BthTX-II, an Asp49 PLA2 from Bothrops jararacussu, Impairs Toxoplasma gondii Infection: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
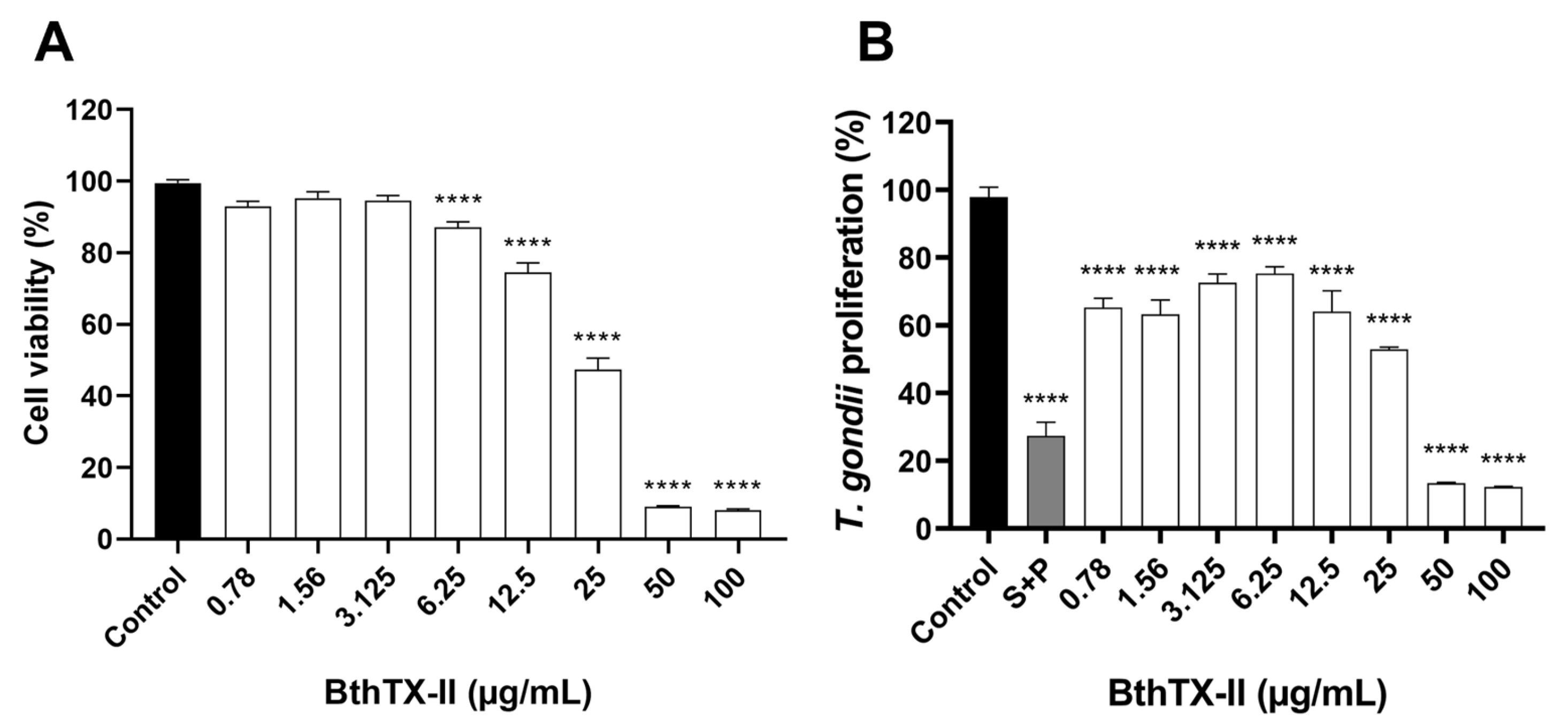
2.1. BthTX-II Inhibits Proliferation of T. gondii Without Causing Toxicity to Trophoblasts
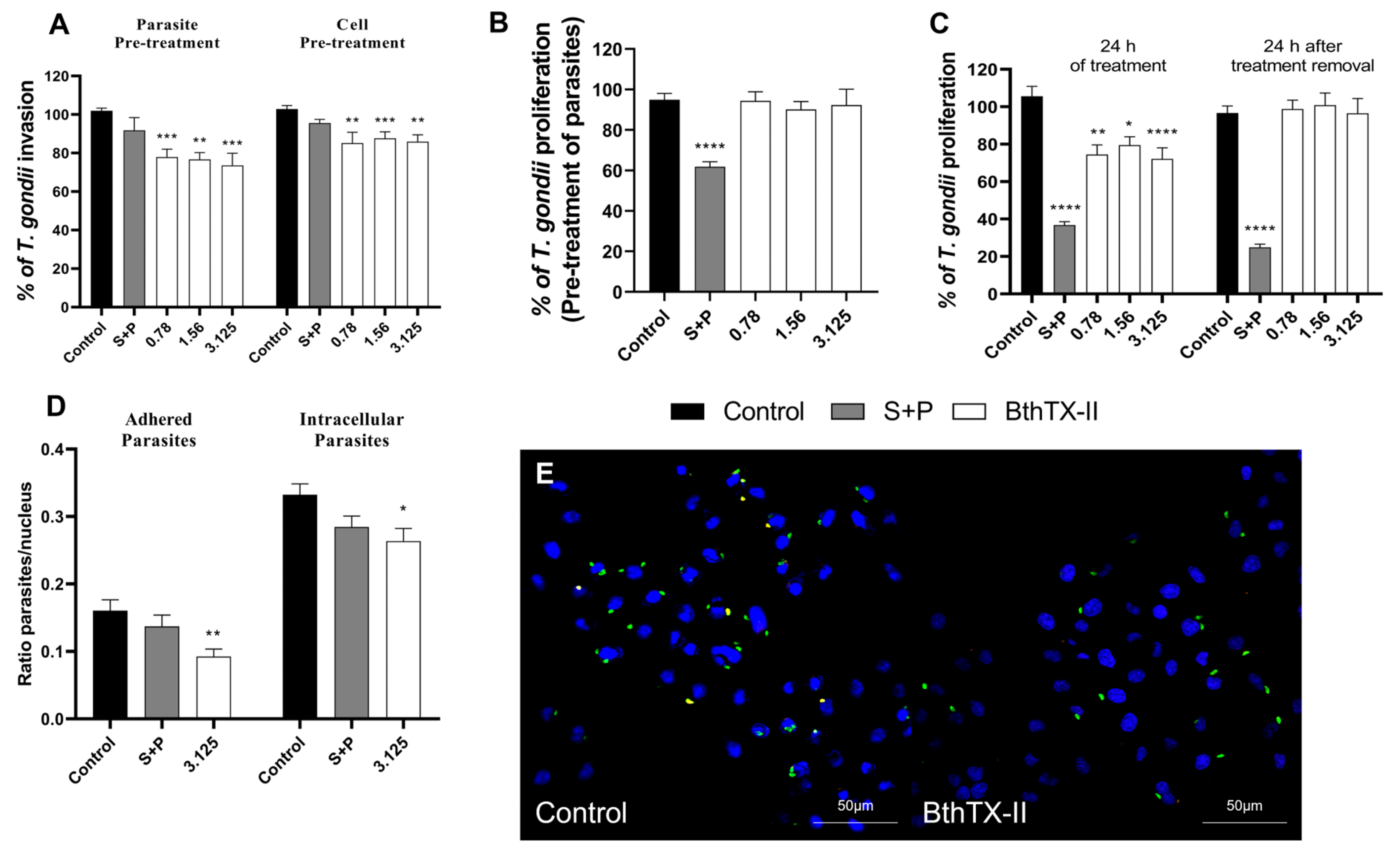
2.2. BthTX-II Directly Affects Parasites and Impairs Early Stages of T. gondii Infection in BeWo Cells, but Its Antiparasitic Effect Is Lost After Treatment Removal
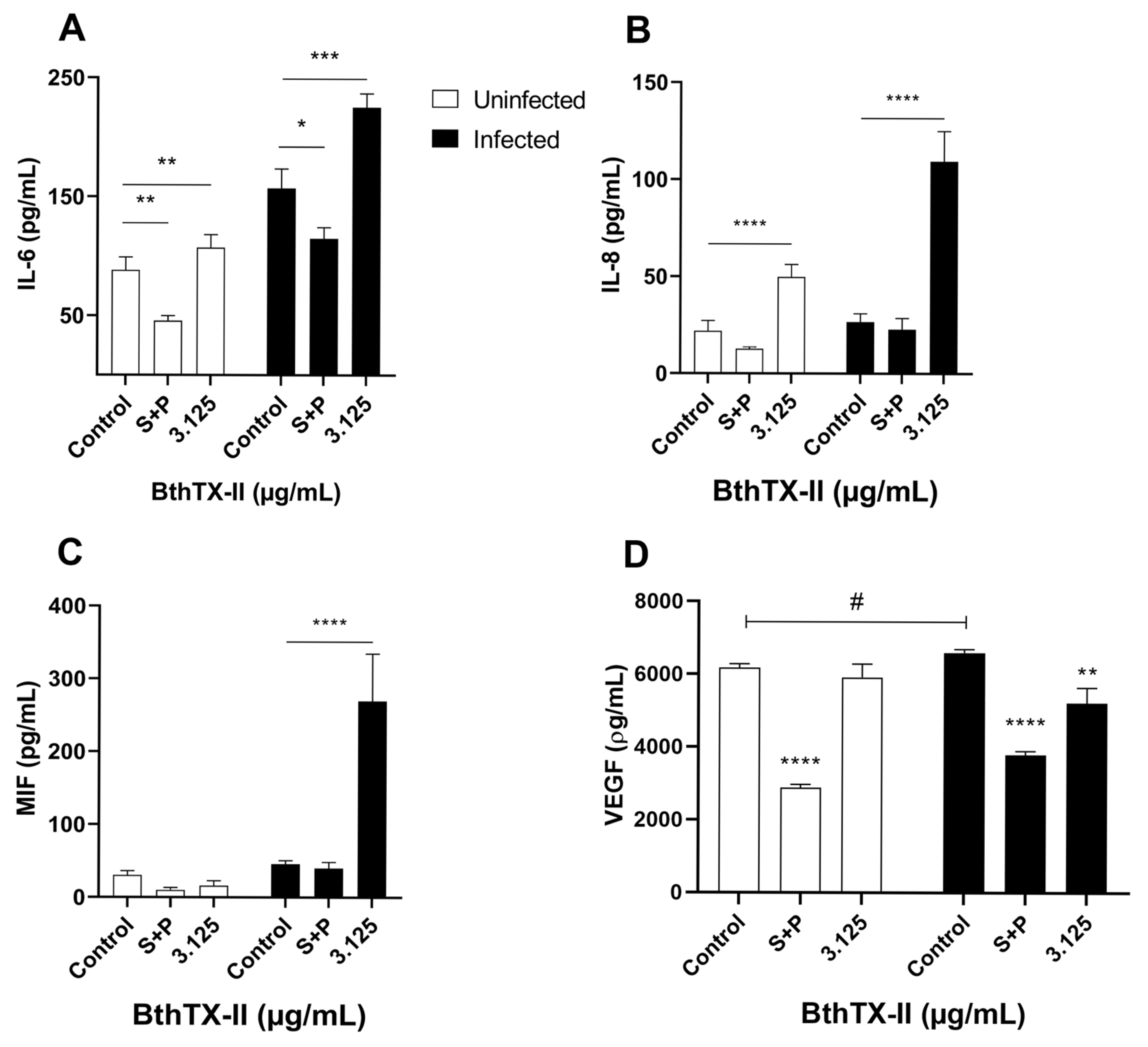
2.3. BthTX-II Upregulates the IL-6, IL-8, and Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) Levels and Downregulates VEGF Production in T. gondii-Infected BeWo Cells
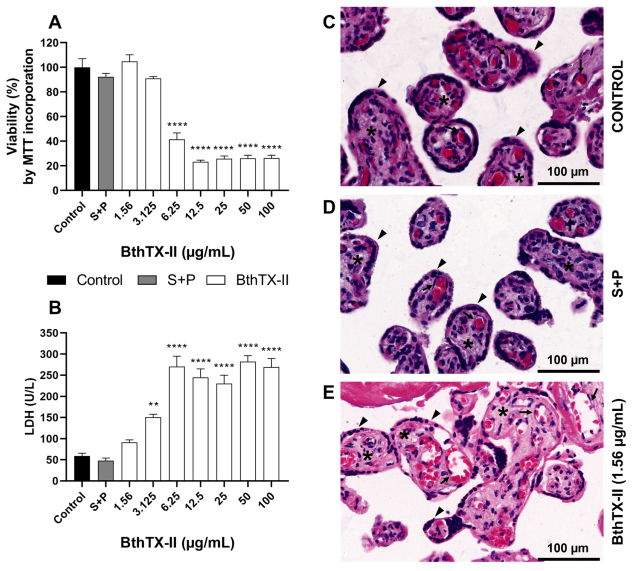
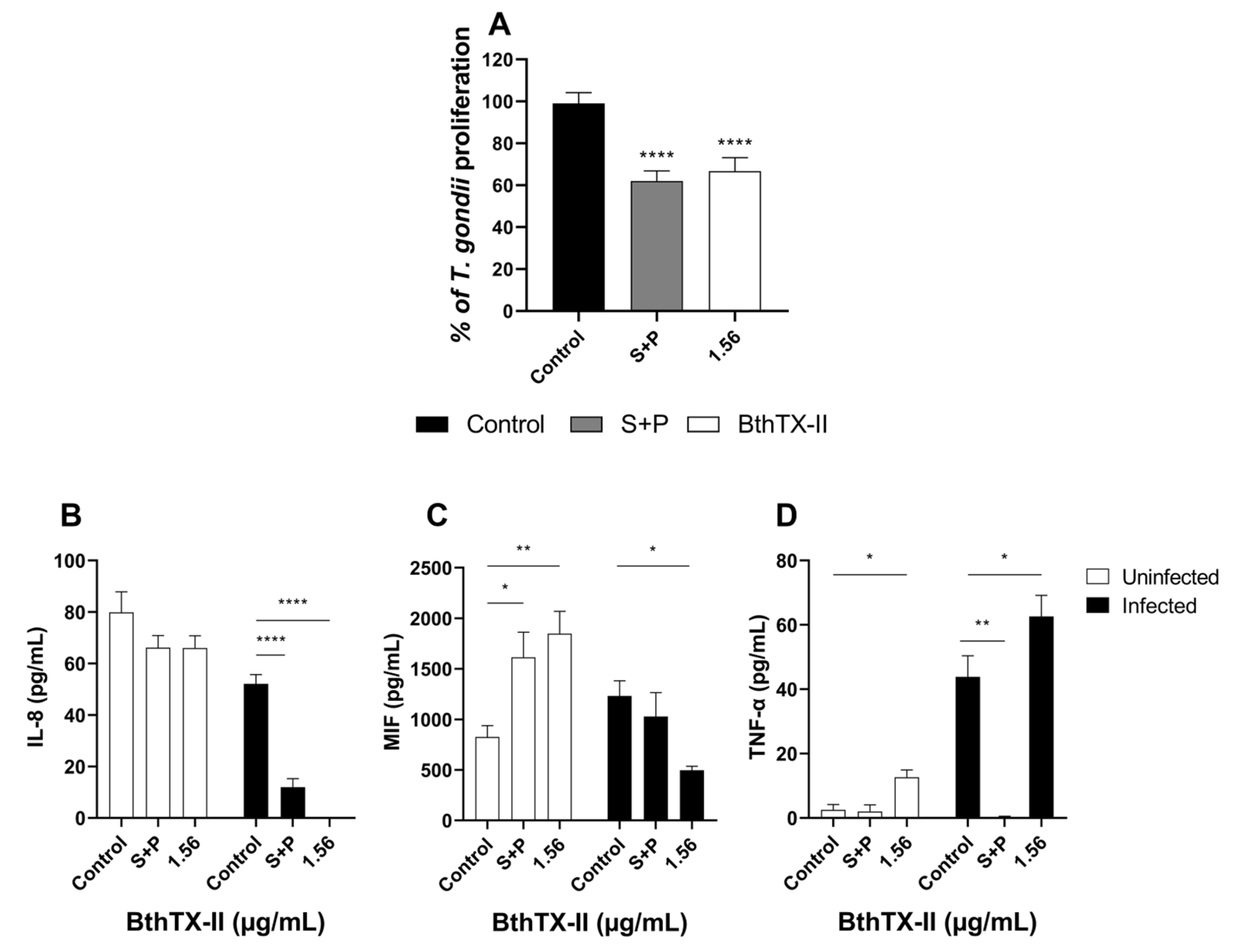
2.4. BthTX-II Reduces T. gondii Proliferation in Human Placental Explants
2.5. BthTX-II Modulates IL-8, MIF, and TNF-α Production in T. gondii-Infected Human Placental Explants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Asp49-PLA2 BthTX-II
4.2. PL Activity of BthTX-II
4.3. Cell Culture and Parasite Maintenance
4.4. Human Placental Explants
4.5. Cell Viability in BeWo Cells
4.6. Proliferation of T. gondii
4.7. Invasion and Proliferation Pre-Treating T. gondii or BeWo
4.8. Reversibility Assay
4.9. Adhesion and Invasion Assay (“Red/Green Assay”)
4.10. Viability of Placental Villous Explants
4.11. T. gondii Infection in Human Placental Villous Explants
4.12. Cytokine and VEGF Determination
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Villena, I. Congenital Toxoplasmosis in Humans: An Update of Worldwide Rate of Congenital Infections. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegr, J.; Prandota, J.; Sovičková, M.; Israili, Z.H. Toxoplasmosis-A Global Threat. Correlation of Latent Toxoplasmosis with Specific Disease Burden in a Set of 88 Countries. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollani, L.; Auriti, C.; Achille, C.; Garofoli, F.; De Rose, D.U.; Meroni, V.; Salvatori, G.; Tzialla, C. Congenital Toxoplasmosis: The State of the Art. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 894573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgerson, P.R.; Mastroiacovo, P. The Global Burden of Congenital Toxoplasmosis: A Systematic Review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2013, 91, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Deus Miranda, G.; Fiori, A.V.D.; Martins, J.P.P.; Vieira, L.G.S.; Ribeiro, T.F.S.; Vitorino, G.H.; da Costa Filho, M.A.L.; Freire, I.F. Um Estudo a Respeito Do Cenário Epidemiológico Da Toxoplasmose Congênita No Brasil. Braz. J. Implantol. Health Sci. 2025, 7, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.A.; Longcore, T.; Barbieri, M.; Dabritz, H.; Hill, D.; Klein, P.N.; Lepczyk, C.; Lilly, E.L.; McLeod, R.; Milcarsky, J.; et al. The One Health Approach to Toxoplasmosis: Epidemiology, Control, and Prevention Strategies. EcoHealth 2019, 16, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Barros, R.A.M.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Marciano, M.A.M.; Mazuz, M.L.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L.; Fux, B. Toxoplasmosis in Human and Animals Around the World. Diagnosis and Perspectives in the One Health Approach. Acta Trop. 2022, 231, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.L. Epidemiology of and Diagnostic Strategies for Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Kong, B.; Qu, X. Human Monocytes Undergo Functional Re-Programming during Differentiation to Dendritic Cell Mediated by Human Extravillous Trophoblasts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.T.M.; Oliveira-Scussel, A.C.M.; Sousa, R.A.P.; Gomes, B.Q.; Félix, J.E.; Silva, R.J.; Millian, I.B.; Assunção, T.S.F.; Teixeira, S.C.; Gomes, M.D.L.M.; et al. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Contributes to Drive Phenotypic and Functional Macrophages Activation in Response to Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, J. Cytokines, Inflammation, and Pain. Int. Anesth. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddami, R.; Mahdipour, M.; Ahmadpour, E. Inflammatory Pathways of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnancy. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 62, 102760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasil, P.; Sleha, R.; Kacerovsky, M.; Bostik, P. Comparison of Adverse Reactions of Spiramycin versus Pyrimethamine/Sulfadiazine Treatment of Toxoplasmosis in Pregnancy: Is Spiramycin Really the Drug of Choice for Unproven Infection of the Fetus? J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023, 36, 2215377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Congenital Toxoplasmosis: Clinical Features, Outcomes, Treatment, and Prevention. Trop. Parasitol. 2016, 6, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneceur, P.; Bouldouyre, M.A.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Menotti, J.; Sauvage, V.; Garin, J.F.; Derouin, F. in vitro Susceptibility of Various Genotypic Strains of Toxoplasma gondii to Pyrimethamine, Sulfadiazine, and Atovaquone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, M.; Mehrzadi, S.; Sharif, M.; Sarvi, S.; Tanzifi, A.; Aghayan, S.A.; Daryani, A. Drug Resistance in Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 299255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.M.; Hafner, R.; Remington, J.; Farthing, C.; Holden-Wiltse, J.; Bosler, E.M.; Harris, C.; Jayaweera, D.T.; Roque, C.; Luft, B.J. Dose-Escalation, Phase 1/11 Study of Azithromycin and Pyrimethamine for the Treatment of Toxoplasmic Encephalitis in AIDS. AIDS 2001, 15, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.A.; Weinberg, W.; Stansell, J.; Leoung, G.; Kovacs, J.; Rogers, M.; Scott, J. Atovaquone for Salvage Treatment and Suppression of Toxoplasmic Encephalitis in Patients with AIDS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.H. A bradykinin-potentiating factor (BPF) present in the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1965, 24, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.F.; Holt, J.C.; Lukasiewicz, H.; Niewiarowski, S. Trigramin. A Low Molecular Weight Peptide Inhibiting Fibrinogen Interaction with Platelet Receptors Expressed on Glycoprotein IIb-IIIa Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 16157–16163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.Y.; Kini, R.M. From Snake Venom Toxins to Therapeutics—Cardiovascular Examples. Toxicon 2012, 59, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, L.M.; Júnior, R.J.O.; Silva, D.A.O.; Mineo, J.R.; Vieira, C.U.; Teixeira, D.N.S.; Homsi-Brandeburgo, M.I.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Hamaguchi, A. Toxoplasma Gondii: Effects of Neuwiedase, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops neuwiedi Snake Venom, on the Invasion and Replication of Human Fibroblasts in Vitro. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 120, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, L. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Effects of Lipopeptide Derivatives of Lycosin-I. Toxins 2023, 15, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, I.P.; Castanheira, L.E.; Barbosa, B.F.; De Souza, D.L.N.; Da Silva, R.J.; Mineo, J.R.; Tudini, K.A.Y.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Ferro, E.A.V.; De Melo Rodrigues, V. Anti-Parasitic Effect on Toxoplasma gondii Induced by BnSP-7, a Lys49-Phospholipase A2 Homologue from Bothrops pauloensis Venom. Toxicon 2016, 119, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.C.; da Silva, M.S.; Gomes, A.A.; Moretti, N.S.; Lopes, D.S.; Ferro, E.A.; de Melo Rodrigues, V. Panacea within a Pandora’s Box: The Antiparasitic Effects of Phospholipases A2 (PLA2s) from Snake Venoms. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.C.; de Melo Fernandes, T.A.; de Souza, G.; Rosini, A.M.; Fajardo Martínez, A.F.; Gomes, A.O.; Alves, R.N.; Lopes, D.S.; da Silva, M.V.; Beraldo-Neto, E.; et al. MjTX-II, a Lys49-PLA2 from Bothrops moojeni Snake Venom, Restricts Toxoplasma gondii Infection via ROS and VEGF Regulation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2025, 409, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Evans, H.J. A Model to Explain the Pharmacological Effects of Snake Venom Phospholipases A2. Toxicon 1989, 27, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.M.; Andrião-Escarso, S.H.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Marangoni, S.; Toyama, M.H.; Arni, R.K.; Giglio, J.R. Structural and Functional Characterization of Myotoxin I, a Lys49 Phospholipase A(2) Homologue from Bothrops moojeni (Caissaca) Snake Venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 373, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filkin, S.Y.; Lipkin, A.V.; Fedorov, A.N. Phospholipase Superfamily: Structure, Functions, and Biotechnological Applications. Biochemistry 2020, 85, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipases A2: Unveiling the Secrets of a Functionally Versatile Group of Snake Venom Toxins. Toxicon 2013, 62, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Sasa, M.; Gutierrez, J. The Phospholipase A2 Homologues of Snake Venoms: Biological Activities and Their Possible Adaptive Roles. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 860–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Calderón, L. An Overview of Lysine-49 Phospholipase A2 Myotoxins from Crotalid Snake Venoms and Their Structural Determinants of Myotoxic Action. Toxicon 2003, 42, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Chioato, L.; Ruller, R.; Sá, J.M. Active-Site Mutagenesis of a Lys49-Phospholipase A2: Biological and Membrane-Disrupting Activities in the Absence of Catalysis. Biochem. J. 2002, 362, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homsi-Brandeburgo, M.I.; Queiroz, L.S.; Santo-Neto, H.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Giglio, J.R. Fractionation of Bothrops jararacussu Snake Venom: Partial Chemical Characterization and Biological Activity of Bothropstoxin. Toxicon 1988, 26, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.F.; Novello, J.C.; Cintra, A.C.O.; Giglio, J.R.; Landucci, E.T.; Oliveira, B.; Marangoni, S. The Amino Acid Sequence of Bothropstoxin-II, an Asp-49 Myotoxin from Bothrops jararacussu (Jararacucu) Venom with Low Phospholipase A2 Activity. J. Protein Chem. 1998, 17, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, L.C.; Marchi-Salvador, D.P.; Cintra, A.C.O.; Sampaio, S.V.; Soares, A.M.; Fontes, M.R.M. Crystal Structure of a Myotoxic Asp49-Phospholipase A2 with Low Catalytic Activity: Insights into Ca2+-Independent Catalytic Mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.J.; Salvador, G.H.M.; Campanelli, H.B.; Pimenta, D.C.; de Oliveira Neto, M.; Usón, I.; Fontes, M.R.M. BthTX-II from Bothrops jararacussu Venom Has Variants with Different Oligomeric Assemblies: An Example of Snake Venom Phospholipases A2 Versatility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrião-Escarso, S.H.; Soares, A.M.; Fontes, M.R.M.; Fuly, A.L.; Corrêa, F.M.A.; Rosa, J.C.; Greene, L.J.; Giglio, J.R. Structural and Functional Characterization of an Acidic Platelet Aggregation Inhibitor and Hypotensive Phospholipase A2 from Bothrops jararacussu Snake Venom. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeno, C.N.; Paloschi, M.V.; Lopes, J.A.; Souza Silva, M.D.; Evangelista, J.R.; dos Reis, V.P.; da Setúbal, S.; Soares, A.M.; Zuliani, J.P. Dynamics of Action of a Lys-49 and an Asp-49 PLA2s on Inflammasome NLRP3 Activation in Murine Macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 112, 109194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, R.C.; Landucci, E.C.T.; Toyama, M.H.; Giglio, J.R.; Marangoni, S.; De Nucci, G.; Antunes, E. Leucocyte Recruitment Induced by Type II Phospholipases A2 into the Rat Pleural Cavity. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landucci, E.C.T.; Castro, R.C.; Pereira, M.F.; Cintra, A.C.O.; Giglio, J.R.; Marangoni, S.; Oliveira, B.; Cirino, G.; Antunes, E.; De Nucci, G. Mast Cell Degranulation Induced by Two Phospholipase A2 Homologues: Dissociation between Enzymatic and Biological Activities. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 343, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, F.V.P.V.; Zóia, M.A.; Lopes, D.S.; Gimenes, S.N.; Vecchi, L.; Alves, P.T.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Silva, A.C.A.; Yoneyama, K.A.G.; Goulart, L.R.; et al. Antitumor and Antimetastatic Effects of PLA2-BthTX-II from Bothrops jararacussu Venom on Human Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, F.V.P.V.; Lopes, D.S.; Zóia, M.A.P.; Correia, L.I.V.; Saito, N.; Fonseca, B.B.; Polloni, L.; Teixeira, S.C.; Goulart, L.R.; de Melo Rodrigues Ávila, V. A New Approach to Inhibiting Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Antiangiogenic Effect of BthTx-II, a PLA2-Asp-49 from Bothrops jararacussu Venom. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.-X.; Wei, S.-S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Peng, H.-J. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Medicines in Humans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 138204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieler, H.; Keister, D.B.; Dvorak, J.A.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. A Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 Blocks Malaria Parasite Development in the Mosquito Midgut by Inhibiting Ookinete Association with the Midgut Surface. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 4157–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adade, C.M.; Carvalho, A.L.O.; Tomaz, M.A.; Costa, T.F.R.; Godinho, J.L.; Melo, P.A.; Lima, A.P.C.A.; Rodrigues, J.C.F.; Zingali, R.B.; Souto-Padrón, T. Crovirin, a Snake Venom Cysteine-Rich Secretory Protein (CRISP) with Promising Activity against Trypanosomes and Leishmania. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, N.M.; Santos, I.A.; Grosche, V.R.; Ferreira, G.M.; Guevara-Vega, M.; Rosa, R.B.; Pena, L.J.; Nicolau-Junior, N.; Cintra, A.C.O.; Mineo, T.P.; et al. Roles of Bothrops jararacussu Toxins I and II: Antiviral Findings against Zika Virus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilio, A.B.; Caldas, S.; De Oliveira, R.A.; Santos, A.S.B.; Richardson, M.; Naumann, G.B.; Schneider, F.S.; Alvarenga, V.G.; Estevão-Costa, M.I.; Fuly, A.L.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Lys49 and Asp49 Phospholipases A2 from Snake Venom and Their Antiviral Activities Against Dengue Virus. Toxins 2013, 5, 1780–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarshan, S.; Dhananjaya, B.L. Antibacterial Activity of an Acidic Phospholipase A2 (NN-XIb-PLA2) from the Venom of Naja naja (Indian Cobra). Springerplus 2016, 5, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudharshan, S.; Dhananjaya, B.L. Antibacterial Potential of a Basic Phospholipase A2 (VRV-PL-VIIIa) from Daboia russelii pulchella (Russell’s Viper) Venom. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Barros, N.B.; Macedo, S.R.A.; Ferreira, A.S.; Tagliari, M.P.; Zanchi, F.B.; Kayano, A.M.; Soares, A.M.; Nicolete, R. Liposomes Containing an ASP49-Phospholipase A2 from Bothrops jararacussu Snake Venom as Experimental Therapy against Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 36, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.S.; Alves, C.M.O.S.; Angeloni, M.B.; Gomes, A.O.; Barbosa, B.F.; Franco, P.S.; Silva, D.A.O.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Mineo, J.R.; Mineo, T.W.P.; et al. Trophoblast Cells Are Able to Regulate Monocyte Activity to Control Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Placenta 2013, 34, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, B.F.; Paulesu, L.; Ietta, F.; Bechi, N.; Romagnoli, R.; Gomes, A.O.; Favoreto-Junior, S.; Silva, D.A.O.; Mineo, J.R.; Mineo, T.W.P.; et al. Susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii Proliferation in BeWo Human Trophoblast Cells Is Dose-Dependent of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF), via ERK1/2 Phosphorylation and Prostaglandin E2 Production. Placenta 2014, 35, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, G.; Silva, R.J.; Milián, I.C.B.; Rosini, A.M.; de Araújo, T.E.; Teixeira, S.C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Franco, P.S.; da Silva, C.V.; Mineo, J.R.; et al. Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 Modulates Toxoplasma gondii Infection, Immune Response and Lipid Droplets Formation in Human Trophoblast Cells and Villous Explants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebbari, H.; Roberts, C.W.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; Bluethmann, H.; Alexander, J. A Protective Role for IL-6 during Early Infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Parasite Immunol. 1998, 20, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, T.R.; Leeper, N.J.; Hynes, K.L.; Gewertz, B.L. Interleukin-6 Causes Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction via the Protein Kinase C Pathway. J. Surg. Res. 2002, 104, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Takai, R.; Bürgin, H.; Ishihara, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Amano, J.; Higuchi, Y.; Chiba, S.; Singer, T.; Kawamura, A.; et al. The Effects of Interleukin-6 Signal Blockade on Fertility, Embryo-Fetal Development, and Immunization in vivo. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 95, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.P.O.; Mota, C.M.; Mineo, T.W.P.; Ferro, E.A.V.; Barbosa, B.F.; Silva, N.M. Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction in Human BeWo Trophoblast Cells Decreases Toxoplasma gondii Proliferation in Association with the Upregulation of P38 MAPK Phosphorylation and IL-6 Production. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 659028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, M.; Saavedra, R.; Bautista, R.; Viedma, R.; Tenorio, E.P.; Leng, L.; Sanchez, Y.; Juárez, I.; Satoskar, A.A.; Shenoy, A.S.; et al. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) Is Critical for the Host Resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 3661–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.B.; Gomes, M.S.R.; de Souza, D.L.N.; Gimenes, S.N.C.; Castanheira, L.E.; Borges, M.H.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Yoneyama, K.A.G.; Brandeburgo, M.I.H.; Rodrigues, V.M. Molecular Cloning and Pharmacological Properties of an Acidic PLA2 from Bothrops pauloensis Snake Venom. Toxins 2013, 5, 2403–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, E.A.V.; Roberto Mineo, J.; Ietta, F.; Bechi, N.; Romagnoli, R.; Aparecida Oliveira Silva, D.; Sorda, G.; Bevilacqua, E.; Ricci Paulesu, L. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Is Up-Regulated in Human First-Trimester Placenta Stimulated by Soluble Antigen of Toxoplasma Gondii, Resulting in Increased Monocyte Adhesion on Villous Explants. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gomes, A.O.; De Oliveira Silva, D.A.; Silva, N.M.; De Freitas Barbosa, B.; Silva Franco, P.; Angeloni, M.B.; Fermino, M.L.; Roque-Barreira, M.C.; Bechi, N.; Paulesu, L.R.; et al. Effect of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) in Human Placental Explants Infected with Toxoplasma gondii Depends on Gestational Age. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2792–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejad, M.R.; Sherafat, S.J.; Roshani, M.; Telkabadi, M.; Lahmi, F.; Cheraghipour, K.; Kaboli, A.R.; Alavi-Moghaddam, M. The Evaluation of Interleukin-8 Chemokine in Chronic and Acute Toxoplasma gondii Infection The Evaluation of Interleukin-8 Chemokine in Chronic and Acute Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed To. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2011, 4, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, S.C.; Paschoalino, M.; de Souza, G.; Rosini, A.M.; de Lima Junior, J.P.; Luz, L.C.; Fajardo Martínez, A.F.; Alves, R.N.; Almeida, M.P.O.; Damasceno, J.L.; et al. Rottlerin Impairs Early and Late Steps of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Human Trophoblast Cells and Villous Explants. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 384, 110716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denney, C.F.; Eckmann, L.; Reed, S.L. Chemokine Secretion of Human Cells in Response to Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navia, B.A.; Petito, C.K.; Gold, J.W.M.; Cho, E.-S.; Jordan, B.D.; Price, R.W. Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Complicating the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome: Clinical and Neuropathological Findings in 27 Patients. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.B.; Remington, J.S. Activity of Human Blood Leukocytes against Toxoplasma gondii. J. Infect. Dis. 1979, 140, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chan, H.M.; Li, Z.; Lin, C.; Nicholls, J.; Chen, C.F.; Lee, P.Y.; Lui, V.; Bacher, M.; Tam, P.K.H. Upregulation of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Contributes to Induced N-Myc Expression by the Activation of ERK Signaling Pathway and Increased Expression of Interleukin-8 and VEGF in Neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4146–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, K.R.; Stephens, R.S. The Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Induces the Inflammatory Factor Interleukin-8 Following Chlamydia Trachomatis Infection. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5924–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.S.; Izidoro, L.F.M.; de Oliveira, R.J., Jr.; Soares, A.M.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Sampaio, S.V. Snake Venom Phospholipases A2: A New Class of Antitumor Agents. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Matsunaga, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Morita, T. Identification of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-Binding Protein in the Venom of Eastern Cottonmouth: A New Role of Snake Venom Myotoxic LYS49-Phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29989–29992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.H.; Ismail, H.A.H.A.; Cha, G.H.; Jo, Y.J.; Gao, F.F.; Choi, I.W.; Chu, J.Q.; Yuk, J.M.; Lee, Y.H. VEGF Production Is Regulated by the AKT/ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway and Controls the Proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii in ARPE-19 Cells. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 517925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.C.; Oliveira, V.Q.; Teixeira, S.C.; Correia, T.M.L.; Andrade, L.O.S.B.; Polloni, L.; Marques, L.M.; Clissa, P.B.; Baldo, C.; Ferro, E.A.V.; et al. PLA2-MjTX-II from Bothrops moojeni Snake Venom Exhibits Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenic Effects on Human Lung Cancer Cells. Toxicon 2024, 243, 107742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polloni, L.; Azevedo, F.V.P.V.; Teixeira, S.C.; Moura, E.; Costa, T.R.; Gimenes, S.N.C.; Correia, L.I.V.; Freitas, V.; Yoneyama, K.A.G.; Rodrigues, R.S.; et al. Antiangiogenic Effects of Phospholipase A2 Lys49 BnSP-7 from Bothrops pauloensis Snake Venom on Endothelial Cells: An in vitro and ex vivo Approach. Toxicol. Vitr. 2021, 72, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.D.; Christian, D.A.; Hunter, C.A. Immune Response and Immunopathology during Toxoplasmosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzinelli, R.T.; Eltoum, I.; Wynn, T.A.; Sher, A. Acute Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Is Induced by in Vivo Neutralization of TNF-Alpha and Correlates with the down-Regulated Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Other Markers of Macrophage Activation. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 3672–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, A.C.A.V.; Machado, A.S.; Béla, S.R.; Costa, J.G.L.; Andrade, G.M.Q.; Vasconcelos-Santos, D.V.; Januário, J.N.; Coelho-Dos-Reis, J.G.; Ferro, E.A.V.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; et al. Cytokine Signatures Associated with Early Onset, Active Lesions and Late Cicatricial Events of Retinochoroidal Commitment in Infants with Congenital Toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, M.Y.; Moffett, A. Development of the Human Placenta. Development 2019, 146, dev163428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrião-Escarso, S.H.; Soares, A.M.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Angulo, Y.; Díaz, C.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Giglio, J.R. Myotoxic Phospholipases A(2) in Bothrops Snake Venoms: Effect of Chemical Modifications on the Enzymatic and Pharmacological Properties of Bothropstoxins from Bothrops jararacussu. Biochimie 2000, 82, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, G.H.; Postema, N.M.; Nieuwenhuizen, W.; van Deenen, L.L.M. Purification and Properties of Phospholipase A from Porcine Pancreas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1968, 159, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, F.; Huang, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, Y. Effects of Long-Term Serial Cell Passaging on Cell Spreading, Migration, and Cell-Surface Ultrastructures of Cultured Vascular Endothelial Cells. Cytotechnology 2013, 66, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.C.; de Souza, G.; Borges, B.C.; de Araújo, T.E.; Rosini, A.M.; Aguila, F.A.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Bastos, J.K.; Silva, M.J.B.; et al. Copaifera Spp. Oleoresins Impair Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Both Human Trophoblastic Cells and Human Placental Explants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, R.d.P.; Bessa, M.A.d.S.; Siqueira, C.d.P.; Teixeira, S.C.; Ferro, E.A.V.; Martins, M.M.; Cunha, L.C.S.; Martins, C.H.G. Antimicrobial, Antivirulence, and Antiparasitic Potential of Capsicum chinense Jacq. Extracts and Their Isolated Compound Capsaicin. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.J.M.; Crevelin, E.J.; Carneiro, L.J.; Rogez, H.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Beraldo Moraes, L.A.; Bastos, J.K. Development of a Validated Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Determination of Acid Diterpenes in Copaifera Oleoresins. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1515, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Murata, Y.; Sugi, T.; Kato, K. Inorganic Nanoparticles Kill Toxoplasma Gondii via Changes in Redox Status and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1647–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, M.B.; dos Santos, V.C.O.; Teixeira, S.C.; Silva, N.B.S.; de Oliveira, P.F.; Ozelin, S.D.; Furtado, R.A.; Tavares, D.C.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; et al. Polyalthic Acid from Copaifera Lucens Demonstrates Anticariogenic and Antiparasitic Properties for Safe Use. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.S.Y.; Chua, K.H.; Nölke, G.; Spiegel, H.; Goh, W.L.; Chow, S.C.; Kee, B.P.; Fischer, R.; Schillberg, S.; Othman, R.Y. Plant-Derived Toxoplasma gondii. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, V.Q.; Ferreira, E.L.; Morais, L.P.; Garcia, L.A.; Sousa, G.d.O.; Almeida, M.P.O.; de Souza, G.; Júnior, J.P.d.L.; dos Santos, N.C.L.; de Oliveira, R.M.; et al. BthTX-II, an Asp49 PLA2 from Bothrops jararacussu, Impairs Toxoplasma gondii Infection: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Approaches. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091260
Oliveira VQ, Ferreira EL, Morais LP, Garcia LA, Sousa GdO, Almeida MPO, de Souza G, Júnior JPdL, dos Santos NCL, de Oliveira RM, et al. BthTX-II, an Asp49 PLA2 from Bothrops jararacussu, Impairs Toxoplasma gondii Infection: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Approaches. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091260
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Vinícius Queiroz, Emanuelle Lorrayne Ferreira, Lorena Pinheiro Morais, Leonardo Alves Garcia, Gabriel de Oliveira Sousa, Marcos Paulo Oliveira Almeida, Guilherme de Souza, Joed Pires de Lima Júnior, Natália Carine Lima dos Santos, Rafael Martins de Oliveira, and et al. 2025. "BthTX-II, an Asp49 PLA2 from Bothrops jararacussu, Impairs Toxoplasma gondii Infection: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Approaches" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091260
APA StyleOliveira, V. Q., Ferreira, E. L., Morais, L. P., Garcia, L. A., Sousa, G. d. O., Almeida, M. P. O., de Souza, G., Júnior, J. P. d. L., dos Santos, N. C. L., de Oliveira, R. M., Costa, T. R., Soares, A. M., Santos, L. C., Lopes, D. S., Beraldo-Neto, E., Gomes, A. O., Madeira, J. E. G. C., Barbosa, B. F., Ferro, E. A. V., ... Ávila, V. d. M. R. (2025). BthTX-II, an Asp49 PLA2 from Bothrops jararacussu, Impairs Toxoplasma gondii Infection: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Approaches. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091260







