Echinops as a Source of Bioactive Compounds—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
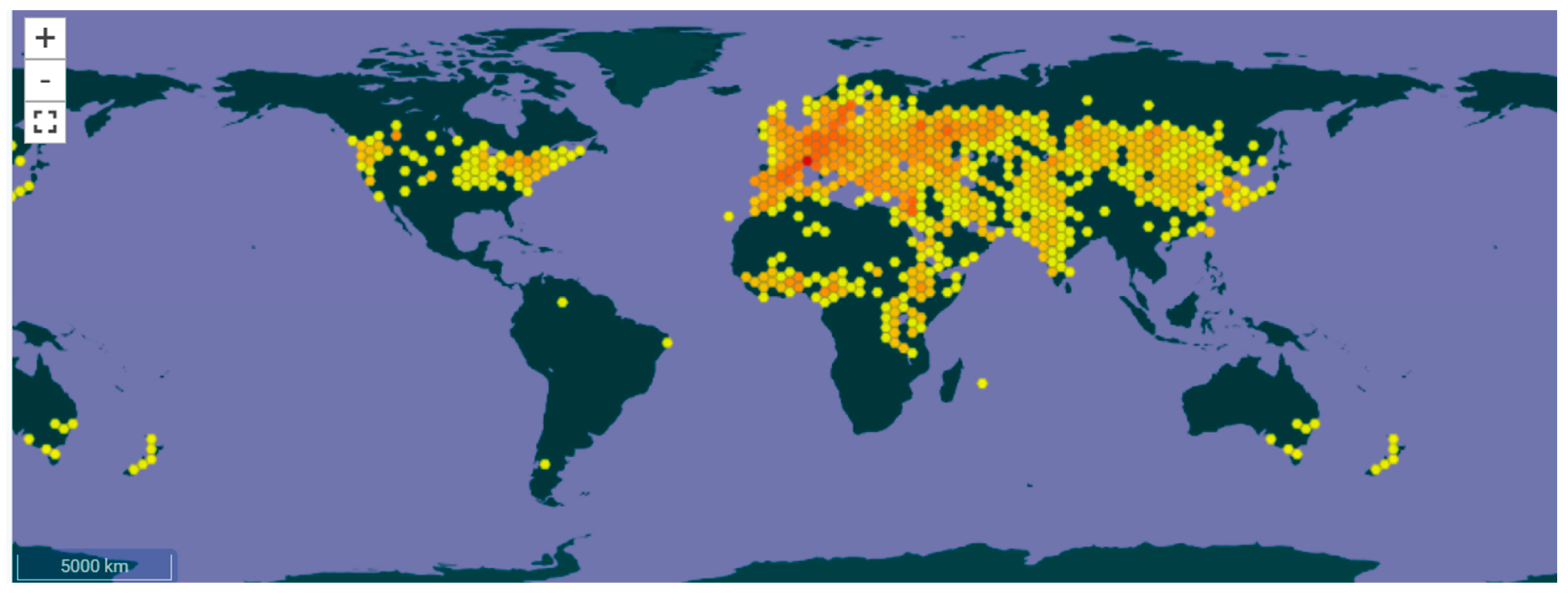
Botanical Identity, Taxonomy, and Cultivation
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thiophenes
3.2. Terpenes
3.3. Flavonoids
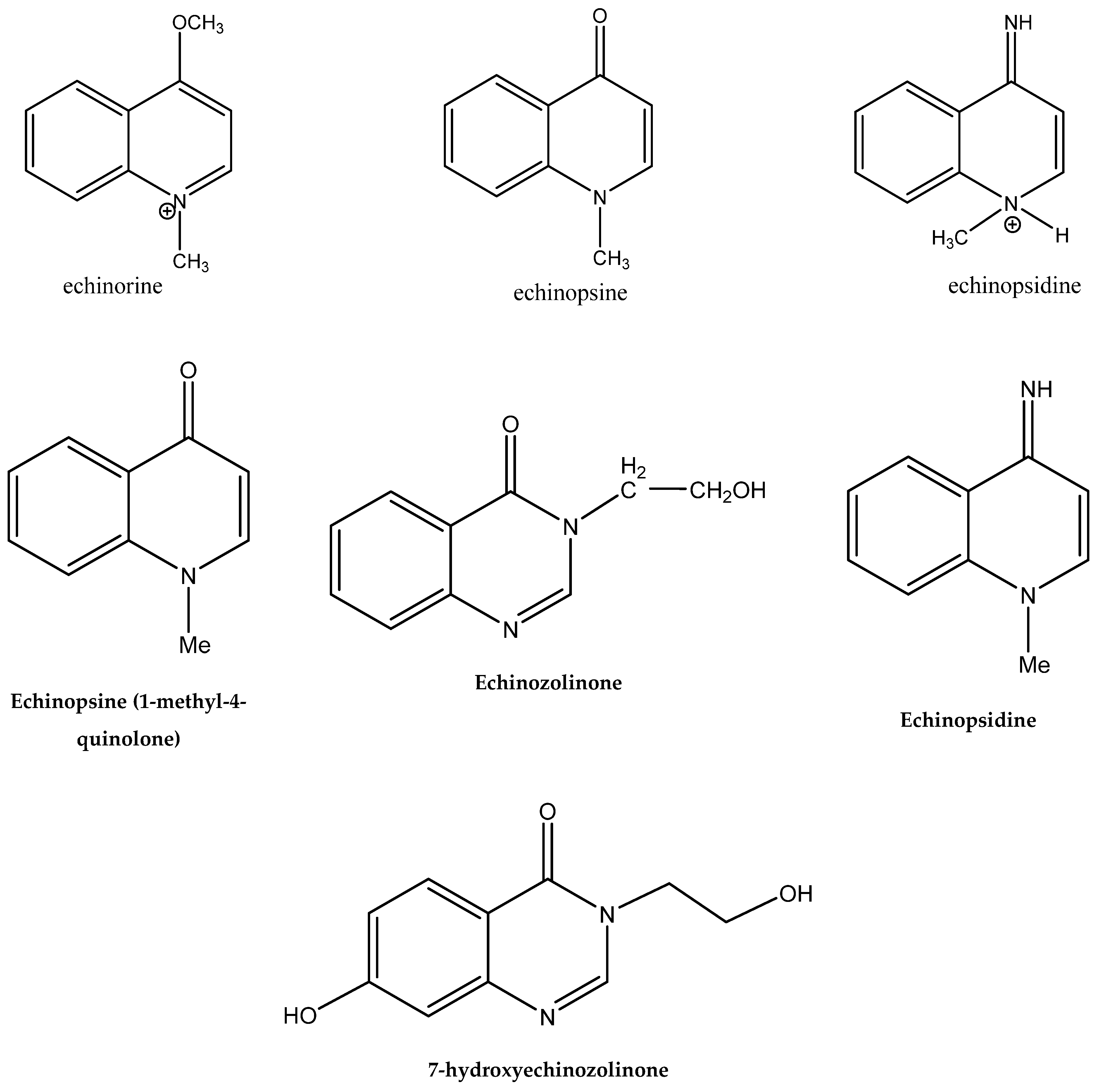
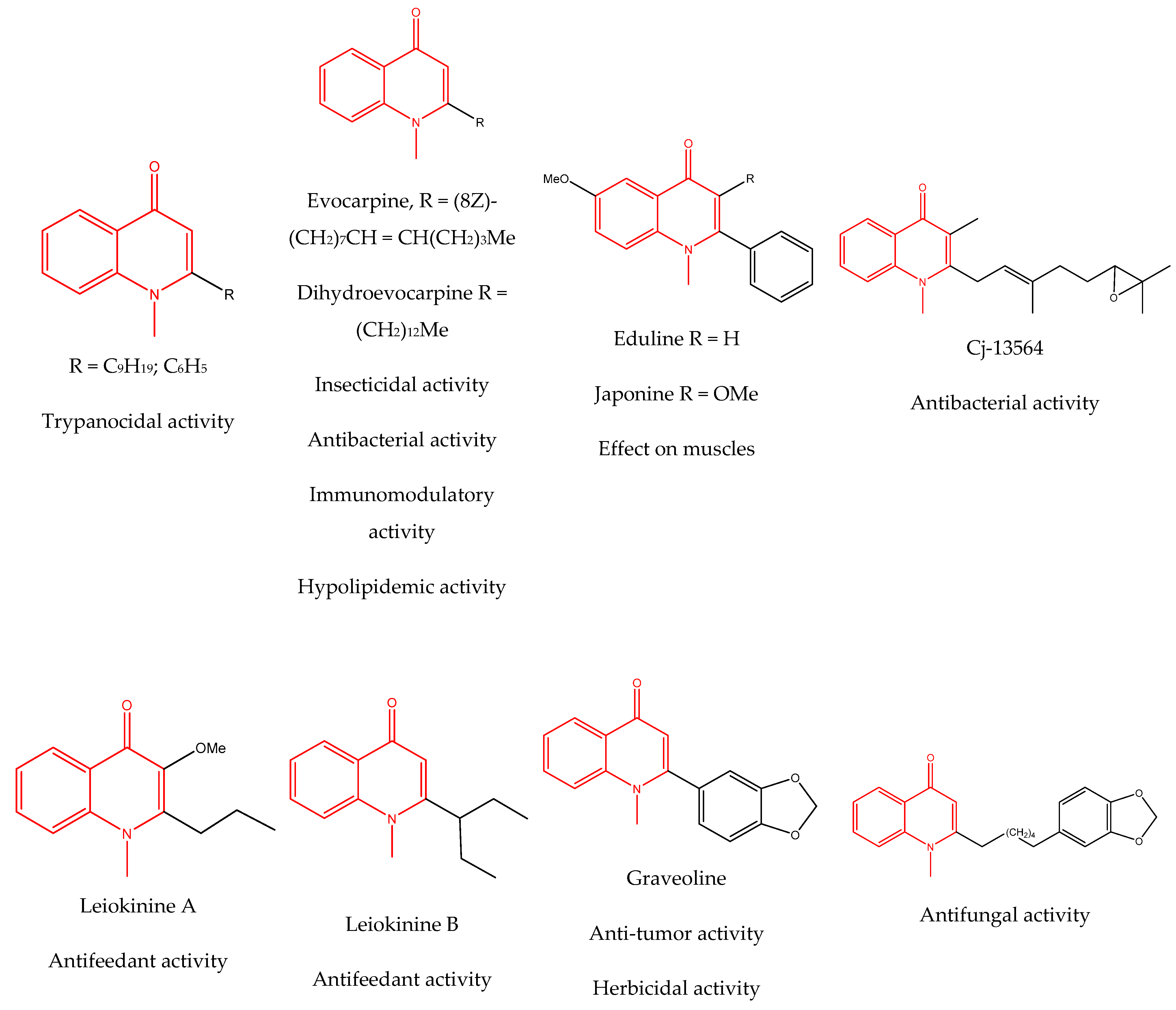
3.4. Alkaloids
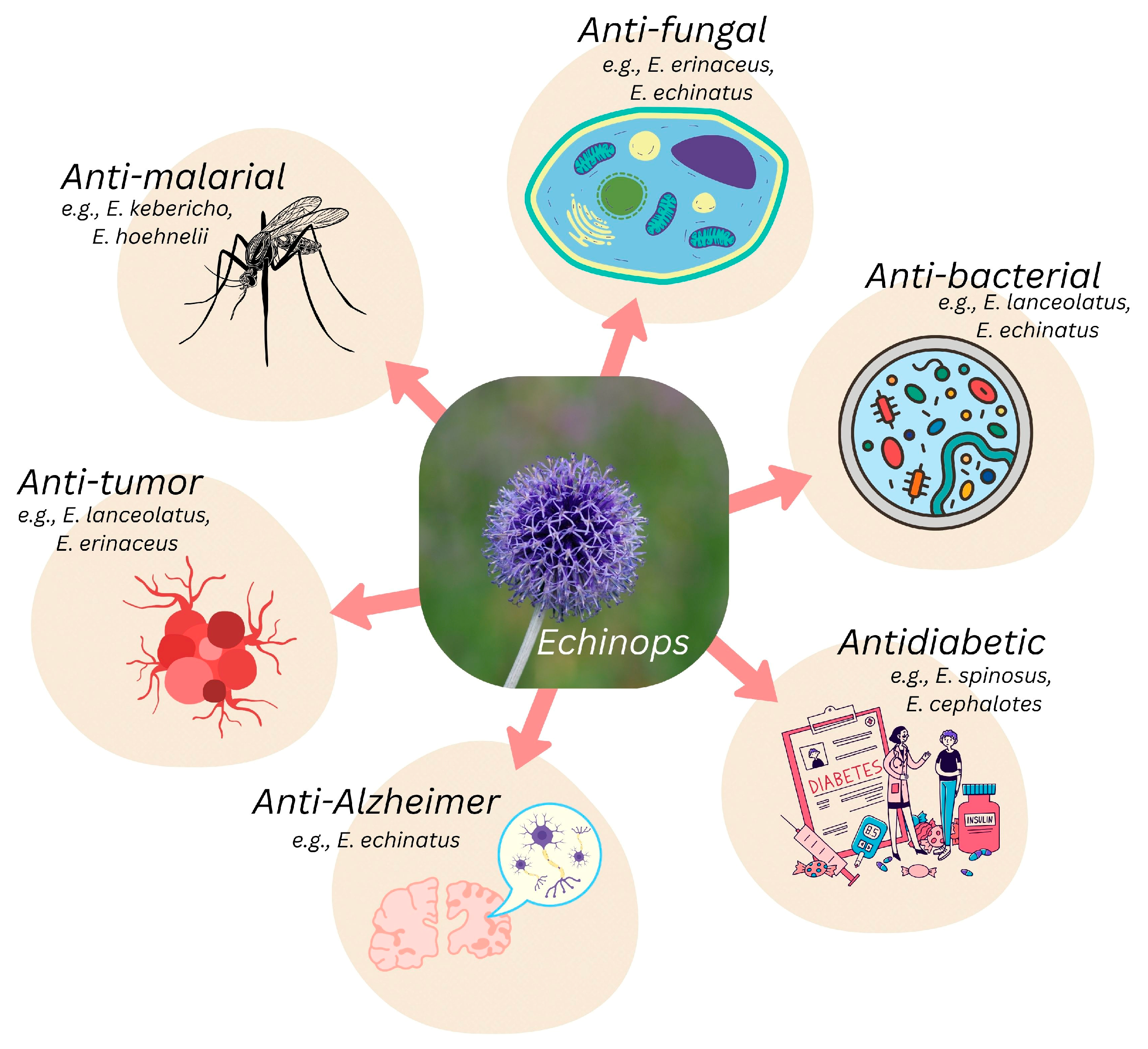
3.5. Therapeutic Potential of the Genus Echinops
3.5.1. Antioxidant Activity
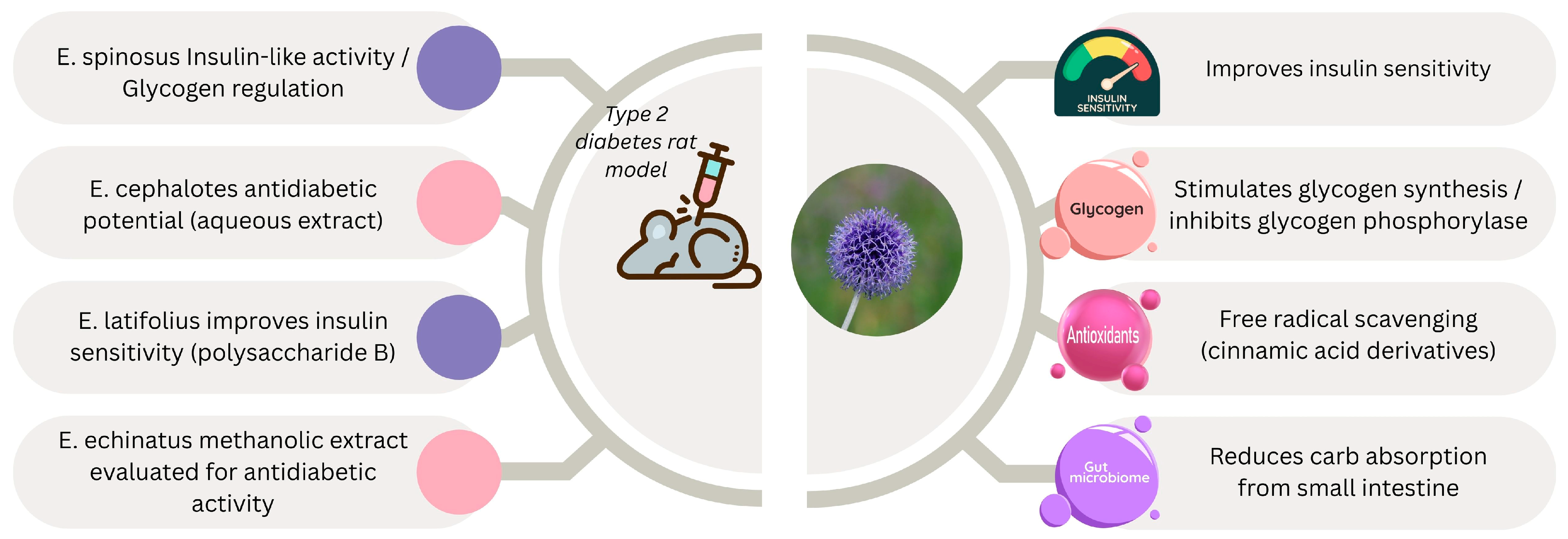
3.5.2. Antidiabetic Properties
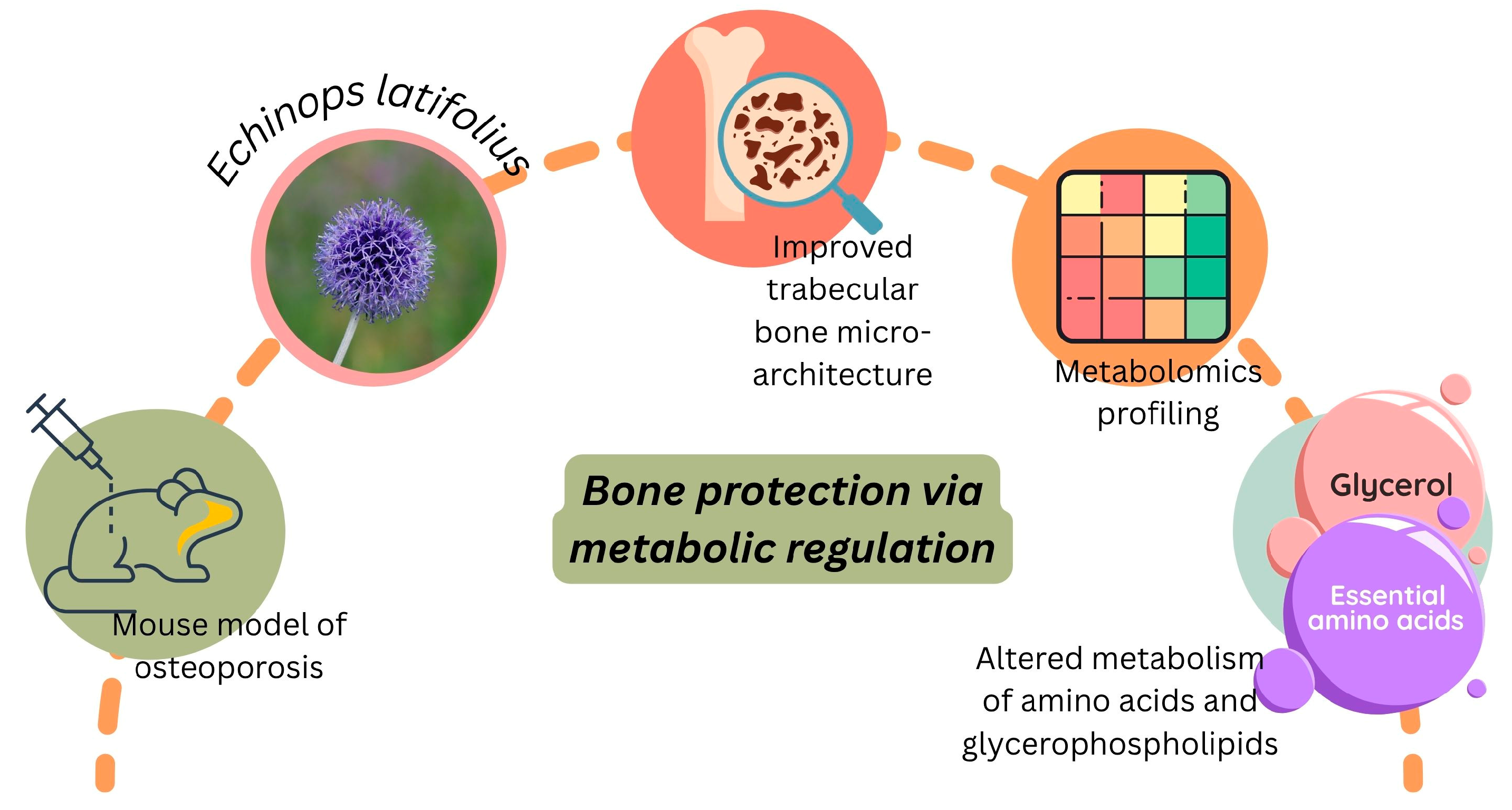
3.5.3. Anti-Osteoporosis Efficacy of Echinops latifolius
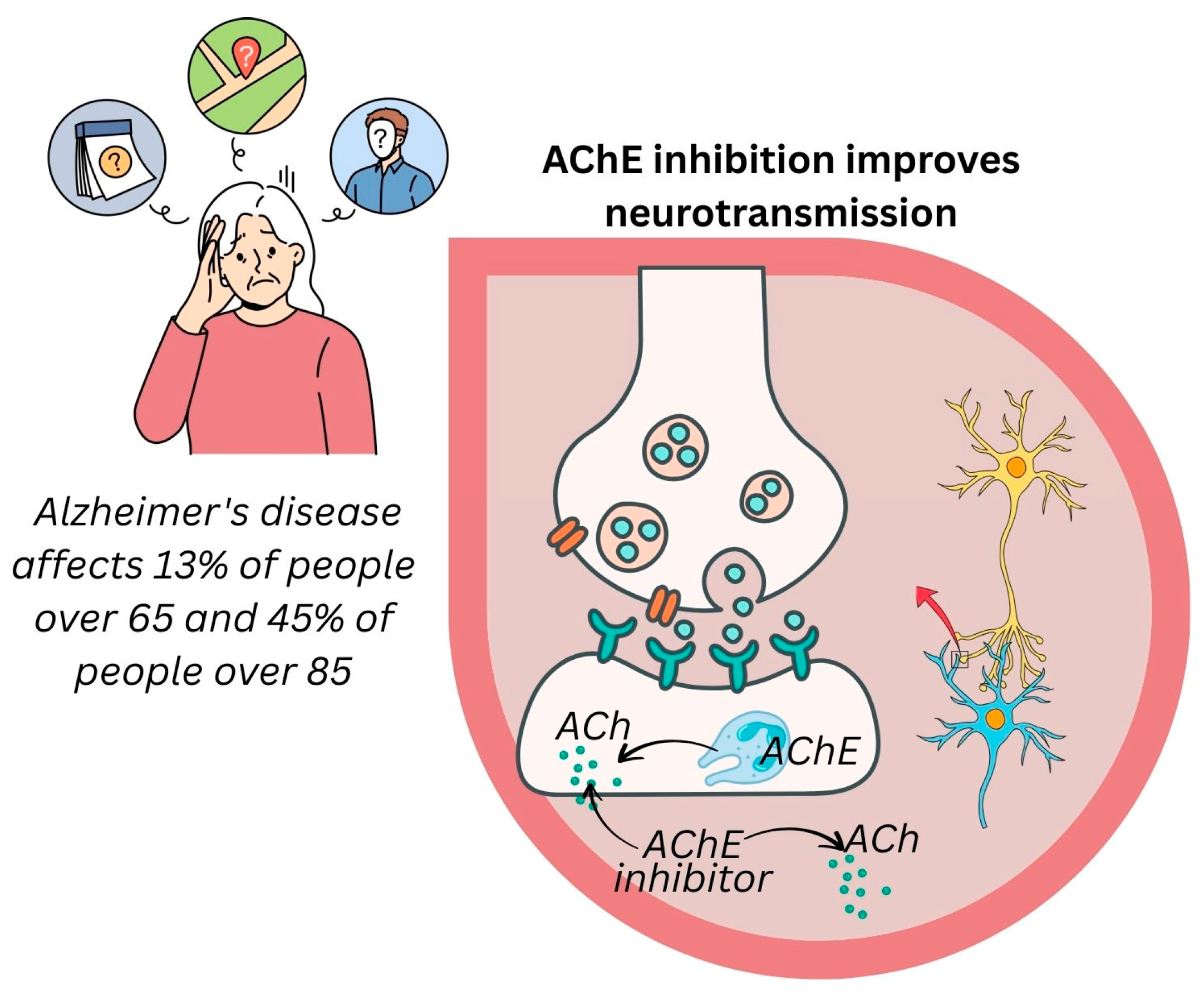
3.5.4. Alzheimer’s Disease Prevention
3.5.5. Antimicrobial Activities
3.5.6. Insecticidal Properties
3.5.7. Anti-Malarial Activity
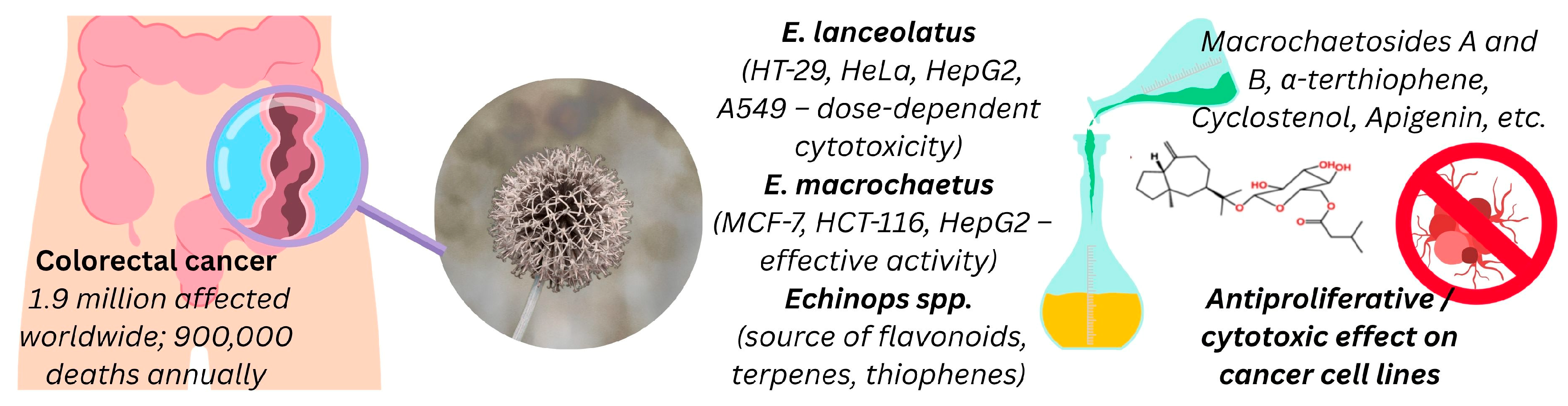
3.5.8. Cytotoxicity
3.5.9. Food Supplement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garnatje, T.; Vallès, J.; Garcia, S.; Hidalgo, O.; Sanz, M.; Canela, M.Á.; Siljak-Yakovlev, S. Genome Size in Echinops L. and Related Genera (Asteraceae, Cardueae): Karyological, Ecological and Phylogenetic Implications. Biol. Cell 2004, 96, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnatje, T.; Susanna, A.; Garcia-Jacas, N.; Vilatersana, R.; Vallès, J. A First Approach to the Molecular Phylogeny of the GenusEchinops (Asteraceae): Sectional Delimitation and Relationships with the GenusAcantholepis. Folia Geobot. 2005, 40, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Jimenez, I.; Lazkov, G.; Hidalgo, O.; Garnatje, T. Molecular Systematics of Echinops L. (Asteraceae, Cynareae): A Phylogeny Based on ITS and TrnLtrnF Sequences with Emphasis on Sectional Delimitation. Taxon 2010, 59, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falah, F.; Shirani, K.; Vasiee, A.; Tabatabaee Yazdi, F.; Alizadeh Behbahani, B. In Vitro Screening of Phytochemicals, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Activity of Echinops Setifer Extract. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 35, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBIF.org. GBIF Backbone Taxonomy: Echinops L. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/species/3109550 (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Hedge, I.C. Vergleichende Chorologie Der Zentraleuropaischen Flora. Band III. Ed. H. Meusel & E.J. Jager. Edinb. J. Bot. 2010, 50, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, L.R. The Flight Directionality of Honeybees Foraging on Real and Artificial Inflorescences. Can. J. Zool. 1987, 65, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigó, A.; Malatinszky, Á.; Barina, Z. Inventory of the Urban Flora of Budapest (Hungary) Highlighting New and Noteworthy Floristic Records. Biodivers. Data J. 2023, 11, e110450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginko, E.; Dobeš, C.; Saukel, J. Suitability of Root and Rhizome Anatomy for Taxonomic Classification and Reconstruction of Phylogenetic Relationships in the Tribes Cardueae and Cichorieae (Asteraceae). Sci. Pharm. 2016, 84, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuhrovec, J.; Volovnik, S.; Gosik, R. Description of the Immature Stages of Larinus vulpes and Notes on Its Biology (Coleoptera, Curculionidae, Lixinae). ZooKeys 2017, 679, 107–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řezáčová, V.; Řezáč, M.; Wilson, G.W.T.; Michalová, T. Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Can Be Disadvantageous for Weedy Annuals in Competition with Paired Perennial Plants. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greuter, W. Euro+Med PlantBase—The Information Resource for Euro-Mediterranean Plant Diversity. 2006. Available online: https://ww2.bgbm.org/EuroPlusMed/PTaxonDetail.asp?NameId=122540&PTRefFk=7000000 (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Rameshk, M.; Khoshbin, E.; Moeinzadeh, M.; Sharififar, K.; Bahrami, D.; Sharififar, F. Mannas, Unique Products of a Dynamic Insect-Plant Interaction: Biodiversity, Conservation and Ethnopharmacological Considerations. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M. A Revision of the Genus Echinops (Compositae-Cardueae) in Tropical Africa. Kew Bull. 1997, 52, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friis, I.; Boulos, L. 2002. Flora of Egypt. Vol. 3. (Verbenaceae-Compositae). Nord. J. Bot. 2002, 22, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, V.; Ghahreman, A. Three New Species of Echinops (Compositae, Cynareae) from Iran. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2002, 140, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echinops ritro Subsp. Ruthenicus (Small Globe Thistle). Available online: https://www.gardenia.net/plant/echinops-ritro-subsp-ruthenicus (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Patel, A.J.; Patel, N.M.; Patel, A.A.; Patel, J.; Patel, S. Comparative Analgesic Activity of Root and Aerial Part Methanolic Extracts of Echinops echinatus Roxb. Pharm. Lett. 2011, 3, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Raškauskas, P. Echinops Sphaerocephalus and Chrysochromulina Polylepis Algae Fractionation, Analysis and Evaluation. Master’s Thesis, Kauno Technologijos Universitetas, Kaunas, Lithuania, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bitew, H.; Hymete, A. The Genus Echinops: Phytochemistry and Biological Activities: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroo, R.R.J.; Jacobs, J.J.M.R.; Van Gestel, J.A.M.; Kenkel, H.; Jannik, W.; Croes, A.F.; Wullems, G.J. Regulation of Thiophene Biosynthesis by Sulphate in Roots of Marigolds. New Phytol. 1997, 135, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H. 2-(Penta-1,3-Diynyl)-5-(3,4-Dihydroxybut-1-Ynyl)Thiophene, a Novel NQO1 Inducing Agent from Echinops grijsii Hance. Molecules 2010, 15, 5273–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegaz, B.M.; Tadesse, M.; Majinda, R. Distribution of Sesquiterpene Lactones and Polyacetylenic Thiophenes in Echinops. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2003, 19, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegaz, B.M. Polyacetylenic Thiophenes and Terpenoids from the Roots of Echinops pappii. Phytochemistry 2001, 30, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokialakis, N.; Cantrell, C.L.; Duke, S.O.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Wedge, D.E. Antifungal Activity of Thiophenes from Echinops ritro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1651–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokialakis, N.; Osbrink, W.L.; Mamonov, L.K.; Gemejieva, N.G.; Mims, A.B.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Lax, A.R.; Cantrell, C.L. Antifeedant and Toxicity Effects of Thiophenes from Four Echinops Species against the Formosan Subterranean Termite, Coptotermes formosanus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgumbayeva, A. A Review on the Medicinal Plant Echinops ritro Species: Phytochemistry and Biological Activity. Farmacia 2023, 71, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-P.; Chen, C.-C.; Huang, H.-C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, J.-J.; Yang, C.-S.; Ou, C.-Y.; Wu, J.-B.; Huang, G.-J.; Kuo, Y.-H. A New Bithiophene from the Root of Echinops grijsii. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 2147–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, Z. Characterization of Bioactive Thiophenes from the Dichloromethane Extract of Echinops grijisii as Michael Addition Acceptors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liang, D.; Jin, W.; Qu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, Z. Cytotoxic Thiophenes from the Root of Echinops grijisii Hance. Z. Naturforsch C. J. Biosci. 2009, 64, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandjo, L.P.; Kuete, V.; Siwe, X.N.; Poumale, H.M.P.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity of an Unprecedented Brominated Oleanolide and a New Furoceramide from the Cameroonian Spice, Echinops giganteus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 2529–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuete, V.; Sandjo, L.P.; Wiench, B.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity and Modes of Action of Four Cameroonian Dietary Spices Ethno-Medically Used to Treat Cancers: Echinops giganteus, Xylopia aethiopica, Imperata cylindrica and Piper capense. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymete, A.; Rohloff, J.; KjØsen, H.; Iversen, T. Acetylenic Thiophenes from the Roots of Echinops ellenbeckii from Ethiopia. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.; Christensen, L.P.; Thomasen, T. Thiophene Derivatives from Echinops Species. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 1157–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, H.-Z.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Guo, D.-A. New Thiophenes from Echinops grijisii. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2002, 4, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Li, N.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Z.; Li, X. Chemical Constituents of the Root of Echinops grijisii Hance. Shenyang Yao Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2008, 8, 007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.-B.; Xiao, G.-D.; Xiang, W.; Yang, X.; Cao, K.-X.; Huang, R.-S. Novel Substituted Thiophenes and Sulf-Polyacetylene Ester from Echinops ritro L. Molecules 2019, 24, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Ali, A.; Ur Rehman, J.; Mamonov, L.K.; Cantrell, C.L.; Khan, I.A. Toxicity of Thiophenes from Echinops transiliensis (Asteraceae) against Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) Larvae. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, H.; Mammo, W.; Hymete, A.; Yeshak, M. Antimalarial Activity of Acetylenic Thiophenes from Echinops Hoehnelii Schweinf. Molecules 2017, 22, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Cantrell, C.L.; Mamonov, L.K.; Osbrink, W.L.A.; Ross, S.A. Echinopsacetylenes a and B, New Thiophenes from Echinops transiliensis. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 6228–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Cantrell, C.L.; Mamonov, L.K.; Kustova, T.S.; Fronczek, F.R.; Ross, S.A. Chemical Constituents from Echinops nanus and Echinops transiliensis. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 45, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, L.-H.; Meng, D.-L.; Li, Z.-L.; Li, N. Two New Thiophenes from Echinops latifolius and Their Phototoxic Activities. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Shi, Q.; Hong, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Qu, H. Cytotoxic Properties of Thiophenes from Echinops grijissi Hance. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Lee, J.W.; Jang, H.; Choi, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.; Hong, J.T.; Lee, M.K.; Hwang, B.Y. Dimeric Sesquiterpene and Thiophenes from the Roots of Echinops latifolius. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5995–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Kang, H.; Zhou, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Shu, P. A Review of the Phytochemistry and Biological Activities of Echinopsis radix. Molecules 2024, 29, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, D.-L.; Li, Z.-L.; Zhang, P.; Xu, J. Thiophenes from Echinops latifolius. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyekbayeva, L.; Mohamed, N.M.; Yerkebulan, O.; Mohamed, E.I.; Ubaidilla, D.; Nursulu, A.; Assem, M.; Srivedavyasasri, R.; Ross, S.A. Phytochemical Constituents and Antioxidant Activity of Echinops albicaulis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 32, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; Todd, M.; Rutledge, P. Recent Advances in Macrocyclic Fluorescent Probes for Ion Sensing. Molecules 2017, 22, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Jin, W.-R.; Shi, Q.; He, H.; Ma, Z.-J.; Qu, H.-B. Two Novel Thiophenes from Echinops grijissi Hance. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Sauriol, F.; Shi, Q.; Yang, J. New Thiophene Acetylene from Echinops spinosissimus subsp. spinosus. Chem. Nat. Comp. 2017, 53, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Omar, A.M.; Bagalagel, A.A.; Diri, R.M.; Noor, A.O.; Almasri, D.M.; Mohamed, S.G.A.; Mohamed, G.A. Thiophenes—Naturally Occurring Plant Metabolites: Biological Activities and in Silico Evaluation of Their Potential as Cathepsin D Inhibitors. Plants 2022, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neenu Krishna, P.U.; Muraleedharan, K. Alpha-Terthiophene and Its Functionalized Derivatives from Roots of Echinops grijisii to Produce Potential Organic Semiconductor Materials: A Theoretical Study. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheleva-Dimitrova, D.; Simeonova, R.; Kondeva-Burdina, M.; Savov, Y.; Balabanova, V.; Zengin, G.; Petrova, A.; Gevrenova, R. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Potential of Echinops ritro L. Extracts on Induced Oxidative Stress in Vitro/in Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitouni-Nourine, S.H.; Belyagoubi-Benhammou, N.; El-Houaria Zitouni-Haouar, F.; Douahi, O.; Chenafi, F.; Fetati, H.; Chabane Sari, S.; Benmahieddine, A.; Zaoui, C.; Mekaouche, F.Z.N.; et al. Echinops spinosissimus Turra Root Methanolic Extract: Characterization of the Bioactive Components and Relative Wound Healing, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties. Plants 2022, 11, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, M.; Trewin, H.; Gawthrop, F.; Wagstaff, C. Sesquiterpenoids Lactones: Benefits to Plants and People. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12780–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, P.K. 7-Hydroxyechinozolinone, a New Alkaloid from the Flowers of Echinops echinatus. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenler, R.; Yilmaz, S.; Aksit, H.; Sen, O.; Demirtas, I. Antioxidant Activities of Chemical Constituents Isolated from Echinops orientalis Trauv. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2014, 8, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Radulović, N.S.; Denić, M.S. Essential Oils from the Roots of Echinops bannaticus Rochel ex Schrad. and Echinops sphaerocephalus L. (Asteraceae): Chemotaxonomic and Biosynthetic Aspects. Chem. Biodiv. 2013, 10, 658–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Cong, B.; Yu, S.-H.; Sauriol, F.; Huo, C.-H.; Shi, Q.-W.; Gu, Y.-C.; Zamir, L.O.; Kiyota, H. Echinopines A and B: Sesquiterpenoids Possessing an Unprecedented Skeleton from Echinops spinosus. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ren, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, H. Three New Sesquiterpenoids from Echinops ritro L. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, D.I.; Fayed, A.; Adel, R. Echinops taeckholmiana Amin: Optimization of a Tissue Culture Protocol, Biological Evaluation, and Chemical Profiling Using GC and LC-MS. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 13105–13115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, K.A. A Pseudoguaiane Sesquiterpene Xylopyranoside from Echinops hussoni. Pharmazie 2001, 56, 415–417. [Google Scholar]
- Zamzami, T.A.; Abdallah, H.M.; Shehata, I.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Koshak, A.E.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Macrochaetosides A and B, New Rare Sesquiterpene Glycosides from Echinops macrochaetus and Their Cytotoxic Activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 30, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Singh, K.N.; Pande, V.B. Onstituents of Echinops niveus. Fitoterapia 1990, 61, 279–281. [Google Scholar]
- Tene, M.; Tane, P.; Sondengam, B.L.; Connolly, J.D. Lignans from the Roots of Echinops giganteus. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 2101–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senejoux, F.; Demougeot, C.; Karimov, U.; Muyard, F.; Kerram, P.; Aisa, H.A.; Girard-Thernier, C. Chemical Constituents from Echinops integrifolius. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 47, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A. Isolation and Characterization of Lupeol from Echinops echinatus Roxb. Root. Eur. J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2016, 3, 385–387. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Gambhir, S.S.; Pandey, V.B.; Joshi, V.K. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Echinops echinatus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1989, 25, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafantakis, N.; Zelianeos, K.; Termentzi, A.; Vontzalidou, A.; Aligiannis, N.; Fokialakis, N. Triterpenes from Echinops spinosissimus Turra subsp. spinosissimus. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 30, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chao, Q.; Li, R.; Lin, G.; Huang, H. A New Pentacyclic Triterpene, Gmeliniin A, from Echinops gmelinii Turcz. Chin. J. Chem. 2000, 18, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.M.; Ezzat, S.M.; El Dine, R.S.; Abdel-Sattar, E.; Abdel-Naim, A.B. Protective Effect of Echinops Galalensis against CCl4-Induced Injury on the Human Hepatoma Cell Line (Huh7). Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 6, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, K.A.; Fahmy, M.A.; Hassan, E.E.; Nagy, A.M.; Farghaly, A.A.; Hassan, E.M.; Omara, E.A. Safety Evaluation of Ethanolic Extract from Aerial Flowering Part of Spiny Globe Thistle (Echinops spinosus) in Mice: Phytochemical Screening and Genotoxicity. MRGTEM 2025, 902, 503854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Pandey, V.B. Nivetin, a Neoflavonoid from Echinops niveus. Phytochemistry 2001, 29, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Upadhyay, R.K.; Pandey, M.B.; Singh, J.P.; Pandey, V.B. Flavonoids from Echinops echinatus. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panero, J.L.; Funk, V.A. The Value of Sampling Anomalous Taxa in Phylogenetic Studies: Major Clades of the Asteraceae Revealed. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 47, 757–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.N.; Roy, R.; Singh, B.; Singh, R.P.; Pandey, V.B. An Acylflavone Glucoside of Echinops echinatus Flowers. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaraf, M.; Benyahia, S.; Mekkiou, R.; Benayache, S.; Benayache, F. Flavonoids from Ethyl Acetate Extract of Echinops spinosus (Asteraceae). Der Pharma Chem. 2016, 8, 158–160. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Ahamad, T.; Mishra, D.P.; Khan, M.F. Plant Neoflavonoids: Chemical Structures and Biological Functions. In Plant-derived Bioactives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čižmárová, B.; Hubková, B.; Tomečková, V.; Birková, A. Flavonoids as Promising Natural Compounds in the Prevention and Treatment of Selected Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengin, G.; Fahmy, N.M.; Sinan, K.I.; Uba, A.I.; Bouyahya, A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Yıldıztugay, E.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Fayez, S. Differential Metabolomic Fingerprinting of the Crude Extracts of Three Asteraceae Species with Assessment of Their in Vitro Antioxidant and Enzyme-Inhibitory Activities Supported by in Silico Investigations. Processes 2022, 10, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.A.R.; Khadeem, E.J. Phytochemical Investigation of Flavonoids Glycoside in the Ira-Qi Echinops Heterophyl-Lus (Compositae). Pharm. Glob 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yadava, R.N.; Singh, S.K. New Anti-Inflammatory Active Flavanone Glycoside from the Echinops echinatus Roxb. Indian J. Chem. 2006, 45, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Balabanova, V.; Zheleva-Dimitrova, D.; Voynikov, Y.; Zengin, G.; Joubert, O.; Gevrenova, R. New Insight into Enzyme Inhibitory and Anti-Proliferative Activity of Echinops ritro L. (Asteraceae). C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2023, 76, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padashetty, S.A.; Mishra, S.H. An HPTLC Method for the Evaluation of Two Medicinal Plants Commercially Available in the Indian Market under the Common Trade Name Brahmadandi. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videla, L.A. Oxidative Stress Signaling Underlying Liver Disease and Hepatoprotective Mechanisms. World J. Hepatol. 2009, 1, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.-W.; Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Xia, Y.; Gao, Z.; Song, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Y. Transcriptome Analysis to Reveal the Mechanism of the Effect of Echinops latifolius Polysaccharide B on Palmitate-Induced Insulin-Resistant. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafay, M. Phytochemicals Analysis and Antimicrobial Activities of Echinops echinatus from Cholistan Desert, Pakistan. Agrobiol. Rec. 2021, 5, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Ma, F.; Li, C.; Bu, R.; Lu, J.; Gao, J.; Xue, P. Metabolomics Profiling Reveals Echinops latifolius Tausch Improves the Trabecular Micro-Architecture of Ovariectomized Rats Mainly via Intervening Amino Acids and Glycerophospholipids Metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 260, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, N.N.; Aly, H.F.; Fouad, G.I.; Abd El-Karim, S.S.; Anwar, M.M.; Syam, Y.M.; Elseginy, S.A.; Ahmed, K.A.; Booles, H.F.; Shalaby, M.B.; et al. Anti-Alzheimer Activity of New Coumarin-Based Derivatives Targeting Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 18496–18510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, I.Y.; Mohsen, E.; Ibrahim, R.M.; Fernie, A.R.; Alseekh, S.; Salem, M.A. Non-Targeted Metabolomics and Chemometrics for Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Authentication and Adulteration Detection in Relation to Its Anticholinesterase Activity. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamila, N.; Khan, N.; Hwang, I.M.; Khan, S.N. Elemental Analysis and Bioactivities of Echinops echinatus Roxb. (Globe Thistle) via Spectroscopic Techniques. Pak. J. Bot. 2019, 52, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamać, M.; Kosińska, A.; Estrella, I.; Hernández, T.; Dueñas, M. Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds Identified in Sunflower Seeds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, G.; Kupfer, A.; Kalbitz, J.; Gerdelbracht, H.-J.; Kluge, H.; Eder, K.; Dräger, B. Great Globe Thistle Fruit (Echinops sphaerocephalus L.), a Potential New Oil Crop. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, C.; Di Ferdinando, M.; Fini, A.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as Antioxidants and Developmental Regulators: Relative Significance in Plants and Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3540–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deavall, D.G.; Martin, E.A.; Horner, J.M.; Roberts, R. Drug-Induced Oxidative Stress and Toxicity. J. Toxicol. 2012, 2012, 645460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.K.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, C.R.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, J.H.; Song, S.; Kim, C.; Park, G.G.; Park, C.-S.; et al. Antioxidant and Cognitive-Enhancing Activities of Arctium lappa L. Roots in Aβ1-42-Induced Mouse Model. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-González, A.; Figueroa-Hernández, C.Y.; González-Rios, O.; Suárez-Quiroz, M.L.; González-Amaro, R.M.; Hernández-Estrada, Z.J.; Rayas-Duarte, P. Coffee Chlorogenic Acids Incorporation for Bioactivity Enhancement of Foods: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouba A, A. Phenolic Compounds and Radical Scavenging Potential of Twenty Cameroonian Spices. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. 2010, 1, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivó-Barrachina, L.; Rojas-Chacón, M.J.; Navarro-Salazar, R.; Belda-Sanchis, V.; Pérez-Murillo, J.; Peiró-Puig, A.; Herran-González, M.; Pérez-Bermejo, M. The Role of Natural Products on Diabetes Mellitus Treatment: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.S.; Khaled, A.M.; Al-Bagawi, A.H.; Fareid, M.A.; Hameed, R.A.; Zahra, F.A.A.; Moneim, A.E.A. Echinops Spinosus Effect against Diabetes and Its Hepatorenal Complications: Total Extract and Flavonoids Fraction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 38606–38617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.; Sarker, M.M.R.; Sultana, T.N.; Chowdhury, M.N.R.; Rashid, M.A.; Chaity, N.I.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, J.; Hafez, E.E.; Khan, S.A.; et al. Antidiabetic Phytochemicals from Medicinal Plants: Prospective Candidates for New Drug Discovery and Development. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 800714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, S.; Afroz, S.; Qureshi, A.S. Anti-Diabetic Activity of Hydro-Alcoholic Root Extract of Echinops echinatus and Its Beneficial Effects on Nephropathy in Experimental Rats. Indian J. Res. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sarvaiya, D.D.; Sheth, N.R.; Dudhrejiya, A.V. Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Activity of Roots of Echinops echinatus Roxb. Pharmacologyonline 2017, 2, 10–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, S.R.Y.; Akram, A.; Aslam, N.; Wajid, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Nazir, I.; Jabeen, Q.; Muhammad, S. Antidiabetic and Antidyslipidemic Potential of Echinops echinatus in Rat Models of Type I and Type II Diabetes. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32, 505–514. [Google Scholar]
- Benrahou, K.; Doudach, L.; Mrabti, H.N.; El Guourrami, O.; Zengin, G.; Bouyahya, A.; Cherrah, Y. Acute Toxicity, Phenol Content, Antioxidant and Postprandial Anti-Diabetic Activity of Echinops spinosus Extracts. Int. J. Second. Metab. 2022, 9, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, H.; Azizi, Y.; Maleki-Ravasan, N.; Tahghighi, A.; Khalaj, A.; Pourhamzeh, M. Nature׳s Gifts to Medicine: The Metabolic Effects of Extracts from Cocoons of Larinus hedenborgi (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Their Host Plant Echinops cephalotes (Asteraceae) in Diabetic Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 284, 114762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chang, H.; Gao, X.; Dong, C.; Li, Z.; Hao, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, Q. Mongolian Medicine Echinops Prevented Postmenopausal Osteoporosis and Induced ER/AKT/ERK Pathway in BMSCs. Biosci. Trends 2018, 12, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyno, S.; Mtewa, A.G.; Hope, D.; Bazira, J.; Makonnen, E.; Alele, P.E. Antibacterial Activities of Echinops kebericho Mesfin Tuber Extracts and Isolation of the Most Active Compound, Dehydrocostus Lactone. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 608672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seukep, A.J.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Xu, Y.-B.; Guo, M.-Q. In Vitro Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Potential of Echinops lanceolatus Mattf. (Asteraceae) and Identification of Potential Bioactive Compounds. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameya, G.; Gure, A.; Dessalegn, E. Antimicrobial Activity of Echinops kebericho against Human Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 13, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Tian, S.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yi, J.; Yu, C.; et al. Antibacterial Activity and Action Mechanism of the Echinops ritro L. Essential Oil against Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2017, 20, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, L.; Sleiman, A.; Abdel-Massih, R.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenols and Alkaloids in Middle Eastern Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.G.; Lv, W.; Dai, C.Y.; Zhu, F.F.; Xu, G.H.; Ma, Z.J.; Chen, Z. 2-(Pro-1-Ynyl)-5-(5,6-Dihydroxypenta-1,3-Diynyl) Thiophene Induces Apoptosis through Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated JNK Activation in Human Colon Cancer SW620 Cells. Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweilam, S.H.; Abdel, M.; Foudah, A.I.; Alqarni, M.H.; Elattal, N.A.; El-Gindi, O.D.; El-Sherei, M.M.; Abdel-Sattar, E. Phytochemical, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and in Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Echinops erinaceus Kit Tan. Separations 2022, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemberie, W.; Tadie, A.; Enyew, A.; Debebe, A.; Raja, N. Repellent Activity of Plant Essential Oil Extracts against Malaria Vector Anopheles arabiensis Patton (Diptera: Culicidae). Entomon 2016, 41, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymete, A.; Iversen, T.-H.; Rohloff, J.; Erko, B. Screening of Echinops ellenbeckii and Echinops longisetus for Biological Activities and Chemical Constituents. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Cai, M.; Meng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Design, Synthesis and Biological Activities of Echinopsine Derivatives Containing Acylhydrazone Moiety. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadache, M.; Benkortbi, O.; Hanini, S.; Amrane, A.; Khaouane, L.; Si-Moussa, C. A Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship for Acute Oral Toxicity of Pesticides on Rats: Validation, Domain of Application and Prediction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 303, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarz, M.H.; Pouretedal, H.R. Simple and Reliable Prediction of Toxicological Activities of Benzoic Acid Derivatives without Using Any Experimental Data or Computer Codes. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 22, 1238–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.C. Phytolacca Dodecandra Berries as a Means of Controlling Bilharzia Transmitting Snails. By Lugt Ch. B. Amsterdam: Royal Tropical Institute (1986), Bulletin 812, pp. 61, Guilders 10.00. Exp. Agric. 1988, 24, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.D.H.; Temmink, J.H.M.; Marquis, J.; Parkhurst, R.M.; Lugt, C.B.; Lemmich, E.; Wolde-Yohannes, L.; de Savigny, D. Endod: Safety Evaluation of a Plant Molluscicide. Regulat. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1991, 14, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biruksew, A.; Zeynudin, A.; Alemu, Y.; Golassa, L.; Yohannes, M.; Debella, A.; Urge, G.; Spiegeleer, B.D.; Suleman, S. Zingiber Officinale Roscoe and Echinops kebericho Mesfin Showed Antiplasmodial Activities against Plasmodium Berghei in a Dosedependent Manner in Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2018, 28, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, P.K. Echinozolinone, an Alkaloid from Echinops echinatus. Phytochemistry 2001, 26, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global Burden of Colorectal Cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and Mortality Estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2022, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil Mohamed, A.; Mohamed, E.; Mohamed, A. Evaluation of Anticancer Activities of Ulva Lactuca Ethanolic Extract on Colorectal Cancer Cells. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 66, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.R.; Heer, E.; Sutherland, R.L.; Ruan, Y.; Tinmouth, J.; Heitman, S.J.; Hilsden, R.J. National Trends in Colorectal Cancer Incidence among Older and Younger Adults in Canada. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e198090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuete, V.; Krusche, B.; Youns, M.; Voukeng, I.; Fankam, A.G.; Tankeo, S.; Lacmata, S.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity of Some Cameroonian Spices and Selected Medicinal Plant Extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Dini, M. Identification of Manna Sources, Production Mechanism and Utilization in Iran. Iran. J. Med. Aromat. Plants Res. 2003, 17, 75–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, Y. Managing Rangeland as a Complex System: How Government Interventions Decouple Social Systems from Ecological Systems. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, M.; Pishva, H.; Mohammadi; Alinejad, F. Effect of Manna from Cotoneaster Discolor on Infant Jaundice (Effect on Blood Bilirubin Level). J. Med. Plants 2005, 4, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Azadbakht, M.; Dehkordi, N.G.; Sadjadi, S.E.; Ghannadi, A.; Taleb, M. Iranian Herbal Pharmacopoeia. Depart. Med. Sci. 2003, 6, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Takavar, S.; Mohamadi, M. Producer’s Factors and Mechanisms of Manna in Iran. J. Med. Plants 2008, 7, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nasirzadeh, A.A.R.; Javidtash, I.; Riasat, M. Identification of Echinops Species and Study on Some Biological Characteristics of Larinus Vulpes Oliv. As Manna Producer in Fars Province. Iran. J. Med. Aromat. Plants Res. 2005, 21, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name of the Secondary Metabolite | Chemical Structure | Isolated from | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| monothiophenes | |||
| 2-(Penta-1,3-diynyl)-5-(3,4-dihydroxybut-1-ynyl)thiophene | 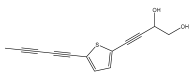 | E. grijsii Hance | [22] |
| 5-(penta-1,3-diynyl)-2-(3-chloro-4-hydoxy-but-1-ynyl)-thiophene |  | E. ellenbeckii | [23] |
| E. giganteus | [20] | ||
| E. hispidus Fresen. | [20] | ||
| E. longisetus | [20] | ||
| E. macrochaetus | [20] | ||
| 2-(pent-3-en-1-ynyl)-5-(4-hydroxybut-1-ynyl)-thiophene | 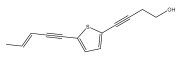 | E. pappii | [24] |
| 5-(4-hydroxybut-1-ynyl)-2-(pent-1,3-diynyl)-thiophene | 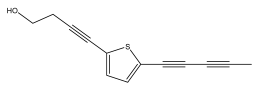 | E. pappii | [24] |
| E. ritro | [25,26,27] | ||
| E. grijsii | [28,29,30] | ||
| E. giganteus | [20,31,32] | ||
| 5-(penta-1,3-diynyl)-2-(but-3-en-1-ynyl)-thiophene | 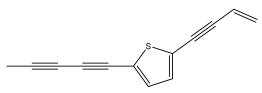 | E. ellenbeckii | [33] |
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| E. humilis Bieb. | [34] | ||
| E. niveus Walb. ex Royle | [34] | ||
| E. orientalis Trautv. | [34] | ||
| E. sphaerocephalus L. | [34] | ||
| E. dahuricus Fisch. | [34] | ||
| E. latijolius Tausch. | [34] | ||
| E. leiopolyceras Bomm. | [34] | ||
| E. microcephalus Sibth. et Sm. | [34] | ||
| E. ruthenicus’ | [34] | ||
| E. spinosissimus Turra | [34] | ||
| E. spinosus L. | [34] | ||
| E. tschimganicus B. Fedtsch. | [34] | ||
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| E. gmelini Turcz | [34] | ||
| 5-(penta-1,3-diynyl)-2-(4-acetoxy-but-1-ynyl)-thiophene | 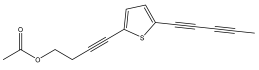 | E. ellenbeckii | [33] |
| E. humilis Bieb. | [34] | ||
| E. niveus Walb. ex Royle | [34] | ||
| E. orientalis Trautv. | [34] | ||
| E. sphaerocephalus L. | [34] | ||
| E. dahuricus Fisch. | [34] | ||
| E. latijolius Tausch. | [34] | ||
| E. leiopolyceras Bomm. | [34] | ||
| E. microcephalus Sibth. et Sm. | [34] | ||
| E. ruthenicus’ | [34] | ||
| E. spinosissimus Turra | [34] | ||
| E. spinosus L. | [34] | ||
| E. tschimganicus B. Fedtsch. | [34] | ||
| E. humilis Bieb. | [34] | ||
| E. commutatus Juratzka | [34] | ||
| E. gmelini Turcz. | [34] | ||
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| 5-(5,6-dihydroxy-hexa-1,3-diynyl)-2-(prop-1-ynyl)-thiophene (echinoynethiophene A) | 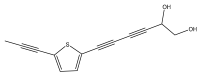 | E. grijsii | [35,36] |
| E. grijsii | [30] | ||
| 5-(penta-1,3-diynyl)-2-(3,4-dihydroxybut-1-ynyl)-thiophene | 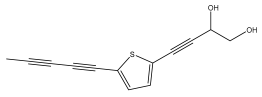 | E. grijsii | [28,35,36] |
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| E. grijsii | [22,29] | ||
| E. grijsii | [30] | ||
| E. giganteus | [31] | ||
| E. transiliensis | [38] | ||
| E. hoehnelii | [39] | ||
| Echinopsacetylenes B | 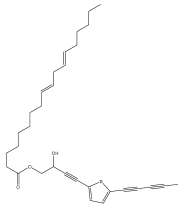 | E. transiliensis | [40] |
| Echinothiophenegenol ((R)-5-hydroxy-6-((1E,3E)-6-hydroxyhexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)thieno[2,3-e]isobenzofuran-8(6H)-one) | 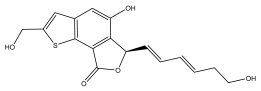 | E. grijsii | [30] |
| E. nanus | [41] | ||
| 5-(4-acetoxy-3-chlorobut-1-ynyl)-2-(pent-1,3-diynyl)-thiophene | 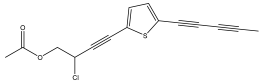 | E. ritro | [25] |
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| E. humilis Bieb. | [34] | ||
| E. niveus Walb. ex Royle | [34] | ||
| E. orientalis Trautv. | [34] | ||
| E. sphaerocephalus L. | [34] | ||
| E. tschimganicus B. Fedtsch. | [34] | ||
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| E. gmelini Turcz | [34] | ||
| 5-(prop-1-ynyl)- 2-(3,4-diacetoxybut-1-ynyl)-thiophene | 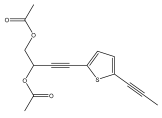 | E. latifolius | [42] |
| E. grijsii | [43] | ||
| 5-(1,2-dihydroxy-ethyl)-2-(Z)-hept-5-ene-1,3-diynylthiophene | 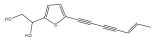 | E. latifolius | [44] |
| 5-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-2-(E)-hept-5-ene-1,3-diynylthiophene |  | E. latifolius | [44] |
| 5-(penta-1,3-diynyl)-2-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-but-1-ynyl)-thiophene | 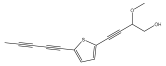 | E. hoehnelii | [39] |
| 5-(penta-1,3-diynyl)-2-(3-methoxy-4-acetoxy-but-1-ynyl)-thiophene | 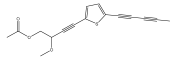 | E. hoehnelii | [39] |
| 2-(penta-1, 3-diynyl)-5-(3, 4-dihydroxybut-1-ynyl) thiophene | 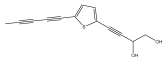 | [22,45] | |
| 5-(penta-1,3-diynyl)-2-(3-acetoxy-4-hydroxy-but-1-ynyl)-thiophene | 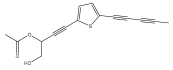 | E. transiliensis | [38] |
| Junipic acid (5-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)thiophene-2-carboxylic acid) |  | E. ritro | [37] |
| dithiophenes | |||
| 5-(but-3-en-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene (1) | 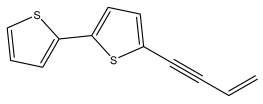 | E. macrochaetus | [23] |
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| E. humilis Bieb. | [34] | ||
| E. niveus Walb. ex Royle | [34] | ||
| E. orientalis Trautv. | [34] | ||
| E. sphaerocephalus L. | [34] | ||
| E. dahuricus Fisch. | [34] | ||
| E. latijolius Tausch. | [34,46] | ||
| E. leiopolyceras Bomm. | [34] | ||
| E. microcephalus Sibth. et Sm. | [34] | ||
| E. ruthenicus’ | [34] | ||
| E. spinosissimus Turra | [26,34] | ||
| E. spinosus L. | [34] | ||
| E. tschimganicus B. Fedtsch. | [34] | ||
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| E. gmelini Turcz | [34] | ||
| E. pappii Chiov. | [23] | ||
| E. ritro | [25,27] | ||
| E. grijsii | [28] | ||
| E. nanus Bunge | [41] | ||
| E. albicaulis | [26,47] | ||
| 5-[(5-acetoxymethyl-2-thienyl)-2-(but-3-en-1-ynyl)]-thiophene | 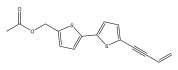 | E. ellenbeckii | [33] |
| 5-(3,4-dihydroxybut-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene |  | E. grijsii | [28,29,30,35,36] |
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| E. latifolius | [42] | ||
| E. transiliensis | [38] | ||
| 2,2′-bithiophene-5-carboxylic acid | 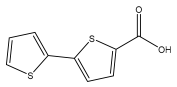 | E. grijsii | [28,35] |
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| 5-(3-buten-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene | 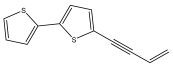 | E. grijsii | [35] |
| 5-(4-isovaleroyloxybut-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene |  | E. grijsii | [28,35] |
| E. grijsii | [46] | ||
| E. grijsii | [43] | ||
| E. grijsii | [48] | ||
| E. ritro | [25,26] | ||
| Grijisone A | 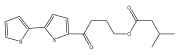 | E. grijsii | [49] |
| 5-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-1-butyny)-2,2′-bithiophene (4-([2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)-2-methoxybut-3-yn-1-ol) |  | E. grijsii | [28] |
| 1-([2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)ethan-1-one | 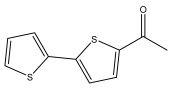 | E. latifolius | [42] |
| E. grijsii | [28] | ||
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| 5-formyl-2,2′-bithiophene | 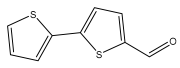 | E. grijsii | [28] |
| 5′-(3,4-Dihydroxybut-1-yn-1-yl)-[2,2′-bithiophene]-5-carbaldehyde | 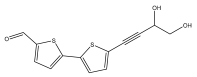 | E. ritro | [37] |
| 4-Hydroxy-1-(5′-methyl-[2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)butan-1-one | 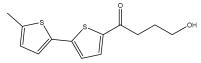 | E. ritro | [37] |
| 5′-(3,4-Dihydroxybut-1-yn-1-yl)-[2,2′-bithiophene]-5-carboxylic acid | 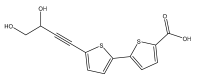 | E. ritro | [37] |
| Methyl 2,2′-bithiophene-5-carboxylate |  | E. grijsii | [28] |
| 5-(3-hydroxymethyl-3-isovaleroyloxyprop-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene | 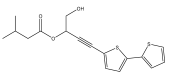 | E. latifolius | [46] |
| E. grijsii | [28] | ||
| 5-(4-hydroxy-1-butynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene | 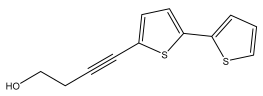 | E. latifolius | [42] |
| E. ritro | [25] | ||
| E. latifolius | [42] | ||
| E. grijsii | [28,30] | ||
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| E. ritro | [26] | ||
| 5-(4-acetoxy-1-butynl)-2,2′-bithiophene (4-([2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)but-3-yn-1-yl acetate) | 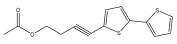 | E. grijsii | [28] |
| 5-(3-hydroxy-4-isovaleroyloxybut-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene | 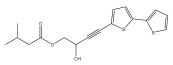 | E. latifolius | [46] |
| 5-(3-acetoxy-4-isovaleroyloxybut-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene | 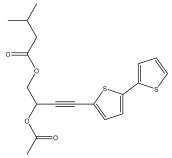 | E. latifolius | [46] |
| 5-(3,4-diacetoxybut-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene |  | E. ritro | [25,26] |
| E. latifolius | [34] | ||
| E. niveus Walb. ex Royle | [34] | ||
| E. orientalis Trautv. | [34] | ||
| E. gmelini Turcz. | [34] | ||
| E. giganteum | [34] | ||
| E. sphaerocephalus L. | [34] | ||
| E. dahuricus Fisch. | [34] | ||
| E. ruthenicus | [34] | ||
| E. commutatus Juratzka | [34] | ||
| E. spinosus L. | [34] | ||
| E. tschimganicus B. Fedtsch. | [34] | ||
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| E. gmelini Turcz | [34] | ||
| E. grijsii | [43] | ||
| E. grijsii | [29] | ||
| E. grijsii | [43] | ||
| E. transiliensis | [38] | ||
| 5-(4-hydroxybut-1-one)-2,2′-bithiophene (1-([2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)-4-hydroxybutan-1-one) |  | E. latifolius | [42] |
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| Methoxy-arctinol-b (2-methoxy-2-(3′-methoxy-5′-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-[2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)ethan-1-ol) |  | E. latifolius | [44] |
| Arctinol-b (1-(5′-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-[2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)ethane-1,2-diol) | 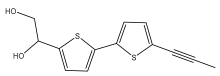 | E. grijsii | [30,37] |
| E. latifolius | [44] | ||
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| Arctinol a ((5′-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-[2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)methanol) | 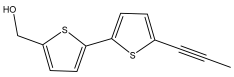 | E. latifolius | [37,44] |
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| E. ritro | [37] | ||
| Methyl [5′-(1-propynyf)-2,2′-bithienyl-5-yl] carboxylate | 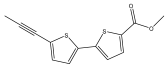 | E. latifolius | [44] |
| 5-(3-hydroxy-4-acetoxybut-1-ynyl)-2,2′-bithiophene (4-([2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)-2-hydroxybut-3-yn-1-yl acetate) | 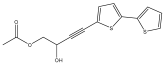 | E. transiliensis | [38] |
| E. transiliensis | [38] | ||
| 5′-(3,4-dihydroxybut-1-yn-1-yl)-[2,2′-bithiophene]-5-carbaldehyde | 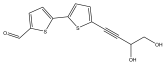 | E. ritro | [37] |
| 5′-(3,4-dihydroxybut-1-yn-1-yl)-[2,2′-bithiophene]-5-carboxylic acid | 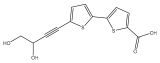 | E. ritro | [37] |
| 4-hydroxy-1-(5′-methyl-[2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)butan-1-one | 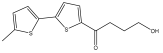 | E. ritro | [37] |
| Arctinal (5′-(prop-1-yn-1-yl)-[2,2′-bithiophene]-5-carbaldehyde) |  | E. ritro | [37] |
| 4-(5′-methyl-[2,2′-bithiophen]-5-yl)but-3-yn-1-ol | 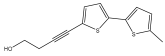 | E. ritro | [37] |
| Arctic acid | 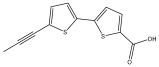 | E. ritro | [37] |
| 2,2-Dimethyl-4-[5-(prop-1-ynyl)-2,2-bithiophen-5-yl]-1,3-dioxolane | 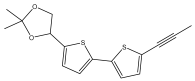 | E. spinosus | [50] |
| terthiophenes | |||
| α-terthiophene (2) |  | E. ellenbeckii | [23] |
| E. pappii | [23] | ||
| E. niveus Walb. ex Royle | [34] | ||
| E. orientalis Trautv. | [34] | ||
| E. gmelini Turcz. | [34] | ||
| E. giganteum | [34] | ||
| E. sphaerocephalus L. | [34] | ||
| E. dahuricus Fisch. | [34] | ||
| E. ruthenicus | [34] | ||
| E. commutatus Juratzka | [34] | ||
| E. spinosus L. | [34] | ||
| E. tschimganicus B. Fedtsch. | [34] | ||
| E. exaltatus Schrad | [34] | ||
| E. gmelini Turcz | [34] | ||
| E. macrochaetus | [23] | ||
| E. grijsii | [28,48,51,52] | ||
| E. latifolius | [34,46] | ||
| E. ritro | [25,53] | ||
| E. ritro | [26] | ||
| E. nanus | [41] | ||
| E. albicaulis | [25,26,47] | ||
| E. transiliensis | [41] | ||
| Echinops spinosissimus Turra | [34,54] | ||
| 5-chloro- α-terthiophene | 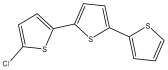 | E. grijsii | [35,52] |
| 5-acetyl α-terthiophene | 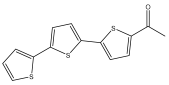 | E. grijsii | [35,52] |
| 5,5′-dichloro-α-terthiophene | 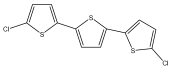 | E. grijsii | [35,52] |
| Grijisyne A | 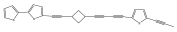 | E. grijsii | [49] |
| 5-{4-[4-(5-pent-1,3-diynylthiophen-2-yl)-but-3-ynyloxy]-but-ynyl}-2,2′-bithiophene | 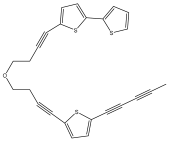 | E. latifolius | [42] |
| Cardopatine | 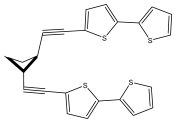 | E. grijsii | [28,35,45] |
| E. latifolius | [45,46] | ||
| E. ritro | [25,26] | ||
| Isocardopatine | 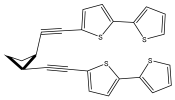 | E. grijsii | [28,29,35,43] |
| E. ritro | [25] | ||
| Echinopsacetylenes A | 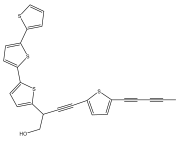 | E. transiliensis | [40] |
| Name of the Terpene | Chemical Structure | Isolated from | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dehydrocostus lactone | 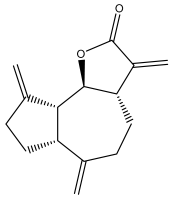 | E. amplexicauli | [23] |
| E. kebericho | [23] | ||
| Costunolide | 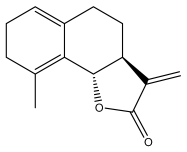 | E. amplexicaulis, | [23,24] |
| E. kebericho, | [23,24] | ||
| E. pappii | [23,24] | ||
| Dihydrocostunolide |  | E. amplexicaulis | [23] |
| Echinopines A |  | E. spinosus | [59] |
| Echinopines B | 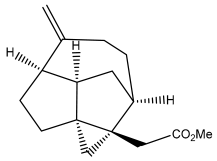 | E. spinosus | [59] |
| (3α,4α,6α)-3,13-dihydroxyguaia-7(11),10(14)-dieno-12,6-lactone) | 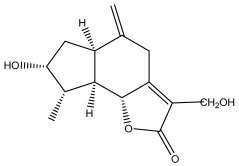 | E. ritro | [60] |
| β-vatirenene | 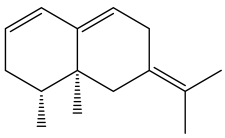 | E. taeckholmiana | [61] |
| jatamol A | 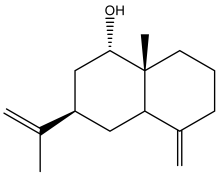 | E. taeckholmiana | [61] |
| (3α,4α,6α,11ß)-3-hydroxyguai-1(10)-eno-12,6-lactone) | 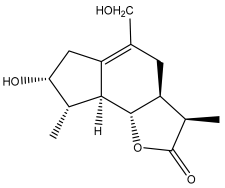 | E. ritro | [60] |
| (11α)-11,13-dihydroarglanilic acid methyl ester | 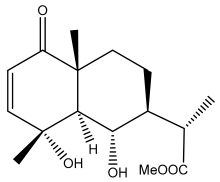 | E. ritro | [60] |
| Vulgarin | 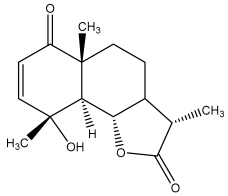 | E. ritro | [60] |
| (3R,3aS,6aR,9S,9aR,9bS)-octahydro-3,9-dimethyl-6-methyleneazuleno[4,5-b]furan2,8(3H,9bH)-d ione |  | E. ritro | [60] |
| (3aS,6aR,8S,9S,9aR,9bR)-decahydro-8-hydroxy-9-methyl-3,6 dimethyleneazuleno[4,5-b]furan-2(9bH)-one | 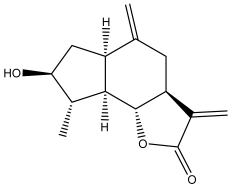 | E. ritro | [60] |
| (3aS,6aR,8R,9R,9aR,9bR)-decahydro-8-hydroxy-3,3,9-trimethyl-6-methyleneazuleno[4,5-b]furan-2(9bH)-one | 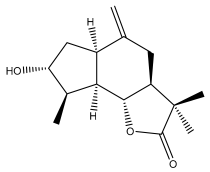 | E. ritro | [60] |
| (3R,3aS,6aR,8S,9S,9aR,9bS)-decahydro-8-hydroxy-3,9-dimethyl-6-methyleneazuleno[4,5-b]furan-2(9bH)-one | 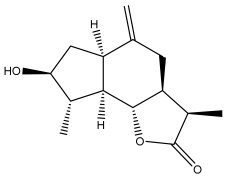 | E. ritro | [60] |
| Santamarin | 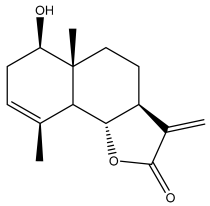 | E. pappii | [24] |
| E. ritro | [60] | ||
| Reynosin |  | E. pappii | [24] |
| Caryophyllene epoxide | 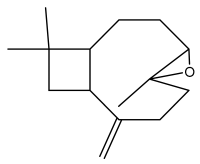 | E. giganteus | [23] |
| E. hispidus | [23] | ||
| Echusoside | 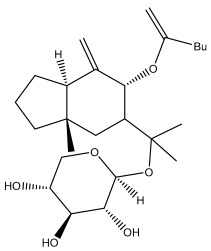 | E. hussoni Boiss. | [62] |
| (3S,3aS,5aR,6R,8R,9bS)-decahydro-6,8-dihydroxy-3,5a-dimethyl-9-methylenenaphtho[1,2-b]furan-2(9bH)-one | 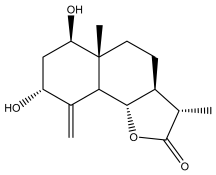 | E. ritro | [60] |
| (3S,3aS,5aR,6S,9bS)-3,3a,4,5,5a,6-hexahydro-6-hydroxy-3,5a,9-trimethylnaphtho[1,2-b]furan-2,7(9aH,9bH)-dione | 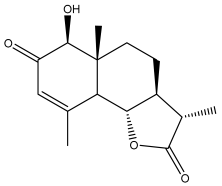 | E. ritro | [60] |
| 2,6,10-trimethyldodeca-2,6,10-triene | 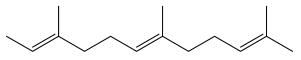 | E. albicaulis | [47] |
| Macrochaetosides A | 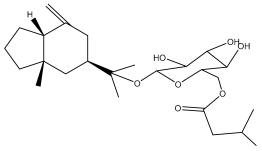 | E. macrochaetus | [63] |
| Macrochaetosides B | 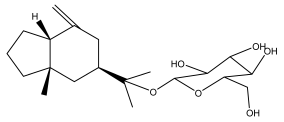 | E. macrochaetus | [63] |
| Latifolanone A | 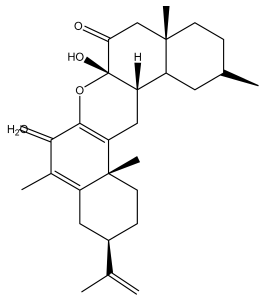 | E. latifolius | [44] |
| Atractylenolide-II | 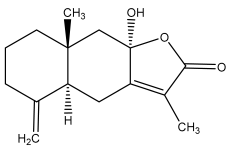 | E. latifolius | [44] |
| ß-amyrin |  | E. niveus | [64] |
| Betulinic acid | 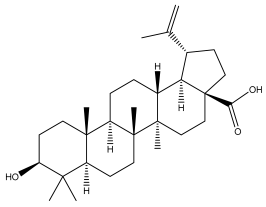 | E. niveus | [64] |
| Lupeol | 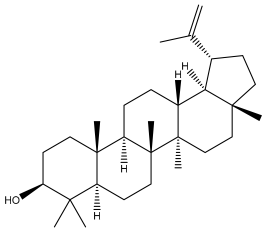 | E. niveus | [64] |
| E. giganteus | [65] | ||
| E. integrifolius | [66] | ||
| E. echinatus | [67] | ||
| Taraxasterol | 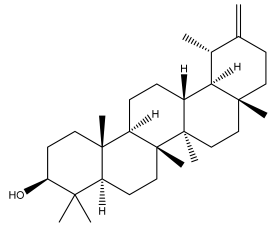 | E. niveus | [64] |
| Taraxasterol acetate | 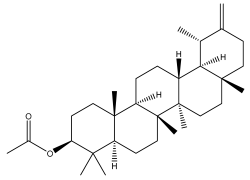 | E. niveus | [64] |
| E. echinatus | [68] | ||
| 20-oxo-30-nortaraxast-21-en-3β-ol |  | Echinops latifolius Tausch | [69] |
| Taraxeryl acetate | 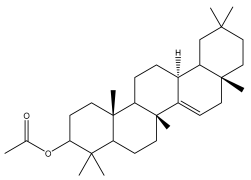 | E. taeckholmiana | [61] |
| ß-sitosterol | 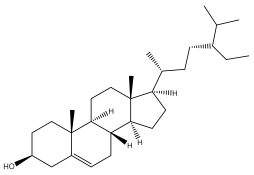 | E. niveus | [64] |
| E. transiliensis | [41] | ||
| E. giganteus | [32] | ||
| E. orientalis | [57] | ||
| ß-sitosterol glucoside | 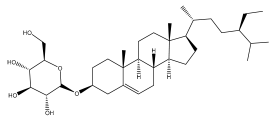 | E. niveus | [64] |
| E. giganteus | [65] | ||
| E. integrifolius | [66] | ||
| E. albicaulis | [47] | ||
| Reynosin | 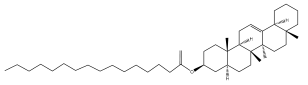 | E. pappii | [24] |
| Gmeliniin A |  | E. gmelinii | [70] |
| Stigmasterol | 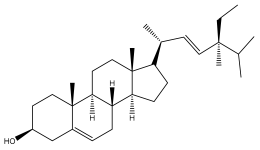 | E. transiliensis | [41] |
| E. macrochaetus | [63] | ||
| E. integrifolius | [66] | ||
| E. giganteus | [32] | ||
| Lupeol acetate | 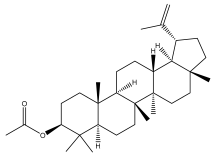 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| E. echinatus | [67] | ||
| E. albicaulis | [47] | ||
| Lupeol linoleate | 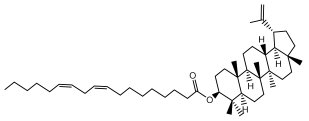 | E. albicaulis | [47] |
| Ajugasterone C |  | E. grijisii | [36] |
| Ursolic acid | 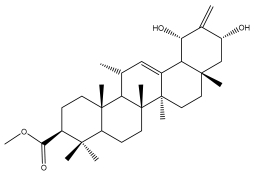 | E. giganteus | [32] |
| Echinopsolide A (3ß-acetoxy-15α-bromoolean-13ß,28-olide) | 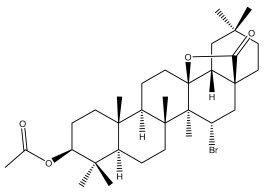 | E. giganteus | [31] |
| ß-amyrin acetate |  | E. giganteus | [31] |
| 3ß-acetoxy-taraxast-12,20(30)-diene-11α-21α-diol |  | E. galalensis | [71] |
| α-amyrin | 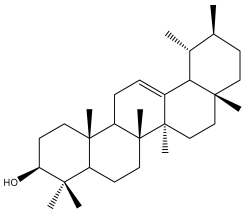 | E. galalensis | [71] |
| Erythrodiol | 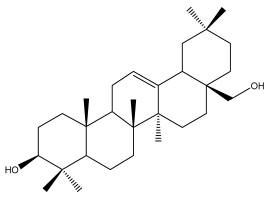 | E. galalensis | [71] |
| Lup-20(29)-ene-1,3-diol | 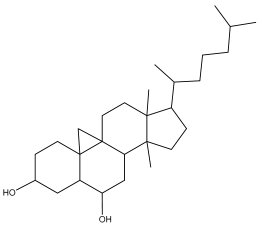 | E. galalensis | [63] |
| Cyclostenol | 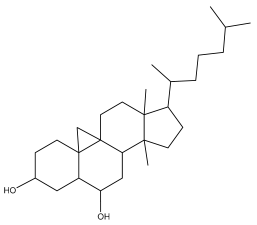 | E. macrochaetus | [63] |
| Flavonoids and Other Phenolic Compounds | Chemical Structure | Isolated from | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apigenin |  | E. niveus | [64] |
| E. echinatus | [76] | ||
| E. integrifolius | [66] | ||
| E. spinosus | [77] | ||
| E. albicaulis | [47] | ||
| Luteolin | 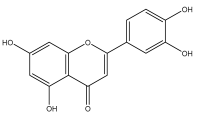 | E. niveus | [64] |
| E. grijisii | [36] | ||
| Nivegin (5,7-dihydroxy-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2H-chromen-2-one) |  | E. niveus | [64,78] |
| Nivetin (5,7-dihydroxy-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2H-chromen-2-one) | 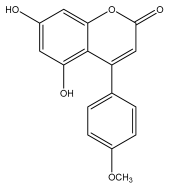 | E. niveus | [73,79] |
| Apigenin 7-O-glucoside |  | E. echinatus | [76] |
| E. spinosus | [77] | ||
| E. orientalis | [57] | ||
| E. ritro | [80] | ||
| Echitin | 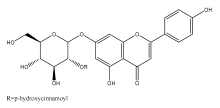 | E. echinatus | [76] |
| Echinoside | 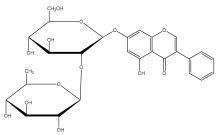 | E. echinatus | [74] |
| 7-hydroxyisoflavone | 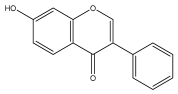 | E. echinatus | [74] |
| Kaempferol |  | E. echinatus | [74] |
| Kaempferol-4′-methylether | 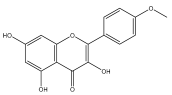 | E. echinatus | [74] |
| Kaempferol-7-methylether | 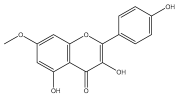 | E. echinatus | [74] |
| Kaempferol-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside | 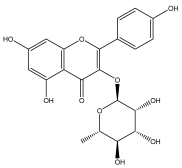 | E. echinatus | [74] |
| E. heterophyllus | [81] | ||
| Myrecetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnoside | 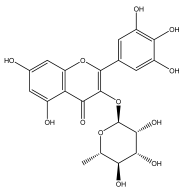 | E. echinatus | [74] |
| Chrysoeriol | 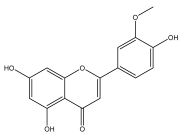 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| Hispidulin | 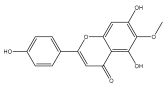 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| Jaceidin |  | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| Centaureidin |  | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| Axillarin | 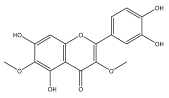 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| Genkwanin |  | E. albicaulis | [47] |
| Apigenin-7-O-(6″-trans-pcoumaroyl- ß -D-glucopyranoside | 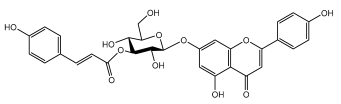 | E. orientalis | [57] |
| E. spinosus | [77] | ||
| 5,7-dihydroxy-8,4′-dimethoxyflavanone-5-O-α-L-rhamno-pyranosyl-7-O-ß-D-arabinopyranosyl (1→4)-O-ß-D-glucopyranoside | E. echinatus | [82] | |
| Candidone | 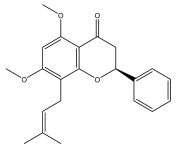 | E. giganteus | [32] |
| Chlorogenic acid | 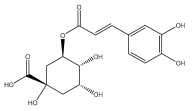 | E. grijisii | [36] |
| Cynarin | 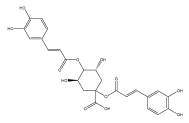 | E. grijisii | [36] |
| Rutin |  | E. heterophyllus | [81] |
| E. albicaulis | [47] | ||
| (+)-4-(3-methylbutanoyl)-2,6-di(3,4-dimethoxy)phenyl-3,7-dioxabicyclo[3.3.0]octane | 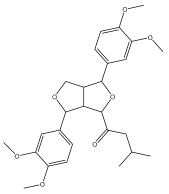 | E. giganteus | [65] |
| (+)-4-hydroxy-2,6- di(3,4-dimethoxy)phenyl-3,7-dioxabicyclo[3.3.0]octane | 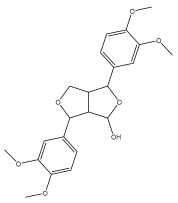 | E. giganteus | [65] |
| E. giganteus | [31] | ||
| E. giganteus | [32] | ||
| Jaceidin (5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3,6-dimethoxychromen-4-one) | 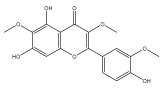 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| centaureidin (5,7,3′-Trihydroxy-3,6,4′-trimethoxyflavone) | 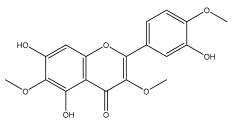 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| Hispidulin (4′,5,7-Trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone) | 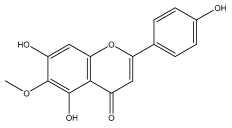 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| axillarin | 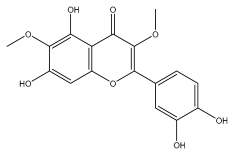 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| Hexacosyl-(E)-ferulate | 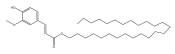 | E. nanus | [41] |
| Umbelliferone | 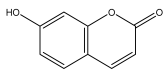 | E. integrifolius | [66] |
| Syringin |  | E. grijisii | [36] |
| 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid | 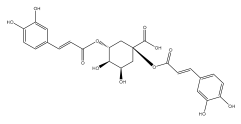 | E. galalensis | [71] |
| E. ritro | [83] | ||
| 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (isochlorogenic acid A) | 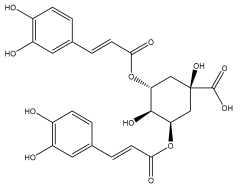 | E. ritro | [83] |
| 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (isochlorogenic acid C) | 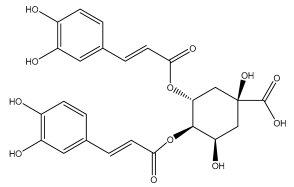 | E. ritro | [53] |
| 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid | 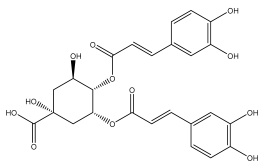 | E. ritro | [53] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanova, S.; Ivanova, A.; Todorova, M.; Gledacheva, V.; Nikolova, S. Echinops as a Source of Bioactive Compounds—A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091353
Ivanova S, Ivanova A, Todorova M, Gledacheva V, Nikolova S. Echinops as a Source of Bioactive Compounds—A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091353
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanova, Simona, Alexandra Ivanova, Mina Todorova, Vera Gledacheva, and Stoyanka Nikolova. 2025. "Echinops as a Source of Bioactive Compounds—A Systematic Review" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091353
APA StyleIvanova, S., Ivanova, A., Todorova, M., Gledacheva, V., & Nikolova, S. (2025). Echinops as a Source of Bioactive Compounds—A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091353







