Natural Killer Cell Activation Signature Identifies Cyclin B1/CDK1 as a Druggable Target to Overcome Natural Killer Cell Dysfunction and Tumor Invasiveness in Melanoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
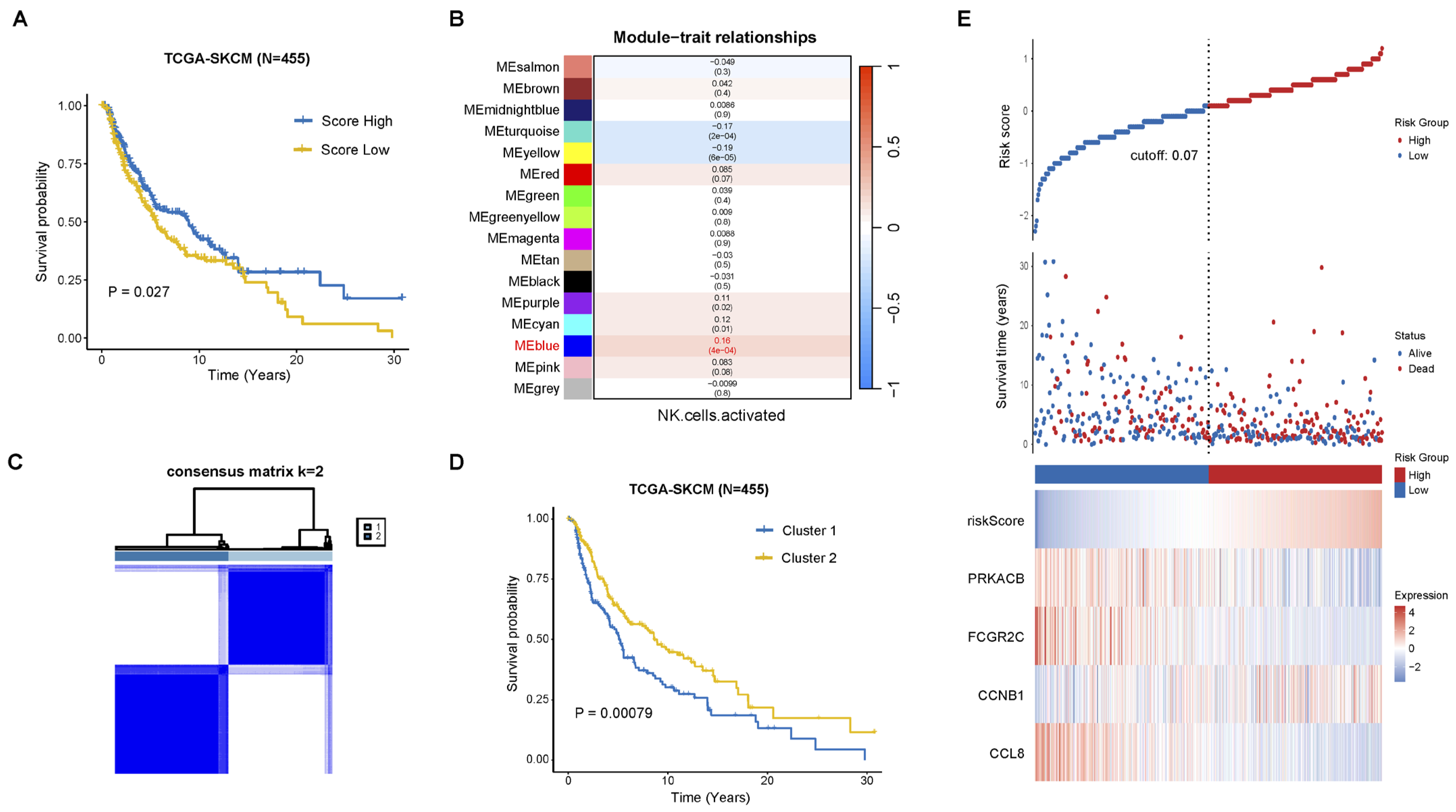
2.1. Construction of Prognostic Signature Associated with NK Cell Activation
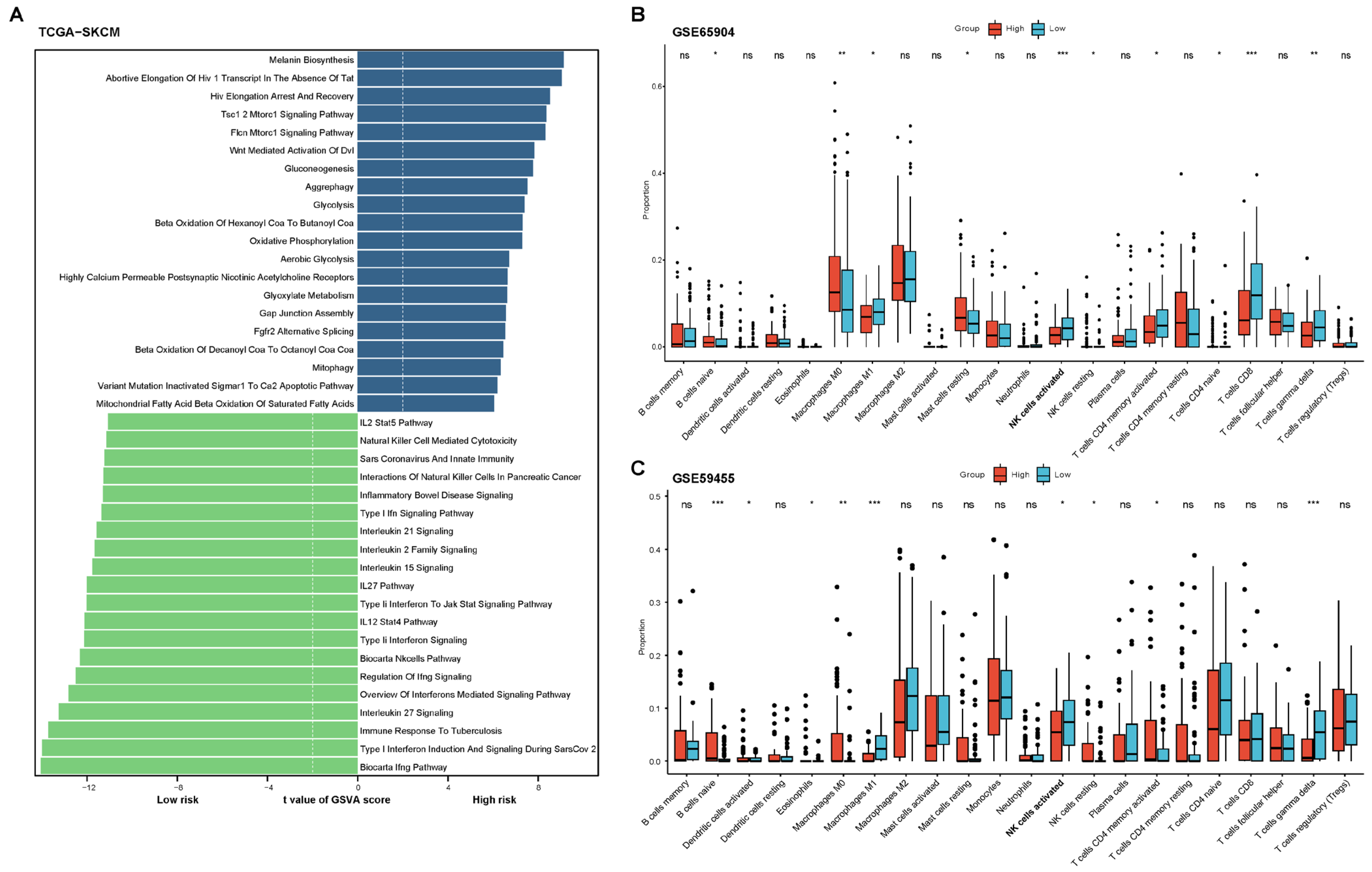
2.2. Functional and Immune Infiltration Analysis of the Prognostic Model
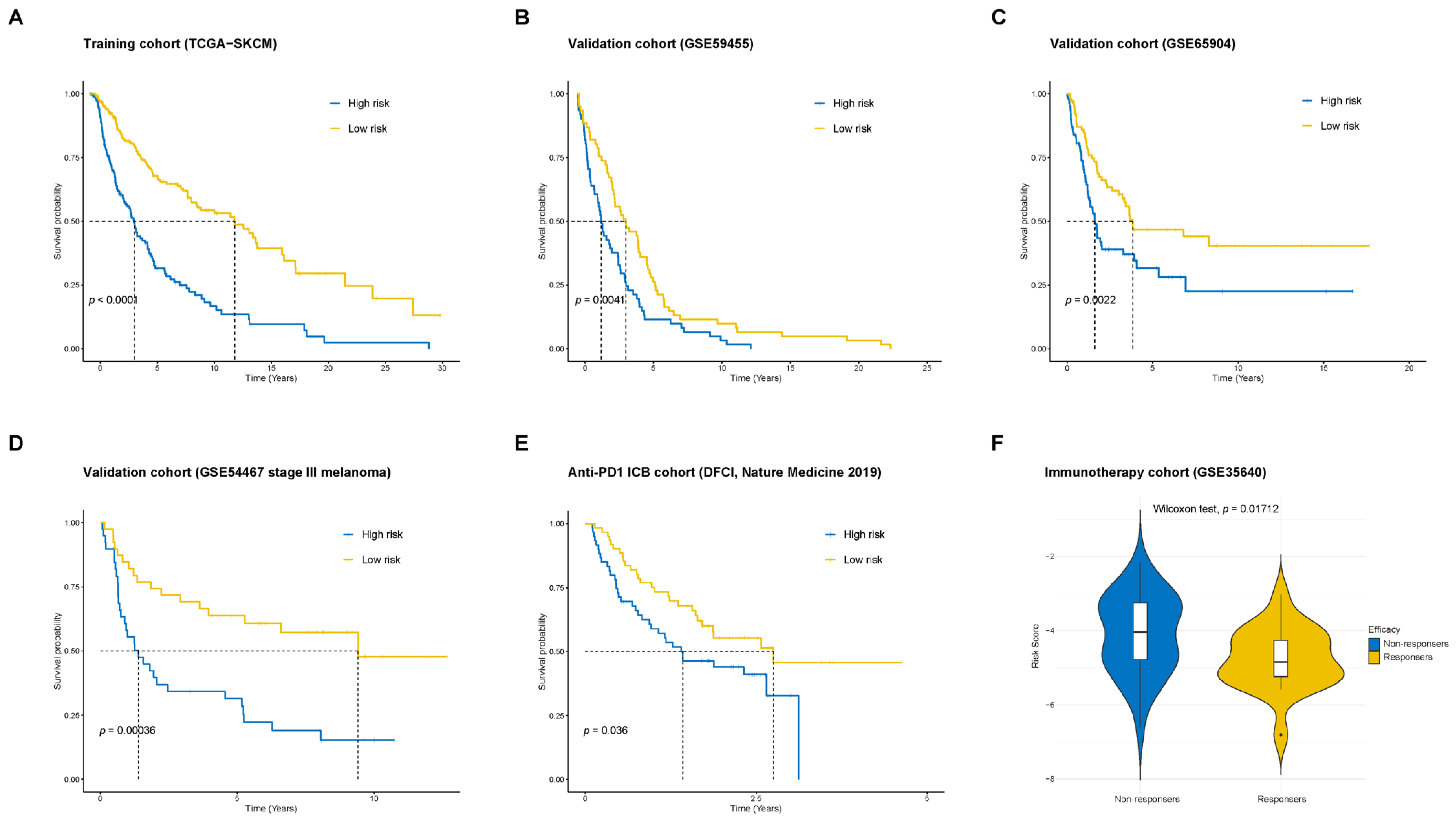
2.3. Validation of the Prognostic Model in Multiple Cohorts
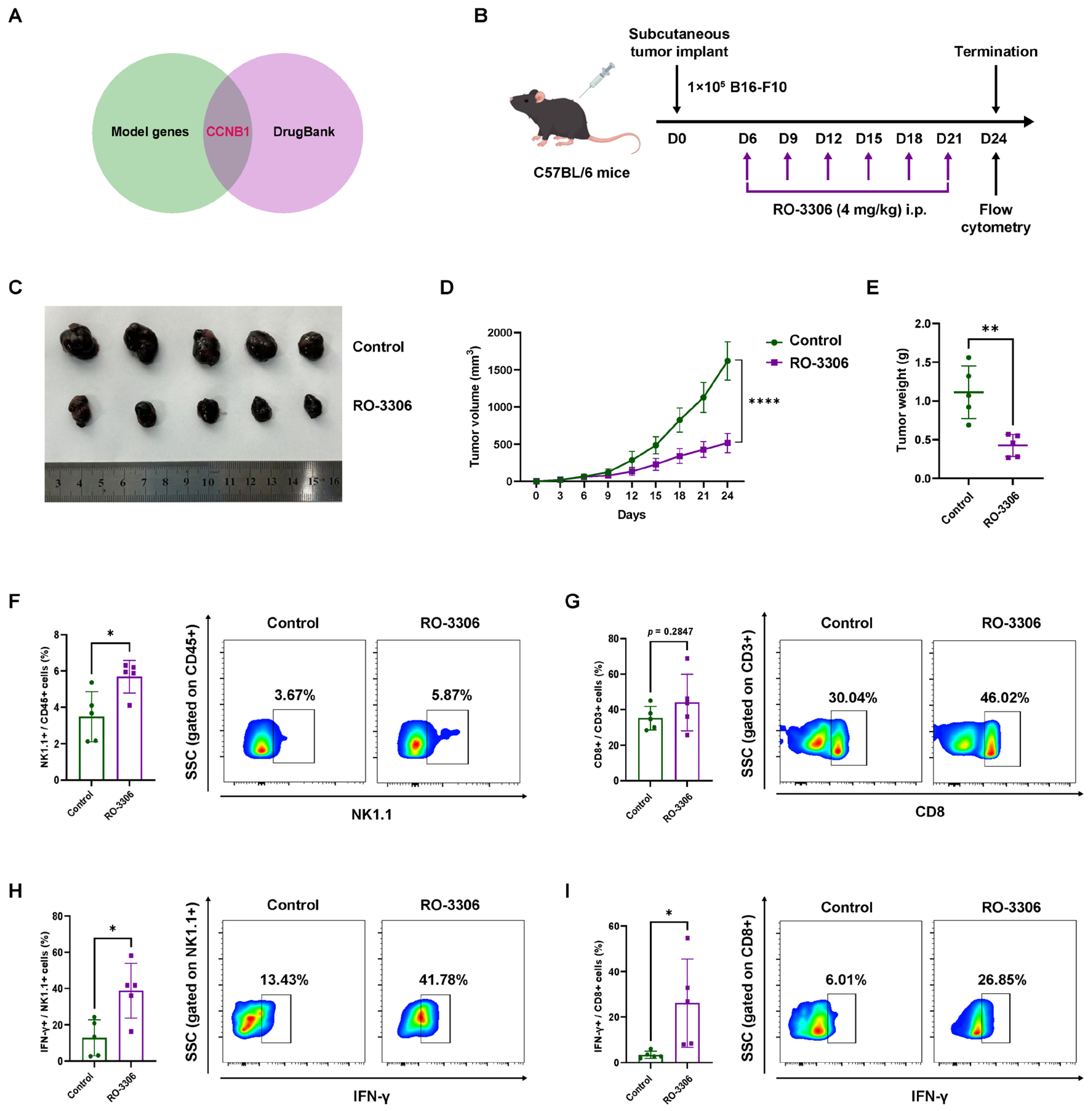
2.4. Pharmacological CCNB1 Inhibition (RO-3306) Suppresses Melanoma Growth by Enhancing NK Infiltration and Cytotoxicity In Vivo
2.5. CCNB1 Knockdown in Melanoma Cells Enhances NK-92MI Activation and Cytotoxicity
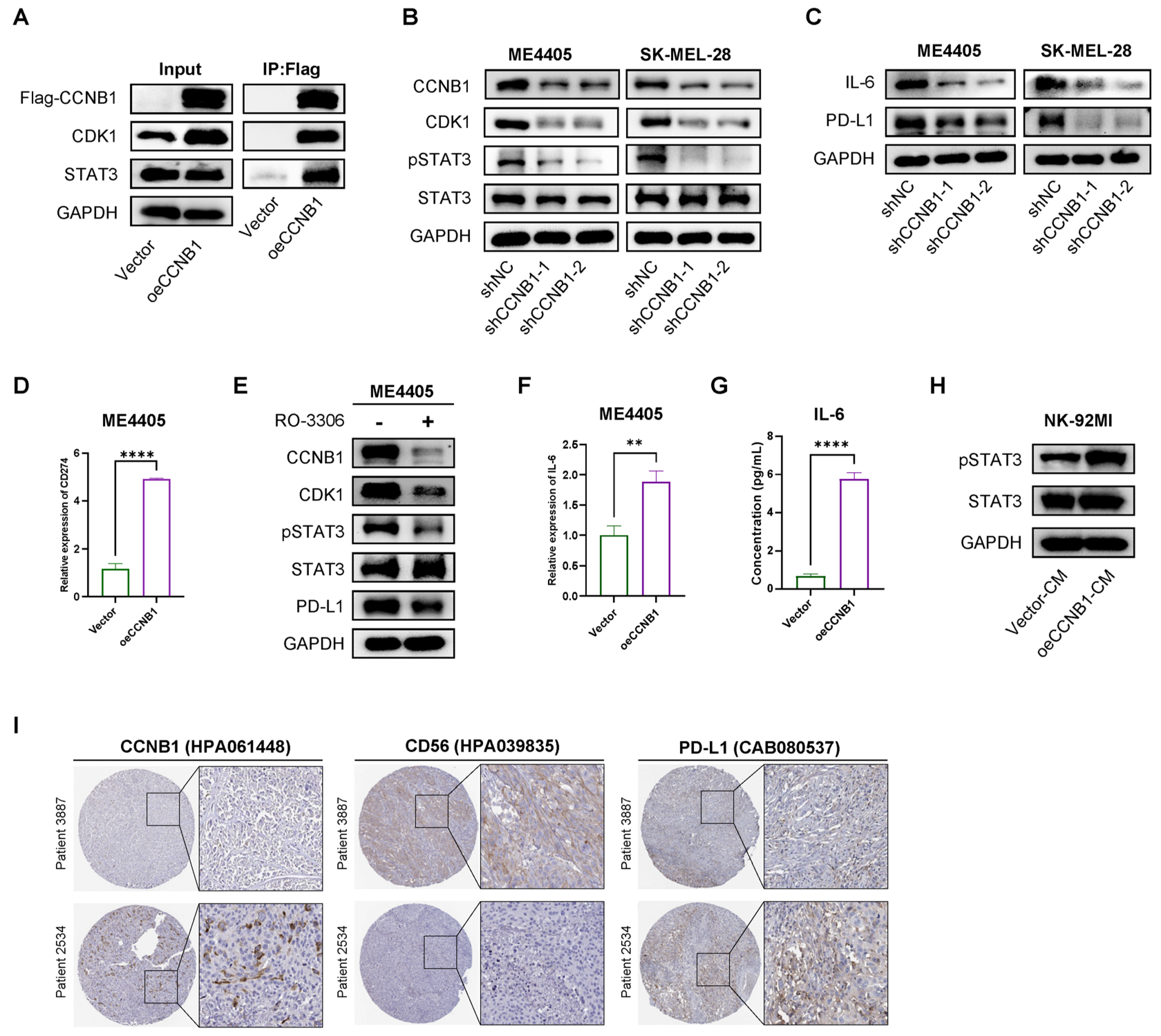
2.6. CCNB1/CDK1 Upregulates STAT3-PD-L1 in Melanoma Cells and Secretes IL-6 to Enhance STAT3 Signaling in NK-92 Cells
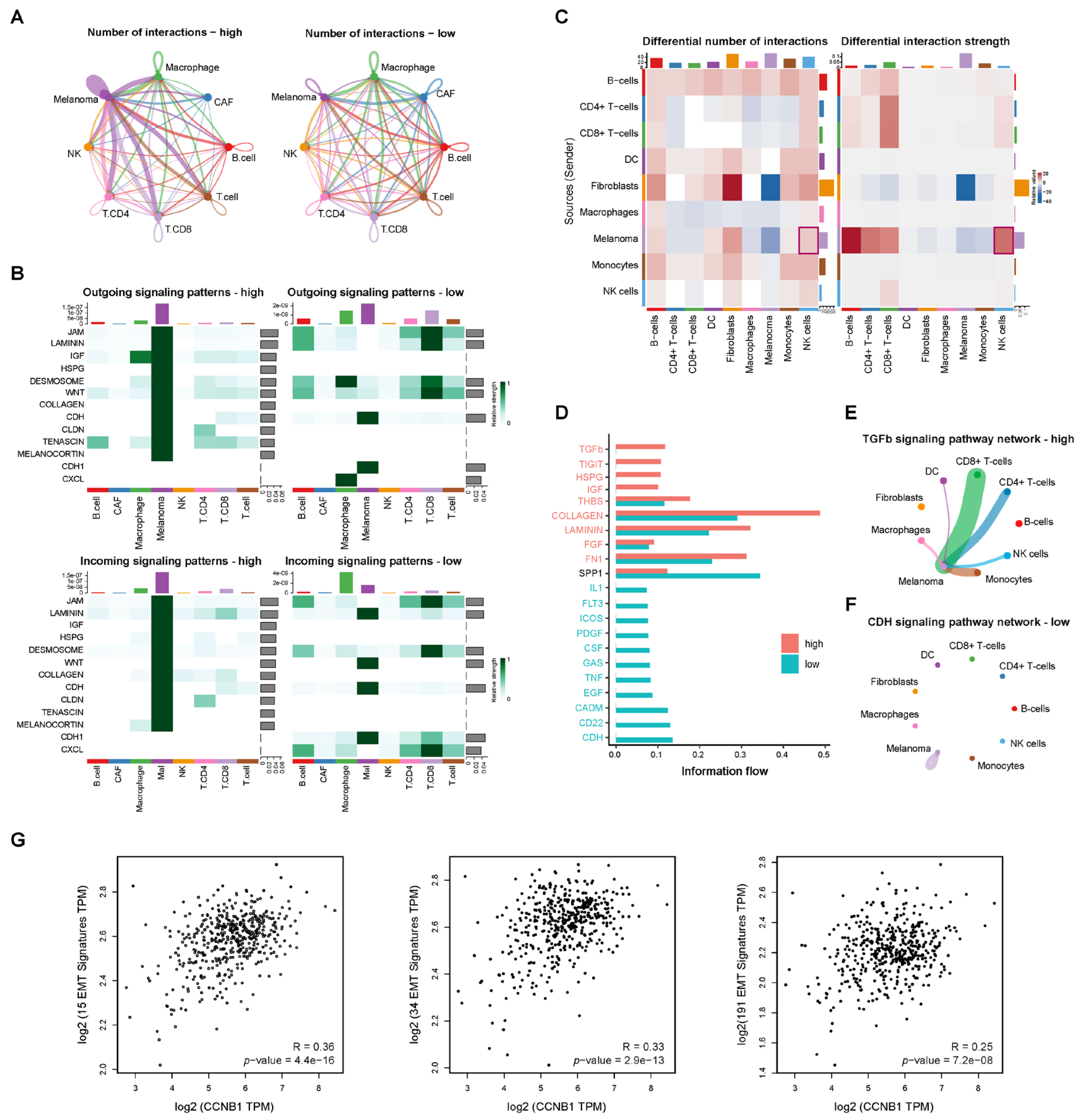
2.7. Cell–Cell Communication Reveals TGF-β Signaling in CCNB1-High Melanoma Linked to EMT
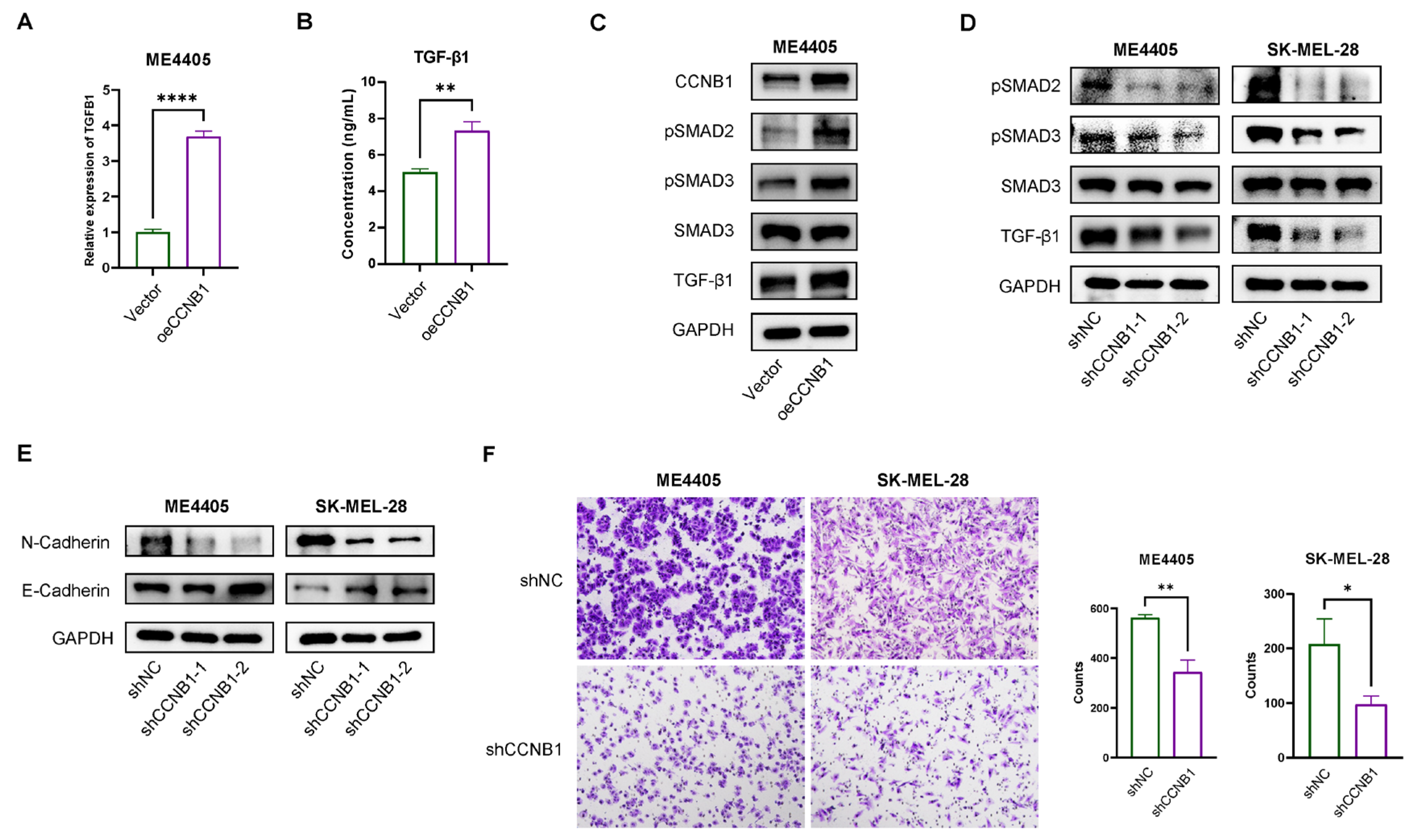
2.8. CCNB1 Promotes EMT and Melanoma Invasiveness Through the TGF-β-SMAD2/3 Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source
4.2. Development NK Activation-Related Prognostic Model
4.3. Gene Set Variation Analysis
4.4. Cell–Cell Communication Analysis
4.5. Cell Culture and Stable Cell Line Generation
4.6. Co-Culture of NK-92MI Cells with Melanoma Cells and Assessment by Flow Cytometry
4.7. Western Blotting and Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
4.8. RT-qPCR
4.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.10. Cell Invasion Assay
4.11. Animal Models and Treatment
4.12. Statistical Analysis
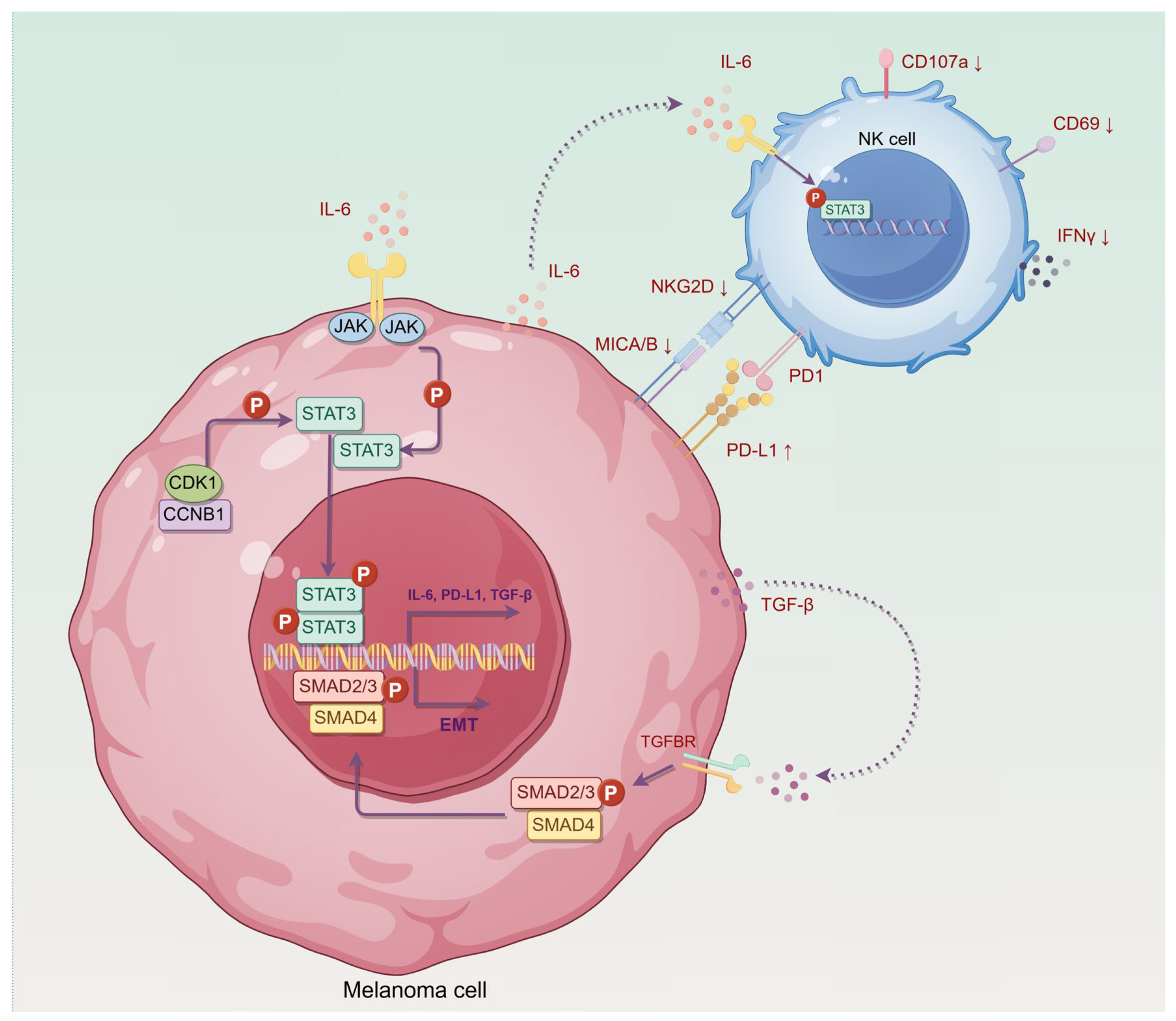
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Shain, A.H.; Bastian, B.C. From Melanocytes to Melanomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.V.; Swetter, S.M.; Menzies, A.M.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Scolyer, R.A. Cutaneous Melanoma. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2023, 402, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk-Krauss, J.; Stein, J.A.; Weber, J.; Polsky, D.; Geller, A.C. New Systematic Therapies and Trends in Cutaneous Melanoma Deaths Among US Whites, 1986–2016. Am. J. Public Health 2020, 110, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.P.; Othus, M.; Chen, Y.; Wright, G.P.; Yost, K.J.; Hyngstrom, J.R.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Lao, C.D.; Fecher, L.A.; Truong, T.-G.; et al. Neoadjuvant-Adjuvant or Adjuvant-Only Pembrolizumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Ribas, A.; Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Schachter, J.; Nyakas, M.; Kee, D.; Petrella, T.M.; Blaustein, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab for Advanced Melanoma: 10-Year Follow-up of the Phase III KEYNOTE-006 Study. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2024, 35, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.C.; Zappasodi, R. A Decade of Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy in Melanoma: Understanding the Molecular Basis for Immune Sensitivity and Resistance. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziogas, D.C.; Theocharopoulos, C.; Koutouratsas, T.; Haanen, J.; Gogas, H. Mechanisms of Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Melanoma: What We Have to Overcome? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 113, 102499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, N.K.; Kissiov, D.U.; Raulet, D.H. Roles of Natural Killer Cells in Immunity to Cancer, and Applications to Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delconte, R.B.; Kolesnik, T.B.; Dagley, L.F.; Rautela, J.; Shi, W.; Putz, E.M.; Stannard, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Teh, C.; Firth, M.; et al. CIS Is a Potent Checkpoint in NK Cell-Mediated Tumor Immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, R.; Wu, C.; Bassoy, E.Y.; Rubino, T.E.; Utagawa, E.C.; Magtibay, P.M.; Butler, K.A.; Curtis, M. PP4 Inhibition Sensitizes Ovarian Cancer to NK Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity via STAT1 Activation and Inflammatory Signaling. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.; Chuvin, N.; Valladeau-Guilemond, J.; Depil, S. Development of NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapies through Receptor Engineering. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis-Marcisak, E.F.; Fitzgerald, A.A.; Kessler, M.D.; Danilova, L.; Jaffee, E.M.; Zaidi, N.; Weiner, L.M.; Fertig, E.J. Transfer Learning between Preclinical Models and Human Tumors Identifies a Conserved NK Cell Activation Signature in Anti-CTLA-4 Responsive Tumors. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Ryan, J.; Pan, D.; Wucherpfennig, K.W.; Letai, A. Augmenting NK Cell-Based Immunotherapy by Targeting Mitochondrial Apoptosis. Cell 2022, 185, 1521–1538.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Tovar, C.; Chen, S.; Knezevic, D.; Zhao, X.; Sun, H.; Heimbrook, D.C.; Chen, L. Selective Small-Molecule Inhibitor Reveals Critical Mitotic Functions of Human CDK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10660–10665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran Menon, D.; Luo, Y.; Arcaroli, J.J.; Liu, S.; KrishnanKutty, L.N.; Osborne, D.G.; Li, Y.; Samson, J.M.; Bagby, S.; Tan, A.-C.; et al. CDK1 Interacts with Sox2 and Promotes Tumor Initiation in Human Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6561–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, M.; Candas, D.; Zhang, T.-Q.; Qin, L.; Eldridge, A.; Wachsmann-Hogiu, S.; Ahmed, K.M.; Chromy, B.A.; Nantajit, D.; et al. Cyclin B1/Cdk1 Coordinates Mitochondrial Respiration for Cell-Cycle G2/M Progression. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Kao, T.P.; Huang, H. CDK1 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Survival via Phosphorylation and Inhibition of FOXO1 Transcription Factor. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4733–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Breyssens, H.; Salter, V.; Zhong, S.; Hu, Y.; Baer, C.; Ratnayaka, I.; Sullivan, A.; Brown, N.R.; Endicott, J.; et al. Restoring P53 Function in Human Melanoma Cells by Inhibiting MDM2 and Cyclin B1/CDK1-Phosphorylated Nuclear iASPP. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Guo, W.; Ling, J.; Xu, D.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Du, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, M.; Song, H.; et al. Iron-Dependent CDK1 Activity Promotes Lung Carcinogenesis via Activation of the GP130/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ding, Y.; Jin, J.; Xu, C.; Hu, W.; Wu, S.; Ding, G.; Cheng, R.; Cao, L.; Jia, S. Post-Translational Modification of CDK1-STAT3 Signaling by Fisetin Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer Stem Cell Properties. Cell Biosci. 2023, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 Signalling Axis in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, L.L.; Yu, G.T.; Wu, L.; Mao, L.; Deng, W.W.; Liu, J.F.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Zhang, W.F.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.J. STAT3 Induces Immunosuppression by Upregulating PD-1/PD-L1 in HNSCC. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-Beta-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Sferruzza, G.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, S. CAR-T and CAR-NK as Cellular Cancer Immunotherapy for Solid Tumors. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 1089–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedrahmati, F.; Esmaeil, N.; Abbaspour, M. Targeting Immune Checkpoints: How to Use Natural Killer Cells for Fighting against Solid Tumors. Cancer Commun. Lond. Engl. 2023, 43, 177–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Kalimuthu, S.; Gangadaran, P.; Oh, J.M.; Lee, H.W.; Baek, S.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.-C. Exosomes Derived from Natural Killer Cells Exert Therapeutic Effect in Melanoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2732–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, S.; Sung, H.-M.; Ickes, C.; Gibhardt, C.S.; Vultur, A.; Bhat, H.; Hu, Z.; Brafford, P.; Denger, A.; Stejerean-Todoran, I.; et al. Protein Signatures of NK Cell-Mediated Melanoma Killing Predict Response to Immunotherapies. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5540–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, U.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Turner, N.C.; Knudsen, E.S. The History and Future of Targeting Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, M.; Le Calvé, B.; Ferbeyre, G.; Blank, V.; Lessard, F. New Insights into CDK Regulators: Novel Opportunities for Cancer Therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Palbociclib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Ribociclib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S. Trilaciclib: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelliott, E.J.; Sheppard, K.E.; McArthur, G.A. Harnessing the Immunotherapeutic Potential of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Melanoma: Is Timing Everything? NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Pang, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, X.; Tu, L.; Shen, Y.; Jia, X.; Lee, J.-C.; Wang, Y. Integrated Screens Identify CDK1 as a Therapeutic Target in Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2481–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, L.; Abd El-Hafeez, A.A.; Ibrahim, T.M.; Salem, R.; Marzouk, H.M.M.; El-Domany, R.A.; Ghosh, P.; Eldehna, W.M.; Abou-Seri, S.M. Identification of Novel Piperazine-Tethered Phthalazines as Selective CDK1 Inhibitors Endowed with in Vitro Anticancer Activity toward the Pancreatic Cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mirlekar, B.; Johnson, B.M.; Brickey, W.J.; Wrobel, J.A.; Yang, N.; Song, D.; Entwistle, S.; Tan, X.; Deng, M.; et al. STING-Induced Regulatory B Cells Compromise NK Function in Cancer Immunity. Nature 2022, 610, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, F.; Yin, L.; Wang, F.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, F.; Chen, D.; Dong, X.; Gu, Y.; et al. The Establishment of Polypeptide PSMA-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Engineered Natural Killer Cells for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer and the Induction of Ferroptosis-Related Cell Death. Cancer Commun. Lond. Engl. 2022, 42, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, H.J.; Rees, E.; Lanfredini, S.; Powell, K.A.; Gore, J.; Gibbs, A.; Lovatt, C.; Davies, G.E.; Olivero, C.; Shorning, B.Y.; et al. CD200 Ectodomain Shedding into the Tumor Microenvironment Leads to NK Cell Dysfunction and Apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e150750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Liu, E.T.; Shultz, L.D.; Ren, G. Lipid-Laden Lung Mesenchymal Cells Foster Breast Cancer Metastasis via Metabolic Reprogramming of Tumor Cells and Natural Killer Cells. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1960–1976.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari de Andrade, L.; Tay, R.E.; Pan, D.; Luoma, A.M.; Ito, Y.; Badrinath, S.; Tsoucas, D.; Franz, B.; May, K.F.; Harvey, C.J.; et al. Antibody-Mediated Inhibition of MICA and MICB Shedding Promotes NK Cell-Driven Tumor Immunity. Science 2018, 359, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cell Cycle, CDKs and Cancer: A Changing Paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, C.; Li, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, C.; Yu, L. CDK1 Inhibitor RO-3306 Enhances BTKi Potency in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma by Suppressing JAK2/STAT3 Signaling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 297, 139893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neo, S.Y.; Yang, Y.; Record, J.; Ma, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Tobin, N.P.; Blake, E.; Seitz, C.; Thomas, R.; et al. CD73 Immune Checkpoint Defines Regulatory NK Cells within the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, S.Y.; Oliveira, M.M.S.; Tong, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cismas, S.; Burduli, N.; Malmerfelt, A.; Teo, J.K.H.; Lam, K.-P.; et al. Natural Killer Cells Drive 4-1BBL Positive Uveal Melanoma towards EMT and Metastatic Disease. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2024, 43, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, I.S.; Knútsdóttir, H.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Padmanaban, V.; Warrier, M.; Ramirez, J.C.; Dunworth, M.; Zhang, H.; Jaffee, E.M.; Bader, J.S.; et al. Cancer Cells Educate Natural Killer Cells to a Metastasis-Promoting Cell State. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e202001134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacalano, N.A. Regulation of Natural Killer Cell Function by STAT3. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatelli, S.S.; Zhou, J.-M.; Gilvary, D.L.; Eksioglu, E.A.; Chen, X.; Cress, W.D.; Haura, E.B.; Schabath, M.B.; Coppola, D.; Wei, S.; et al. TGF-β-Inducible microRNA-183 Silences Tumor-Associated Natural Killer Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4203–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.; Deng, J.; Chinnadurai, R.; Yuan, S.; Pennati, A.; Galipeau, J. Stimulation of Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Tumor Immunity by an IL15/TGFβ-Neutralizing Fusion Protein. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5683–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Schilling, B.; Liu, D.; Sucker, A.; Livingstone, E.; Jerby-Arnon, L.; Zimmer, L.; Gutzmer, R.; Satzger, I.; Loquai, C.; et al. Integrative Molecular and Clinical Modeling of Clinical Outcomes to PD1 Blockade in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust Enumeration of Cell Subsets from Tissue Expression Profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R Package for Weighted Correlation Network Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N. ConsensusClusterPlus: A Class Discovery Tool with Confidence Assessments and Item Tracking. Bioinform. Oxf. Engl. 2010, 26, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma Powers Differential Expression Analyses for RNA-Sequencing and Microarray Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene Set Variation Analysis for Microarray and RNA-Seq Data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Liao, W.; Huang, J.; Ding, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Wen, X.; et al. Natural Killer Cell Activation Signature Identifies Cyclin B1/CDK1 as a Druggable Target to Overcome Natural Killer Cell Dysfunction and Tumor Invasiveness in Melanoma. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050666
Chen L, Liao W, Huang J, Ding Q, Wu J, Zhang Q, Ding Y, Li D, Li J, Wen X, et al. Natural Killer Cell Activation Signature Identifies Cyclin B1/CDK1 as a Druggable Target to Overcome Natural Killer Cell Dysfunction and Tumor Invasiveness in Melanoma. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050666
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Linbin, Wanqian Liao, Jing Huang, Qiuyue Ding, Junwan Wu, Qiong Zhang, Ya Ding, Dandan Li, Jingjing Li, Xizhi Wen, and et al. 2025. "Natural Killer Cell Activation Signature Identifies Cyclin B1/CDK1 as a Druggable Target to Overcome Natural Killer Cell Dysfunction and Tumor Invasiveness in Melanoma" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050666
APA StyleChen, L., Liao, W., Huang, J., Ding, Q., Wu, J., Zhang, Q., Ding, Y., Li, D., Li, J., Wen, X., & Zhang, X. (2025). Natural Killer Cell Activation Signature Identifies Cyclin B1/CDK1 as a Druggable Target to Overcome Natural Killer Cell Dysfunction and Tumor Invasiveness in Melanoma. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050666







