Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Tanshinone IIA in Bone Injury Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview of Bone Injury
1.2. Pharmacological Potential and Research Value of Tanshinone IIA
1.3. Active Constituents of Salvia miltiorrhiza: Tanshinone IIA, Related Diterpenoids, and Salvianolic Acids
2. Chemical Properties and Pharmacokinetics of Tanshinone IIA
2.1. Plasma Half-Life and Bioavailability
2.2. Drug Delivery and Formulation Advances
2.3. Pharmacokinetics of Tanshinone IIA (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion)
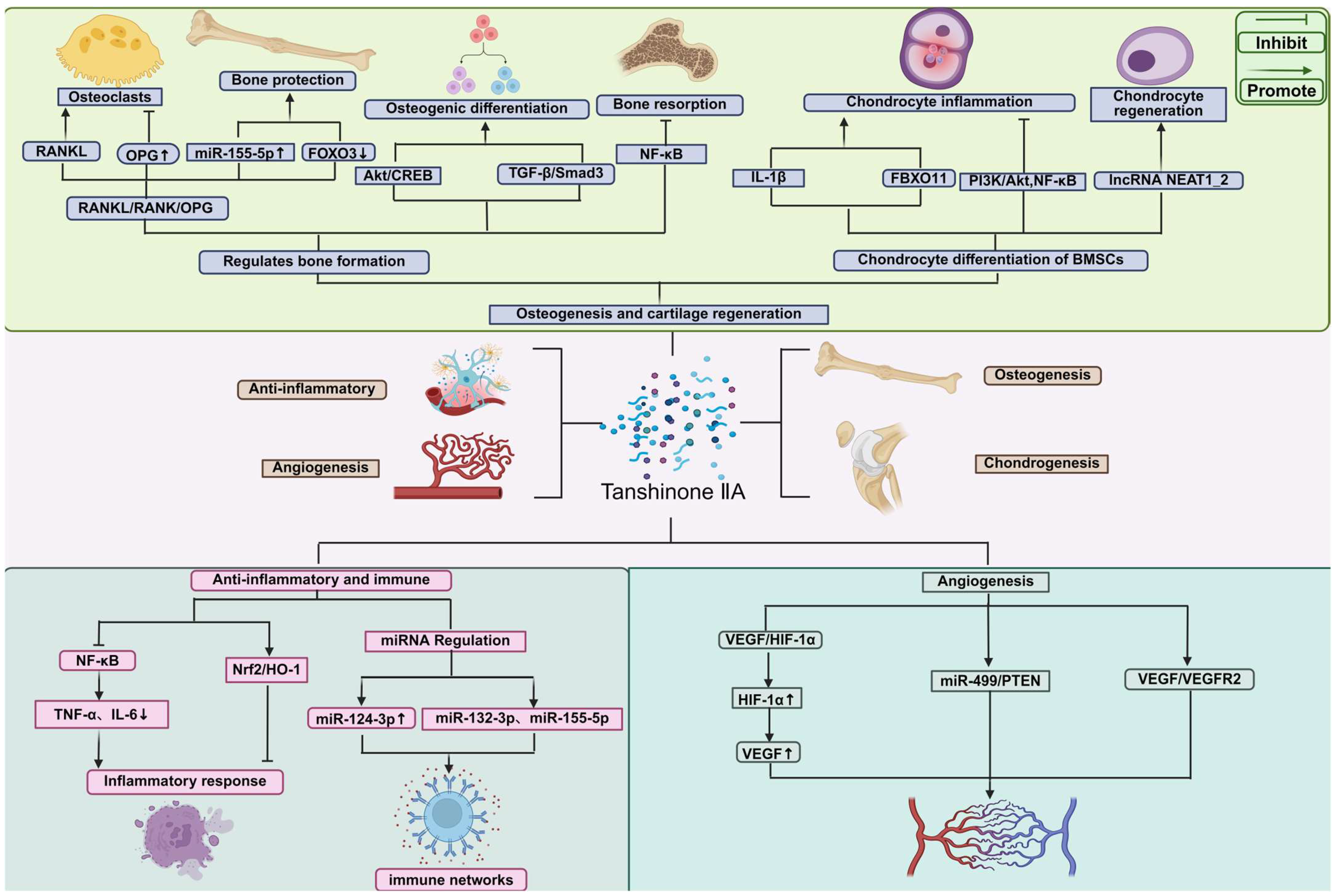
3. Mechanisms of Tanshinone IIA in Bone Tissue Repair
3.1. Osteogenesis-Promoting Effects and Signaling Pathway
3.2. Cartilage Protection and Regeneration
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Mechanisms
3.4. Angiogenic Effects
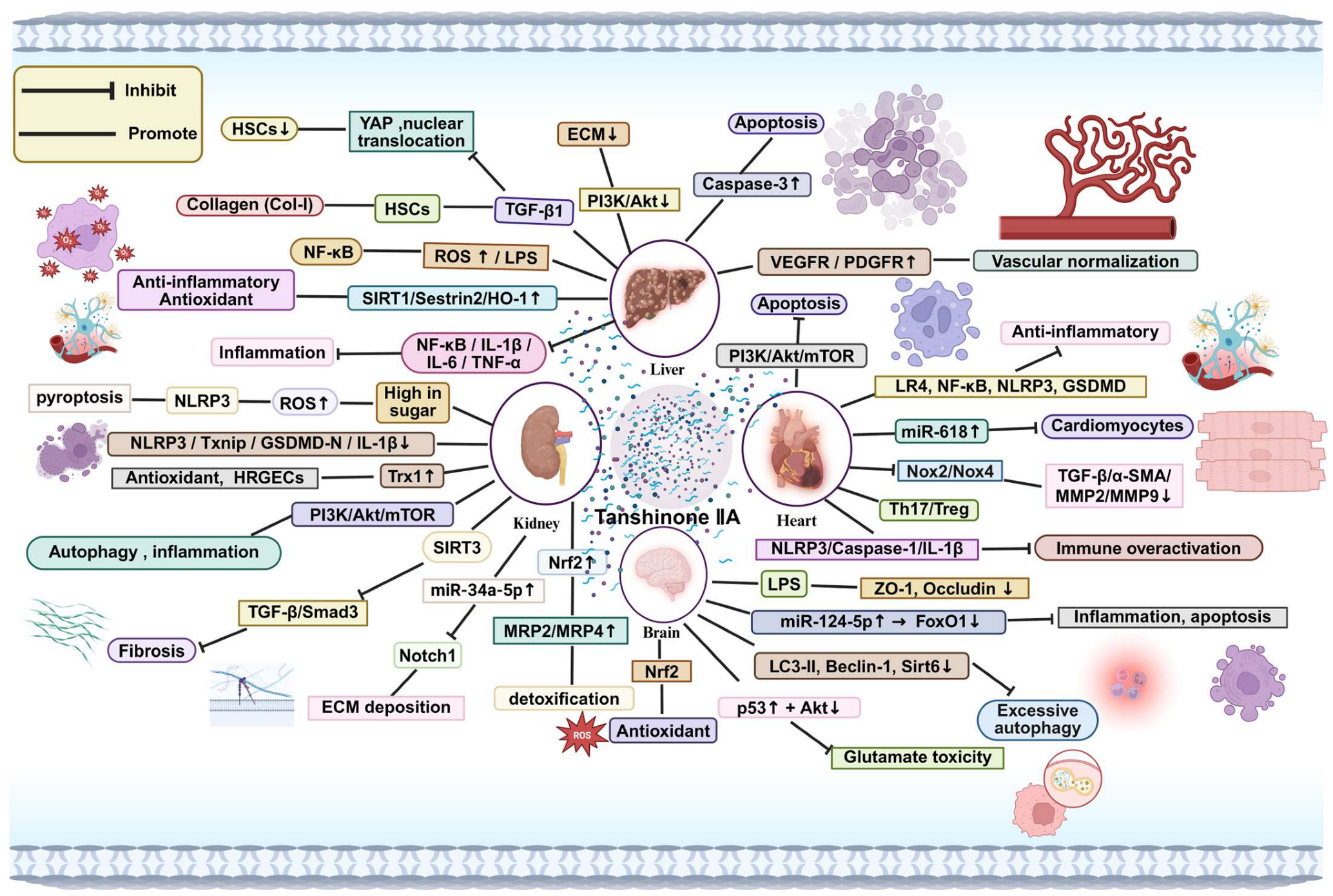
4. Systemic Effects of Tanshinone IIA
4.1. Effects on the Liver
4.2. Effects on the Kidney
4.3. Effects on the Heart
4.4. Effects on the Brain
4.5. Effects on the Nervous System
4.6. Effects of Tanshinone IIA on Genetic Material
5. Efficacy and Toxicity Evaluation of Tanshinone IIA in Animal Models of Bone Repair
5.1. Preclinical Studies on Tanshinone IIA-Promoted Bone Repair in Animal Models
5.2. Effective Concentration Range of Tanshinone IIA in Bone Injury Repair
5.3. Challenges in Drug Delivery: Design and Implementation Strategies
5.4. Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety Monitoring of Tanshinone IIA
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muñoz, M.B.; Robinson, K.; Shibli-Rahhal, A.M. Bone Health and Osteoporosis Prevention and Treatment. Clin. Obs. Gynecol. 2020, 63, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBoff, M.S.; Greenspan, S.L.; Insogna, K.L.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Saag, K.G.; Singer, A.J.; Siris, E.S. The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 2049–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.P. Long-Term Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arceo-Mendoza, R.M.; Camacho, P.M. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Latest Guidelines. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, J.; Gao, Y.; Fang, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liao, W.; Cui, L.; Liu, Y. Expanding the therapeutic potential of Salvia miltiorrhiza: A review of its pharmacological applications in musculoskeletal diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1276038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, W. Mechanisms and new advances in the efficacy of plant active ingredients in tendon-bone healing. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2025, 20, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, L.; Su, J.; Li, S.; Duncan, S.E.; Liu, Z.; Fan, G. Pharmacological Activity and Mechanism of Tanshinone IIA in Related Diseases. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 4735–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Feng, H.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Gao, H.; Tang, S.; Xie, C. Renoprotective Effects of Tanshinone IIA: A Literature Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Luo, Y. Tanshinone IIA delays liver aging by modulating oxidative stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1434024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeuku, S.O.; Pang, K.L.; Chin, K.Y. The Skeletal Effects of Tanshinones: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Su, S.; Xiang, X.; Sha, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.; Yan, H.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Comparative Analysis of the Major Chemical Constituents in Salvia miltiorrhiza Roots, Stems, Leaves and Flowers during Different Growth Periods by UPLC-TQ-MS/MS and HPLC-ELSD Methods. Molecules 2017, 22, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Lin, Z.; Ke, L.; Shi, P.; Li, S.; Huang, L.; Lin, X.; Yao, H. Recent Research Progress (2015–2021) and Perspectives on the Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Tanshinone IIA. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 778847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhao, W.R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.L.; Tang, J.Y. Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate: A review of pharmacological activity and pharmacokinetics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Shi, X.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Jiang, W.; Fang, Z. Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Injection on Hypertensive Nephropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Ke, L.; Ye, S.; Shi, P.; Yao, H. Pharmacological Mechanisms of Cryptotanshinone: Recent Advances in Cardiovascular, Cancer, and Neurological Disease Applications. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 6031–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. A comprehensive review of tanshinone IIA and its derivatives in fibrosis treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, W.; Mu, Y.P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.N.; Zhao, C.Q.; Chen, J.M.; Liu, P. Pharmacological Effects of Salvianolic Acid B Against Oxidative Damage. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 572373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Chen, G.; Liu, W.; Ye, D.; Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Song, J. Salvianolic Acid B: A Review of Pharmacological Effects, Safety, Combination Therapy, New Dosage Forms, and Novel Drug Delivery Routes. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Tan, Z.R.; Cheng, J.L.; Huang, W.H.; Zhang, W.; Deng, W.; Yuan, C.S.; Zhou, H.H. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetic comparison of tanshinones between two formulations of Salvia miltiorrhiza in healthy volunteers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Fu, W.; Zhou, P.; He, Y.; Fang, M.; Wan, H.; Zhou, H. Pharmacokinetic Comparison of Nine Bioactive Compounds of Guanxinshutong Capsule in Normal and Acute Myocardial Infarction Rats. Eur. J. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 47, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadoriya, A.; Shah, P.A.; Shrivastav, P.S.; Bharwad, K.D.; Singhal, P. Determination of terbinafine in human plasma using UPLC-MS/MS: Application to a bioequivalence study in healthy subjects. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, W.; Cao, L.; Xu, C.; Tan, G.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, M.; Jin, J. Comparative pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of cryptotanshinone, tanshinone IIA, dihydrotanshinone I, and tanshinone I after oral administration of pure tanshinones and liposoluble extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza to rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2020, 41, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.A.; Ramadan, A.A.; Abdelmonsif, D.A.; El-Kamel, A.H. Enhanced oral bioavailability of Tanshinone IIA using lipid nanocapsules: Formulation, in-vitro appraisal and pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.-M.; Sun, E.; Cui, L.; Jia, X.-B.; Jin, X. Improvement in oral bioavailability and dissolution of tanshinone IIA by preparation of solid dispersions with porous silica. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, Z.; Feng, N. Biotinylated-lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for improving the bioavailability and anti-leukaemia activity of Tanshinone IIA. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. S1), 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Zhang, W.; Tang, S.Y.; Luo, S.M.; Xiong, P.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Hu, H.C.; Chen, Y.Q.; Jia, B.; Yan, Q.H.; et al. Natural products in traditional Chinese medicine: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets of renal fibrosis and state-of-the-art drug delivery systems. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 116039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Kong, L.; Guo, R.B.; He, S.Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.T.; Cheng, L. Multifunctional icariin and tanshinone IIA co-delivery liposomes with potential application for Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 1648–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Ashour, A.; El-Kamel, A.H.; A Abdelmonsif, D.; Khalifa, H.M.; A Ramadan, A. Modified Lipid Nanocapsules for Targeted Tanshinone IIA Delivery in Liver Fibrosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 8013–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Liu, K.; Yang, D.; Wu, J.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xi, J.; Xie, F.; Li, X. The nanocrystal-loaded liposome of tanshinone IIA with high drug loading and stability towards efficient liver fibrosis reversion. Nanomedicine 2025, 63, 102797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Ye, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Jiang, C.; Lü, J. Tanshinones: Sources, pharmacokinetics and anti-cancer activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13621–13666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Chiu, T.L.; Kuo, S.J.; Chien, S.Y.; Chen, D.R.; Su, C.C. Tanshinone IIA inhibits the growth of pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 cells by decreasing protein expression of TCTP, MCL-1 and Bcl-xL. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang Ouyang, D.-S.; Huang, W.H.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Tan, Z.R.; Peng, J.B.; Wang, Y.C.; Guo, Y.; Hu, D.L.; Xiao, J.; et al. Kinetics of cytochrome P450 enzymes for metabolism of sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate in vitro. Chin. Med. 2016, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.; Dai, X.; Qin, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. Rapid Identification of Tanshinone IIA Metabolites in an Amyloid-β(1–42) Induced Alzherimer’s Disease Rat Model using UHPLC-Q-Exactive Qrbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2019, 24, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, S.; Cai, X.; Wang, W.; Luo, K.; Huang, D.; Gao, J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of tanshinone IIA after oral administration of Bushen Huoxue Qubi granules to rats with blood stasis syndrome. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudha, S.; Upmanyu, A.; Saraswat, D.; Singh, M. Pharmacological impacts of tanshinone on osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis: A review. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayanagi, H.; Kim, S.; Koga, T.; Nishina, H.; Isshiki, M.; Yoshida, H.; Saiura, A.; Isobe, M.; Yokochi, T.; Inoue, J.I.; et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Molon, R.S. Therapeutic Potential of Tanshinones in Osteolytic Diseases: From Molecular and Cellular Pathways to Preclinical Models. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, J.; Yuan, G. Tanshinone IIA attenuates polyethylene-induced osteolysis in a mouse model: The key role of miR-155-5p/FOXO3 axis. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, C.; Tong, W.; Zou, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W. Tanshinone IIA blocks dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts through inhibiting Nox4-derived ROS production. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 13695–13706. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wu, H.; Feng, S.; Huang, X.; Xu, H.; Shen, X.; Fu, Y.; Fang, S. Tanshinone IIA promotes osteogenic differentiation potential and suppresses adipogenic differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Hu, X.; Sun, K.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, B.; Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; Lu, S.; et al. Local Application of Tanshinone IIA protects mesenchymal stem cells from apoptosis and promotes fracture healing in ovariectomized mice. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Lv, H.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Shen, Y. Tanshinone I IA Reverses Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Impaired by Glucocorticoids via the ERK1/2-CREB Signaling Pathway. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2025, 105, e70069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, R. Tanshinone IIA alleviates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation by regulating FBXO11 expression. Clinics 2024, 79, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Zuo, Y.; He, J.; Liu, H. Tanshinone IIA Facilitates Efficient Cartilage Regeneration under Inflammatory Factors Caused Stress via Upregulating LncRNA NEAT1_2. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Han, D.; Ao, R.F.; Cai, Z.H.; Zhu, G.Z.; Wu, D.Z.; Gao, J.W.; Zhuang, J.S.; Tu, C.; Zhao, K.; et al. Tanshinone IIA attenuates osteoarthritis via inhibiting aberrant angiogenesis in subchondral bone. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 753, 109904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, L.H.; Tan, L.M.; Luo, W.B.; Xiong, H.; Lu, X.L.; Liu, D.; Li, W.Y.; Guo, Y.X.; Tang, Z.; et al. Tanshinone IIA Ameliorates Inflammation Response in Osteoarthritis via Inhibition of miR-155/FOXO3 Axis. Pharmacology 2021, 106, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Peng, H.; Yao, R.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, G.; Yu, H.; Qiu, Y. Inhibition of cellular communication network factor 1 (CCN1)-driven senescence slows down cartilage inflammaging and osteoarthritis. Bone 2020, 139, 115522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Lin, C.; Liu, Q.; He, Y.; Ruganzu, J.B.; Jin, H.; Peng, X.; Ji, S.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W. Tanshinone IIA attenuates neuroinflammation via inhibiting RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Feng, C.; Shao, L.; Mei, L.; Cao, R. Tanshinone IIA exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects in LPS-stimulated bovine endometrial epithelial cells by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 136, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Song, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wei, F. Tanshinone I and Tanshinone IIA/B attenuate LPS-induced mastitis via regulating the NF-κB. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, S.; Quarta, S.; Doccini, S.; Saviano, A.; Marigliano, N.; Polini, B.; Massaro, M.; Carluccio, M.A.; Calabriso, N.; Wabitsch, M.; et al. Tanshinone IIA and Cryptotanshinone Counteract Inflammation by Regulating Gene and miRNA Expression in Human SGBS Adipocytes. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Song, X.R.; Niu, Q.; Sun, Q.S.; Li, X.N.; Li, N.; Liu, B.L.; Huang, F.; Qiu, Z.X. Tanshinone IIA prevents LPS-induced inflammatory responses in mice via inactivation of succinate dehydrogenase in macrophages. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, P.; Su, E.; Jia, J.; Zhang, C.; Xie, S.; Huang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Ding, J.; Zou, Y.; et al. Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Improves Adverse Ventricular Remodeling Post-MI by Reducing Myocardial Necrosis, Modulating Inflammation, and Promoting Angiogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhao, S.; Fang, Q.; Qiao, Z.; Meng, Y.; Jin, Q.; Zong, L.; Shui, L.; Chen, S.; Han, H.; et al. Tanshinone IIA improved psychological stress-induced embryo implantation disorders by inhibiting GC/GR signaling and promoting angiogenesis. Phytomedicine 2025, 144, 156946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, C. Tanshinone IIA improves cardiac function via regulating miR-499–5p dependent angiogenesis in myocardial ischemic mice. Microvasc. Res. 2022, 143, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Luan, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate ameliorates cerebral ischemic injury through regulation of angiogenesis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Hu, W.; Wu, Z.; Xu, H.; Yao, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, B.; Wen, L.; Gong, D.; et al. Tanshinone II A attenuates vascular remodeling through klf4 mediated smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, P.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Z. Tanshinone IIA and hepatocellular carcinoma: A potential therapeutic drug. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1071415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, D.; Liao, W.; Su, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Fang, M.; Liu, Y. Tanshinone IIA regulates CCl4 induced liver fibrosis in C57BL/6J mice via the PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2024, 38, e23648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Kou, H.; Liu, P. Tanshinone IIA alleviate atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis via down-regulation of MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 152, 114465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tan, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, Y.; Feng, L. Tanshinone IIA attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation, oxidative stress, and liver fibrosis by inhibiting YAP signaling. Eur. J. Histochem. 2025, 69, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, S.; Xia, X.; Hu, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, D. Tanshinone IIA promotes vascular normalization and boosts Sorafenib’s anti-hepatoma activity via modulating the PI3K-AKT pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1189532. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W.; Song, P.; Zang, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Fang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Tanshinone IIA, a component of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, attenuated sepsis-induced liver injury via the SIRT1/Sestrin2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 340, 119169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Guan, Y.B.; Zhang, K.J.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y. Tanshinone IIA mediates protection from diabetes kidney disease by inhibiting oxidative stress induced pyroptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 316, 116667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Xu, H. Tanshinone IIA Promoted Autophagy and Inhibited Inflammation to Alleviate Podocyte Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 2709–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Kang, S.; Shao, T.; Xu, L.; Chen, J. Activation of SIRT3 by Tanshinone IIA ameliorates renal fibrosis by suppressing the TGF-β/TSP-1 pathway and attenuating oxidative stress. Cell. Signal. 2024, 122, 111348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, F. Tanshinone IIA improves diabetes-induced renal fibrosis by regulating the miR-34-5p/Notch1 axis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 4019–4040. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Long, F.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; He, Q.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X. Tanshinone IIA prevents acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity through the activation of the Nrf2-Mrp2/4 pathway in mice. Env. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Gu, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, J. Tanshinone IIA attenuates renal injury during hypothermic preservation via the MEK/ERK1/2/GSK-3β pathway. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Zou, H.-X.; Le, S.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Qiao, Y.M.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.C.; Lai, S.Q.; Huang, H. Tanshinone IIA confers protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and apoptosis via VDAC1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Ye, Z.; Xue, W.; Shi, S.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, H. Tanshinone IIA inhibits cardiomyocyte pyroptosis through TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathway after acute myocardial infarction. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1252942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Xiao, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, J. Tanshinone IIA from Salvia miltiorrhiza exerts anti-fibrotic effects on cardiac fibroblasts and rat heart tissues by suppressing the levels of pro-fibrotic factors: The key role of miR-618. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14078. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Rui, Q. Tanshinone IIA attenuates heart failure via inhibiting oxidative stress in myocardial infarction rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Fan, G. Tanshinone IIA ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Th17 cells differentiation. Acta Cir. Bras. 2022, 37, e370701. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Han, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Yu, J.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Liu, X.T.; Shan, H.; Wu, S.C. Tanshinone IIA protected against lipopolysaccharide-induced brain injury through the protective effect of the blood-brain barrier and the suppression of oxidant stress and inflammatory response. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 8304–8312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Lv, M.; Wang, D.; He, Y.; Han, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, S.; Yao, L.; Zhang, F. Tanshinone IIA Alleviates Traumatic Brain Injury by Reducing Ischemia-Reperfusion via the miR-124-5p/FoxO1 Axis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2024, 2024, 7459054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, S.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Tanshinone IIA Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Microglial Activation and Polarization via NF-κB Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 641848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Hu, Z.C.; Long, Y.; Cheng, L.C.; Zhao, C.Y.; Shao, M.K. Tanshinone IIA Microemulsion Protects against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via Regulating H3K18ac and H4K8ac In Vivo and In Vitro. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 1845–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Su, P.; Jiang, X.; Jin, Z. The protective effect of an extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen) on cerebral ischemic injury in animal models: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 317, 116772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherawat, K.; Mehan, S. Tanshinone-IIA mediated neuroprotection by modulating neuronal pathways. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 1647–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Q.; Hu, T.; Wu, G.L.; Qiao, L.J.; Cai, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.J. Tanshinone IIA, the key compound in Salvia miltiorrhiza, improves cognitive impairment by upregulating Aβ-degrading enzymes in APP/PS1 mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254 Pt 2, 127923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Peng, X.; He, Y.; Ruganzu, J.B.; Yang, W. Tanshinone IIA suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammatory responses through NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathways in human U87 astrocytoma cells. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 164, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Li, C.; Xiang, Z.; Jiao, B. Tanshinone IIA reduces the risk of Alzheimer’s disease by inhibiting iNOS, MMP-2 and NF-κBp65 transcription and translation in the temporal lobes of rat models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y. Tanshinone IIA attenuates Aβ-induced neurotoxicity by down-regulating COX-2 expression and PGE2 synthesis via inactivation of NF-κB pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Biol. Res. 2019, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chang, T.W.; Hsieh, W.H.; Hung, M.C.; Lin, I.H.; Lai, S.C.; Tzeng, Y.J. Simultaneous induction of apoptosis and necroptosis by Tanshinone IIA in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, J.Y.; Liu, S.D.; Fu, K.; Liu, H.Y. Tanshinone IIA induces cytochrome c-mediated caspase cascade apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells via the JNK pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Huang, C.C.; Huang, W.L.; Lin, T.K.; Liao, P.L.; Wang, P.W.; Liou, C.W.; Chuang, J.H. Tanshinone IIA induces intrinsic apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells both in vivo and in vitro associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.N.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Fang, L. Tanshinone IIA: A Review of its Anticancer Effects. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 611087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.T.; Zhang, X.L.; Zuo, H.N.; Lu, X.; Li, L. Articular cartilage degradation is prevented by tanshinone IIA through inhibiting apoptosis and the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6285–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, N.; Wang, F. Tanshinone prevents alveolar bone loss in ovariectomized osteoporosis rats by up-regulating phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 376, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, Z.; Yang, M.; Tong, L.; Zhang, Y. Inhibition of tanshinone IIA on renin activity protected against osteoporosis in diabetic mice. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Tong, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y. Recovery of chicken growth plate by TanshinoneⅡA through wnt/β-catenin pathway in thiram-induced Tibial Dyschondroplasia. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2019, 183, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Wang, J.; Han, M.; Zhao, M.; Li, K.; Lu, T.; Guo, Q.; Jiang, Q. Tanshinone IIA inhibits osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis via LDHC-regulated ROS generation. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yuan, B.; Chen, X. Tanshinone IIA attenuates osteoclastogenesis in ovariectomized mice by inactivating NF-kB and Akt signaling pathways. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Qu, Z.; Wang, D.; Huang, W.; Kong, L.; Yan, L. Tanshinone Ameliorates Glucocorticoid-Induced Bone Loss via Activation of AKT1 Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 878433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Ma, S.; Feng, W.; Wei, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhong, G.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; Li, J. Tanshinone IIA protects against polyethylene particle-induced osteolysis response in a mouse calvarial model. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 4461–4471. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Xu, H.; Dai, T.; Shi, K. Effects of Tanshinone IIA on osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Niu, Y.; Xie, W.; Wei, D.; Du, Q. Tanshinone IIA promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via ERK1/2-dependent Runx2 induction. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, H.B.; Yang, D.; Ha, H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.N.; Woo, E.R.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, Z.H. Tanshinone IIA inhibits osteoclast differentiation through down-regulation of c-Fos and NFATc1. Exp. Mol. Med. 2006, 38, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, J. Influence of release rate, dose and co-administration on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and PK-PD relationship of tanshinone IIA and tanshinol. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Tang, H.; Jiang, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, J. Development of sustained-release pellets to modulate the in vivo processes of the main active components of Danshen: A pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation. Phytomedicine 2019, 58, 152793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Moslemany, R.M.; El-Kamel, A.H.; Allam, E.A.; Khalifa, H.M.; Hussein, A.; Ashour, A.A. Tanshinone IIA loaded bioactive nanoemulsion for alleviation of lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury via inhibition of endothelial glycocalyx shedding. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yi, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Biomimetic metal-phenolic nanocarrier for co-delivery of multiple phytomedical bioactive components for anti-atherosclerotic therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 671, 125228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, B.; Feng, D.; Jiang, R.; Wang, X. Efficacy and safety of tanshinone IIA in combination with mesalazine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, A.; Zhao, P.; Soukup, S.T.; Guigas, C.; Stärke, J.; Kulling, S.E.; Diel, P. Chemical Stability and Bioactivity of tanshinone I, tanshinone IIA, cryptotanshinone and dihydrotanshinone in in vitro test systems. Toxicol. Lett. 2023, 375, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, W.; Han, W.; Wang, Z.; Ren, X.; Wang, D.; Pan, G.; Lin, Q.; Wang, X. Effect of Sodium Tanshinone IIA Sulfonate Injection on Blood Lipid in Patients With Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 770746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.S.; Andersson, I.J.; Cheung, P.-Y.; Baker, P.; Davidge, S.T.; Torrens, C. The vascular effects of sodium tanshinone IIA sulphonate in rodent and human pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fan, M.; Wei, S.; Guo, D.; Ong, H.T. The efficacy and safety of sodium tanshinone ⅡA sulfonate injection in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Wu, J.R.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B. Sodium Tanshinone II A Sulfonate Injection as Adjuvant Treatment for Unstable Angina Pectoris: A Meta-Analysis of 17 Randomized Controlled Trials. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 24, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cell/Disease-Related Model | Major Effect | Mechanism/Pathway Axis |
|---|---|---|
| BMSCs (under hypoxia/osteogenic induction) | ↑ ALP and mineralization; ↓ adipogenic differentiation | Synergistic activation of Akt/CREB and TGF-β/Smad3 signaling |
| Osteoblasts (e.g., MC3T3-E1) | Antioxidative/anti-apoptotic; maintenance of osteogenic phenotype | Inhibits Nox4-ROS and NF-κB; activates Nrf2 antioxidant pathway |
| Osteoclast precursors/osteoclasts (RANKL-induced) | Inhibits differentiation and bone resorption | ↓ RANKL/↑ OPG; suppression of c-Fos/NFATc1 and NF-κB |
| Chondrocytes (CHON-001; human chondrocytes) | Anti–IL-1β inflammation and protection from matrix degradation | ↓ FBXO11 → inhibition of PI3K/Akt and NF-κB; ↑ NEAT1_2 to maintain chondrocyte phenotype |
| Synovial fibroblast-like cells (RA-FLS) | Anti-TNF-α inflammatory cascade | ↑ miR-124-3p; ↓ miR-132-3p/miR-155-5p |
| Endothelial cells (HUVEC; CD31^hi Emcn^hi) | Context-dependent regulation of angiogenesis | ↑ HIF-1α/VEGF–VEGFR2 signaling or inhibition of OA-related VEGFR2–MAPK axis |
| Macrophages/immune cells | Anti-inflammatory and immunometabolic reprogramming | Inhibits SDH–HIF-1α and NLRP3; ↑ NAD⁺/Sirt2; activates Nrf2/HO-1 |
| Osteosarcoma/bone-related tumor cells | Induces apoptosis; inhibits proliferation | Mitochondrial dysfunction; JNK-dependent and extrinsic apoptosis pathways |
| Animal Model | Key Target(s) | Mechanism/Pathway |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis (rat; ACLT + MMx) | MMPs ↓; TIMPs ↑; BMP ↑; TGF-β ↑; IL-1β/TNF-α/NO ↓ | Inhibits MMPs; enhances TIMPs and anabolic factors; suppresses inflammatory mediators |
| Osteoporosis (rat; OVX—alveolar bone/BMSCs) | PHGDH ↑ (via promoter demethylation) | Restores PHGDH expression; delays BMSC senescence; preserves stemness |
| Diabetic bone loss (mouse; STZ) | Renin activity ↓; Ang II ↓ | Inhibits renin activity and Ang II signaling in bone |
| Tibial dyschondroplasia (TD) (experimental model) | Wnt5α ↑; BMP-2 ↑; moderated β-catenin | Activates noncanonical Wnt/β-catenin; restrains excessive canonical β-catenin |
| Rheumatoid arthritis–related bone loss (rat; adjuvant-induced) | LDHC inhibition; osteoclast markers ↓ | Binds/inhibits LDHC → reduces ROS → blocks RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis |
| Osteoporosis (mouse; OVX—general bone loss) | Bone indices improved: BV/TV, BS/TV, Tb.N, Tb.Pf, BMD | Exerts antiresorptive and osteoprotective effects on trabecular bone |
| Particle-induced calvarial osteolysis (mouse; polyethylene particles) | OPG ↑; OSCAR ↓; CTX-1 ↓ | Inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption around implant |
| Fracture repair (mouse; OVX, hydrogel delivery) | Nrf2 ↑; apoptosis ↓ | Activates Nrf2 antioxidant pathway; reduces TUNEL-positive cells |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, W.; Si, Y.; Wen, X.; Lin, D.; Yu, Z.; Xie, X.; Xu, J. Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Tanshinone IIA in Bone Injury Repair. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091338
Hu W, Si Y, Wen X, Lin D, Yu Z, Xie X, Xu J. Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Tanshinone IIA in Bone Injury Repair. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091338
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Weijian, Yameng Si, Xinru Wen, Duan Lin, Zihao Yu, Xin Xie, and Jiabin Xu. 2025. "Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Tanshinone IIA in Bone Injury Repair" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091338
APA StyleHu, W., Si, Y., Wen, X., Lin, D., Yu, Z., Xie, X., & Xu, J. (2025). Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Tanshinone IIA in Bone Injury Repair. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091338






