Network Pharmacology and Machine Learning Identify Flavonoids as Potential Senotherapeutics
Abstract
1. Introduction
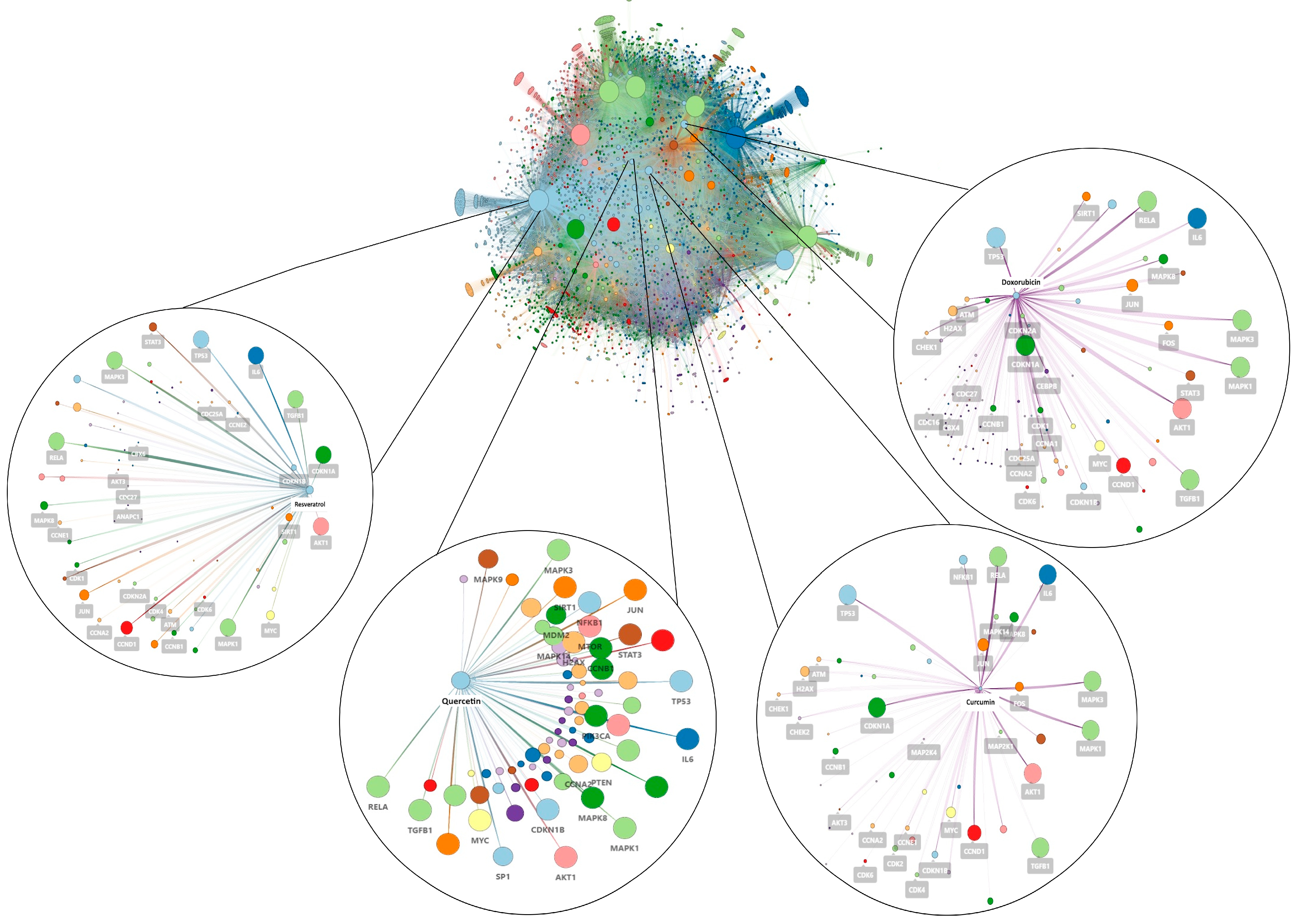
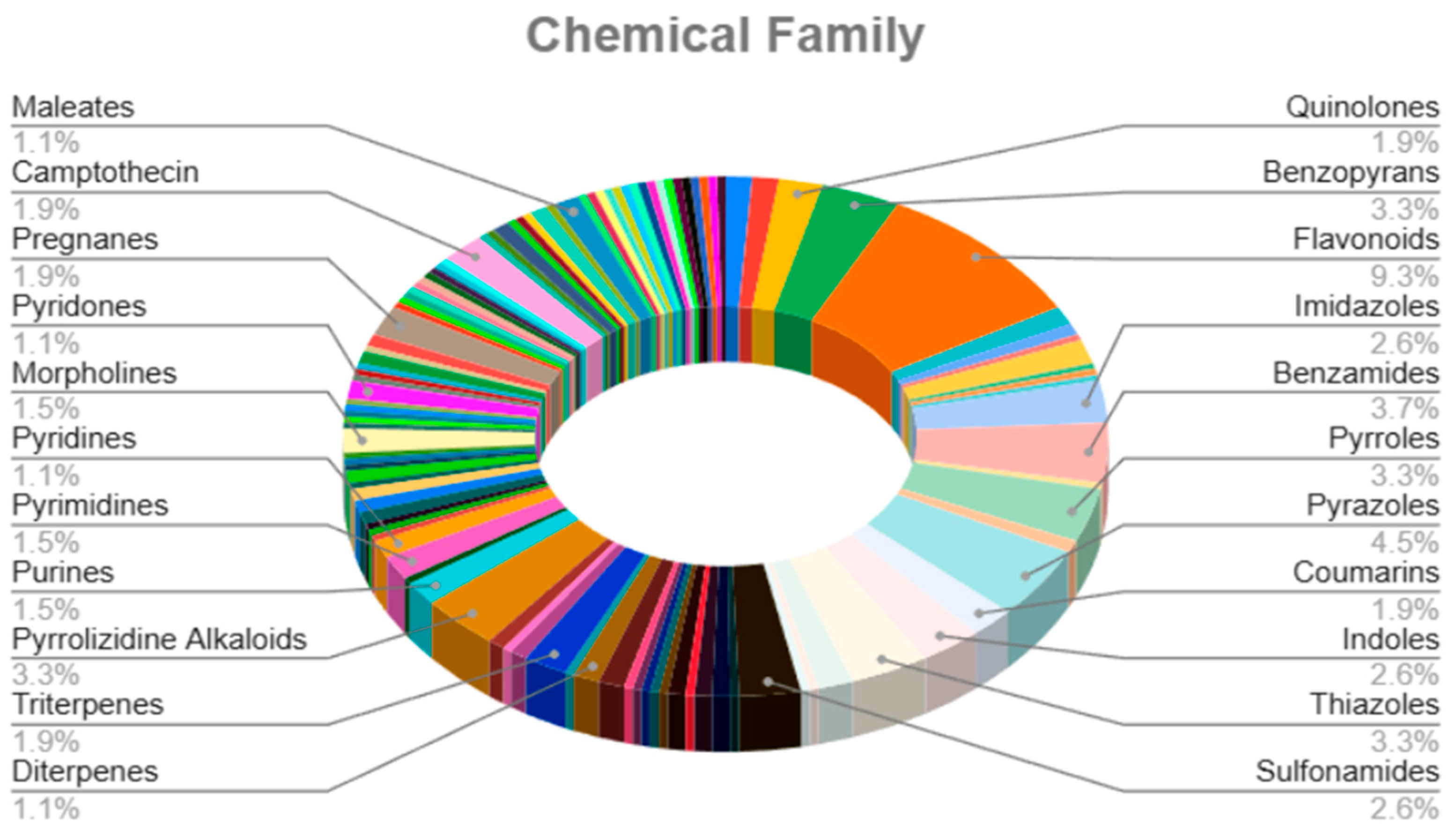
2. Results
3. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Network Pharmacology
4.2. Molecular Descriptors
4.3. Supervised ML Analysis (SVM, KNN, and RFC)
4.4. Druglikeness by Lipinski Rules
4.5. Development of a Web Tool and Chemical Classification
4.6. Docking Analysis
4.6.1. Protein Structures Acquisition
4.6.2. Compounds Structure Obtention for Docking Analysis
4.6.3. Molecular Docking
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SASP | Senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ML | Machine learning |
| RFC | Random Forest Classifier |
| SVM | Supand Vector Machine |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| CTD | Comparative Toxicogenomics Database |
| PPI | Protein-Protein Interactions |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
References
- Huang, W.; Hickson, L.J.; Eirin, A.; Kirkland, J.L.; Lerman, L.O. Cellular Senescence: The Good, the Bad and the Unknown. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, B.G.; Durik, M.; Baker, D.J.; van Deursen, J.M. Cellular Senescence in Aging and Age-Related Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapy. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, A.; O’Loghlen, A. Cellular Senescence and Ageing: Mechanisms and Interventions. Front. Aging 2022, 3, 866718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarneshan, S.N.; Fakhri, S.; Bachtel, G.; Bishayee, A. Exploiting Pivotal Mechanisms behind the Senescence-like Cell Cycle Arrest in Cancer. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2023, 135, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Borghesan, M.; Hoogaars, W.M.H.; Varela-Eirin, M.; Talma, N.; Demaria, M. A Senescence-Centric View of Aging: Implications for Longevity and Disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.D.; Wu, D.; Meydani, S.N. Age-Associated Alterations in Immune Function and Inflammation. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 118, 110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeldine, J.; Lord, J.M. Immunesenescence and Compromised Removal of Senescent Cells: Implications for Health in Old Age. In Healthy Ageing and Longevity; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 23–52. ISBN 9783030875312. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, D.; Gil, J. Senescence and Aging: Causes, Consequences, and Therapeutic Avenues. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Vázquez, O.S.; Magos-Guerrero, G.A.; Escobar-Ramírez, J.L.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C. Natural Products as a Major Source of Candidates for Potential Senolytic Compounds Obtained by Screening. Med. Chem. 2023, 19, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D. Senotherapeutics for Healthy Ageing. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Salekeen, R.; Soto-Palma, C.; He, Y.; Elsallabi, O.; Hughes, B.; Nunes, A.; Xu, W.; Zhang, B.; Mohamed, A.; et al. Development of Novel Flavonoid Senolytics through Phenotypic Drug Screening and Drug Design. bioRxiv 2024, 10, 620529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, F.; Magni, F.; Leonardi, A.; Crescenzi, E. Therapy-Induced Senescence: Novel Approaches for Markers Identification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, R.; Su, D.; Zhou, N.; Qi, Y. Metformin Protects Lens Epithelial Cells against Senescence in a Naturally Aged Mouse Model. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walaszczyk, A.; Dookun, E.; Redgrave, R.; Tual-Chalot, S.; Victorelli, S.; Spyridopoulos, I.; Owens, A.; Arthur, H.M.; Passos, J.F.; Richardson, G.D. Pharmacological Clearance of Senescent Cells Improves Survival and Recovery in Aged Mice Following Acute Myocardial Infarction. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Tuday, E.; Allen, S.; Kim, J.; Trott, D.W.; Holland, W.L.; Donato, A.J.; Lesniewski, L.A. Senolytic Drugs, Dasatinib and Quercetin, Attenuate Adipose Tissue Inflammation, and Ameliorate Metabolic Function in Old Age. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickson, L.J.; Langhi Prata, L.G.P.; Bobart, S.A.; Evans, T.K.; Giorgadze, N.; Hashmi, S.K.; Herrmann, S.M.; Jensen, M.D.; Jia, Q.; Jordan, K.L.; et al. Senolytics Decrease Senescent Cells in Humans: Preliminary Report from a Clinical Trial of Dasatinib plus Quercetin in Individuals with Diabetic Kidney Disease. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzforum Dasatinib + Quercetin. Available online: https://www.alzforum.org/therapeutics/dasatinib-quercetin (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- He, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, D. Senolytic Drug Development. In Healthy Ageing and Longevity; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 3–20. ISBN 9783030449025. [Google Scholar]
- Muthuramalingam, P.; Jeyasri, R.; Varadharajan, V.; Priya, A.; Dhanapal, A.R.; Shin, H.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Ramesh, M.; Krishnan, M.; Omosimua, R.O.; et al. Network Pharmacology: An Efficient but Underutilized Approach in Oral, Head and Neck Cancer Therapy-a Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1410942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smer-Barreto, V.; Quintanilla, A.; Elliott, R.J.R.; Dawson, J.C.; Sun, J.; Campa, V.M.; Lorente-Macías, Á.; Unciti-Broceta, A.; Carragher, N.O.; Acosta, J.C.; et al. Discovery of Senolytics Using Machine Learning. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, M.; Ruban, S.; Nandhini, T.J.; Loganayagi, S.; Sayed, R.M.; Hassan, E.; Al-Saidi, I.A.-D.H. A Framework Design of ML Classifier Algorithm for Retrieve the Information about the Drugs and Its Quality. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 14 May 2024; pp. 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, S.; Tripathi, G.; Singh, D.B.; Jain, P.; Kumar, A. Machine Learning Approaches and Their Applications in Drug Discovery and Design. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, F.J.N.; Carneiro, A.S. AI-Driven Drug Discovery: A Comprehensive Review. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 23889–23903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Patel, V.; Jain, M.; Parmar, G. Network Pharmacology and Systems Biology in Drug Discovery. In Interdisciplinary Biotechnological Advances; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 231–252. ISBN 9789819913152. [Google Scholar]
- Arrell, D.K.; Terzic, A. Network Systems Biology for Drug Discovery. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 88, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knegtel, R.M.A.; Grootenhuis, P.D.J. Binding Affinities and Non-Bonded Interaction Energies. In 3D QSAR in Drug Design; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 99–114. ISBN 9780792347903. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Xu, J.; Hussain, S.A.; Alrubie, T.M.; Maddu, N.; Wei, H. Combination of Quercetin and Curcumin modulates NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway in murine model of esophageal erosive reflux disease erosive reflux disease. Folia Morphol. (Warsz), Online ahead of print. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadinejad, F.; Bos, T.; Hu, B.; Britt, E.; Koblinski, J.; Souers, A.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Faber, A.C.; Gewirtz, D.A.; Harada, H. Senolytic-Mediated Elimination of Head and Neck Tumor Cells Induced Into Senescence by Cisplatin. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022, 101, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshkina, E.; Koval, L.; Platonova, E.; Golubev, D.; Ulyasheva, N.; Babak, T.; Shaposhnikov, M.; Moskalev, A. Polyphenols as Potential Geroprotectors. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2024, 40, 564–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, M.V. Insights into the Origin and Therapeutic Implications of Benzopyran and Its Derivatives. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202300220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Guo, Y.; Pu, F.; Yang, C.; Xiao, X.; Du, H.; He, J.; Lu, S. Opportunities and Challenges in Enhancing the Bioavailability and Bioactivity of Dietary Flavonoids: A Novel Delivery System Perspective. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y. Improvement Strategies for the Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Flavonoids: An Overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallance, T.M.; Ravishankar, D.; Albadawi, D.A.I.; Osborn, H.M.I.; Vaiyapuri, S. Synthetic Flavonoids as Novel Modulators of Platelet Function and Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisson, J.; McAlpine, J.B.; Friesen, J.B.; Chen, S.-N.; Graham, J.; Pauli, G.F. Can Invalid Bioactives Undermine Natural Product-Based Drug Discovery? J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1671–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baell, J.; Walters, M.A. Chemistry: Chemical Con Artists Foil Drug Discovery. Nature 2014, 513, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uivarosi, V.; Munteanu, A.-C.; Nițulescu, G.M. An Overview of Synthetic and Semisynthetic Flavonoid Derivatives and Analogues: Perspectives in Drug Discovery. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Studies in natural products chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 29–84. ISBN 9780444641816. [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly, C.J.; Rosenstein, M.C.; Davis, A.P.; Colby, G.T.; Forrest, J.N., Jr.; Boyer, J.L. The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: A Cross-Species Resource for Building Chemical-Gene Interaction Networks. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An Open-Source Program for Chemistry Aware Data Visualization and Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.A.; Kalakech, A.; Steiti, A. Random Forest Algorithm Overview. Babylon. J. Mach. Learn. 2024, 2024, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonlau, M. Support Vector Machines. In Statistics and Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 237–266. ISBN 9783031333897. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenova, T.; Valova, I. Classification with K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm: Comparative Analysis between the Manual and Automatic Methods for K-Selection. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 14, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pitcher, L.E.; Prahalad, V.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D. Targeting Cellular Senescence with Senotherapeutics: Senolytics and Senomorphics. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 1362–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, G.; Zuva, T.; Sibanda, E.M. A Review of Evaluation Metrics in Machine Learning Algorithms. In Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 15–25. ISBN 9783031353130. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, O.; Dhanikula, A.B.; Panchagnula, R. Drug Delivery: An Odyssey of 100 Years. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
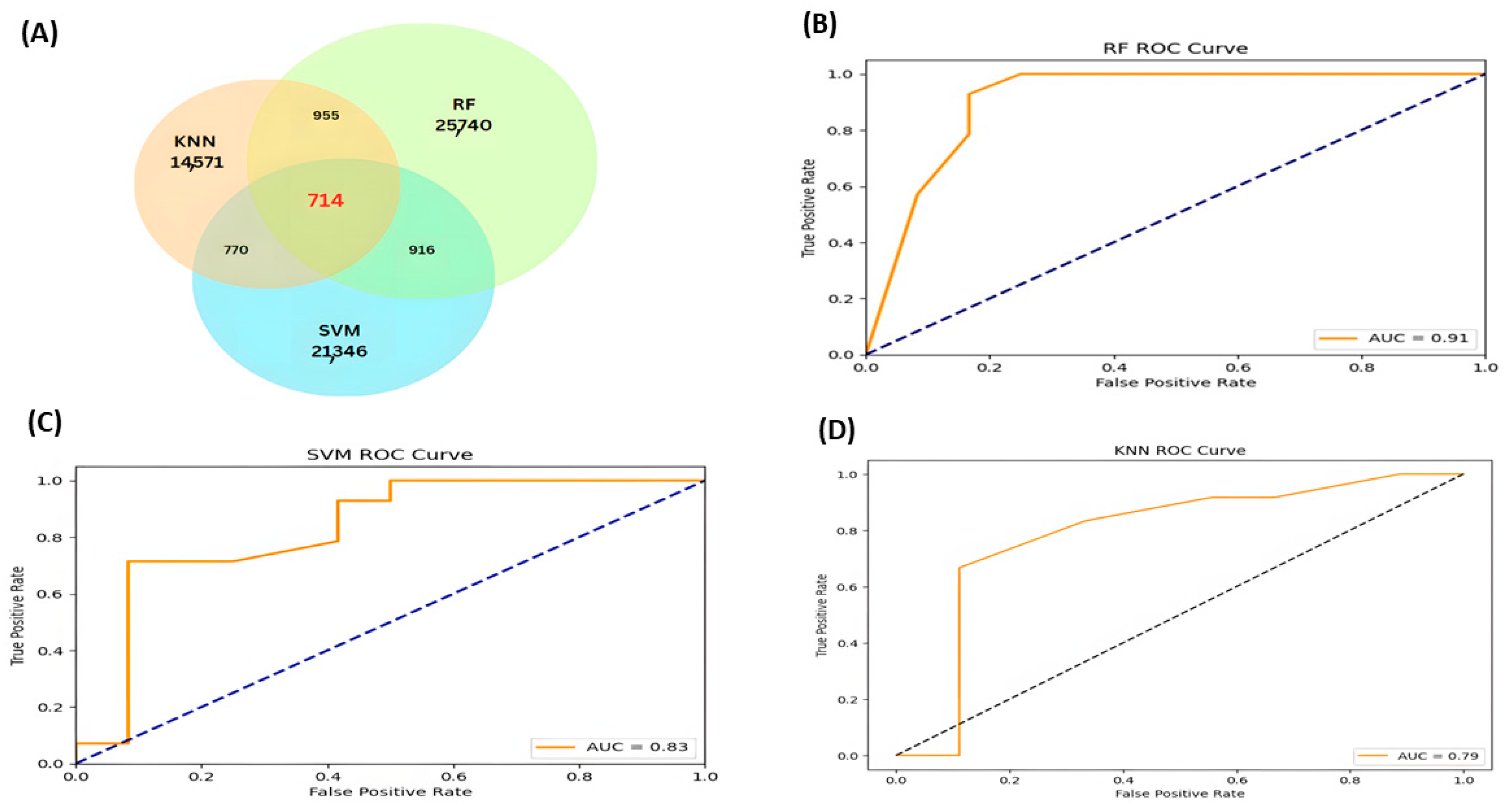
| RF | SVM | KNN | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.88 * | 0.76 | 0.76 |
| Specificity | 0.92 | 0.71 | 0.88 |
| Precision | 0.90 | 0.71 | 0.88 |
| Recall | 0.92 | 0.83 | 0.67 |
| F1-Score | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.76 |
| Kappa | 0.76 * | 0.54 | 0.53 |
| Protein Target | Flavonoid | ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| p53 | 3′,4′,7-trihydroxyisoflavone | −6.3 |
| Catechin | −6.8 | |
| Auriculasin | −7.4 | |
| Glycitein | −6.1 | |
| Silybin | −7.3 | |
| AKT1 | Tephrosin | −11.2 |
| 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl)-6-methoxychroman-4-one | −9.2 | |
| Trx | Pomiferin | −6.9 |
| Calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside | −6.1 | |
| Cyclin D1 | Eriodictyol | −7.2 |
| p21 | 4′-O-methylalpinumisoflavone | −6.4 |
| c-Fos | Daidzin | −6.0 |
| CDK1 | 5,7,3′-trihydroxy-3,4′-dimethoxyflavone | −8.9 |
| NORE1 | Glycitin | −7.0 |
| p65 | Jaceosidin | −4.4 |
| CDK1 | Isosilybin A | −9.7 |
| c-Jun | Eupafolin | −5.9 |
| p38α | Skullcapflavone II | −8.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santiago-de-la-Cruz, J.A.; Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, M.E.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C. Network Pharmacology and Machine Learning Identify Flavonoids as Potential Senotherapeutics. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081176
Santiago-de-la-Cruz JA, Rivero-Segura NA, Alvarez-Sánchez ME, Gomez-Verjan JC. Network Pharmacology and Machine Learning Identify Flavonoids as Potential Senotherapeutics. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081176
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantiago-de-la-Cruz, Jose Alberto, Nadia Alejandra Rivero-Segura, María Elizbeth Alvarez-Sánchez, and Juan Carlos Gomez-Verjan. 2025. "Network Pharmacology and Machine Learning Identify Flavonoids as Potential Senotherapeutics" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081176
APA StyleSantiago-de-la-Cruz, J. A., Rivero-Segura, N. A., Alvarez-Sánchez, M. E., & Gomez-Verjan, J. C. (2025). Network Pharmacology and Machine Learning Identify Flavonoids as Potential Senotherapeutics. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081176











