Ferroptosis as a Form of Cell Death—Medical Importance and Pharmacological Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Iron Homeostasis
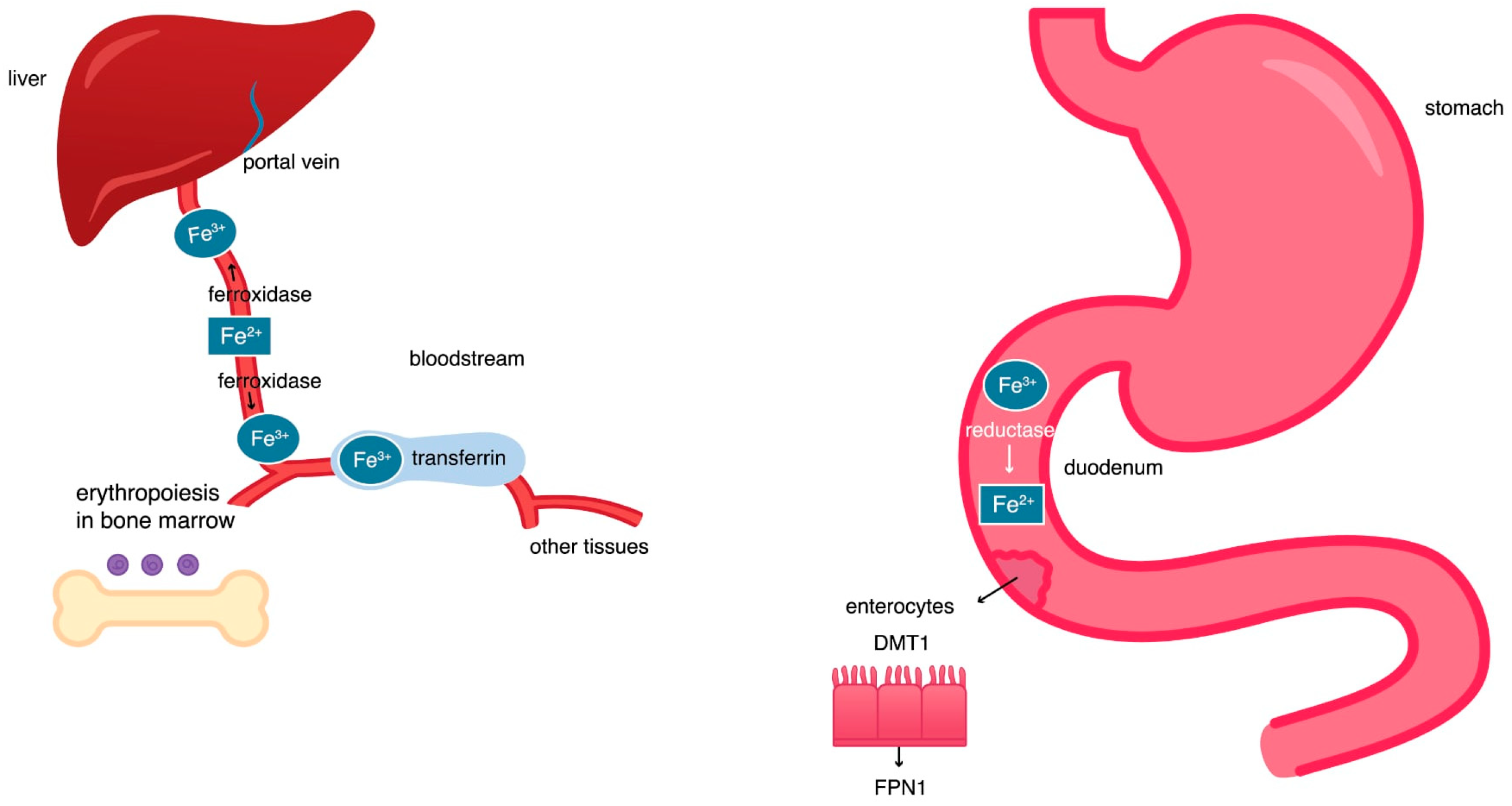
2.1. Iron Circulation in the Body
2.2. The Hephaestin, Ceruloplasmin, and Transferrin Activity
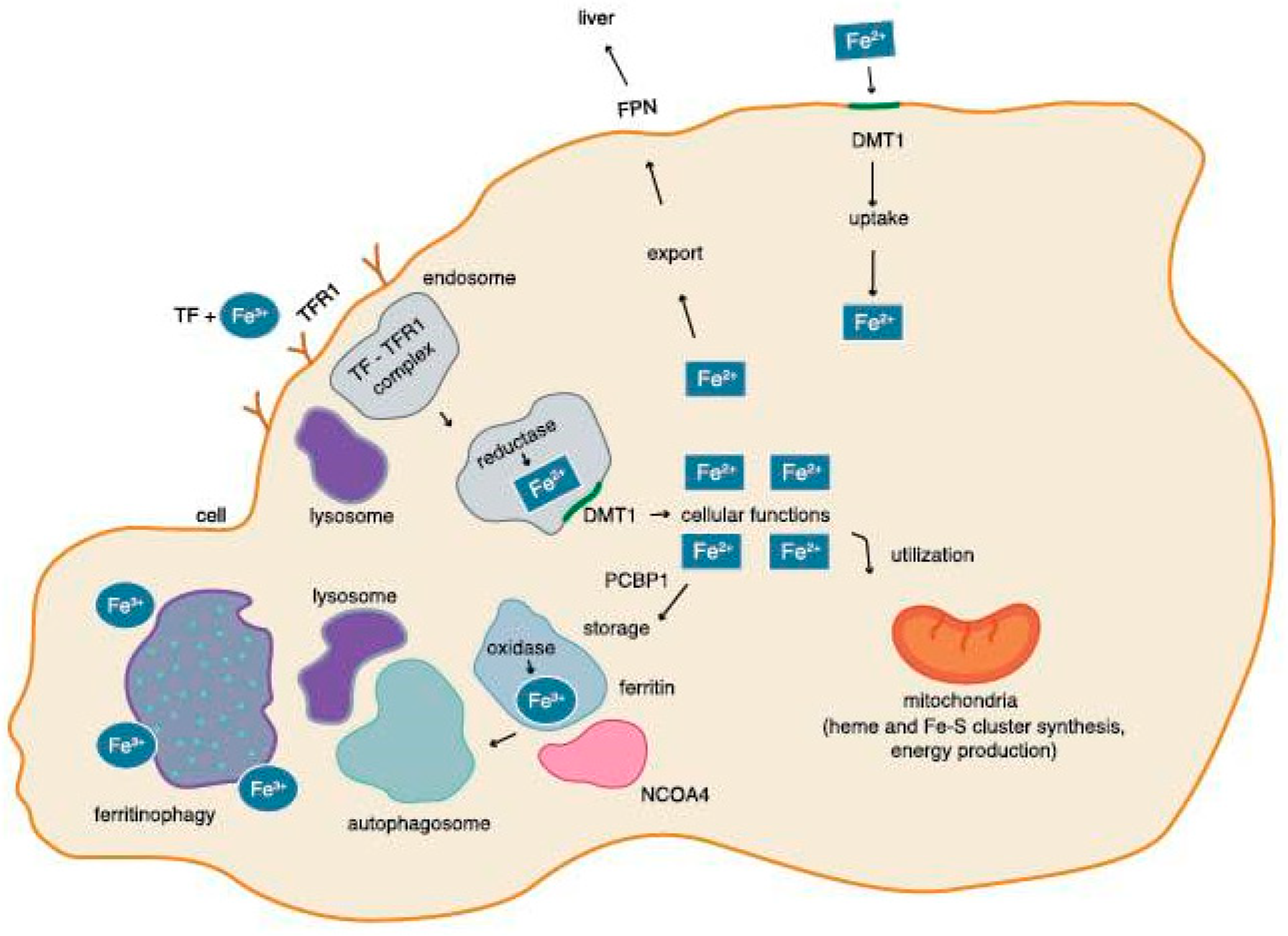
2.3. Iron Circulation in a Cell
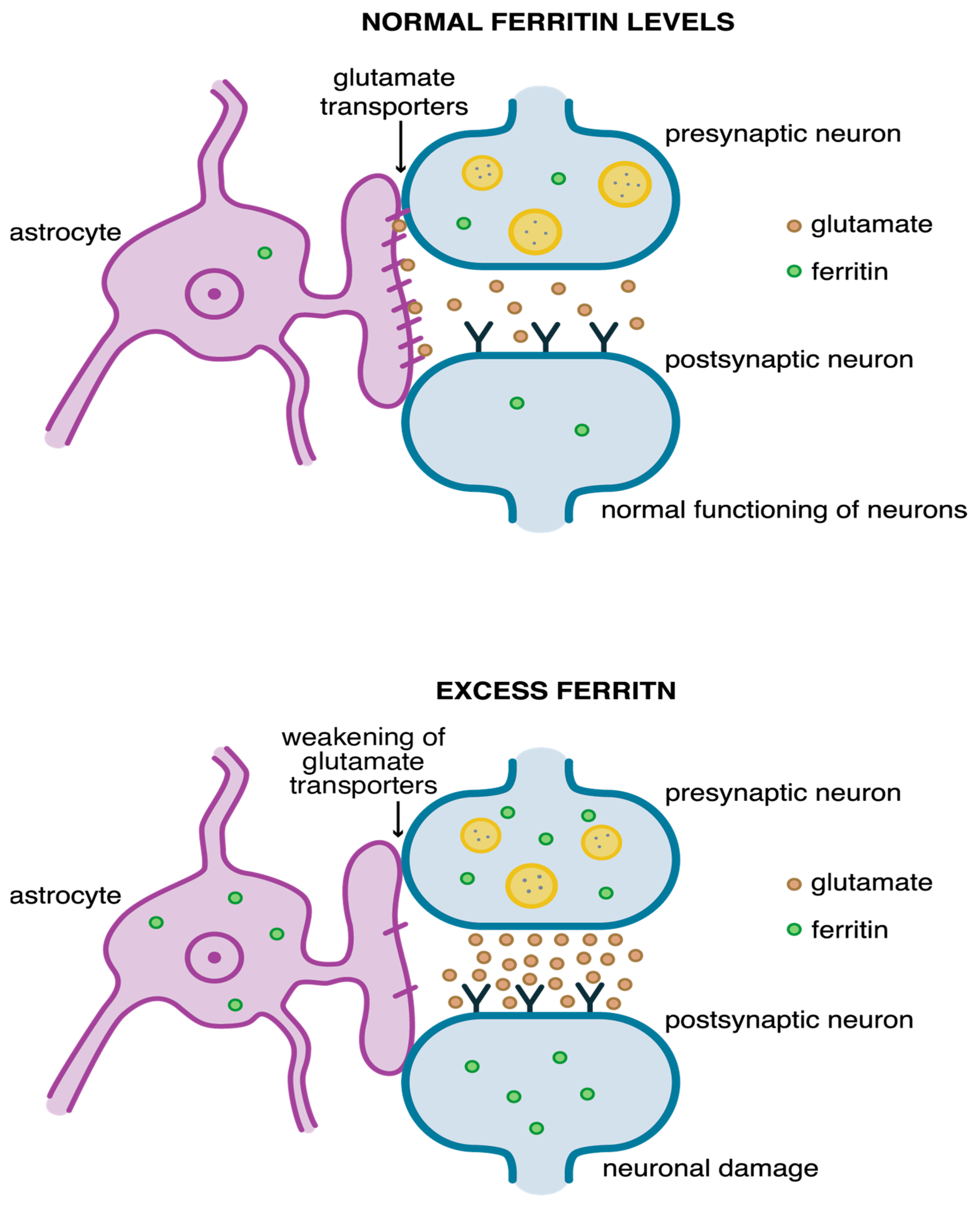
2.4. Regulation of the Level of Tron in a Cell by Ferritinophagy
2.5. Regulation of the Level of Iron in the Cell by IRP-1 and IRP-2
3. Excess Iron During Pathology Processes
3.1. The Fenton Reaction and the Haber–Weiss Reaction
3.2. Non-Transferrin-Bound Iron
3.3. Antioxidant and Oxidative Factors
3.4. Iron Regulatory Proteins
4. The Body’s Antioxidant System
4.1. Glutathione Peroxidase 4 as Component of Antioxidant System
4.2. Other Components of Antioxidant System
4.3. System Xc
4.4. CoQ10
5. Oxidative Effect
5.1. Oxidative Processes
5.2. ACSL4 and LPCAT3
6. Other Factors Regulating Ferroptosis
6.1. ACSL3 and Ferroptosis Inhibition
6.2. MBOAT1, MBOAT 2, and Ferroptosis Inhibition
6.3. Factors Leading to Induction of Ferroptosis
6.4. Factors Leading to Inhibition of Ferroptosis
7. Selected Clinical Implications
7.1. Cancer Diseases
7.2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH), Ischemic Stroke
7.3. Autoimmune Diseases
7.4. Neurodegenerative Diseases
7.5. Kidney Diseases
7.6. Cardiovascular System
7.7. General Anesthesia
7.8. Intestinal Diseases
8. Summary and Outlook
9. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Cellular degradation systems in ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Krusenstiern, A.N.; Robson, R.N.; Qian, N.; Qiu, B.; Hu, F.; Reznik, E.; Smith, N.; Zandkarimi, F.; Estes, V.M.; Dupont, M.; et al. Identification of essential sites of lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.N.; Carmicheal, J.; Jiang, L.; Lei, Y.L.; Green, M.D. Contribution of Lipid Oxidation and Ferroptosis to Radiotherapy Efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xin, L.; Xiang, M.; Shang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X.; Lu, Y. The molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cardiovascular disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Su, J.; Zeng, F.; Deng, G.; Chen, X. Targeting Ferroptosis by Ubiquitin System Enzymes: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5475–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarangelo, A.; Dixon, S.J. Lipid Metabolism and Ferroptosis. In Ferroptosis in Health and Disease; Tang, D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y. Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhai, B.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, Y.; Fang, J.; Xu, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Sui, X.; et al. The emerging role of ferroptosis in inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Tang, R.; Xiao, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: Recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschhorn, T.; Stockwell, B.R. The development of the concept of ferroptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Liu, Y.; Dai, R.; Ismail, N.; Su, W.; Li, B. Ferroptosis and Its Potential Role in Human Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Lei, G.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. PARP inhibition promotes ferroptosis via repressing SLC7A11 and synergizes with ferroptosis inducers in BRCA-proficient ovarian cancer. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, W.X.; Gupta, R.; Zhai, K.; Wang, Y.R.; Xu, W.H.; Cui, Y. Current and Potential Roles of Ferroptosis in Bladder Cancer. Curr. Med. Sci. 2024, 44, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Xia, H.; Cui, Y.; Yam, J.W.P.; Xu, Y. Ferroptosis: From Basic Research to Clinical Therapeutics in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2023, 11, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Su, H.; Yin, M.Z.; Zeng, F.R.; Chen, X.; Deng, G.T. BET inhibitors potentiate melanoma ferroptosis and immunotherapy through AKR1C2 inhibition. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoochani, A.; Hsu, E.C.; Aslan, M.; Rice, M.A.; Nguyen, H.M.; Brooks, J.D.; Corey, E.; Paulmurugan, R.; Stoyanova, T. Ferroptosis Inducers Are a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertheloot, D.; Latz, E.; Franklin, B.S. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: An intricate game of cell death. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2022, 22, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yin, H.L.; Huang, Z.J.; Lin, Z.T.; Mao, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Wang, W.; Dong, J.; Wei, Y. The crosslinks between ferroptosis and autophagy in asthma. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1140791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, P.; Coy, S.; Petrova, B.; Dreishpoon, M.; Verma, A.; Abdusamad, M.; Rossen, J.; Joesch-Cohen, L.; Humeidi, R.; Spangler, R.D.; et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 2022, 375, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Y.Z. Cellular Iron Metabolism and Regulation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1173, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toyokuni, S.; Yanatori, I. Iron Metabolism and Ferroptosis. In Ferroptosis in Health and Disease; Tang, D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lanser, L.; Fuchs, D.; Kurz, K.; Weiss, G. Physiology and Inflammation Driven Pathophysiology of Iron Homeostasis-Mechanistic Insights into Anemia of Inflammation and Its Treatment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Kalra, P.R.; Mentz, R.J. Ponikowski Identification of three mechanistic pathways for iron-deficient heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 2281–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T. Hepcidin and Iron in Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2023, 74, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helman, S.L.; Zhou, J.; Fuqua, B.K.; Lu, Y.; Collins, J.F.; Chen, H.; Vulpe, C.D.; Anderson, G.J.; Frazer, D.M. The biology of mammalian multi-copper ferroxidases. Biometals 2023, 36, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Schorpp, K.; Jin, J.; Yozwiak, C.E.; Hoffstrom, B.G.; Decker, A.M.; Rajbhandari, P.; Stokes, M.E.; Bender, H.G.; Csuka, J.M.; et al. Transferrin Receptor Is a Specific Ferroptosis Marker. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3411–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Shen, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Fang, X.; Duan, L.; et al. Hepatic transferrin plays a role in systemic iron homeostasis and liver ferroptosis. Blood 2020, 136, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokuni, S.; Kong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Maeda, Y.; Motooka, Y.; Akatsuka, S. Iron as spirit of life to share under monopoly. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2022, 71, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knovich, M.A.; Storey, J.A.; Coffman, L.G.; Torti, S.V.; Torti, F.M. Ferritin for the clinician. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Codina, N.; Gikandi, A.; Mancias, J.D. The Role of NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy in Ferroptosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1301, 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Quiles Del Rey, M.; Mancias, J.D. NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy: A Potential Link to Neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Codina, N.; Mancias, J.D. The Role of NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy in Health and Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, S.; Sawamura, T.; Shibuya, Y.; Kono, M.; Ohbuchi, A.; Suzuki, T.; Mizokoshi, Y.; Saigo, K. Labile iron, ROS, and cell death are prominently induced by haemin, but not by non-transferrin-bound iron. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2022, 61, 103319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Guo, Y.; Wu, F.G. Chemodynamic Therapy via Fenton and Fenton-Like Nanomaterials: Strategies and Recent Advances. Small 2022, 18, 2103868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Guo, S.; Wang, D.; An, Q. Fenton-Like Reaction: Recent Advances and New Trends. Chemistry 2024, 30, e202304337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipovic, M.R.; Koppenol, W.H. The Haber-Weiss reaction—The latest revival. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 145, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka, D.; Gromadzka, G. Ceruloplazmina, hefajstyna i cyklopen: Trzy multimiedziowe oksydazy uczestniczące w metabolizmie żelaza u człowieka. Postęp. Hig. Med. Dośw. 2014, 68, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaris, D.; Barbouti, A.; Pantopoulos, K. Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: An intimate relationship. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z. Hydroxyl radical generations form the physiologically relevant Fenton-like reactions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 208, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppenol, W.H.; Hider, R.H. Iron and redox cycling. Do’s and don’ts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angoro, B.; Motshakeri, M.; Hemmaway, C.; Svirskis, D.; Sharma, M. Non-transferrin bound iron. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 531, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, C.C.; Patel, S.J.; Protchenko, O. Management versus miscues in the cytosolic labile iron pool: The varied functions of iron chaperones. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandhan, A.; Dodson, M.; Shakya, A.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, K.; et al. NRF2 controls iron homeostasis and ferroptosis through HERC2 and VAMP8. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci-Çekiç, S.; Özkan, G.; Avan, A.N.; Uzunboy, S.; Çapanoğlu, E.; Apak, R. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 209, 114477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, A.; Li, L.; Liang, Q.; Wang, S.; Dong, Q.; Fu, M.; Lan, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Repression of the antiporter SLC7A11/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 axis drives ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells to facilitate vascular calcification. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 1259–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Zhang, J.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A.; Peng, Z. Mitochondria ROS and mitophagy in acute kidney injury. Autophagy 2023, 19, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheff, D.M.; Huang, C.; Scholzen, K.C.; Gencheva, R.; Ronzetti, M.H.; Cheng, Q.; Hall, M.D.; Arnér, E.S.J. The ferroptosis inducing compounds RSL3 and ML162 are not direct inhibitors of GPX4 but of TXNRD1. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kroemer, G. Ferroptosis. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R1292–R1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppula, P.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: Ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, J.; Adla, S.K.; Markowicz-Piasecka, M.; Huttunen, K.M. Increased/Targeted Brain (Pro)Drug Delivery via Utilization of Solute Carriers (SLCs). Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.J.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J. Role of ferroptosis in neurological diseases. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 747, 135614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Freitas, F.P.; Shah, R.; Aldrovandi, M.; da Silva, M.C.; Ingold, I.; Goya Grocin, A.; Xavier da Silva, T.N.; Panzilius, E.; Scheel, C.H.; et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 2019, 575, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, C.; Alborzinia, H.; Amen, V.S.; Ayton, S.; Barayeu, U.; Bartelt, A.; Bayir, H.; Bebber, C.M.; Birsoy, K.; Böttcher, J.P.; et al. Ferroptosis in health and disease. Redox Biol. 2024, 75, 103211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersuker, K.; Hendricks, J.M.; Li, Z.; Magtanong, L.; Ford, B.; Tang, P.H.; Roberts, M.A.; Tong, B.; Maimone, T.J.; Zoncu, R.; et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 2019, 575, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, A.; Wu, L.; Zhang, B.X.; Yang, Q.C.; Liu, Y.T.; Li, H.; Mao, L.; Xiong, D.; Yu, H.J.; Sun, Z.J. Glutamine inhibition combined with CD47 blockade enhances radiotherapy-induced ferroptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2024, 588, 216727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.X.; Sun, X.; Yan, X.L.; Guo, Z.N.; Yang, Y. Ferroptosis in Neurological Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Roh, J.L. SLC7A11 as a Gateway of Metabolic Perturbation and Ferroptosis Vulnerability in Cancer. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Kryczek, I.; Li, X.; Bian, Y.; Sell, A.; Wei, S.; Grove, S.; Johnson, J.K.; et al. CD8+ T cells and fatty acids orchestrate tumor ferroptosis and immunity via ACSL4. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Feng, Y.; Zandkarimi, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kim, J.; Cai, Y.; Gu, W.; Stockwell, B.R.; Jiang, X. Ferroptosis surveillance independent of GPX4 and differentially regulated by sex hormones. Cell 2023, 186, 2748–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstorum, A.; Tesfay, L.; Paul, B.T.; Torti, F.M.; Laubenbacher, R.C.; Torti, S.V. Systems biology of ferroptosis: A modeling approach. J. Theor. Biol. 2020, 493, 110222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Kang, R.; Tang, D.; Liu, J. Ferroptosis: Principles and significance in health and disease. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Xie, R.; Cao, Y.; Tang, J.; Men, Y.; Peng, H.; Yang, W. Simvastatin induced ferroptosis for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, D.; Li, S.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, Z. Ferroptosis: The emerging player in remodeling triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1284057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Gao, T.; Connell, D.O.; Yao, F.; Mu, C.; Cai, B.; Shang, Y.; et al. Nedd4 ubiquitylates VDAC2/3 to suppress erastin-induced ferroptosis in melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Peng, Z. ROS-induced lipid peroxidation modulates cell death outcome: Mechanisms behind apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, T.; Yang, H.; Lei, L.; Guo, M.; Ding, H.F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; et al. ATF3 promotes erastin-induced ferroptosis by suppressing system Xc. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lu, D.; Yin, M.; Shan, M.; Gao, Y. Erastin induces ferroptosis via ferroportin-mediated iron accumulation in endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 36, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Xu, X.; Kong, X.; Ren, J.; Yao, X.; Wen, Q.; et al. Microglia and macrophage exhibit attenuated inflammatory response and ferroptosis resistance after RSL3 stimulation via increasing Nrf2 expression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, W.; Wei, H.; Chang, C.; Yang, L.; Meng, J.; Long, T.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, C. Srs11-92, a ferrostatin-1 analog, improves oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via Nrf2 signal following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, J.; Wray, A.A. Deferoxamine; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Lin, J.; Sun, K.; Guo, J.; Yao, X.; Wang, G.; Hou, L.; Xu, J.; Guo, J.; Guo, F. Deferoxamine Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Chondrocyte Ferroptosis and Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 791376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Kaempferol Ameliorates Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Neuronal Ferroptosis by Activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Axis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xiao, Q.X.; Wu, M.; Luo, M.Y. Deferoxamine in intracerebral hemorrhage: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2023, 227, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.C.; Chai, T.T. Bioactive Peptides and Protein Hydrolysates as Lipoxygenase Inhibitors. Biology 2023, 12, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.M.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhu, K.F.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Z.C.; Chang, J. The ALOX5 inhibitor Zileuton regulates tumor-associated macrophage M2 polarization by JAK/STAT and inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion and metastasis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S. Zileuton inhibits arachidonate-5-lipoxygenase to exert antitumor effects in preclinical cervical cancer models. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Song, Y. Baicalein inhibits RLS3-induced ferroptosis in melanocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 561, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.Q.; Zhao, L.L.; Hong, C.; Zou, Q.M.; Su, J.X.; Li, S.J.; Zhou, X.F.; Li, Z.S.; Deng, B.; Cao, J.; et al. Baicalein triggers ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells via blocking the JAK2/STAT3/GPX4 axis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Miura, K.; Aizawa, K.; Bat-Erdene, O.; Sashikawa-Kimura, M.; Noguchi, E.; Watanabe, M.; Yamada, N.; Osaka, H.; Morimoto, N.; et al. Apomorphine Suppresses the Progression of Steatohepatitis by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, J. Ferroptosis in Nervous System Diseases. In Ferroptosis in Health and Disease; Tang, D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Dong, X. Recent Progress in Ferroptosis Inducers for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, R.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Ren, K.; Jia, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Insight into the Double-Edged Role of Ferroptosis in Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, L. New knowledge of the mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in liver cancer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Chen, L. Ferritinophagy/ferroptosis: Iron-related newcomers in human diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9179–9190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Glandorff, C.; Sun, M. Ferroptosis: A new hunter of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; He, D.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Li, B. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: Opportunities and challenges in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Mau, C.Z.; Chen, Y.C.; Su, Y.H.; Chen, H.A.; Huang, S.Y.; Chang, J.S.; Chiu, C.F. A case-control study in Taiwanese cohort and meta-analysis of serum ferritin in pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yan, J.; Huang, L.; Araujo, C.; Peng, J.; Gao, L.; Liu, S.; Tang, J.; Zuo, G.; Zhang, J.H. INT-777 attenuates NLRP3-ASC inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation via TGR5/cAMP/PKA signaling pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 91, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Tian, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Bihl, J.; Shi, H. Inhibition oFerroptosis Alleviates Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage In Vitro and In Vivo via Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 41, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tuo, Q.Z.; Lei, P. Iron, ferroptosis, and ischemic stroke. J. Neurochem. 2023, 165, 487–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; He, C.; Yan, F.; Li, J.R.; Xu, H.Z.; Zhuang, J.F.; Zhou, H.; Peng, Y.C.; Fu, X.J.; et al. Selective Ferroptosis Inhibitor Liproxstatin-1 Attenuates Neurological Deficits and Neuroinflammation After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, L.; Lu, J.; Fang, Y.; Wu, H.; Xu, W.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Cepharanthine Attenuates Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice via Inhibiting 15-Lipoxygenase-1-Mediated Microglia and Endothelial Cell Ferroptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 4295208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Tian, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G. Ferroptosis in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage: Review of literature. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2024, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; et al. Ferritinophagy is Involved in Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Neuronal Ferroptosis. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jiang, M.; Li, K.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xu, Y.; Krishfield, S.; Lipsky, P.E.; Tsokos, G.C.; et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4-regulated neutrophil ferroptosis induces systemic autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; Li, J.Y. Ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease: Glia-neuron crosstalk. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.D.; Pang, P.; Zhou, X.T.; Hu, F.; Xiong, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Xie, D.; Hu, Y.Z.; et al. Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1548–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N.; Zhang, J. Iron Metabolism, Ferroptosis, and the Links with Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Mohammad, T.; Malik, A.; Hassan, M.I.; Domashevskiy, A.V. Iron response elements (IREs)-mRNA of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein binding to iron regulatory protein (IRP1): A combined molecular docking and spectroscopic approach. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupershmidt, L.; Youdim, M.B.H. The Neuroprotective Activities of the Novel Multi-Target Iron-Chelators in Models of Alzheimer’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Aging. Cells 2023, 12, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseenko, A.V.; Waseem, T.V.; Fedorovich, S.V. Ferritin, a protein containing iron nanoparticles, induces reactive oxygen species formation and inhibits glutamate uptake in rat brain synaptosomes. Brain Res. 2008, 1241, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, P.; Porcelli, G.; Bavisotto, C.C.; Nuzzo, D.; Galizzi, G.; Biagio, P.L.S.; Bulone, D.; Di Carlo, M. Synaptosomes: New vesicles for neuronal mitochondrial transplantation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarillo, E.; Rizor, A.; Lee, J.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics. Neuropharmacology 2019, 161, 107559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Ma, P.; Yang, P.; Zhai, S.; He, M.; Zhang, X.; Tu, Q.; Jiao, L.; Ye, L.; Feng, Z.; et al. Alpha lipoic acid ameliorates motor deficits by inhibiting ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 810, 137346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Dong, H.; Yu, H.; Huang, M.; Gao, X. Ferroptosis Enhanced Diabetic Renal Tubular Injury via HIF-1α/HO-1 Pathway in db/db Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 626390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Bi, R.; Su, Y.; Quan, F.; Lin, Y.; Yue, C.; Cui, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, S.; et al. ACSL4 deficiency confers protection against ferroptosis-mediated acute kidney injury. Redox Biol. 2022, 51, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Guan, B.; Wang, X.; An, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Jia, J.; Song, L.; et al. Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule inhibits ferroptosis and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the GPX4/xCT signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, J.J.; Cao, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Yang, S.; Li, K. Iron overload contributes to general anaesthesia-induced neurotoxicity and cognitive deficits. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.; Chen, F.; He, Y.; Tan, Z.; Han, X.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Leng, Y. Dexmedetomidine against intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 959, 176090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, J.; Duan, H.Q.; Zhao, C.X.; Sun, C.; Li, B.; Fan, B.Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.X.; et al. Deferoxamine promotes recovery of traumatic spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 532–541. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.R.; Shi, C.; Song, Q.Y.; Kang, M.J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, H.; Pei, D.S. Sorafenib induces ferroptosis by promoting TRIM54-mediated FSP1 ubiquitination and degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inductors of Ferroptosis | Inhibitors of Ferroptosis |
|---|---|
System Xc inhibitors
| Lipophilic antioxidants
|
HMG-CoA reductase
| Iron chelators
|
TXNRD1 inhibitors
| Lipoxygenase inhibitors
|
GPX4 inhibitors
| Others
|
GPX4 degradation compounds
| |
GSH depletion compounds
| |
Lipid peroxidation inducers
| |
|
| Research | Disease | Ferroptotic Cells | Cell Features | Effective Inhibitors of Ferroptosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al., 2021 [98] | Systemic lupus erythematosus Lupus prone mice | Neutrophils | Mitochondrial vacuole creation, enlargement mitochondrial membrane density, atrophy of mitochondrial cristae | Liproxstatin-1 Deferoxamine |
| Ye et al., 2022 [47] | Chronic kidney disease | Vascular smooth muscle cells | High calcium and phosphate levels, high lipid ROS in cytoplasm | Ferrostatin-1 |
| Feng et al., 2021 [108] | Diabetes | Renal tubule cells | High HIF-1α, HO-1, and iron levels, high lipid ROS, reduced SOD, GPX4, CAT | Ferrostatin-1 |
| Zhang et al., 2023 [110] | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases | Macrophage | Atherosclerotic cells: Swollen mitochondria, increased membrane density, atrophy of mitochondrial cristae | QXJYG–Qing-Xin-Jie-Yu Granule |
| Li et al., 2021 [70] | Endometriosis | Ectopic endometrium stromal cells | Shorter, condensed, shrunken mitochondria, increased membrane density | Ferrostatin-1, Liproxstatin-1, Deferoxamine |
| Yao et al., 2019 [113] | Spinal cord injury | Spinal cord cells | Shrunken mitochondria, rupture outer membrane | Deferoxamine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kielan, B.; Pałasz, A.; Krysta, K.; Krzystanek, M. Ferroptosis as a Form of Cell Death—Medical Importance and Pharmacological Implications. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081183
Kielan B, Pałasz A, Krysta K, Krzystanek M. Ferroptosis as a Form of Cell Death—Medical Importance and Pharmacological Implications. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081183
Chicago/Turabian StyleKielan, Blanka, Artur Pałasz, Krzysztof Krysta, and Marek Krzystanek. 2025. "Ferroptosis as a Form of Cell Death—Medical Importance and Pharmacological Implications" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081183
APA StyleKielan, B., Pałasz, A., Krysta, K., & Krzystanek, M. (2025). Ferroptosis as a Form of Cell Death—Medical Importance and Pharmacological Implications. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081183