Pharmacogenomics of Tirzepatide: Genomic Insights into Dual GIP/GLP-1 Agonist Response in Type 2 Diabetes and Atherosclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
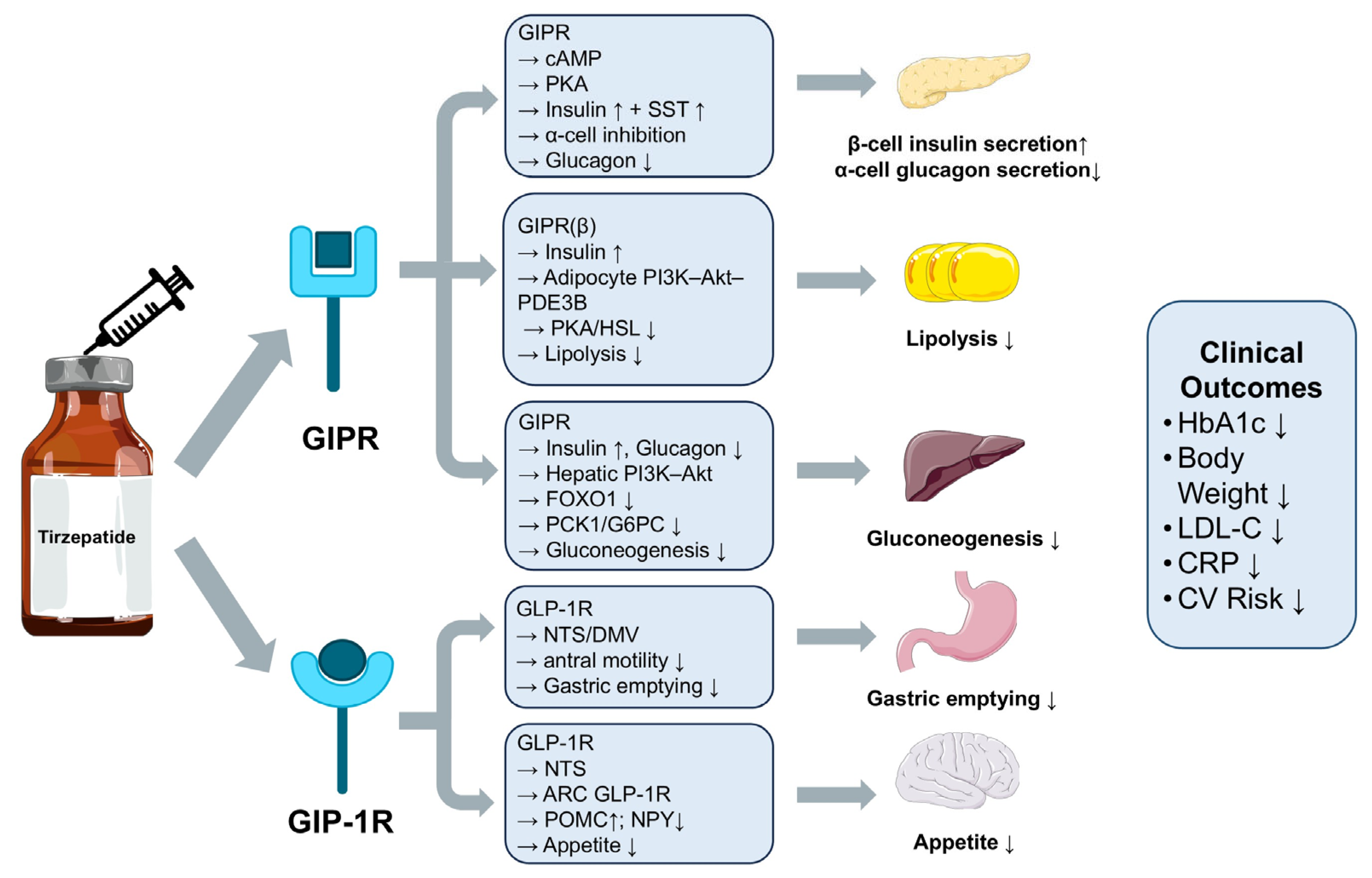
2. Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Effects of Tirzepatide
3. Genetic Variants Associated with Tirzepatide Response
3.1. GLP1R Genetic Variants and Their Impact on Tirzepatide Response
3.2. GIPR Genetic Variants and Their Impact on Tirzepatide Response
3.3. TCF7L2 Genetic Variation and Their Impact on Tirzepatide Response
3.4. Obesity-Related Genetic Variants and Their Impact on Tirzepatide-Induced Weight Loss
3.5. Genomic Insights from GWAS and Pharmacogenomic Databases
3.6. Tirzepatide Toxicity and Safety
4. Genetic Determinants Influencing Tirzepatide Efficacy in T2DM and AS Comorbidity
4.1. T2DM-Associated Genetic Variants Modulating GLP-1RA Therapeutic Efficacy
4.2. AS-Related Genetic Background Shapes Cardiovascular Benefits of Tirzepatide
4.3. Disease-Related Downregulation of GLP1R Expression
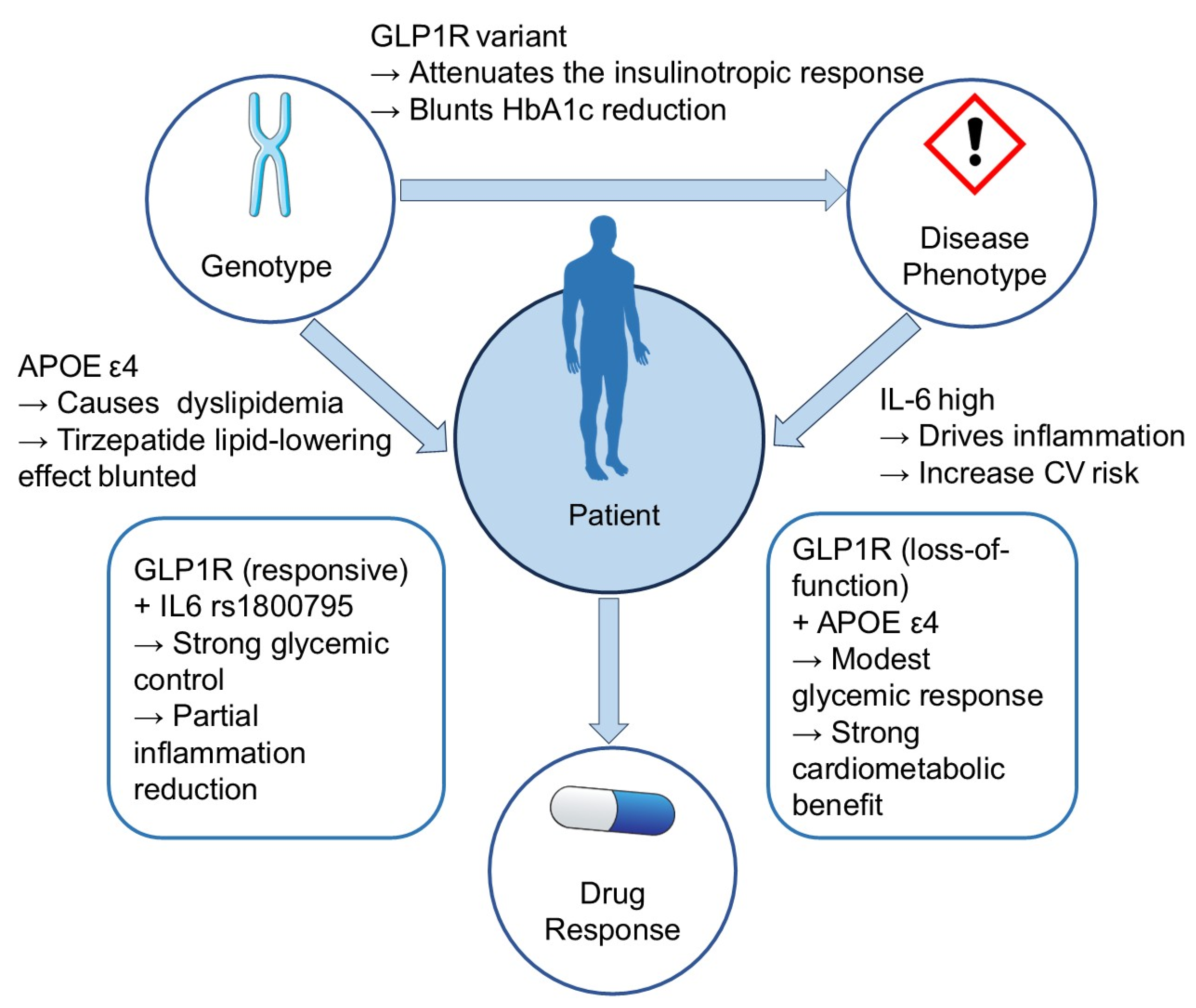
4.4. Toward a Gene–Disease–Drug Interaction Model for Tirzepatide
5. Pharmacogenomic Stratification and Precision Treatment Potential
5.1. Integrating Key Pharmacogenomic Markers
5.2. Multi-Omics Data Fusion for Enhanced Stratification
5.3. Personalized Therapeutic Algorithms
5.4. Clinical Translation of Pharmacogenomic Stratification
6. Challenges and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Provost, P.; Doucet, J.; Hammarberg, T.; Gerisch, G.; Samuelsson, B.; Radmark, O. 5-Lipoxygenase interacts with coactosin-like protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16520–16527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh-Swaby, O.R.; Goodman, S.G.; Leiter, L.A.; Cheng, A.; Connelly, K.A.; Fitchett, D.; Jüni, P.; Farkouh, M.E.; Udell, J.A. Glucose-lowering drugs or strategies, atherosclerotic cardiovascular events, and heart failure in people with or at risk of type 2 diabetes: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarson, T.R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U.H. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: A systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007–2017. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low Wang, C.C.; Hess, C.N.; Hiatt, W.R.; Goldfine, A.B. Clinical Update: Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus: Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—Mechanisms, Management, and Clinical Considerations. Circulation 2016, 133, 2459–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakasis, P.; Theofilis, P.; Patoulias, D.; Vlachakis, P.K.; Antoniadis, A.P.; Fragakis, N. Diabetes-Driven Atherosclerosis: Updated Mechanistic Insights and Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanrewaju, O.A.; Sheeba, F.; Kumar, A.; Ahmad, S.; Blank, N.; Kumari, R.; Kumari, K.; Salame, T.; Khalid, A.; Yousef, N.; et al. Novel Therapies in Diabetes: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, SGLT2 Inhibitors, and Beyond. Cureus 2023, 15, e51151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pérez, L.E.; Alvarez, M.; Dilla, T.; Gil-Guillén, V.; Orozco-Beltrán, D. Adherence to therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2013, 4, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabhi, K.N.; Gohil, N.V.; Tanveer, N.; Hussein, S.; Pingili, S.; Makkena, V.K.; Jaramillo, A.P.; Awosusi, B.L.; Ayyub, J.; Nath, T.S. Assessing the Link Between Statins and Insulin Intolerance: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e42029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; D’Alessio, D.A. Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor co-agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with unmatched effectiveness regrading glycaemic control and body weight reduction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prato, S.; Kahn, S.E.; Pavo, I.; Weerakkody, G.J.; Yang, Z.; Doupis, J.; Aizenberg, D.; Wynne, A.G.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Heine, R.J.; et al. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Hong, L.; Li, B.; Yang, L. Tirzepatide’s innovative applications in the management of type 2 diabetes and its future prospects in cardiovascular health. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1453825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawed, A.Y.; Mari, A.; Brown, A.; McDonald, T.J.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Hong, M.G.; Sharma, S.; Robertson, N.R.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Pharmacogenomics of GLP-1 receptor agonists: A genome-wide analysis of observational data and large randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, K.R.; Hicks, J.K.; Pui, C.H.; Relling, M.V.; Evans, W.E. Pharmacogenomics and individualized medicine: Translating science into practice. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, P.; Mousa, S.S.; Mousa, S.A. Pharmacogenomics in type II diabetes mellitus management: Steps toward personalized medicine. Pharmacogenom. Pers. Med. 2009, 2, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Taliun, D.; Thurner, M.; Robertson, N.R.; Torres, J.M.; Rayner, N.W.; Payne, A.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Scott, R.A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Block, C.; Bailey, C.; Wysham, C.; Hemmingway, A.; Allen, S.E.; Peleshok, J. Tirzepatide for the treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes: An endocrine perspective. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.K.; Nikooienejad, A.; Bray, R.; Cui, X.; Wilson, J.; Duffin, K.; Milicevic, Z.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.A. Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Tirzepatide Improves Beta-cell Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Pérez Manghi, F.C.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvik, B.; Giorgino, F.; Jódar, E.; Frias, J.P.; Fernández Landó, L.; Brown, K.; Bray, R.; Rodríguez, Á. Once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Wysham, C.; Frías, J.P.; Kaneko, S.; Lee, C.J.; Fernández Landó, L.; Mao, H.; Cui, X.; Karanikas, C.A.; Thieu, V.T. Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltis, J.P.; Marathe, J.A.; Nguyen, M.T.; Le, R.; Bursill, C.A.; Marathe, C.S.; Nelson, A.J.; Psaltis, P.J. Incretin-based therapies for the management of cardiometabolic disease in the clinic: Past, present, and future. Med. Res. Rev. 2025, 45, 29–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, M.U.; Mahmud, O.; Ahmed, S.; Qureshi, S.A.; Kakar, W.G.; Fatima, S.S. The Effects of Tirzepatide on Lipid Profile: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 33, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.M.; Nikooienejad, A.; Robins, D.A.; Roell, W.C.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Haupt, A.; Duffin, K.L.; Taskinen, M.R.; Ruotolo, G. The dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, tirzepatide, improves lipoprotein biomarkers associated with insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, H.; Lv, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Hu, K.; Sun, H. Exploring the molecular mechanisms of tirzepatide in alleviating metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver in mice through integration of metabolomics, lipidomics, and proteomics. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongejan, Y.K.; Eikenboom, J.C.J.; Gijbels, M.J.J.; Berbée, J.F.P.; van Vlijmen, B.J.M. Atherothrombosis model by silencing of protein C in APOE*3-Leiden.CETP transgenic mice. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eenige, R.; Ying, Z.; Tramper, N.; Wiebing, V.; Siraj, Z.; de Boer, J.F.; Lambooij, J.M.; Guigas, B.; Qu, H.; Coskun, T.; et al. Combined glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonism attenuates atherosclerosis severity in APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice. Atherosclerosis 2023, 372, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.K.; Carr, M.J.; Kontopantelis, E.; Leelarathna, L.; Thabit, H.; Emsley, R.; Buchan, I.; Mamas, M.A.; van Staa, T.P.; Sattar, N.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular and Heart Failure Events with SGLT2 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, and Their Combination in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganakumar, V.; Fernandez, C.J.; Pappachan, J.M. Antidiabetic combination therapy and cardiovascular outcomes: An evidence-based approach. World J. Diabetes 2025, 16, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiao, B.; He, C. Combination treatment of SGLT2i and GLP-1RA associated with improved cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes patients with acute coronary syndrome: A propensity score-matched cohort study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2025, 431, 133229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez, J.C.; Jablonski, K.A.; Bayley, N.; Pollin, T.I.; de Bakker, P.I.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Knowler, W.C.; Nathan, D.M.; Altshuler, D. TCF7L2 polymorphisms and progression to diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The genetics of obesity: From discovery to biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chedid, V.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Carlson, P.; Van Malderen, K.; Acosta, A.; Zinsmeister, A.; Camilleri, M. Allelic variant in the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor gene associated with greater effect of liraglutide and exenatide on gastric emptying: A pilot pharmacogenetics study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, M.; Gill, D.; Ahlqvist, E.; Robinson, T.; Mariosa, D.; Johansson, M.; Cortez Cardoso Penha, R.; Dossus, L.; Gunter, M.J.; Moreno, V.; et al. Genetically proxied impaired GIPR signaling and risk of 6 cancers. iScience 2023, 26, 106848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavi Nameghi, S. Association of GIPR gene variant on the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A case-control study. Endocr. Metab. Sci. 2023, 13, 100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Bray, G.A.; Hu, F.B.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Weight-loss diets modify glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor rs2287019 genotype effects on changes in body weight, fasting glucose, and insulin resistance: The Preventing Overweight Using Novel Dietary Strategies trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Hivert, M.-F.; Langenberg, C.; Tanaka, T.; Pankow, J.S.; Vollenweider, P.; Lyssenko, V.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Dupuis, J.; Jackson, A.U.; et al. Genetic variation in GIPR influences the glucose and insulin responses to an oral glucose challenge. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilgaard, K.; Jensen, C.B.; Schou, J.H.; Lyssenko, V.; Wegner, L.; Brøns, C.; Vilsbøll, T.; Hansen, T.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J.; et al. The T allele of rs7903146 TCF7L2 is associated with impaired insulinotropic action of incretin hormones, reduced 24 h profiles of plasma insulin and glucagon, and increased hepatic glucose production in young healthy men. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropano, C.; Santoro, N.; Groop, L.; Dalla Man, C.; Cobelli, C.; Galderisi, A.; Kursawe, R.; Pierpont, B.; Goffredo, M.; Caprio, S. The rs7903146 Variant in the TCF7L2 Gene Increases the Risk of Prediabetes/Type 2 Diabetes in Obese Adolescents by Impairing β-Cell Function and Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Nie, H.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Li, M.; Song, Y. The rs17782313 polymorphism near MC4R gene confers a high risk of obesity and hyperglycemia, while PGC1α rs8192678 polymorphism is weakly correlated with glucometabolic disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1210455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magno, F.; Guaraná, H.C.; Fonseca, A.C.P.; Cabello, G.M.K.; Carneiro, J.R.I.; Pedrosa, A.P.; Ximenes, A.C.; Rosado, E.L. Influence of FTO rs9939609 polymorphism on appetite, ghrelin, leptin, IL6, TNFα levels, and food intake of women with morbid obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2018, 11, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Bachiller, R. Role of rs6923761 gene variant in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in basal GLP-1 levels, cardiovascular risk factor and serum adipokine levels in naïve type 2 diabetic patients. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2014, 38, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javorský, M.; Gotthardová, I.; Klimčáková, L.; Kvapil, M.; Židzik, J.; Schroner, Z.; Doubravová, P.; Gala, I.; Dravecká, I.; Tkáč, I. A missense variant in GLP1R gene is associated with the glycaemic response to treatment with gliptins. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.; Carette, C.; Narjoz, C.; Rives-Lange, C.; Rassy, N.; Czernichow, S.; Pallet, N. A GLP1R gene variant and sex influence the response to semaglutide treatment in patients with severe obesity. Obesity 2025, 33, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Eid, L.; Reynolds, C.A.; Tomas, A.; Ben, J. Biased agonism and polymorphic variation at the GLP-1 receptor: Implications for the development of personalised therapeutics. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 184, 106411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, S.F.; Khajavi, N.; Kleinau, G.; Teumer, A.; Scheerer, P.; Homuth, G.; Völzke, H.; Wiegand, S.; Kühnen, P.; Krude, H.; et al. Evaluation of a rare glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor variant in a patient with diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeini, M.; Laurenti, M.C.; Egan, A.M.; Muthusamy, K.; Ramar, A.; Vella, E.; Bailey, K.R.; Cobelli, C.; Dalla Man, C.; Vella, A. The Longitudinal Effect of Diabetes-Associated Variation in TCF7L2 on Islet Function in Humans. Diabetes 2024, 73, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurenti, M.C.; Dalla Man, C.; Varghese, R.T.; Andrews, J.C.; Rizza, R.A.; Matveyenko, A.; De Nicolao, G.; Cobelli, C.; Vella, A. Diabetes-associated genetic variation in TCF7L2 alters pulsatile insulin secretion in humans. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e136136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Loh, N.Y.; Sabaratnam, R.; Vasan, S.K.; van Dam, A.D.; Todorčević, M.; Neville, M.J.; Toledo, E.; Karpe, F.; Christodoulides, C. TCF7L2 plays a complex role in human adipose progenitor biology, which might contribute to genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorling, J.L.; Clayton, D.J.; Jones, J.; Carter, W.G.; Thackray, A.E.; King, J.A.; Pucci, A.; Batterham, R.L.; Stensel, D.J. A randomized crossover trial assessing the effects of acute exercise on appetite, circulating ghrelin concentrations, and butyrylcholinesterase activity in normal-weight males with variants of the obesity-linked FTO rs9939609 polymorphism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melhorn, S.J.; Askren, M.K.; Chung, W.K.; Kratz, M.; Bosch, T.A.; Tyagi, V.; Webb, M.F.; De Leon, M.R.B.; Grabowski, T.J.; Leibel, R.L.; et al. FTO genotype impacts food intake and corticolimbic activation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iepsen, E.W.; Zhang, J.; Thomsen, H.S.; Hansen, E.L.; Hollensted, M.; Madsbad, S.; Hansen, T.; Holst, J.J.; Holm, J.-C.; Torekov, S.S. Patients with Obesity Caused by Melanocortin-4 Receptor Mutations Can Be Treated with a Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 23–32.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinkova, M.; Kadiyska, T.; Handjieva-Darlenska, T. Pharmacogenetics of Glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor in diabetes management. Pharmacia 2023, 70, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney, G.I.; Do, T.; West, W.A.; Uwaifo, G.I. Cystic Fibrosis and Hemochromatosis Carriers May Be Prone to Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Agonist Pancreatitis: 3 Cases. JCEM Case Rep. 2025, 3, luaf104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Raj, R.; Elshimy, G.; Zapata, I.; Kannan, L.; Majety, P.; Edem, D.; Correa, R. Adverse Events Related to Tirzepatide. J. Endocr. Soc. 2023, 7, bvad016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mando, N.; Thomson, E.; Fowler, M.; Short, L.; Gillen, N. Acute Pancreatitis Caused by Tirzepatide. Cureus 2024, 16, e76007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Nauck, M.A.; Van, J.; Benson, C.; Bray, R.; Cui, X.; Milicevic, Z.; Urva, S.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.A. Efficacy and tolerability of tirzepatide, a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate different dose-escalation regimens. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, D.; Onishi, Y.; Norwood, P.; Huh, R.; Bray, R.; Patel, H.; Rodríguez, Á. Effect of Subcutaneous Tirzepatide vs Placebo Added to Titrated Insulin Glargine on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS-5 Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2022, 327, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, D.A.; Witt, H.; Rahman, S.H.; Schulz, H.U.; Sargen, K.; Kage, A.; Cartmell, M.T.; Landt, O.; Larvin, M.; Demaine, A.G.; et al. The SPINK1 N34S variant is associated with acute pancreatitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 20, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Association between different GLP-1 receptor agonists and acute pancreatitis: Case series and real-world pharmacovigilance analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1461398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.-B.; Tang, X.-Y.; Zhou, D.-Z.; Qian, Y.-Y.; Hu, L.-H.; Yu, F.-F.; Yu, D.; Wu, H.; Deng, S.-J.; Lin, J.-H.; et al. SPINK1, PRSS1, CTRC, and CFTR Genotypes Influence Disease Onset and Clinical Outcomes in Chronic Pancreatitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furihata, K.; Mimura, H.; Urva, S.; Oura, T.; Ohwaki, K.; Imaoka, T. A phase 1 multiple-ascending dose study of tirzepatide in Japanese participants with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Nauck, M.A.; Van, J.; Kutner, M.E.; Cui, X.; Benson, C.; Urva, S.; Gimeno, R.E.; Milicevic, Z.; Robins, D.; et al. Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 2180–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, T.; Sloop, K.W.; Loghin, C.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Urva, S.; Bokvist, K.B.; Cui, X.; Briere, D.A.; Cabrera, O.; Roell, W.C.; et al. LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol. Metab. 2018, 18, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, G.; Yin, S.; Yang, X.; Zhou, M.; Jian, W. Optimal dose of tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 990182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankner, R.; Murad, H.; Agay, N.; Olmer, L.; Freedman, L.S. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Pancreatic Cancer Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2350408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, H.; Loley, C.; Lieb, W.; Pencina, M.J.; Nelson, C.P.; Kathiresan, S.; Peloso, G.M.; Voight, B.F.; Reilly, M.P.; Assimes, T.L.; et al. Genetic variants primarily associated with type 2 diabetes are related to coronary artery disease risk. Atherosclerosis 2015, 241, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Yu, X.; Zhu, X.; Song, Y.; Gao, F.; Yu, B.; Qu, A. Diabetes Mellitus to Accelerated Atherosclerosis: Shared Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2024, 17, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.; Grechko, A.V.; Poggio, P.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Alfieri, V.; Orekhov, A.N. The Diabetes Mellitus-Atherosclerosis Connection: The Role of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.A.; Tschritter, O.; Machicao, F.; Thamer, C.; Stefan, N.; Gallwitz, B.; Holst, J.J.; Dekker, J.M.; t Hart, L.M.; Nijpels, G.; et al. Impaired glucagon-like peptide-1-induced insulin secretion in carriers of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphisms. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyssenko, V.; Jonsson, A.; Almgren, P.; Pulizzi, N.; Isomaa, B.; Tuomi, T.; Berglund, G.; Altshuler, D.; Nilsson, P.; Groop, L. Clinical risk factors, DNA variants, and the development of type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruchat, S.M.; Elks, C.E.; Loos, R.J.; Vohl, M.C.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Rankinen, T.; Bouchard, C.; Perusse, L. Association between insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity and type 2 diabetes susceptibility variants identified in genome-wide association studies. Acta Diabetol. 2009, 46, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, M.; Fujitani, Y.; Hara, A.; Uchida, T.; Tamura, Y.; Takeno, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Watanabe, T.; Ogihara, T.; Fukunaka, A.; et al. The diabetes-susceptible gene SLC30A8/ZnT8 regulates hepatic insulin clearance. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4513–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakidou, A.; Kyriazou, A.V.; Koufakis, T.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Avramidis, I.; Baltagiannis, S.; Goulis, D.G.; Kotsa, K. Association between variants in TCF7L2, CTRB1/2, and GLP-1R genes and response to therapy with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Postgrad. Med. 2024, 136, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, Y.A.; Rabes, J.P.; Boileau, C.; Varret, M. APOE gene variants in primary dyslipidemia. Atherosclerosis 2021, 328, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankosky, E.R.; Wang, H.; Neff, L.M.; Kan, H.; Wang, F.; Ahmad, N.N.; Griffin, R.; Stefanski, A.; Garvey, W.T. Tirzepatide reduces the predicted risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and improves cardiometabolic risk factors in adults with obesity or overweight: SURMOUNT-1 post hoc analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, W.; Kong, W.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zeng, T. The effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on circulating inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 3607–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Obata, A.; Shimoda, M.; Okauchi, S.; Hirukawa, H.; Kohara, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Nogami, Y.; Nakanishi, S.; Mune, T.; et al. Decreased glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor expression in endothelial and smooth muscle cells in diabetic db/db mice: TCF7L2 is a possible regulator of the vascular glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Diab Vasc. Dis. Res. 2017, 14, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornholm, K.D.; Povlsen, G.K.; Ougaard, M.E.; Pyke, C.; Rakipovski, G.; Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Skovsted, G.F. Decreased expression of the GLP-1 receptor after segmental artery injury in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 248, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneto, H.; Kimura, T.; Shimoda, M.; Obata, A.; Sanada, J.; Fushimi, Y.; Nakanishi, S.; Mune, T.; Kaku, K. Favorable Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist against Pancreatic beta-Cell Glucose Toxicity and the Development of Arteriosclerosis: “The Earlier, the Better” in Therapy with Incretin-Based Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michałowska, J.; Miller-Kasprzak, E.; Seraszek-Jaros, A.; Mostowska, A.; Bogdański, P. Association of GLP1R variants rs2268641 and rs6923761 with obesity and other metabolic parameters in a Polish cohort. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1000185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; La Lee, Y.; Jung, C.H. The Cardiovascular Effect of Tirzepatide: A Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Dual Agonist. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2023, 12, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samms, R.J.; Coghlan, M.P.; Sloop, K.W. How May GIP Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of GLP-1? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Castro, T.B.; Hernández-Díaz, Y.; Pérez-Hernández, N.; Tovilla-Zárate, C.A.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E.; López-Narvaez, M.L.; Blachman-Braun, R.; Posadas-Sánchez, R.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; García-Flores, E.; et al. Interleukin 6 (rs1800795) gene polymorphism is associated with cardiovascular diseases: A meta-analysis of 74 studies with 86,229 subjects. EXCLI J. 2019, 18, 331–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.; Previde, P.; Cole, J.; Thomas, B.; Laxmeshwar, N.; Mallory, E.; Lever, J.; Petkovic, D.; Altman, R.B.; Kulkarni, A. Search and visualization of gene-drug-disease interactions for pharmacogenomics and precision medicine research using GeneDive. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 117, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Du, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yin, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; et al. Association between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene polymorphism and treatment response to GLP1R agonists in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Yanez, R.L.; Markova, M.; Dambeck, U.; Honsek, C.; Machann, J.; Schuler, R.; Kabisch, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. Predictive effect of GIPR SNP rs10423928 on glucose metabolism liver fat and adiposity in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. Peptides 2020, 125, 170237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villareal, D.T.; Robertson, H.; Bell, G.I.; Patterson, B.W.; Tran, H.; Wice, B.; Polonsky, K.S. TCF7L2 variant rs7903146 affects the risk of type 2 diabetes by modulating incretin action. Diabetes 2010, 59, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahley, R.W. Apolipoprotein E: From cardiovascular disease to neurodegenerative disorders. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Liu, J.; Lau, C.W.; Huang, Y. IL-6 in diabetes and cardiovascular complications. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3595–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, K.; Becker, M.; Zugwurst, J.; Biller-Friedmann, I.; Spoettl, G.; Greif, M.; Leber, A.W.; Becker, A.; Laubender, R.P.; Lebherz, C.; et al. Circulating concentrations of GLP-1 are associated with coronary atherosclerosis in humans. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.E.; Li, C.; Rabinovic, A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 2007, 8, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villikudathil, A.T.; Mc Guigan, D.H.; English, A. Computational approaches for clinical, genomic and proteomic markers of response to glucagon-like peptide-1 therapy in type-2 diabetes mellitus: An exploratory analysis with machine learning algorithms. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2024, 18, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.O.; Cui, Y.C.; Lin, P.C.; Chiang, J.H. An Innovative Multi-Omics Model Integrating Latent Alignment and Attention Mechanism for Drug Response Prediction. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J. BANDRP: A bilinear attention network for anti-cancer drug response prediction based on fingerprint and multi-omics. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privé, F.; Arbel, J.; Vilhjálmsson, B.J. LDpred2: Better, faster, stronger. Bioinformatics 2021, 36, 5424–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J.; Holst, J.J. The expanding incretin universe: From basic biology to clinical translation. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1765–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B.; An, J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Lien, L.F.; Haqq, A.M.; Shah, S.H.; Arlotto, M.; Slentz, C.A.; et al. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klau, S.; Jurinovic, V.; Hornung, R.; Herold, T.; Boulesteix, A.L. Priority-Lasso: A simple hierarchical approach to the prediction of clinical outcome using multi-omics data. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, A.J.; Elkin, E.B. Decision curve analysis: A novel method for evaluating prediction models. Med. Decis. Mak. 2006, 26, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simona, A.; Song, W.; Bates, D.W.; Samer, C.F. Polygenic risk scores in pharmacogenomics: Opportunities and challenges-a mini review. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1217049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsgaard, H.; Seelig, E.; Timper, K.; Coslovsky, M.; Soederlund, L.; Lyngbaek, M.P.; Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Hanssen, H.; Frey, W.O.; et al. GLP-1 secretion is regulated by IL-6 signalling: A randomised, placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, E.P.; Cheng, S.; Larson, M.G.; Walford, G.A.; Lewis, G.D.; McCabe, E.; Yang, E.; Farrell, L.; Fox, C.S.; O’Donnell, C.J.; et al. Lipid profiling identifies a triacylglycerol signature of insulin resistance and improves diabetes prediction in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Gang, X.; Wang, G. The Relationship between Branched-Chain Amino Acid Related Metabolomic Signature and Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2794591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Stampfer, M.J.; Liu, S. Meta-analysis: Apolipoprotein E genotypes and risk for coronary heart disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonin, G.; Goričar, K.; Blagus, T.; Janež, A.; Dolžan, V.; Klen, J. Genetic variability in sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor effect on glycemic and pressure control in type 2 diabetes patients treated with SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1RA in the everyday clinical practice. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1547920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgren, P.; Lindqvist, A.; Krus, U.; Hakaste, L.; Ottosson-Laakso, E.; Asplund, O.; Sonestedt, E.; Prasad, R.B.; Laurila, E.; Orho-Melander, M.; et al. Genetic determinants of circulating GIP and GLP-1 concentrations. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e93306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magavern, E.F.; Gurdasani, D.; Ng, F.L.; Lee, S.S. Health equality, race and pharmacogenomics. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, A.; Kim, H.H.; Shah-Williams, E.; Zhang, L. Racial and Ethnic Differences in Drug Disposition and Response: Review of New Molecular Entities Approved Between 2014 and 2019. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S. Pharmacogenomics and the challenge of health disparities. Public Health Genom. 2009, 12, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolio, T.A.; Chisholm, R.L.; Ozenberger, B.; Roden, D.M.; Williams, M.S.; Wilson, R.; Bick, D.; Bottinger, E.P.; Brilliant, M.H.; Eng, C.; et al. Implementing genomic medicine in the clinic: The future is here. Genet. Med. 2013, 15, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | SNP Variant | Associated Effect | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLP1R | rs6923761 (G>A) | ↑ delayed gastric emptying | Affecting appetite and postprandial glucose [34] |
| GIPR | rs1800437 (G>C) | ↓ early-phase insulin secretion | Reduces receptor signaling [35,36] |
| rs2287019 (C>T) | ↓ 30 min insulin | Influence gene–diet interaction [37] | |
| rs10423928(T>A) | ↓ insulin secretion | Modulate glucose metabolism [38] | |
| TCF7L2 | rs7903146 (C>T) | ↓ insulin secretion | Reduces β-cell responsiveness [39,40] |
| MC4R | rs17782313 (T>C) | ↑ obesity risk | Involved in the regulation of glucose metabolism [41] |
| FTO | rs9939609 (T>A) | ↓ satiety | Affects adipocyte response to satiety signal [42] |
| Modality | Example Features | Preprocessing | Feature Engineering/Selection | Fusion/Model Candidates | Primary Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genomics (PRS) | PRS from GWAS SNPs | Quality control (QC); ancestry-stratified standardization | LD-aware PRS (LDpred2) | Early fusion + LASSO/Priority LASSO | AUROC, AUPRC |
| Transcriptomics (bulk/scRNA-seq) | Gene counts/pathways | Normalization; batch correction (ComBat) | Variance filtering | Multiblock or attention-based fusion | AUROC, AUPRC |
| Proteomics | Targeted panel intensities | Normalization; outlier handling | Panel-level z-scores | RF | AUROC, AUPRC |
| Metabolomics/lipidomics | BCAA; TAG species | Drift correction; scaling | Pathway aggregates | Elastic-net/RF | AUROC, AUPRC |
| Clinical (EHR/RWD) | HbA1c, BMI, meds, duration | Data harmonization; MICE/KNN | Domain composites (e.g., ASCVD risk) | Multiblock or attention-based fusion | AUROC, AUPRC; calibration (Brier); DCA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Tang, Y.; Peng, M.; Han, R.; He, P. Pharmacogenomics of Tirzepatide: Genomic Insights into Dual GIP/GLP-1 Agonist Response in Type 2 Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091261
Song Z, Tang Y, Peng M, Han R, He P. Pharmacogenomics of Tirzepatide: Genomic Insights into Dual GIP/GLP-1 Agonist Response in Type 2 Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091261
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zihang, Yifan Tang, Mao Peng, Ruoyu Han, and Pingping He. 2025. "Pharmacogenomics of Tirzepatide: Genomic Insights into Dual GIP/GLP-1 Agonist Response in Type 2 Diabetes and Atherosclerosis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091261
APA StyleSong, Z., Tang, Y., Peng, M., Han, R., & He, P. (2025). Pharmacogenomics of Tirzepatide: Genomic Insights into Dual GIP/GLP-1 Agonist Response in Type 2 Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091261





