Daptomycin-Loaded Nano-Drug Delivery System Based on Biomimetic Cell Membrane Coating Technology: Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of M1-Type Macrophage Membrane
2.2. Particle Size, Zeta Potential, and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.3. Characterization of Membrane Proteins
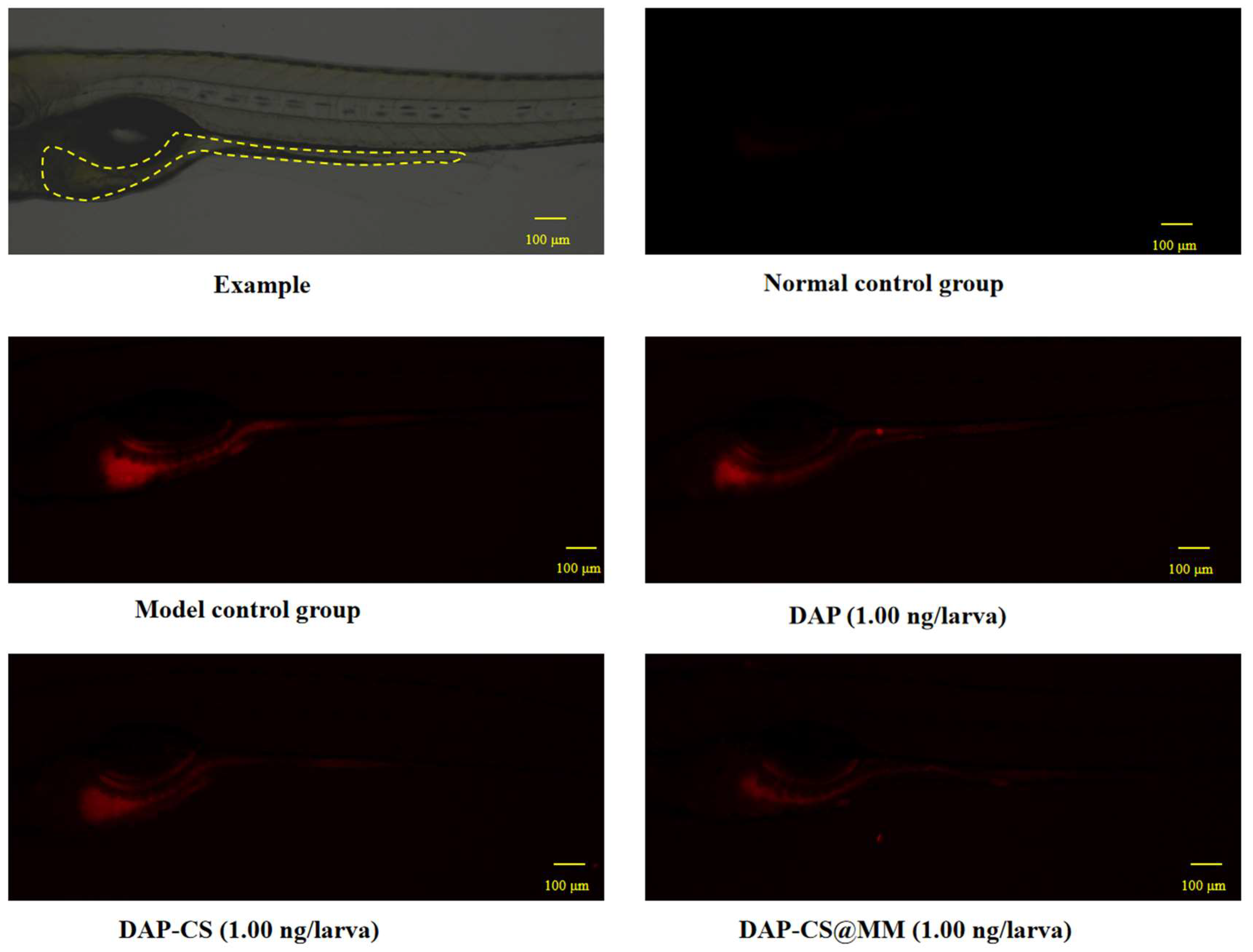
2.4. Immune Escape Assay In Vitro
2.5. Evaluation of Antibacterial Efficacy In Vivo
2.5.1. Determination of Maximum Tolerated Dose
2.5.2. Assessment of Antibacterial Efficacy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.1.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.1.2. Biological Materials
3.2. M1-Type Macrophage Membranes
3.2.1. Polarization and Characterization
3.2.2. Extraction of M1-Type Macrophage Membranes
3.3. Preparation of Biomimetic Nano-Drug Delivery System
3.3.1. Preparation of DAP-CS
3.3.2. Phospholipid Materials
3.3.3. Preparation of DAP-CS@MM
3.4. Characterization of DAP-CS@MM
3.4.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
3.4.2. Encapsulation Efficiency
3.4.3. Membrane Protein Characterization
3.5. In Vitro Immune Escape Assay
3.6. Evaluation of Antibacterial Efficacy
3.6.1. Maximum Tolerated Dose
3.6.2. Antibacterial Efficacy
3.7. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silverman Jared, A.; Perlmutter Nancy, G.; Shapiro Howard, M. Correlation of daptomycin bactericidal activity and membrane depolarization in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukada, H.; Tsuji, Y.; Yamashina, T.; Tsuruta, M.; Hiraki, Y.; Tsuruyama, M.; Ogami, C.; Kawasuji, H.; Sakamaki, I.; Yamamoto, Y. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of daptomycin in a clinical setting. J. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 26, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.Y.; Chen, H.B.; Li, S.G.; Gao, H.; Sun, S.J.; Li, H.N.; Wang, R.B.; Jin, L.Y.; Liu, Y.D.; Wang, H. Daptomycin resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is conferred by IS256 insertion in the promoter of mprF along with mutations in mprF and walK. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangili, A.; Bica, I.; Snydman, D.R.; Hamera, D.H. Daptomycin-resistant, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1058–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, F.M.; Yeh, W.W.; Wennersten, C.B.; Venkataraman, L.; Albano, E.; Alyea, E.P.; Gold, H.S.; Baden, L.R.; Pillai, S.K. Emergence of a clinical daptomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolate during treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and osteomyelitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiya, H.; Haruki, Y.; Uchida, T.; Wada, T.; Shiota, S.; Ishida, T.; Ogawa, H.; Murase, T.; Otsuka, F. Emergence of Daptomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus during Treatment. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Coombs, G.W.; Daley, D.A.; Shoby, P.; Mowlaboccus, S. Whole-genome sequencing identifies MprF mutations in a genetically diverse population of daptomycin non-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in Australia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, G.; Du, B.; Liu, B.; Gao, T.; Zhao, P.; Yang, Y.; Rong, R. Polysaccharides from traditional Chinese medicine and their nano-formulated delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 357, 123416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoveidaei, A.H.; Sadat-Shojai, M.; Mosalamiaghili, S.; Salarikia, S.R.; Roghani-shahraki, H.; Ghaderpanah, R.; Ersi, M.H.; Conway, J.D. Nano-hydroxyapatite structures for bone regenerative medicine: Cell-material interaction. Bone 2024, 179, 116956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Bhaskar, R.; Han, S.S. Leveraging the nanotopography of filamentous fungal chitin-glucan nano/microfibrous spheres (FNS) coated with collagen (type I) for scaffolded fibroblast spheroids in regenerative medicine. Tissue Cell 2025, 93, 102734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Meng, T.T.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhou, B.L.; Du, S.H.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F.Q. Difenoconazole-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Yu, Y.F.; Qiu, W.; Tian, K.S.; Guo, Z.W.; Qian, J.; Lu, H.P.; Zhan, C.Y. Protein corona on brain targeted nanocarriers: Challenges and prospects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 202, 115114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Samadian, H.; Hamidi, M.; Seidi, K.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Yazdi, A.A.; Shavandi, A.; Laurent, S.; Be Omide Hagh, M.; et al. Multifunctional nanostructures: Intelligent design to overcome biological barriers. Mater. Today Bio. 2023, 20, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Ahmed, M.M.S.; Islam, M.A.; Hossain, N.; Chowdhury, M.A. Advances in nanoparticles in targeted drug delivery—A review. Results Surf. Interf. 2025, 19, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Tian, X.R.; Zhang, D.Y.; Cui, H.X.; Du, W.; Yang, Z.H.; Li, J.Y.; Li, W.S.; Xu, J.H.; et al. Stealth missiles with precision guidance: A novel multifunctional nano-drug delivery system based on biomimetic cell membrane coating technology. Mater. Today Bio. 2025, 33, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhu, L.; An, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.W.; Yan, F.; Zhang, W.J.; Qu, K.; Zhang, K.; Wu, W.; et al. Hybrid cell membranes camouflaged copper-loaded nano-prodrug for tumor angiogenesis inhibition and cell cuproptosis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ma, X.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, L.; Shi, Y.J. Precision delivery of pretreated macrophage-membrane-coated Pt nanoclusters for improving Alzheimer’s disease-like cognitive dysfunction induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Biomaterials 2025, 319, 123211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, K.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, Y.X.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Qian, R.J.; Deng, Z.P.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.L.; et al. N-acetyl-L-cysteine-modified macrophage membrane-coated VEGF sustained-release nanoparticles for treatment of myocardial infarction: A biomimetic nano-buffer for neutralization of detrimental factors and promotion of mature angiogenesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.T.; Pang, S.C.; Li, C.L.; Song, J.M.; Wang, M.; Chen, M.L.; Ren, X.L. Breast cancer-targeted therapy and doxorubicin multidrug resistance are reversed via macrophage membrane-camouflaged liposomes. Colloid Surf. B 2025, 245, 114310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.J.; Zhang, L.N.; You, J.; Zhan, J.C.; Liang, H.; Gu, X.; Zhu, Y. Biomimetic nanoparticles functionalized by macrophage membrane ameliorate heart failure in mouse and human cardiac organoid model. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Li, Y.M.; Shi, H.; Wang, B.B.; Tian, H.; Mei, X.F.; Wu, C. Berberine-calcium alginate-coated macrophage membrane-derived nanovesicles for the oral treatment of ulcerative colitis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 294, 139114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Ren, X.H.; Cao, P.P.; Chu, X.Q.; Wei, P.H.; Liu, Q.L.; Lu, Y.C.; Fu, B.; Li, W.Y.; Li, Y.H.; et al. Macrophage membrane-biomimetic nanoparticles target inflammatory microenvironment for epilepsy treatment. Theranostics 2024, 14, 6652–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Xiong, J.M.; Hu, Y.; Miao, W.J.; Huang, H. Wrapping collagen-based nanoparticle with macrophage membrane for treating multidrug-resistant bacterial infection. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2022, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawaratsumida, K.; Furuyashiki, M.; Katsumoto, M.; Fujimoto, Y.; Fukase, K.; Suda, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Characterization of N-terminal Structure of TLR2-activating Lipoprotein in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9147–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Ye, C.H.; Jiang, L.F.; Zhu, X.W.; Zhou, F.Y.; Xia, M.Z.; Chen, Y.H. The bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-146a-5p promotes diabetic wound healing in mice via macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2024, 579, 112089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.H.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, M.Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Feng, B. FHL2 regulates microglia M1/M2 polarization after spinal cord injury via PARP14-depended STAT1/6 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 110853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Li, K.; Li, J.P.; Ding, Y.; Yang, G.Z.; Zheng, X.B. Ferrocene-functionalized polydopamine film timely mediates M1-to-M2 macrophage polarization through adaptive wettability. Colloid Surf. B 2024, 236, 113825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.P.; Xu, S.; Pan, X.H.; Xin, W.Y.; Cao, W.L.; Ma, W.Y.; Li, L.; Shen, Q.; Li, Z.P. Psoralen protects neurons and alleviates neuroinflammation by regulating microglial M1/M2 polarization via inhibition of the Fyn-PKCδ pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 137, 112493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.T.; Wan, Z.J.; Sheng, X.P.; Rao, W.; Zhan, X.H.; Gu, J.L.; Wei, X.Z.; Fan, T.Y. Effects of higenamine on M1/M2 polarization and osteoclast differentiation in rheumatoid arthritis via the THBS-1/TGF-β signaling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2025, 134, 111905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.Z.; Jiang, S.N.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.P.; Di, L.F.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, H.M.; Hong, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.A.; et al. “Seesaw effect” between daptomycin and ceftobiprole in daptomycin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2025, 65, 107469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, K.K.; Zhu, Y.F.; Wan, J.Q.; Zhan, C.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Xie, B.B.; Xu, P.R.; Pan, H.M.; Wang, H.X. Macrophage membrane-biomimetic adhesive polycaprolactone nanocamptothecin for improving cancer-targeting efficiency and impairing metastasis. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadvand, S.; Kaveh Zenjanab, M.; Mashinchian, M.; Shayegh, J.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R. Recent advances in biomimetic cell membrane–Camouflaged nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 116951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Liao, Y.H.; Chen, W.X.; Luo, J.N.; Li, D.D.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, F.X. Bone-targeted nanomedicine based on red blood cell membrane-coated polymeric carriers for effective osteoporosis reversal. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 110, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Ye, P.J.; Zhou, Y.C.; He, D.X.; Wei, H.; Yu, C.Y. Cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles as drug carriers for cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Liu, J.Y.; Jiang, Q.K.; Mi, Y.; Meng, Q.Q.; Mu, D.Y.; Hou, Y. Biomimetic cell membrane vesicles as promising delivery carriers for dietary polyphenols in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 93, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.J.; Xie, Z.Y.; Gao, S.; Teng, T.L.; Zhou, W.Q.; Shang, Y.Y.; Jing, W.; Shi, W.H.; Wang, Q.F.; Huang, X.R.; et al. Efficacy of Moxifloxacin against Mycobacterium abscessus in Zebrafish Model in vivo. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 350–358. [Google Scholar]


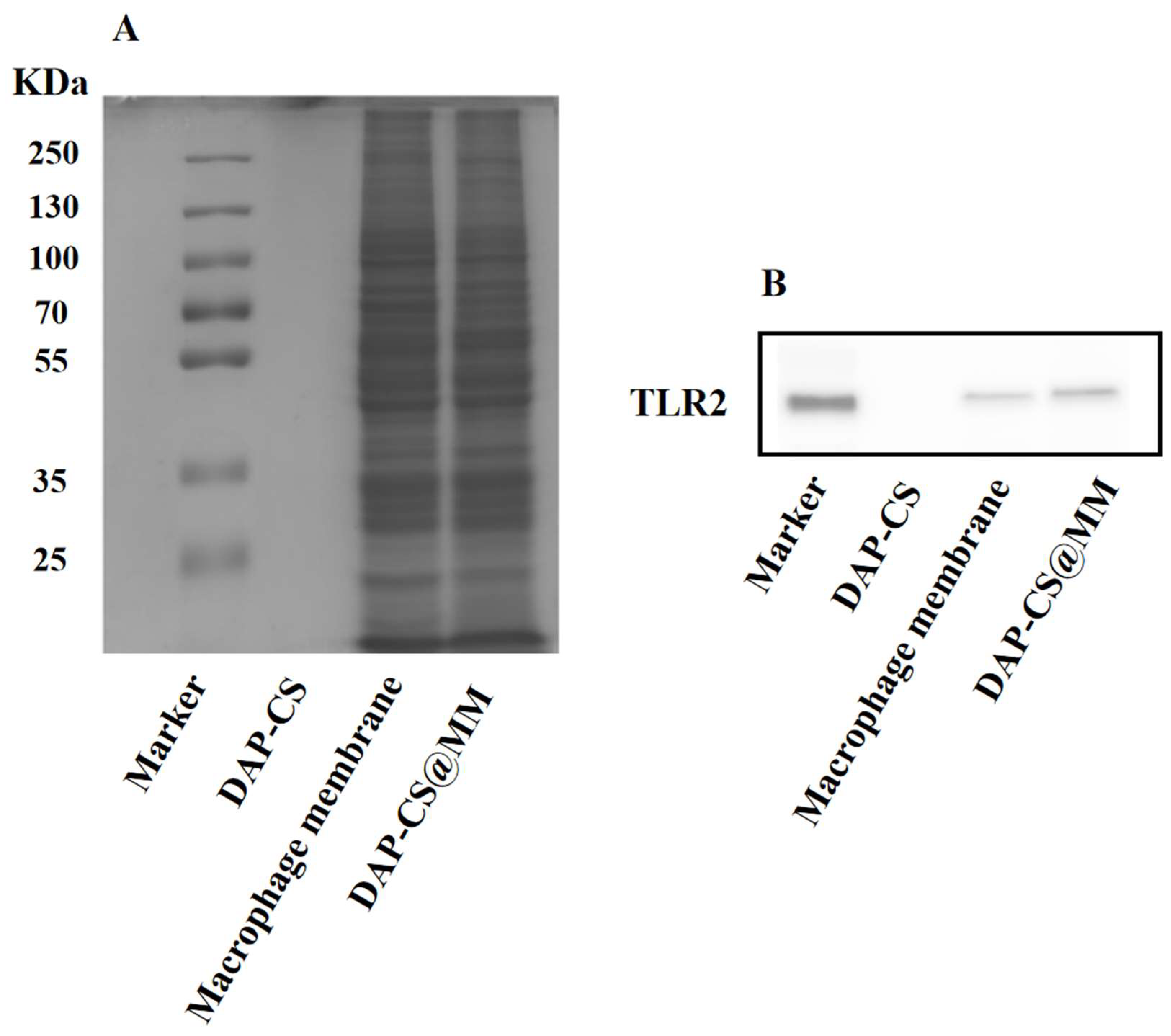

| Sample | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | Entrapment Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAP-CS | 90.93 ± 5.38 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 27.48 ± 0.53 | 76.09 ± 0.42 |
| DAP-CS@MM | 110.9 ± 13.72 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 11.90 ± 1.90 | 70.43 ± 1.29 |
| Group | Dose (ng/Larva) | Mortality (%) | Behaviors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Control Group | - | 0 | normal |
| Model Control Group | 0 | 0 | normal |
| DAP | 125 | 0 | normal |
| 250 | 0 | normal | |
| 500 | 0 | abnormal * | |
| 1000 | 0 | abnormal * | |
| 2000 | 17 | - |
| Group | Concentration (ng/larva) | Fluorescence Intensity (Pixels) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Control Group | - | 45,925 ± 3577 a |
| Model Control Group | - | 864,890 ± 39,470 d |
| DAP | 1.00 | 766,996 ± 16,054 c |
| DAP-CS | 1.00 | 754,545 ± 32,188 c |
| DAP-CS@MM | 1.00 | 660,482 ± 29,038 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Du, S.; He, K.; Zhou, B.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, M.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Daptomycin-Loaded Nano-Drug Delivery System Based on Biomimetic Cell Membrane Coating Technology: Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081169
Zhou Y, Du S, He K, Zhou B, Chen Z, Zheng C, Zhou M, Li J, Chen Y, Zhang H, et al. Daptomycin-Loaded Nano-Drug Delivery System Based on Biomimetic Cell Membrane Coating Technology: Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081169
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuqin, Shihan Du, Kailun He, Beilei Zhou, Zixuan Chen, Cheng Zheng, Minghao Zhou, Jue Li, Yue Chen, Hu Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Daptomycin-Loaded Nano-Drug Delivery System Based on Biomimetic Cell Membrane Coating Technology: Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081169
APA StyleZhou, Y., Du, S., He, K., Zhou, B., Chen, Z., Zheng, C., Zhou, M., Li, J., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Yuan, H., Li, Y., Chen, Y., & Hu, F. (2025). Daptomycin-Loaded Nano-Drug Delivery System Based on Biomimetic Cell Membrane Coating Technology: Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081169









