., Nicolotti, O., Di Maro, S., Zappalà, M., & Ettari, R. (2026). Development of Novel Proline- and Pipecolic Acid-Based Allosteric Inhibitors of Dengue and Zika Virus NS2B/NS3 Protease. Pharmaceuticals, 19(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19010024












