Abstract
Background/Objectives: Iron deficiency anemia remains a primary global health concern, affecting millions worldwide. Despite the widespread availability of iron supplements, their efficacy is often hindered by poor bioavailability and adverse gastrointestinal effects. This study explores the potential of probiotics to enhance the bioavailability of Fe3O4 NPs through probiotic-mediated mechanisms. Methods: Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Lactobacillus plantarum were utilized to investigate their interactions with Fe3O4 NPs, synthesized via co-precipitation and characterized using transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction. Results: The results indicated that probiotics adhere to the nanoparticle surface, with L. fermentum exhibiting the highest adhesion and internalization capacity, leading to a significant increase in 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (4-HPLA) production (11.73 ± 0.09 mg/mL at 24 h, p < 0.05). Spectroscopic analyses further revealed that probiotic metabolism facilitates the oxidation of Fe3O4 to Fe2O3. Additionally, Fe3O4 nanoparticle-treated cultures demonstrated enhanced bacterial viability and metabolic activity, highlighting a synergistic effect between probiotics and iron nanoparticles. Conclusions: These findings provide compelling evidence for probiotic-assisted iron supplementation as a promising strategy to enhance iron bioavailability while mitigating the gastrointestinal side effects of conventional iron supplements.
1. Introduction
Iron deficiency is one of the most widespread nutritional deficiencies globally, affecting millions of individuals, particularly including vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, children, and individuals with chronic diseases [1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 24.8% of the population (1.62 billion people) suffers from anemia, a condition primarily caused by iron deficiency [2]. As iron is fundamental in oxygen transport, redox reactions, energy metabolism, and enzymatic functions, iron deficiency anemia is quite detrimental and develops when iron levels are insufficient, leading to fatigue, weakness, cognitive impairment, and increased susceptibility to infections [3].
As such, various supplementation strategies have been developed to address iron deficiency, including ferrous sulfate, iron salts, and iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) [4]. Although existing conventional iron supplements have been effective in restoring iron levels, they often come with significant drawbacks, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, low bioavailability, and interactions with dietary components. As a result, Fe3O4 NPs have been acknowledged as an innovative alternative due to their stability, biocompatibility, and ability to resist degradation in the stomach’s acidic environment [5], offering Fe3O4 NPs promising advantages. However, their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract remains a significant challenge, requiring innovative strategies to enhance their bioavailability. One such approach involves using acid-resistant probiotics that can survive gastric transit and maintain functional viability in the gut, thereby supporting nutrient absorption. Lactobacillus rhamnosus, particularly strain GG, is well known for its acid tolerance and ability to adhere to intestinal epithelial cells. These properties support its survival in the gastrointestinal environment and its efficacy in promoting intestinal health and improving the absorption of micronutrients such as iron [6,7]. Lactobacillus fermentum and Lactobacillus plantarum have also shown excellent survival in simulated gastric juice, with viability rates reaching up to 86.7% and 96.97%, respectively [8,9,10].
Emerging research suggests that probiotics can significantly enhance iron bioavailability by improving solubilization, facilitating absorption, and reducing iron-related oxidative stress [11,12,13,14,15]. Certain probiotic strains, such as L. fermentum, L. acidophilus, and Bifidobacterium breve, have demonstrated the ability to modulate iron metabolism through multiple mechanisms [11]. These bacteria lower the intestinal pH, primarily through acid production, which enhances iron solubility and promotes gut absorption. One of their key excreted metabolites, p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid (HPLA), produced by L. fermentum, exhibits potent ferric-reducing activity under acidic conditions. Studies have shown that HPLA efficiently reduces ferric iron (Fe3+) to its more bioavailable ferrous form (Fe2+) at pH 3.8, though this activity significantly diminishes at higher pH values [16]. Moreover, probiotics have been found to upregulate divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), a key protein responsible for iron uptake in intestinal cells, further improving iron assimilation [3]. In addition to their direct role in iron metabolism, probiotics support the balance of the gut microbiota, which is essential for optimal nutrient absorption [17,18,19]. Reducing intestinal inflammation and preventing microbial imbalances creates a more favorable environment for iron uptake [18]. Integrating probiotics into iron supplementation strategies may enhance iron absorption while minimizing these adverse effects [18,20].
Recent advances in probiotic research have contributed to a deeper understanding of the molecular pathways involved in the probiotic-mediated regulation of iron metabolism [21]. Beyond increasing solubility and reducing ferric iron to its more bioavailable ferrous form, specific probiotic strains have been shown to modulate the expression of host genes involved in iron transport and storage [18,22]. For instance, the upregulation of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) and ferroportin and the modulation of ferritin expression are crucial in enhancing cellular iron uptake and systemic distribution [23]. Moreover, probiotics have demonstrated the ability to influence signaling pathways such as TLR2/NF-κB, involved in immune response and inflammatory regulation, thereby indirectly supporting a gut environment that is more conducive to iron absorption [3,11,13]. In addition, probiotics contribute to intestinal barrier integrity by modulating mucin expression and tight junction proteins such as MUC2, CLDN, and ZO-1, facilitating nutrient permeability and reducing inflammation [17]. Their antioxidant properties also play a role in mitigating the oxidative stress associated with iron metabolism [24], with emerging evidence suggesting that certain lactic acid bacteria may utilize extracellular electron transfer mechanisms to enhance ferric iron reduction, representing a novel metabolic pathway that supports iron solubilization and absorption [13].
The combined use of Fe3O4 NPs and probiotics as a novel supplementation strategy is gaining increasing attention due to the challenges related to the bioavailability of nanoparticles and the beneficial effects of probiotics on iron absorption. Recent studies have demonstrated that certain probiotic strains, such as L. plantarum, enhance iron absorption through multiple mechanisms [22,24]. Specifically, probiotics can regulate the expression and activity of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), an activator protein responsible for iron absorption in the gut, thereby facilitating the absorption of dietary iron [18]. Additionally, probiotics exhibit anti-inflammatory properties that may reduce intestinal inflammation, creating a more favorable environment for optimal nutrient absorption [25]. Studies indicate that probiotics may act as protective carriers for Fe3O4 NPs, enhancing their stability and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract [26,27]. For example, encapsulating iron dextran with probiotic bacteria in pH-triggered hydrogels prevents iron aggregation in the acidic gastric environment, thereby ensuring efficient delivery to the gut, where absorption occurs [28]. In addition, probiotics may alleviate the oxidative stress and inflammation associated with Fe3O4 NP administration, supporting their role in promoting iron homeostasis [29]. Despite the present research in this field, a pressing need remains to explore how the probiotic-mediated biotransformation of Fe3O4 NPs enhances iron absorption.
As such, this study aims to investigate the underlying molecular and biochemical mechanisms by which select probiotic strains, L. fermentum, L. rhamnosus, and L. plantarum, synergistically interact with Fe3O4 NPs to enhance iron solubilization.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphological and Structural Characterization of Fe3O4 NPs
The physical characteristics of Fe3O4 NPs, such as their aggregation state and surface area, directly affect their dissolution behavior, redox activity, and interaction with probiotic metabolic pathways [5,30]. Therefore, a detailed morphological and structural analysis was used to establish the Fe3O4 NPs’ properties after synthesis and their potential bioavailability enhancement via probiotics.
The TEM image (Figure 1A) highlights the nanoscale dimensions of the Fe3O4 particles, exhibiting a quasi-spherical morphology with an aggregation tendency. This fact can be attributed to a direct consequence of strong dipole–dipole magnetic interactions, which is a common feature of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles [31]. The uniform particle distribution suggests a controlled synthesis process. The SEM image (Figure 1B) provides a detailed view of the surface topology, emphasizing the rough and clustered structure of the Fe3O4 NPs. The degree of aggregation observed in the SEM image suggests a high surface-area-to-volume ratio, which can benefit probiotic adhesion and biofilm formation [32]. The clustered porous nature of Fe3O4 NPs provides a favorable environment for probiotic adhesion, where bacterial exopolysaccharides and surface proteins can establish strong interactions with the nanoparticles, facilitating biofilm-mediated iron uptake. This is consistent with studies that have shown probiotics to be able to significantly enhance intestinal iron absorption by releasing metabolites that facilitate this conversion [3,28]. Moreover, the degree of Fe3O4 NP aggregation influences the NPs’ behavior in simulated gastrointestinal conditions, where probiotic-secreted metabolites may act as natural dispersing agents, preventing excessive nanoparticle clustering and ensuring sustained iron release [33].

Figure 1.
TEM (A) and SEM (B) images of Fe3O4 NPs synthesized by the co-precipitation method.
Furthermore, the complementary structural and chemical data of the synthesized Fe3O4 NPs were investigated through FT-IR and XRD methods. The FT-IR spectrum (Figure 2A) displays an absorption band near 570 cm−1, which is typically assigned to the Fe–O stretching vibration in magnetite, confirming the formation of the Fe3O4 phase. Subsequent FT-IR analyses confirmed that no residual ethanol or ethyl acetate reagents were detectable on the nanoparticle surfaces. Meanwhile, the XRD pattern (Figure 2B) confirmed the inverse spinel crystal structure characteristic of magnetite, indicated by the intense diffraction peaks at 2θ values corresponding to planes such as (220), (311), (400), (422), (511), and (440). The sharpness and intensity of these peaks attest to the high crystallinity of the NPs. At the same time, the average crystallite size, determined by the Debye–Scherrer formula (16.9 nm), places them in the nanometer range.

Figure 2.
FT-IR spectra (A) and XRD patterns (B) of Fe3O4 NPs synthesized by the co-precipitation method.
Therefore, the synergistic results collected from the morphological and structural characterization of the Fe3O4 NPs underscore the successful synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles via co-precipitation.
2.2. Impact of Fe3O4 NPs on Bacterial Fermentation
The presence of Fe3O4 NPs in fermentation systems has been explored by examining how these nanoparticles influence bacterial physiology, fermentation kinetics, and the ultimate bioavailability of iron in the context of probiotic-mediated iron supplementation. Iron is a vital cofactor for numerous enzymes that drive energy production, growth, and overall fermentative performance in probiotic bacteria [4,29,34]. By modulating iron availability, Fe3O4 NPs may stimulate key metabolic pathways, potentially boosting the fermentation rate and efficiency [16,22,30].
SEM images (Figure 3) confirmed the adhesion of Fe3O4 NPs to the surfaces of all three probiotic strains, with L. fermentum exhibiting the most pronounced attachment. Variations in cell surface charge, hydrophobicity, or extracellular polymeric substances may influence this strain-dependent affinity [35]. This interaction likely stems from the binding affinities between the nanoparticle surface functional groups (hydroxyls) and the exopolysaccharides or proteinaceous layers on the bacterial cell wall [36]. Similar adherence has been suggested to facilitate localized iron reduction and uptake, as probiotic cells secrete organic acids and siderophores that enhance iron solubility [35,36].

Figure 3.
SEM images of probiotics with Fe3O4 NPs: LP-Fe3O4 for L. plantarum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs; LR-Fe3O4 for L. rhamnosus after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs; LF-Fe3O4 for L. fermentum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs.
The TEM results (Figure 4) further revealed the internalization of Fe3O4 NPs within L. fermentum cells, while L. plantarum and L. rhamnosus showed lower degrees of internalization. Notably, L. fermentum maintained a smooth cell surface post-exposure, indicating potential membrane adaptations that facilitate nanoparticle uptake without compromising cellular integrity. These findings align with those of previous researchers investigating maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles in combination with L. fermentum. They found that these nanoparticles not only adhered to the bacterial surface but also significantly improved the accumulation of magnetic particles in the gastrointestinal tract, supporting their potential as iron delivery systems [4,37].

Figure 4.
TEM images of probiotics with Fe3O4 NPs: LP-Fe3O4 for L. plantarum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs; LR-Fe3O4 for L. rhamnosus after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs; LF-Fe3O4 for L. fermentum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs.
In contrast, L. rhamnosus exhibited signs of osmotic stress upon exposure to Fe3O4 NPs. SEM images revealed morphological changes indicative of cell stress, corroborated by a TEM analysis showing an increased presence of ribozymes, thus suggesting upregulated stress-related metabolic activity. These observations imply that Fe3O4 NPs may impose a metabolic burden on L. rhamnosus, potentially affecting its viability and probiotic functionality. For instance, it has been shown that L. rhamnosus can regulate mRNA abundance to recover translation efficiency under osmotic stress, an essential parameter for maintaining cellular functions during stress conditions [38,39]. The coordinated increase in transcript abundance ensures that ribosomes have a readily available pool of mRNAs encoding proteins that are critical for stabilizing the cell membrane, preventing protein aggregation, and maintaining overall cellular homeostasis [40]. Fe3O4 NPs have also been described to adhere to the surface of probiotics, thus enhancing their solubility and bioavailability [41,42]. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species have been stated to possess surface structures (exopolysaccharides, lipoteichoic acids, surface proteins) that enable adhesion to mineral surfaces [42]. Nevertheless, beyond these physicochemical properties, strain-specific differences in gene expression and metabolic pathways may explain these effects [43,44]. For example, Lactobacillus spp. may upregulate genes (expression of lar) involved in organic acid production [44], thereby enhancing Fe3O4 solubility, while Bifidobacterium spp. might rely on iron-binding proteins for nanoparticle interaction [43]. Another key factor could be the differential expression of siderophore-related genes, as most probiotic bacteria have been found to lack traditional siderophores [45,46]. However, the Lactobacillus genus has been reported to produce siderophores (peptides) that can chelate Fe3+ and facilitate transport [46]. Additionally, gene expression in metal ion homeostasis, such as that relating to DNA-binding proteins from starved cells and ferritin-like proteins, may contribute to intracellular iron sequestration and storage [46,47].
The presence of Fe3O4 NPs notably influenced the fermentation profiles of the tested probiotic strains, suggesting a potential synergistic relationship between iron oxide nanostructures and probiotic metabolism. As shown in Figure 5, each bacterial species (L. plantarum, L. rhamnosus, and L. fermentum) exhibited distinct viability patterns in response to Fe3O4 supplementation over the incubation period. Fe3O4 NPs influenced the cell viability relative to that of the control (bacteria without nanoparticles), particularly at the end of fermentation. As incubation progressed, L. plantarum consistently exhibited higher viable cell counts when Fe3O4 NPs were added, as compared to the control. Similar trends were observed for L. fermentum viability. This enhancement became more pronounced at the end time points (12–24 h), suggesting that the nanoparticle-provided iron may have bolstered key metabolic pathways involved in cell division and energy production [48]. Nonetheless, the results showed that iron supplementation via nanoparticles did not inhibit bacterial viability. On the other hand, the elevated viable cell counts in Fe3O4-supplemented cultures at the mid-to-late fermentation stages suggest that L. rhamnosus can harness the iron from the nanoparticles to sustain growth. Moreover, differences among the three species’ response profiles highlight strain-specific iron acquisition and regulation pathways. This observation resonates with the concept that certain probiotics possess specialized mechanisms (iron chelation or reduction) to facilitate iron acquisition from mineral complexes.
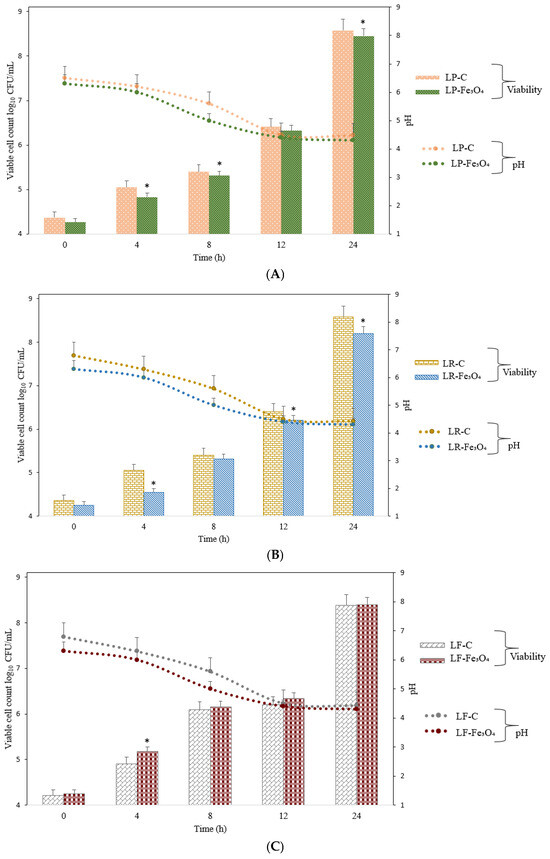
Figure 5.
Viable cell counts for L. plantarum, L. rhamnosus, and L. fermentum in the presence of Fe3O4 NPs. (A) L. plantarum cultured under control conditions (LP-C) and in the presence of Fe3O4 NPs (LP-Fe3O4) for 24 h. (B) L. rhamnosus cultured under control conditions (LR-C) and in the presence of Fe3O4 NPs (LR-Fe3O4) for 24 h; (C) L. fermentum cultured under control conditions (LF-C) and in the presence of Fe3O4 NPs (LF-Fe3O4) for 24 h. The values for bacterial viable cell growth and pH are displayed as mean values ± SDs, log10 CFU/g, n = 3 (CFU/mL—colony-forming units/mL of the sample). A two-way ANOVA was applied to compare differences between the bacterial species through the Tukey multiple comparisons method with a p-value provided if p < 0.05, and the symbols for the Tukey interpretation are as follows: * p < 0.05. LP-C for L. plantarum (control); LR-C for L. rhamnosus (control); LF-C for L. fermentum (control); LP-Fe3O4 for L. plantarum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs; LR-Fe3O4 for L. rhamnosus after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs; LF-Fe3O4 for L. fermentum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs.
Regarding pH levels during the cultivation of the bacteria with or without Fe3O4 NPs, it was noticeable that the three bacteria had similar behaviors regarding their acidification profiles. A more rapid decline in pH values occurred when Fe3O4 NPs were present, although the final pH values remained similar. Even though the cultures of L. plantarum and L. rhamnosus with Fe3O4 showed a more rapid pH drop, the bacterial proliferation was lower than that of cultures without Fe3O4, which suggests that the Fe3O4 NPs may have slowed down their proliferation. Even more interestingly, the bacterial proliferation of L. fermentum with Fe3O4 was slightly higher than that of L. fermentum without Fe3O4, and the pH values followed the same trend as in the cases of the other two bacteria. These differences likely reflect inherent species-level variations in carbohydrate metabolism, acid production, and iron uptake by bacteria [4]. Furthermore, the notable drop in pH aligns with the enhanced growth observed in the Fe3O4-supplemented cultures by the end of the fermentation, supporting the conclusion that nanoparticle-provided iron catalyzes more vigorous fermentation.
2.3. Ferric-Reducing Activity of Probiotics
The ferric-reducing power of certain probiotic bacteria is central to improving iron absorption in the gut. In simple terms, most dietary iron is ingested as ferric iron (Fe3+), which is not easily absorbed by the body. For iron to be taken up by intestinal cells, it must first be reduced to its ferrous form (Fe2+). This conversion is crucial because Fe2+ can be readily transported into enterocytes via DMT1. In this respect, it was shown that the reduction efficiency was mainly influenced by the probiotic production of metabolites like 4-HPLA and the pH [16].
The metabolism of three probiotic strains, L. plantarum, L. rhamnosus, and L. fermentum, was analyzed under fermentation conditions in the presence of Fe3O4 NPs (Table 1). Several parameters were monitored, including energy substrate utilization (glucose and fructose), the production of organic acids (lactic, acetic, and propionic acids), the accumulation of 4-HPLA, and ethanol formation.

Table 1.
Secondary metabolite (mg/mL) profiling of L. plantarum, L. rhamnosus, and L. fermentum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs.
The observed progressive decline in glucose and fructose levels indicates active bacterial metabolism, consistent with the fermentative pathways characteristic of lactic acid bacteria. L. rhamnosus and L. fermentum initially had higher sugar concentrations than L. plantarum. However, after 24 h, the sugar dropped to low levels, indicating complete fermentation. Notably, the incorporation of Fe3O4 NPs did not restrict sugar metabolism, whereas, for L. rhamnosus, a slight enhancement in the rate of sugar consumption was observed. These findings align with those of studies suggesting that metal-based nanoparticles can modulate bacterial metabolism [34,49]. The impact of Fe3O4 NPs on bacterial activity is highly dependent on their physicochemical properties, particularly their particle size, surface charge, and synthesis method [50]. Shen et al. (2018) [51] showed that Fe3O4 NPs synthesized by co-precipitation exhibit high aqueous medium dispersions, which can facilitate their interaction with microbial cells, potentially modulating metabolic pathways [51].
One of the most significant metabolites excreted after the fermentation was 4-HPLA, detected in the highest concentration for L. fermentum, significantly exceeding the levels observed for L. plantarum and L. rhamnosus. Previous studies have suggested that 4-HPLA significantly affects iron metabolism, particularly concerning ferric reduction [4,16,23]. This metabolite has been reported to efficiently reduce Fe3+ to Fe2+ under acidic conditions, potentially enhancing iron’s bioavailability in the gut. González et al. (2017) [16] investigated the iron-reducing capacity of L. fermentum CECT5716, indicating that this strain excretes 4-HPLA in significant amounts, mimicking the function of duodenal cytochrome B (DcytB), an endogenous iron-reducing enzyme in enterocytes. Their findings confirmed that 4-HPLA actively reduces iron forms at pH 3.8, making iron more bioavailable for absorption. Moreover, they demonstrated that the iron-reducing activity of L. fermentum is predominantly extracellular, as evidenced by the retained reducing power in the cell-free supernatant [16]. This aligns with our results, where L. fermentum indicates the highest levels of 4-HPLA, further reinforcing its role in iron metabolism.
Beyond its role in iron reduction, 4-HPLA has also been associated with modulating organic acid metabolism. Previous studies have shown that elevated 4-HPLA concentrations correlate with increased acetate accumulation, suggesting that this metabolite influences key pathways involved in organic acid biosynthesis [52]. Acetate is a key metabolic byproduct in lactic acid bacterium fermentation and serves as an essential precursor for energy metabolism and bacterial growth regulation [3,23,24]. Higher acetate levels contribute to a more favorable intestinal environment by modulating the pH and supporting the growth of beneficial microbiota [30]. Moreover, probiotic fermentation contributes to gut acidification by producing organic acids (short-chain fatty acids), which enhance iron solubility and absorption [53]. The reduction in pH due to short-chain fatty acid production has been suggested to directly influence iron solubility in the intestinal environment. For instance, lower fecal pH levels, which have been linked to probiotic administration, enhance iron absorption by mechanisms that facilitate the dissolution of ferric iron into its soluble form [54]. Ji et al. (2021) [55] also established that elevated levels of Corynebacterium and Lactobacillus (5 × 109) species enhance the production of short-chain fatty acids, which subsequently stimulate interferon-β secretion in alveolar macrophages, thereby influencing iron absorption. Additionally, probiotic immunomodulation exerts anti-inflammatory effects, which downregulate hepcidin. This relationship was further supported by Vonderheid et al. (2019) [56] and Rusu et al. (2020) [23], who independently confirmed the positive correlation between probiotic supplementation and improved iron uptake. Specifically, L. plantarum 299v (109 CFU/g) has been shown to lead to a significant increase in ferritin levels in women of reproductive age (mean increase 2.45 ng/mL, 95% CI 0.61–4.3, n = 320) [24]. Furthermore, L. curvatus (109 CFU/g) with Fe gluconate at 120 mg Fe/kg diet supplementation re-established anemia parameters in 8 weeks of oral treatment [57]. These mechanisms collectively contribute to improved iron absorption and probiotic viability, resulting in a synergistic effect. Thus, probiotics influence iron metabolism through multiple mechanisms, including pH reduction, organic acid secretion, and direct iron chelation via metabolites like 4-HPLA [4,16,22,30]. These combined effects create an environment conducive to increased iron bioavailability, highlighting the role of L. fermentum in iron homeostasis [5].
FT-IR and XRD analyses were conducted to confirm the structural and chemical transformation of Fe3O4 NPs into Fe2O3 during probiotic fermentation. The FT-IR spectrum (Figure 6A) provides the results of this structural transition. The characteristic Fe–O stretching vibration typically observed around 570 cm−1 in pure magnetite was slightly shifted across the different bacterial treatments, with the most pronounced alteration occurring in L. fermentum-treated samples. This indicates structural perturbations resulting from bacterial enzymatic or metabolic activity, particularly the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+. Additionally, variations in absorbance intensity suggest differential interactions at the bacterial cell–nanoparticle interface, likely mediated by secreted metabolites, siderophores, or reductases. Previous studies have demonstrated that bacterial strains with high ferric reductase activity can modulate the electronic structure of iron oxides, thereby enhancing their dissolution [12,48]. Beyond the Fe–O vibrational region, other subtle spectral changes can be noted in the 1200–1600 cm−1 range, where bacterial exopolysaccharides, proteins, and other organic compounds exhibit characteristic absorbance peaks. These features are particularly relevant because bacterial surface biomolecules can act as ligands that chelate iron, further enhancing its solubility and bioavailability. The observed spectral changes suggest the involvement of multiple biogenic factors in iron reduction.

Figure 6.
FT-IR spectra (A) and XRD patterns (B) of Fe3O4 NPs after fermentation with probiotic bacteria. LP-Fe3O4 for L. plantarum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs; LR-Fe3O4 for L. rhamnosus after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs; LF-Fe3O4 for L. fermentum after fermentation with Fe3O4 NPs.
The XRD pattern further corroborated the microbial-induced oxidation process. The hexagonal hematite structure of Fe2O3 (α-Fe2O3) formed after fermentation, and the crystalline phase was analyzed (Figure 6B). The reflections were assigned to Miller indices (104), (110), (113), (024), (116), (018), (214), (030), which could be indexed by the JCPDS sheet—PDF no. 20-1096. The results suggest substantial oxidation of Fe3O4 (magnetite) into Fe2O3 (hematite) in the case of L. fermentum and L. plantarum fermentation. The disappearance of magnetite-specific peaks and the emergence of hematite-specific diffraction patterns indicate a complete phase transformation. This transformation is driven by the acidic and redox-active microenvironment generated by a high concentration of 4-HPLA. The increased crystallinity of L. fermentum–Fe2O3 post-fermentation suggests a controlled oxidation mechanism, likely involving direct microbial interactions with the nanoparticle surface. From a mechanistic perspective, the microbial secretion of metabolites capable of chelating Fe3+ plays a crucial role in this transformation, with L. fermentum known to enhance iron bioavailability through extracellular electron transfer [13,16]. On the other hand, L. rhamnosus and L. plantarum induce noticeable modifications and exhibit less pronounced peak broadening than L. fermentum, suggesting a more moderate interaction with the iron oxide lattice. These results suggest that probiotic-fermented Fe3O4 NPs could be an effective dietary iron source.
These study findings should be interpreted with consideration of their limitations. First, although 4-HPLA has been identified as a key metabolite in iron reduction, a direct functional validation of its role in promoting iron absorption was not conducted herein. As such, future in vitro assays using intestinal cell models must confirm its biological activity. Second, additional in vivo studies are necessary to assess the impact of probiotic-fermented Fe3O4 NPs on iron bioavailability. Third, the results were obtained using specific probiotic strains (L. fermentum, L. plantarum, and L. rhamnosus), and further studies should investigate whether strain-specific metabolic variations influence the strains’ ability to enhance iron absorption. While several studies have explored the influence of probiotics on iron bioavailability, less attention has been given to how this intervention may affect other key probiotic functions, such as immunomodulation, enhancement of gut barrier integrity, and modulation of the host microbiota [58,59]. This represents an important gap, and it remains unclear whether co-administration of iron and probiotics may significantly alter the functional properties of probiotic strains, either through direct metabolic interactions or by influencing the intestinal environment. Future studies should aim to elucidate these potential effects in order to ensure that improvements in iron status do not come at the expense of other health-promoting activities of probiotics.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate, FeSO4·7H2O (ACS, 98–102%, VWR, Radnor, PA, USA); potassium nitrate, KNO3 (Sigma Aldrich, 99%; St. Louis, MO, USA); potassium hydroxide, KOH (Alfa Aesar, 99.8%; Haverhill, MA, USA); and ethanol absolute were used without further purification.
The fermentation process involved three probiotic strains, Lactobacillus fermentum (LMG 6902), Lactobacillus plantarum (ATCC 8014), and Lactobacillus rhamnosus (LMG 25626), acquired from the BCCM/LMG Bacteria Collection. The bacterial cultures were cultivated in de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth, supplied in dried form by HIMEDIA (Einhausen, Germany). Acetonitrile, HPLC gradient-grade, was provided by Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), while water was purified with a Direct-Q UV system by Millipore (Burlington, MA, USA). Pure standards of glucose, fructose, lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (4-HPLA), and ethanol (>98%) were purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry (Tokyo, Japan).
3.2. Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
The co-precipitation method was applied to obtain Fe3O4 NPs. Briefly, FeSO4·7H2O was dissolved in MiliQ water at a molar ratio of 1:1 under continuous stirring to obtain a homogeneous solution [21]. The reaction underlying the formation of the iron oxide matrix (Equation (1)) is based on the partial oxidation of divalent iron to trivalent iron, simultaneously with the reduction of the nitrate ion:
3FeSO4 + 2KNO3 + 4KOH → Fe3O4↓+ 3K2SO4 + 2NO2↑ + 2H2O
The mixture was heated to 80 °C, and 25% NH3·H2O was added dropwise until the pH reached 11, ensured by the presence of OH− ions. The reaction mixture was maintained in these conditions for 60 min, with constant stirring to promote crystal growth and maturation. The resulting black precipitate was magnetically separated using a 0.3 T magnetic field, then thoroughly washed with MiliQ water and a 4:1 ethanol and ethyl acetate combination (v/v). The produced Fe3O4 NPs were suspended in MiliQ water, resulting in a stable black solution.
3.3. Characterization of the Fe3O4 NPs
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyses were conducted using a HITACHI HD-2700 STEM microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a digital image recording system alongside an SU8230 scanning electron microscope (SEM) from the same manufacturer [19]. Dehydration was achieved using an ethanol series (30%), with SEM samples dried using a liquid CO2 critical point dryer (1200 psi, 31 °C, 30 min) to eliminate surface tension artifacts, while TEM samples were air-dried on carbon-coated 400-mesh copper grids under low humidity with 0.1% BSA to prevent aggregation. The electron microscope was coupled with an Aztec X-Max 1160 EDX detector (Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, UK) for energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). SEM/EDS images were acquired under 30 kV and 10 μA operating conditions. Image acquisition and particle size measurements were performed using Hitachi acquisition software (version 8.1). To ensure statistical reliability, n ≥ 100 measurements were made across multiple images, and the data were fitted to a Gaussian distribution using Origin 2019b (ver. 9.65) [60].
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) was conducted to analyze the chemical nature of the nanoparticle surfaces using a Shimadzu IR-Prestige FTIR Spectrometer equipped with a diamond PIKEMIRacle single reflection plate unit. The spectra were taken in the 600–4000 cm−1 range with a resolution of 4 cm−1 [61].
An X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed at ambient temperature using a Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer to investigate the crystal structure of the synthesized Fe3O4 NPs. The instrument was equipped with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å), and diffraction patterns were recorded over a suitable 2θ range to capture all characteristic peaks. Subsequently, the Scherrer method was used to estimate the average crystallite size [62].
3.4. Probiotic Inoculum Preparation with Fe3O4 NPs
The lactic acid bacterium strains L. fermentum LMG 6902, L. rhamnosus LMG 25626, and L. plantarum ATCC 8014 were cultivated under aerobic conditions in de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth medium. The medium was sterilized by autoclaving at 121 °C for 15 min. The bacterial cultures were incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 h, followed by an additional inoculum and incubation period under the same conditions until they reached the stationary growth phase (~20 h post-inoculation) [63]. The bacterial suspensions were assessed for viable cell counts, reaching approximately 10 log CFU/mL. The bacterial optical density (OD) at 600 nm (OD600) was measured using a NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA). The recorded OD600 values ranged between 0.009 and 0.011. For Fe3O4 nanoparticle (NP) exposure, a 100 mL bacterial suspension was supplemented with 120 µg/mL of Fe3O4 NPs [64]. The bacterial NP suspension was then incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 h under static conditions to allow potential bacterial interactions and uptake of Fe3O4 NPs. All these processes were carried out in a sterile environment.
3.5. Ferric-Reducing Activity of Probiotics
3.5.1. Secondary Metabolite Identification
To identify excreted bacterial compound(s) with ferric-reducing activity, the samples were centrifuged at 12,298× g and 4 °C for 30 min [65]. The supernatant was then filtered through a 0.45 μm nylon filter and analyzed using an HPLC system. The analysis was performed using an HP-1200 liquid chromatograph equipped with a quaternary pump, autosampler, DAD detector, and MS-6110 single-quadrupole API–electrospray detector (Agilent Technologies, Clara, CA, USA). The separation of compounds was performed on a Polaris Hi-Plex H column (300 × 7.7 mm, Agilent Technologies), employing a mobile phase of 5 mM H2SO4 at a rate of 0.6 mL/min. The column temperature was adjusted to 80 °C, while the RID temperature was maintained at 35 °C. The elution process for the compounds took 25 min. Data were acquired and interpreted using the OpenLab software ChemStation (Agilent Technologies, Clara, CA, USA). The identified compounds in the analyzed samples were recognized by comparing the duration of their stay within the system with those of standard reference compounds. The compounds analyzed during fermentation included glucose, fructose, lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, 4-HPLA, and ethanol. Chromatograms were recorded at wavelengths of λ = 210 and 280 nm, and data acquisition was performed with Agilent ChemStation software (ver. C.01.08).
3.5.2. Characterization of the Probiotic Biomass Enriched with Fe3O4 NPs
The structural, morphological, and chemical properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticle-enriched probiotic biomass were characterized using electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction techniques [66,67].
3.6. Statistical Analysis
All the values are displayed as means ± standard deviations (SDs) from three independent experiments. All continuous variables were tested for normality using the Shapiro–Wilk test before the statistical analysis. Data following a normal distribution were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey’s comparison test, and post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests. Minitab statistical software (version 16.1.0; LEAD Technologies, Inc., Charlotte, NC, USA) and Graph Prism Version 8.0.1. (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) were used to analyze the differences among samples with significance levels of p < 0.05. Statistical significance was assumed at the 95% confidence level for differences in mean values.
4. Conclusions
The present study validates the hypothesis that probiotic intervention significantly enhances the bioavailability of Fe3O4 NPs through several synergistic mechanisms. Probiotics, particularly L. fermentum, exhibit strong adhesion and internalization of the nanoparticles, facilitating more effective interactions at the microbial interface. This strain’s elevated production of 4-HPLA plays a crucial role in reducing ferric ions, thus improving iron solubility and subsequent uptake. Additionally, spectroscopic analyses revealed microbial-induced oxidation of Fe3O4 to Fe2O3, which further contributes to enhanced iron release and bioavailability. These findings underscore the potential of integrating probiotic formulations with iron oxide nanoparticles as a novel supplementation strategy to overcome the limitations of traditional iron therapies, mainly by reducing gastrointestinal side effects while optimizing iron absorption. Future research should focus on elucidating the precise molecular pathways involved and validating these results in clinical settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C., E.S., D.C.V. and O.L.P.; methodology, C.C., A.M., A.M.C. and R.A.V.; software, B.-E.T.; validation, L.B.-T., F.R. and L.M.; formal analysis, O.L.P.; investigation, C.C., A.M., L.B.-T. and F.R.; resources, D.C.V. and O.L.P.; data curation, O.L.P.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C., A.M., A.M.C. and R.A.V.; writing—review and editing, C.C., A.M. and E.S.; visualization, D.C.V. and O.L.P.; supervision, D.C.V.; project administration, O.L.P.; funding acquisition, O.L.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the Romanian Ministry of Education and Research, CNCS—UEFISCDI, project number PN-III-P4-ID-PCE-2020-2126, within PNCDI III.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Ma, Y.; Wu, H.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, T. Construction of iron oxide nanoparticles modified with Angelica sinensis polysaccharide for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia. J. Nanopart. Res. 2024, 26, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, N.U.; von Siebenthal, H.K.; Moretti, D.; Zimmermann, M.B. Oral iron supplementation in iron-deficient women: How much and how often? Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 75, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewska, Z.; Zawartka, A.; Schab, M.; Martyniak, A.; Skoczen, S.; Tomasik, P.J.; Wedrychowicz, A. Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Postbiotics in the Prevention and Treatment of Anemia. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garces, V.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Galvez, N.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Garcia-Martin, M.L.; Gutierrez, L.; Rondon, D.; Olivares, M.; Galvez, J.; et al. Bacteria-Carried Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Treatment of Anemia. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciont, C.; Mesaros, A.; Pop, O.L.; Vodnar, D.C. Iron oxide nanoparticles carried by probiotics for iron absorption: A systematic review. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, M.; Lebeer, S. Towards a Better Understanding of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG—Host Interactions. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13 (Suppl. S1), S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.-Z.; Wu, K.; Deng, L.-X.; Hu, M.; Luo, Y.-X.; Zhang, L.-Y. Probiotics to Prevent Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: A Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1095368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, A.C.; Halami, P.M. Probiotic attributes of Lactobacillus fermentum isolated from human feces and dairy products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8113–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumu, S.C.R.; Halami, P.M. In Vivo Safety Assessment of Lactobacillus fermentum Strains, Evaluation of Their Cholesterol-lowering Ability and Intestinal Microbial Modulation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 100, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegaray, N.; Yilmaz, B.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, M.; Pateiro, M.; Ozogul, F.; Lorenzo, J.M. A novel approach to Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: From probiotic properties to the omics insights. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 268, 127289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averina, O.V.; Poluektova, E.U.; Marsova, M.V.; Danilenko, V.N. Biomarkers and utility of the antioxidant potential of probiotic Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria as representatives of the human gut microbiota. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, T.J.; Smith, A.T. Ferric iron reductases and their contribution to unicellular ferrous iron uptake. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 218, 111407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejedor-Sanz, S.; Stevens, E.T.; Li, S.; Finnegan, P.; Nelson, J.; Knoesen, A.; Light, S.H.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M.; Marco, M.L. Extracellular electron transfer increases fermentation in lactic acid bacteria via a hybrid metabolism. eLife 2022, 11, e70684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Li, L. The influence of microbiota on ferroptosis in intestinal diseases. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2263210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Humaran, L.G.; Chassaing, B.; Langella, P. Exploring the interaction and impact of probiotic and commensal bacteria on vitamins, minerals and short chain fatty acids metabolism. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Gálvez, N.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Dominguez-Vera, J.M. Identification of the key excreted molecule by Lactobacillus fermentum related to host iron absorption. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, K.C.; Samanta, S.; Mondal, S.; Mondal, S.P.; Mondal, K.; Halder, S.K. Navigating the frontiers of mineral absorption in the human body: Exploring the impact of probiotic innovations: Impact of probiotics in mineral absorption by human body. Indian J. Exp. Biol. (IJEB) 2024, 62, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, R.A.; Vodnar, D.C. Probiotic-driven advancement: Exploring the intricacies of mineral absorption in the human body. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciont, C.; Difonzo, G.; Pasqualone, A.; Chis, M.S.; Ranga, F.; Szabo, K.; Simon, E.; Naghiu, A.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Caponio, F.; et al. Phenolic profile of micro- and nano-encapsulated olive leaf extract in biscuits during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2023, 428, 136778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Fei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, S.; Zou, H.; Zhu, F. Efficacy of probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotics supplements in individuals with anemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesaros, A.; Neamțu, B.V.; Marinca, T.F.; Popa, F.; Cupa, G.; Vasile, O.R.; Chicinaș, I. Preparation of Fe@Fe3O4/ZnFe2O4 Powders and Their Consolidation via Hybrid Cold-Sintering/Spark Plasma-Sintering. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sara, S.H.; Yasser, J.J.; Latif, I.K. Influence of Zinc and Probiotics on Productive Performance, Immune Response and Mineral Content in Muscle of Broiler Chickens. Acad. Int. J. Vet. Med. 2023, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, I.G.; Suharoschi, R.; Vodnar, D.C.; Pop, C.R.; Socaci, S.A.; Vulturar, R.; Istrati, M.; Morosan, I.; Farcas, A.C.; Kerezsi, A.D.; et al. Iron Supplementation Influence on the Gut Microbiota and Probiotic Intake Effect in Iron Deficiency—A Literature-Based Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, A.; Parge, A.; Nimkar, R.; Sinha, A. Effect of probiotic and prebiotics supplementation on hemoglobin levels and iron absorption among women of reproductive age and children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nutr. 2025, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazawal, S.; Dhingra, U.; Hiremath, G.; Sarkar, A.; Dhingra, P.; Dutta, A.; Menon, V.P.; Black, R.E. Effects of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 and prebiotic oligosaccharide added to milk on iron status, anemia, and growth among children 1 to 4 years old. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Mandal, S. Bifidobacteria—Insight into clinical outcomes and mechanisms of its probiotic action. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 192, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhidarian, B.; Roldos, L.; Iskandar, M.M.; Saedisomeolia, A.; Kubow, S. Probiotic Supplementation and Micronutrient Status in Healthy Subjects: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, P.; Singh, V.; Gupta, R.; Kaul, S.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, S.; Bhunia, R.K.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Singhal, N.K. pH-Triggered, Synbiotic Hydrogel Beads for In Vivo Therapy of Iron Deficiency Anemia and Reduced Inflammatory Response. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 7467–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.K.; Schwartz, A.J.; Barthel, G.; Inohara, N.; Liu, Q.; Sankar, A.; Hill, D.R.; Ma, X.; Lamberg, O.; Schnizlein, M.K.; et al. Microbial Metabolite Signaling Is Required for Systemic Iron Homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 115–130.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, M.; Onning, G.; Berggren, A.; Hulthen, L. Probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum 299v increases iron absorption from an iron-supplemented fruit drink: A double-isotope cross-over single-blind study in women of reproductive age. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besenhard, M.O.; LaGrow, A.P.; Hodzic, A.; Kriechbaum, M.; Panariello, L.; Bais, G.; Loizou, K.; Damilos, S.; Margarida Cruz, M.; Thanh, N.T.K.; et al. Co-precipitation synthesis of stable iron oxide nanoparticles with NaOH: New insights and continuous production via flow chemistry. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausova, G.; Hyrslova, I.; Hynstova, I. In Vitro Evaluation of Adhesion Capacity, Hydrophobicity, and Auto-Aggregation of Newly Isolated Potential Probiotic Strains. Fermentation 2019, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Surface components and metabolites of probiotics for regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campaña, A.L.; Saragliadis, A.; Mikheenko, P.; Linke, D. Insights into the bacterial synthesis of metal nanoparticles. Front. Nanotechnol. 2023, 5, 1216921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albutt, N.; Sonsupup, S.; Sinprachim, T.; Thonglor, P. Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Chitosan for Biomedical Applications. Key Eng. Mater. 2024, 1005, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.L.D.C.; Silva, I.M.B.; Magdalena, A.G. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4-NH2 and Fe3O4-NH2-chitosan nanoparticles. Cerâmica 2021, 67, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Garces, V.; Galvez, N.; Gutierrez, L.; Galvez, J.; Rondon, D.; Olivares, M.; Dominguez-Vera, J.M. Magnetic study on biodistribution and biodegradation of oral magnetic nanostructures in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15041–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Bao, T.; Yi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Z. Ribosome Profiling and RNA Sequencing Reveal Genome-Wide Cellular Translation and Transcription Regulation Under Osmotic Stress in Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 53103. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 781454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Blanco, D.A.; Shell, S.S. Regulation of mRNA Stability During Bacterial Stress Responses. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, B.; Kos-Braun, I.C.; Henras, A.K.; Dez, C.; Rueda, M.P.; Zhang, X.; Gadal, O.; Kos, M.; Shore, D. A ribosome assembly stress response regulates transcription to maintain proteome homeostasis. eLife 2019, 8, e45002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.Y.J.; Quek, S.Y. Probiotics: Health benefits, food application, and colonization in the human gastrointestinal tract. Food Bioeng. 2024, 3, 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamarlapudi, S.L.; Muddada, S. Biosorption of Iron (II) by Lactobacillus fermentum from Aqueous Solutions. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Bautista, A.; de la Garza, M.; Carrero, J.C.; Campos-Rodriguez, R.; Godinez-Victoria, M.; Drago-Serrano, M.E. The Impact of Lactoferrin on the Growth of Intestinal Inhabitant Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Bae, M.; Hwang, I.M.; Lee, J.H. Transcriptional analysis of the molecular mechanism underlying the response of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum to lactic acid stress conditions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.H.; Goli, J.K.; Das, S.; Mohanty, N. Production, optimization and probiotic characterization of potential lactic acid bacteria producing siderophores. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yang, T.; Chakravorty, S.; Majumdar, A.; Nairn, B.L.; Six, D.A.; Marcondes Dos Santos, N.; Price, S.L.; Lawrenz, M.B.; Actis, L.A.; et al. Fluorescent sensors of siderophores produced by bacterial pathogens. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiousi, D.E.; Efstathiou, C.; Tzampazlis, V.; Plessas, S.; Panopoulou, M.; Koffa, M.; Galanis, A. Genetic and phenotypic assessment of the antimicrobial activity of three potential probiotic lactobacilli against human enteropathogenic bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1127256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.M.; Svistunenko, D.A.; Wilson, M.T.; Hemmings, A.M.; Moore, G.R.; Le Brun, N.E. Bacterial iron detoxification at the molecular level. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 17602–17623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Gomes, D.; Esteruelas, G.; Bonilla, L.; Lopez-Machado, A.L.; Galindo, R.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents: An Overview. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algadi, H.; Alhoot, M.A.; Al-Maleki, A.R.; Purwitasari, N. Effects of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles against Biofilm-Forming Bacteria: A Systematic Review. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Li, B.; Qiao, Y. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in Targeted Drug/Gene Delivery Systems. Materials 2018, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.; Yang, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B. Production of 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid by Lactobacillus sp. SK007 fermentation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 109, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Myojin, T.; Li, K.; Kurita, A.; Seto, M.; Motoyama, A.; Liu, X.; Satoh, A.; Munemasa, S.; Murata, Y.; et al. A Major Intestinal Catabolite of Quercetin Glycosides, 3-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid, Protects the Hepatocytes from the Acetaldehyde-Induced Cytotoxicity through the Enhancement of the Total Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrypnik, K.; Bogdanski, P.; Schmidt, M.; Suliburska, J. The Effect of Multispecies Probiotic Supplementation on Iron Status in Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 192, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.J.; Sun, Q.M.; Nie, D.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Qin, F.F.; Wang, Q.S.; Lu, S.F.; Pang, G.M.; Lu, Z.G. Probiotics protect against RSV infection by modulating the microbiota-alveolar-macrophage axis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1630–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonderheid, S.C.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Park, C.; Pauls, H.; OjiNjideka Hemphill, N.; LaBomascus, B.; McLeod, A.; Koenig, M.D. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Probiotic Species on Iron Absorption and Iron Status. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrypnik, K.; Olejnik-Schmidt, A.; Mikolajczyk-Stecyna, J.; Schmidt, M.; Suliburska, J. Influence of supplementation with probiotic bacteria Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Latilactobacillus curvatus on selected parameters of duodenum iron metabolism in rats on a high-fat, iron-deficient diet. Nutrition 2025, 129, 112591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.Z.; Badar, S.; O’Callaghan, K.M.; Zlotkin, S.; Roth, D.E. Fecal Iron Measurement in Studies of the Human Intestinal Microbiome. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2022, 6, nzac143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordine, M.L.; Seyoum, Y.; Bruneau, A.; Baye, K.; Lefebvre, T.; Cherbuy, C.; Canonne-Hergaux, F.; Nicolas, G.; Humblot, C.; Thomas, M. The microbiota and the host organism switch between cooperation and competition based on dietary iron levels. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2361660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconeasa, Z.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Coman, C.; Leopold, L.; Mesaros, A.; Pop, O.; RUGINĂ, D.; Socaciu, C. Evaluation of antiproliferative potential of cerium oxide nanoparticles on hela human cervical tumor cell. Bull. UASVM Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vodnar, D.C.; SOCACIU, C. Monitoring lactic acid fermentation in media containing dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) by FTIR spectroscopy. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2012, 40, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.L.; Mesaros, A.; Vodnar, D.C.; Suharoschi, R.; Tăbăran, F.; Magerușan, L.; Tódor, I.S.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Balint, A.; Ciontea, L.; et al. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Efficient Antibacterial Application In Vitro against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Pathogens. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csatlos, N.I.; Simon, E.; Teleky, B.E.; Szabo, K.; Diaconeasa, Z.M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Ciont Nagy, C.; Pop, O.L. Development of a Fermented Beverage with Chlorella vulgaris Powder on Soybean-Based Fermented Beverage. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafazzoli, K.; Ghavami, M.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Production of iron enriched Saccharomyces boulardii: Impact of process variables. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleky, B.E.; Martău, A.G.; Ranga, F.; Chețan, F.; Vodnar, D.C. Exploitation of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Baker’s Yeast as Single or Multiple Starter Cultures of Wheat Flour Dough Enriched with Soy Flour. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.; Poonia, A. Microbial biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using probiotic strain and its characterization. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 5477–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sarkar, B.; Kaushik, A.; Mostafavi, E. Nanobiotechnological prospects of probiotic microflora: Synthesis, mechanism, and applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838 Pt 3, 156212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).