Paeonol Suppresses Bladder Cancer Progression via Apoptotic Pathways: Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Paeonol Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of BC Cells
2.2. Paeonol Induces Apoptosis and Arrests Cell Cycle at the G1 Phase on BC Cells
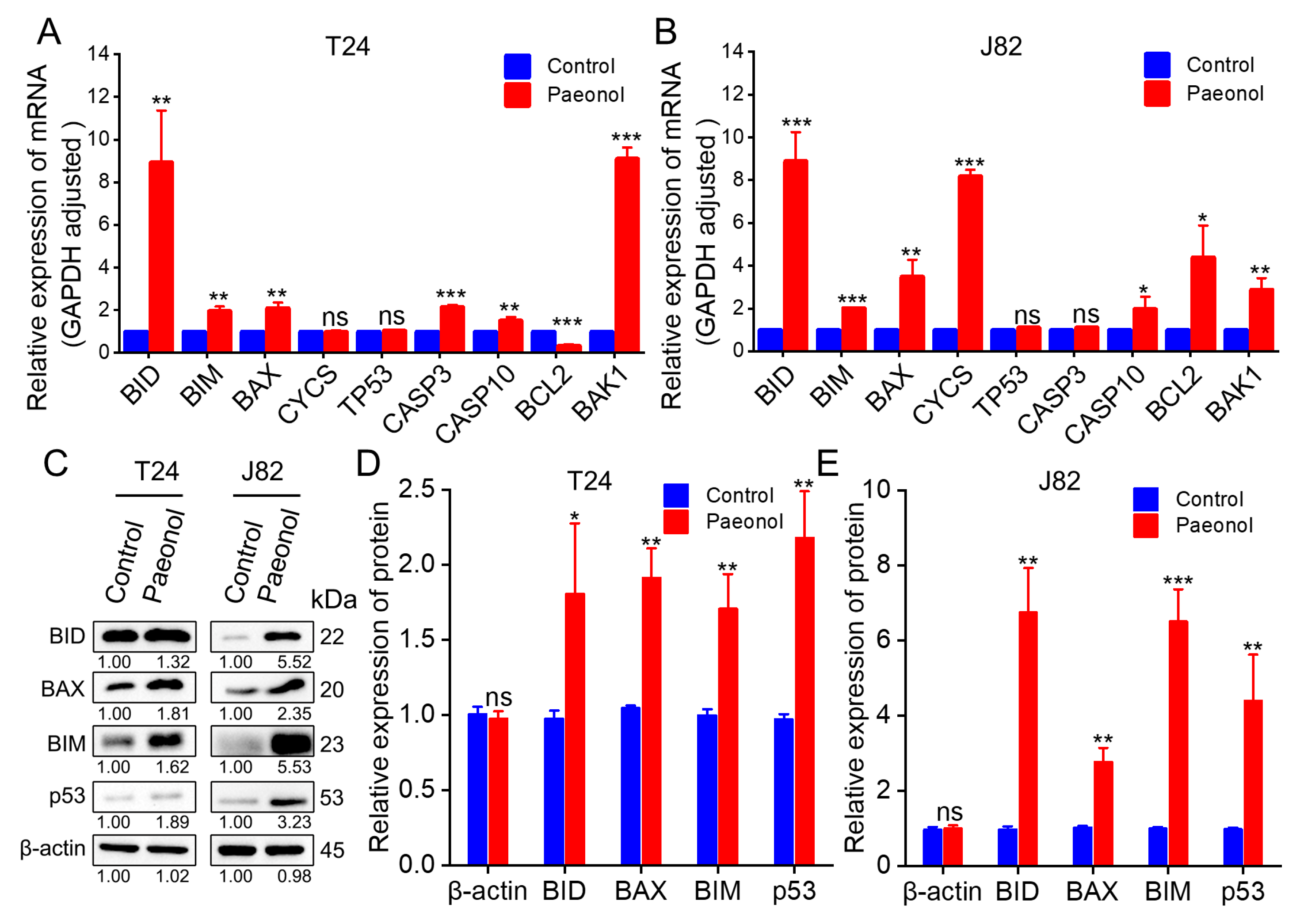
2.3. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Paeonol’s Effects on BC Cells
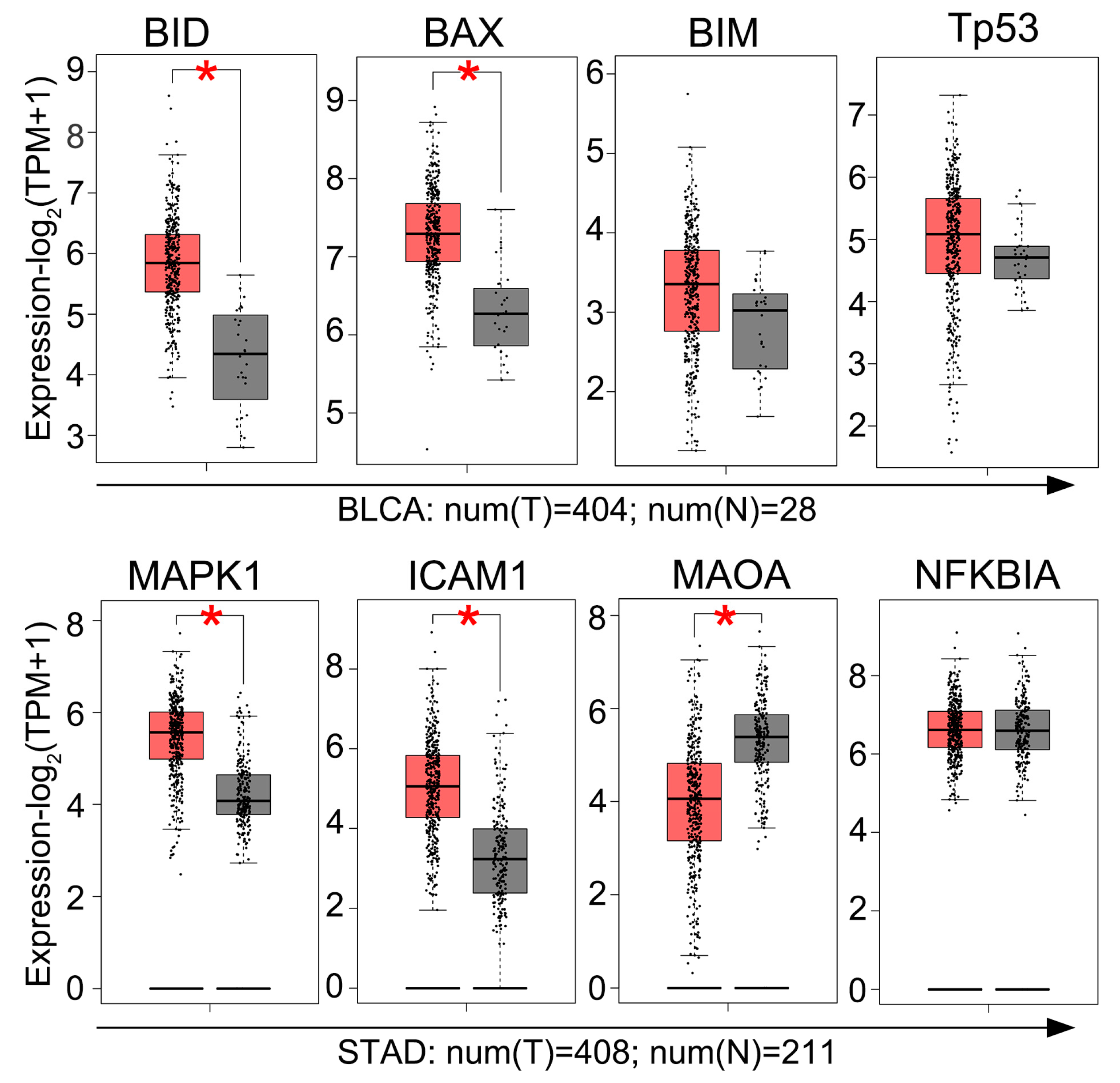
2.4. GEPIA Analysis of Gene Expression in BC Tissues
2.5. Paeonol Inhibits Tumor Growth in a Xenograft Mouse Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Paeonol Preparation and Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Viability Assay and IC50 Determination
4.3. Cell Migration by Wound Healing Assay
4.4. Apoptosis Detection by Annexin V-FITC/PI Staining and Flow Cytometry
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis by PI Staining and Flow Cytometry
4.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
4.8. GEPIA Analysis of Gene Expression
4.9. In Vivo Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | bladder cancer |
| CCK-8 | cell counting kit-8 |
| CDX | cell line-derived xenograft |
| d | day |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| h | hours |
| IC50 | half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| i.g. | intragastric administration |
| MDR | multidrug resistance |
| MIBC | muscle-invasive bladder cancer |
| min | minutes |
| NMIBC | non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer |
| PI | propidium iodide |
| PS | penicillin–streptomycin |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene difluoride |
| RT-qPCR | real-time quantitative PCR |
| SD | standard deviations |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfo-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| TMB | tumor mutational burden |
| WB | Western blotting |
References
- Lai, H.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Q.; Luo, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, M.; Miao, J.; Ji, Z.; Lin, G.N.; Song, W.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the epithelial cell heterogeneity and invasive subpopulation in human bladder cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 2099–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdik, C. Unlocking bladder cancer. Nature 2017, 551, S34–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussinov, R.; Tsai, C.J.; Jang, H. Anticancer drug resistance: An update and perspective. Drug Resist. Updat. 2021, 59, 100796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Akbani, R.; Creighton, C.J.; Lerner, S.P.; Weinstein, J.N.; Getz, G.; Kwiatkowski, D.J. Invasive Bladder Cancer: Genomic Insights and Therapeutic Promise. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4514–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Pei, L.; Li, Y.; Gou, X. EP300 mutation is associated with tumor mutation burden and promotes antitumor immunity in bladder cancer patients. Aging 2020, 12, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, G.; Zhang, D.; Lai, W.F. Mechanisms and strategies to enhance penetration during intravesical drug therapy for bladder cancer. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, J.Y.; Kamat, A.M.; Black, P.C.; Grivas, P.; Shariat, S.F.; Babjuk, M. Recurrence mechanisms of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer—A clinical perspective. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2022, 19, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cookson, M.S.; Guercio, B.J.; Cheng, L. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. BMJ 2024, 384, e076743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.G.; Oh, W.K.; Galsky, M.D. Treatment of muscle-invasive and advanced bladder cancer in 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 404–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigner, P.; Bijak, M.; Saluk-Bijak, J. The Green Anti-Cancer Weapon. The Role of Natural Compounds in Bladder Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, M.; Corno, C.; Colombo, D.; Perego, P. Curcumin and Related Compounds in Cancer Cells: New Avenues for Old Molecules. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 889816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Thai, P.N.; Shivnaraine, R.V.; Ren, L.; Wu, X.; Siepe, D.H.; Liu, Y.; Tu, C.; Shin, H.S.; Caudal, A.; et al. Multiscale drug screening for cardiac fibrosis identifies MD2 as a therapeutic target. Cell 2024, 187, 7143–7163.e7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.J.; Du, S.Y.; Mu, L.S.; Fan, J.J.; Hu, J.C.; Ye, Y.; Ding, M.; Zhou, W.Y.; Yu, Q.H.; et al. Artemisinins ameliorate polycystic ovarian syndrome by mediating LONP1-CYP11A1 interaction. Science 2024, 384, eadk5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Dai, S.; Xue, X.; Peng, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Protective mechanism of Paeonol on central nervous system. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 470–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Du, Y.; Xie, L.; Pu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B. Effects of Paeonol and Gastroretention Tablets of Paeonol on Experimental Gastric Ulcers and Intestinal Flora in Rats. Inflammation 2020, 43, 2178–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, K.; Xi, B.; Xie, J.; Bing, X. Paeonol increases the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacity of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 123, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Feng, X.; Du, M.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P. Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of paeonol on antitumor and prevention of side effects of cancer therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1194861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, D.C.; Liu, L.F. Paeonol: Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.S.; Chen, J.X.; Tang, J.; Geng, Y.W.; Zheng, L.; Lv, L.L.; Chen, L.Y.; Chen, Z. Paeonol Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion Through the Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad Signaling and Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.H.; Shi, R.J.; Chen, Z.C. Paeonol exerts anti-tumor activity against colorectal cancer cells by inducing G0/G1 phase arrest and cell apoptosis via inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, G.; Shi, Y. Investigation on the antitumor effects of paeonol against renal cell carcinoma based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 285, 114857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Zhou, S. Antitumor and Apoptosis Induction Effects of Paeonol on Mice Bearing EMT6 Breast Carcinoma. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Wang, X.F. Paeonol exerts an anticancer effect on human colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of PGE2 synthesis and COX-2 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.S.; Han, X.; Yu, P.J.; Jiao, M.M.; Liu, X.H.; Shi, J.B. Novel paeonol derivatives: Design, synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in vivo. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 98, 103735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Cai, L.J.; Pang, K.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Li, B.B.; Li, R.; Han, C.H. Paeonol inhibits proliferation and induces cell apoptosis of human T24 and 5637 bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, R.; Zhai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z. Paeonol Inhibits Glioma Growth In Vivo and In Vitro by Inducing Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2023, 33, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cai, O.; Yu, Y.; Tan, S. Paeonol inhibits the malignancy of Apatinib-resistant gastric cancer cells via LINC00665/miR-665/MAPK1 axis. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S.Y. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting p53 pathways: Mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, N.J.; Oliveira, R.A.; Körner, P.R.; Kochavi, A.; Mertens, S.; Malka, Y.; Voogd, R.; van der Horst, S.E.M.; Huismans, M.A.; Smabers, L.P.; et al. DNA damage induces p53-independent apoptosis through ribosome stalling. Science 2024, 384, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.W.; Okada, M.; Sayeed, I.; Xiao, G.; Stein, D.; Jin, P.; Ye, K. Gambogic amide, a selective agonist for TrkA receptor that possesses robust neurotrophic activity, prevents neuronal cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16329–16334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Qiu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guan, Z.; Qin, Y.; Sui, T.; Wu, F.; Li, B.; et al. The tumor-enriched small molecule gambogic amide suppresses glioma by targeting WDR1-dependent cytoskeleton remodeling. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.S.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.; Wan, Y.T.; Wu, F.W.; Liu, J.C.; Peng, J.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Hong, L. Paeonol repurposing for cancer therapy: From mechanism to clinical translation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G. Emerging nanomedicines of paclitaxel for cancer treatment. J. Control. Release 2022, 342, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Anand, U.; Pandey, S.K.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Chen, Z.S.; Dey, A. Therapeutic strategies to overcome taxane resistance in cancer. Drug Resist. Updates 2021, 55, 100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adki, K.M.; Kulkarni, Y.A. Chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacology and recent novel drug delivery systems of paeonol. Life Sci. 2020, 250, 117544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Shi, R.; Fu, F.; Li, M.; De, D.; Du, Y.; Li, Z. Paeonol protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by promoting Mfn2-mediated mitochondrial fusion through activating the PKCε-Stat3 pathway. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 47, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.A.; El-Sheikh, A.A.K.; Abdel-Hafez, S.M.N.; Kandeel, M.; Abdel-Gaber, S.A. Paeonol Protects Against Methotrexate-Induced Nephrotoxicity via Upregulation of P-gp Expression and Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 774387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Cancer Type | Potential Targets | 48 h In Vitro | Animal Model (Tumor Volume and Weight Inhibition) | Molecular Mechanism | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μg/mL) | Cell Apoptosis | Cell Cycle Arrest | Cell Migration | ||||
| bladder cancer (this study) | ↑: BID, BIM, BAX, p53 ↑: BID, BIM, BAX, p53 | 225 (T24) 124 (J82) | 7.65% to 11.72% (200 μg/mL) 9.03% to 18.01% (200 μg/mL) | G1 (200 μg/mL) G1 (200 μg/mL) | ↓ (50 μg/mL) ↓ (50 μg/mL) | yes (150 mg/kg i.g. every 3 days for 21 days) ND | apoptotic pathway |
| bladder cancer [28] | ↑: BAX, CASP3, AKT ↓: BCL2 ↑: BAX, CASP3, AKT ↓: BCL2 | 251 (T24) 265 (5637) | 7.83% to 20.47% (200 μg/mL) 5.80% to 14.07% (200 μg/mL) | ND ND | ND ND | yes (100 and 400 mg/kg/day i.g. for 14 days) ND | PI3K/AKT |
| glioma [29] | ↑: BID, BAK, BAX ↓: BCL2 ↑: BID, BAK, BAX ↓: BCL2 | 401 (U87MG) 88 (U251) | 3.65% to 23.90% (200 μg/mL) 4.30% to 33.30% (200 μg/mL) | G1 G1 | ND ND | yes (5 mg/kg i.p. every 3 days for 35 days) ND | the mitochondria-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway |
| apatinib-resistant gastric cancer [30] | ↑: miR-665 ↓: LINC00665, MAPK1 ↑: miR-665 ↓: LINC00665, MAPK1 | 54 (BGC-823/AP) 57 (MGC-803/AP) | ND ND | ND ND | ND ND | yes (30 and 50 mg/kg/day i.p. for 28 days) ND | LINC00665/miR-665/MAPK1 axis |
| colorectal cancer [26] | ↑: BAX, IkBa ↓: COX-2, BCL2, IKKa, NF-Kb/p65 | <120 (LoVo) | 1.10% to 16.10% (30 μg/mL) | ND | ND | yes (100 mg/kg/day i.g. for 11 days) | NF-kb/p65 |
| pancreatic cancer [22] | ↑: E-cadherin ↓: N-cadherin, vimentin, TGF-β1,p-Smad2/Smad2, p-Smad3/Smad3 | 44 (Panc-1) 35 (Capan-1) | ND ND | ND ND | ↓ (17, 25 μg/mL) ↓ (17, 25 μg/mL) | ND ND | TGF-β1/Smad, epithelial-mesenchymal-transition |
| Gene | 5′-3′ | 5′-3′ |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | AAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAA | GGAAGATGGTGATGGGATTT |
| BID | ATGGACCGTAGCATCCCTCC | GTAGGTGCGTAGGTTCTGGT |
| BIM | CTGAGTGTGACCGAGAAG | GATTACCTTGTGGCTCTGT |
| TP53 | GTTCCGAGAGCTGAATGAGG | TCTGAGTCAGGCCCTTCTGT |
| BAX | CCTTTTGCTTCAGGGTTTCA | CAGTTGAAGTTGCCGTCAGA |
| CYCS | GGTGATGTTGAGAAAGGCAAG | GTTCTTATTGGCGGCTGTGT |
| CASP3 | AAGCGAATCAATGGACTCT | TGTACCAGACCGAGATGT |
| CASP10 | TAGGATTGGTCCCCAACAAGA | GAGAAACCCTTTGTCGGGTGG |
| BCL2 | CTAAAACCCTGCCACCTCAA | CTCAGTGCTGAGTCCATCCA |
| BAK1 | TCTGGCCCTACACGTCTACC | ACAAACTGGCCCAACAGAAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, L.; Chen, R.; Guo, R.; Liang, Y.; Hao, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Yu, C.; Yang, Z. Paeonol Suppresses Bladder Cancer Progression via Apoptotic Pathways: Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040472
Ying L, Chen R, Guo R, Liang Y, Hao M, Chen X, Zhang W, Yu C, Yang Z. Paeonol Suppresses Bladder Cancer Progression via Apoptotic Pathways: Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040472
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Lu, Ruolan Chen, Rui Guo, Youfeng Liang, Mingxuan Hao, Xiaoyang Chen, Wenjing Zhang, Changyuan Yu, and Zhao Yang. 2025. "Paeonol Suppresses Bladder Cancer Progression via Apoptotic Pathways: Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040472
APA StyleYing, L., Chen, R., Guo, R., Liang, Y., Hao, M., Chen, X., Zhang, W., Yu, C., & Yang, Z. (2025). Paeonol Suppresses Bladder Cancer Progression via Apoptotic Pathways: Insights from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040472







