Investigating the Mechanism of Yiqi Huoxue Jieyu Granules Against Ischemic Stroke Through Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Active Compounds in YHJGs and Targets Prediction
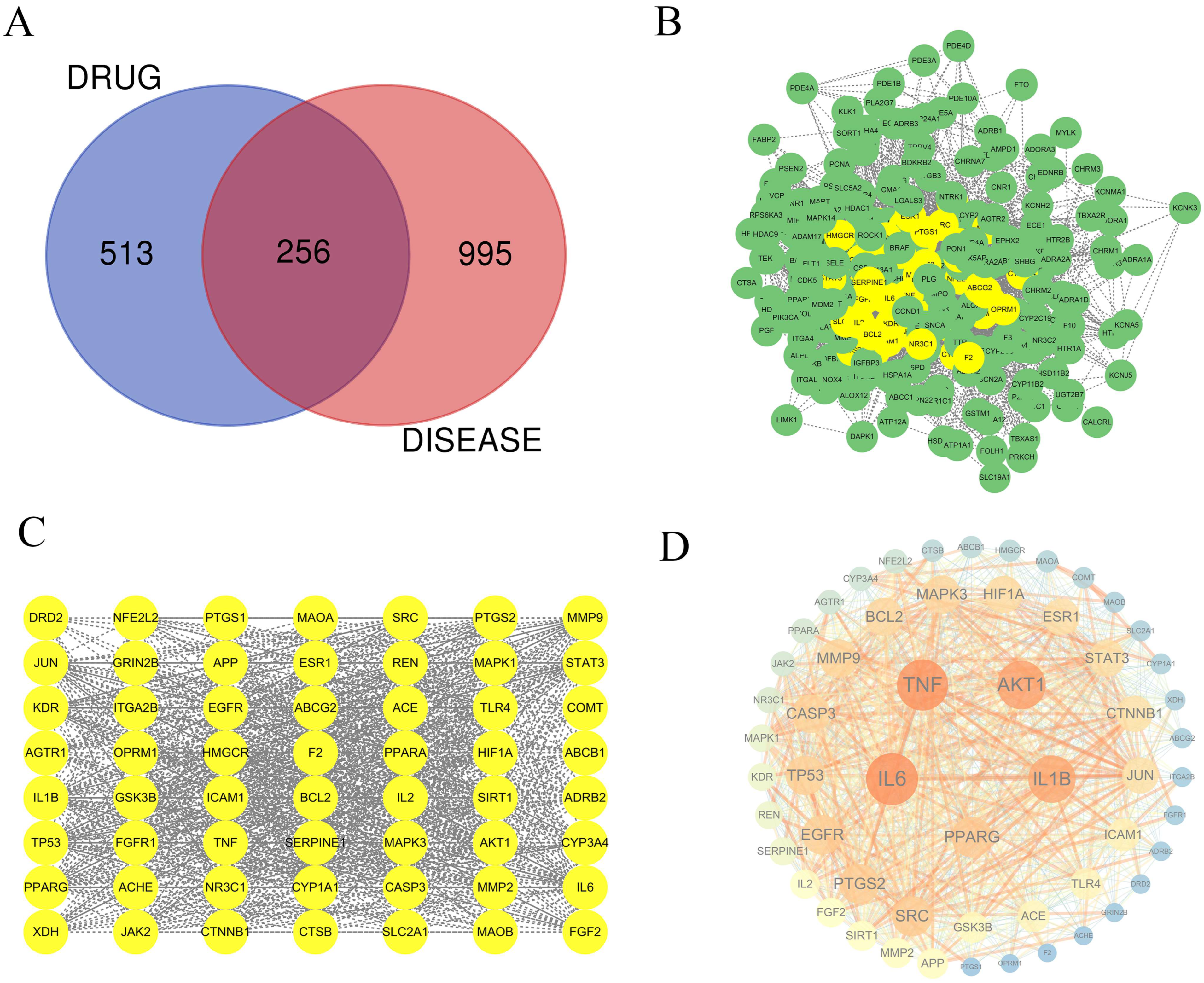
2.2. Drug-Compound-Target Network Construction
2.3. Ischemic Stroke-Related Targets
2.4. PPI Network Construction and Key Target Prediction
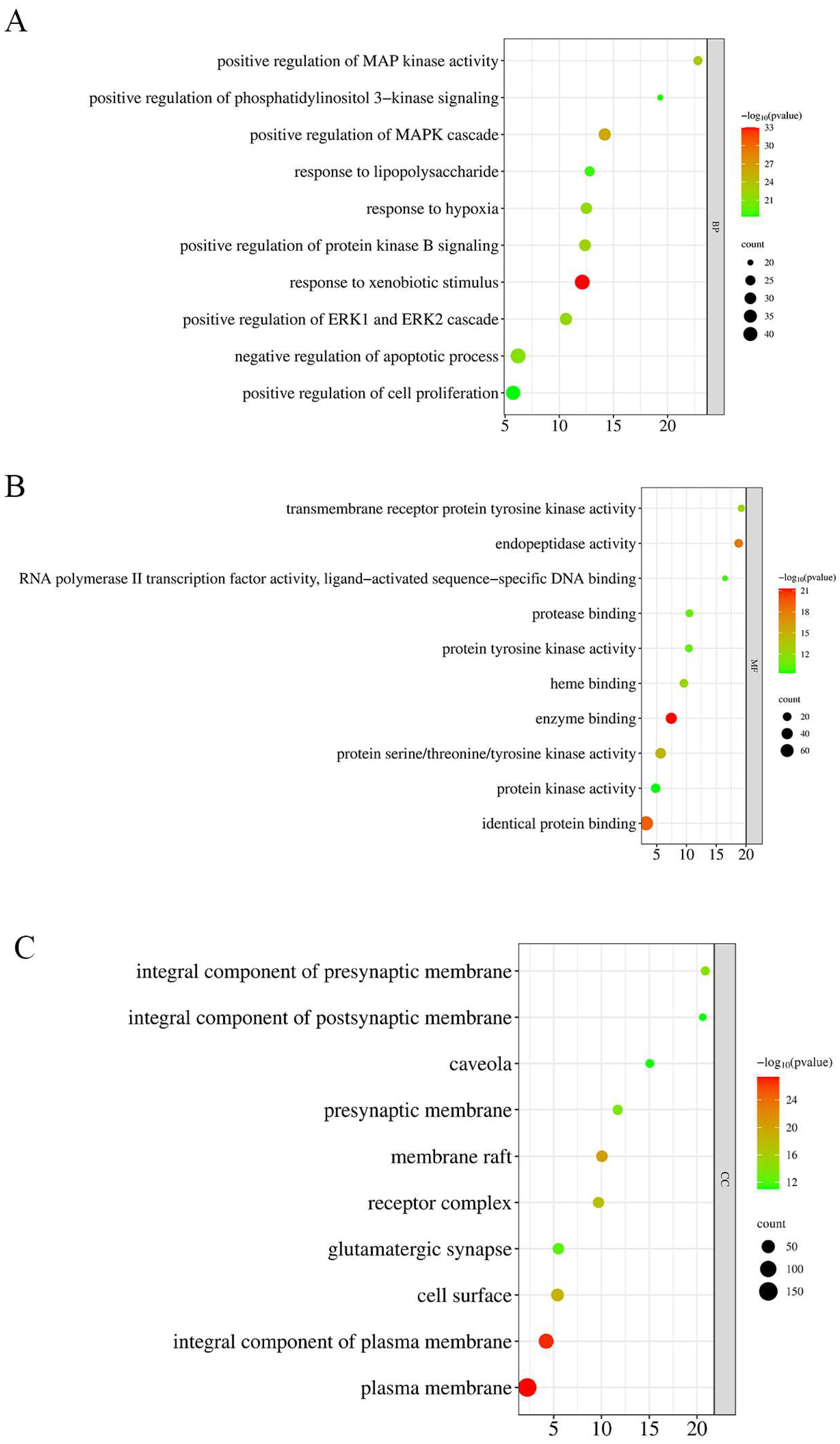
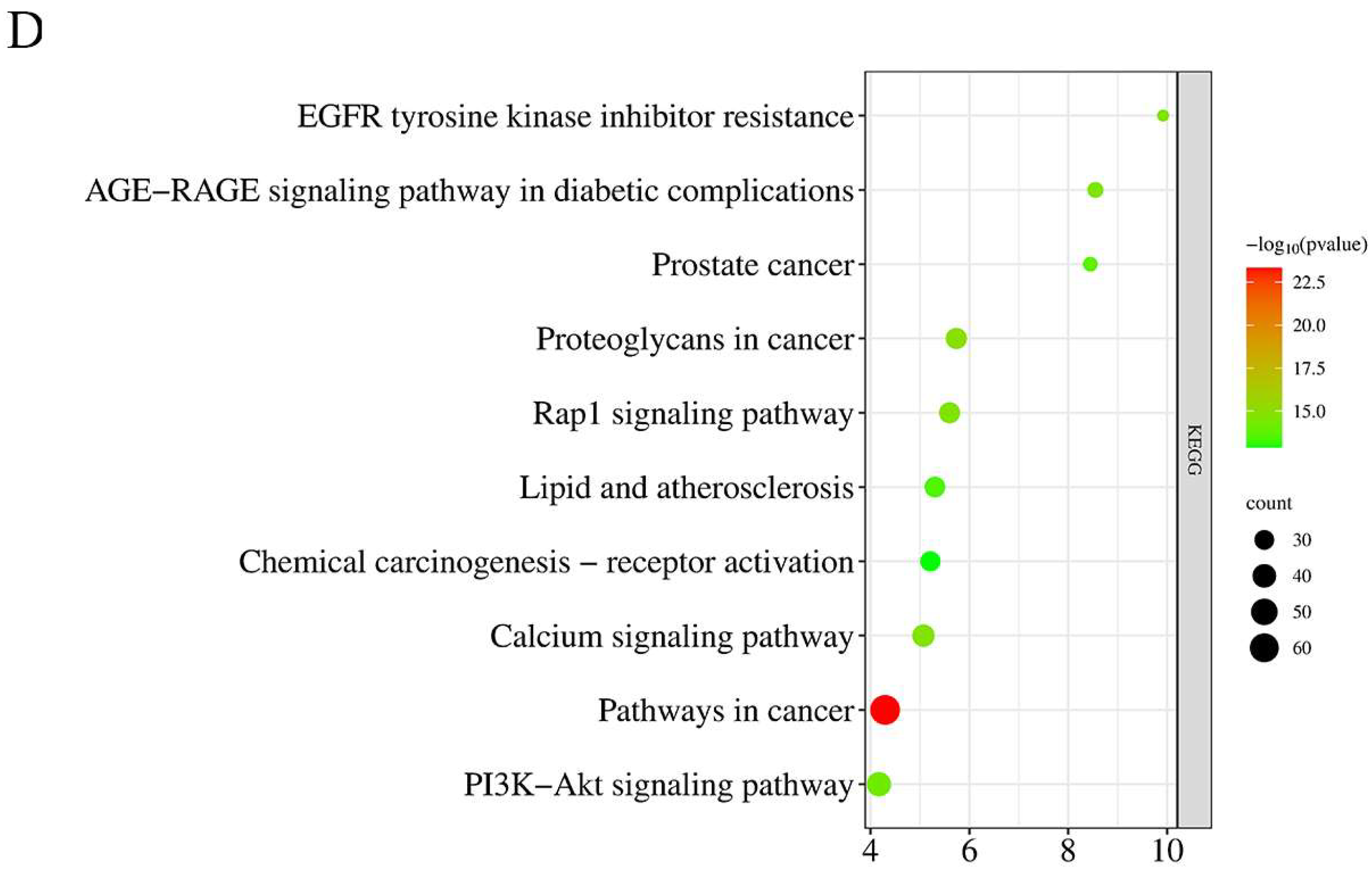
2.5. GO and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
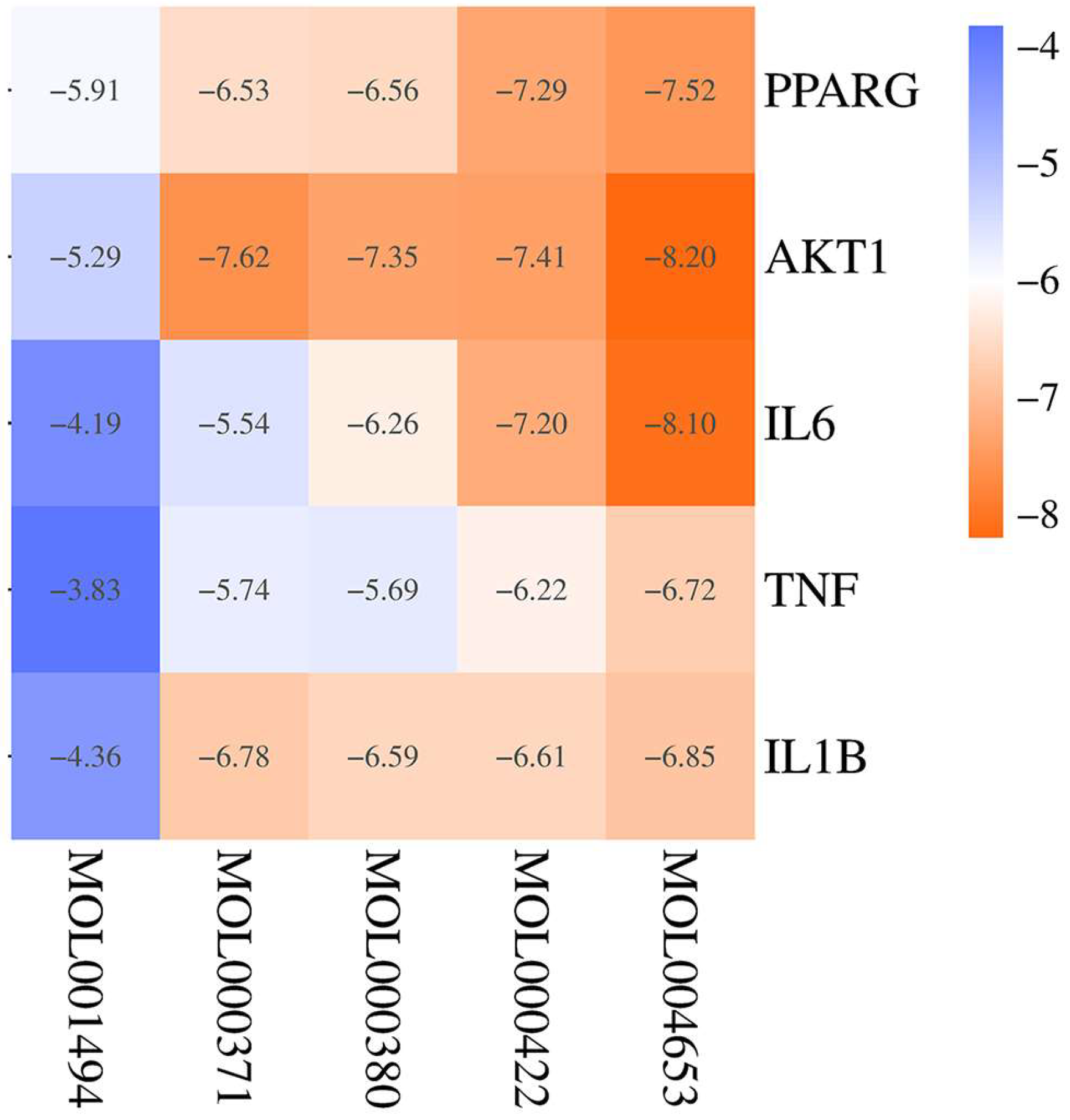
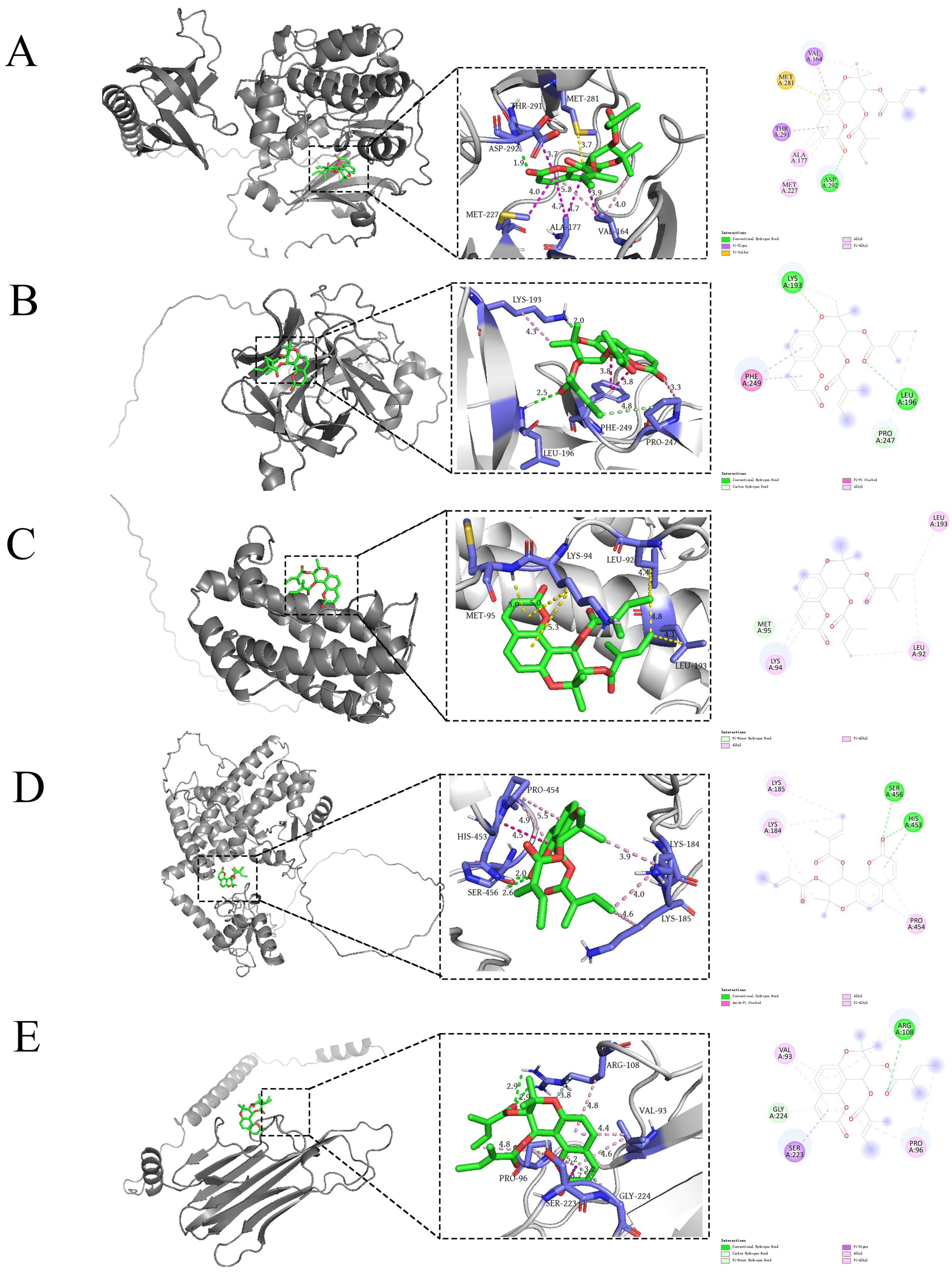
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. Experimental Verification
2.7.1. HPLC Profile of YHJGs
2.7.2. YHJGs Improved Neurological Deficits After MCAO in Rats
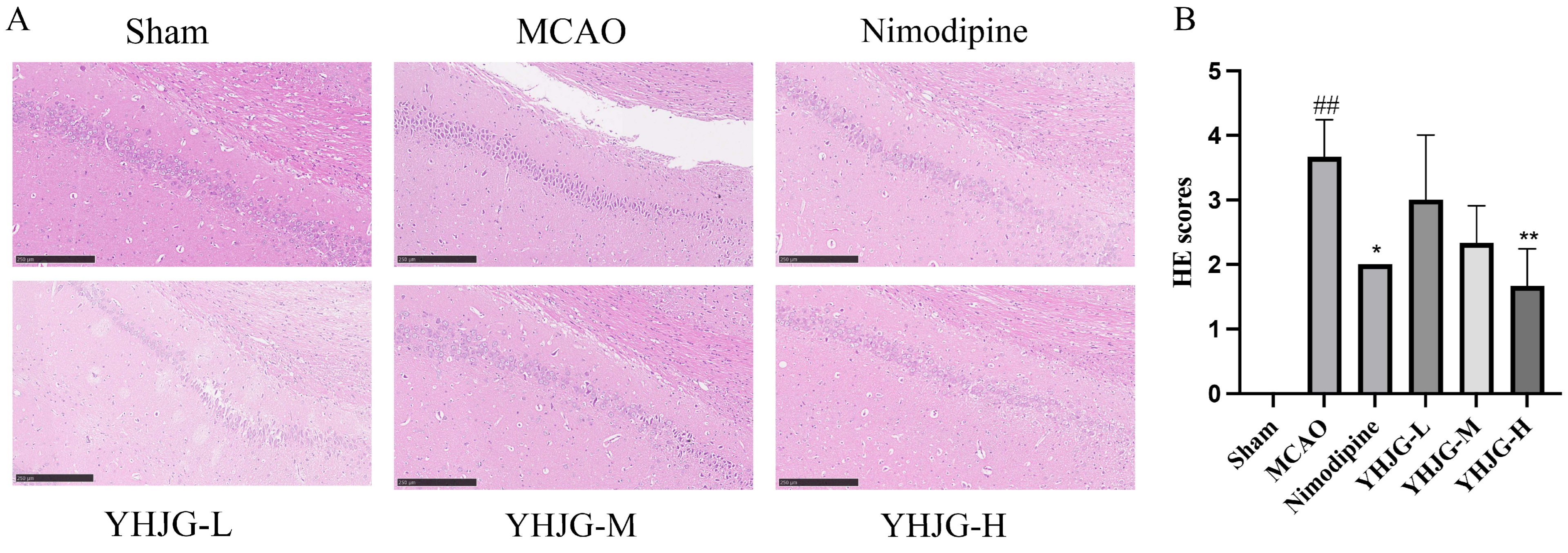
2.7.3. YHJGs Reduced Infarction Volume and Infarction Rate After MCAO in Rats
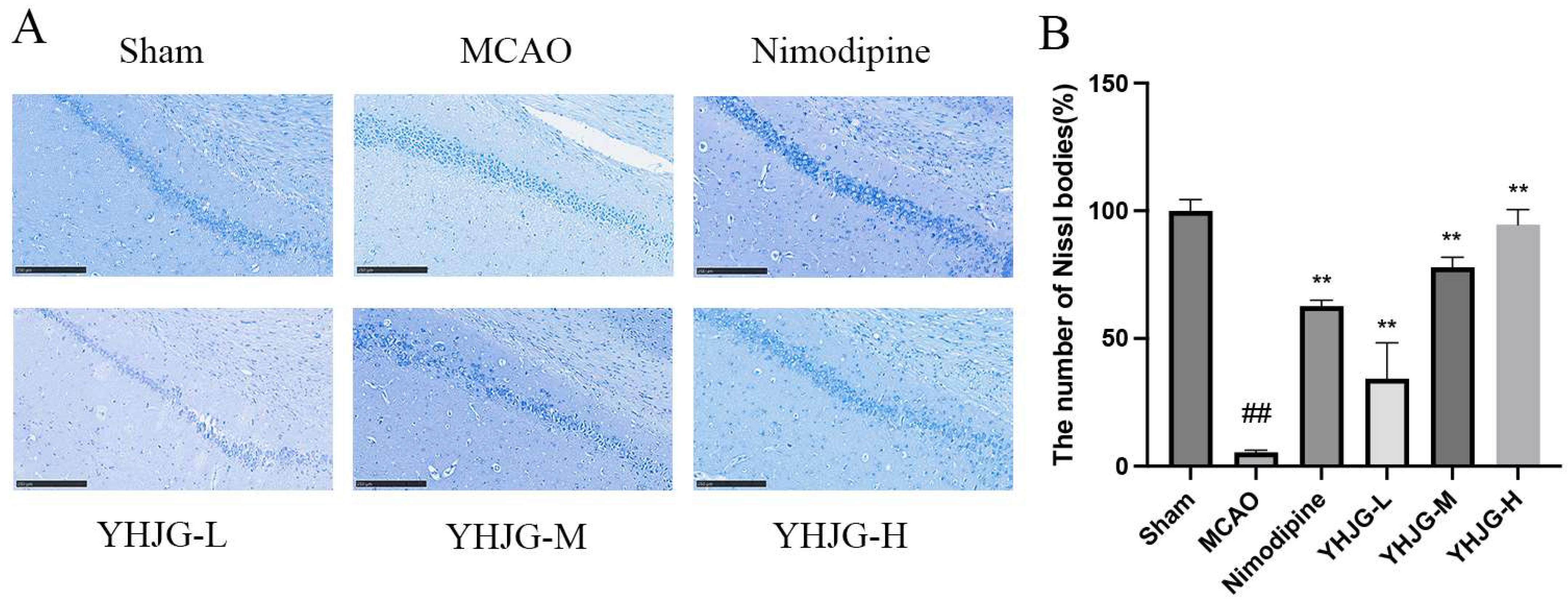
2.7.4. YHJGs Alleviated the Damage to the Nissl Bodies in MCAO Rats
2.7.5. The Effects of YHJGs on the mRNA Levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, AKT1, and PPAR-γ in the MCAO Rat Brain Tissue
2.7.6. YHJGs Down-Regulated the Expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, AKT1, PPAR-γ, and pERK1/2/ERK 1/2 in the Ischemic Hemisphere After MCAO
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection and Processing
4.1.1. Composite Ingredients of YHJGs
4.1.2. Screening of Bioactive Ingredients
4.1.3. Target Prediction of Bioactive Ingredients
4.1.4. Identification of Ischemic Stroke-Related Targets
4.2. Network Construction
4.2.1. Drug–Ingredient–Target Network Construction
4.2.2. Obtaining Shared Targets Between YHJGs and Specific Diseases
4.2.3. Construction of PPI Network Diagram
4.2.4. Key Target Prediction
4.3. GO and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.4. Molecular Docking
4.5. Experimental Verification
4.5.1. Preparation of YHJGs
4.5.2. HPLC Analysis
4.5.3. Animals and Experimental Grouping
4.5.4. Determination of Neurological Defect Score
4.5.5. Measurement of Infarct Volume and Determination of Infarction Rate
4.5.6. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining Was Used to Observe the Pathological Changes in the Brain Tissue
4.5.7. Nissl Staining Was Used to Examine Neuronal Damage in the Rat Brain Tissue
4.5.8. Quantitative RT-PCR Was Used to Examine Gene Expression
4.5.9. Western Blotting Was Used to Examine Protein Expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, AKT1, PPAR-γ and pERK1/2/ ERK 1/2
4.5.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebrahimi, V.; Rastegar-Moghaddam, S.H.; Mohammadipour, A. Therapeutic Potentials of MicroRNA-126 in Cerebral Ischemia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiffge, D.J.; Werring, D.J.; Paciaroni, M.; Dawson, J.; Warach, S.; Milling, T.J.; Engelter, S.T.; Fischer, U.; Norrving, B. Timing of Anticoagulation After Recent Ischaemic Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y. Neuronal Injuries in Cerebral Infarction and Ischemic Stroke: From Mechanisms to Treatment (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e110, Erratum in Stroke 2019, 50, e440–e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turc, G.; Bhogal, P.; Fischer, U.; Khatri, P.; Lobotesis, K.; Mazighi, M.; Schellinger, P.D.; Toni, D.; de Vries, J.; White, P.; et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO)—European Society for Minimally Invasive Neurological Therapy (ESMINT) Guidelines on Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, 15, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Bie, X.; Xu, B.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, T. Clinical Efficacy of Yiqi Huoxue Jieyu Formula in the Treatment of Post—Stroke Depression with Qi Deficiency, Blood Stasis, and Liver Qi Stagnation Syndrome. World J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2023, 18, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Jin, W.; Shi, Y. Integration Strategy of Network Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Narrative Review. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 42, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, K.; Wang, C.; Ma, C.; Gong, L.; Zhou, H.; Xue, X.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Protective Effects of Dietary Quercetin on Cerebral Ischemic Injury: Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability-Enhancing Nanoformulations. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4470–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sánchez, C.; Lagoa, R.; Poejo, J.; García-López, V.; García-Martínez, V.; Gutierrez-Merino, C. An Update of Kaempferol Protection against Brain Damage Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion and by 3-Nitropropionic Acid. Molecules 2024, 29, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przykaza, Ł. Understanding the Connection Between Common Stroke Comorbidities, Their Associated Inflammation, and the Course of the Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Cascade. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 782569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henein, M.Y.; Vancheri, S.; Longo, G.; Vancheri, F. The Role of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tiegs, G.; Horst, A.K. TNF in the Liver: Targeting a Central Player in Inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-W.; Chen, C.-M.; Chang, K.-H. Biomarker of Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, K.; Kawano, T. Akt Is a Molecular Target for Signal Transduction Therapy in Brain Ischemic Insult. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 92, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lang, J.; Zeng, Z.; McCullough, L.D. Akt1 Gene Deletion and Stroke. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 269, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergadi, E.; Ieronymaki, E.; Lyroni, K.; Vaporidi, K.; Tsatsanis, C. Akt Signaling Pathway in Macrophage Activation and M1/M2 Polarization. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2017, 198, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Deng, S.-M.; He, Z.-Y. Association between PPARG Genetic Polymorphisms and Ischemic Stroke Risk in a Northern Chinese Han Population: A Case-Control Study. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Si, X.-M.; Yang, G.-L.; Zhou, L. Relationship Between PPAR-γ Gene Polymorphisms and Ischemic Stroke Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onder, A.; Trendafilova, A. A Review on Anomalin: A Natural Bioactive Pyranocoumarin from the Past to the Future. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Ali, H.; Shah, K.U.; Ali, H.; Shehzad, O.; Onder, A.; Kim, Y.S. Anomalin Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Lungs Injury Through Inhibition of AP-1 Signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, F.-J.; Jia, Z.-Z.; Zhang, T.; Sun, J.; Du, X.-Y.; Wang, S.-X.; Chai, L.-J.; Hu, L.-M. Xueshuantong Injection Combined with Salvianolate Lyophilized Injection Improves the Synaptic Plasticity Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats through PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RhoA/ROCK Pathways. Brain Res. 2022, 1787, 147923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, H.; Liu, X. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling by NDRG2 Contributes to Neuronal Apoptosis and Autophagy in Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2023, 32, 106984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walana, W.; Wang, J.-J.; Yabasin, I.B.; Ntim, M.; Kampo, S.; Al-Azab, M.; Elkhider, A.; Dogkotenge Kuugbee, E.; Cheng, J.-W.; Gordon, J.R.; et al. IL-8 Analogue CXCL8 (3-72) K11R/G31P, Modulates LPS-Induced Inflammation via AKT1-NF-Kβ and ERK1/2-AP-1 Pathways in THP-1 Monocytes. Hum. Immunol. 2018, 79, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamdzyk, M.; Lenahan, C.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in Stroke Prevention and Therapy-The Best Is yet to Come? J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 2275–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Han, J.; Hui, L. MAPK Signaling in Inflammation-Associated Cancer Development. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, Y.T.; Aziz, F.; Guerrero-Castilla, A.; Arguelles, S. Signaling Pathways in Inflammation and Anti-Inflammatory Therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1449–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, A.; Kang, Y. Rational Application of β-Hydroxybutyrate Attenuates Ischemic Stroke by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial-Dependent Apoptosis via Activation of the Erk/CREB/eNOS Pathway. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.; Unsicker, K. ERK and Cell Death: ERK1/2 in Neuronal Death. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawe, N.; Steinberg, G.; Zhao, H. Dual Roles of the MAPK/ERK1/2 Cell Signaling Pathway After Stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, X.; Huang, C.; Chen, J.; Shu, S.; Chen, G.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Y. ERK Inhibition Reduces Neuronal Death and Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses in Forebrain-Specific Ppp2cα Knockout Mice. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, Y. Down-Regulation of NAA10 Mediates the Neuroprotection Induced by Sevoflurane Preconditioning via Regulating ERK1/2 Phosphorylation. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 755, 135897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Li, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Shan, A. Astragalus Polysaccharides Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation via the NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5525–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Cañestro, C.; Reiner, M.F.; Bonetti, N.R.; Liberale, L.; Merlini, M.; Wüst, P.; Amstalden, H.; Briand-Schumacher, S.; Semerano, A.; Giacalone, G.; et al. AP-1 (Activated Protein-1) Transcription Factor JunD Regulates Ischemia/Reperfusion Brain Damage via IL-1β (Interleukin-1β). Stroke 2019, 50, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A Database of Systems Pharmacology for Drug Discovery from Herbal Medicines. J. Cheminformatics 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 Edition—Chinese Pharmacopoeia, Drug Standards, Regulations Online Inquiry—Pubiao Net. Available online: https://db2.ouryao.com/yd2020/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Wang, P.-C.; Wang, S.-X.; Yan, X.-L.; He, Y.-Y.; Wang, M.-C.; Zheng, H.-Z.; Shi, X.-G.; Tan, Y.-H.; Wang, L.-S. Combination of Paeoniflorin and Calycosin-7-Glucoside Alleviates Ischaemic Stroke Injury via the PI3K/AKT Signalling Pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, G.-X.; Liang, C.; Wang, J.; Duan, C.-Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.-L. Astragaloside IV Improves Neurobehavior and Promotes Hippocampal Neurogenesis in MCAO Rats Though BDNF-TrkB Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S.; Deivendran, B.; Perumal, E. Chemotherapeutic Potential of Saikosaponin D: Experimental Evidence. J. Xenobiot. 2022, 12, 378–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, A.-R.; Mi, L.-F.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Hu, M.-Z.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.-B.; Zheng, S. Saikosaponin A Improved Depression-like Behavior and Inhibited Hippocampal Neuronal Apoptosis After Cerebral Ischemia through p-CREB/BDNF Pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 403, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, G. Saikosaponin A Attenuates Neural Injury Caused by Ischemia/Reperfusion. Transl. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, M.; Xie, X.; Xu, Y.; Su, P.; Jin, Z. Efficacy of Ferulic Acid in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Injury in Rats: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1278036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, F.; Zhang, R.; Sun, C.; Gong, C.; Jian, L.; Ding, L. Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Amygdalin and Paeoniflorin After Single and Multiple Intravenous Infusions of Huoxue-Tongluo Lyophilized Powder for Injection in Healthy Chinese Volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, W.; Qi, B.; Zeng, F.; Bao, N.; Li, Q.; Guo, F.; Xia, S. The Potential Drug for Treatment in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Bioinformatical Study Based on Distinct Drug Databases. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, A.; Islam, S.; Tankhilevich, E.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The AlphaFold Database of Protein Structures: A Biologist’s Guide. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Rehmannioside A Improves Cognitive Impairment and Alleviates Ferroptosis via Activating PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 and SLC7A11/GPX4 Signaling Pathway After Ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 289, 115021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; He, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wan, H.; Yang, J. Formononetin Protects against Inflammation Associated with Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fei, Y.; Xu, X.; Yao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Ding, H. Shikonin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting NOD2/RIP2/NF-κB-Mediated Microglia Polarization and Neuroinflammation. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 33, 107689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| MOLDID | Label | Drug | Component Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOL004653 | CH7 | Chai Hu | (+)-Anomalin |
| MOL001494 | CX2 | Chuan Xiong | Mandenol |
| MOL000371 | HQ3 | Huang Qi | 3,9-di-O-Methylnissolin |
| MOL000380 | HQ5 | Huang Qi | (6aR,11aR)-9,10-Dimethoxy-6a,11a-dihydro-6H-benzofurano[3,2-c]chromen-3-ol |
| MOL000422 | F | Huang Qi, Chai Hu, Bai Shao, and Shi Chang Pu | kaempferol |
| Drug Name | Chinese Name | Batch Number | Manufacture Company | Place of Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astragalus membranaceus | Huang Qi | 201222 | Jiaxing Oriental Chinese Medicine Decoction Pieces Co., Ltd., Jiaxing, Zhejiang, China | Neimenggu, China |
| Ligusticum chuanxiong | Chuan Xiong | 201211 | Sichuan, China | |
| Bupleurum chinense | Chai Hu | 201215 | Hebei, China | |
| Prunus persica | Tao Ren | 201123 | Shandong, China | |
| Acorus tatarinowii | Shi Chang Pu | 200826 | Zhejiang, China | |
| Paeonia lactiflora | Bai Shao | 201212 | Anhui, China | |
| Curcuma aromatica | Yu Jin | 201201 | Zhejiang University of Chinese Medicine Decoction Pieces Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China | Zhejiang, China |
| Time (min) | Acetonitrile (A%) | 0.1% Phosphoric Acid–Water (B%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 95 |
| 5 | 5 | 95 |
| 10 | 13 | 87 |
| 16 | 18 | 82 |
| 23 | 19.7 | 80.3 |
| 26 | 19.7 | 80.3 |
| 32 | 25 | 75 |
| 45 | 55 | 45 |
| 55 | 5 | 95 |
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | CTAGAGACAGCCGCATCTTCTTG | GTAGTTGAGGTCAATGAAGGGGT |
| IL-1β | GGCAGGTCTACTTTGGAGTCATT | CTCCACGGGCAAGACATAGG |
| IL-6 | AGGCTGACAGACCCCAAAAG | TAGCCACTCCTTCTGTGACTCTA |
| AKT1 | CGACGTAGCCATTGTGAAGGAG | ATTGTGCCACTGAGAAGTTGTTG |
| PPAR-γ | TGAATCCAGAGTCCGCTGACC | CGCCCTCGCCTTTGCTTTG |
| GAPDH | GACATGCCGCCTGGAGAAAC | AGCCCAGGATGCCCTTTAGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, T.; Wan, H. Investigating the Mechanism of Yiqi Huoxue Jieyu Granules Against Ischemic Stroke Through Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091332
Chen Y, Zhou H, Zhang T, Wan H. Investigating the Mechanism of Yiqi Huoxue Jieyu Granules Against Ischemic Stroke Through Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091332
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ying, Huifen Zhou, Ting Zhang, and Haitong Wan. 2025. "Investigating the Mechanism of Yiqi Huoxue Jieyu Granules Against Ischemic Stroke Through Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091332
APA StyleChen, Y., Zhou, H., Zhang, T., & Wan, H. (2025). Investigating the Mechanism of Yiqi Huoxue Jieyu Granules Against Ischemic Stroke Through Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091332









