Thiopental Versus Propofol in Combination with Remifentanil for Successful Classic Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion: A Prospective, Randomised, Double-Blind Trial †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Study Design
4.3. Anaesthetic Management
4.4. Ethical Statement
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Power Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adnan, M.; Furqan, A.; Sattar, M.K. Effect of Midazolam Premedication on Doses of Propofol for Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion in Children. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad. 2017, 29, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Reier, C.E. Bleeding, Dysphagia, Dysphonia, Dysarthria, Severe Sore Throat, and Possible Recurrent Laryngeal, Hypoglossal, and Lingual Nerve Injury Associated with Routine Laryngeal Mask Airway Management: Where Is the Vigilance? Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 1241–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, P.; Ghai, B. Comparison of butorphanol and thiopentone vs fentanyl and thiopentone for laryngeal mask airway insertion. J. Clin. Anesth. 2006, 18, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoneham, M.D.; Bree, S.E.; Sneyd, J.R. Facilitation of laryngeal mask insertion: Effects of lignocaine given intravenously before induction with propofol. Anaesthesia 1995, 50, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, P.; Carey, M.; Power, M.; Kirby, F. Patient response to laryngeal mask insertion after induction of anaesthesia with propofol or thiopentone. Can. J. Anaesth. 1993, 40, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driver, I.; Wilson, C.; Wiltshire, S.; Mills, P.; Howard-Griffin, R. Co-induction and laryngeal mask insertion# A comparison of thiopentone versus propofol. Anaesthesia 1997, 52, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeating, K.; Bali, I.M.; Dundee, J.W. The effects of thiopentone and propofol on upper airway integrity. Anaesthesia 1988, 43, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.W.; Ellis, F.R. Comparison of propofol and increased doses of thiopentone for laryngeal mask insertion. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1995, 39, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.W.; Jang, D.J.; Shin, O.Y.; Nam, S.B. Effect-site concentration of remifentanil for laryngeal mask airway insertion during target-controlled infusion of propofol. Anaesthesia 2009, 64, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.F.; Chen, F.G.; Cheong, K.F.; Esuvaranathan, V. Laryngeal mask insertion using thiopental and low dose atracurium: A comparison with propofol. Can. J. Anesth./J. Can. Anesth. 1999, 46, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seavell, C.R.; Cook, T.M.; Cox, C.M. Topical lignocaine and thiopentone for the insertion of a laryngeal mask airway: A comparison with propofol. Anaesthesia 1996, 51, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, A.B.; Brohan, J.; Goudra, B. The Role of GABA Receptors in Anesthesia and Sedation: An Updated Review. CNS Drugs 2025, 39, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapat, P.; Joshi, R.N.; Young, E.; Jago, R.H. Comparison of propofol versus thiopentone with midazolam or lidocaine to facilitate laryngeal mask insertion. Can. J. Anaesth. 1996, 43, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloi, D.K.; Bharali, P.; Das, I.; Basumatary, J.; Mahanta, P. To Compare the Intravenous Bolus Dose of Propofol with an Equipotent Dose of Intravenous Thiopentone for the Facilitation of Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion. Cureus 2022, 14, e31917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belete, E.; W/Yahones, M.; Aweke, Z.; Dendir, G.; Mola, S.; Neme, D.; Melaku, G.; Ahmed, S.; Regasa, T.; Tesfaye, B. Comparison of thiopentone with lidocaine spray vs propofol for laryngeal mask airway insertion at tikur anbessa specialized hospital. A prospective cohort study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 66, 102436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetabi, H.; Mahjobipoor, H.; Bahmani, M. Effect of Intranasal Remifentanil versus Lidocaine on Facilitation of Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion and Cardiovascular Response: A Double-blind Clinical Trial Study. Bull. Emerg. Trauma 2024, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apparao, M.; Saraiah, R.; Raju, K.; Arpitha Reddy, A. Comparatıve study between propofol and thiopentone sodium in facilitation of laryngeal mask airway insertion. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2023, 16, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.U. General anesthesia for cesarean section: Are we doing it well? Anesth. Pain Med. 2022, 17, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibiski, J.; Patel, P.; Abdijadid, S. Barbiturates. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539731/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Odor, P.M.; Bampoe, S.; Moonesinghe, S.R.; Andrade, J.; Pandit, J.J.; Lucas, D.N. General anaesthetic and airway management practice for obstetric surgery in England: A prospective, multicentre observational study. Anaesthesia 2021, 76, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, L.; Chassard, D. Choice of hypnotic drug for obstetric and non-obstetric general anaesthesia. Comment on Br J Anaesth 2020; 125: e81-7. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, e452–e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.M.; Seavell, C.R.; Cox, C.M. Lignocaine to aid the insertion of the laryngeal mask airway with thiopentone: A comparison between topical and intravenous administration. Anaesthesia 1996, 51, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, P.S.A.; Gan, T.J.; Howell, S. A Review of the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Remifentanil. Anesth. Analg. 1999, 89, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, S.; Siddik-Sayyid, S.; Alameddine, M.; Wakim, C.; Dahabra, C.; Moussa, A.; Khatib, M.; Baraka, A. Propofol is superior to thiopental for intubation without muscle relaxants. Can. J. Anesth./J. Can. Anesth. 2005, 52, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, L.; Da-Col, X.; Rimmelé, T.; Allaouchiche, B.; Chassard, D.; Boselli, E. Optimal remifentanil dose for laryngeal mask airway insertion when co-administered with a single standard dose of propofol. Can. J. Anesth./J. Can. Anesth. 2010, 57, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, W.J.; Kim, K.H.; Suh, J.K.; Cho, S.Y. The Use of Remifentanil to Facilitate the Insertion of the Cobra Perilaryngeal Airway. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 108, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvet, L.; Stoian, A.; Rimmelé, T.; Allaouchiche, B.; Chassard, D.; Boselli, E. Optimal remifentanil dosage for providing excellent intubating conditions when co-administered with a single standard dose of propofol. Anaesthesia 2009, 64, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.P.; Hall, A.P.; Russell, J.; Rowbotham, D.J. Effect of remifentanil on the haemodynamic response to orotracheal intubation. Br. J. Anaesth. 1998, 80, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemola, U.-M.; Mennander, S.; Saarnivaara, L. Tracheal intubation without the use of muscle relaxants: Remifentanil or alfentanil in combination with propofol. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2000, 44, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmus, M.; Ender, G.; Kadir, B.A.; Nurcin, G.; Erdogan, O.; Ersoy, M.O. Remifentanil with Thiopental for Tracheal Intubation Without Muscle Relaxants. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 96, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Safavi, M.; Honarmand, A. Tracheal intubation without muscle relaxants: A randomized study of remifentanil or alfentanil in combination with thiopental. Ann. Saudi Med. 2008, 28, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jarineshin, H.; Kashani, S.; Vatankhah, M.; Abdulahzade Baghaee, A.; Sattari, S.; Fekrat, F. Better Hemodynamic Profile of Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion Compared to Laryngoscopy and Tracheal Intubation. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2015, 17, e28615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, L.; Stoian, A.; Rousson, D.; Allaouchiche, B.; Chassard, D.; Boselli, E. What is the optimal remifentanil dosage for providing excellent intubating conditions when coadministered with thiopental? A prospective randomized dose–response study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 27, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, H.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwak, H.J.; Oh, S.E.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.Y. Effect of sex differences in remifentanil requirements for the insertion of a laryngeal mask airway during propofol anesthesia: A prospective randomized trial. Medicine 2016, 95, e5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhan, E.; Ugur, G.; Alper, I.; Gunusen, I.; Ozyar, B. Tracheal intubation without muscle relaxants: Remifentanil or alfentanil in combination with propofol. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2005, 20, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, W.; Biedler, A.; Huppert, A.; Kreuer, S.; Bücheler, O.; Ziegenfuss, T.; Larsen, R. Comparison of the effects of remifentanil or fentanyl on anaesthetic induction characteristics of propofol, thiopental or etomidate. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2002, 19, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.; Booth, J.; Olufolabi, A.J.; El-Moalem, H.E.; Glass, P.S. Comparison of remifentanil with alfentanil or suxamethonium following propofol anaesthesia for tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia 1999, 54, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorini, F.; Romano, R.; Ciccaglioni, A.; Pascarella, M.A.; Rocco, A.; Mariani, V.; Pietropaoli, P. Effects of remifentanil on human heart electrical system. A transesophageal pacing electrophysiological study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2003, 69, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mccollum, J.S.C.; Dundee, J.W. Comparison of induction characteristics of four intravenous anaesthetic agents. Anaesthesia 1986, 41, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.B.; Wheatley, L. Tracheal Intubation in Ambulatory Surgery Patients: Using Remifentanil and Propofol Without Muscle Relaxants. Anesth. Analg. 1998, 86, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhan, E.; Ugur, G.; Gunusen, I.; Alper, I.; Ozyar, B. Propofol—Not thiopental or etomidate—With remifentanil provides adequate intubating conditions in the absence of neuromuscular blockade. Can. J. Anesth./J. Can. Anesth. 2003, 50, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.T.; Oh, A.Y.; Park, S.H.; Hwang, J.W.; Park, H.P. Optimal remifentanil dose for lightwand intubation without muscle relaxants in healthy patients with thiopental coadministration: A prospective randomised study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2012, 29, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnappa, S.; Kundra, P. Optimal anaesthetic depth for LMA insertion. Indian J. Anaesth. 2011, 55, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Banerjee, N.; Singh, P.; Saraswat, N.; Agrawal, S. Comparison of Bispectral index-guided propofol and etomidate infusion for Supraglottic airway insertion. Trends Anaesth. Crit. Care 2023, 51, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, Y.; Fatima, N.; Kumar, S.; Nasir, K.K. Laryngeal mask airway placement: A comparison between propofol and thiopentone sodium in the day case surgery. Pak. J. Public Health 1970, 6, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetabi, H.; Jebelli, E.; Shafa, A. Comparing the safety and efficacy of three different doses of atracurium in facilitating the insertion of laryngeal mask airway in patients undergoing phacoemulsification cataract surgery: A randomized clinical trial. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2020, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, Y.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Liu, K. Propofol Causes Less Postoperative Pharyngeal Morbidity Than Thiopental After the Use of a Laryngeal Mask Airway. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, A.; Jacob, R.; Koshy, R. A randomized control study comparing the pharyngolaryngeal morbidity of laryngeal mask airway versus endotracheal tube. Anesth. Essays Res. 2016, 10, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgard, G.; Möllhoff, T.; Prien, T. The effect of laryngeal mask cuff pressure on postoperative sore throat incidence. J. Clin. Anesth. 1996, 8, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chui, P.T.; Cheam, E.W.S. The use of low-dose mivacurium to facilitate insertion of the laryngeal mask airway. Anaesthesia 1998, 53, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khutell, A.; Grover, T.; Singh, A.; Seth, A.; Madan, M.; Yadav, K. A Prospective Comparison of Insertion Characteristics of Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) ProSeal® Using Rotation Techniques vs Standard Techniques in Adults Undergoing Elective Surgery. Cureus 2023, 15, e37976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleña, J.M. Role of laryngeal mask airway in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.L.Y.; Critchley, L.A.H.; Lee, A.; Gin, T. Alfentanil Dosage When Inserting the Classic Laryngeal Mask Airway. Anesthesiology 2006, 105, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueredo, E.; Vivar-Diago, M.; Muñoz-Blanco, F. Laryngo-pharyngeal complaints after use of the laryngeal mask airway. Can. J. Anesth./J. Can. Anesth. 1999, 46, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koay, C.K.; Yoong, C.S.; Kok, P. A Randomized Trial Comparing Two Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion Techniques. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2001, 29, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akan, M.; Çakırgöz, M.; Yılmaz, M. Comparative Effects of Remifentanil and Dexmedetomidine as Thiopental Adjuvants on Classic Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Insertion Conditions: A Randomized Double-Blind Study. In Proceedings of the 11th International Medicine and Health Sciences Research Congress (UTSAK), Online, Turkey, 24–25 December 2022; Presentation ID: 780. p. 548. [Google Scholar]
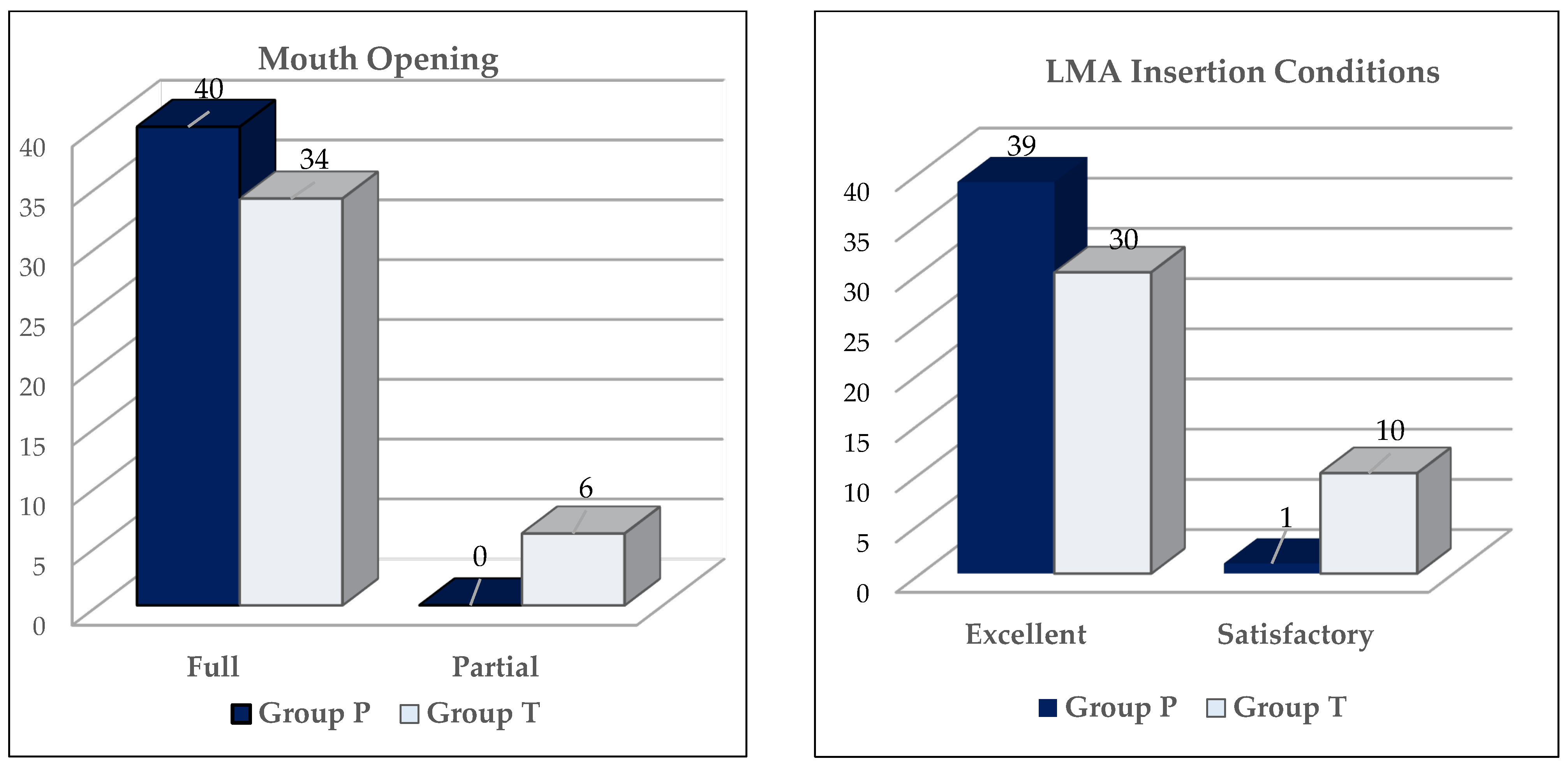
| Group P (n = 40) | Group T (n = 40) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age(year) | Mean ± SD | 44.3 ± 11.1 | 41.6 ± 14 | 0.338 1 | |
| Median (Min.–Max.) | 44.5 (19–63) | 44.5 (18–65) | |||
| Sex | Female | n (%) | 14 (35.0) | 18 (45.0) | 0.361 2 |
| Male | n (%) | 26 (65.0) | 22 (55.0) | ||
| Weight (kg) | Mean ± SD | 73.3 ± 12.7 | 72.4 ± 11.3 | 0.731 1 | |
| Median (Min.–Max.) | 72 (50–102) | 73.5 (48–93) | |||
| Variables | Group P (n = 40) | Group T (n = 40) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration to loss of eyelash reflex (s) | Mean ± SD | 23.8 ± 2.4 | 30.1 ± 2.3 | <0.001 2 |
| Median (Min.–Max.) | 24 (20–29) | 30.5 (25–34) | ||
| Apnoea duration (s) | Mean ± SD | 376.3 ± 42 | 244.1 ± 45.9 | <0.001 1 |
| Median (Min.–Max.) | 377.5 (296–440) | 240 (160–370) | ||
| LMA insertion duration (s) | Mean ± SD | 10.5 ± 1.4 | 12.6 ± 1.7 | <0.001 2 |
| Median (Min.–Max.) | 10 (9–14) | 13 (10–16) | ||
| LMA use duration (min) | Mean ± SD | 50.4 ± 16.9 | 53.4 ± 17.9 | 0.272 2 |
| Median (Min.–Max.) | 44 (35–104) | 49 (32–111) |
| Group P (n = 40) | Group T (n = 40) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Median (Min.–Max.) | Mean ± SD | Median (Min.–Max.) | ||
| Heart Rate (bpm) | |||||
| Baseline | 76.2 ± 11.1 | 76 (56–106) b | 77.2 ± 13.7 | 76 (56–105) b | 0.714 1 |
| 1 min Before | 65.1 ± 9.8 | 64 (50–89) a | 70.7 ± 12.5 | 70 (52–97) a | 0.028 1 |
| 1 min After | 63.7 ± 9.6 | 62 (50–87) a,b | 69.1 ± 11.5 | 68 (51–93) a,b | 0.026 1 |
| 2 min | 62.1 ± 9.5 | 62 (49–85) a,b | 67.6 ± 11 | 67 (51–90) a,b | 0.024 2 |
| 3 min | 59.7 ± 8.6 | 59 (49–81) a,b | 65.2 ± 10.3 | 63.5 (50–88) a,b | 0.014 2 |
| 4 min | 59.2 ± 8.3 | 59 (48–80) a,b | 64.7 ± 10.5 | 63 (50–86) a,b | 0.017 2 |
| 5 min | 58.6 ± 8.5 | 58 (48–82) a,b | 64.1 ± 10.4 | 62.5 (49–87) a,b | 0.014 2 |
| Systolic arterial pressure (mmHg) | |||||
| Baseline | 131.7 ± 17.1 | 132 (95–165) | 130.9 ± 20.7 | 129.5 (94–170) | 0.856 1 |
| 1 min Before | 105.3 ± 12 | 106 (78–125) a | 112.8 ± 16.6 | 113 (82–144) a | 0.023 1 |
| 1 min After | 104.3 ± 12 | 106 (77–123) a,b | 111.6 ± 16.2 | 111 (82–142) a,b | 0.026 1 |
| 2 min | 103.5 ± 12.1 | 105.5 (76–121) a,b | 110.8 ± 16.6 | 110 (80–141) a,b | 0.027 1 |
| 3 min | 99.8 ± 10.5 | 101 (75–117) a,b | 107.2 ± 15.3 | 106.5 (80–138) a,b | 0.014 1 |
| 4 min | 98.2 ± 10.1 | 99 (75–115) a,b | 105.5 ± 14.7 | 104 (82–135) a,b | 0.012 1 |
| 5 min | 97.4 ± 9.9 | 98.5 (74–115) a,b | 104.8 ± 14.8 | 103.5 (81–136) a,b | 0.011 1 |
| Diastolic arterial pressure (mmHg) | |||||
| Baseline | 77 ± 11 | 76 (56–98) b | 78.4 ± 13.6 | 78 (56–106) b | 0.607 1 |
| 1 min Before | 61.2 ± 8.4 | 61.5 (45–78) a | 65.9 ± 11.1 | 65 (49–92) a,b | 0.034 1 |
| 1 min After | 60.7 ± 8 | 60.5 (47–75) a,b | 67.5 ± 11.4 | 67 (48–90) a,b | 0.003 1 |
| 2 min | 59.8 ± 7.7 | 59.5 (46–74) a,b | 65.3 ± 10.9 | 64.5 (48–90) a,b | 0.011 1 |
| 3 min | 58 ± 7.3 | 57 (46–71) a,b | 63.3 ± 10.4 | 62.5 (47–88) a,b | 0.010 1 |
| 4 min | 56.5 ± 6.9 | 55.5 (46–70) a,b | 62.4 ± 10.5 | 62 (47–88) a,b | 0.004 1 |
| 5 min | 55.8 ± 7.3 | 54.5 (45–70) a,b | 61.6 ± 10.6 | 61 (46–87) a,b | 0.017 2 |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | |||||
| Baseline | 95.2 ± 11.6 | 94.5 (70–120) | 95.9 ± 13.2 | 95 (69–125) | 0.808 1 |
| 1 min Before | 75.9 ± 8.7 | 75.5 (57–92) a | 81.5 ± 10.5 | 81 (61–109) a | 0.011 1 |
| 1 min After | 75.3 ± 8.4 | 74 (57–90) a | 82.3 ± 10.6 | 82 (60–107) a,b | 0.002 1 |
| 2 min | 74.3 ± 8.3 | 74 (56–89) a | 80.4 ± 10.5 | 80 (60–107) a,b | 0.005 1 |
| 3 min | 72 ± 7.5 | 72 (56–86) a,b | 77.9 ± 10 | 77.5 (59–105) a,b | 0.004 1 |
| 4 min | 70.4 ± 7 | 71 (56–83) a,b | 76.8 ± 9.9 | 76.5 (59–104) a,b | 0.001 1 |
| 5 min | 69.6 ± 7.2 | 71 (55–82) a,b | 76 ± 10 | 76.5 (58–103) a,b | 0.001 1 |
| Group P (n = 40) | Group T (n = 40) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presence of blood | 1 | 38 | 95% | 37 | 92.5% | 1.000 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 5% | 2 | 5% | ||
| 3 | 0 | 0% | 1 | 2.5% | ||
| Recovery sore throat | 0 | 36 | 90% | 34 | 85 | 0.499 1 |
| 1 | 3 | 7.5% | 4 | 10% | ||
| 2 | 1 | 2.5% | 2 | 5% | ||
| 3 | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | ||
| 4 | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | ||
| Complications | No | 34 | 85% | 40 | 100% | 0.026 2 |
| Bradycardia | 2 | 5% | 0 | 0% | ||
| Hypotension | 3 | 7.5% | 0 | 2.5% | ||
| Hypotension and Bradycardia | 1 | 2.5% | 0 | 0% | ||
| Recovery dysphagia | No | 39 | 97.5% | 36 | 90% | 0.359 2 |
| Yes | 1 | 2.5% | 4 | 10% | ||
| Variables | Ease of LMA Insertion | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent | Satisfactory | Poor | |
| Mouth opening | Full | Partial | None |
| Ease of LMA insertion | Easy | Difficult | Impossible |
| Patient response | |||
| Swallowing | None | Mild | Pronounced |
| Coughing and retching | None | Mild | Pronounced |
| Head and body movements | None | Mild | Pronounced |
| Laryngospasm | None | Partial | Full |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akan, M.; Çakırgöz, M.; Demirel, İ.; Saraç, Ö.; Kar, A.A.; Alaygut, E.; Demirel, O.; Yeniay, H.; Tünay, A. Thiopental Versus Propofol in Combination with Remifentanil for Successful Classic Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion: A Prospective, Randomised, Double-Blind Trial. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081173
Akan M, Çakırgöz M, Demirel İ, Saraç Ö, Kar AA, Alaygut E, Demirel O, Yeniay H, Tünay A. Thiopental Versus Propofol in Combination with Remifentanil for Successful Classic Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion: A Prospective, Randomised, Double-Blind Trial. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081173
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkan, Mert, Mensure Çakırgöz, İsmail Demirel, Ömürhan Saraç, Aysun Afife Kar, Ergin Alaygut, Oğuzhan Demirel, Hicret Yeniay, and Abdurrahman Tünay. 2025. "Thiopental Versus Propofol in Combination with Remifentanil for Successful Classic Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion: A Prospective, Randomised, Double-Blind Trial" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081173
APA StyleAkan, M., Çakırgöz, M., Demirel, İ., Saraç, Ö., Kar, A. A., Alaygut, E., Demirel, O., Yeniay, H., & Tünay, A. (2025). Thiopental Versus Propofol in Combination with Remifentanil for Successful Classic Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion: A Prospective, Randomised, Double-Blind Trial. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081173





