Gum Acacia–Dexamethasone Combination Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats via Targeting SIRT1-HMGB1 Signaling Pathway and Preserving Mitochondrial Integrity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Impact of GA, DEX, and Combination of GA and DEX on LPS-Induced Changes in Body Weight and Kidney Index
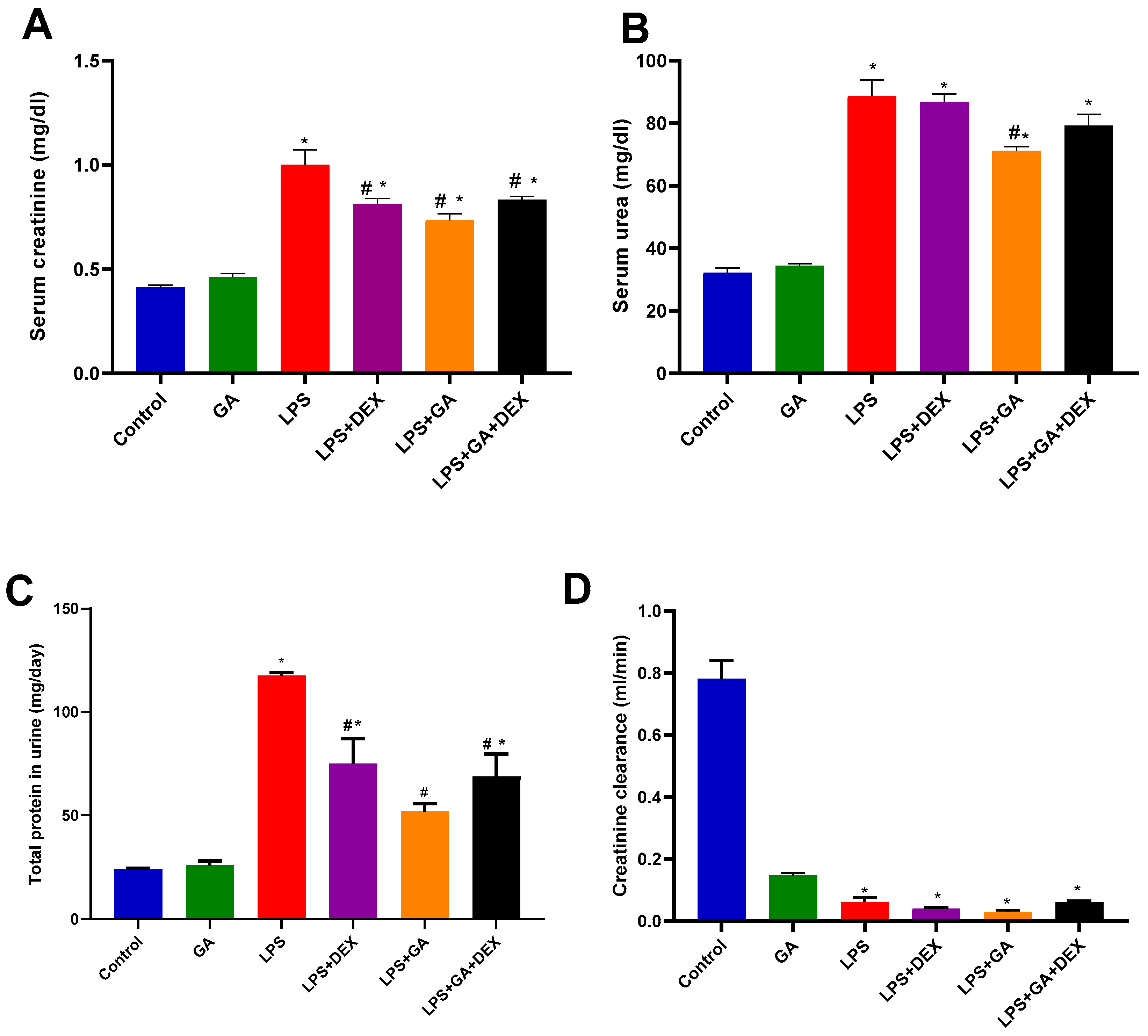
2.2. Impact of GA, DEX, and Combination of GA and DEX on LPS-Induced Changes in Kidney Function Biomarkers
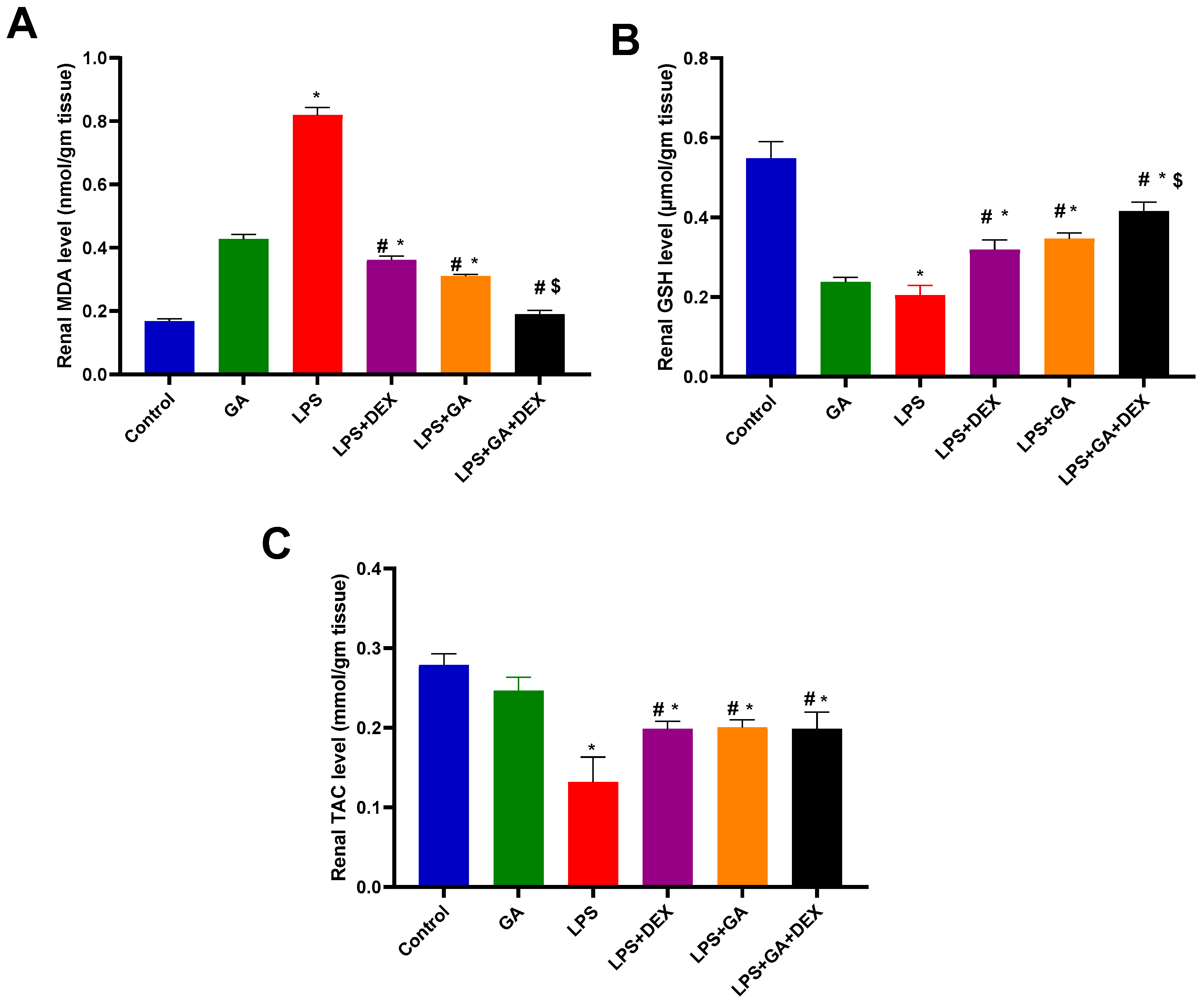
2.3. Impact of GA, DEX, and Combination of GA and DEX on LPS-Induced Changes in Oxidant/Antioxidant Parameters
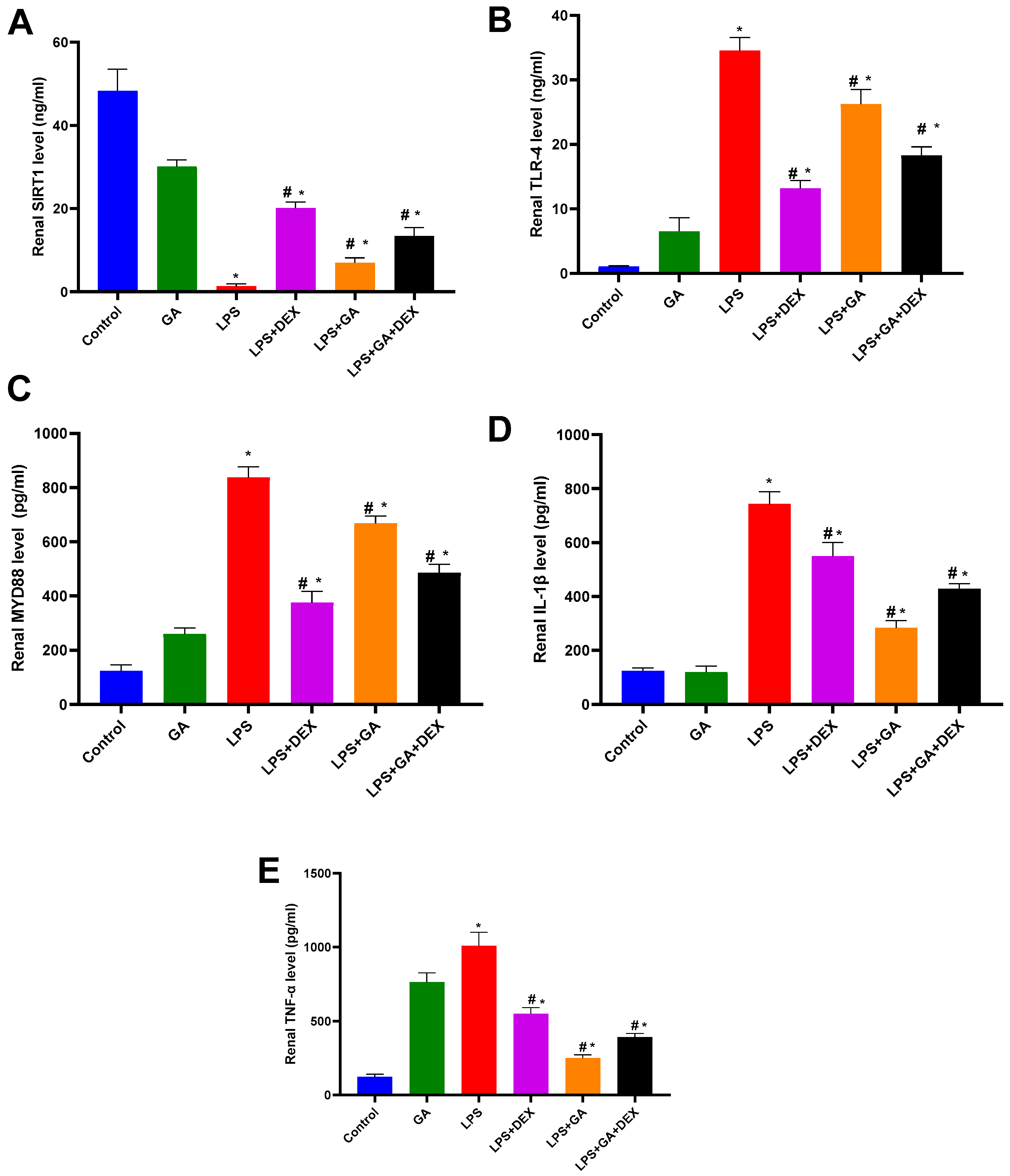
2.4. Impact of GA, DEX, and Combination of GA and DEX on LPS-Induced Changes in Inflammatory Markers
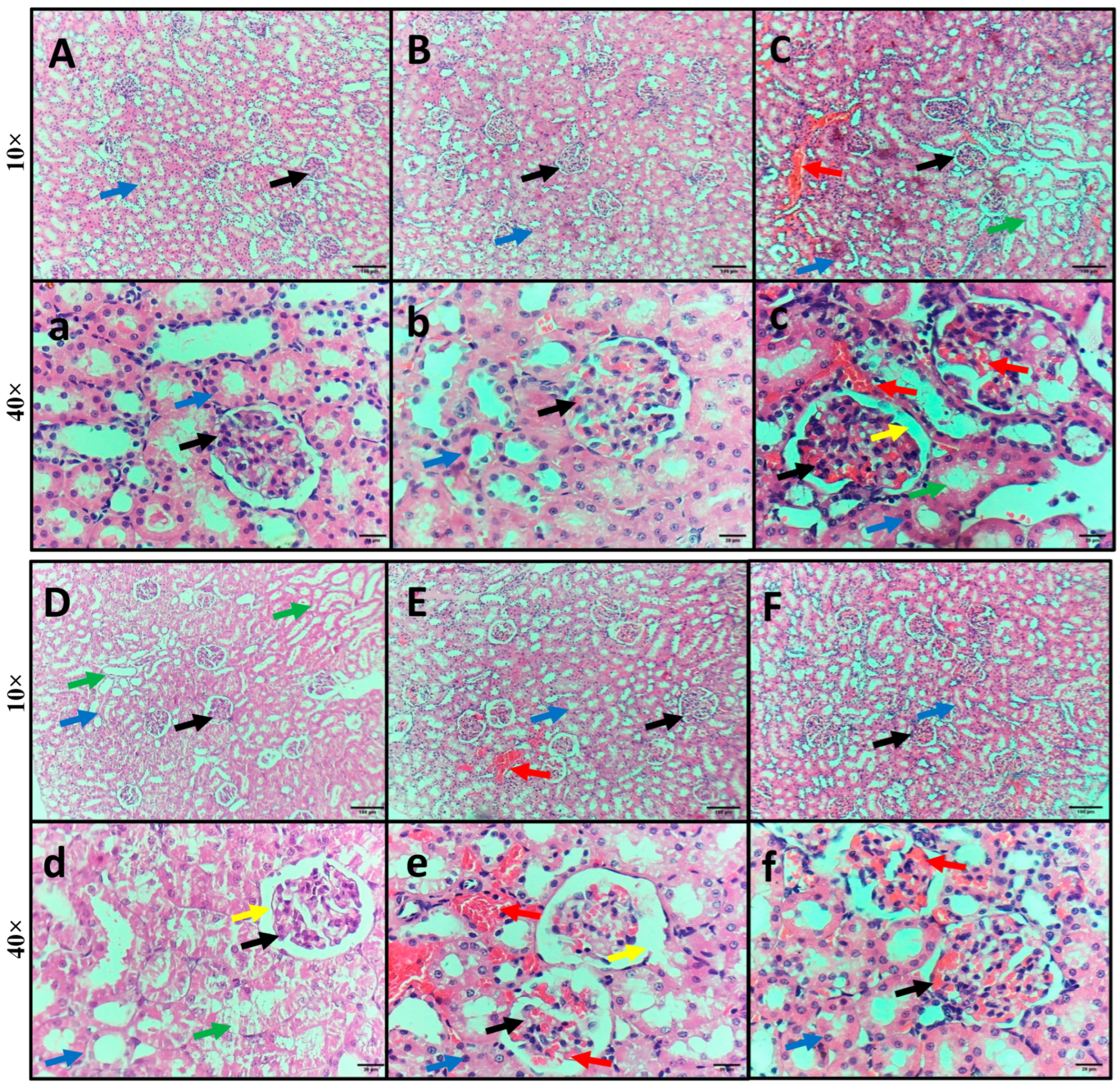
2.5. Impact of GA, DEX, and Combination of GA and DEX on LPS-Induced Histopathological Irregularities in Kidney Tissues
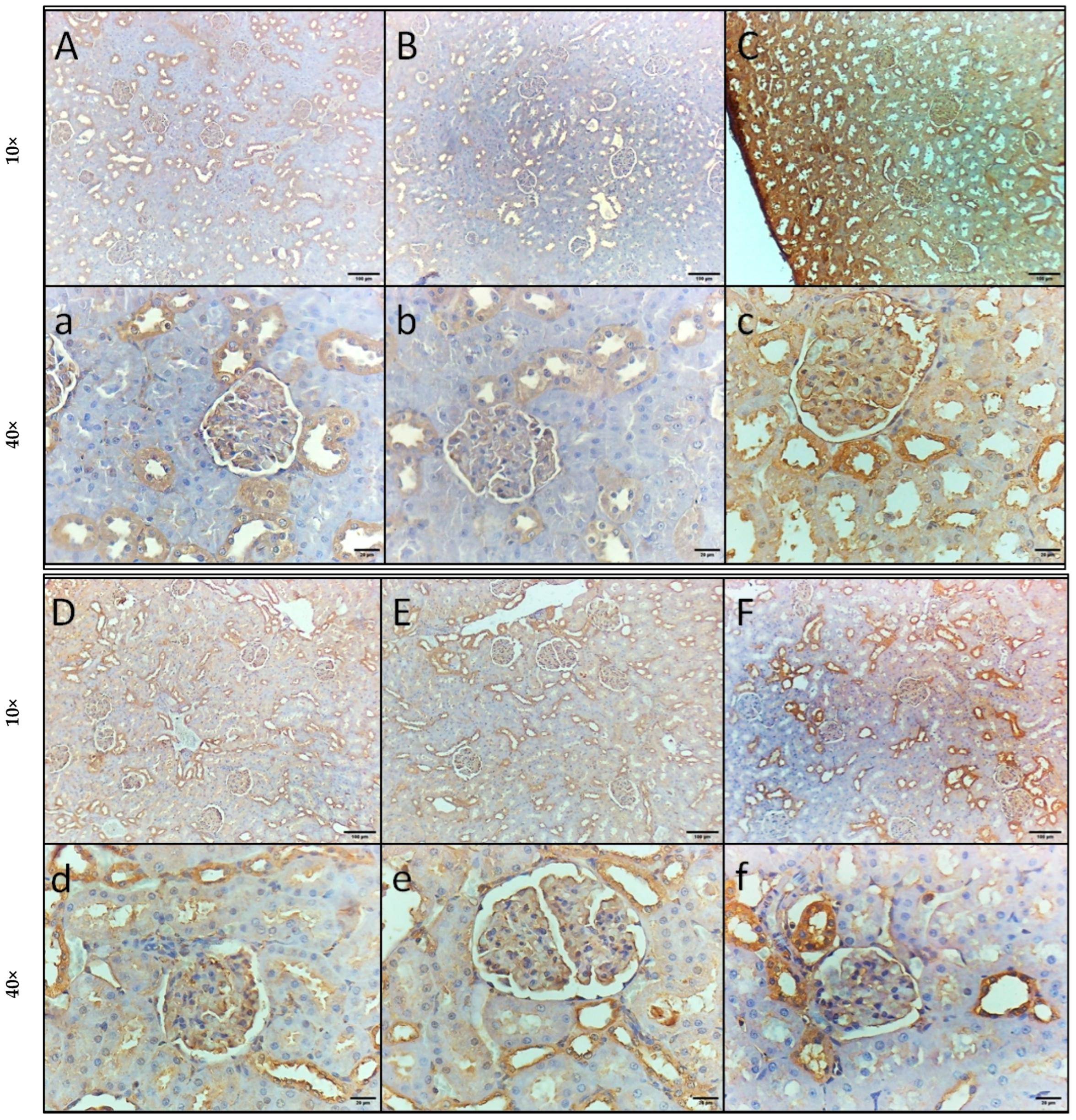
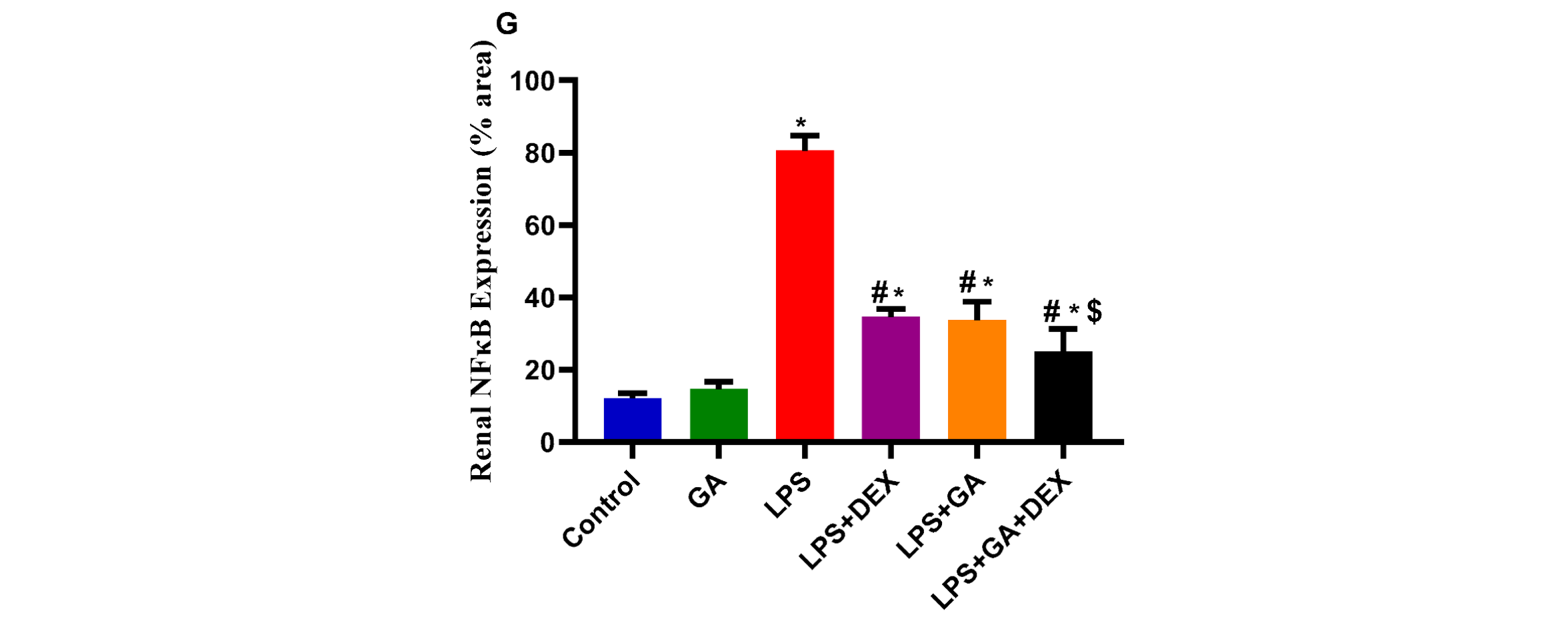
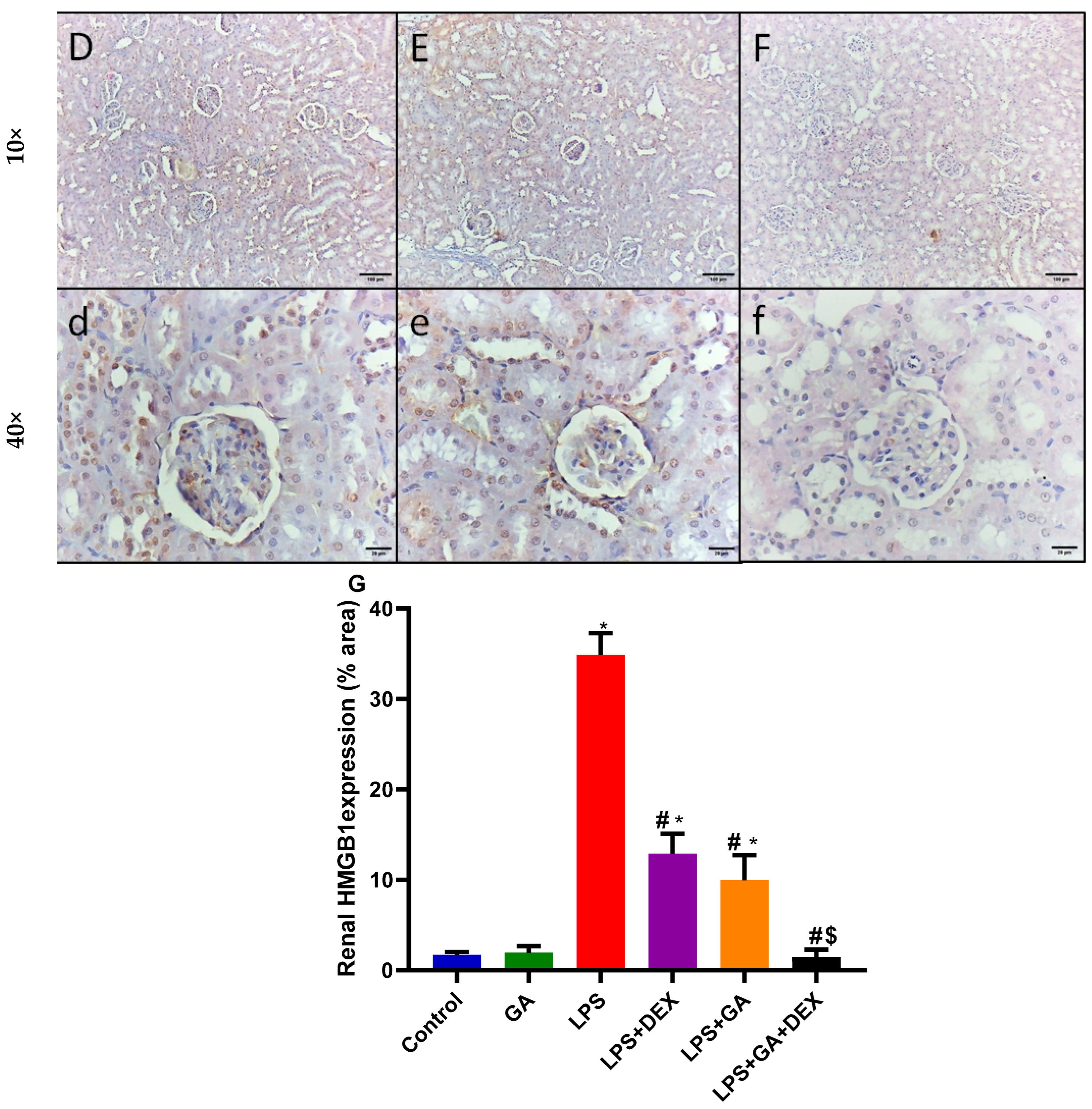
2.6. Impact of GA, DEX, and Combination of GA and DEX on LPS-Induced Changes in NF-κB and HMGB1 Expression
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Chemicals
4.2. Animals
4.3. Induction of AKI
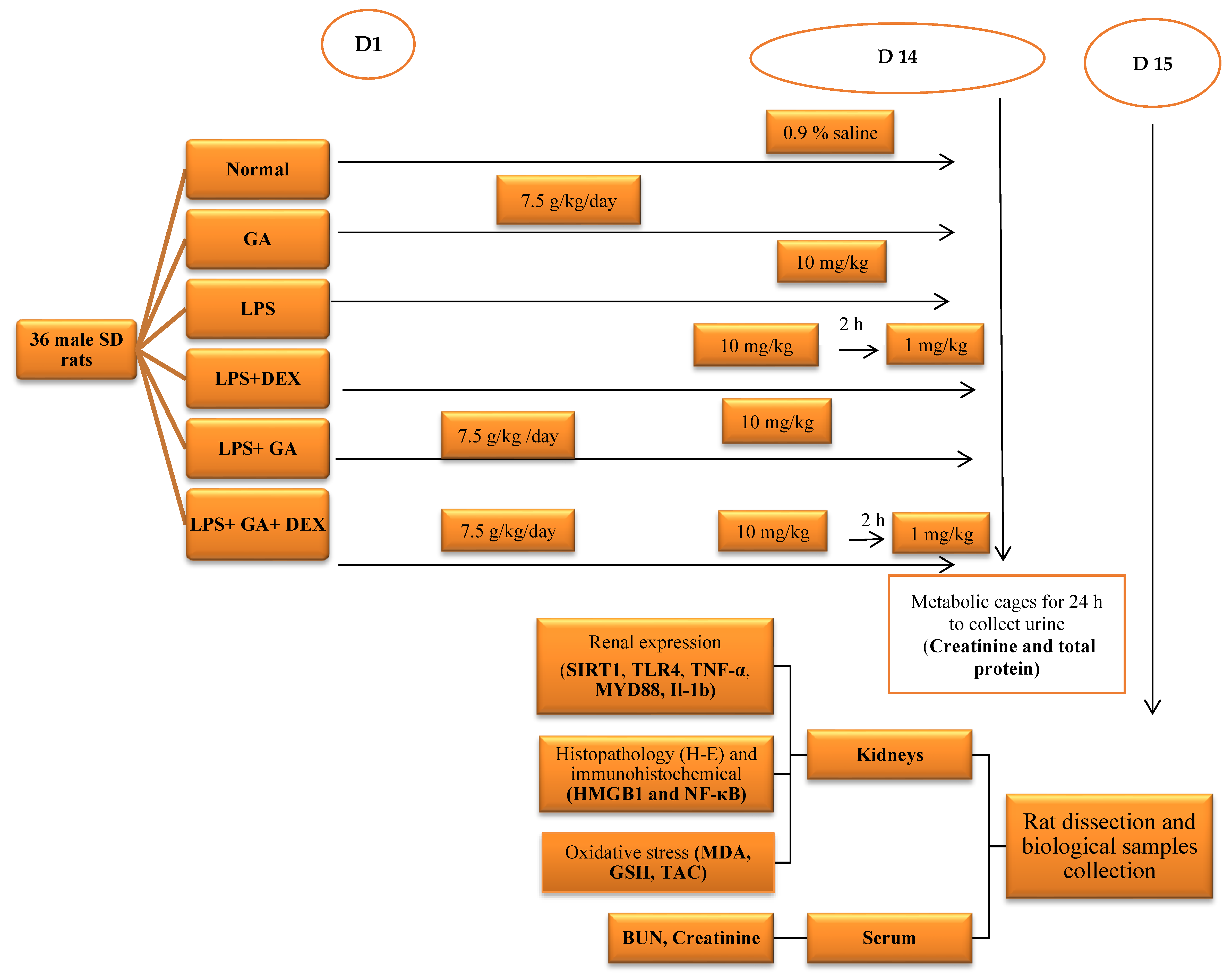
4.4. Experimental Protocol and Sample Collection
4.5. Sample Preparation
4.6. Assessment of Biological Marker Levels in Serum and Tissue Samples
4.7. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Examination
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
The Limitations of This Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, S.; Chen, Y.-H.; Tan, Z.-X.; Xie, D.-D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Yu, D.-X.; Xu, D.-X. Vitamin D3 pretreatment regulates renal inflammatory responses during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gómez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claure-Del Granado, R.; James, M.T.; Legrand, M. Tackling sepsis-associated acute kidney injury using routinely collected data. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 1100–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Gao, J.; Xiang, X.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Wu, W.; Cai, J.; Tang, C.; Zhang, D. Discovery and validation of miR-452 as an effective biomarker for acute kidney injury in sepsis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallés, P.G.; Gil Lorenzo, A.F.; Garcia, R.D.; Cacciamani, V.; Benardon, M.E.; Costantino, V.V. Toll-like receptor 4 in acute kidney injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhai, J. The SIRT1-HMGB1 axis: Therapeutic potential to ameliorate inflammatory responses and tumor occurrence. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 986511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrihastini, V.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Adarshan, S.; Sujitha, M.; Chen, J.-T.; Shin, H.; Ramesh, M. Plant derived bioactive compounds, their anti-cancer effects and in silico approaches as an alternative target treatment strategy for breast cancer: An updated overview. Cancers 2021, 13, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, G.O.; Ogasawara, T.; Ushida, K. The regulatory and scientific approach to defining GA arabic (Acacia senegal and Acacia seyal) as a dietary fibre. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshama, S.S. The preventive role of Arabic GA in the treatment of toxicity. Open Access Toxicol. Res. 2018, 1, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Shafeek, F.; Abu-Elsaad, N.; El-Karef, A.; Ibrahim, T. GA Acacia mitigates diclofenac nephrotoxicity by targeting monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, complement receptor-1 and pro-apoptotic pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 129, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.E.; Kaddam, L.A.; Alkarib, S.Y.; Kaballo, B.G.; Khalid, S.A.; Higawee, A.; AbdElhabib, A.; AlaaAldeen, A.; Phillips, A.O.; Saeed, A.M. GA Arabic (Acacia senegal) Augmented Total Antioxidant Capacity and Reduced C-Reactive Protein among Haemodialysis Patients in Phase II Trial. Int. J. Nephrol. 2020, 2020, 7214673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, V.M.; Rocha, M.; Esplugues, J.V. Role of free radicals in sepsis: Antioxidant therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 3141–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.E.; Abdlrahman, S.; Ahmed Mohamed, S.; Bilal, T.; Elghazali, F.E.; Elbadwi, S.M. Nephroprotective effect of Acacia senegal (GA Arabic) agains t gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int. J. Res.-Granthaalayah 2022, 10, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noha, S.; Fetaih, H.A.; Dessouki, A. Effect of GA Arabic on Chemically Induced Acute Renal Injury in Albino Rats. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. B Zool. 2022, 14, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Jo, S.-K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Cho, E.; Hyun, Y.Y.; Cha, J.J.; Kang, Y.S.; Cha, D.R.; Cho, W.Y. Glucocorticoids attenuate septic acute kidney injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 435, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Nadim, M.K.; Pickkers, P.; Gomez, H.; Bell, S.; Joannidis, M.; Kashani, K.; Koyner, J.L.; Pannu, N.; Meersch, M. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: Consensus report of the 28th Acute Disease Quality Initiative workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, S.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R.; Doig, G.S.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: A multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 2005, 294, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, J.; Valenzuela-Sánchez, F.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, M.; Moyano, S. Sepsis: A review of advances in management. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 2393–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.C.; Serpa-Neto, A.; Hurford, R.; Clement, P.; Laupland, K.B.; See, E.; McCullough, J.; White, H.; Shekar, K.; Tabah, A. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: Incidence, patient characteristics, timing, trajectory, treatment, and associated outcomes. A multicenter, observational study. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, G.; Ugan, R.A.; Cadirci, E.; Halici, Z. Sepsis and septic shock: Current treatment strategies and new approaches. Eurasian J. Med. 2017, 49, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, Z.A. Immunopathogenesis of acute kidney injury. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018, 46, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang-Ting, C.; Tzu-Ching, C.; Ching-Yi, T.; Song-Kuen, S.; Ming-Kuen, L. Adenovirus-mediated bcl-2 gene transfer inhibits renal ischemia/reperfusion induced tubular oxidative stress and apoptosis. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Liu, X.; Chang, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, M.; Liu, M. Rutin prevents inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide in RAW 264.7 cells via conquering the TLR4-MyD88-TRAF6-NF-κB signalling pathway. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farman, M.S.; Salman, M.I.; Hamad, H. Effect of GA arabic administration on some physiological and biochemical parameters in chronic renal failure patients. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Leem, J.; Park, K.-K. Antioxidative, antiapoptotic, and anti-inflammatory effects of apamin in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury. Molecules 2020, 25, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Jin, F.; Liu, D.; Shu, G.; Wang, X.; Qi, J.; Sun, M.; Yang, P.; Jiang, S.; Ying, X. ROS-responsive nano-drug delivery system combining mitochondria-targeting ceria nanoparticles with atorvastatin for acute kidney injury. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z. Salidroside attenuates LPS-induced kidney injury through activation of SIRT1/Nrf2 pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2023, 42, 09603271231169520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Za’abi, A.; Al Salam, S.; Al Suleimani, Y.; Manoj, P.; Nemmar, A.; Ali, B.H. GA acacia improves renal function and ameliorates systemic inflammation, oxidative and nitrosative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats with adenine-induced chronic kidney disease. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 2293–2304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaddam, L.; Fadl-Elmula, I.; Eisawi, O.A.; Abdelrazig, H.A.; Salih, M.A.; Lang, F.; Saeed, A.M. GA Arabic as novel anti-oxidant agent in sickle cell anemia, phase II trial. BMC Hematol. 2017, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, C.; Cunha, C.; Vaz, A.R.; Falcão, A.S.; Barateiro, A.; Seixas, E.; Fernandes, A.; Brites, D. Key aging-associated alterations in primary microglia response to beta-amyloid stimulation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Guo, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Xie, S.M.; Liu, C.; Lv, P.; Xing, L.; Zhang, X. High mobility group box-1 protects against Aflatoxin G1-induced pulmonary epithelial cell damage in the lung inflammatory environment. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 331, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Kang, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, R. EGCG in green tea induces aggregation of HMGB1 protein through large conformational changes with polarized charge redistribution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-w.; Yao, H.; Caito, S.; Sundar, I.K.; Rahman, I. Redox regulation of SIRT1 in inflammation and cellular senescence. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 61, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, M.-H.; Jeong, J.-K.; Lee, Y.-J.; Seol, J.-W.; Jackson, C.; Park, S.-Y. SIRT1, a class III histone deacetylase, regulates TNF-α-induced inflammation in human chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Hao, C.-M. SIRT1 and Kidney Function. Kidney Dis. 2015, 1, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Kitada, M.; Koya, D. Sirtuins and renal oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Zhuo, Y.; Guo, Z.; He, L.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Dai, H. SIRT1/PGC-1 pathway activation triggers autophagy/mitophagy and attenuates oxidative damage in intestinal epithelial cells. Biochimie 2020, 170, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. The mechanism of HMGB1 secretion and release. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venereau, E.; Casalgrandi, M.; Schiraldi, M.; Antoine, D.J.; Cattaneo, A.; De Marchis, F.; Liu, J.; Antonelli, A.; Preti, A.; Raeli, L. Mutually exclusive redox forms of HMGB1 promote cell recruitment or proinflammatory cytokine release. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, J.K.; Choi, S.-E.; Kim, D.H. Sirtuin 1 deacetylase: A key regulator of hepatic lipid metabolism. Vitam. Horm. 2013, 91, 385–404. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Gao, Y.; Dai, X.; Fu, W.; Cai, S.; Fang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Z. SIRT1-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation suppresses sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F20–F31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulskens, W.P.; Teske, G.J.; Butter, L.M.; Roelofs, J.J.; Van Der Poll, T.; Florquin, S.; Leemans, J.C. Toll-like receptor-4 coordinates the innate immune response of the kidney to renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Carballo, C.; Guerrero-Hue, M.; García-Caballero, C.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Opazo-Ríos, L.; Morgado-Pascual, J.L.; Herencia-Bellido, C.; Vallejo-Mudarra, M.; Cortegano, I.; Gaspar, M.L. Toll-like receptors in acute kidney injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Du, S.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Su, Y.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y. Effects of microRNA-208a on inflammation and oxidative stress in ketamine-induced cardiotoxicity through Notch/NF-κB signal pathways by CHD9. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Duan, Q.; Dong, C.; Cui, J. Cul4a attenuates LPS-induced acute kidney injury via blocking NF-kB signaling pathway in sepsis. J. Med. Biochem. 2022, 41, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhong, W.; Lin, Z.; Yan, J. Blockade of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced kidney injury by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2023, 27, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, C.; Lai, J.; Wang, J.; Zhong, H.; Chen, F. Toll-like receptor 4 promotes the inflammatory response in septic acute kidney injury by promoting p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2023, 55, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, F.; Li, H.; Chen, B. Ginkgetin aglycone ameliorates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by activating SIRT1 via inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewalle, J.; Libert, C. Glucocorticoids in sepsis: To be or not to be. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, I.; Dejager, L.; Ballegeer, M.; Lievens, S.; Tavernier, J.; De Bosscher, K.; Libert, C. The Interactome of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Its Influence on the Actions of Glucocorticoids in Combatting Inflammatory and Infectious Diseases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.-L.; Marshall, J.C. Surviving sepsis: A guide to the guidelines. Crit. Care 2008, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, Y.J.; Lee, M.J.; Bae, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.A.R.; Mun, S.; Kim, Y.-s.; Yune, C.J.; Chung, T.N.; Kim, K. Effects of glucocorticoid therapy on sepsis depend both on the dose of steroids and on the severity and phase of the animal sepsis model. Life 2022, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, D.-w.; Tang, L.-n.; Lu, H.-n.; Zhang, F.; Guo, H.-p.; Hu, Z.; Huang, S.-y. The protective effect of different doses of dexamethasone on acute kidney injury induced by sepsis in mice. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2013, 25, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.M.; Ho, S.T.; Chen, A.; Wang, J.J.; Li, C.Y.; Tsai, S.K.; Wu, C.C. Low-dose dexamethasone ameliorates circulatory failure and renal dysfunction in conscious rats with endotoxemia. Shock 2004, 21, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Dutta, M.; Mondal, M.; Sarkar, K.; Paul, G. Effect of Bisphenol S (BPS) on the contraction of duodenal visceral smooth muscle ex vivo in rat. Sci. Arch. 2021, 2, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigis, M.C.; Guarente, L.P. Mammalian sirtuins—Emerging roles in physiology, aging, and calorie restriction. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigis, M.C.; Sinclair, D.A. Mammalian sirtuins: Biological insights and disease relevance. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2010, 5, 253–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencina, A.M.; Franza, T.; Sullivan, M.J.; Ulett, G.C.; Ipe, D.S.; Gaudu, P.; Gennis, R.B.; Schurig-Briccio, L.A. Type 2 NADH dehydrogenase is the only point of entry for electrons into the Streptococcus agalactiae respiratory chain and is a potential drug target. mBio 2018, 9, e01034-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.B.; Yoon, Y.D.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, C.W.; Yoon, W.K.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.M. Toll-like receptor-mediated activation of B cells and macrophages by polysaccharide isolated from cell culture of Acanthopanax senticosus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.-J.; Niu, P.-P.; Cong, J.-Z.; Zhang, B.-K.; Zhao, M. TLR4 signaling: A potential therapeutic target in ischemic coronary artery disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Rangarajan, P.; Ling, E.-A.; Dheen, S.T. Dexamethasone inhibits the Nox-dependent ROS production via suppression of MKP-1-dependent MAPK pathways in activated microglia. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirris, T.; Jansen, J.; Mihajlovic, M.; van den Heuvel, L.; Masereeuw, R.; Russel, F.G. Mild intracellular acidification by dexamethasone attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction in a human inflammatory proximal tubule epithelial cell model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, M.R.; El-Sheakh, A.R.; Suddek, G.M. Saroglitazar, a dual PPAR-α/γ agonist, alleviates LPS-induced hepatic and renal injury in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 115, 109688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, A.M.; Aldahmash, B.A. Antioxidant effect of Arabic GA against mercuric chloride-induced nephrotoxicity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Premachandran, S.; Shukla, J.; Poduval, T. Synergistic therapeutic potential of dexamethasone and L-arginine in lipopolysaccharide-induced septic shock. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 140, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Oikawa, H.; Sato, S.; Satodate, R.; Suzuki, K.; Sato, S. Distinguishing small lymph vessels in the portal tracts of human liver from portal veins by immunohistochemistry for α smooth muscle actin. Int. Hepatol. Commun. 1996, 4, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alruwaili, F.N.; Nour, O.A.; Ibrahim, T.M. Gum Acacia–Dexamethasone Combination Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats via Targeting SIRT1-HMGB1 Signaling Pathway and Preserving Mitochondrial Integrity. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081164
Alruwaili FN, Nour OA, Ibrahim TM. Gum Acacia–Dexamethasone Combination Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats via Targeting SIRT1-HMGB1 Signaling Pathway and Preserving Mitochondrial Integrity. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081164
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlruwaili, Fawaz N., Omnia A. Nour, and Tarek M. Ibrahim. 2025. "Gum Acacia–Dexamethasone Combination Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats via Targeting SIRT1-HMGB1 Signaling Pathway and Preserving Mitochondrial Integrity" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081164
APA StyleAlruwaili, F. N., Nour, O. A., & Ibrahim, T. M. (2025). Gum Acacia–Dexamethasone Combination Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats via Targeting SIRT1-HMGB1 Signaling Pathway and Preserving Mitochondrial Integrity. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081164





