Multiple Strategies Confirm the Anti Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect of Cinnamic Acid Based on the PI3k-AKT Pathway
Abstract
1. Background
2. Results
2.1. Performance of Different Anti-Tumor Prediction Models
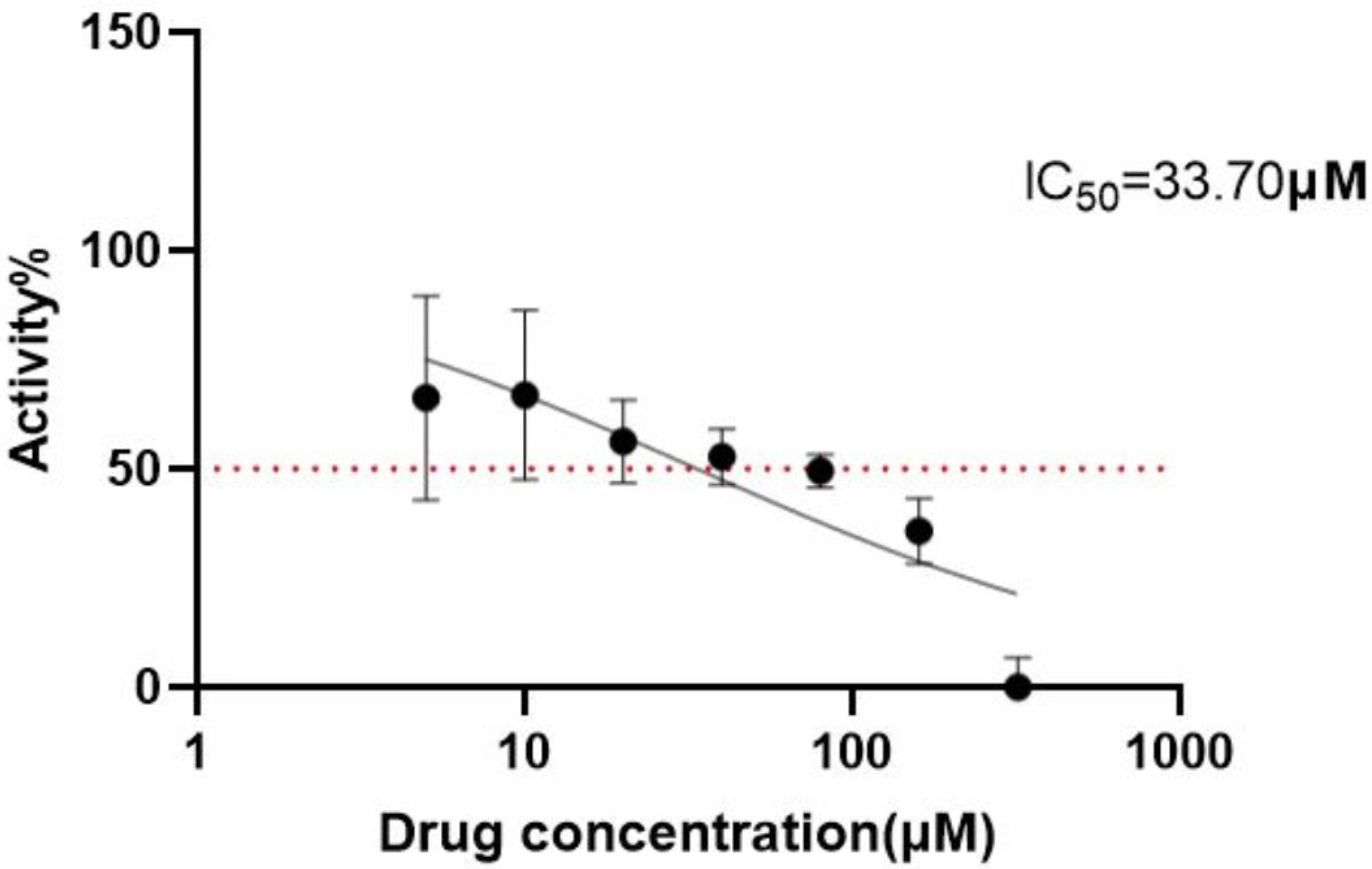
2.2. Prediction of Anti-Tumor Activity of Cinnamic Acid and Verification Set
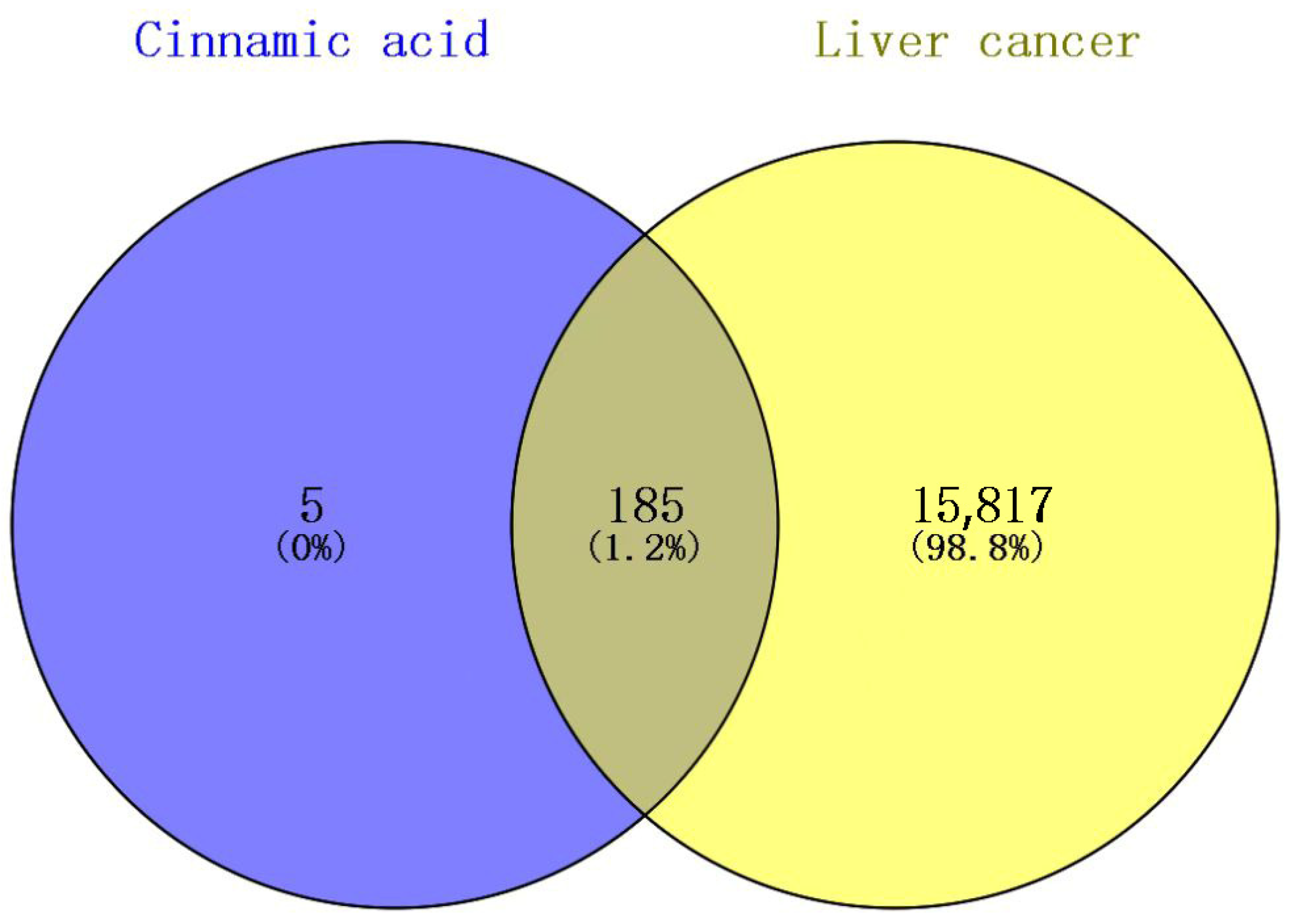
2.3. The Intersection Target Results of Cinnamic Acid and Liver Cancer
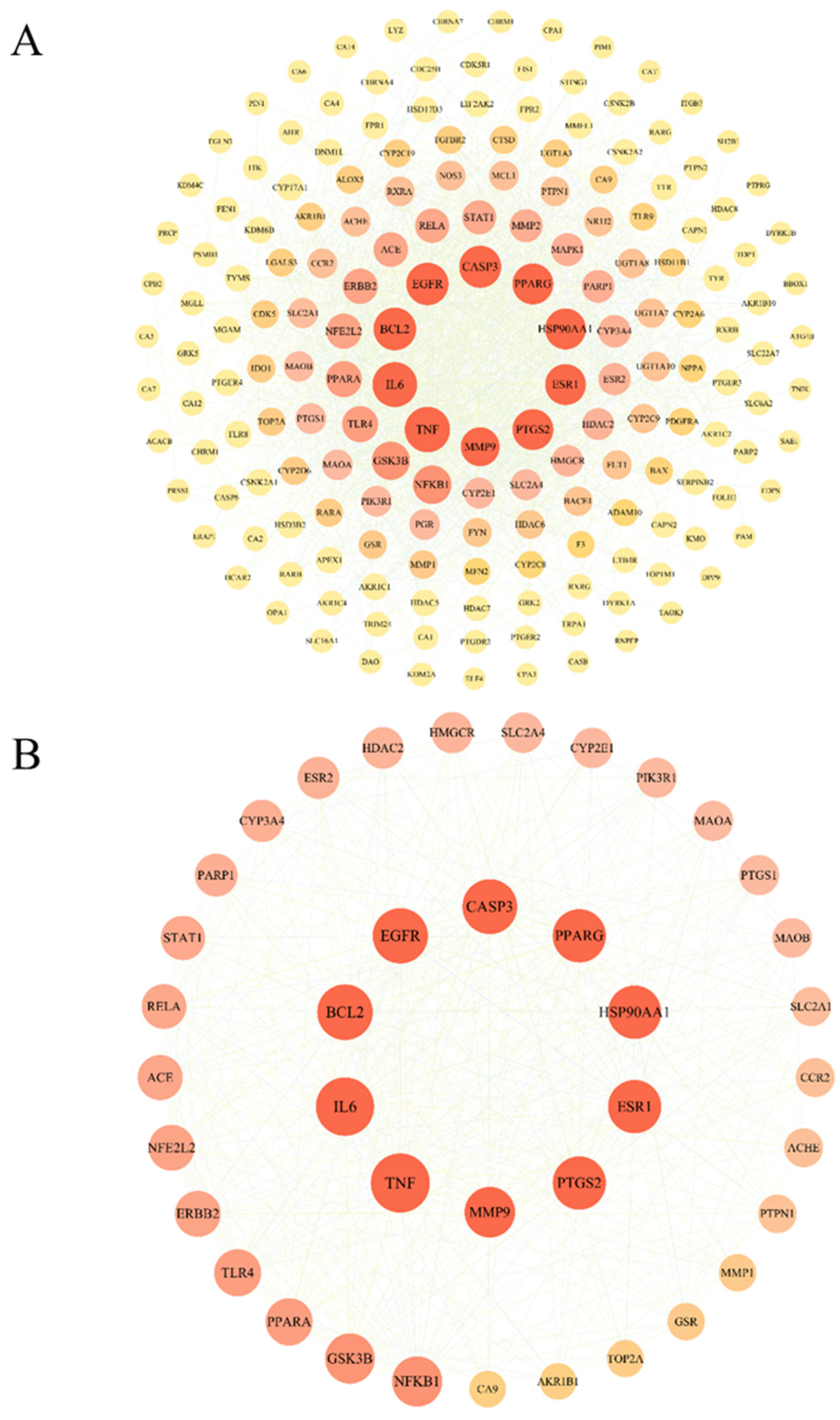
2.4. PPI Network Construction and Core Target Screening
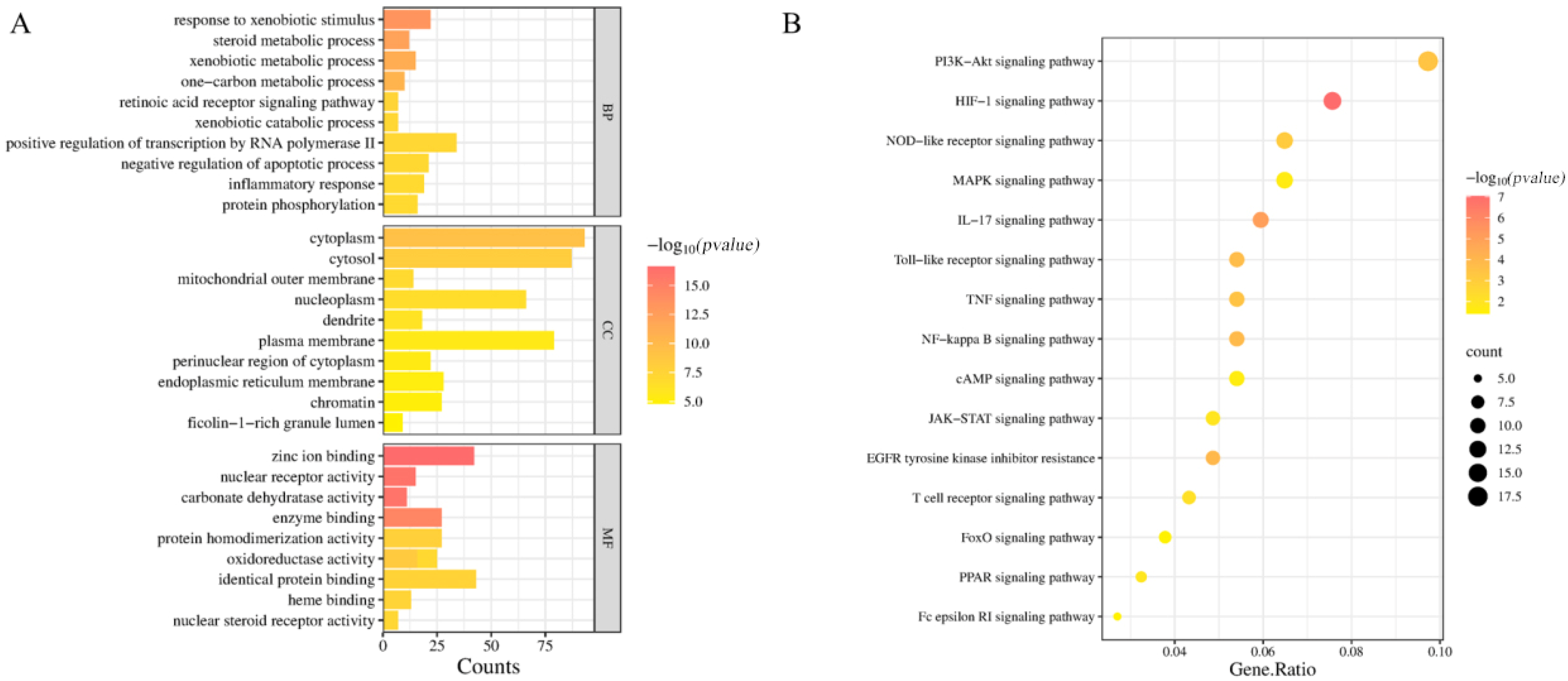
2.5. GO Functional Enrichment Analysis and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
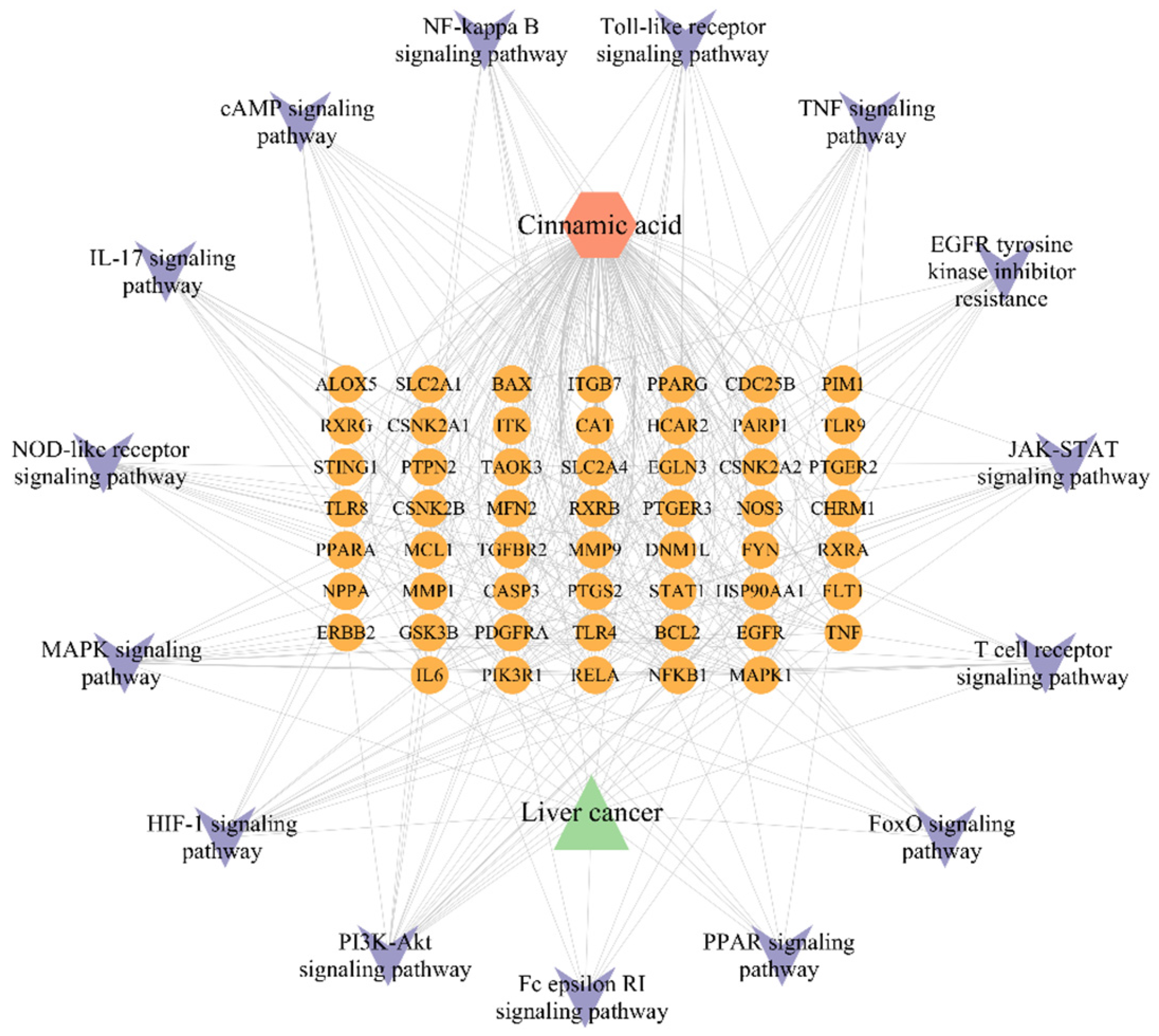
2.6. Component-Pathway-Target-Disease Network Construction
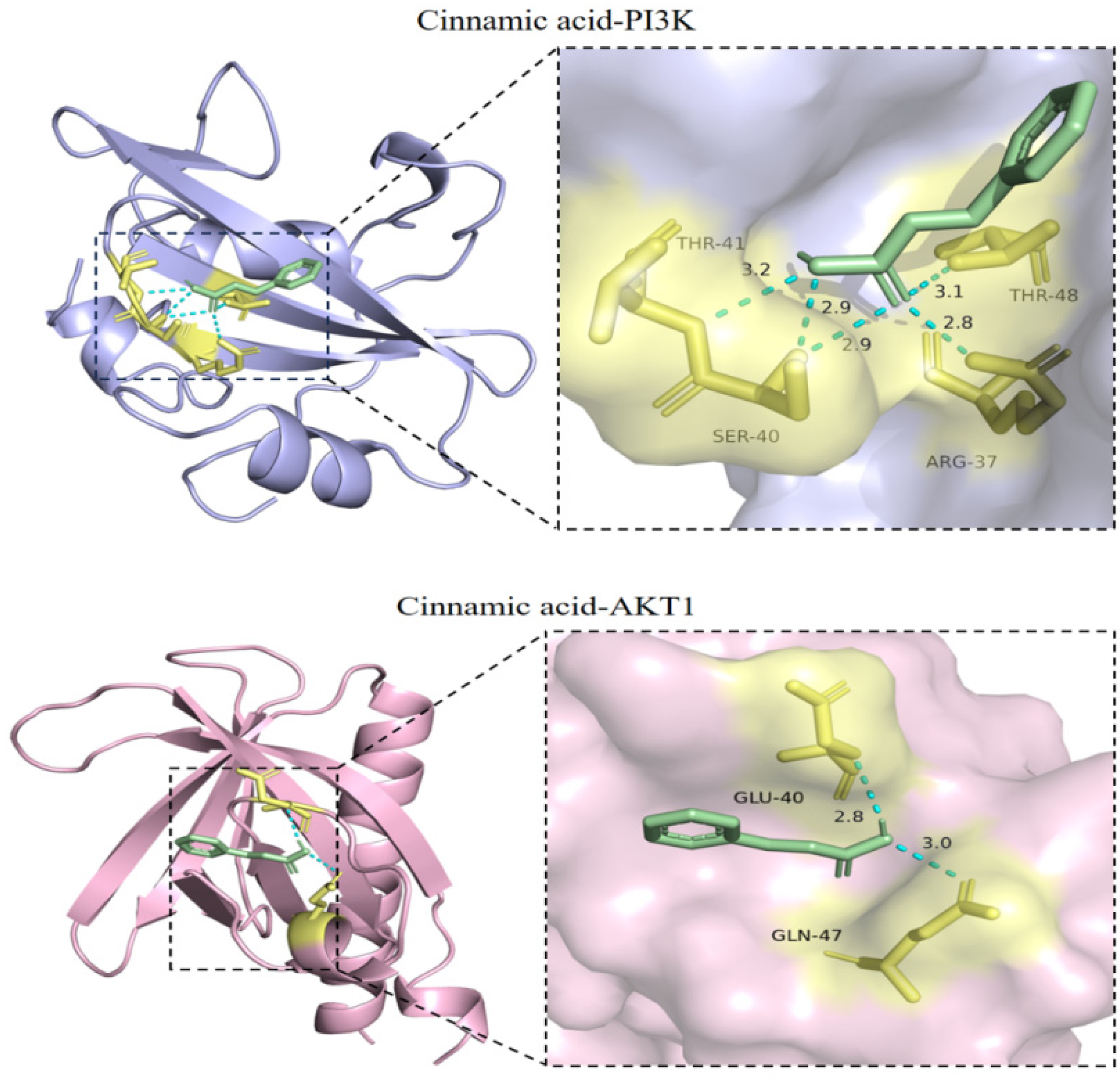
2.7. Verification of the Docking of Cinnamic Acid and PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway-Related Target Proteins
2.8. Cell Viability Assay
2.9. Observation of Morphological Changes
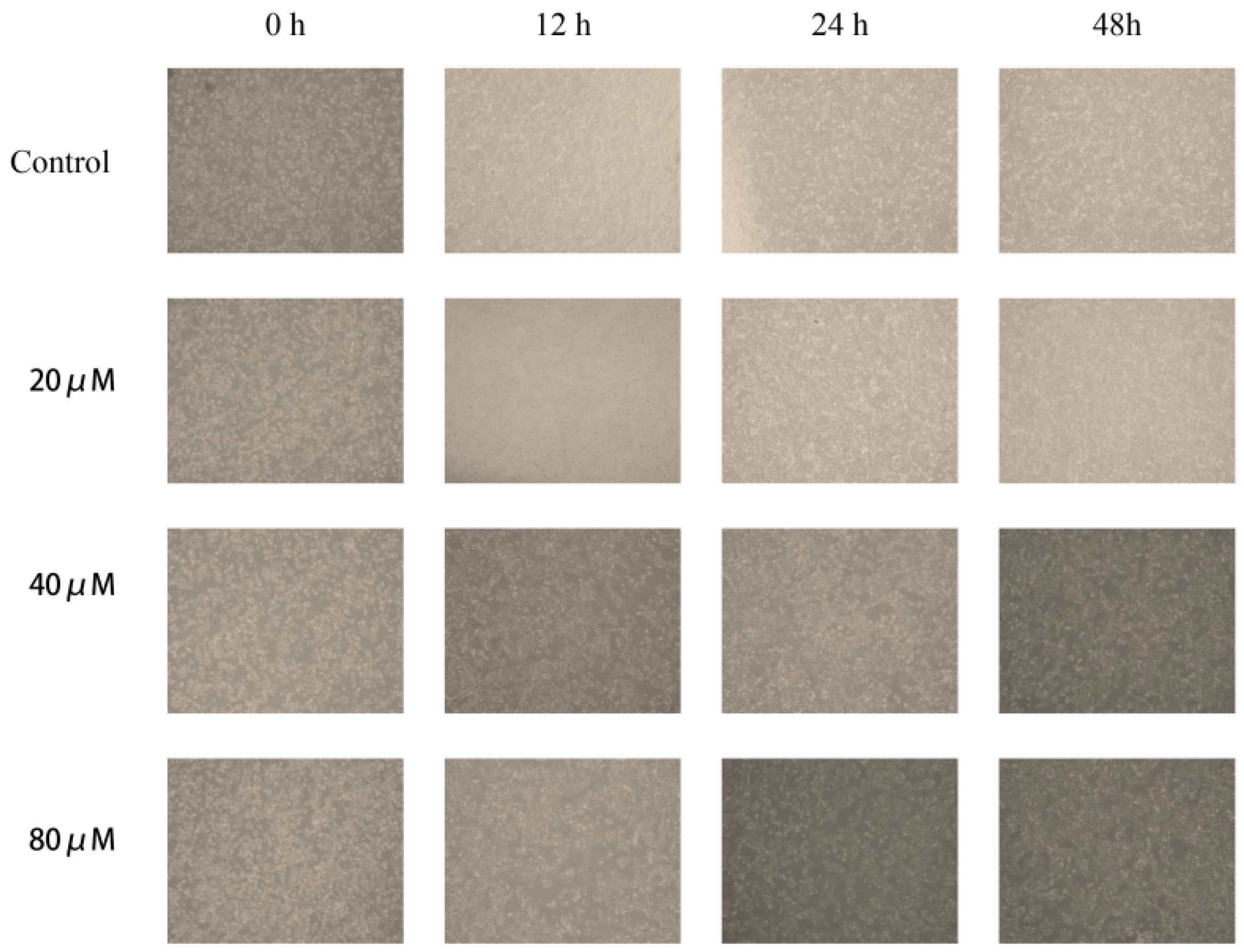
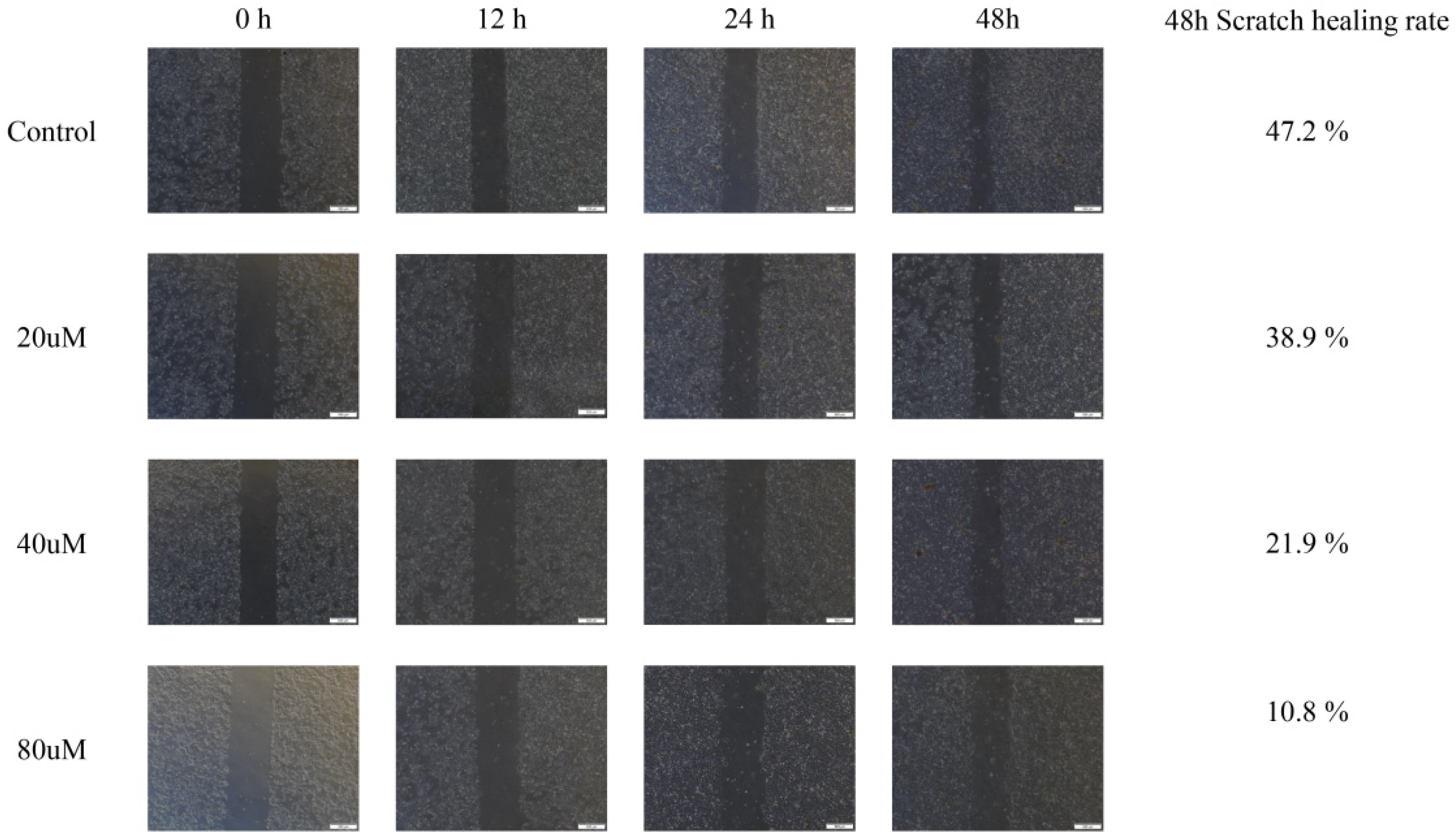
2.10. Cinnamic Acid Inhibits Hep3B Cell Migration
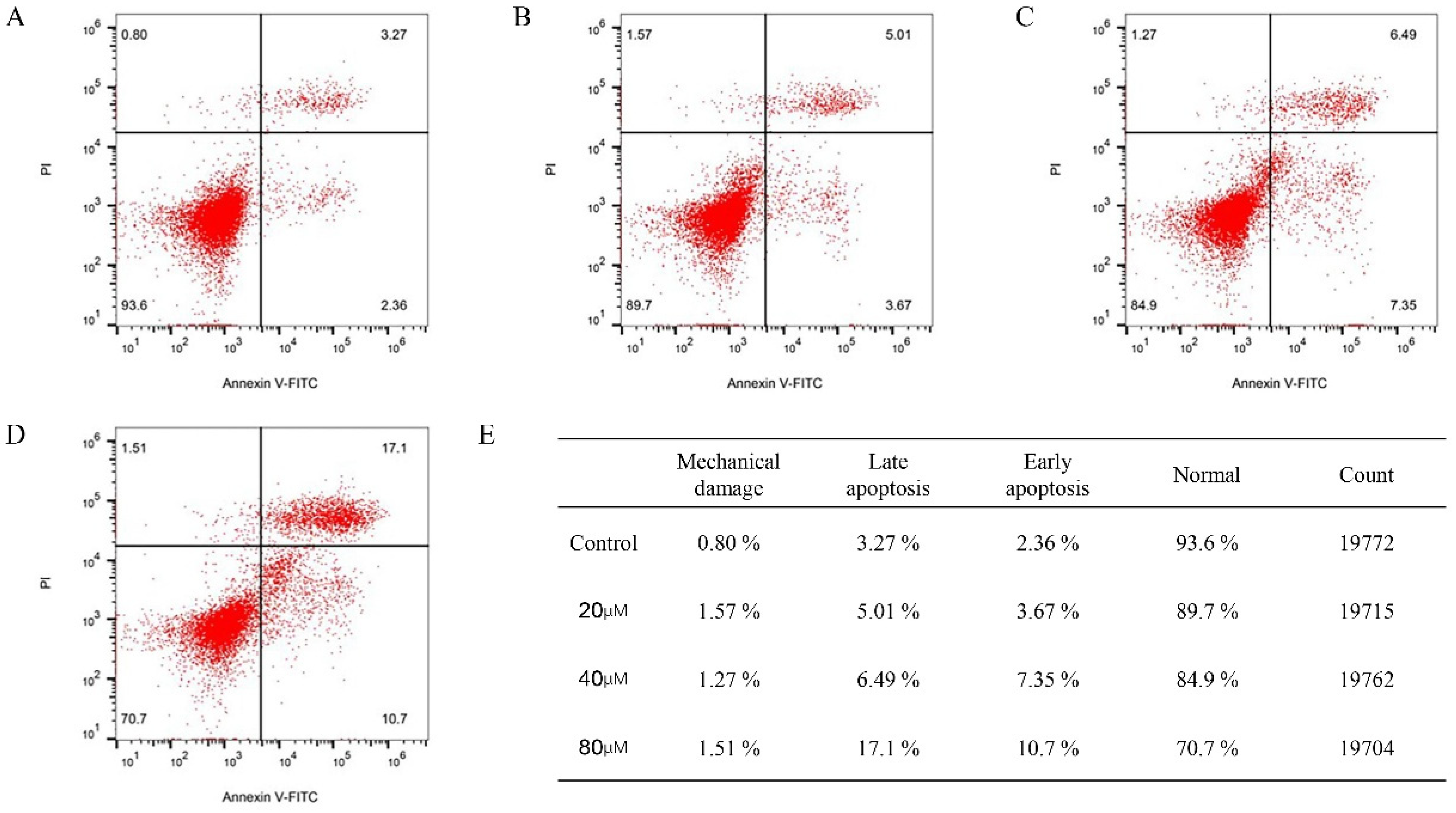
2.11. Cinnamic Acid Promotes Apoptosis of Hep3B Cells
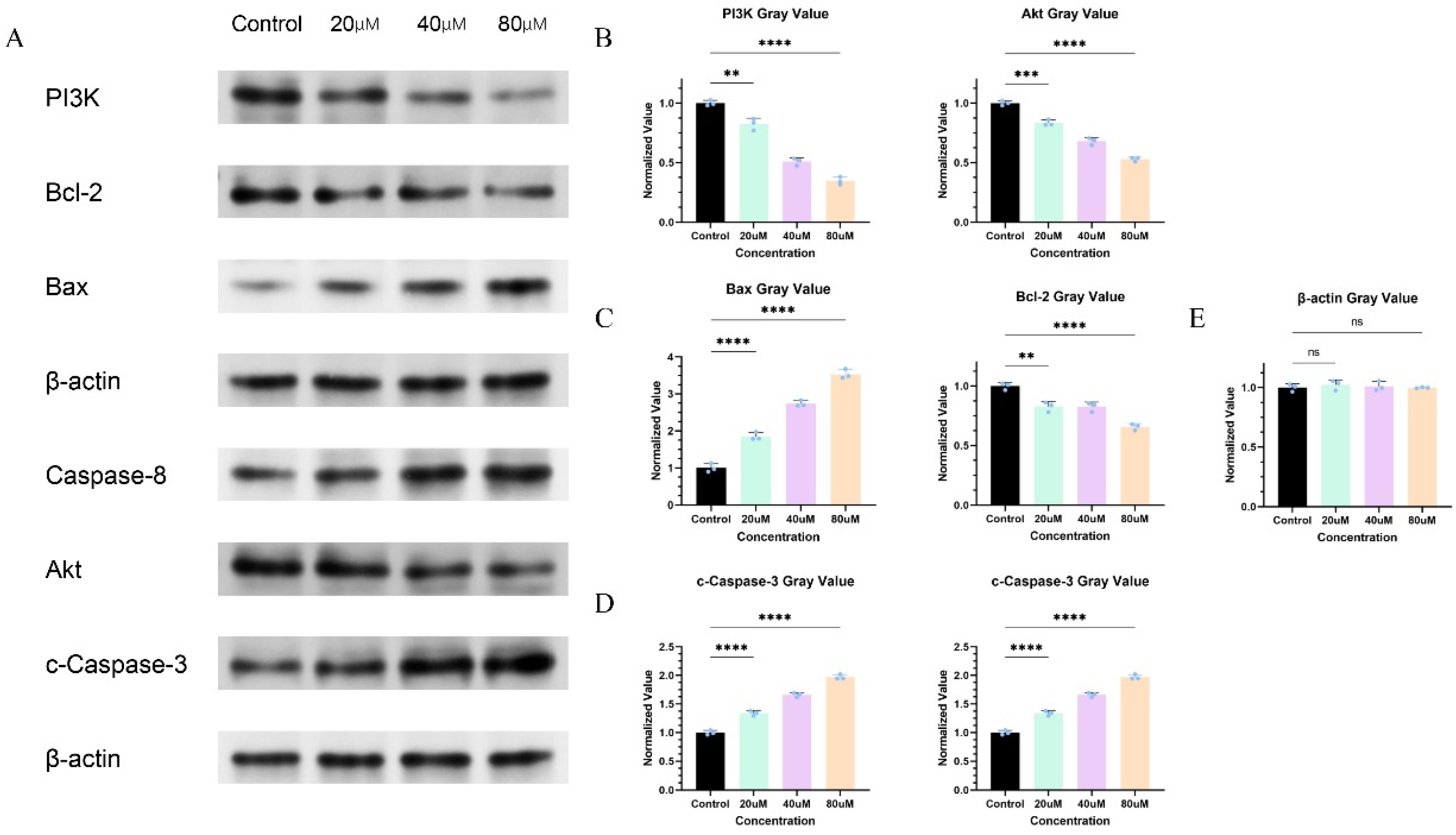
2.12. Cinnamic Acid Regulates PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
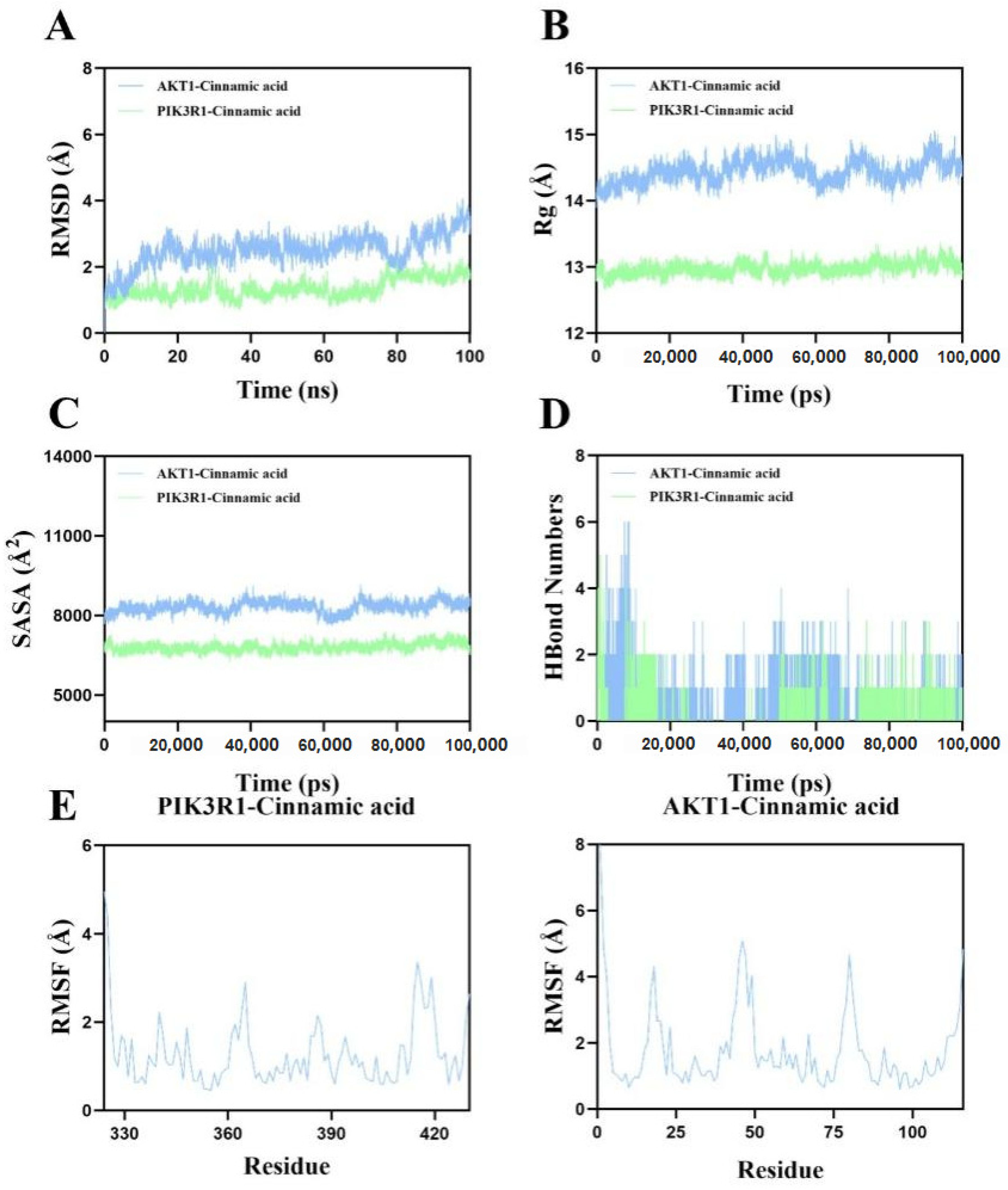
2.13. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Corroborates the Binding Stability of Cinnamic Acid to AKT1 and PIK3R1
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Construction of Anti-Tumor Prediction Model
4.2. Screening and Mechanism Analysis of Network Pharmacological Targets
4.3. Molecular Docking Verification
4.4. Cell Experiments and Mechanism Verification
4.5. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chidambaranathan-Reghupaty, S.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology, etiology and molecular classification. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 149, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Ko, H.; Yun, M. Cancer Metabolism as a Mechanism of Treatment Resistance and Potential Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Yonsei Med. J. 2018, 59, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokhadze, N.; Das, A.; Dizon, D.S. Global cancer statistics: A healthy population relies on population health. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.M.; Mo, N.; Zeng, J.; Ma, F.C.; Jiang, Y.F.; Huang, H.S.; Liao, X.W.; Zhu, G.Z.; Ma, J.; Peng, T. Advances in postoperative adjuvant therapy for primary liver cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1604–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Qu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Sun, K.; Gu, X.; Xia, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, W.; et al. Liver cancer incidence and mortality in China: Temporal trends and projections to 2030. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 30, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Chen, E.; Zhang, Y. Integrated Molecular Modeling and Machine Learning for Drug Design. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2023, 19, 7478–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadybekov, A.V.; Katritch, V. Computational approaches streamlining drug discovery. Nature 2023, 616, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vivo, M.; Masetti, M.; Bottegoni, G.; Cavalli, A. Role of Molecular Dynamics and Related Methods in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4035–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Matteo, A.; Bathon, J.M.; Emery, P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2023, 402, 2019–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Qin, T.; Huang, G.; Luo, P.; Hu, Y.; Xia, X. Cinnamomum cassia Presl flavonoids prevent hyperglycemia-induced cognitive impairment via inhibiting of AGEs accumulation and oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 100, 105374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Hao, E.; Qin, J.; Wei, J.; Jiao, Y.; Yi, X.; Huang, L.; Xie, J.; Hua, L.; Zhang, R.; et al. Prediction and analysis of chemical composition, pharmacological action and quality marker (Q-marker) of cinnamon. Chin. Herb. Med. 2018, 49, 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.S.; Cheng, J.B.; Su, W.Q.; Li, H.Z.; Xiao, T.; Chen, D.A.; Zhang, Z.L. Cinnamic acid hybrids as anticancer agents: A mini-review. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, e2200052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.; Abdulrazzaq, M. The Protective Eff ect of Cinnamic Acid against Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2023, 13, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Pang, D.; Liao, S.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, P.; Li, E.; Wang, W. Synergistic effects of cinnamaldehyde and cinnamic acid in cinnamon essential oil against S. pullorum. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anlar, H.G.; Bacanlı, M.; Çal, T.; Aydın, S.; Arı, N.; Ündeğer Bucurgat, Ü.; Başaran, A.A.; Başaran, A.N. Effects of cinnamic acid on complications of diabetes. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 48, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawiła, T.; Swolana, D.; Rok, J.; Rzepka, Z.; Wojtyczka, R.D. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Cinnamic Acid and Its Derivatives: Synergistic Effects with Cloxacillin. Molecules 2025, 30, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirelles, L.E.F.; Souza, M.V.F.; Carobeli, L.R.; Morelli, F.; Mari, N.L.; Damke, E.; Shinobu Mesquita, C.S.; Teixeira, J.J.V.; Consolaro, M.E.L.; Silva, V. Combination of Conventional Drugs with Biocompounds Derived from Cinnamic Acid: A Promising Option for Breast Cancer Therapy. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Shang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhen, Y. Inhibition of histone deacetylases by trans-cinnamic acid and its antitumor effect against colon cancer xenografts in athymic mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 4159–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, G.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Sun, F.M.; Chiang, Y.L.; Lu, S.H.; Weng, C.J. A comparative study on the effectiveness of cis- and trans-form of cinnamic acid treatments for inhibiting invasive activity of human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Yokoe, H.; Tsubuki, M.; Takahashi, N. Growth Inhibition of Human Breast and Prostate Cancer Cells by Cinnamic Acid Derivatives and Their Mechanism of Action. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, N.; Chen, M.; Horn, H.T.; Choi, S.; Wen, T.; Anderson, R.A. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signalling is spatially organized at endosomal compartments by microtubule-associated protein 4. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, F.; Duan, E. The PI3K-Akt pathway inhibits senescence and promotes self-renewal of human skin-derived precursors in vitro. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Leong, H.C.; Datta, A.; Gopal, V.; Kumar, A.P.; Yap, C.T. PI3K/AKT Signaling Tips the Balance of Cytoskeletal Forces for Cancer Progression. Cancers 2022, 14, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: Theory, methodology and application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.W.; Jia, S.; Ashraf, A.B.; Hu, P. Integrative Data Augmentation with U-Net Segmentation Masks Improves Detection of Lymph Node Metastases in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, H.; Boal, F.; Tronchere, H.; Cinato, M.; Kramar, S.; Oleshchuk, O.; Korda, M.; Kunduzova, O. Metformin Protects the Heart Against Hypertrophic and Apoptotic Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.B.; Lee, S.; Kang, I.; Kim, J.H. Momordica charantia Ethanol Extract Attenuates H2O2-Induced Cell Death by Its Antioxidant and Anti-Apoptotic Properties in Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-MC Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix Metalloproteinases: Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-kappaB in the liver--linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, K.; Bachmayr-Heyda, A.; Aust, S.; Grunt, T.W.; Pils, D. Comparative transcriptome analysis links distinct peritoneal tumor spread types, miliary and non-miliary, with putative origin, tubes and ovaries, in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.; Yeo, Y.H.; Scheiner, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hiraoka, A.; Tantai, X.; Fessas, P.; de Castro, T.; D’Alessio, A.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Child-Pugh Class B Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.M.; Zhou, J. The role of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 123, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayali, S.; Pasta, A.; Plaz Torres, M.C.; Jaffe, A.; Strazzabosco, M.; Marenco, S.; Giannini, E.G. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in malignancies after liver transplantation: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, C.; Paglino, C.; Mosca, A. Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesawa, Y.; Sakagami, H.; Okudaira, N.; Toda, K.; Takao, K.; Kagaya, H.; Sugita, Y. Quantitative Structure-Cytotoxicity Relationship of Cinnamic Acid Phenetyl Esters. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Rommel, C. PI3K and cancer: Lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluis, J.M.; Long, G.V.; Blank, C.U. Learning from clinical trials of neoadjuvant checkpoint blockade. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrián-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D945–D954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodsell, D.S.; Zardecki, C.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; Hudson, B.P.; Persikova, I.; Segura, J.; Shao, C.; Voigt, M.; Westbrook, J.D.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Enabling biomedical research and drug discovery. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, V.; Kalakoti, Y.; Sundar, D. Deep learning assisted multi-omics integration for survival and drug-response prediction in breast cancer. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.; Hahn, M. Extended-connectivity fingerprints. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswat, M.; Arya, K.V. Feature selection and classification of leukocytes using random forest. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2014, 52, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au-Yeung, R.; Camino, B.; Rathore, O.; Kendon, V. Quantum algorithms for scientific computing. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2024, 87, 116001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Odom, P.; Pasunuri, R.; Kersting, K.; Natarajan, S. Learning with privileged and sensitive information: A gradient-boosting approach. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1260583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonte, C.; Vercauteren, F. Privacy-preserving logistic regression training. BMC Med. Genom. 2018, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauner, D.G.; Leal, E.; Adam, T.J.; Zhang, R.; Farley, J.F. Evaluation of four machine learning models for signal detection. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2023, 14, 20420986231219472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Engkvist, O.; Wang, Y.; Olivecrona, M.; Blaschke, T. The rise of deep learning in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, A.; Barham, C.; Li, X.; Hu, H. Interpretation of deep learning in genomics and epigenomics. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S. Building and analyzing machine learning-based warfarin dose prediction models using scikit-learn. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 30, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Witbooi, P.; Christoffels, A.; Hancock, J. Prediction of human-Bacillus anthracis protein–protein interactions using multi-layer neural network. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4159–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, G.; Saito, T.; Rehmsmeier, M. The Precision-Recall Plot Is More Informative than the ROC Plot When Evaluating Binary Classifiers on Imbalanced Datasets. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Iny Stein, T.; Shmoish, M.; Nativ, N.; Bahir, I.; Doniger, T.; Krug, H.; et al. GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database 2010, 2010, baq020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, J.; Gohlke, B.-O.; Erehman, J.; Banerjee, P.; Rong, W.W.; Goede, A.; Dunkel, M.; Preissner, R. SuperPred: Update on drug classification and target prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W26–W31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gfeller, D.; Grosdidier, A.; Wirth, M.; Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. Swiss Target Prediction: A web server for target prediction of bioactive small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W32–W38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Grondin, C.J.; Johnson, R.J.; Sciaky, D.; Wiegers, J.; Wiegers, T.C.; Mattingly, C.J. Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD): Update 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1138–D1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, G. Integrated bioinformatics and network pharmacology to identify the therapeutic target and molecular mechanisms of Huangqin decoction on ulcerative Colitis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Ding, H.; Han, B.; Song, X.; Miao, H.; Cui, X.; Wei, S.; Liu, W.; et al. CDC20 regulates the cell proliferation and radiosensitivity of P53 mutant HCC cells through the Bcl-2/Bax pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 3608–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Z.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.P.; Feng, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H. Cucurbitacin B suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression through inducing DNA damage-dependent cell cycle arrest. Phytomedicine 2024, 126, 155177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Qu, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, K. Royal jelly acid suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenicity by inhibiting H3 histone lactylation at H3K9la and H3K14la sites. Phytomedicine 2023, 118, 154940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnasko, T.S.; Hnasko, R.M. The Western Blot. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1318, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
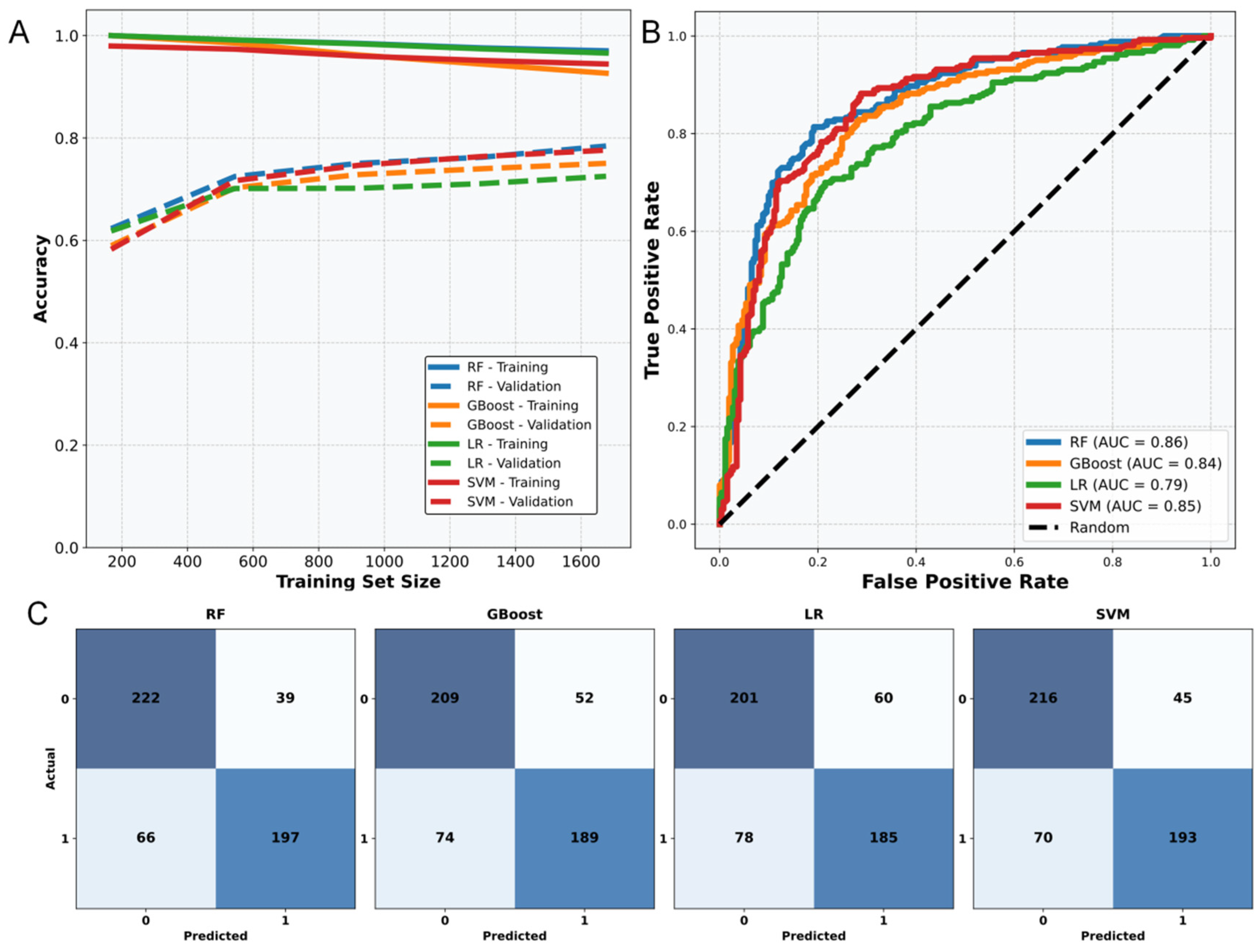
| Model | Accuracy | F1 Score | AUC | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.76 |
| GBoost | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.82 | 0.71 |
| LR | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.77 | 0.69 |
| SVM | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.73 |
| Model | Probability | Compound | Model | Probability | Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.80 | Random 1 | RF | 0.65 | Random 10 |
| RF | 0.76 | Random 2 | RF | 0.65 | Random 11 |
| RF | 0.70 | Random 3 | RF | 0.65 | Random 12 |
| RF | 0.69 | Cinnamic acid | RF | 0.64 | Random 13 |
| RF | 0.69 | Random 4 | RF | 0.63 | Random 14 |
| RF | 0.68 | Random 5 | RF | 0.62 | Random 15 |
| RF | 0.68 | Random 6 | RF | 0.62 | Random 16 |
| RF | 0.66 | Random 7 | RF | 0.62 | Random 17 |
| RF | 0.65 | Random 8 | RF | 0.62 | Random 18 |
| RF | 0.65 | Random 9 | RF | 0.62 | Random 19 |
| Target Protein | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Target Protein | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RXRA | −7.1 | PIK3R1 | −5.4 |
| CHRM1 | −6.7 | NFKB1 | −5.4 |
| PDGFRA | −6.3 | MAPK1 | −5.4 |
| BCL2 | −6.0 | FLT1 | −5.2 |
| GSK3B | −5.9 | NOS3 | −5.2 |
| TLR4 | −5.9 | ITGB7 | −5.2 |
| RELA | −5.8 | MCL1 | −5.2 |
| HSP90AA1 | −5.7 | IL6 | −5.1 |
| ERBB2 | −5.6 | AKT1 | −5.1 |
| EGFR | −5.5 |
| Database | Website |
|---|---|
| DAVID [56] | https://david.ncifcrf.gov/ accessed on 24 January 2025 |
| GeneCards [57] | https://www.genecards.org/ accessed on 24 January 2025 |
| PubChem [40] | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ accessed on 24 January 2025 |
| STRING [58] | https://cn.string-db.org/ accessed on 24 January 2025 |
| Superpred [59] | https://prediction.charite.de/index.php accessed on 24 January 2025 |
| TCMSP [60] | https://www.91tcmsp.com/ accessed on 24 January 2025 |
| SwissTargetPrediction [61] | http://swisstargetprediction.ch/ accessed on 24 January 2025 |
| CTD [62] | https://ctdbase.org/ accessed on 25 January 2025 |
| UniPort [63] | https://www.uniprot.org/ accessed on 26 January 2025 |
| Venny 2.1.0 | https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/ accessed on 24 January 2025 |
| Weisheng Xin | https://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/ accessed on 26 January 2025 |
| Cytoscape 3.10.2 [64] | http://www.cytoscape.org accessed on 27 January 2025 |
| PDB | https://www.rcsb.org/ accessed on 22 January 2025 |
| GenBank | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ accessed on 23 January 2025 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Yan, L.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Tian, Y.; Yang, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, F.; Hao, E. Multiple Strategies Confirm the Anti Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect of Cinnamic Acid Based on the PI3k-AKT Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081205
Guo J, Yan L, Yang Q, Li H, Tian Y, Yang J, Xie J, Zhang F, Hao E. Multiple Strategies Confirm the Anti Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect of Cinnamic Acid Based on the PI3k-AKT Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081205
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jiageng, Lijiao Yan, Qi Yang, Huaying Li, Yu Tian, Jieyi Yang, Jinling Xie, Fan Zhang, and Erwei Hao. 2025. "Multiple Strategies Confirm the Anti Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect of Cinnamic Acid Based on the PI3k-AKT Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081205
APA StyleGuo, J., Yan, L., Yang, Q., Li, H., Tian, Y., Yang, J., Xie, J., Zhang, F., & Hao, E. (2025). Multiple Strategies Confirm the Anti Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect of Cinnamic Acid Based on the PI3k-AKT Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081205









