Secondary Metabolites from Rehmannia glutinosa Protect Mitochondrial Function in LPS-Injured Endothelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
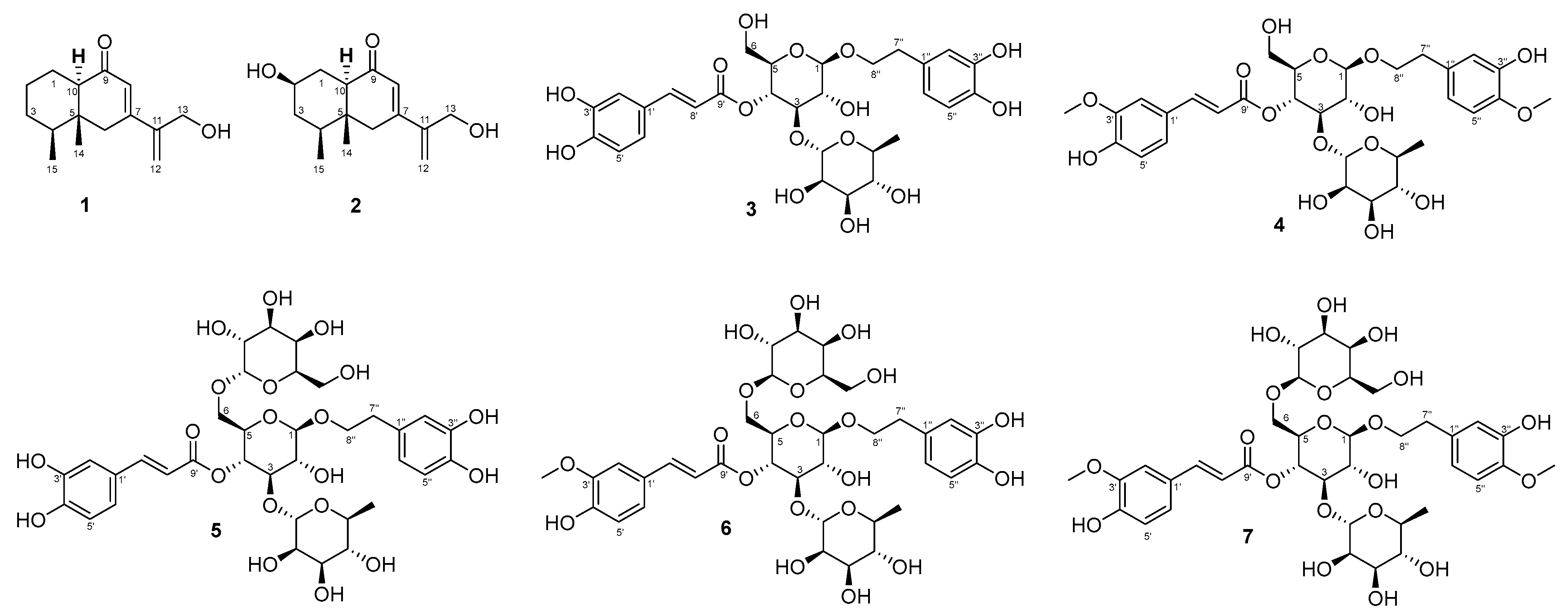
2.1. Structure Determination
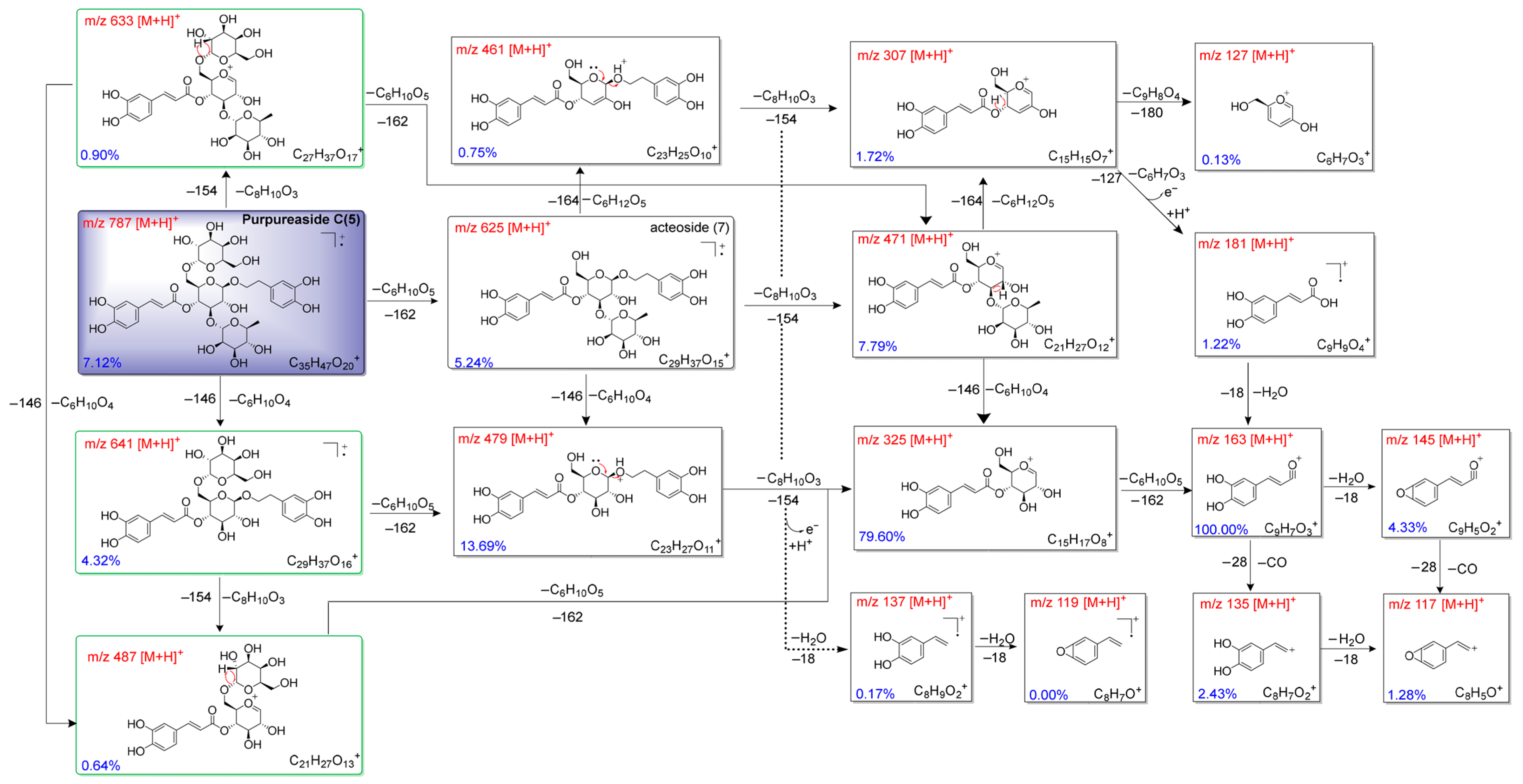
2.2. Fragmentation Mechanisms of Compounds (3–7)
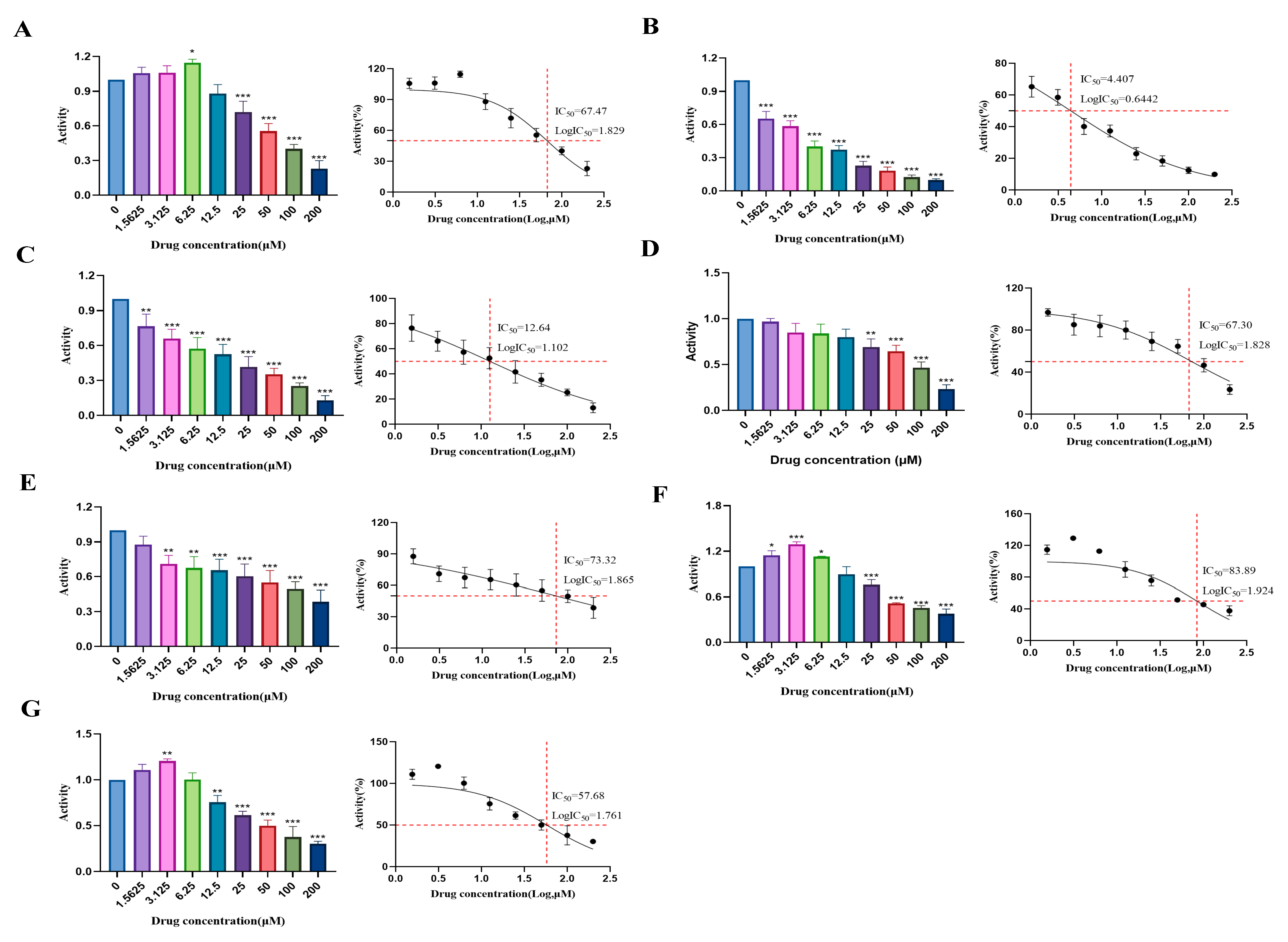
2.3. Determination of Cytotoxic Effects and Experimental Concentrations of Compounds (1–7) in HUVECs
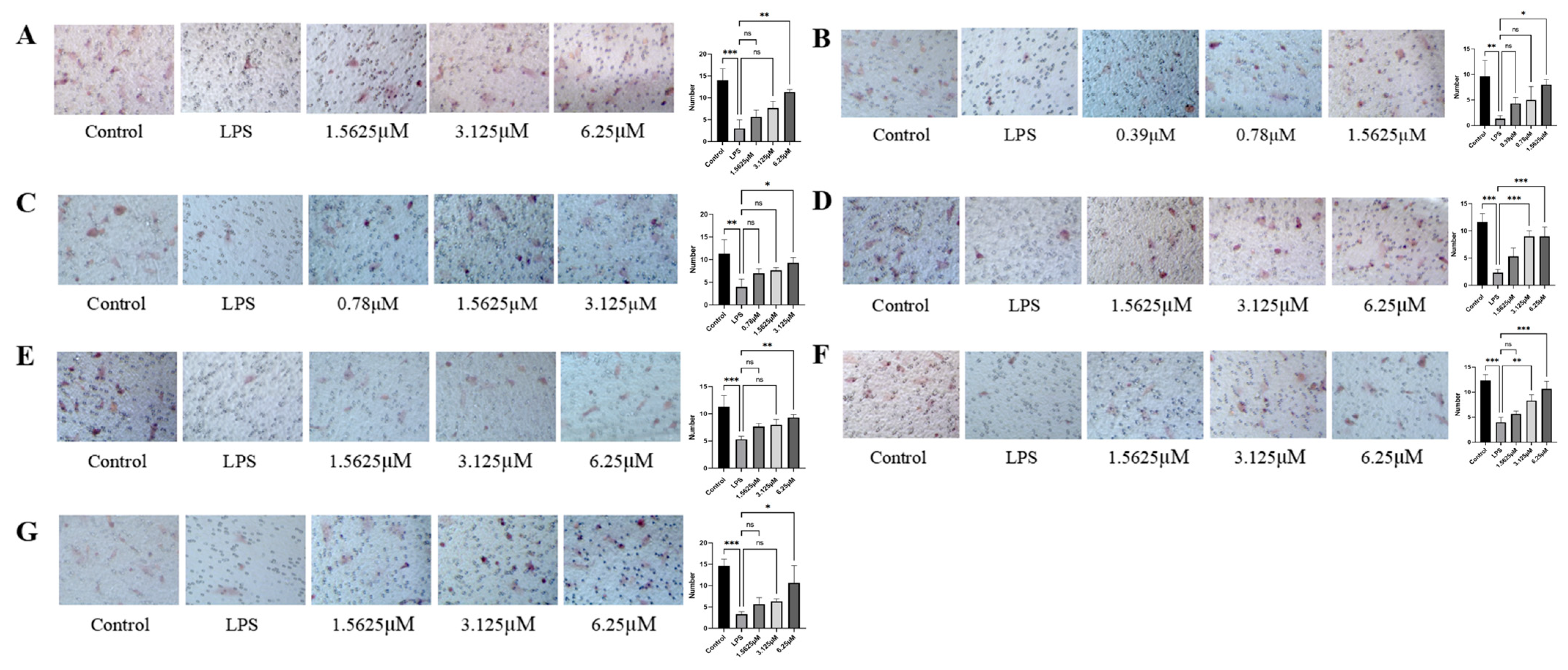
2.4. Effects of Diverse Compound Interventions on LPS-Induced Endothelial Cell Migration Impairment
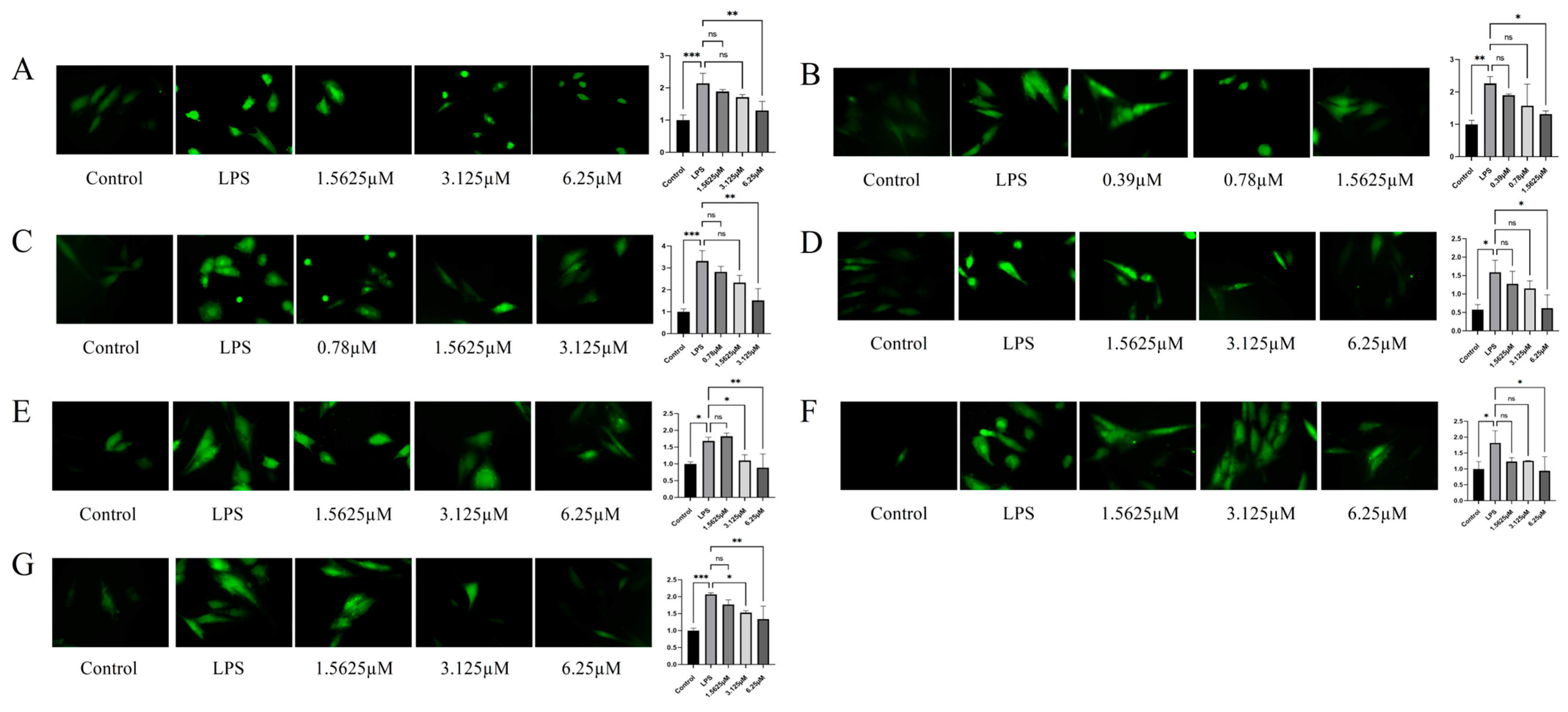
2.5. Inhibitory Potency of Compounds Against ROS Levels in LPS-Induced HUVECs
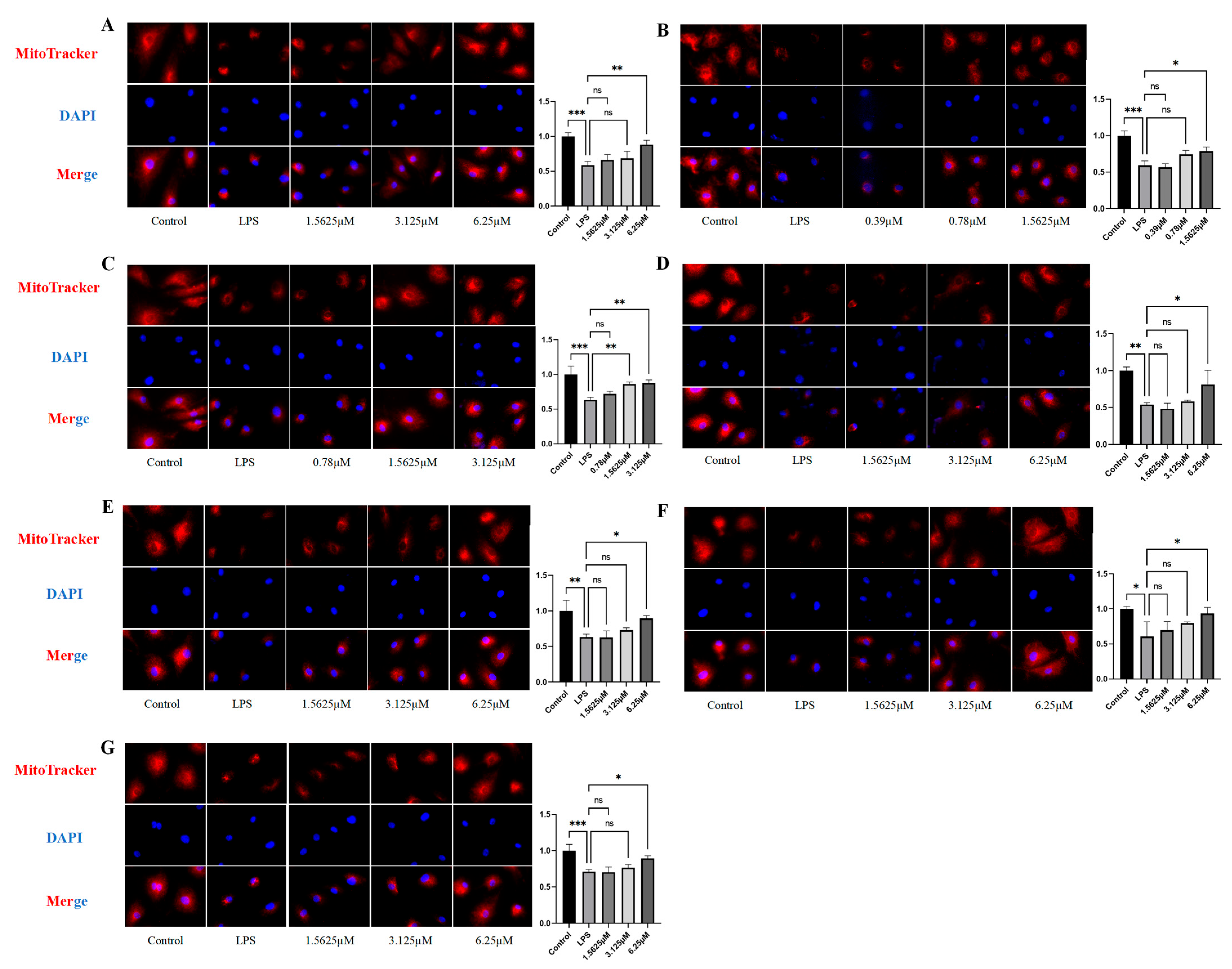
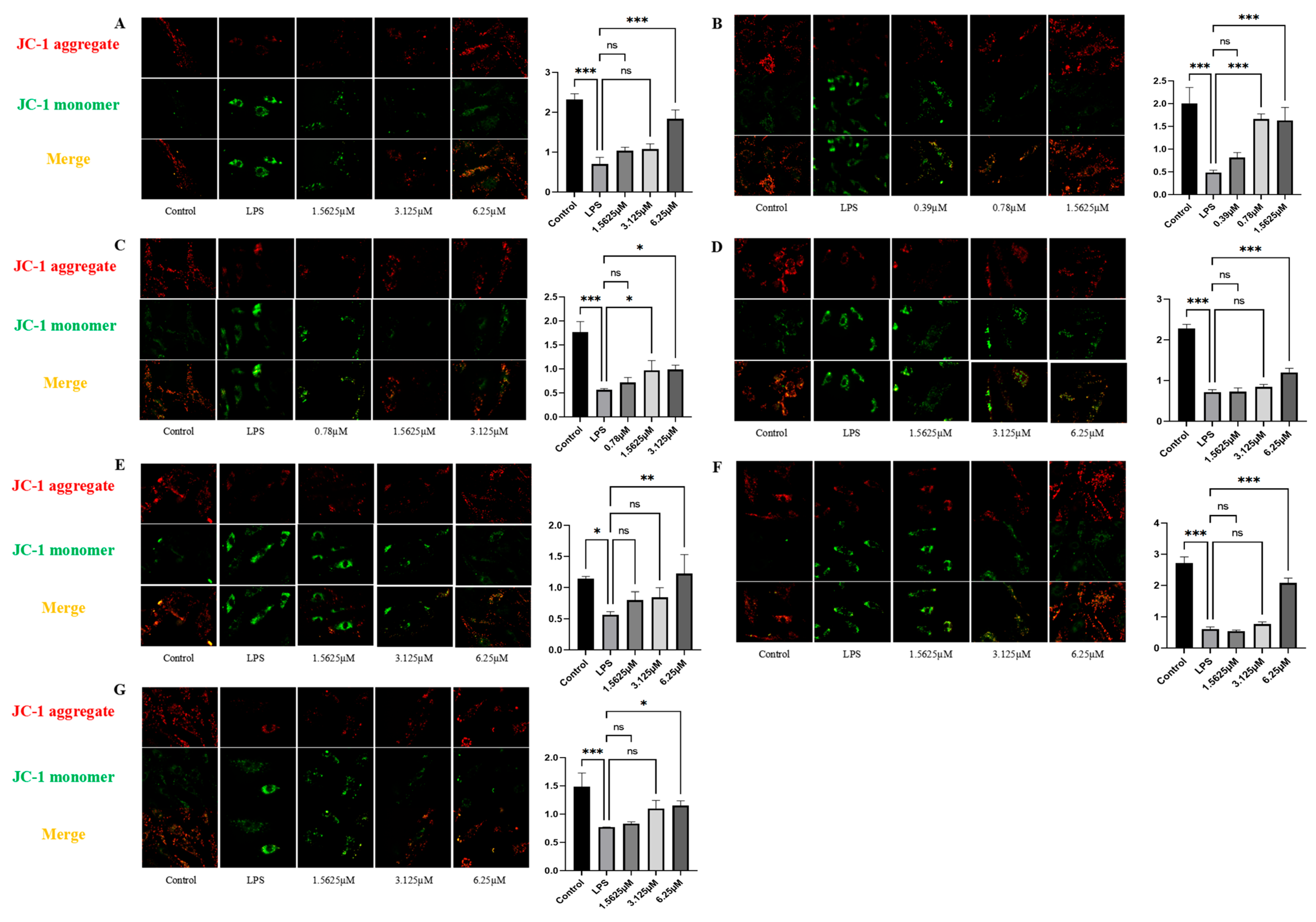
2.6. Effects of Compound Intervention on Mitochondrial Function in LPS-Induced HUVECs
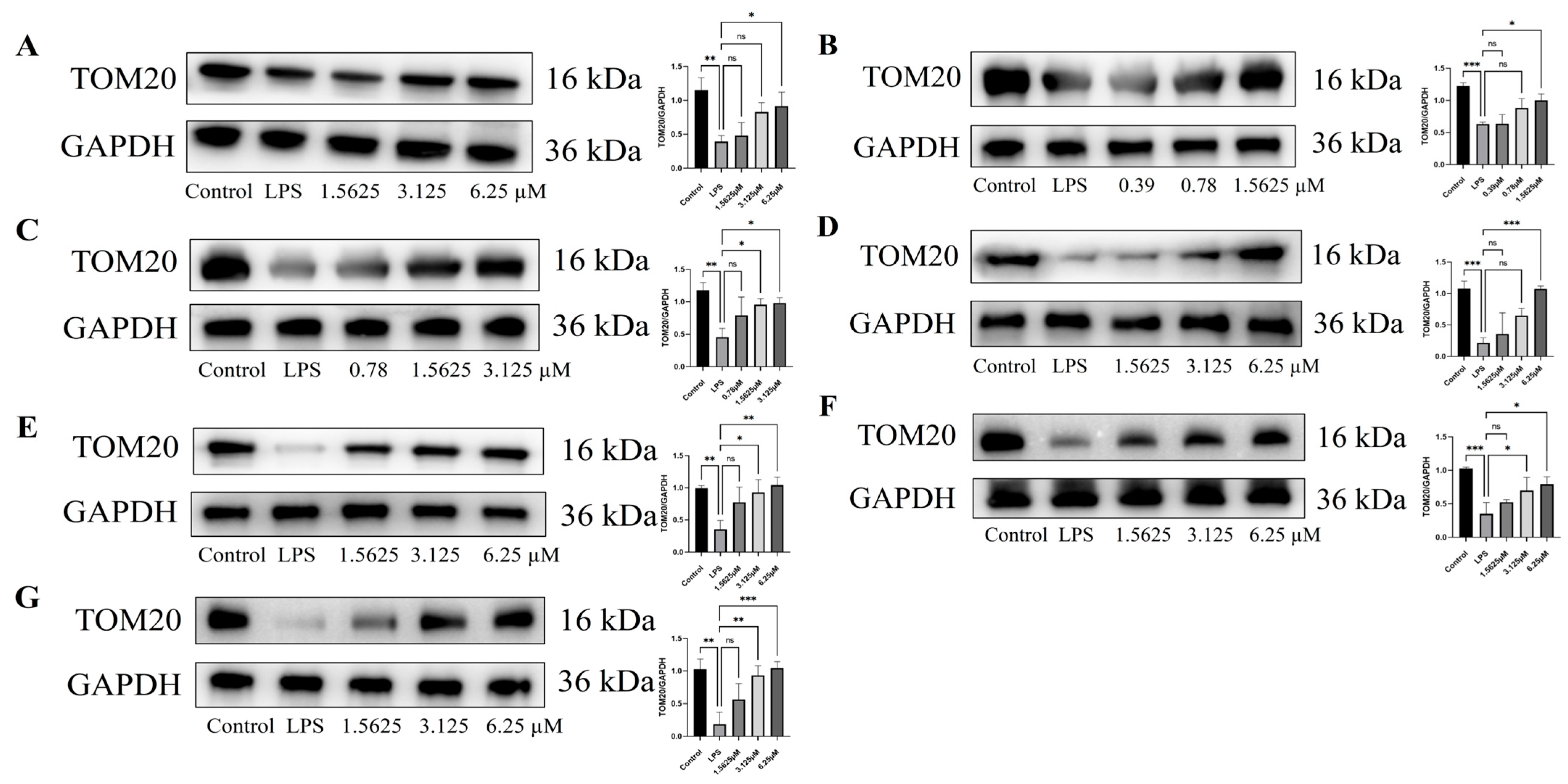
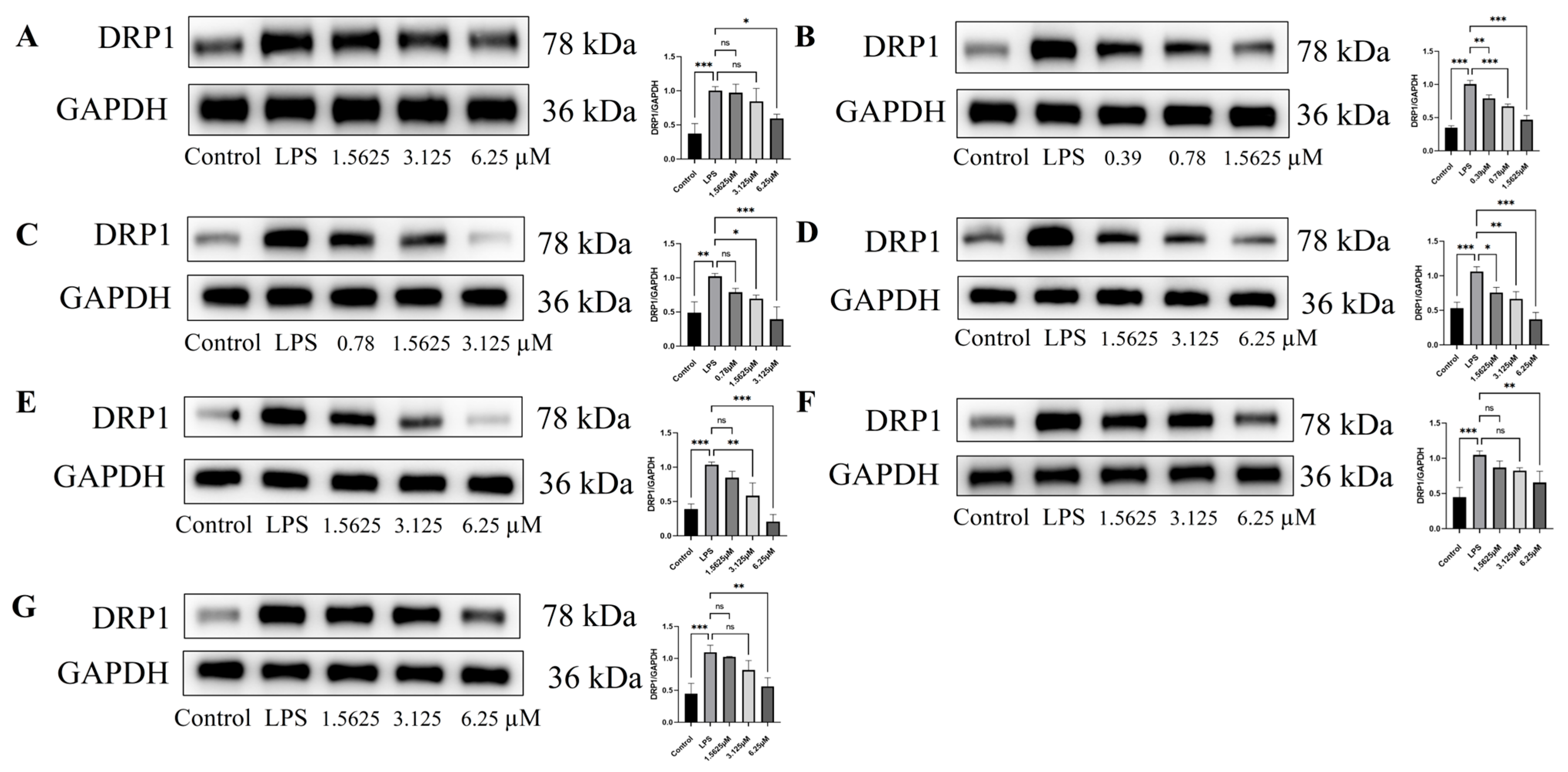
2.7. Effect of Compound Intervention on LPS-Induced Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Endothelial Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Protocols
3.2. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS Parameters
3.3. Plant Material
3.4. Purification of Compounds
3.5. ECD Calculations
3.6. HUVEC Cultivation and Compound Treatment
3.7. CCK-8 Assay
3.8. Transwell Assay
3.9. ROS Detection
3.10. Mitotracker Staining
3.11. JC-1 Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Staining
3.12. Western Blot
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IR | Infrared Radiation |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| MS | Mass Spectrum |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| ECD | Electronic Circular Dichroism |
| HUVECs | Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| ECM | Endothelial Cell Medium |
References
- Qin, Y.; Zhu, J.G. Textual research on the efficacy of Rehmanniae Radix. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 33, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Zhang, K.X.; Liu, Y.; Gai, X.H.; Ren, T.; Liu, S.X.; Tian, C.W. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological actions of Rehmannia glutinosa. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2021, 52, 1772–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, H.; Hao, Y.; Du, K.; Du, H.; Ma, C.; Tu, H.; He, Y. A systematic review on botany, processing, application, phytochemistry and pharmacological action of Radix Rehmnniae. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 285, 114820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; 2020 ed.; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 1, p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, T.; Kox, W.J. Endothelium function in sepsis. Inflamm. Res. 2000, 49, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dolmatova, E.V.; Wang, K.; Mandavilli, R.; Griendling, K.K. The effects of sepsis on endothelium and clinical implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zou, Q.L.; Feng, L.N.; Fan, S.Y.; He, C.; Zhang, D.D.; Kong, P. Mitochondrial dynamics homeostasis and vascular remodeling diseases. Chem. Life 2024, 44, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X.S.; Yang, S.; Chen, X.M. Role of mitochondrial injury in lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular endothelial cell apoptosis. J. Chongqing Med. Univ. 2020, 45, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.X.; Zhang, T.G.; Miao, C.Y. Mitochondrial oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cell and atherosclerosis. Pharm. Pract. Serv. 2023, 41, 329–334+388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Zeng, M.N.; Kan, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Jia, J.F.; Liu, M.; Guo, P.L.; Wang, R.; Feng, W.S.; Zheng, X.K. Effects of Rehmannia glutinosa on LPS-induced septic acute kidney injury through estrogen receptors. Chin. J. New Drugs Clin. Rem. 2023, 42, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.P. Clinical Study of Xijiao Dihuang Decoction in the Treatment of Sepsis (Tipe of Terrific Heat In Vivo). Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, C.; Kulka, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, F. Occurrence and biological activities of eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuyama, K.T.; Fortkamp, D.; Abraham, W.R. Eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from fungi and their medicinal potential. Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.K.; Liu, Y.Y.; Feng, W.S.; Wang, Y.Z.; Guo, Y.H. Development in research of natural phenylethanoid glycosides. Chin. J. New Drugs. 2011, 20, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H. Remophilanetriol: A new eremophilane from the roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005, 26, 1303–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.; Wang, Y.D.; Fang, H.Q.; Sun, G.B.; Ding, G. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS-based targeted discovery of chetomin analogues from Chaetomium cochliodes. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Fang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Ding, G. Bioactive metabolites from the dusty seeds of Gastrodia elata Bl., based on metabolomics and UPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with molecular network strategy. Plants 2025, 14, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Cao, Y.G.; Kan, Y.X.; Ren, Y.J.; Zeng, M.N.; Wang, M.N.; He, C.; Chen, X.; Zheng, X.K.; Feng, W.S. Two new eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from the fresh roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Phytochem. Lett. 2021, 42, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Fu, H.Z.; Zhou, G.P.; Liao, Y.Y.; Yuan, M.M.; Guo, Q.; Yan, Q.W. Chemical constituents of Callicarpa kwangtungensis. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form. 2015, 21, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Zhou, M.Y.; Shen, P.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Chu, C.; Ge, Z.W.; Yan, J.Z. Chemical constituents from Rehmannia glutinosa. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2011, 36, 3125–3129. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, H.; Nishimura, H.; Chin, M.; Mitsuhashi, H. Hydroxycinnamic acid esters of phenethylalcohol glycosides from Rehmannia glutinosa var. purpurea. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Guo, Z.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Wu, Z.J. Recent (2000-2015) developments in the analysis of minor unknown natural products based on characteristic fragment information using LC-MS. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Study on the Mass Spectrometric Analytical Method and Correlation Spectroscopy of LC-MS/NMR of Phenylethanoid Glycosides and Their Complex Mixtures. Master’s Thesis, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, K.E.; Tagliaferro, A.R.; Bobilya, D.J. Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Muzashvili, T.S.; Georgiev, M.I. Advances in the biotechnological glycosylation of valuable flavonoids. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Zhao, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wu, C.L.; Lai, X.F.; Zhao, W.X.; Zhang, M. The synthesis of methylated epigallocatechin gallate. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2015, 51, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Hou, B.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.-L.; Huang, Y.-W.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Z.-M.; Zi, C.-T.; et al. Synthesis, antioxidant activity, and density functional theory study of catechin derivatives. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 54136–54141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorova, L.D.; Popkov, V.A.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Silachev, D.N.; Pevzner, I.B.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Babenko, V.A.; Zorov, S.D.; Balakireva, A.V.; Juhaszova, M.; et al. Mitochondrial membrane potential. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 552, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagawati, M.; Arroum, T.; Webeling, N.; Montoro, A.G.; Mootz, H.D.; Busch, K.B. The receptor subunit Tom20 is dynamically associated with the TOM complex in mitochondria of human cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2021, 32, br1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araiso, Y.; Imai, K.; Endo, T. Role of the TOM complex in protein import into mitochondria: Structural views. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2022, 91, 679–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacinska, A.; Koehler, C.M.; Milenkovic, D.; Lithgow, T.; Pfanner, N. Importing mitochondrial proteins: Machineries and mechanisms. Cell 2009, 138, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Ren, K.D.; Luan, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y. Mitochondrial dynamics: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets of vascular diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 770574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Zablocki, D.; Sadoshima, J. The role of Drp1 in mitophagy and cell death in the heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 142, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, J.Y.; Connor, M.K.; Gordon, J.W.; Yano, M.; Mori, M.; Hood, D.A. Tom20-mediated mitochondrial protein import in muscle cells during differentiation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000, 279, C1393–C1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Pei, H.F.; Duan, H.X.; Wei, F.P.; Yan, B.W.; Wang, W.; Tao, L. Research on mitochondrial translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane complex in cardiovascular diseases. Chin. Heart J. 2014, 26, 214–217+221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youle, R.J.; van der Bliek, A.M. Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress. Science 2012, 337, 1062–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandan, P.K.; Job, A.T.; Ramasamy, T. DRP1 association in inflammation and metastasis: A review. Curr. Drug Targets 2024, 25, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.F.; Chen, L.; Ning, E.J.; Gui, R.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Wang, X.B.; Li, X. Study on antioxidant activity of seven components in Forsythia suspensa leaves. Feed Res. 2023, 46, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, S.; D’Abrosca, B.; Pascarella, M.T.; Letizia, M.; Uzzo, P.; Piscopo, V.; Fiorentino, A. Antioxidant efficacy of iridoid and phenylethanoid glycosides from the medicinal plant Teucrium chamaedris in cell-free systems. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6173–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Cao, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.H.; Ren, Y.J.; Zeng, M.N.; Liu, Y.L.; Chen, X.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhao, B.X.; Zheng, X.K.; et al. Five new eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from the fresh roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Fitoterapia 2024, 175, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubiani, J.R.; Zeraik, M.L.; Oliveira, C.M.; Ximenes, V.F.; Nogueira, C.R.; Fonseca, L.M.; Silva, D.H.; Bolzani, V.S.; Araujo, A.R. Biologically active eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from Camarops sp., an endophytic fungus isolated from Alibertia macrophylla. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tao, P.; Wang, Y.J.; Hou, Y.F.; He, S.M. Molecular mechanism of antioxidant activity of phenylethanoid glycosides from Cistanches Herba based on network pharmacology. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2022, 39, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Qi, S.M.; Ling, L.F.; Feng, Z.Y.; Li, Q. Salidroside protects PC12 cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis via suppressing NOX2-ROS-MAPKs signaling pathway. J. South. Med. Univ. 2016, 37, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Cao, Y.G.; Zeng, M.N.; Wang, M.N.; Chen, X.; Fang, X.L.; He, C.; Ren, Y.J.; Zheng, X.K.; Feng, W.S. A new eremophilanolide from the fresh roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. R. Nat. Prod. 2022, 16, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.S.; Li, M.; Zheng, X.K.; Song, K.; Wang, J.C.; Li, C.G.; Zhang, M.H. Study on chemical constituents of immunosuppressive parts from the roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Chin. Pharm. J. 2014, 49, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar]
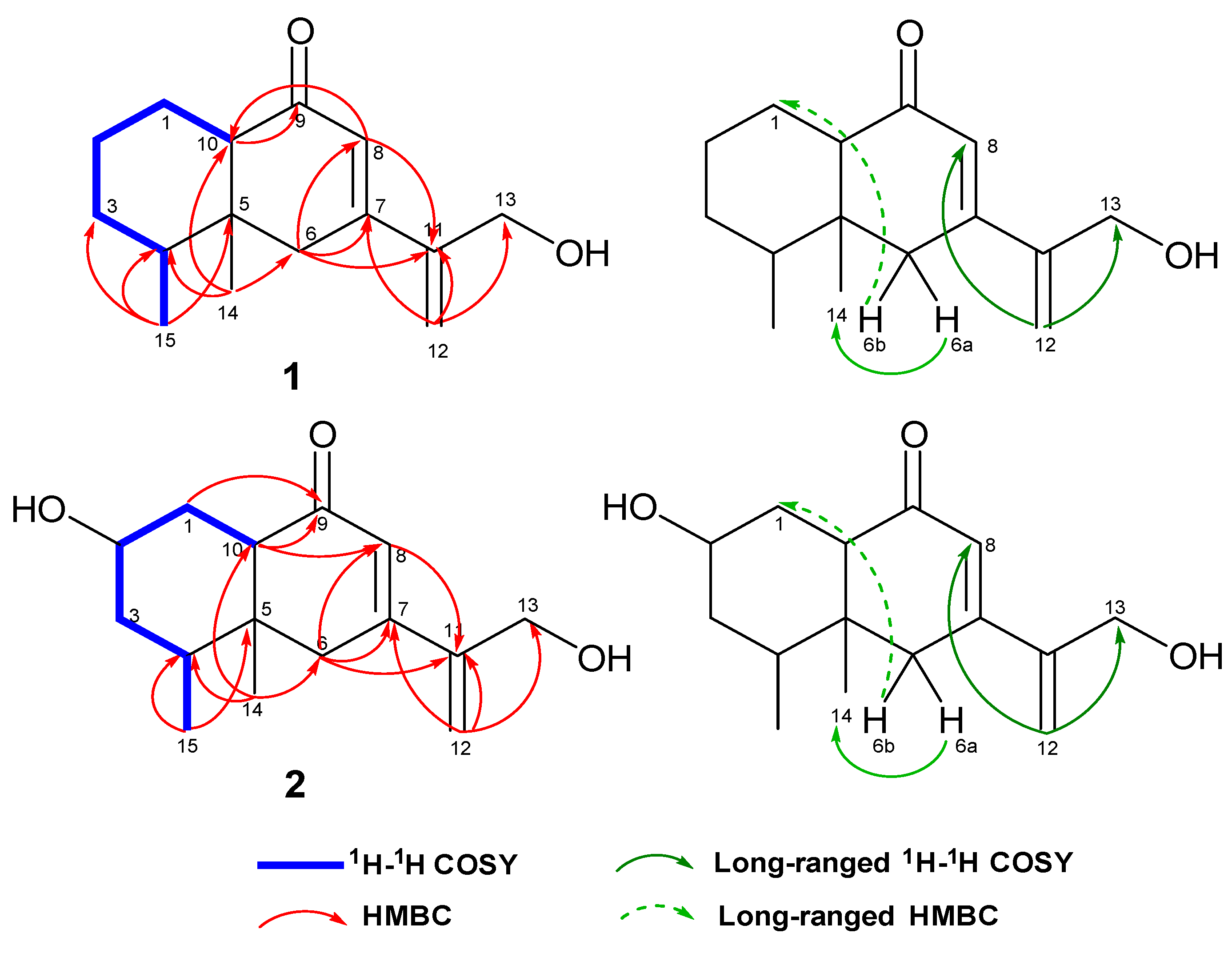
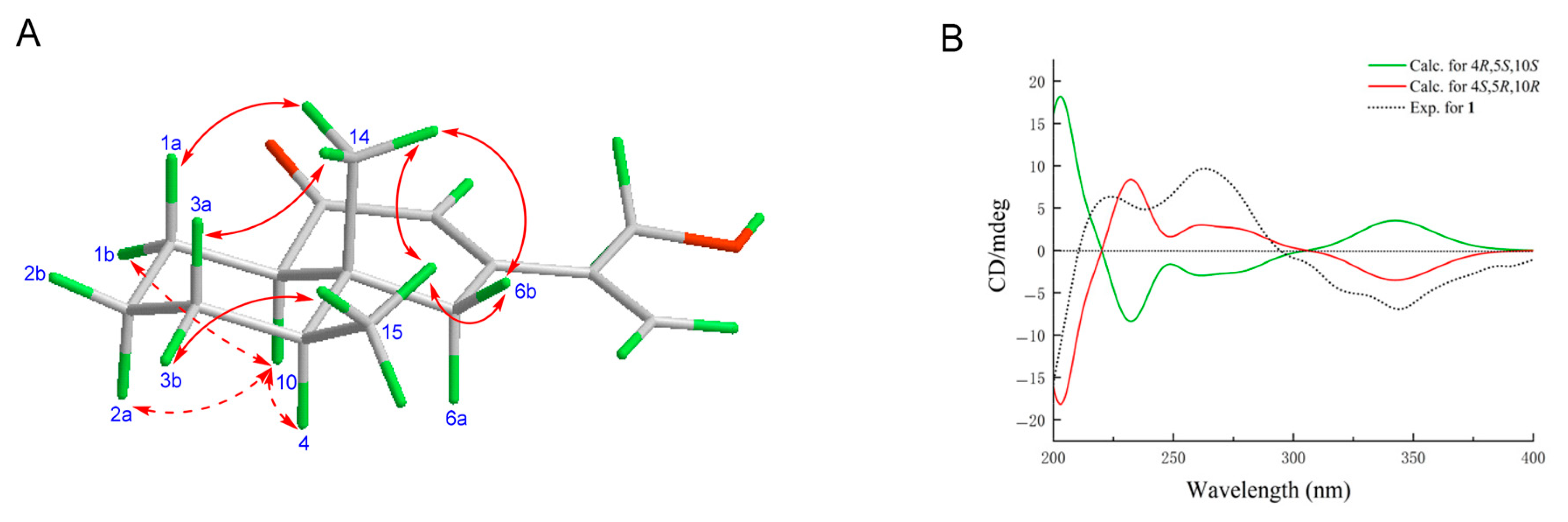
| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH a (mult, J in Hz) | δC b, Type | δH a (mult, J in Hz) | δC b, Type | |
| 1a | 1.29, overlapped | 20.7, CH2 | 1.32, dd, (11.5, 13.0) | 30.1, CH2 |
| 1b | 2.00, ddd, (11.5, 3.0, 1.5) | 2.31, ddd, (13.0, 4.5, 2.5) | ||
| 2a | 1.30, overlapped | 25.3, CH2 | 3.70, tt, (11.5, 4.5) | 69.9, CH |
| 2b | 1.83, m | |||
| 3a | 1.25, overlapped | 30.2, CH2 | 1.28, td, (13.0, 11.5) | 39.1, CH2 |
| 3b | 1.44, ddd, (13.0, 5.0, 2.5) | 1.78, ddd, (13.0, 4.5, 2.5) | ||
| 4 | 1.55, m | 43.3, CH | 1.63, overlapped | 41.4, CH |
| 5 | 40.0, C | 38.9, C | ||
| 6a | 2.30, dd, (2.5, 17.5) | 41.1, CH2 | 2.27, overlapped | 40.7, CH2 |
| 6b | 2.68, d, (17.5) | 2.70, d, (17.5) | ||
| 7 | 151.8, C | 151.9, C | ||
| 8 | 6.05, d, (2.5) | 124.0, CH | 6.08, d, (2.5) | 123.6, CH |
| 9 | 201.9, C | 200.2, C | ||
| 10 | 2.21, dd, (3.5, 11.5) | 55.2, CH | 2.26, overlapped | 53.1, CH |
| 11 | 146.4, C | 145.9, C | ||
| 12 | 5.58, s 5.60, s | 117.3, CH2 | 5.60, s 5.61, s | 117.5, CH2 |
| 13 | 4.38, s | 63.8, CH2 | 4.39, s | 63.4, CH2 |
| 14 | 0.77, s | 11.9, CH3 | 0.78, s | 11.7, CH3 |
| 15 | 0.90, d, (7.0) | 15.4, CH3 | 0.96, d, (7.0) | 14.9, CH3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, L.; Lu, M.; Fang, H.; Li, C.; Qu, H.; Ding, G. Secondary Metabolites from Rehmannia glutinosa Protect Mitochondrial Function in LPS-Injured Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081125
Zhong L, Lu M, Fang H, Li C, Qu H, Ding G. Secondary Metabolites from Rehmannia glutinosa Protect Mitochondrial Function in LPS-Injured Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(8):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081125
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Liwen, Mengkai Lu, Huiqi Fang, Chao Li, Hua Qu, and Gang Ding. 2025. "Secondary Metabolites from Rehmannia glutinosa Protect Mitochondrial Function in LPS-Injured Endothelial Cells" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 8: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081125
APA StyleZhong, L., Lu, M., Fang, H., Li, C., Qu, H., & Ding, G. (2025). Secondary Metabolites from Rehmannia glutinosa Protect Mitochondrial Function in LPS-Injured Endothelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 18(8), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18081125









