Modulation of SIRT-1, NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6, and ERK/Caspase-3 by Lutein Mitigates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of MTX and/or Lutein on Markers of Hepatic Performance
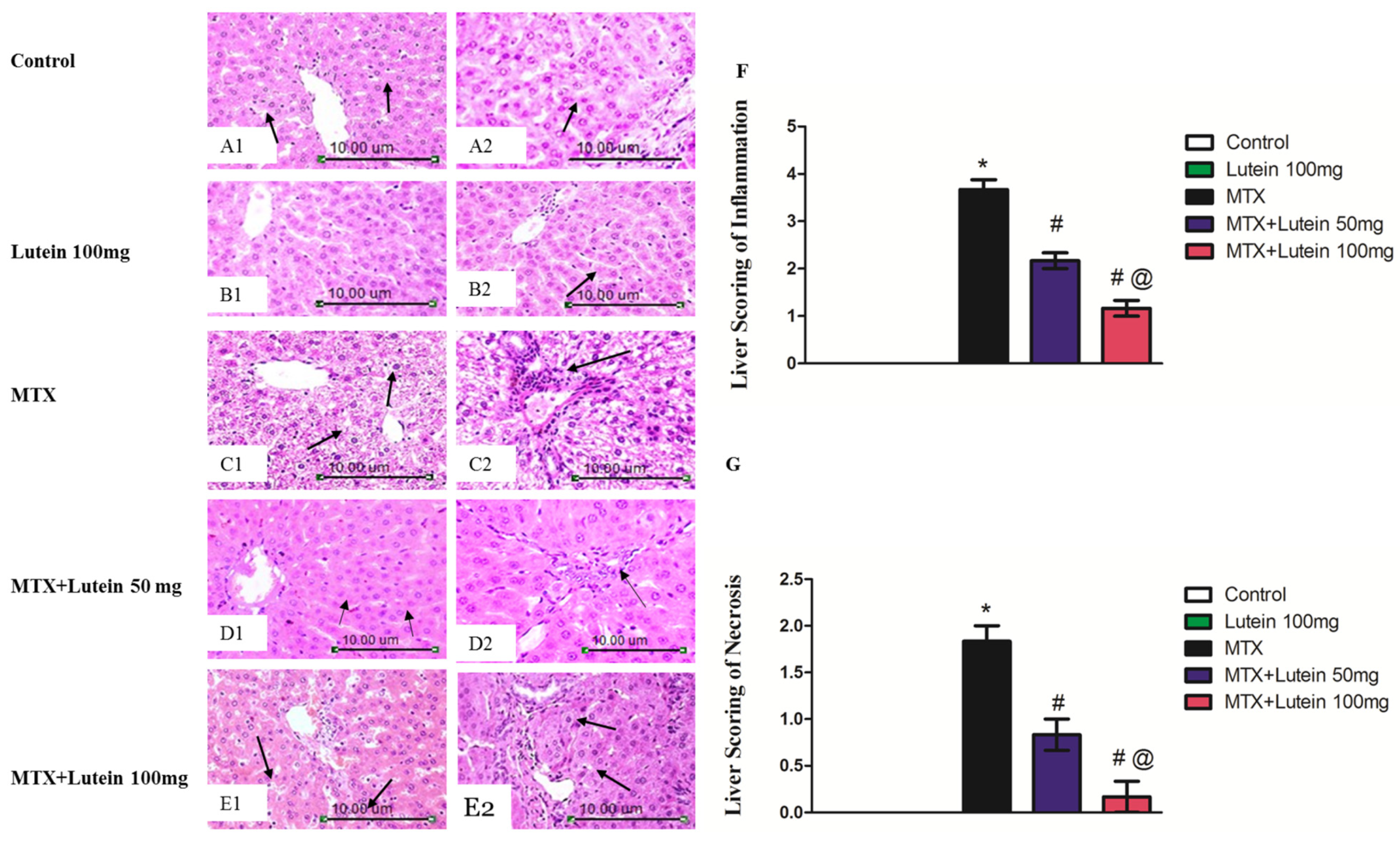
2.2. Effect of MTX and/or Lutein on Hepatic Histopathological Features
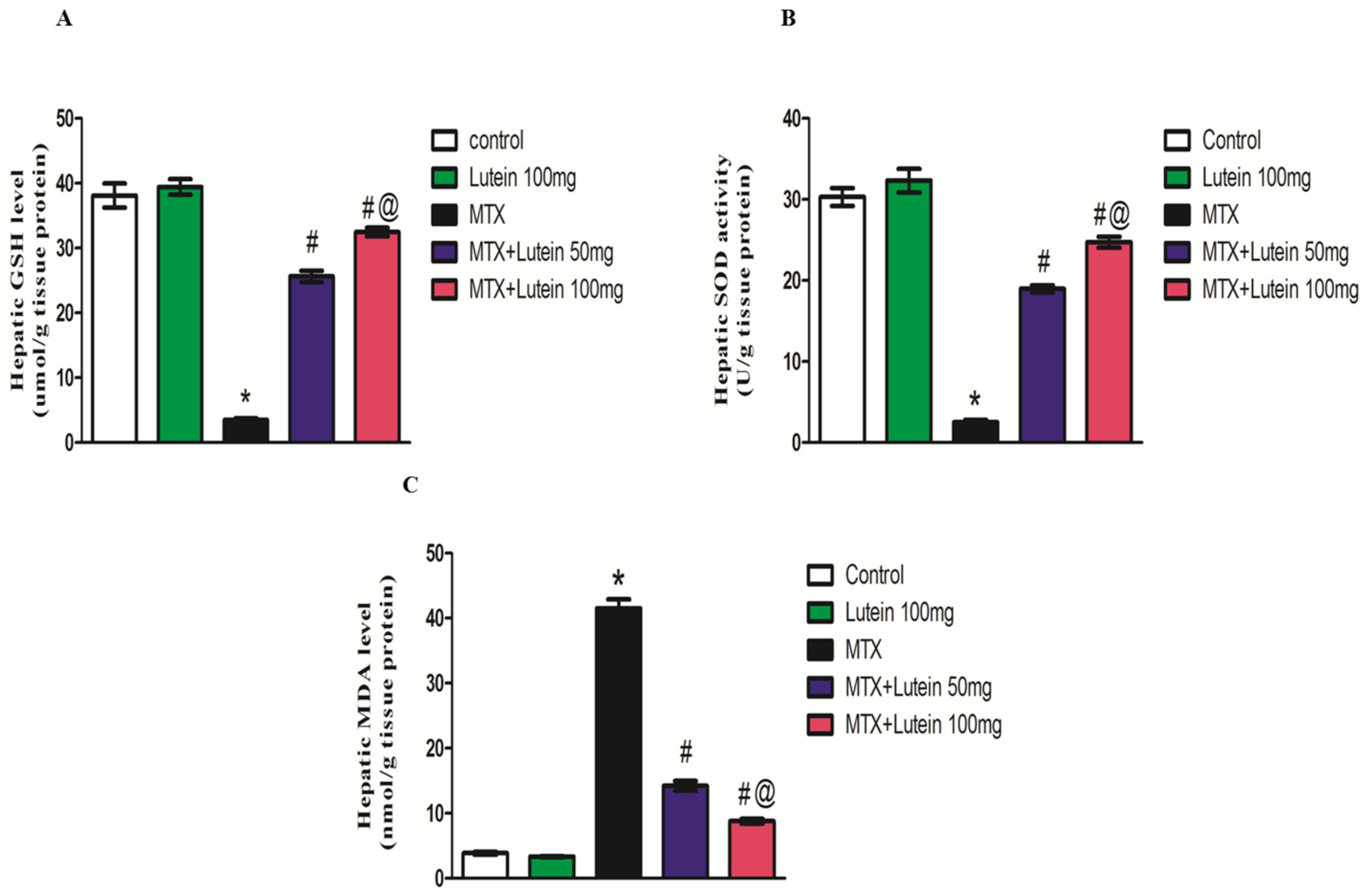
2.3. Effect of MTX and/or Lutein on Hepatic Oxidative Status
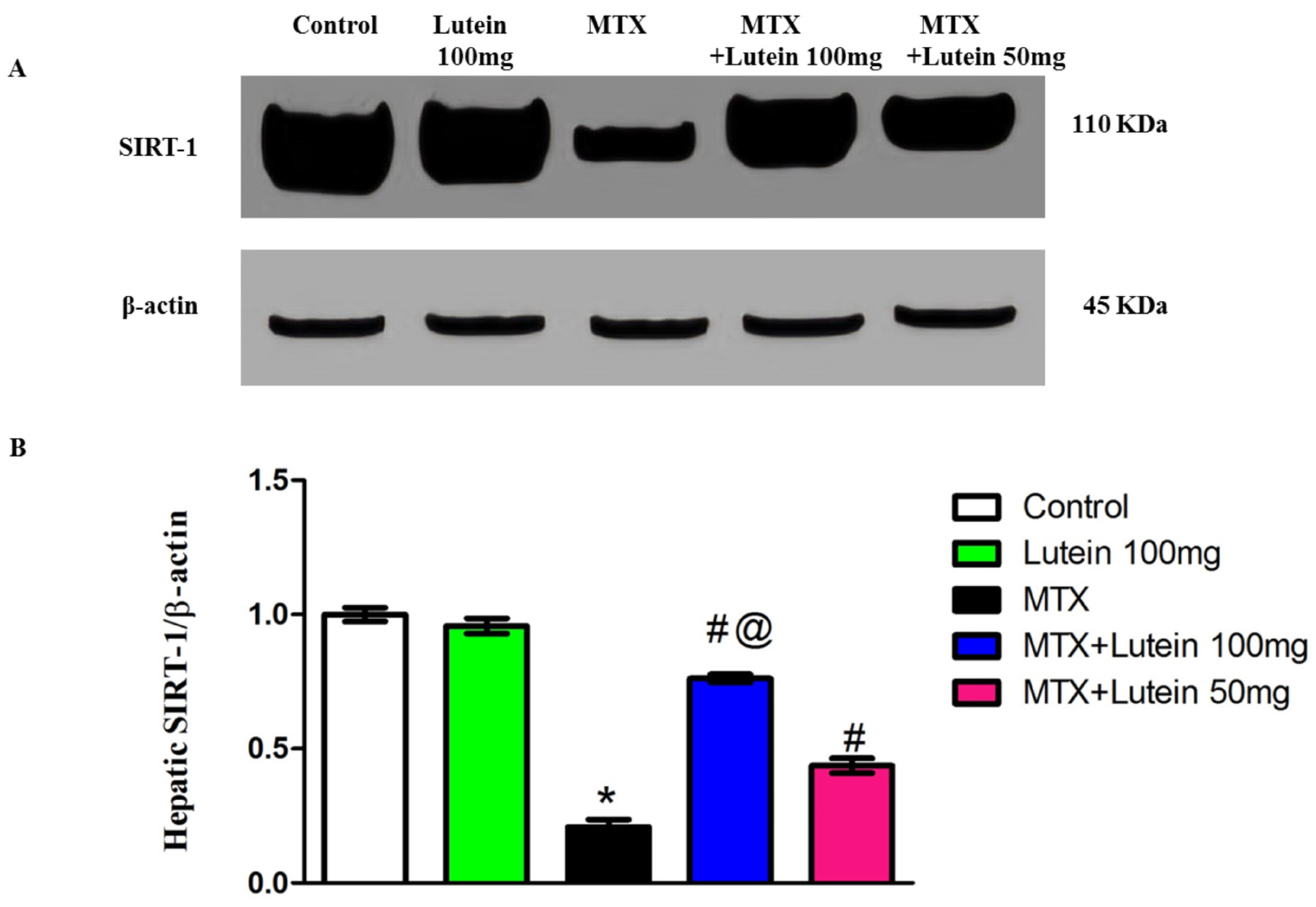
2.4. Effect of MTX and/or Lutein on Expression of SIRT-1 in Hepatic Tissue
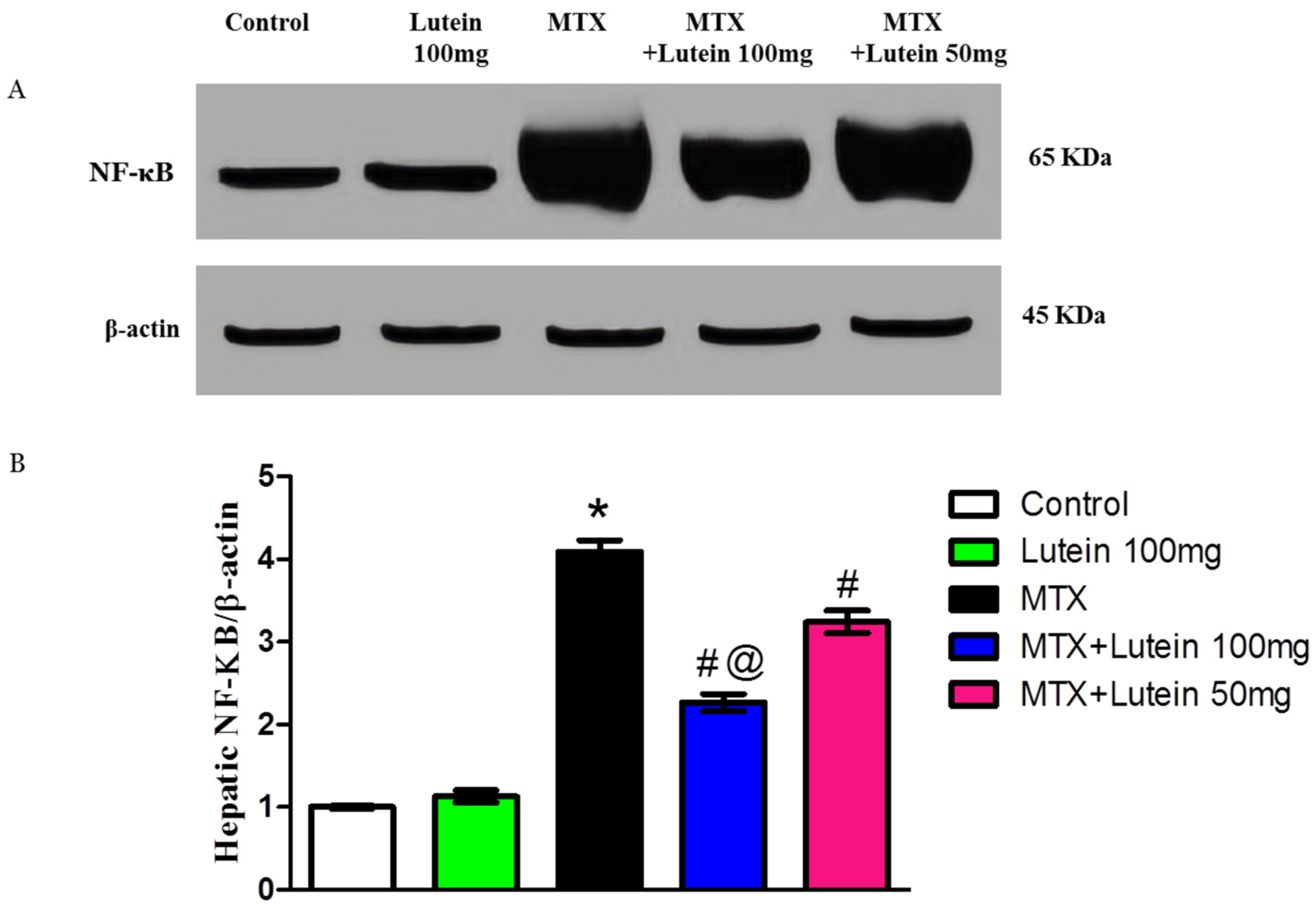
2.5. Effect of MTX and/or Lutein on Expression of NF-κB in Hepatic Tissue
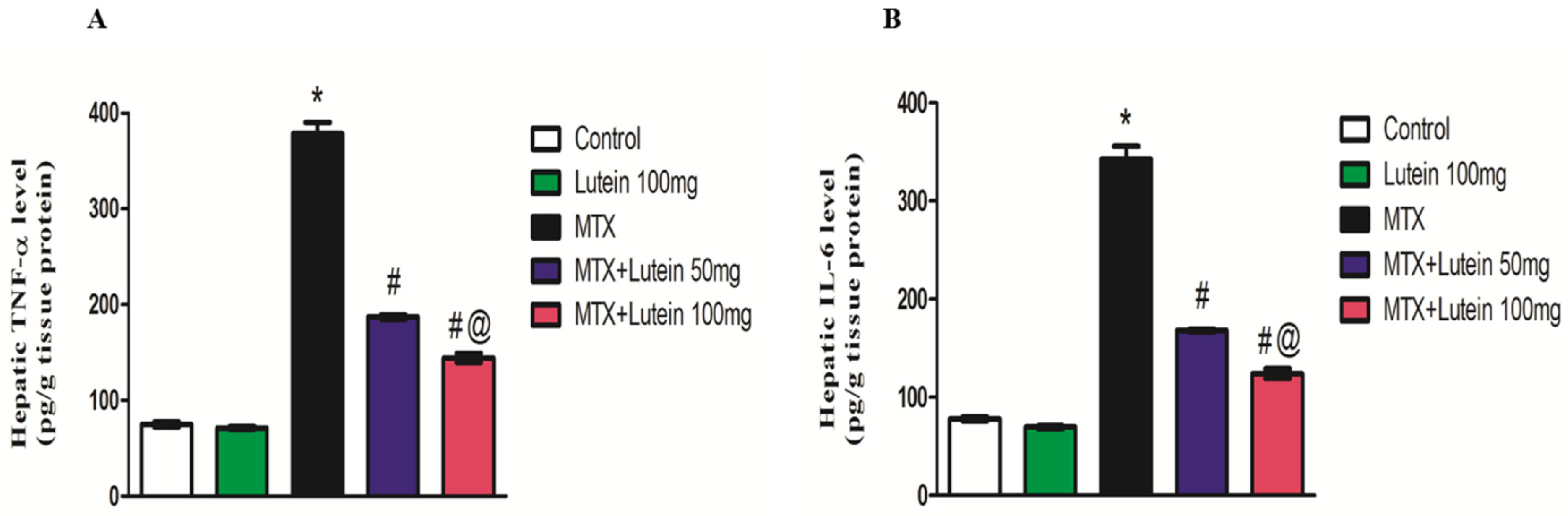
2.6. Effect of MTX and/or Lutein on TNF-α and IL-6 in Hepatic Tissue
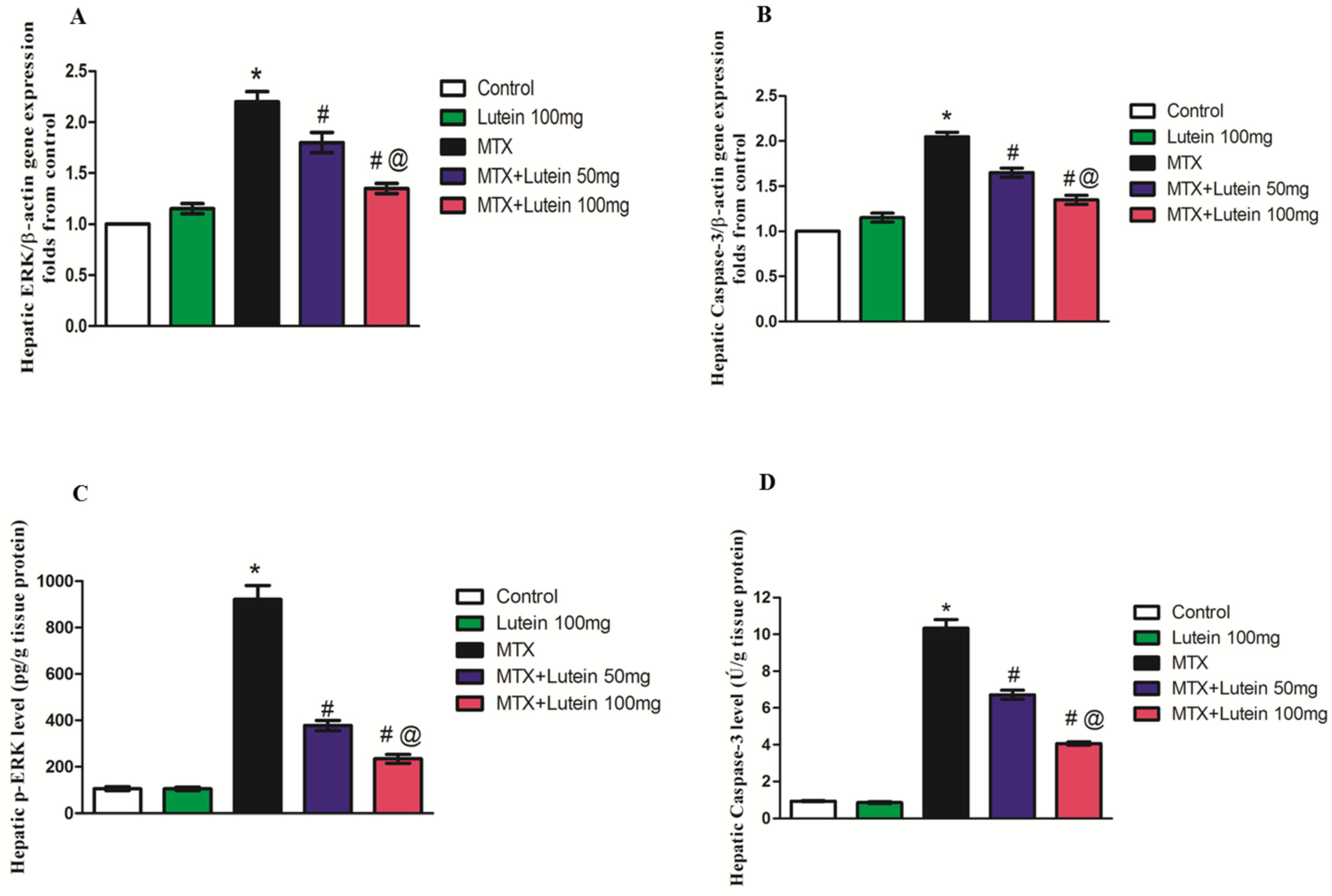
2.7. Effect of MTX and/or Lutein on Gene Expression and Levels of ERK and Caspase-3 in Hepatic Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs
4.2. Animals
4.3. Experimental Design and Induction of Hepatotoxicity
4.4. Blood and Tissue Sampling
4.5. Determination of Liver Function Markers
4.6. Liver Histopathology
4.7. Assessment of Oxidative Status
4.8. Determination of SIRT-1 and Nf-ķB Using Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Determination of TNF-α, IL-6, pERK, and Caspase-3 Using ELISA Technique
4.10. Determination of ERK and Caspase-3 Using qRT-PCR
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| DHFR | Dihydrofolate reductase |
| FPGS | Folylpolyglutamate synthetase |
| MTX-PGs | MTX polyglutamates |
| SIRT-1 | Sirtuin-1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| H and E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| I.G. | Intragastric |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction |
| Bax | Bcl-2 associated X protein |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| I.P. | Intraperitoneal |
References
- de Medeiros, P.d.C.; Nascimento, C.C.; Perobelli, J.E. Antineoplastic drugs in environmentally relevant concentrations cause endocrine disruption and testicular dysfunction in experimental conditions. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 100, 104122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katturajan, R.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Rasool, M.; Prince, S.E. Molecular toxicity of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis treatment: A novel perspective and therapeutic implications. Toxicology 2021, 461, 152909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muanda, F.T.; Blake, P.G.; Weir, M.A.; Ahmadi, F.; McArthur, E.; Sontrop, J.M.; Urquhart, B.L.; Kim, R.B.; Garg, A.X. Low-dose methotrexate and serious adverse events among older adults with chronic kidney disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2345132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellette, S.; Shah, R.; Razi, S.; Ashforth, G.; Wassef, C. Fatal low-dose methotrexate toxicity: A case report and literature review. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.C. Methotrexate for gestational choriocarcinoma: A paradigm shift in oncology. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.M.; Dighriri, I.M.; Baomar, A.F.; Alharthy, B.T.; Alenazi, F.E.; Alali, G.H.; Alenazy, R.H.; Alhumaidi, N.T.; Alhulayfi, D.H.; Alotaibi, Y.B. Overview of methotrexate toxicity: A comprehensive literature review. Cureus 2022, 14, e29518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, R.K.; Brar, N.K.; Forouhar, F.A.; Wu, G.Y. A review of methotrexate-associated hepatotoxicity. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, K.; Honma, T.; Masuyama, K. Methotrexate-related adverse events and impact of concomitant treatment with folic acid and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors: An assessment using the FDA adverse event reporting system. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1030832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghani, M.; Kalantari, H.; Khodayar, M.J.; Khorsandi, L.; Kalantar, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Kalantar, H. Alleviation of Liver Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Underlies the Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid in Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, A.; Jiyad, Z.; O’Beirne, J. Is methotrexate hepatotoxicity associated with cumulative dose? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 62, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, V.; Verhoeven, D.W.; Verhoeven, F.; Aubin, F.; Avouac, J.; Vuitton, L.; Lioté, F.; Thévenot, T.; Wendling, D. Busting the myth of methotrexate chronic hepatotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kashef, D.H.; Sewilam, H.M. Empagliflozin mitigates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity: Targeting ASK-1/JNK/Caspase-3 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 114, 109494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, M.; Kalantar, M.; Sadeghi, E.; Karamallah, M.H.; Kalantar, H. Protective effects of apigenin on altered lipid peroxidation, inflammation, and antioxidant factors in methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilarasan, D. Hepatotoxic potentials of methotrexate: Understanding the possible toxicological molecular mechanisms. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfwuaires, M.A. Galangin mitigates oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in a rat model of methotrexate hepatotoxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 20279–20288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Xu, H.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Shao, A.; Lou, M. Natural compounds for SIRT1-mediated oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in stroke: A potential therapeutic target in the future. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1949718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, W.W.; Cheng, X.; Xiang, H.R.; He, B.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Peng, W.X. Curcumin attenuates isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity by upregulating the SIRT1/PGC-1α/NRF1 pathway. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2022, 42, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, I.; Asci, H.; Candan, I.A.; Savran, M.; Imeci, O.B.; Sevuk, M.A. Cannabidiol mitigates methotrexate-induced hepatic injury via SIRT-1/p53 signaling and mitochondrial pathways: Reduces oxidative stress and inflammation. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2025, 48, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusan, M.; Erdogan, M.A.; Simsek, O.; Ustundag, H.; Dogan, Z.; Ciftci, B.B.; Kocamuftuoglu, M.; Orhan, I.; Erbas, O. Pyridostigmine Mitigates Methotrexate-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats: Association with Changes in BMP-9, SIRT1, and Endoglin Expression. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.-B.; Bao, J.; Deng, C.-X. Emerging roles of SIRT1 in fatty liver diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Long, T.; Xu, M.; Luo, T.; Che, Q.; He, Y.; Xu, D. The role of sirtuin1 in liver injury: Molecular mechanisms and novel therapeutic target. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Lee, J.; Jeon, W.; Yeo, C.; Lee, Y.; Baek, S.; Ha, I. Curcuma aromatica Salisb. Protects from acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by regulating the Sirt1/Ho-1 signaling pathway. Nutrients 2023, 15, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, H.; Soccol, C.R.; Molina-Aulestia, D.T.; Cardoso, J.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Manzoki, M.C.; Ambati, R.R.; Ravishankar, G.A.; De Carvalho, J.C. Lutein from microalgae: An industrial perspective of its production, downstream processing, and market. Fermentation 2024, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkewar, A.S.; Mishra, K.A.; Kamble, M.G.; Kumar, S.; Dey, J.; Sethi, K.K. A mechanistic review on growing multiple therapeutic applications of lutein and its global market research. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 3190–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, N.S.; Hariri, M.L.M.; Mohammed, H.S.; Shafaa, M.W. Lutein and β-carotene characterization in free and nanodispersion forms in terms of antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity. J. Pharm. Innov. 2023, 18, 1727–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbahzadeh, B.; Hassanzadeh-Taheri, M.; Aliparast, M.-s.; Baniasadi, P.; Hosseini, M. The protective effect of crocin on cisplatin-induced testicular impairment in rats. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, M.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Essam, R.M.; Amin, H.A.A.; Abd-Elmawla, M.A. Lutein exerts its cardioprotective effect against the experimental model of isoprenaline-induced myocardial infarction via MIAT/miR-200a/Nrf2/TXINP pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, E.R.; Firdous, A.P.; Preethi, K.C.; Kuttan, R. Carotenoid lutein protects rats from paracetamol-, carbon tetrachloride-and ethanol-induced hepatic damage. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adikwu, E.; Bokolo, B.; Nnanna, T.B.; Yaakor, F. Preclinical Protective Activity of Lutein on Diclofenac-induced Hepatotoxicity. Arch. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 7, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Hu, S.; Wu, X.; Ma, A.; Ma, Y. Lutein prevents liver injury and intestinal barrier dysfunction in rats subjected to chronic alcohol intake. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Gao, D.-H.; Xiang, X.; Xiong, Y.-F.; Zhu, T.-S.; Liu, L.-G.; Sun, X.-F.; Hao, L.-P. Ameliorative effects of lutein on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2015, 21, 8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, T.; Ajibade, A.; Edward, S.; Umeaku, U. Histological and biochemical effects of Lutein on the liver of adult Wistar rats following Paraquat-induced toxicity. J. Exp. Clin. Anat. 2024, 21, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson Sundbaum, J.; Eriksson, N.; Hallberg, P.; Lehto, N.; Wadelius, M.; Baecklund, E. Methotrexate treatment in rheumatoid arthritis and elevated liver enzymes: A long-term follow-up of predictors, surveillance, and outcome in clinical practice. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Arima, N.; Ito, M.; Fujiyama, S.; Kamo, Y.; Ueki, Y. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-like pattern in liver biopsy of rheumatoid arthritis patients with persistent transaminitis during low-dose methotrexate treatment. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, W.H.; Ali, M.F.; Afifi, S.H. Histopathological and Biochemical Studies of Methotrexate Hepatotoxicity on Albino Rats. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2023, 69, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- AbdelKader, G.; Abdelaziz, E.Z.; Hassan, R.; Greish, S.M.; Abogresha, N.M.; Sultan, B.O.; Yousef, E.M.; Morsi, S.; Abdelaziz, E.; Greish, S. Protective effects of crocin against methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in adult male albino rats: Histological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical study. Cureus 2023, 15, e34468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.R. The past and present of serum aminotransferases and the future of liver injury biomarkers. EXCLI J. 2016, 15, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, F.H.; Saadany, A.A.E.; Dawood, L.; Elkaliny, H.H.; Sarhan, N.I.; Badawi, R.; Abd-Elsalam, S. Metformin ameliorated methotrexate-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats in addition to its antitumor activity: Two birds with one stone. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pınar, N.; Kaplan, M.; Özgür, T.; Özcan, O. Ameliorating effects of tempol on methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawwa, A.F.; AlBawab, A.; Rooney, M.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Beresford, M.W.; McElnay, J.C. Methotrexate polyglutamates as a potential marker of adherence to long-term therapy in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis and juvenile dermatomyositis: An observational, cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Shikano, K.; Nanki, T.; Kawai, S. Folylpolyglutamate synthase is a major determinant of intracellular methotrexate polyglutamates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalaklioglu, S.; Genc, G.E.; Aksoy, N.H.; Akcit, F.; Gumuslu, S. Resveratrol ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via inhibition of lipid peroxidation. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kury, L.T.; Dayyan, F.; Ali Shah, F.; Malik, Z.; Khalil, A.A.K.; Alattar, A.; Alshaman, R.; Ali, A.; Khan, Z. Ginkgo biloba extract protects against methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity: A computational and pharmacological approach. Molecules 2020, 25, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardi, N.; Parlakpinar, H.; Cetin, A.; Erdogan, A.; Cetin Ozturk, I. Protective effect of beta-carotene on methotrexate-induced oxidative liver damage. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 38, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, T.; Gedikli, S.; Ozturk, N.; Aydemir Celep, N. The protective effect of N-acetylcysteine against methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Eurasian J. Med. Investig. 2019, 3, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, H.; Salah, A.; Elshatory, A.; Elkholy, O.; Nazih, G.; Awad, W.; Shehab, A. N-acytel cysteine ameliorates methotrexate induced hepatic toxicity and genotoxicity in male albino rats. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 16, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.A.; Qatea, F.K.; Qasim, B.J.; Nashtar, S.B.; Al-Radeef, M.Y. Effects of Silymarin against Hepatic and Renal Toxicity Induced by Methotrexate in Rats. Tikrit J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 17, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Moreno, M.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Caloca-Camarena, F.; Arceo-Orozco, S.; Muriel, P.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; García-Bañuelos, J.; García-González, A.; Navarro-Partida, J.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. A new opportunity for N-acetylcysteine. An outline of its classic antioxidant effects and its pharmacological potential as an epigenetic modulator in liver diseases treatment. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 2365–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavari, K.; Ardekani, S.S.; Ardekani, M.R.S.; Esfahani, M.M.; Kazemizadeh, H.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Iranshahi, M.; Khanavi, M.; Hasanpour, M. Are alterations needed in Silybum marianum (Silymarin) administration practices? A novel outlook and meta-analysis on randomized trials targeting liver injury. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2025, 25, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-A.; Hayden, M.M.; Bannerman, S.; Jansen, J.; Crowe-White, K.M. Anti-apoptotic effects of carotenoids in neurodegeneration. Molecules 2020, 25, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gür, F.M.; Bilgiç, S.; Aktaş, İ. Lutein, a non-provitamin A carotenoid, reduces cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2025, 177, 106965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.-Y.; Min, K.-B. Serum lycopene, lutein and zeaxanthin, and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease mortality in older adults. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2014, 37, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-J.; Lin, J.-F.; Chang, H.-H.; Lee, G.-A.; Hung, C.-F. Lutein protects against methotrexate-induced and reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptotic cell injury of IEC-6 cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, I.; Gur, F.M.; Bilgiç, S. Protection of Lutein Against the Toxic Effect of Cisplatin on Liver in Male Rat. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2025, 178, 106995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, S.M.; Hall, J.D.; Patel, J.; Lee, J.R.; Marcus, D.M.; Sridhar, S.; Romero, M.J.; Labazi, M.; Caldwell, R.W.; Bartoli, M. Protective effects of the carotenoid zeaxanthin in experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Huang, J.; Nisar, M.F.; Wan, C.; Huang, W. The beneficial roles of SIRT1 in drug-induced liver injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8506195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, D.; Luo, G.; Zhou, J.; Tan, Z.; Du, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Hao, L. Lutein attenuates excessive lipid accumulation in differentiated 3T3-L1 cells and abdominal adipose tissue of rats by the SIRT1-mediated pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 133, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Duan, J.; Duan, W.; Pu, X.; Ma, C.; Xu, Z. Lutein ameliorates Parkinson’s disease by regulating miR-135b-5p/SIRT1 to inhibit microglial M1 polarization and inflammation. Brain Res. Bull. 2025, 230, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, K.; Khan, Z.S.; Saha, M.; Mishra, S.; Gaikwad, N.; Bhakta, J.N.; Banerjee, K.; Das Saha, K. Manjari Medika Grape Seed Extract Protects Methotrexate-Induced Hepatic Inflammation: Involvement of NF-κB/NLRP3 and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling System. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matouk, A.I.; Awad, E.M.; El-Tahawy, N.F.; El-Sheikh, A.A.; Waz, S. Dihydromyricetin alleviates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity via suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome/caspase 1 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.J.; Gu, T.J.; Wei, D.Y. Emodin alleviates sepsis-mediated lung injury via inhibition and reduction of NF-kB and HMGB1 pathways mediated by SIRT1. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, R.; Min, Y.; Guo, P.-T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.-K.; Jin, L.; Gao, Y.-Y. The anti-inflammatory effect of lutein in broilers is mediated by regulating Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid-differentiation-factor 88 signaling pathway. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firozjae, A.A.; Shiran, M.R.; Rashidi, M. The neuropharmacological and clinical effects of lutein: A systematic review. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2025, 46, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammadov, R.; Suleyman, B.; Akturan, S.; Cimen, F.K.; Kurt, N.; Suleyman, Z.; Malkoc, İ. Effect of lutein on methotrexate-induced oxidative lung damage in rats: A biochemical and histopathological assessment. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskender, H.; Yenice, G.; Dokumacioglu, E.; Hayirli, A.; Sevim, C.; Dokumacioglu, A.; Terim Kapakin, K.A. Astaxanthin alleviates renal damage of rats on high fructose diet through modulating NFκB/SIRT1 pathway and mitigating oxidative stress. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 126, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dessouki, A.M.; Kaml, M.E.; El-Yamany, M.F. Modulation of AMPK by esomeprazole and canagliflozin mitigates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity: Involvement of MAPK/JNK/ERK, JAK1/STAT3, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 10901–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, Z.; Chen, F.; Li, B.; Jin, H. Lutein inhibits glutamate-induced apoptosis in HT22 cells via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1432969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chucair, A.J.; Rotstein, N.P.; SanGiovanni, J.P.; During, A.; Chew, E.Y.; Politi, L.E. Lutein and zeaxanthin protect photoreceptors from apoptosis induced by oxidative stress: Relation with docosahexaenoic acid. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 5168–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppinen, A.; Suuronen, T.; Ojala, J.; Kaarniranta, K.; Salminen, A. Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelzaher, W.Y.; Geddawy, A.; Attya, M.E.; Ali, A.H.S.A.; Elroby Ali, D.M.; Waggas, D.S.; Alshaeri, H.K.; Ibrahim, Y.F. Sirt1/Nrf2/TNFα; TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB signaling pathways are involved in mediating hepatoprotective effect of bupropion in rat model of myocardial infarction. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2024, 46, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Smith, J.R.; Swanson, H.M.; Rubin, L.P. Carotenoid lutein selectively inhibits breast cancer cell growth and potentiates the effect of chemotherapeutic agents through ROS-mediated mechanisms. Molecules 2018, 23, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavalappa, Y.P.; Gopal, S.S.; Ponesakki, G. Lutein inhibits breast cancer cell growth by suppressing antioxidant and cell survival signals and induces apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-A.; Kang, N.; Heo, S.-Y.; Oh, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Cha, S.-H.; Kim, W.-K.; Heo, S.-J. Antioxidant, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities of lutein-enriched extract of Tetraselmis species. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrzadeh, M.; Mortazavi, P.; Moghadami, A.; Khayambashi, B.; Motafeghi, F. Synergistic antiproliferative and anticancer activity of carotenoid lutein or coenzyme Q10 in combination with doxorubicin on the MCF7 cell line. Appl. Vitr. Toxicol. 2021, 7, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, R.; Habib, H.A.; Anter, A.F.; Amin, A.; Heeba, G.H. Modified citrus pectin ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatic and pulmonary toxicity: Role of Nrf2, galectin-3/TLR-4/NF-κB/TNF-α and TGF-β signaling pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1528978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özgöçmen, M.; Aşcı, H.; Doğan, H.K.; İlhan, İ.; Pekgöz, Ş.; Mustafaoğlu, A. A study on Wistar Albino rats: Investigating protective role of ramelteon on liver damage caused by methotrexate. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzaid, S.M.M.; Ali Abd El-Meguid, E.; El-Tahawy, N.F.; Seleem, H.S.; Khalifa Abd-Elhady, H.; Abdel-kareem, M.A. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic impact of Moringa leave extract supplementation in livers of methotrexate treated rat. Minia J. Med. Res. 2025, 36, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, A.; Gupta, D.; Bag, S.; Ahmed, I.; Bhatt, S.; Nehra, E.; Dhiman, S.; Kumar, A.; Singh, G.; Abdullah, S.T. Glabridin ameliorates methotrexate-induced liver injury via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgiç, S.; Gür, F.M.; Aktaş, İ. Biochemical and histopathological investigation of the protective effect of lutein in rat kidney exposed to cisplatin. Med. Rec. 2022, 4, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.J. Clinical Chemistry: Principles and Technics; Hoeber Medical Division, Harper and Row: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, C.A.F.; Sá, R.d.C.d.S.; Alves, M.F.; Benedito, R.B.; de Sousa, D.P.; Diniz, M.d.F.F.; Araújo, M.S.T.; de Almeida, R.N. Histopathological and biochemical assessment of d-limonene-induced liver injury in rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullazade, S.; Kav, T.; Gököz, Ö.; Önder, S.; Sökmensüer, C. The relationship between treatment response and histological scoring systems applied in chronic hepatitis B. Kafkas J. Med. Sci. 2017, 7, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, M.; Mihara, M. Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, S.L. Superoxide dismutase isoenzymes in tissues and plasma from New Zealand black mice, nude mice and normal BALB/c mice. Mutat. Res./Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1985, 148, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups | Relative Hepatic Weight | Serum ALT (U/L) | Serum AST (U/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.92 ± 0.16 | 33.27 ± 1.08 | 39.53 ± 0.77 |
| Lutein 100 mg | 3.00 ± 0.16 | 33.50 ± 1.01 | 48.95 ± 2.14 |
| MTX | 3.12 ± 0.10 | 77.88 ± 2.29 * | 156.1 ± 10.34 * |
| MTX + Lutein 50 mg | 2.97 ± 0.12 | 50.55 ± 2.17 # | 88.25 ± 7.63 # |
| MTX + Lutein 100 mg | 2.90 ± 0.13 | 37.41 ± 3.64 #@ | 43.90 ± 2.47 #@ |
| Gene | Sequences (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Forwarded | Reverse | |
| ERK | CCCTCTAAAACCAA GGTGGCT | CATCCAATCACCCACACAC AG |
| Caspase-3 | TGAGCATTGA CACAATACAC | AAGCCGAA ACTCTTCATC |
| β-actin | ACCCACACTGTGCCC ATCTATG | AGAGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAG GA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelwahab, A.M.; Habib, H.A.; Darwish, M.A.; Bin Jardan, Y.A.; Heeba, G.H. Modulation of SIRT-1, NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6, and ERK/Caspase-3 by Lutein Mitigates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121787
Abdelwahab AM, Habib HA, Darwish MA, Bin Jardan YA, Heeba GH. Modulation of SIRT-1, NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6, and ERK/Caspase-3 by Lutein Mitigates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(12):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121787
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelwahab, Areej M., Heba A. Habib, Mostafa A. Darwish, Yousef A. Bin Jardan, and Gehan H. Heeba. 2025. "Modulation of SIRT-1, NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6, and ERK/Caspase-3 by Lutein Mitigates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 12: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121787
APA StyleAbdelwahab, A. M., Habib, H. A., Darwish, M. A., Bin Jardan, Y. A., & Heeba, G. H. (2025). Modulation of SIRT-1, NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6, and ERK/Caspase-3 by Lutein Mitigates Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Pharmaceuticals, 18(12), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121787








