Nanoemulsions of Cannabidiol, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, and Their Combination Similarly Exerted Anticonvulsant and Antioxidant Effects in Mice Treated with Pentylenetetrazole
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Licuri Oil
2.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurement
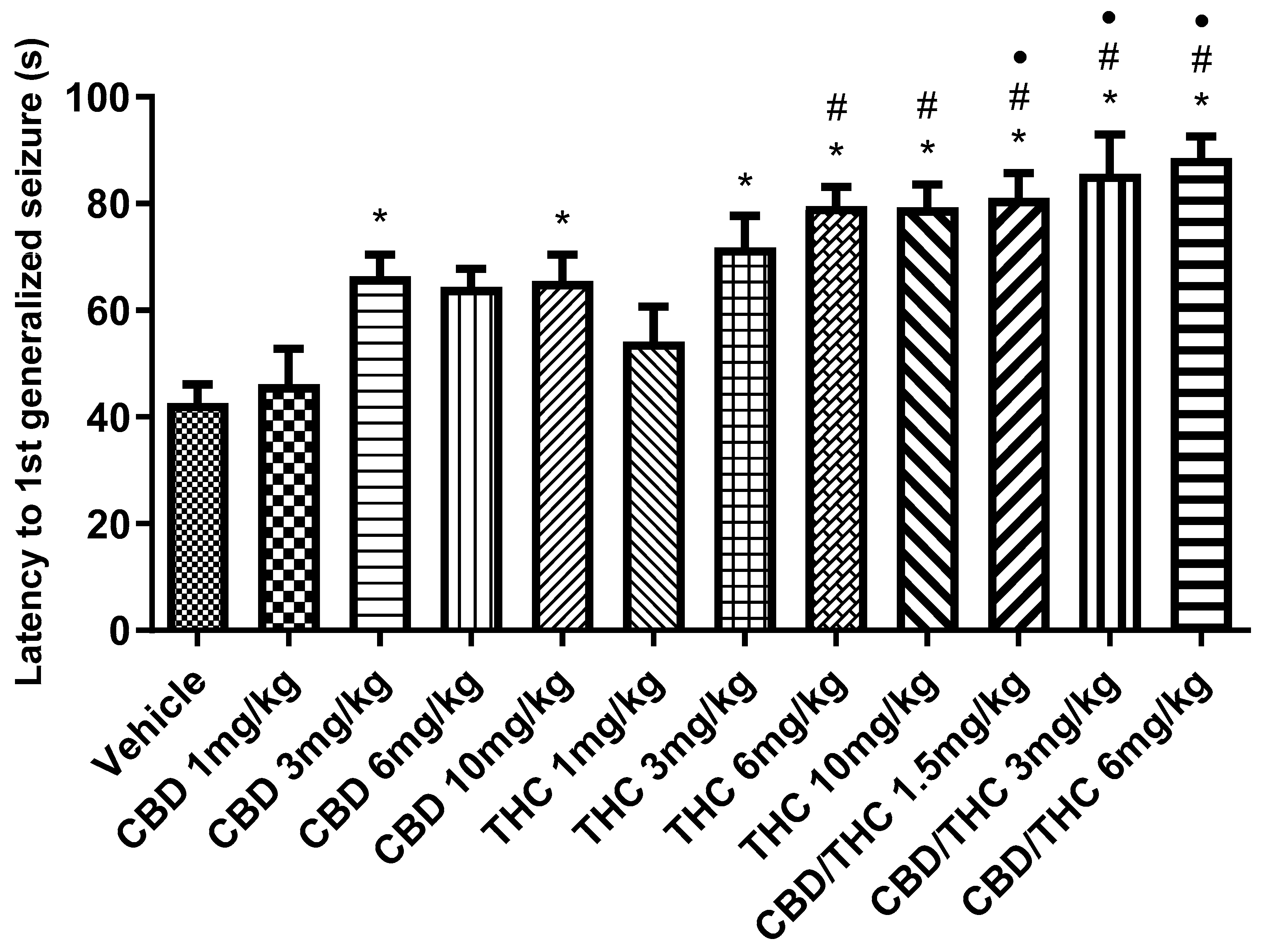
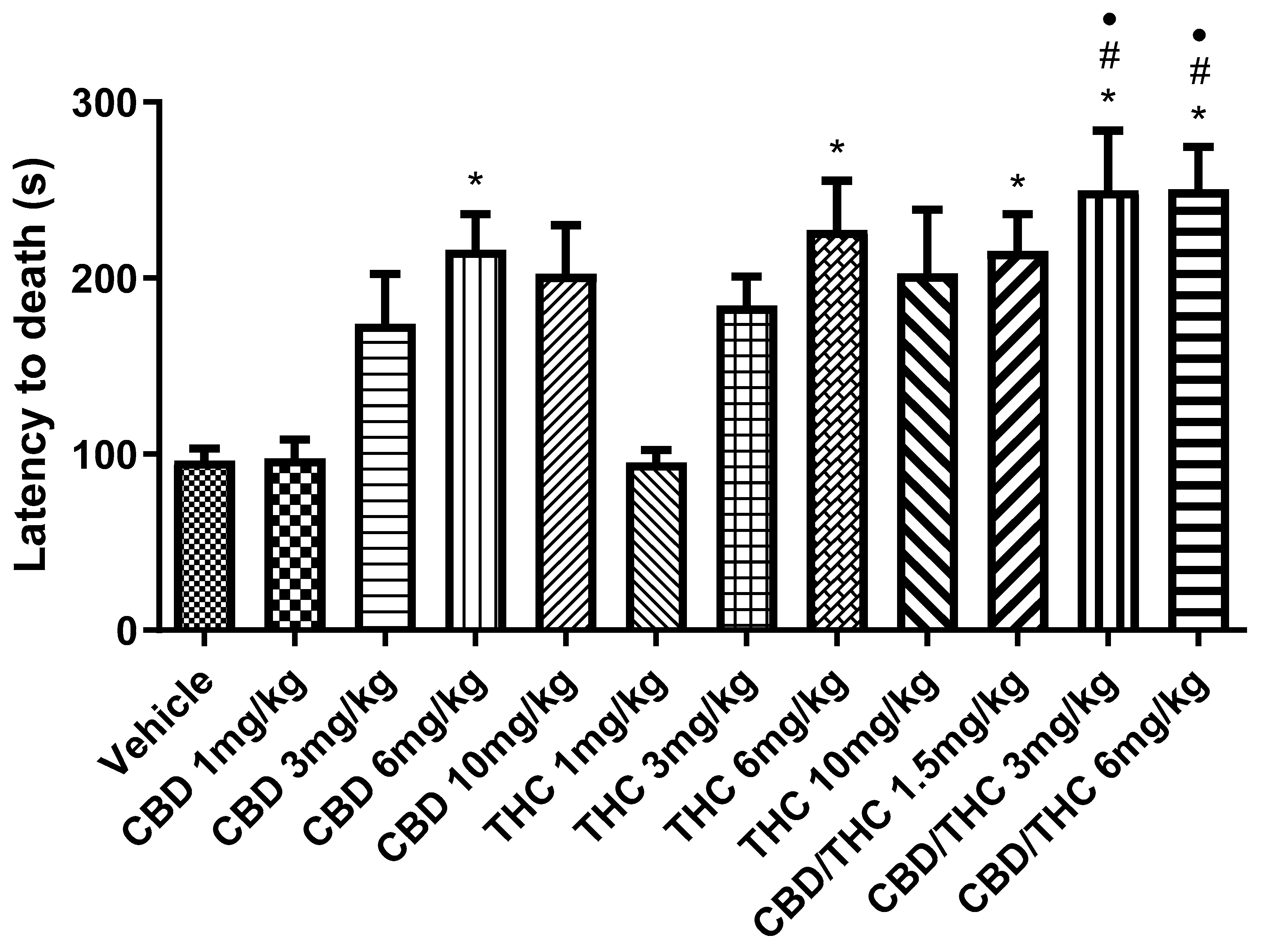
2.3. Effects of Combined or Separately Administered Cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) on Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Acute Seizures
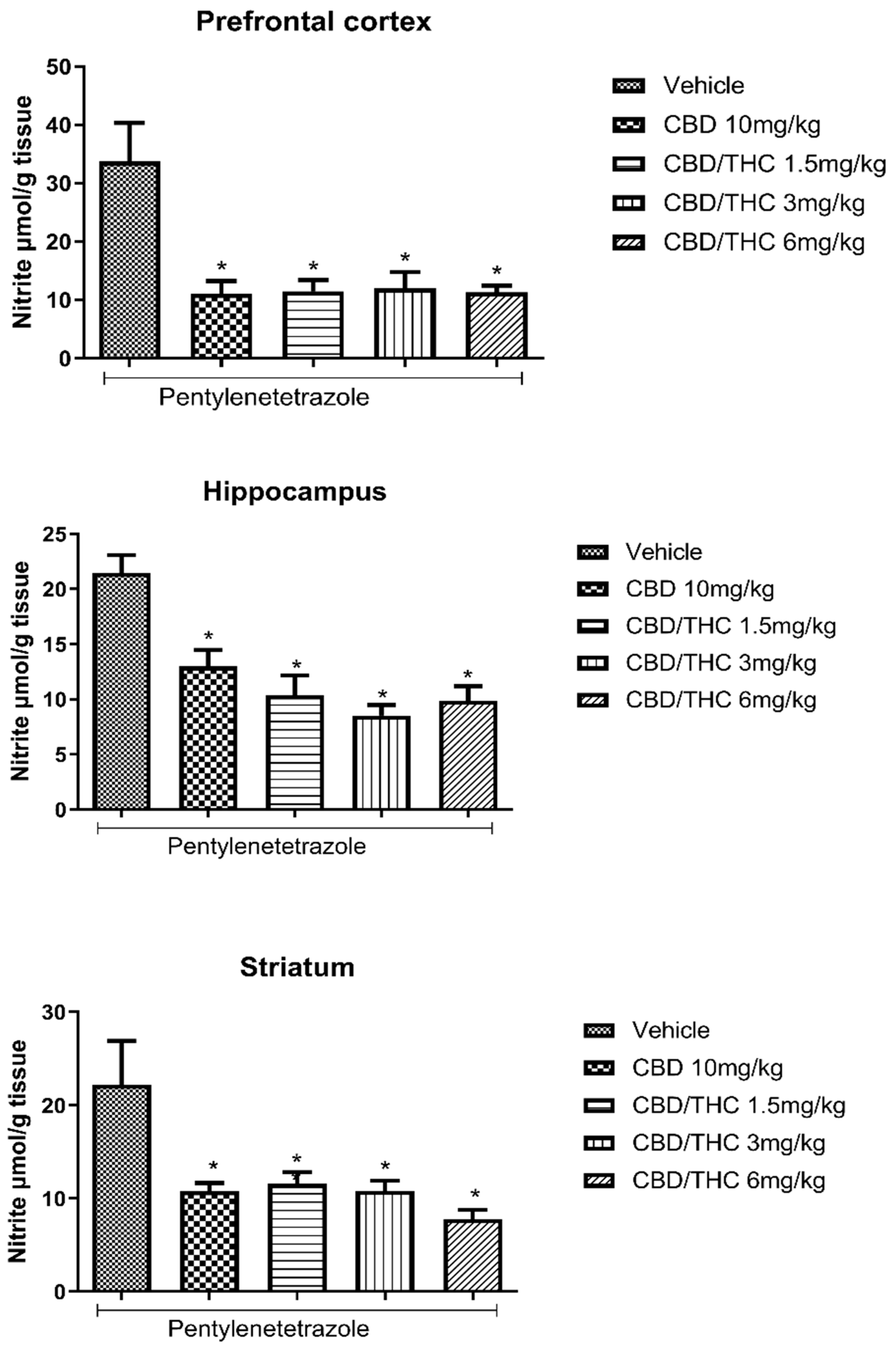
2.4. Effect of Cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD/Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Combination on the Brain Content of Nitrate/Nitrite in the Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) Model of Acute Seizures
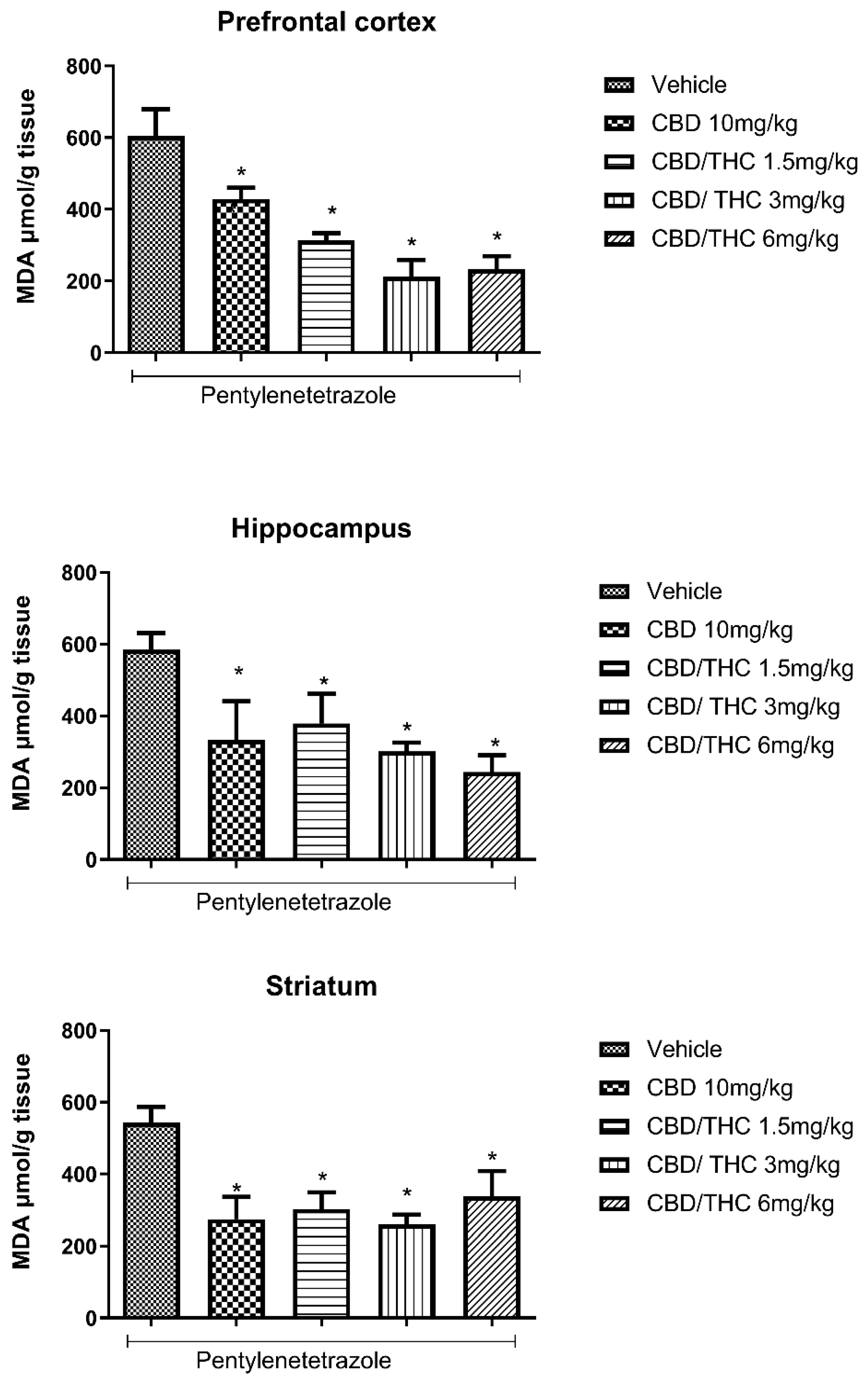
2.5. Effect of Cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD/Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Combination on Lipid Peroxidation in the Brain of Pentylenetetrazole Acutely Treated Mice
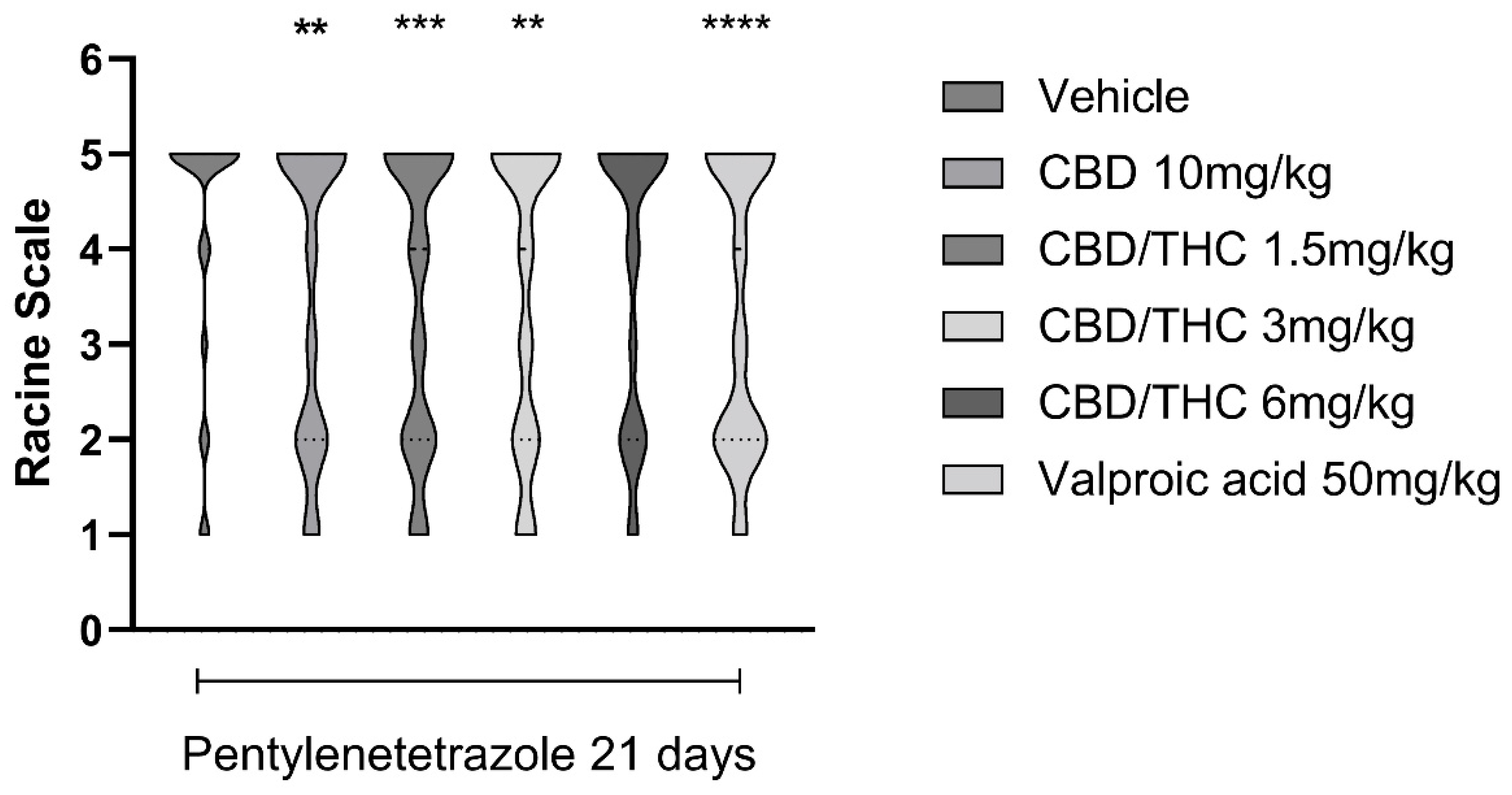
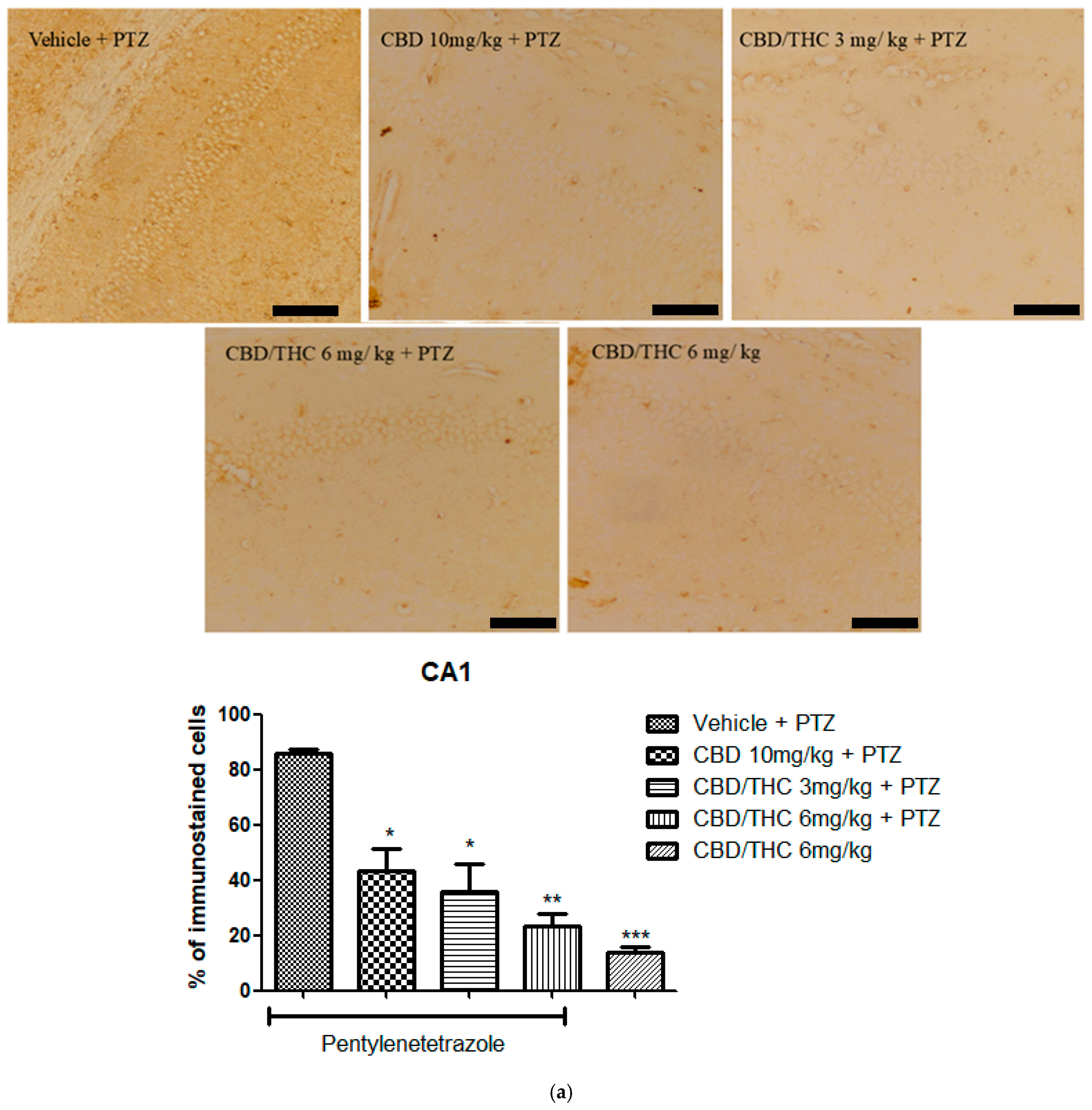
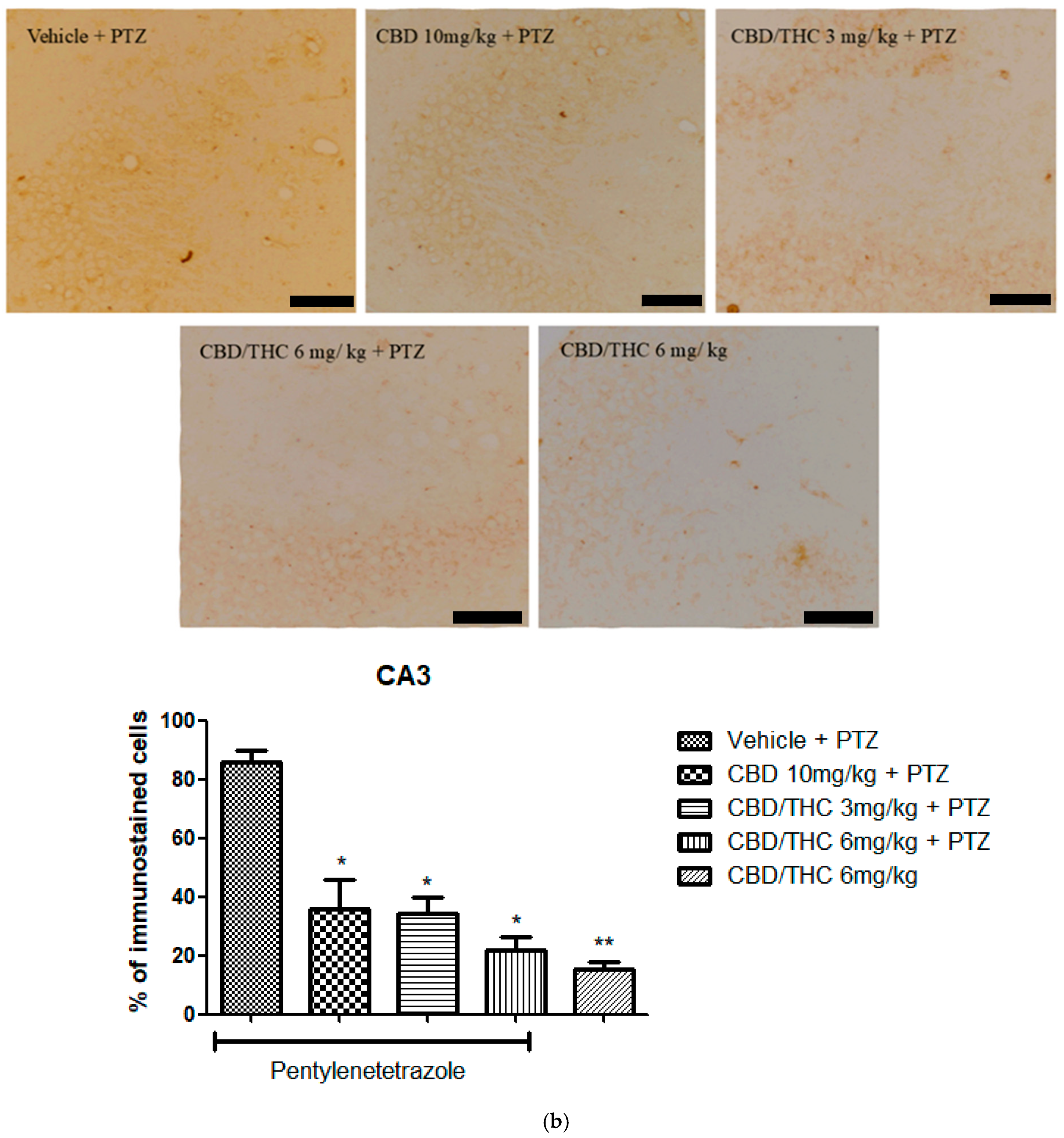
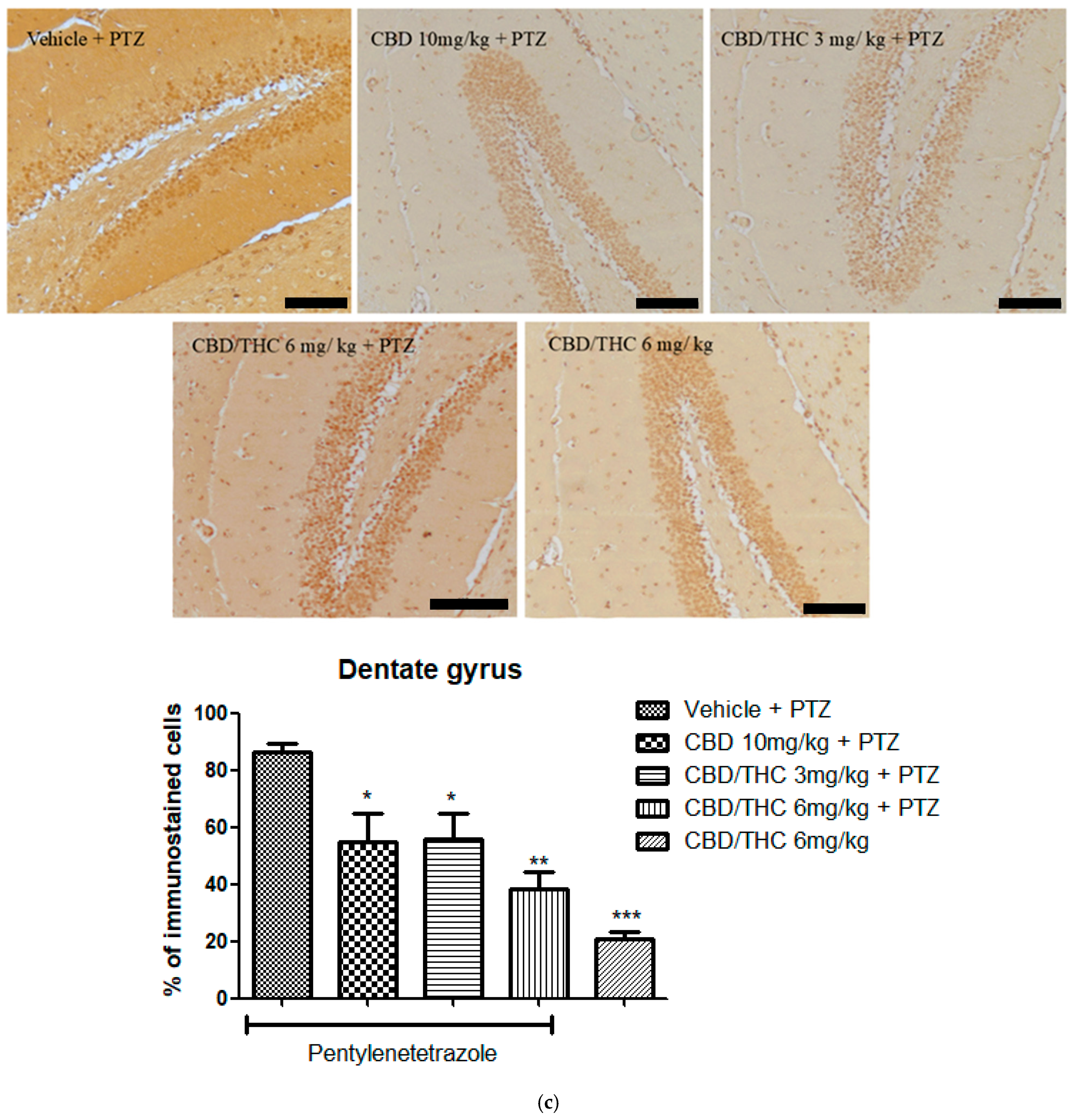
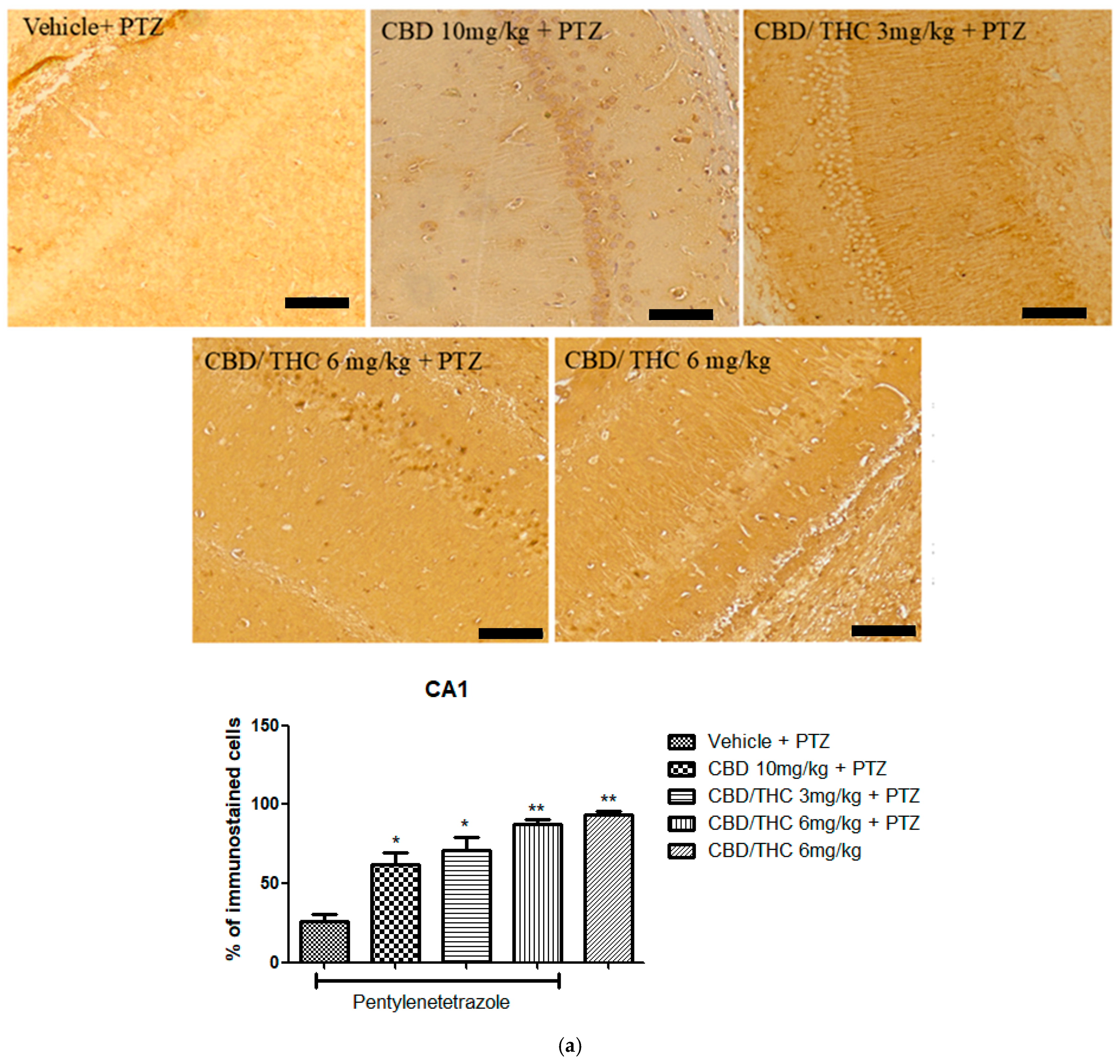
2.6. Effects of Cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD/Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Combination on Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Kindling
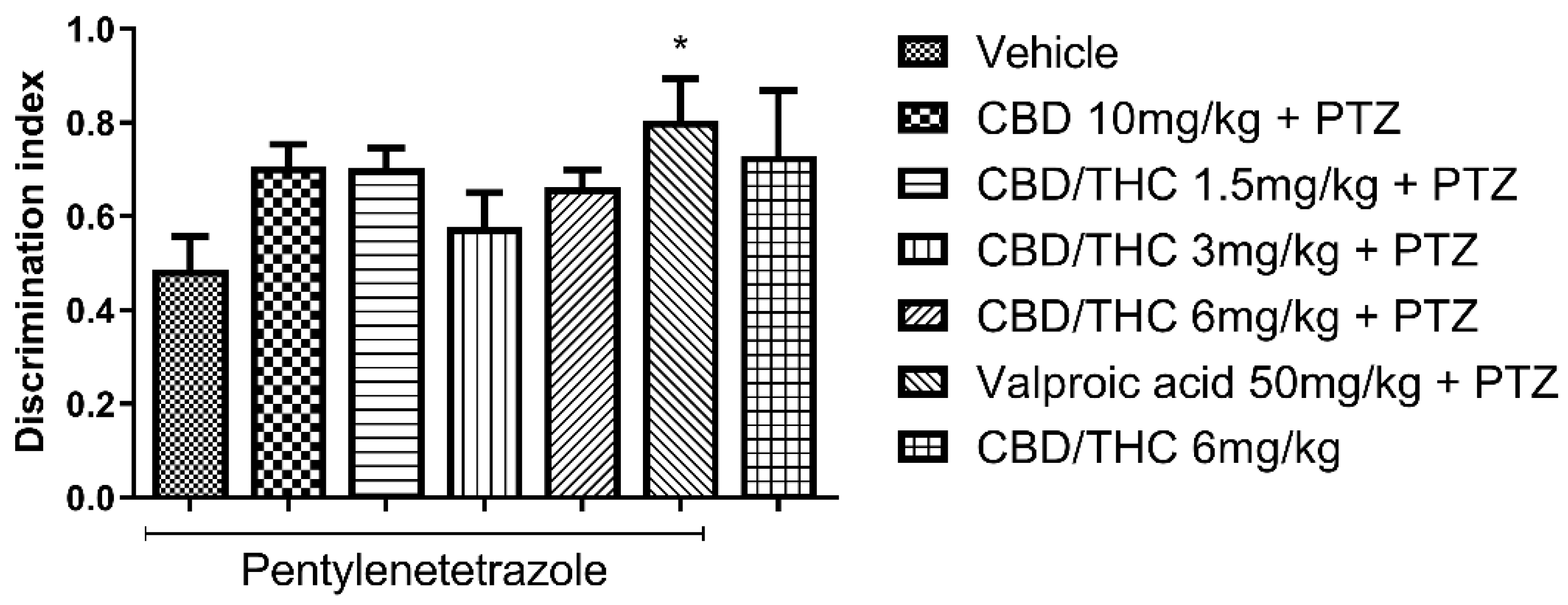
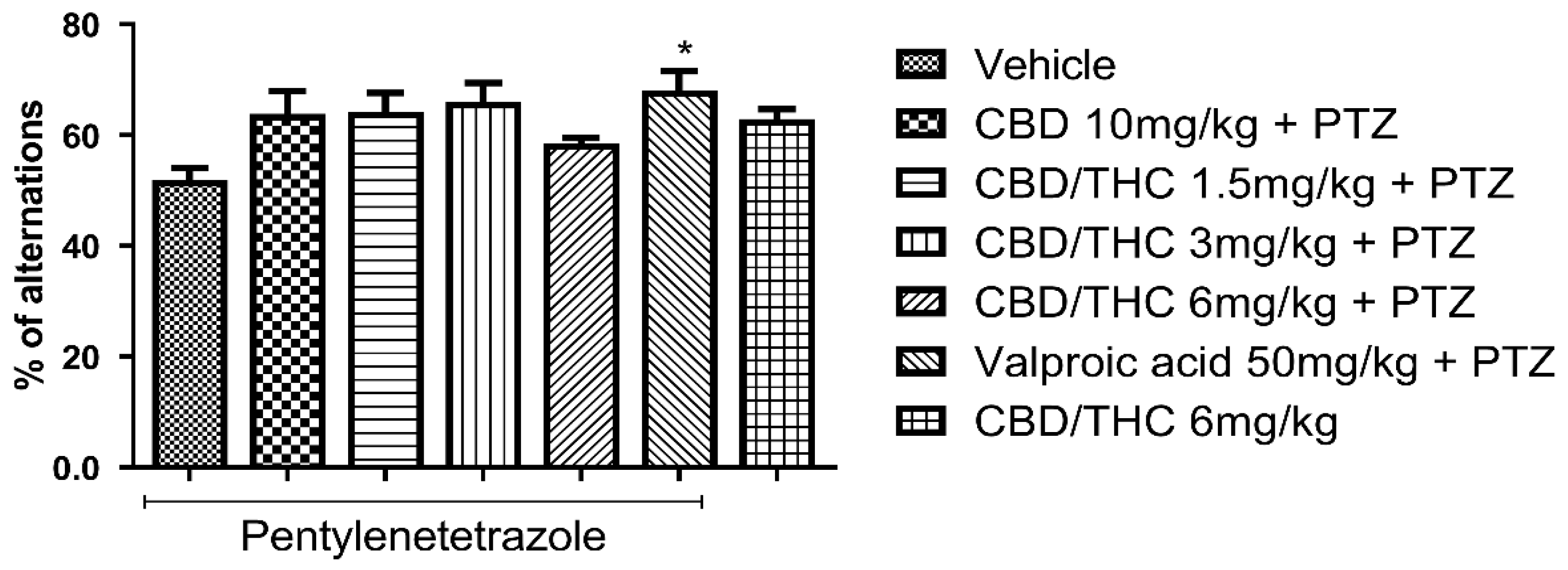
2.7. Changes in Behavioral Test Performance of Cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD/Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Combination-Treated Mice in Consequence of Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Kindling
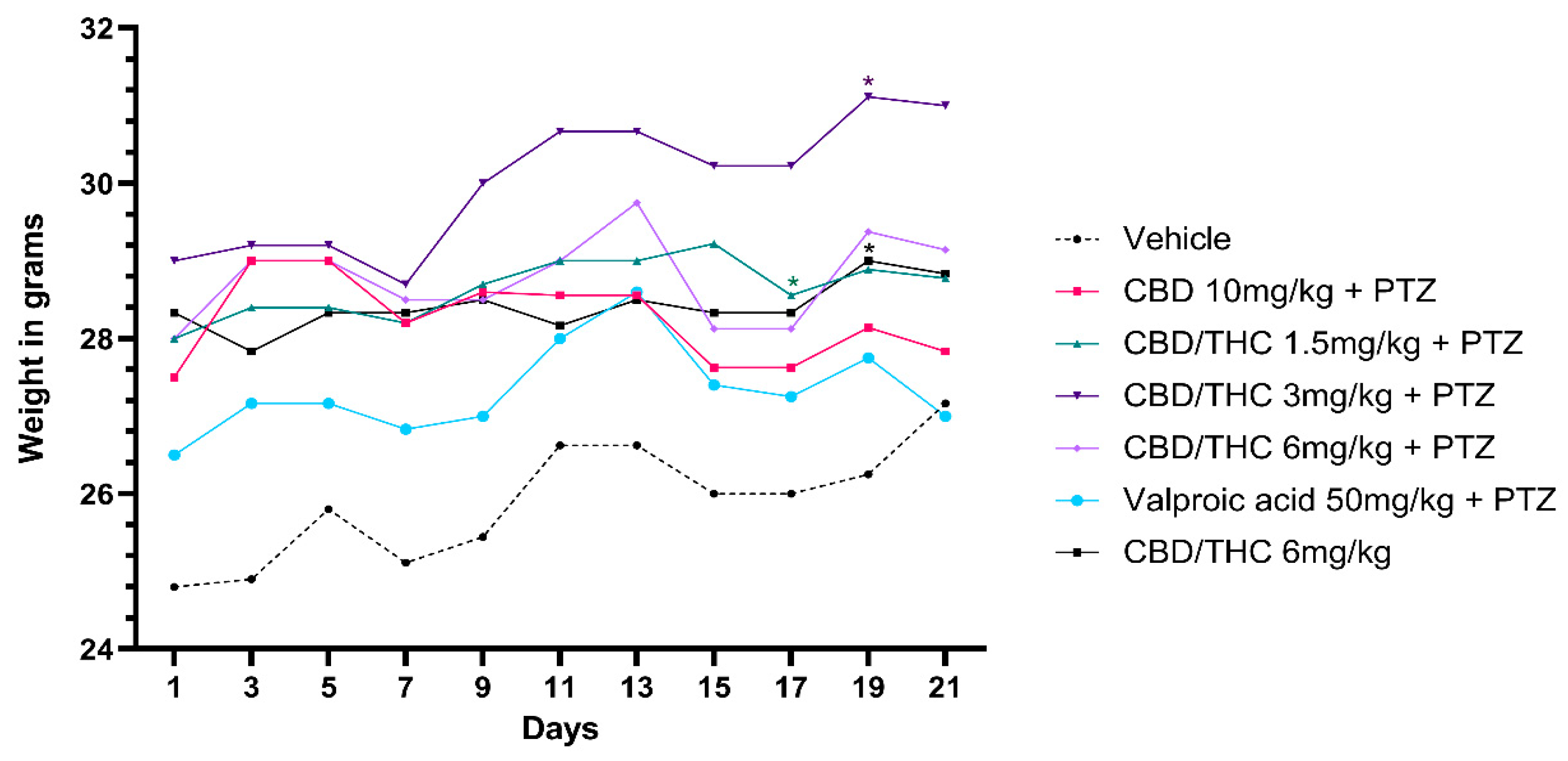
2.8. Effects of Cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD/Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Combination on Body Weight
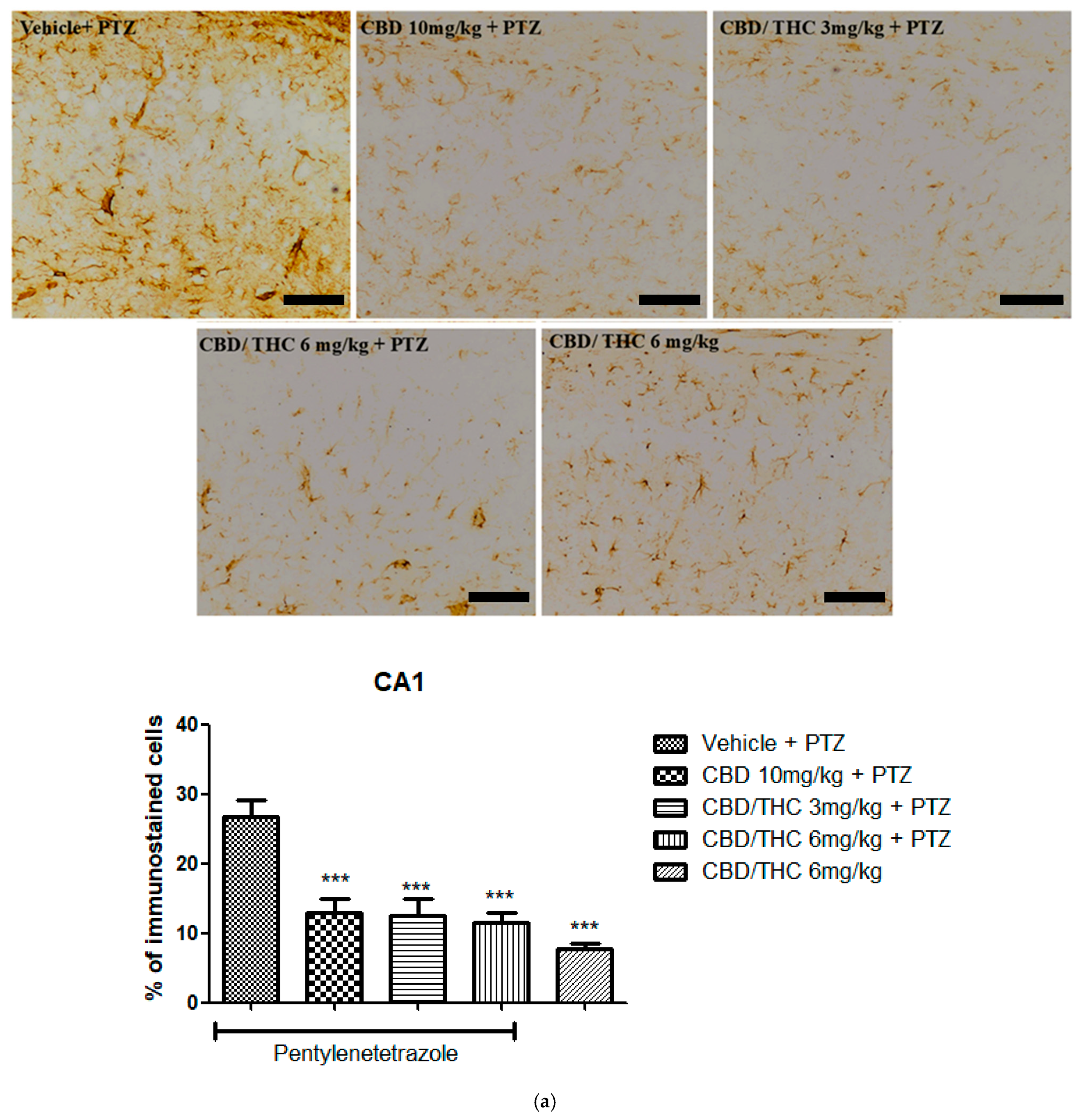
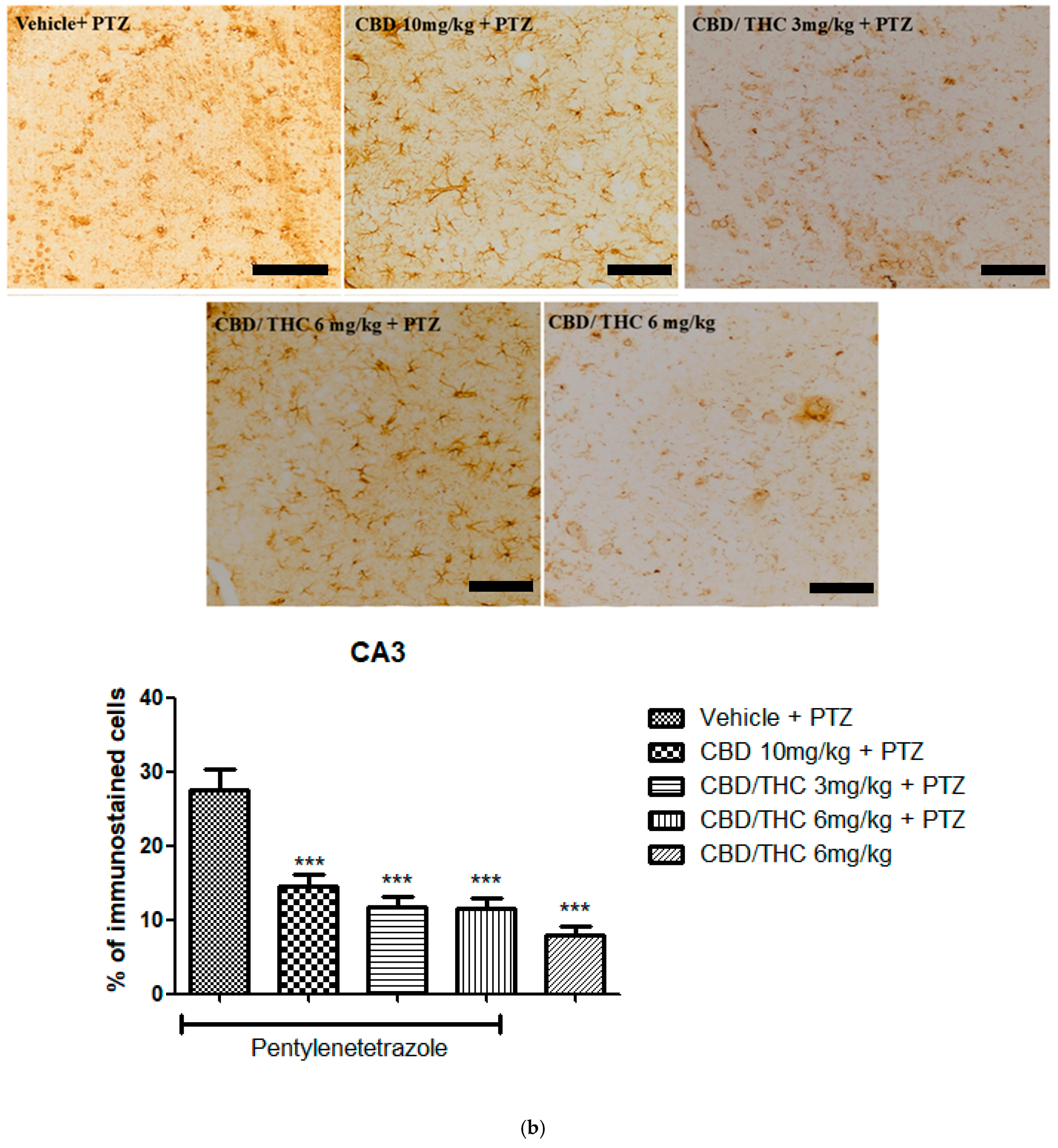
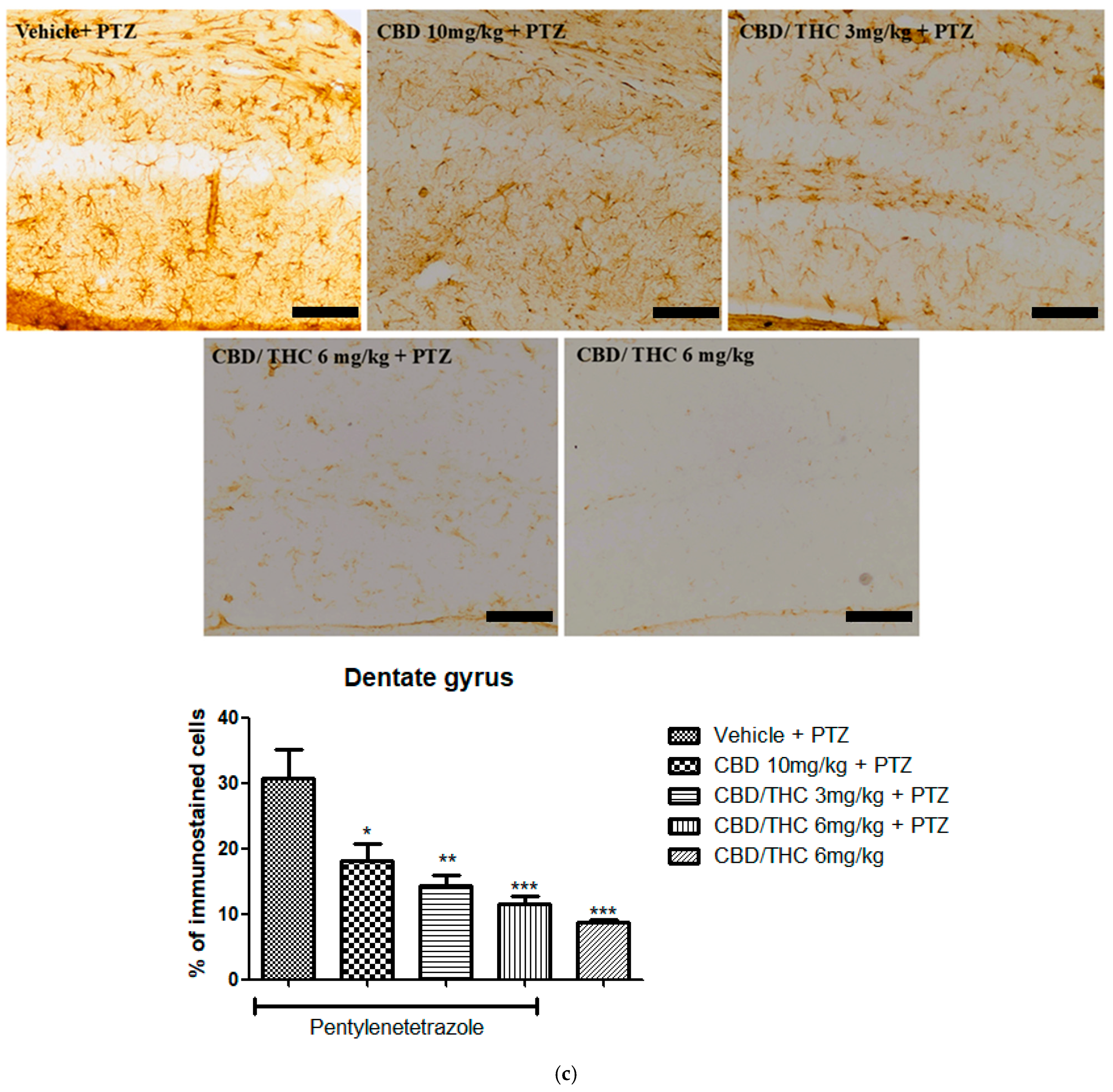
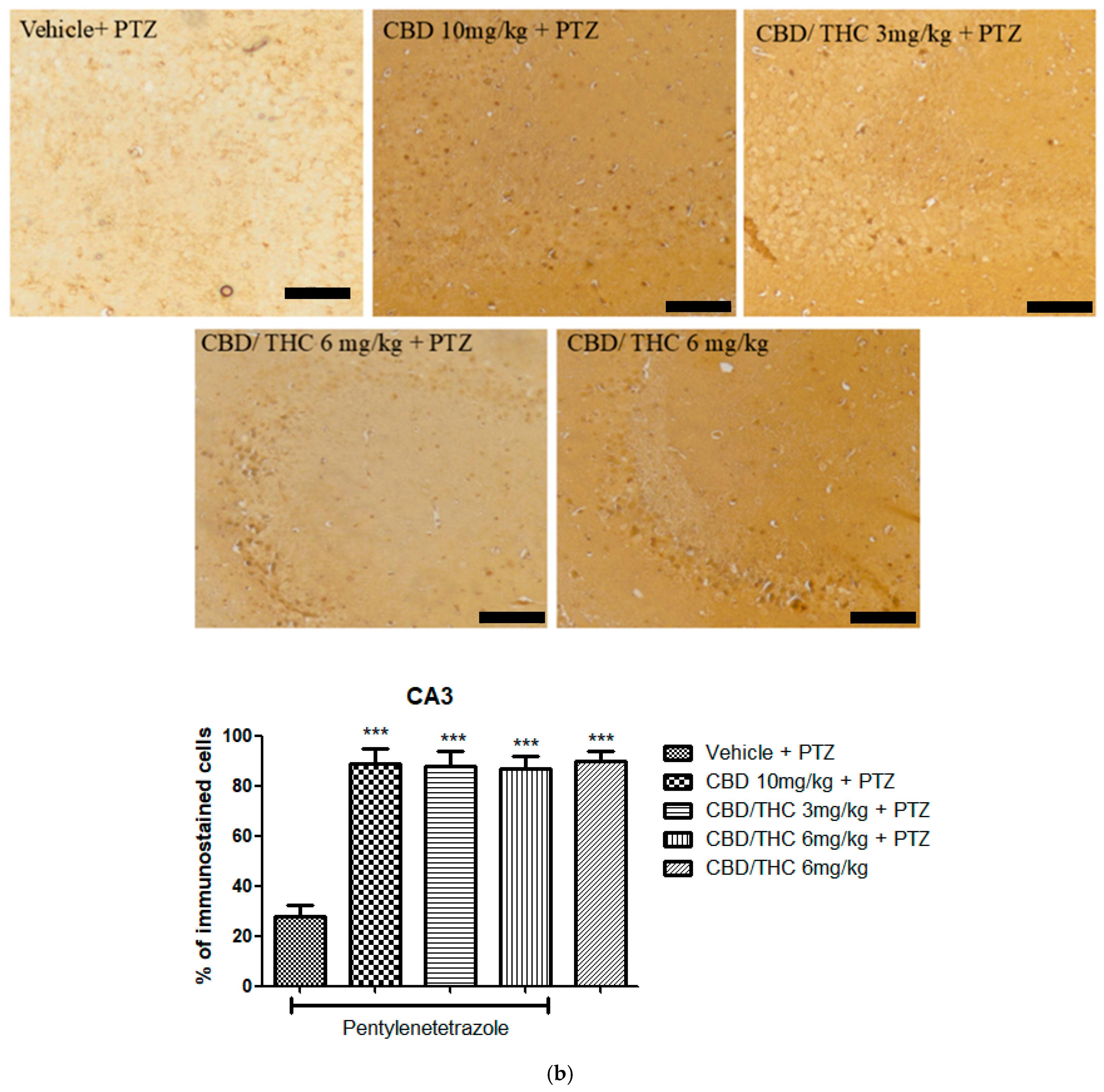
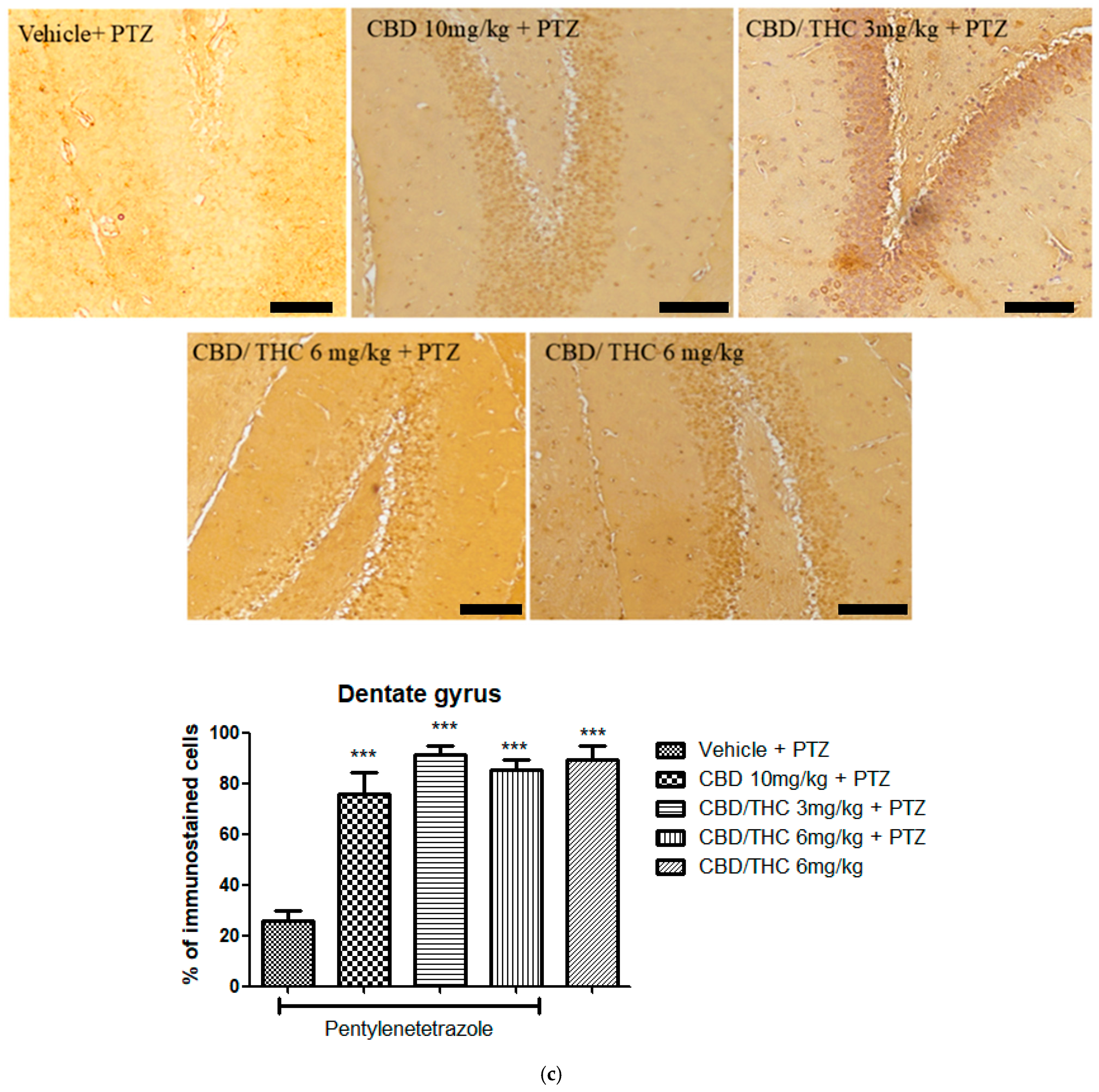
2.9. Effects of Cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD/Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Combination on Astrocyte Activation and After Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Kindling
2.10. Effects of Cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD/Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Combination on Markers of Network Activity After Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-Induced Kindling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Preparation of Nanoemulsions
4.3. Animals and Treatments
4.4. Behavioral Analysis
4.5. Evaluation of Oxidation in the Brain
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Beghi, E. The Epidemiology of Epilepsy. Neuroepidemiology 2020, 54, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.; French, J.A.; Maccarrone, M. Safety, efficacy, and mechanisms of action of cannabinoids in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, M.-; Ben-Eltriki, M.; Mansell, H.; Lê, M.L.; Huntsman, R.J.; Finkelstein, Y.; Kelly, L.E. Cannabinoids used for medical purposes in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Jama Pediatr. 2024, 178, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva Júnior, W.S.; Farias, M.R. A eficácia terapêutica da Cannabis no tratamento da Epilepsia: Uma revisão sistemática. Braz. J. Dev. 2021, 7, 70956–70963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Hai, A.; Domb, A.J.; Hoffman, A. Strategies for enhancing the oral bioavailability of cannabinoids. Expert Op. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, M.; Nakano, Y.; Tajima, M.; Sugiyama, E.; Sato, V.H.; Inada, M.; Sato, H. Nonlinear disposition and metabolic interactions of cannabidiol through CYP3A inhibition in vivo in rats. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2020, 5, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, N.V.L.S.; Ganga Raju, M.; Edunoori, K.; Papani, J. Nano Emulsion: The Targeted Drug Delivery in the Therapy of Epilepsy. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2023, 24, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Bonvento, G.; Bolaños, J.P. Astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation shapes brain activity. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1546–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet, J.; Vainchtein, I.D.; Spano, C.; Giordano, C.; Bordini, D.; Curia, G.; Dominici, M.; Boddeke, H.W.G.M.; Eggen, B.J.L.; Biagini, G. Microglia are less pro-inflammatory than myeloid infiltrates in the hippocampus of mice exposed to status epilepticus. Glia 2016, 64, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.T.; Kim, R.D.; Molofsky, A.V.; Liddelow, S.A. Astrocyte-immune cell interactions in physiology and pathology. Immunity 2021, 54, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Farina, C. Astrocytes as key regulators of brain inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curia, G.; Lucchi, C.; Vinet, J.; Gualtieri, F.; Marinelli, C.; Torsello, A.; Costantino, L.; Biagini, G. Pathophysiogenesis of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: Is prevention of damage antiepileptogenic? Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escartin, C.; Galea, E.; Lakatos, A.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Petzold, G.C.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; Steinhäuser, C.; Volterra, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Agarwal, A.; et al. Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, F.; Miyajima, M.; Maeda, Y.; Tsuzukiyama, H.; Saito, K.; Mikoshiba, K.; Horiuchi, H.; Cheung, D.L.; Nabekura, J.; Sugita, K.; et al. Reactive astrocyte-driven epileptogenesis is induced by microglia initially activated following status epilepticus. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e135391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.W.; Ben Haim, L.; Schirmer, L.; Tyzack, G.E.; Tolman, M.; Miller, J.G.; Tsai, H.H.; Chang, S.M.; Molofsky, A.M.; Yang, J.; et al. Kir4.1-dependent astrocyte-fast motor neuron interactions are required for peak strength. Neuron 2018, 98, 306–319.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinboshi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Ohno, Y. Role of astrocytic inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) 4.1 channels in epileptogenesis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 626658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, N.; Kunisawa, T.; Shimizu, K. Emerging Roles of Astrocyte Kir4.1 Channels in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Brain Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łątka, K.; Jończyk, J.; Bajda, M. γ-Aminobutyric acid transporters as relevant biological target: Their function, structure, inhibitors and role in the therapy of different diseases. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 750–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.K.; Clausen, R.P.; Larsson, O.M.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Schousboe, A.; White, H.S. Synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA transporters as targets for antiepileptic drugs. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Zheng, J.C. Astrocytes: GABAceptive and GABAergic cells in the brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 892497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.L.; Schousboe, A.; Wellendorph, P. GABA transporters in the brain: Pharmacology and implications for epilepsy. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 162, 105375. [Google Scholar]
- Schijins, O.E.M.G.; Bisschop, J.; Rijkers, K.; Dings, J.; Vanherle, S.; Lindsey, P.; Smeets, H.J.; Hoogland, G. GAT-1 (rs2697153) and GAT-3 (rs2272400) polymorphisms are associated with febrile seizures and temporal lobe epilepsy. Epil. Disord. 2020, 22, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuskaitis, C.J.; Rossitto, L.A.; Groff, K.J.; Dhamne, S.C.; Zhang, B.; Lalani, L.K.; Singh, A.K.; Rotenberg, A.; Sahin, M. Factors influencing the acute pentylenetetrazole-induced seizure paradigm and a literature review. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, Á.B.; Alves, A.F.; Ribeiro Portela, A.C.; Oliveira Pires, H.F.; Pessoa de Melo, M.; Medeiros Vilar Barbosa, N.M.; Bezerra Felipe, C.F. Pentylenetetrazole: A review. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 180, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Souza, T.G.; da Silva, M.M.; Feitoza, G.S.; de Melo Alcântara, L.F.; da Silva, M.A.; de Oliveira, A.M.; de Oliveira Farias de Aguiar, J.C.R.; do Amaral Ferraz Navarro, D.M.; de Aguiar Júnior, F.C.A.; da Silva, M.V.; et al. Biological safety of Syagrus coronata (Mart.) Becc. Fixed oil: Cytotoxicity, acute oral toxicity, and genotoxicity studies. J. Ethnopharm. 2021, 272, 113941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Tajima, M.; Sugiyama, E.; Sato, V.H.; Sato, H. Development of a novel nanoemulsion formulation to improve intestinal absorption of cannabidiol. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2019, 2, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Rizwanullah, M.; Mir, R.S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Amin, S. Development of cannabidiol nanoemulsion for direct nose to brain delivery: Statistical optimization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 065009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sohly, M.A.; Shahzadi, S.; Gul, W. Absorption and bioavailability of novel ultrashear nanoemulsion of cannabidiol in rats. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2023, 6, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namvar, S.A.; Mirzae, R.; Pourabdolhossein, F. Study of anti-epileptic effect of Cannabis sativa extract on pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling in male rats. J. Babol Univ. Med. Sci. 2016, 18, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Senn, L.; Cannazza, G.; Biagini, G. Receptors and channels possibly mediating the effects of phytocannabinoids on seizures and epilepsy. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, J.M.; Boison, D. The metabolic basis of epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olowe, R.; Sandouka, S.; Saadi, A.; Shekh-Ahmad, T. Approaches for reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress quantification in epilepsy. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.K.; Chen, S.D.; Lin, K.J.; Chuang, Y.C. Seizure-induced oxidative stress in status epilepticus: Is antioxidant beneficial? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Shi, R.X.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.L.; Tong, X.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wang, N.; Li, M.X.; Tong, Y.; Wang, W. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase/reactive oxygen species pathway is involved in apoptosis and pyroptosis in epilepsy. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Fabisiak, T.; Patel, M. Crosstalk between neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in epilepsy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 976953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, A.L.M.; Bucknor, E.M.V.; Castroflorio, E.; Soares, T.R.; Oliver, P.L.; Rial, D. The interconnected mechanisms of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in epilepsy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrone, G.; Balosso, S.; Pauletti, A.; Ravizza, T.; Vezzani, A. Inflammation and reactive oxygen species as disease modifiers in epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 107742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantseva, M.V.; Perez Velazquez, J.L.; Tsoraklidis, G.; Mendonca, A.J.; Adamchik, Y.; Mills, L.R.; Carlen, P.L.; Burnham, M.W. Oxidative stress is involved in seizure-induced neurodegeneration in the kindling model of epilepsy. Neuroscience 2000, 97, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.L.; Absalom, N.L.; Abelev, S.V.; Low, I.K.; Doohan, P.T.; Martin, L.J.; Chebib, M.; McGregor, I.S.; Arnold, J.C. Interactions between cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in modulating seizure susceptibility and survival in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4261–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, T.E.; Martin, R.C.; Szaflarski, J.P. Cannabidiol (CBD) and cognition in epilepsy. Epil. Behav. 2021, 124, 108316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gáll, Z.; Kelemen, K.; Tolokán, A.; Zolcseak, I.; Sável, I.; Bod, R.; Ferencz, E.; Vancea, S.; Urkon, M.; Kolcsár, M. Anticonvulsant action and long-term effects of chronic cannabidiol treatment in the rat pentylenetetrazole-kindling model of epilepsy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Baos, A.; Puig-Reyne, X.; García-Algar, Ó.; and Valverde, O. Cannabidiol attenuates cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation induced by early alcohol exposure in a mice model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk-Slomka, M.; Biala, G. Cannabidiol attenuates MK-801-induced cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia in the passive avoidance test in mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk-Slomka, M.; Slomka, T.; Biala, G. The Influence of an Acute Administration of cannabidiol or rivastigmine, alone and in combination, on scopolamine-provoked memory impairment in the passive avoidance test in mice. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.Q.; Jia, J.X.; Wang, H.; Li, S.J.; Yang, Z.J.; Wang, X.X.; Yan, X.S. Cannabidiol improves the cognitive function of SAMP8 AD model mice involving the microbiota-gut-brain axis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2024, 87, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobue, A.; Komine, O.; Endo, F.; Kakimi, C.; Miyoshi, Y.; Kawade, N.; Watanabe, S.; Saito, Y.; Murayama, S.; Saido, T.C.; et al. Microglial cannabinoid receptor type II stimulation improves cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease mice by controlling astrocyte activation. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, M.J. Cellular neuroadaptations to chronic opioids: Tolerance, withdrawal and addiction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devinsky, O.; Cilio, M.R.; Cross, H.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; French, J.; Hill, C.; Katz, R.; Di Marzo, V.; Jutras-Aswad, D.; Notcutt, W. Cannabidiol: Pharmacology and potential therapeutic role in epilepsy and other neuropsychiatric disorders. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbadugha, C.C.; Ekanem Theresa, B.; Ekandem Gabriel, J.; Mbagwu Herbert, O.; Okwudili Udemezuo, O.; Oyebadejo Samson, A. Cannabis sativa and the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the rat hippocampal astrocytes. J. Appl. Life Sci. Int. 2015, 3, 183–197. [Google Scholar]
- Kozela, E.; Juknat, A.; Vogel, Z. Modulation of astrocyte activity by cannabidiol, a nonpsychoactive cannabinoid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; You, C.; Lei, D.; Zhang, H. High dosage of cannabidiol (CBD) alleviates pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy in rats by exerting an anticonvulsive effect. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 8820–8827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagao, Y.; Harada, Y.; Mukai, T.; Shimizu, S.; Okuda, A.; Fujimoto, M.; Ono, A.; Sakagami, Y.; Ohno, Y. Expressional analysis of the astrocytic Kir4.1 channel in a pilocarpine-induced temporal lobe epilepsy model. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorini, G.; Melone, M.; Conti, F. A Reappraisal of GAT-1 localization in neocortex. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvill, G.L.; McMahon, J.M.; Schneider, A.; Zemel, M.; Myers, C.T.; Saykally, J.; Nguyen, J.; Robbiano, A.; Zara, F.; Specchio, N.; et al. Mutations in the GABA transporter SLC6A1 cause epilepsy with myoclonic-atonic seizures. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 96, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, L.L.; Hazekamp, A. Cannabis oil: Chemical evaluation of an upcoming Cannabis-based medicine. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2013, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, Y.; D’Antuono, M.; Bertazzoni, G.; Biagini, G.; Avoli, M. Dysfunctional presynaptic GABAB receptors in the neocortex of a genetic model of absence epilepsy. Neurosignals 2009, 17, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Fernandes, C.C.; Ewell, L.A.; John, D.; Romoli, B.; Curia, G.; Taylor, S.R.; Frady, E.P.; Jensen, A.B.; Chaabane, M.M.; et al. MicroRNA-101 regulates multiple developmental programs to constrain excitation in adult neural networks. Neuron 2016, 92, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of Seizure Activity by Electrical Stimulation. II. Motor Seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A. Pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) kindling model of epilepsy. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2012, 58, 9.37.1–9.37.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.M.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, I.Y.; Cho, K.O. Assessment of memory function in pilocarpine-induced epileptic mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 160, e60751. [Google Scholar]
- Dix, S.L.; Aggleton, J.P. Extending the spontaneous preference test of recognition: Evidence of object location discrimination. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 99, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarter, M.; Bodewitz, G.; Stephens, D.N. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced impairment of spontaneous alternation behaviour by nicotine in rats. Psychopharmacology 1988, 94, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, H.H.; Hadley, M. Malondialdehyde determination as an index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.M.; Raine, L.; Fanger, H. Use of Avidin-Biotin-Peroxidase Complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: A comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1981, 29, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
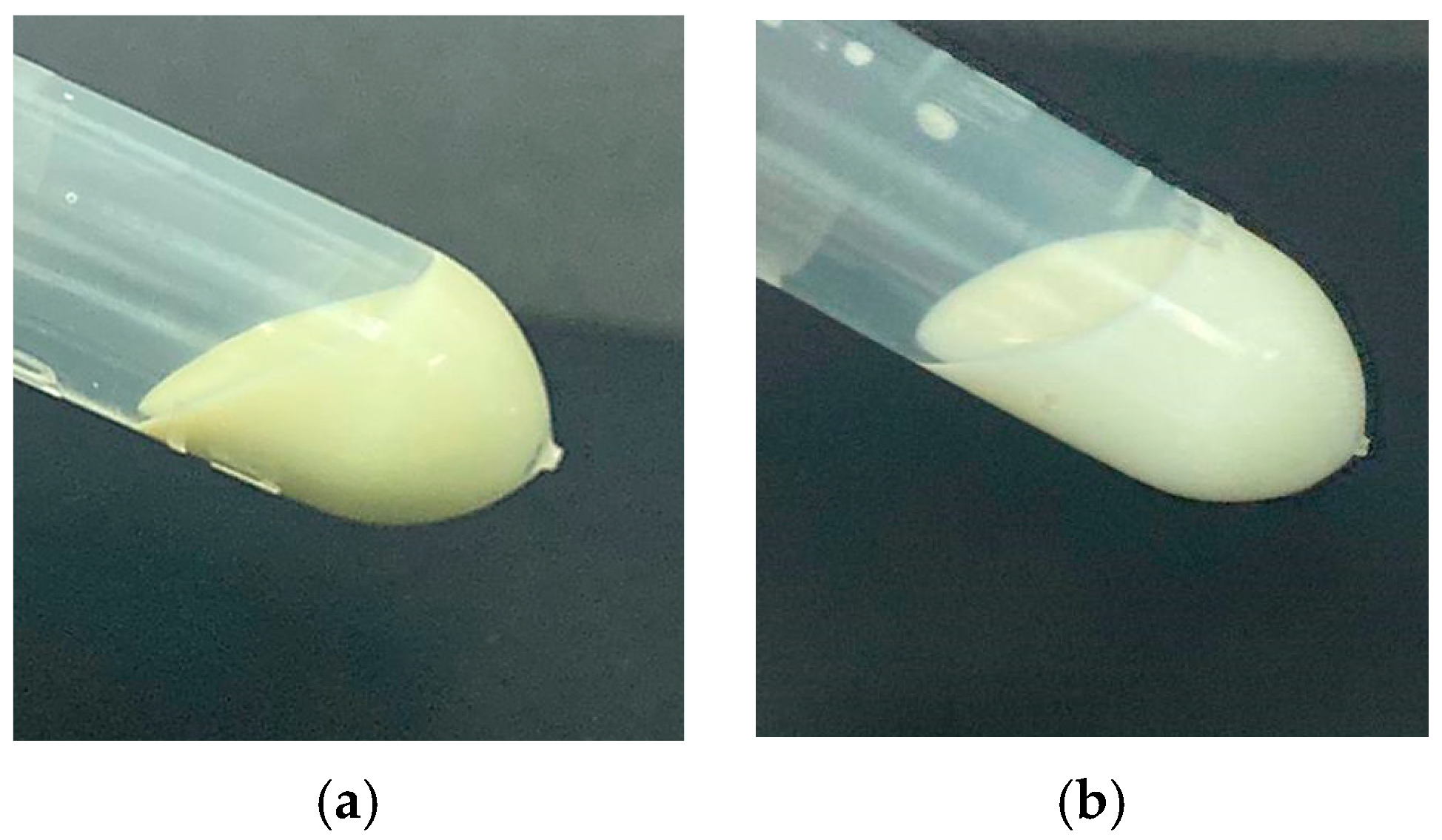
| Fatty Acid | Symbol | Peak Area (%) | Peak Area (%) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| capric | C 10:0 | 7.87 | 6.40 |
| lauric | C 12:0 | 42.13 | 43.64 |
| myristic | C 14:0 | 16.14 | 14.32 |
| palmitic | C 16:0 | 9.18 | 6.89 |
| oleic | C 18:1 | 19.52 | 11.78 |
| stearic | C 18:0 | 5.15 | 3.83 |
| caprylic | C 8:0 | - | 10.05 |
| linoleic | C 18:2 | - | 3.1 |
| Formulation | Droplet Size (nm) | PDI | ZP (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| THC nanoemulsion | 237.5 ± 1.46 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | −33.9 ± 2.14 |
| CBD nanoemulsion | 247.2 ± 1.15 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | −32.4 ± 1.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Aquino, P.E.A.; Júnior, F.J.G.; de Souza Nascimento, T.; Rosal Lustosa, Í.; de Andrade, G.M.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S.; de Brito, D.H.A.; de Almeida, G.É.P.; Silveira, K.B.; Zampieri, D.; et al. Nanoemulsions of Cannabidiol, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, and Their Combination Similarly Exerted Anticonvulsant and Antioxidant Effects in Mice Treated with Pentylenetetrazole. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060782
de Aquino PEA, Júnior FJG, de Souza Nascimento T, Rosal Lustosa Í, de Andrade GM, Ricardo NMPS, de Brito DHA, de Almeida GÉP, Silveira KB, Zampieri D, et al. Nanoemulsions of Cannabidiol, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, and Their Combination Similarly Exerted Anticonvulsant and Antioxidant Effects in Mice Treated with Pentylenetetrazole. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(6):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060782
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Aquino, Pedro Everson Alexandre, Francisco Josimar Girão Júnior, Tyciane de Souza Nascimento, Ítalo Rosal Lustosa, Geanne Matos de Andrade, Nágila Maria Pontes Silva Ricardo, Débora Hellen Almeida de Brito, Gabriel Érik Patrício de Almeida, Kamilla Barreto Silveira, Davila Zampieri, and et al. 2025. "Nanoemulsions of Cannabidiol, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, and Their Combination Similarly Exerted Anticonvulsant and Antioxidant Effects in Mice Treated with Pentylenetetrazole" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 6: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060782
APA Stylede Aquino, P. E. A., Júnior, F. J. G., de Souza Nascimento, T., Rosal Lustosa, Í., de Andrade, G. M., Ricardo, N. M. P. S., de Brito, D. H. A., de Almeida, G. É. P., Silveira, K. B., Zampieri, D., de França Fonteles, M. M., Silveira, E. R., Biagini, G., & de Barros Viana, G. S. (2025). Nanoemulsions of Cannabidiol, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, and Their Combination Similarly Exerted Anticonvulsant and Antioxidant Effects in Mice Treated with Pentylenetetrazole. Pharmaceuticals, 18(6), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18060782







