Identification of Deregulated miRNAs and mRNAs Involved in Tumorigenesis and Detection of Glioblastoma Patients Applying Next-Generation RNA Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Differently Expressed (DE) miRNAs in Tissue Samples of GBM Patients and Control Group
2.1.1. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
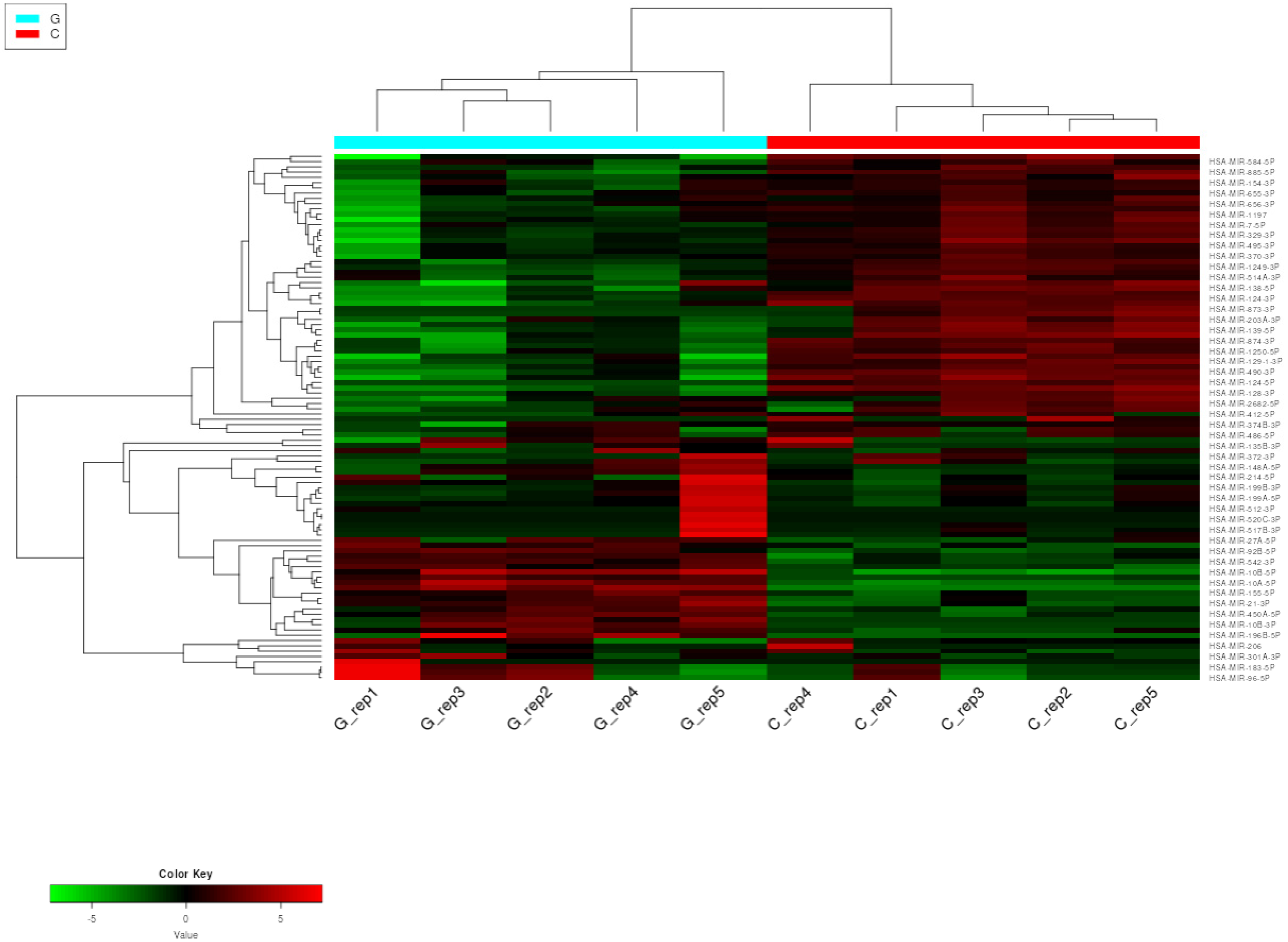
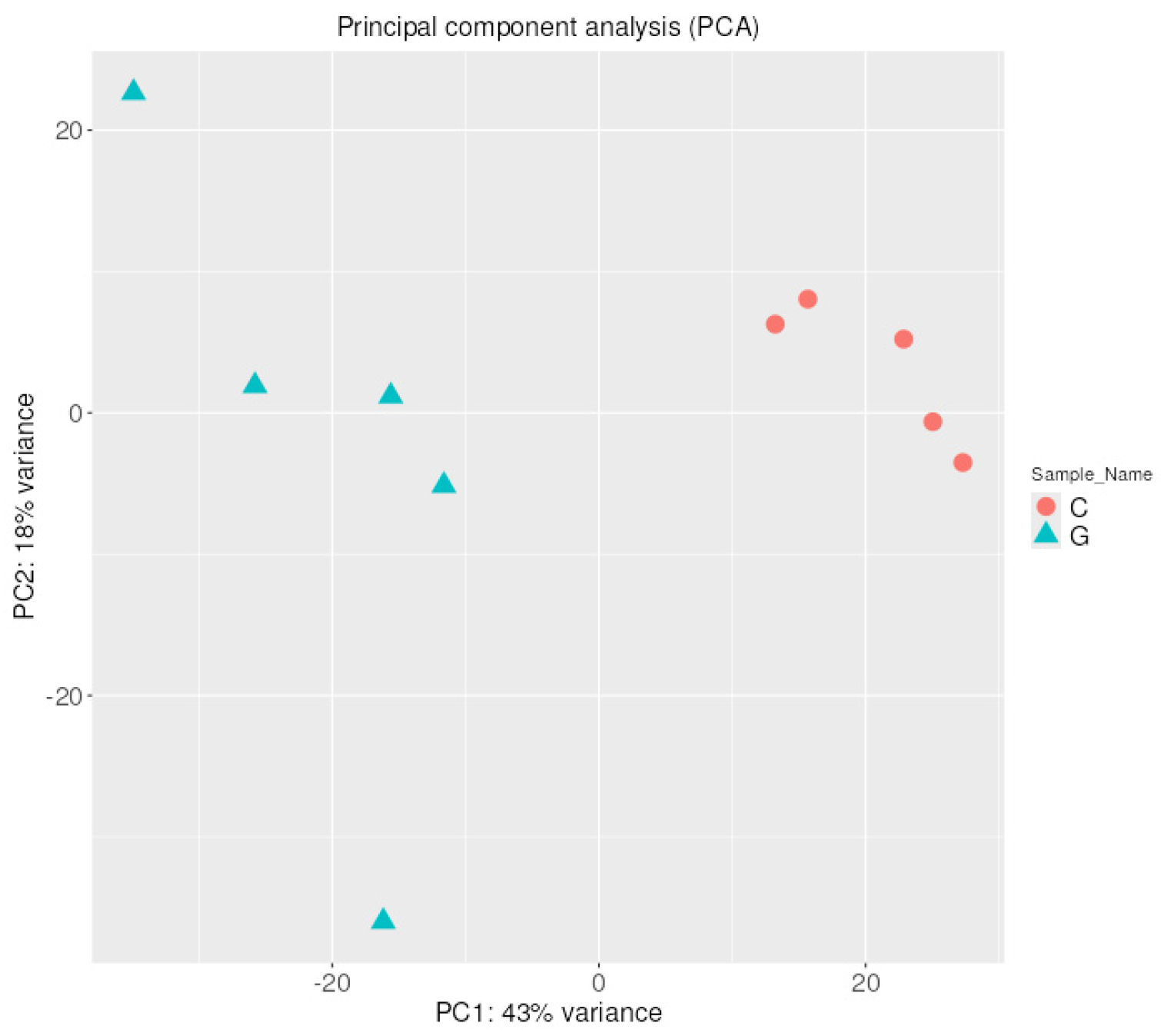
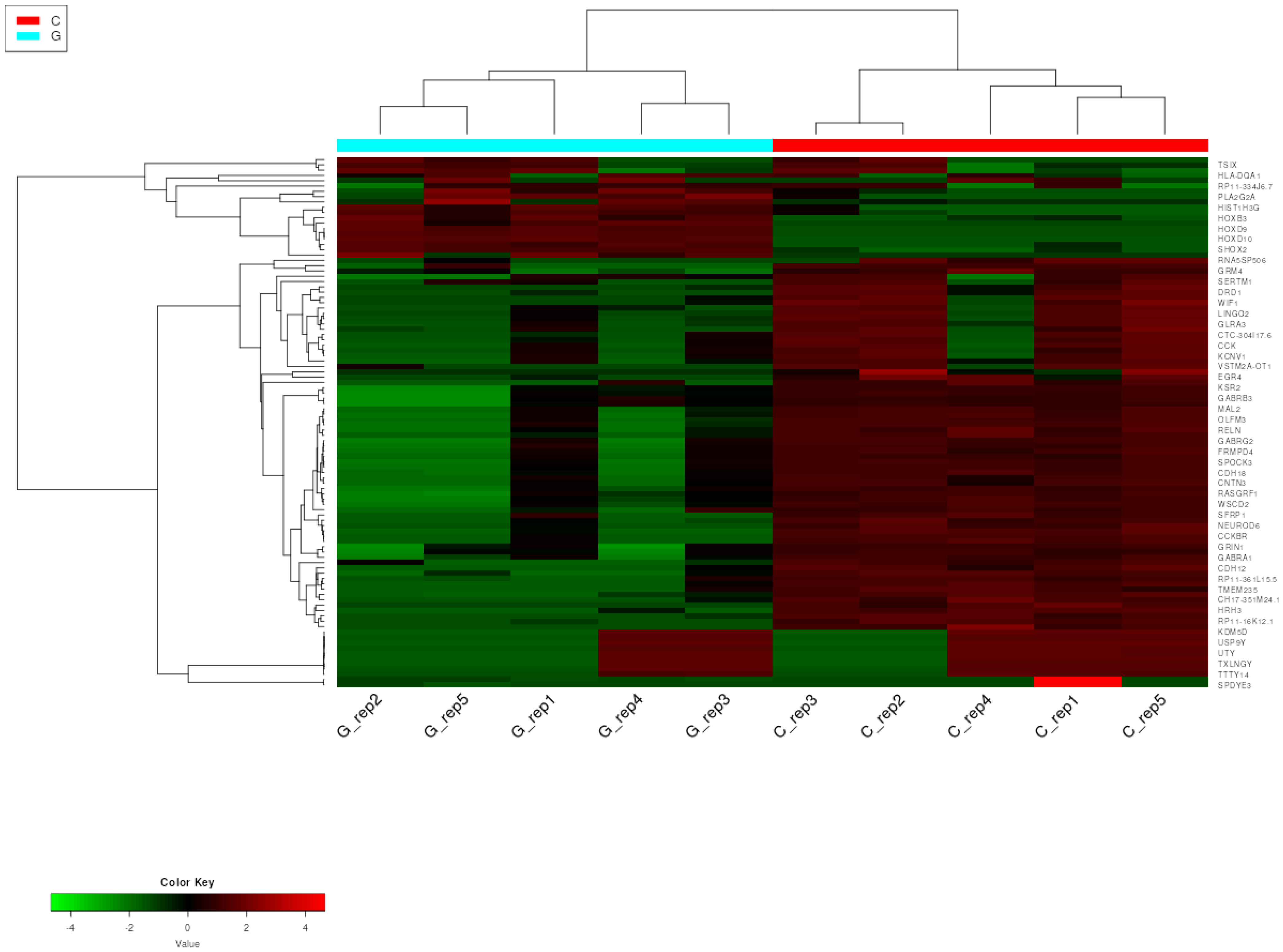
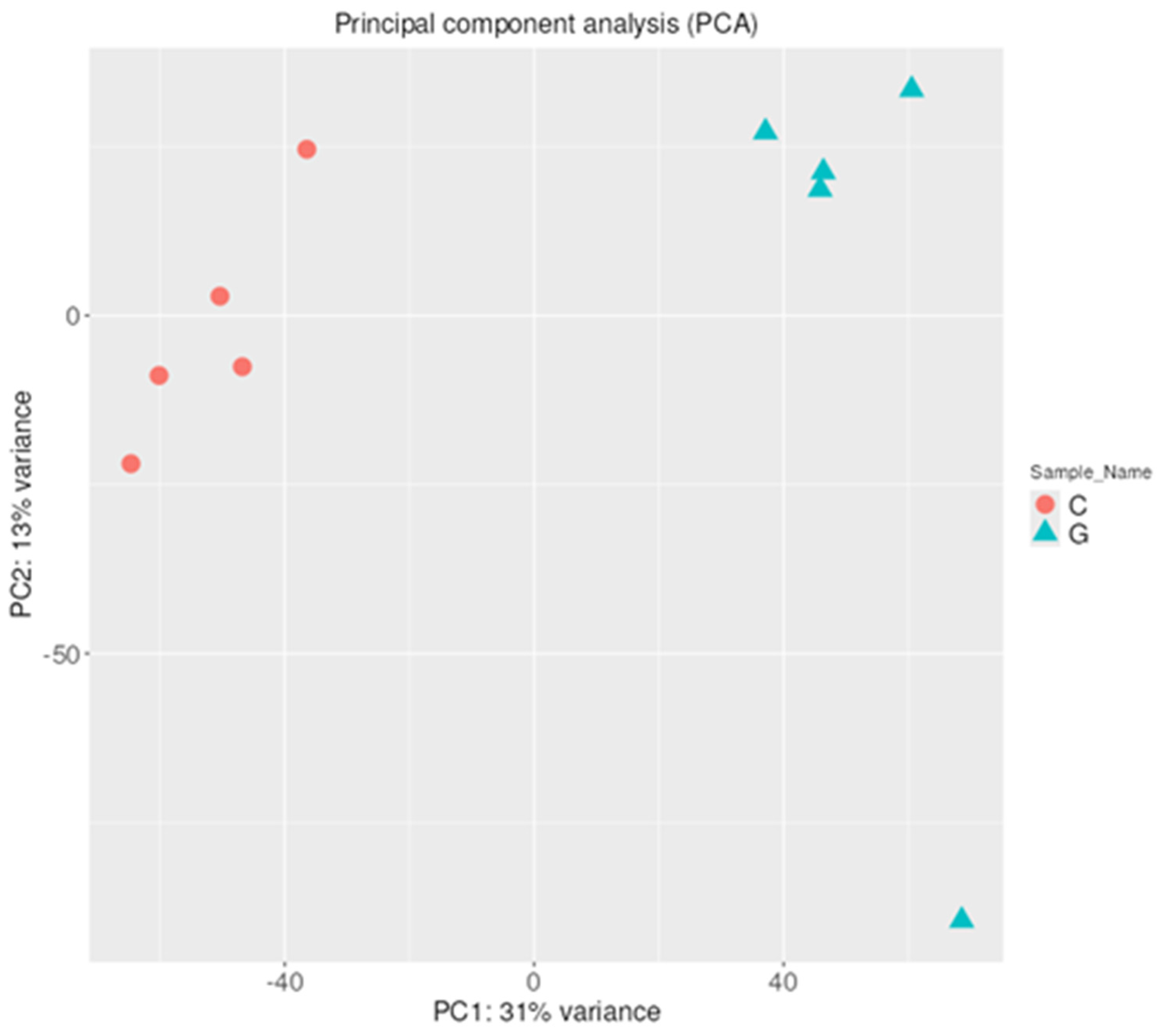
2.1.2. Hierarchical Clustering with Heatmap and Principal Component (PCA) Analysis
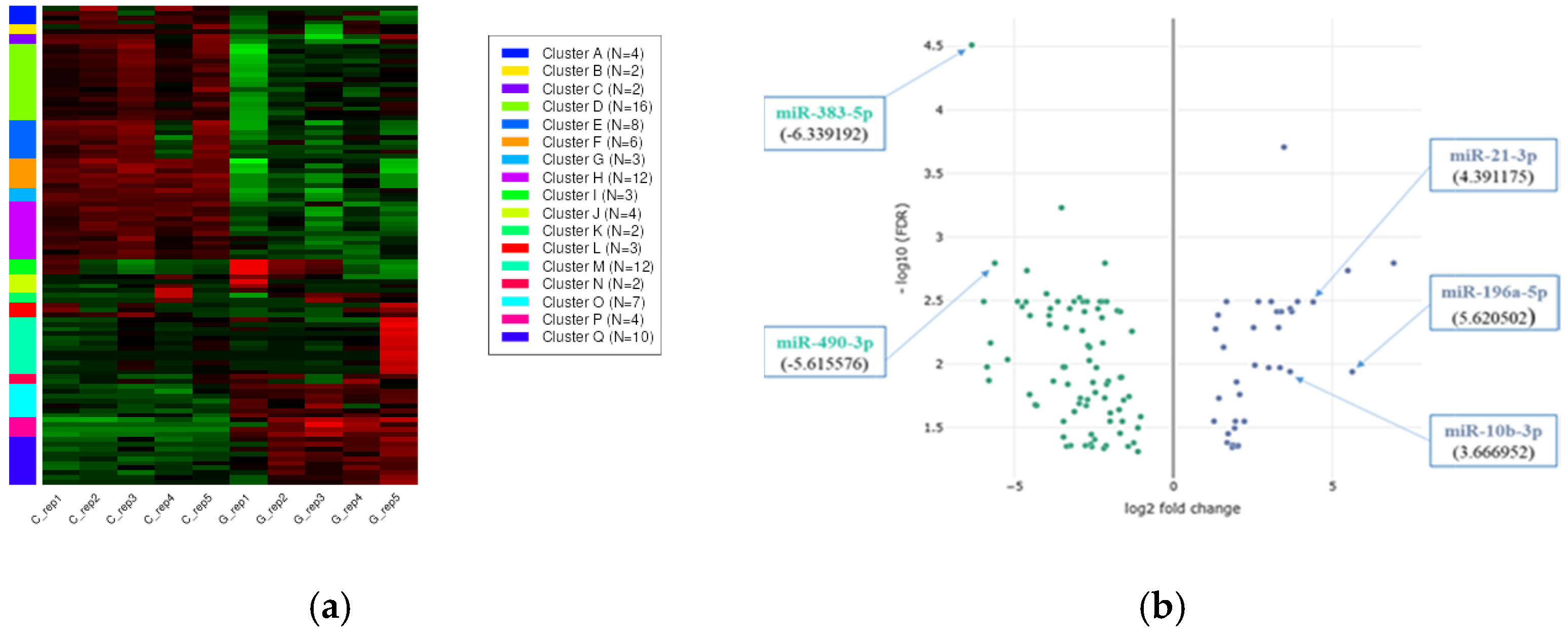
2.1.3. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
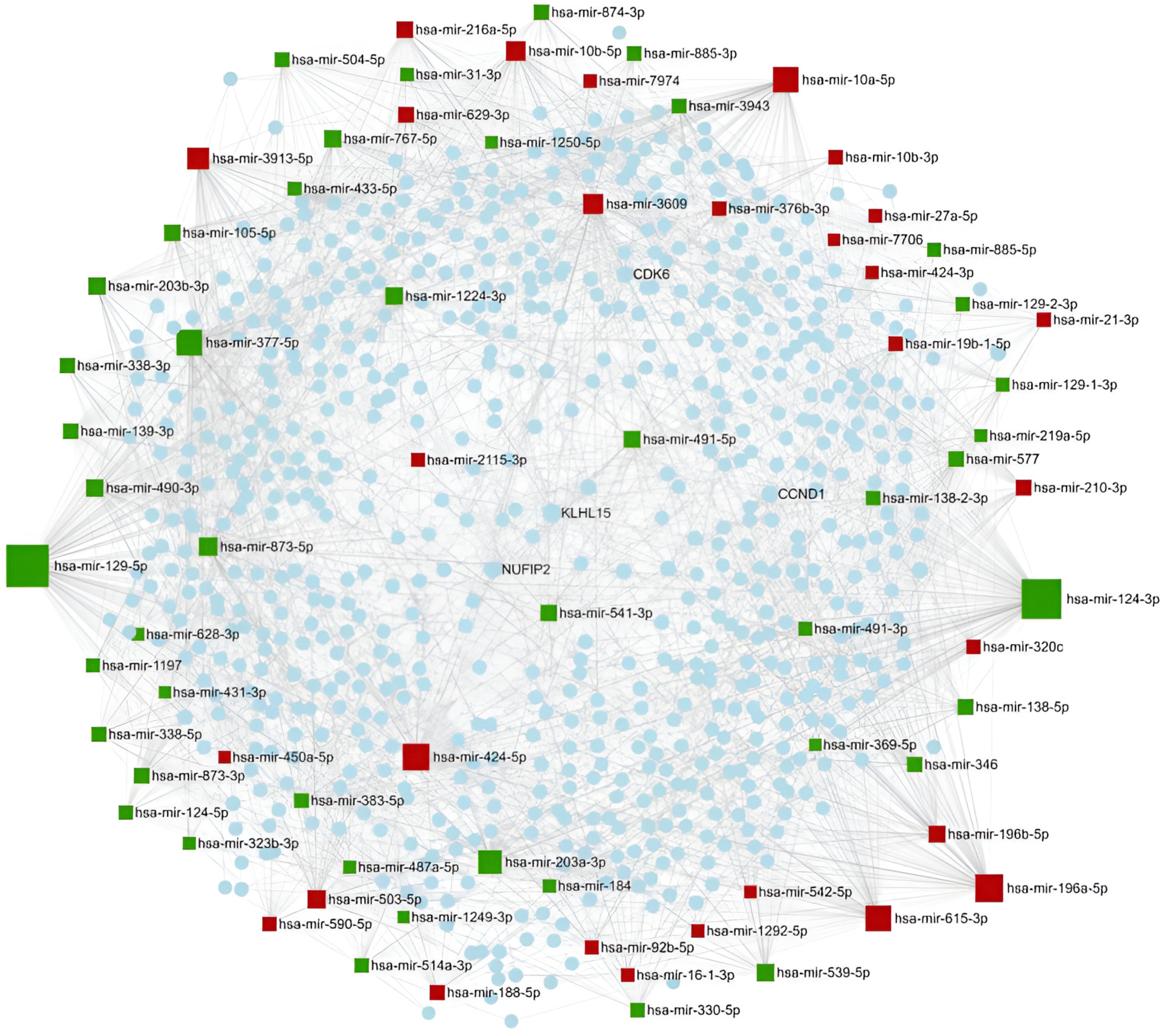
2.1.4. miRNA Ranking by Network-Based Analysis
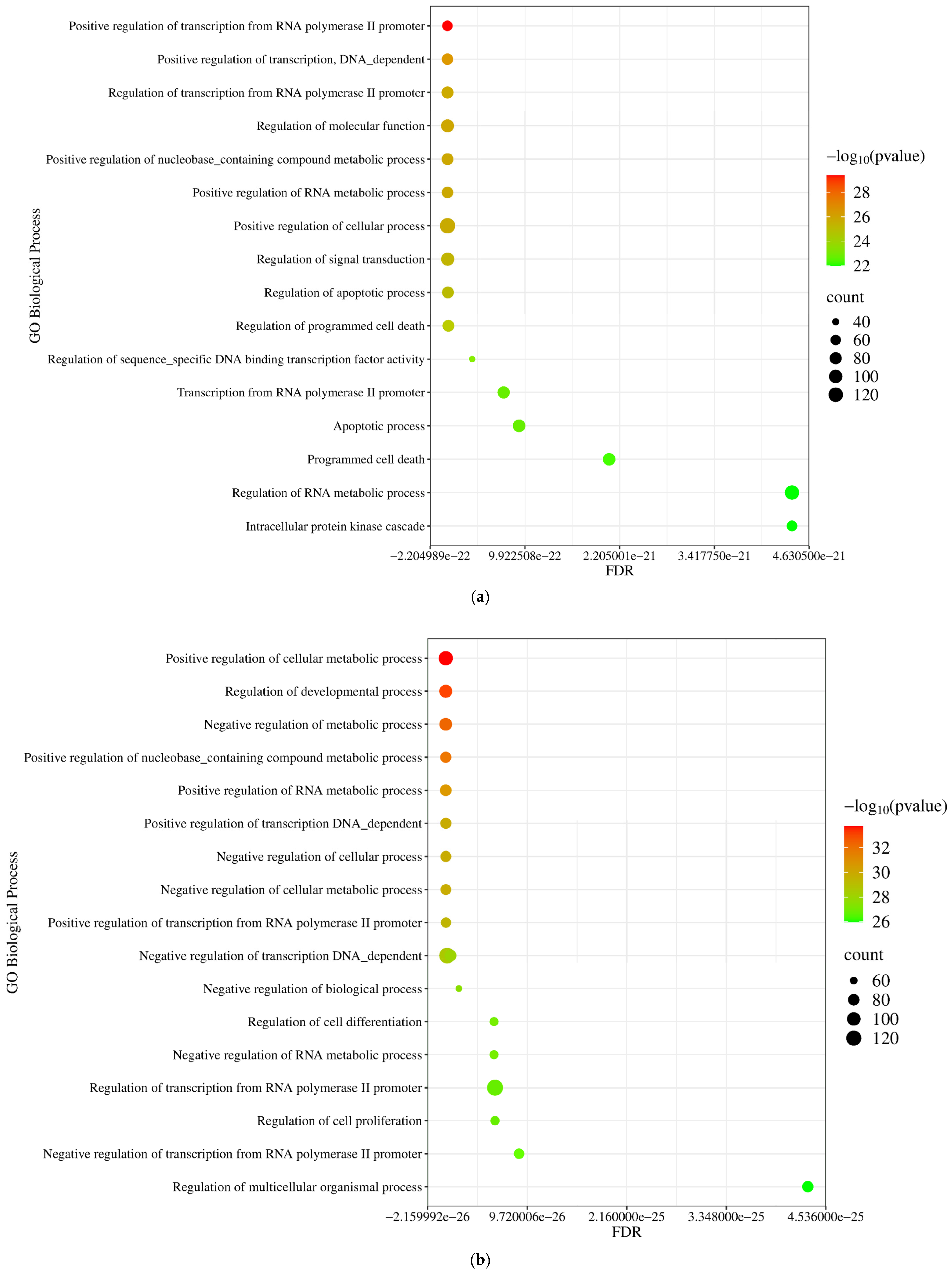
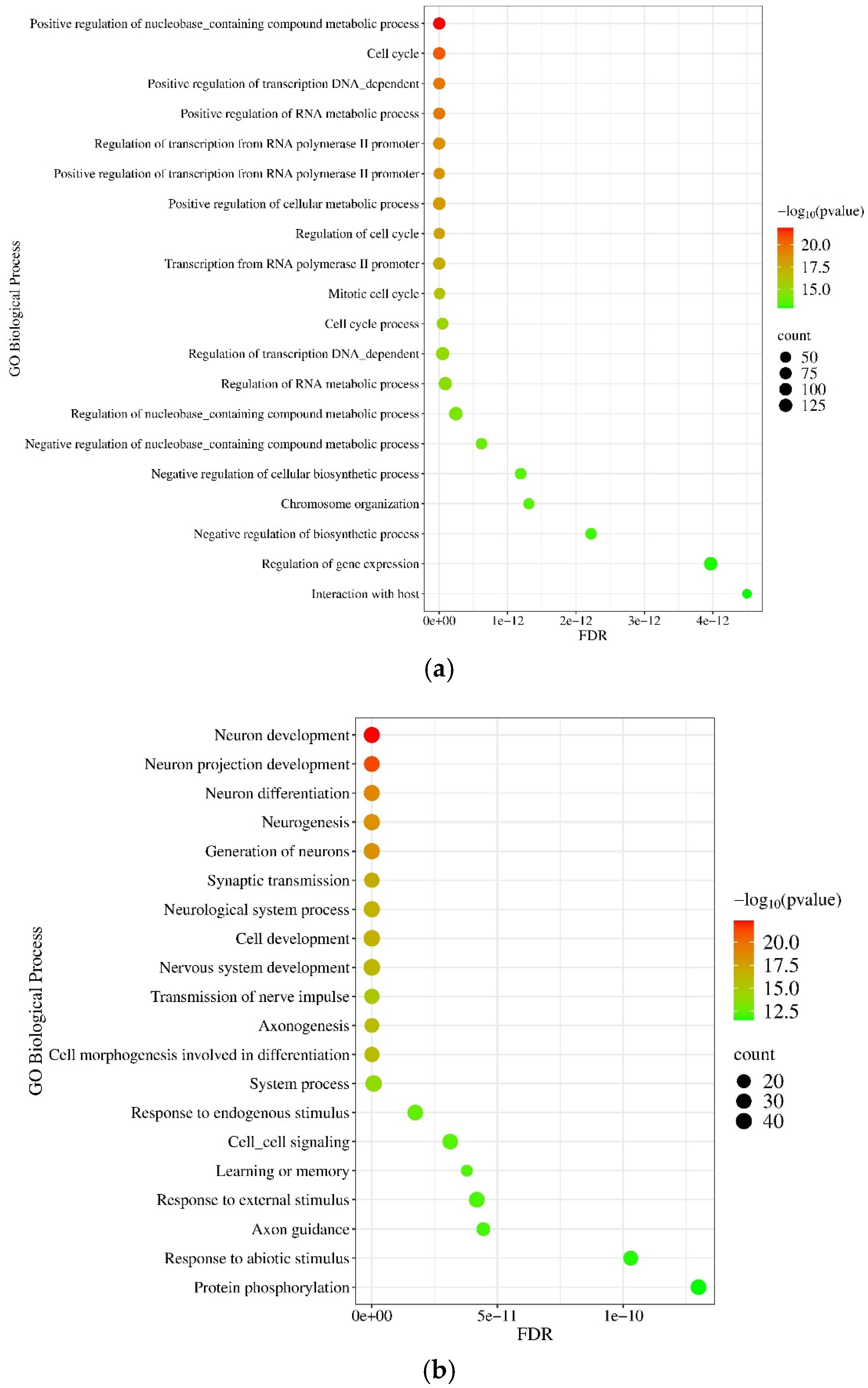
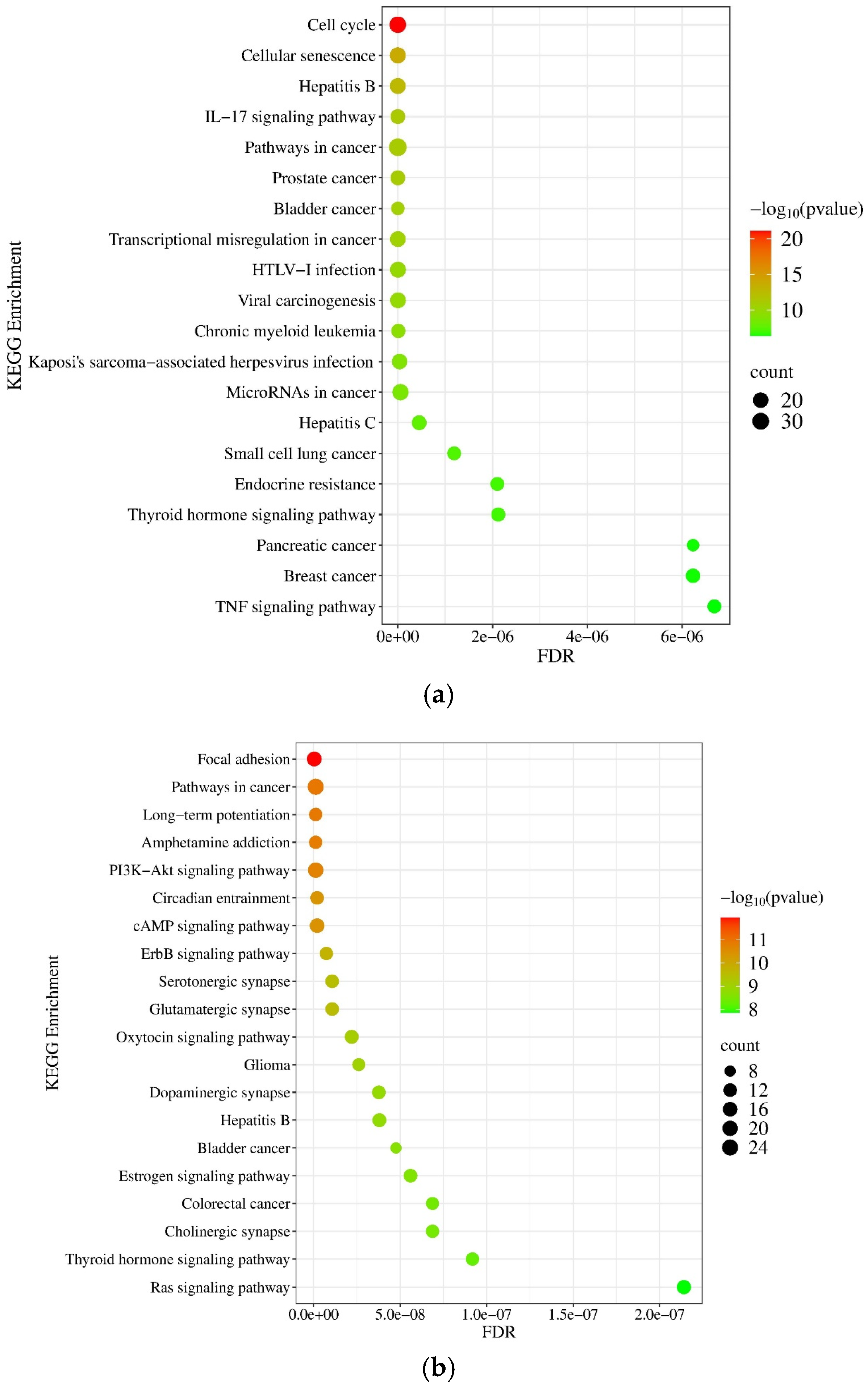
2.1.5. Gene Ontology (GO) and Pathway Enrichment Analysis of miRNA Targets
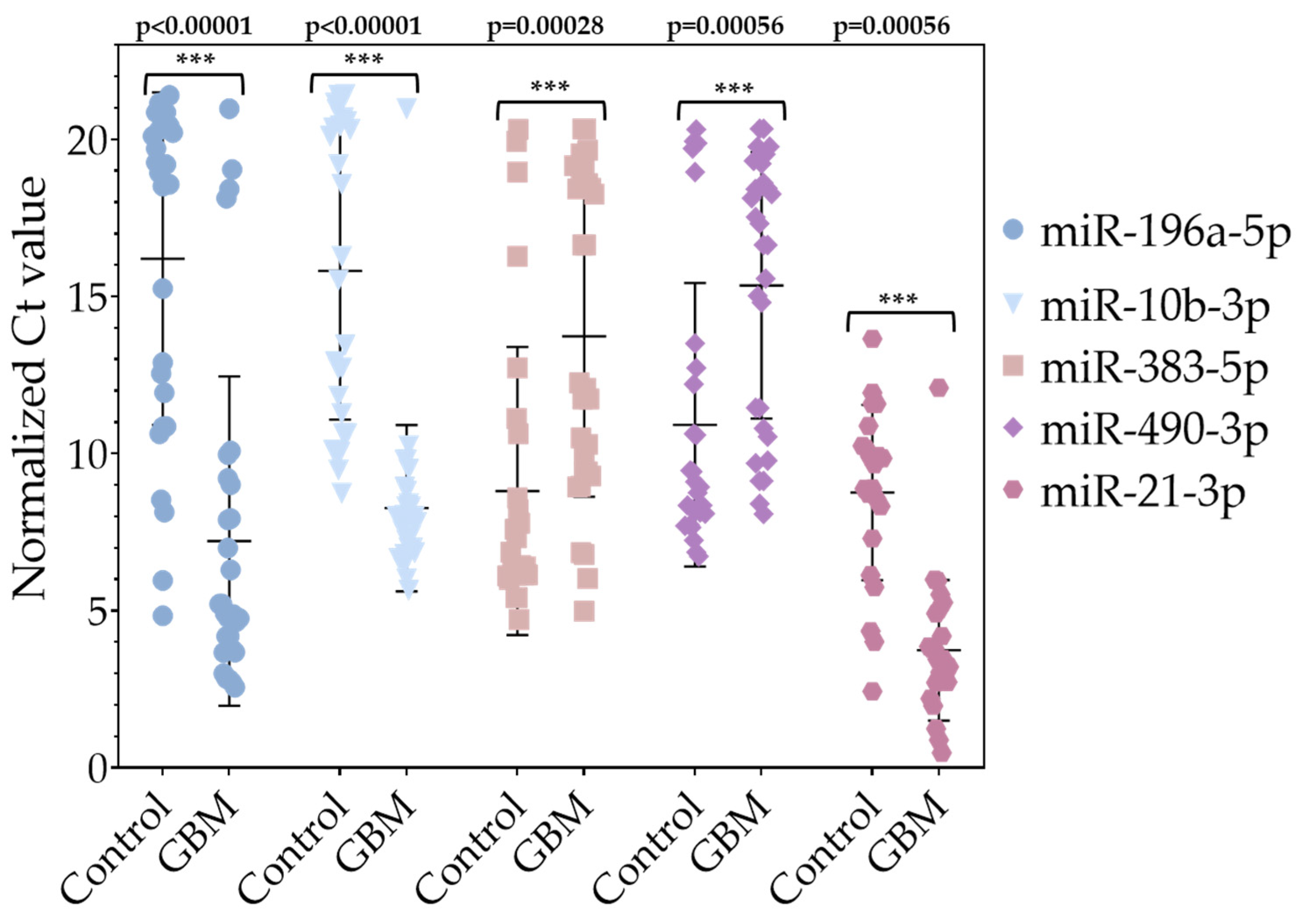
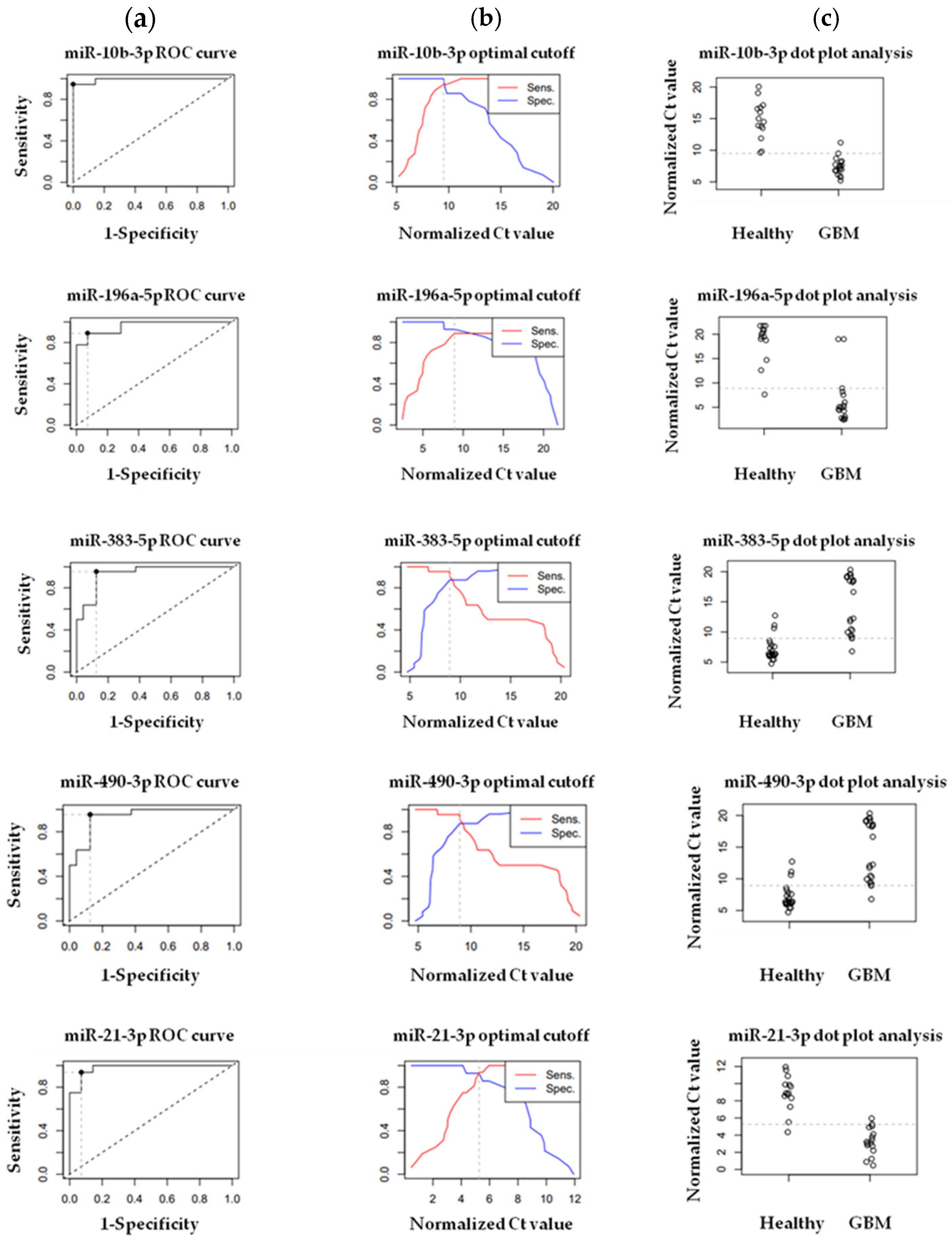
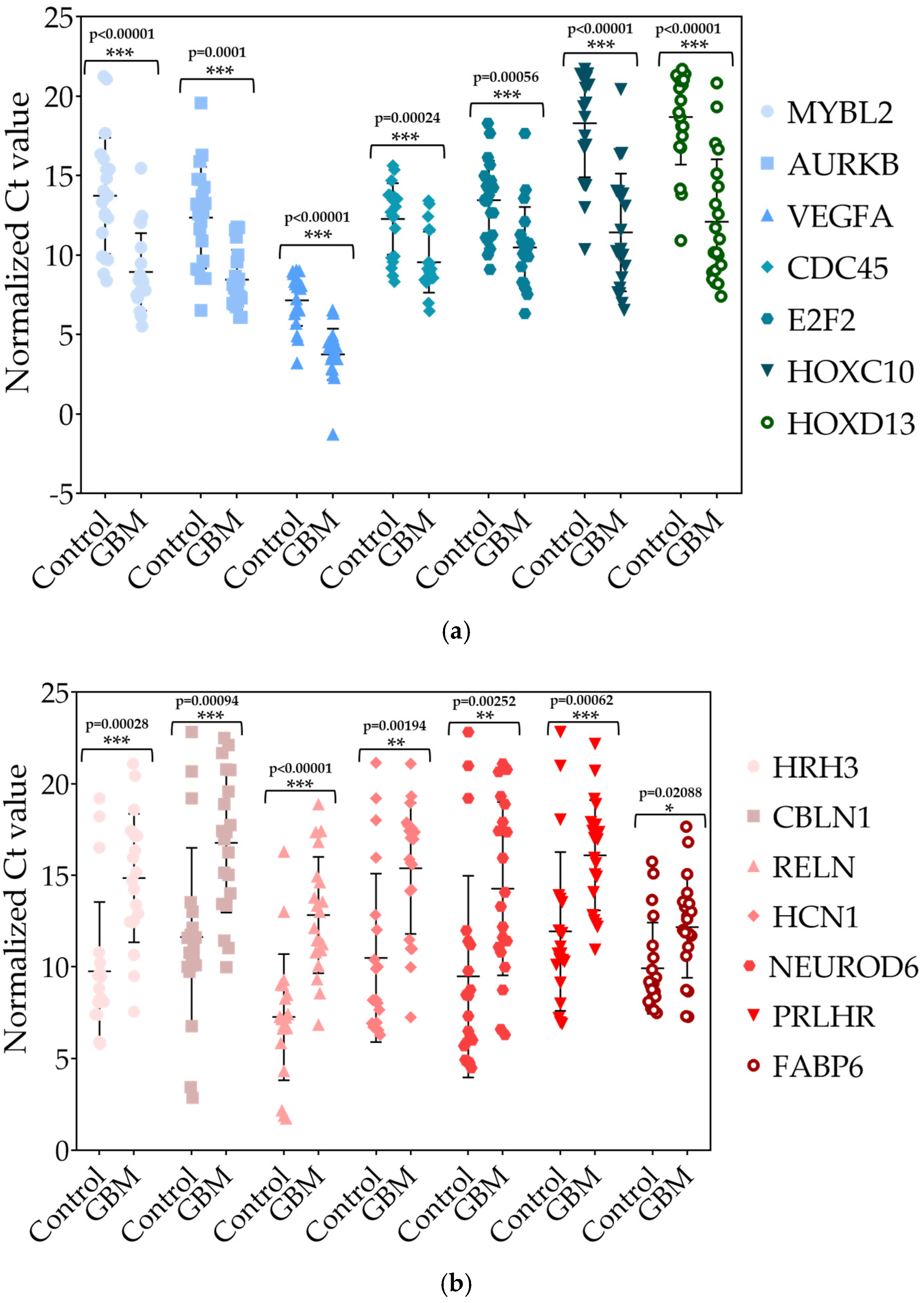
2.1.6. Validation of Differentially Expressed (DE) miRNAs by RT-qPCR in Tissue Samples
2.2. Identification of Differently Expressed (DE) mRNAs in Tissue Samples of GBM Patients and Control Group
2.2.1. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.2.2. Hierarchical Clustering with Heatmap and Principal Component (PCA) Analysis
2.2.3. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis of Deregulated mRNAs
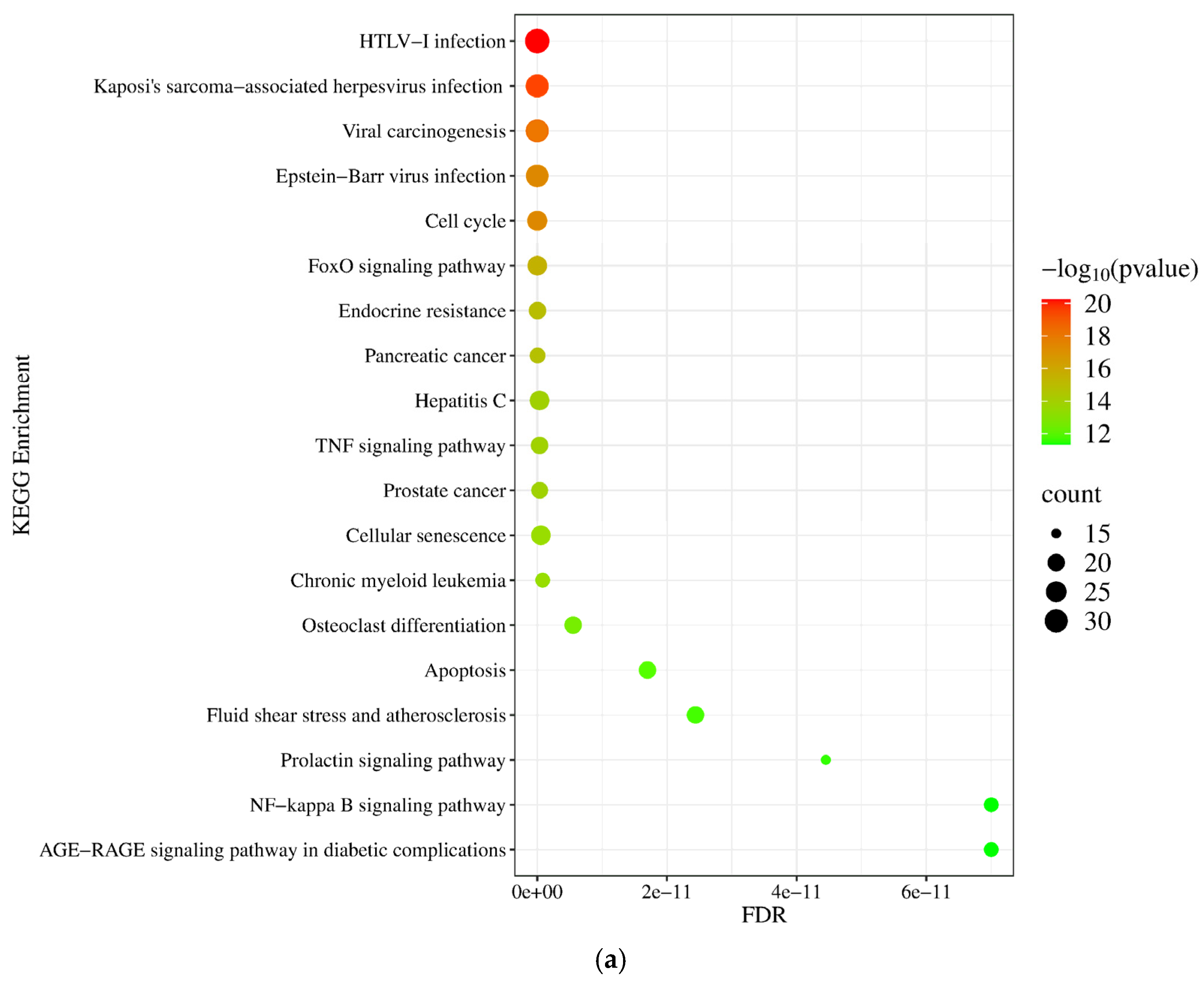
2.2.5. Gene Ontology (GO) and Pathway Enrichment Analysis of mRNA Molecules
2.2.6. Validation of Differentially Expressed (DE) mRNAs by RT-qPCR in Tissue Samples
2.3. The Correlation Between miRNA and mRNA Expression Determined by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
3. Discussion
3.1. Identification of Differently Expressed (DE) miRNAs and mRNAs in Tissue Samples of GBM Patients in Combination with Pathway and Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis
3.2. Validation of Differentially Expressed (DE) miRNAs by RT-qPCR in Tissue Samples
3.3. Validation of Differentially Expressed (DE) mRNAs by RT-qPCR in Tissue Samples
3.4. The Correlation Between miRNA and mRNA Expression Determined by Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. Tissue Exploration and RNA Isolation and Purification for Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
4.3. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) and Determination of Differentially Expressed (DE) miRNAs and mRNAs
4.4. Prediction of Targets of Differentially Expressed (DE) miRNAs, Construction of PPI Networks, Gene Ontology (GO), and Functional Annotation and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.5. Validation of miRNA-Seq Results by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.6. Validation of mRNA-Seq Results by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martínez-Garcia, M.; Álvarez-Linera, J.; Carrato, C.; Ley, L.; Luque, R.; Maldonado, X.; Martínez-Aguillo, M.; Navarro, L.M.; Vaz-Salgado, M.A.; Gil-Gil, M. SEOM clinical guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of glioblastoma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bianco, J.; Bastiancich, C.; Jankovski, A.; Rieux, A.D.; Préat, V.; Danhier, F. On glioblastoma and the search for a cure: Where do we stand? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 2451–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuka, S.; Van Meir, E.G. Overcoming therapeutic resistance in glioblastoma: The way forward. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.D.; Issa, J.J. The promise of epigenetic herapy: Reprogramming the cancer epigenome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2017, 42, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Tian, F.; Yu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zan, L.; Updike, M.S.; Song, J. miRNA-dysregulation associated with tenderness variation induced by acute stress in Angus cattle. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Horton, S.; Saldivar, J.C.; Miuma, S.; Stampfer, M.R.; Heerema, N.A.; Huebner, K. Common chromosome fragile sites in human and murine epithelial cells and FHIT/FRA3B loss-induced global genome instability. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2013, 52, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or Tumor Suppressor? The Duplicity of MicroRNAs in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempere, L.F.; Azmi, A.S.; Moore, A. microRNA-based diagnostic and therapeutic applications in cancer medicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2021, 12, e1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Nguyen, H.P.T.; Luwor, R.B.; Stylli, S.S.; Gogos, A.; Paradiso, L.; Kaye, A.H.; Morokoff, A.P. A comprehensive meta-analysis of circulation miRNAs in glioma as potential diagnostic biomarker. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Che, F.; Zhang, J. Cell-free microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers in glioma: A diagnostic meta-analysis. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2019, 34, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, F.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, N.; et al. Identification of seven serum microRNAs from a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profile as potential noninvasive biomarkers for malignant astrocytomas. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veryaskina, Y.A.; Titov, S.E.; Zhimulev, I.F. Reference Genes for qPCR-Based miRNA Expression Profiling in 14 Human Tissues. Med. Princ. Pract. 2022, 31, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maksoud, S. The Role of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Glioma: Analysis Emphasizing the Main Molecular Players and Therapeutic Strategies Identified in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3252–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scholz, N.; Kurian, K.M.; Siebzehnrubl, F.A.; Licchesi, J.D.F. Targeting the Ubiquitin System in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 574011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kreth, S.; Heyn, J.; Grau, S.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Egensperger, R.; Kreth, F.W. Identification of valid endogenous control genes for determining gene expression in human glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, C.; Xia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, P.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Zhou, X.; Tu, Y.; Kong, F.; et al. Micro124-mediated AHR expression regulates the inflammatory response of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) with nasal polyps. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Wei, W.; Cao, W.; Zhang, R.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N. MiR-218 Inhibited Growth and Metabolism of Human Glioblastoma Cells by Directly Targeting E2F. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, C.; Jiao, J.; Huang, W.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Shao, J. MircoRNA-129-5p suppresses the development of glioma by targeting HOXC10. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, S.L.C.; Sivakamasundari, V.; Shao, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhang, L.-F.; Lufkin, T.; Featherstone, M. Nuclear accumulation of an uncapped RNA produced by Drosha cleavage of a transcript encoding miR-10b and HOXD4. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deforzh, E.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Das, E.; Galitsyna, A.; Arora, R.; Saravanan, H.; Rabinovsky, R.; Wirawan, A.D.; Teplyuk, N.M.; El Fatimy, R.; et al. Promoter and enhancer RNAs regulate chromatin reorganization and activation of miR-10b/HOXD locus, and neoplastic transformation in glioma. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 1894–1908.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, K.; Fu, G.; Pan, G.; Li, C.; Shen, L.; Hu, R.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Cui, H. Demethylzeylasteral inhibits glioma growth by regulating the miR-30e-5p/MYBL2 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Agrawal, R.; Garg, A.; Malgulwar, P.B.; Sharma, V.; Sarkar, C.; Kulshreshtha, R. p53 and miR-210 regulated NeuroD2, a neuronal basic helix–loop–helix transcription factor, is downregulated in glioblastoma patients and functions as a tumor suppressor under hypoxic microenvironment. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 142, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takkar, S.; Sharma, V.; Ghosh, S.; Suri, A.; Sarkar, C.; Kulshreshtha, R. Hypoxia-inducible miR-196a modulates glioblastoma cell proliferation and migration through complex regulation of NRAS. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. miR-490-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma by inhibiting high-mobility group AT-hook 2 expression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; He, L.; Peng, Y. An miR-340-5p-macrophage feedback loop modulates the progression and tumor microenvironment of glioblastoma multiforme. Oncogene 2019, 38, 7399–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.-F.; Lv, G.-X.; Zhang, D.-H. miR-381 Mediates the Development of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Targeting STC2. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 4485–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- D’Urso, P.I.; D’Urso, O.F.; Storelli, C.; Mallardo, M.; Gianfreda, C.D.; Montinaro, A.; Cimmino, A.; Pietro, C.; Marsigliante, S. miR-155 is up-regulated in primary and secondary glioblastoma and promotes tumour growth by inhibiting GABA receptors. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Grigore, I.A.; Rajagopal, A.; Chow, J.T.-S.; Stone, T.J.; Salmena, L. Discovery of miRNA–mRNA regulatory networks in glioblastoma reveals novel insights into tumor microenvironment remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, A.; Zhao, H.; Sun, B.; Han, X.; Zhou, D.; Cui, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, L. A predictive analysis approach for paediatric and adult high-grade glioma: miRNAs and network insight. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Valle-Garcia, D.; de la Cruz, V.P.; Flores, I.; Salazar, A.; Pineda, B.; Meza-Sosa, K.F. Use of microRNAs as Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Tools for Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, S. Multi-omics analysis identifies potential mechanisms of AURKB in mediating poor outcome of lung adenocarcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 5946–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, R.; Dai, W.; Wu, A.; Li, Y. CircCDC45 promotes the malignant progression of glioblastoma by modulating the miR-485-5p/CSF-1 axis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, P.; Qin, K.; Fa, Z.-Q.; Liu, Y.-J.; Ke, Y.-Q.; Jiang, X.-D. P53-induced microRNA-107 inhibits proliferation of glioma cells and down-regulates the expression of CDK6 and Notch-2. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 534, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefas, B.; Godlewski, J.; Comeau, L.; Li, Y.; Abounader, R.; Hawkinson, M.; Lee, J.; Fine, H.; Chiocca, E.A.; Lawler, S.; et al. microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3566–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L. mirna-383-5p Functions as an Anti-oncogene in Glioma through the Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway by Targeting VEGFA. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2024, 24, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Guan, H.; Cai, J.; Fang, L.; Li, J.; Li, M. MiR-136 promotes apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting AEG-1 and Bcl-2. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3608–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Huang, D.; Yin, D.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Kung, H.-F.; Peng, Y. Suppression of tumorigenicity by MicroRNA-138 through inhibition of EZH2-CDK4/6-pRb-E2F1 signal loop in glioblastoma multiforme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinchure, O.S.; Sharma, V.; Tabasum, S.; Ghosh, S.; Singh, R.P.; Sarkar, C.; Kulshreshtha, R. Polycomb complex mediated epigenetic reprogramming alters TGF-β signaling via a novel EZH2/miR-490/TGIF2 axis thereby inducing migration and EMT potential in glioblastomas. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimunde, P.; Pensado-López, A.; Crende, M.C.; Iglesias, V.L.; Sánchez, L.; Torrecilla-Parra, M.; Ramírez, C.M.; Anfray, C.; Andón, F.T. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Glioblastoma and Zebrafish Models for the Discovery of New Treatments. Cancers 2021, 13, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Rouse, C.; Chen, Y.; Dowling, J.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Xu, J.; et al. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16 (Suppl S4), iv1–iv63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shea, A.; Harish, V.; Afzal, Z.; Chijioke, J.; Kedir, H.; Dusmatova, S.; Roy, A.; Ramalinga, M.; Harris, B.; Blancato, J.; et al. MicroRNAs in glioblastoma multiforme pathogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1917–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shaji, S.K.; Sunilkumar, D.; Mahalakshmi, N.V.; Kumar, G.B.; Nair, B.G. Analysis of microarray data for identification of key microRNA signatures in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Belotti, Y.; Tolomeo, S.; Yu, R.; Lim, W.-T.; Lim, C.T. Prognostic Neurotransmitter Receptors Genes Are Associated with Immune Response, Inflammation and Cancer Hallmarks in Brain Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Farhan, M.; Silva, M.; Xingan, X.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, W. Role of FOXO Transcription Factors in Cancer Metabolism and Angiogenesis. Cells 2020, 9, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wade, A.; Robinson, A.E.; Engler, J.R.; Petritsch, C.; James, C.D.; Phillips, J.J. Proteoglycans and their roles in brain cancer. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 2399–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Monin, L.; Gaffen, S.L. Interleukin 17 Family Cytokines: Signaling Mechanisms, Biological Activities, and Therapeutic Implications. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, G.; Han, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Shi, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; et al. MiR-196a exerts its oncogenic effect in glioblastoma multiforme by inhibition of IκBα both in vitro and in vivo. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Teplyuk, N.M.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Gabriely, G.; Volfovsky, N.; Wang, Y.; Teng, J.; Karmali, P.; Marcusson, E.; Peter, M.; Mohan, A.; et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting micro RNA-10b in established intracranial glioblastoma: First steps toward the clinic. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gabriely, G.; Yi, M.; Narayan, R.S.; Niers, J.M.; Wurdinger, T.; Imitola, J.; Ligon, K.L.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.; Stephens, R.M.; et al. Human glioma growth is controlled by MicroRNA-10b. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3563–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- El Fatimy, R.; Subramanian, S.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Krichevsky, A.M. Genome Editing Reveals Glioblastoma Addiction to MicroRNA-10b. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yekta, S.; Tabin, C.J.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs in the Hox network: An apparent link to posterior prevalence. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Beylerli, O.; Gareev, I.; Sufianov, A.; Ilyasova, T.; Zhang, F.; Guang, Y. The role of microRNA in the pathogenesis of glial brain tumors. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022, 7, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gwak, H.-S.; Kim, T.H.; Jo, G.H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kwak, H.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Yin, J.; Yoo, H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.B. Silencing of microRNA-21 Confers radio-sensitivity through Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway and enhancing autophagy in malignant glioma cell lines. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, X.; Choudhury, S.N.; Hua, X.; Dai, Z.; Li, Y. Interaction of the oncogenic miR-21 microRNA and the p53 tumor suppressor pathway. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, G.; Mu, J.; Liu, X.; Peng, X.; Zhong, F.; Yuan, W.; Deng, F.; Peng, X.; Peng, S.; Zeng, X. Prognostic value of miR-21 in gliomas: Comprehensive study based on meta-analysis and TCGA dataset validation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, D.; Ma, P.; Gao, G.; Gui, Y.; Niu, X.; Jin, B. MicroRNA-383 expression regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis in human glioma cells. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 7743–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- He, Z.; Cen, D.; Luo, X.; Li, D.; Li, P.; Liang, L.; Meng, Z. Downregulation of miR-383 promotes glioma cell invasion by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Quan, J.; Liu, W.; Tan, H.; Li, W. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Colopi, A.; Fuda, S.; Santi, S.; Onorato, A.; Cesarini, V.; Salvati, M.; Balistreri, C.R.; Dolci, S.; Guida, E. Impact of age and gender on glioblastoma onset, progression, and management. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 211, 111801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.S.; Le Boiteux, E.; Arnaud, P.; Costa, B.M. HOX gene cluster (de)regulation in brain: From neurodevelopment to malignant glial tumours. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3797–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Peng, J.; Tu, G. Knockdown MTDH Inhibits Glioma Proliferation and Migration and Promotes Apoptosis by Downregulating MYBL. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 1706787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alafate, W.; Wang, M.; Zuo, J.; Wu, W.; Sun, L.; Liu, C.; Xie, W.; Wang, J. Targeting Aurora kinase B attenuates chemoresistance in glioblastoma via a synergistic manner with temozolomide. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Mikoshiba, K.; Nakajima, K. Regulation of cortical neuron migration by the reelin signaling pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Washiyama, K.; Ikeda, K. Inhibition of G-Protein-Activated Inwardly Rectifying K+ Channels by the Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors Atomoxetine and Reboxetine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-J.; Zhao, T.-Z.; Cai, W.-K.; Yang, Y.-X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Chang, T.; Li, Z.-Y. Inhibition of histamine receptor 3 suppresses glioblastoma tumor growth, invasion, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17107–17120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nong, Y.; Stoppel, D.C.; Johnson, M.A.; Boillot, M.; Todorovic, J.; Shen, J.; Zhou, X.; Nadler, M.J.S.; Rodriguez, C.; Huo, Y.; et al. UBE3A and transsynaptic complex NRXN1-CBLN1-GluD1 in a hypothalamic VMHvl-arcuate feedback circuit regulates aggression. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pai, F.-C.; Huang, H.-W.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Tsai, W.-C.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-H.; Chen, Y. Inhibition of FABP6 Reduces Tumor Cell Invasion and Angiogenesis through the Decrease in MMP-2 and VEGF in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Asad, A.S.; Candia, A.J.N.; Gonzalez, N.; Zuccato, C.F.; Abt, A.; Orrillo, S.J.; Lastra, Y.; De Simone, E.; Boutillon, F.; Goffin, V.; et al. Prolactin and its receptor as therapeutic targets in glioblastoma multiforme. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yun, E.-J.; Kim, D.; Hsieh, J.-T.; Baek, S.T. Stanniocalcin 2 drives malignant transformation of human glioblastoma cells by targeting SNAI2 and Matrix Metalloproteinases. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ke, S.Q.; Huang, Z.; Flavahan, W.; Fang, X.; Paul, J.; Wu, L.; Sloan, A.E.; McLendon, R.E.; Li, X.; et al. Periostin secreted by glioblastoma stem cells recruits M2 tumour-associated macrophages and promotes malignant growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


| Regulated Gene | Biological Process | Expression Status (Up/Down) | miRNA | Expression Status (Up/Down) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHR | regulation of transcription | up | hsa-mir-124-3p | down | [19] |
| E2F2 | regulation of transcription | up | hsa-mir-218-5p | down | [20] |
| HOXC10 | regulation of transcription | up | hsa-mir-129-5p | down | [21] |
| HOXD4 | regulation of transcription | up | hsa-mir-10b | up | [22,23] |
| MYBL2 | regulation of transcription | up | hsa-mir-30e-5p | down | [24] |
| NEUROD2 | regulation of transcription | down | hsa-mir-210-3p | up | [25] |
| AJAP1 | cell adhesion | down | hsa-mir-196a-5p | up | [26] |
| MMP9 | cell migration | up | hsa-mir-490-3p | down | [27] |
| POSTN | cell migration | up | hsa-mir-340-5p | down | [28] |
| STC2 | cell migration | up | hsa-mir-381-3p | down | [29] |
| GABRA1 | synaptic transmission | down | hsa-mir-155 -5p | up | [30] |
| GABRB2 | synaptic transmission | down | hsa-mir-10a-5p hsa-mir-10b-5p | up | [31,32] |
| HCN1 | transmission of nerve impulse | down | hsa-mir-10a-5p hsa-mir-10b-5p | up | [33] |
| AURKA | cell cycle regulation | up | hsa-mir-124-3p | down | [34] |
| AURKB | cell cycle regulation | up | hsa-miR-93-5p, hsa-miR-17-5p, hsa-miR-130b-3p | up | [34] |
| CDC45 | cell cycle regulation | up | hsa-mir-485-5p | down | [35] |
| CDK6 | cell cycle regulation | up | hsa-mir-107 | down | [36] |
| EGFR | cell proliferation | up | hsa-mir-7 | down | [37] |
| VEGFA | cell proliferation angiogenesis | up | hsa-mir-383-5p | down | [38] |
| LTBP-1 | regulation of tumor-associated macrophages | up | hsa-mir-340-5p | down | [28] |
| POSTN | regulation of tumor-associated macrophages | up | hsa-mir-340-5p | down | [28] |
| BCL2 | apoptosis | up | hsa-mir-136-3p | down | [39] |
| EZH2 | epigenetic regulation | up | hsa-miR-138-5p, hsa-miR-490-3p | down | [40,41] |
| (a) | |||
| Members of NGS | Gender | Age | Immunohistochemical characteristics |
| Control_1 | M | 70 | - |
| Control_2 | M | 52 | - |
| Control_3 | M | 52 | - |
| Control_4 | F | 71 | - |
| Control_5 | F | 80 | - |
| GBM_1 | M | 65 | IDH wild type |
| GBM_2 | M | 57 | IDH wild type |
| GBM_3 | M | 70 | IDH wild type- |
| GBM_4 | F | 60 | IDH wild type- |
| GBM_5 | F | 56 | IDH wild type- |
| (b) | |||
| Characteristic | Control Group (number) | GBM Group (number) | |
| Sex (M/F) | 14/14 | 15/15 | |
| Age | |||
| Median | 63 | 61 | |
| Range | 38–78 | 37–80 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Géczi, D.; Klekner, Á.; Balogh, I.; Penyige, A.; Szilágyi, M.; Virga, J.; Bakó, A.; Nagy, B.; Torner, B.; Birkó, Z. Identification of Deregulated miRNAs and mRNAs Involved in Tumorigenesis and Detection of Glioblastoma Patients Applying Next-Generation RNA Sequencing. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030431
Géczi D, Klekner Á, Balogh I, Penyige A, Szilágyi M, Virga J, Bakó A, Nagy B, Torner B, Birkó Z. Identification of Deregulated miRNAs and mRNAs Involved in Tumorigenesis and Detection of Glioblastoma Patients Applying Next-Generation RNA Sequencing. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(3):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030431
Chicago/Turabian StyleGéczi, Dóra, Álmos Klekner, István Balogh, András Penyige, Melinda Szilágyi, József Virga, Andrea Bakó, Bálint Nagy, Bernadett Torner, and Zsuzsanna Birkó. 2025. "Identification of Deregulated miRNAs and mRNAs Involved in Tumorigenesis and Detection of Glioblastoma Patients Applying Next-Generation RNA Sequencing" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 3: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030431
APA StyleGéczi, D., Klekner, Á., Balogh, I., Penyige, A., Szilágyi, M., Virga, J., Bakó, A., Nagy, B., Torner, B., & Birkó, Z. (2025). Identification of Deregulated miRNAs and mRNAs Involved in Tumorigenesis and Detection of Glioblastoma Patients Applying Next-Generation RNA Sequencing. Pharmaceuticals, 18(3), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030431








