Astragaloside–Brucea Javanica Oil Nanoemulsion Regulates Glycolysis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through AURKA-Mediated PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Network Pharmacological Analysis of AS/BJO-NEs Against OSCC
2.1.1. Acquisition of Target Sites for AS/BJO-NEs in the Treatment of OSCC
2.1.2. Construction and Enrichment Analysis of PPI Network
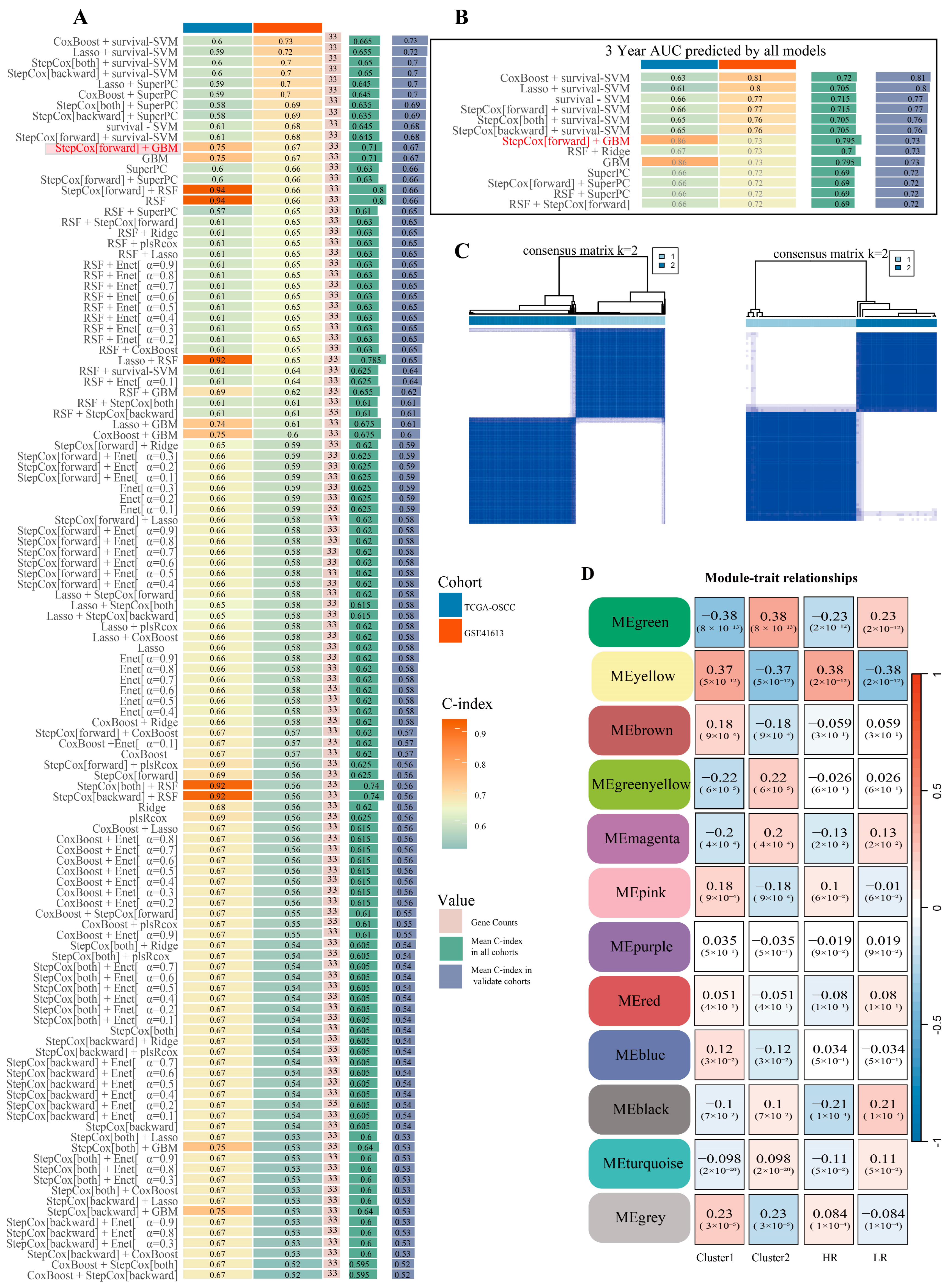
2.2. OSCC Machine Learning Prognostic Risk Model for Glycolysis and Consistency Clustering Analysis
2.2.1. Construct and Screen a Prognostic Risk Model for OSCC Glycolysis-Related Genes
2.2.2. Consistency Clustering Analysis and External Verification Based on the Optimal Model Genes
2.3. WGCNA Identified the Core Targets Related to Glycolysis That Are Targeted by AS/BJO-NEs
2.3.1. WGCNA Identifies the Modules Associated with High Risk and Poor Prognosis
2.3.2. Analysis of Poor Prognosis of GHGs and GRGs and Correlation Analysis with Glycolysis
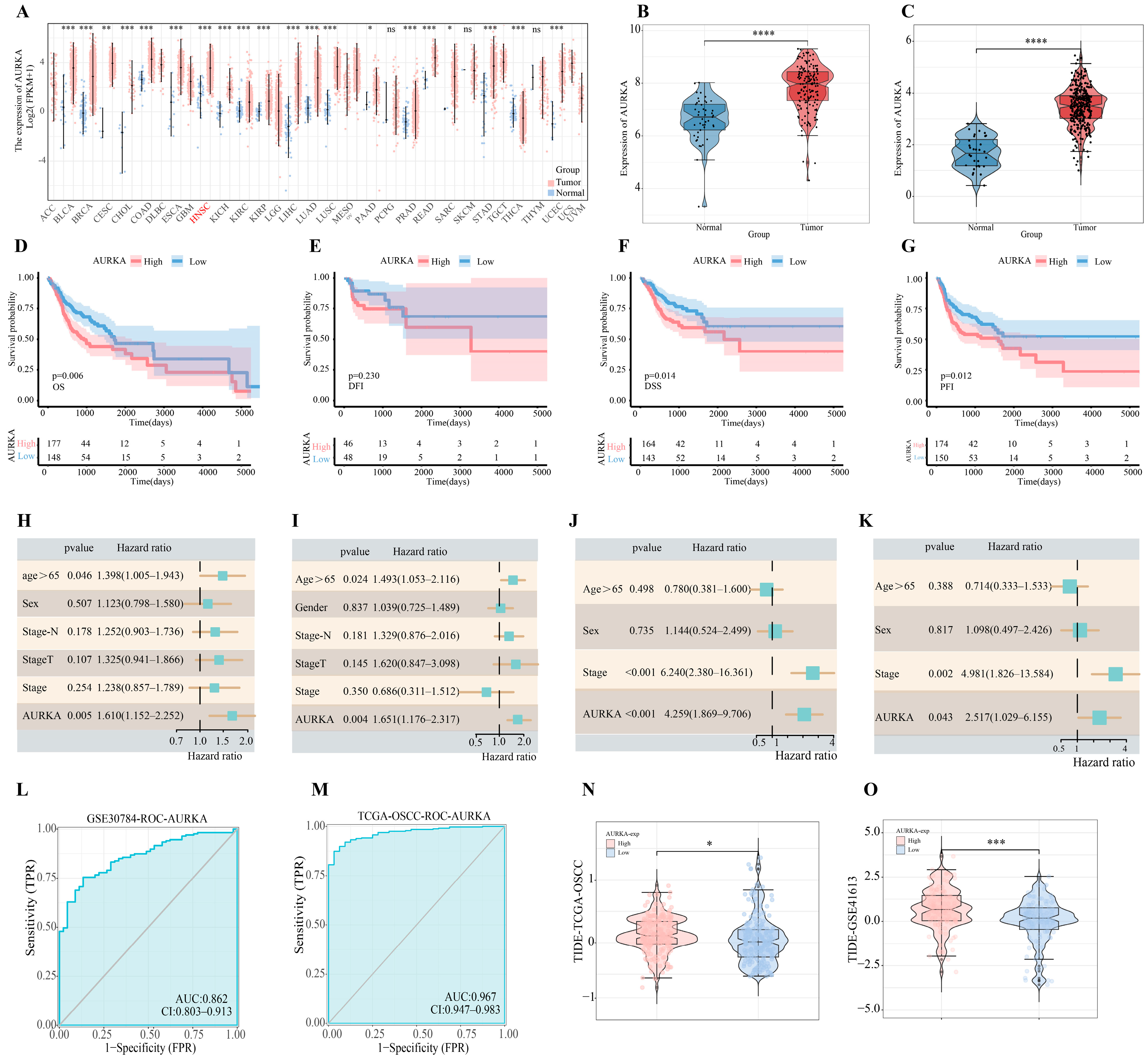
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of AURKA
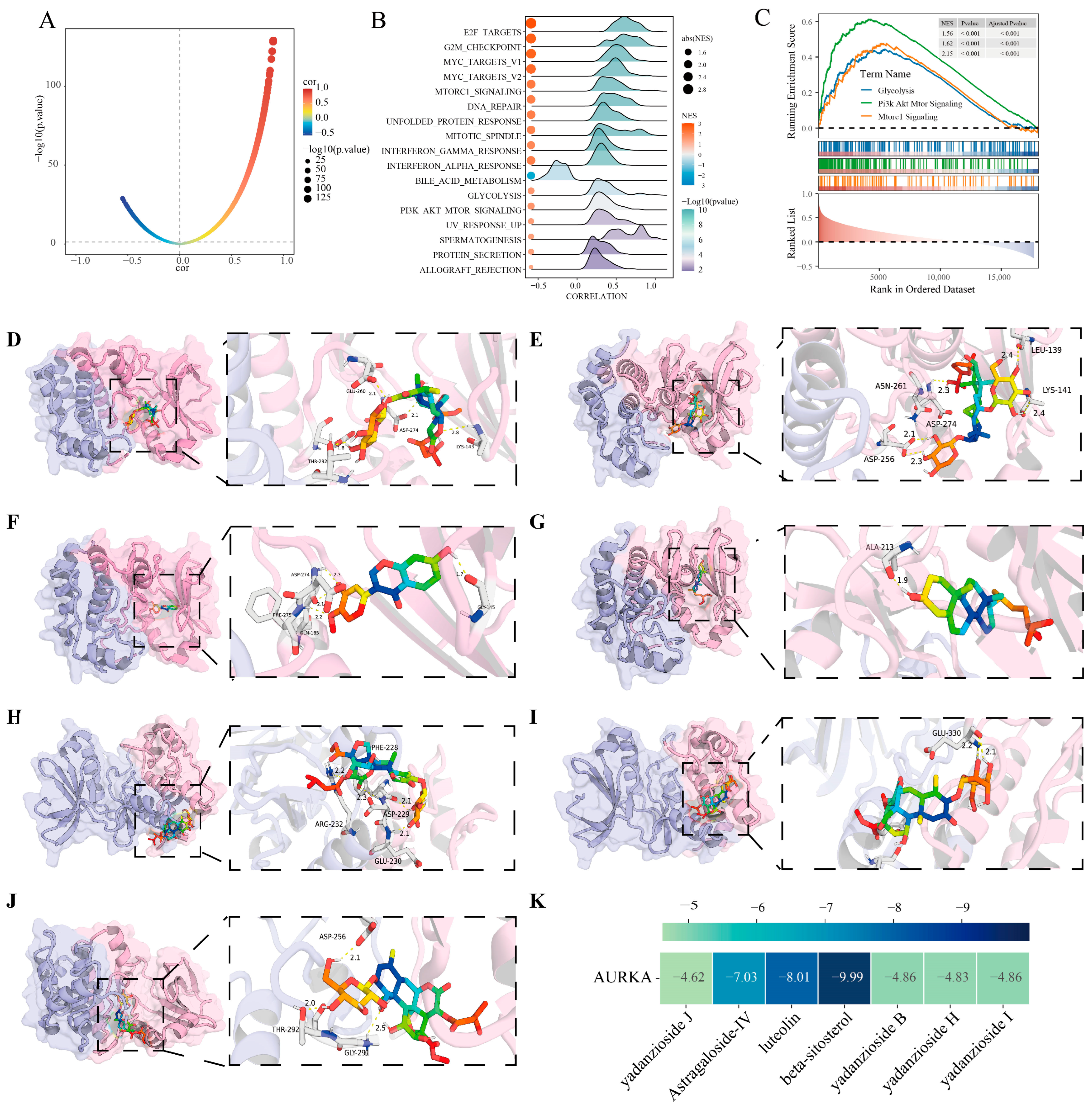
2.5. Analysis of AURKA-Related Pathways and Their Correlation with Glycolysis
2.5.1. Transcriptomic Analysis of Enrichment of AURKA-Related Pathway
2.5.2. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Validate the AURKA-Related Pathways
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. Composition and Preparation of AS/BJO-NEs
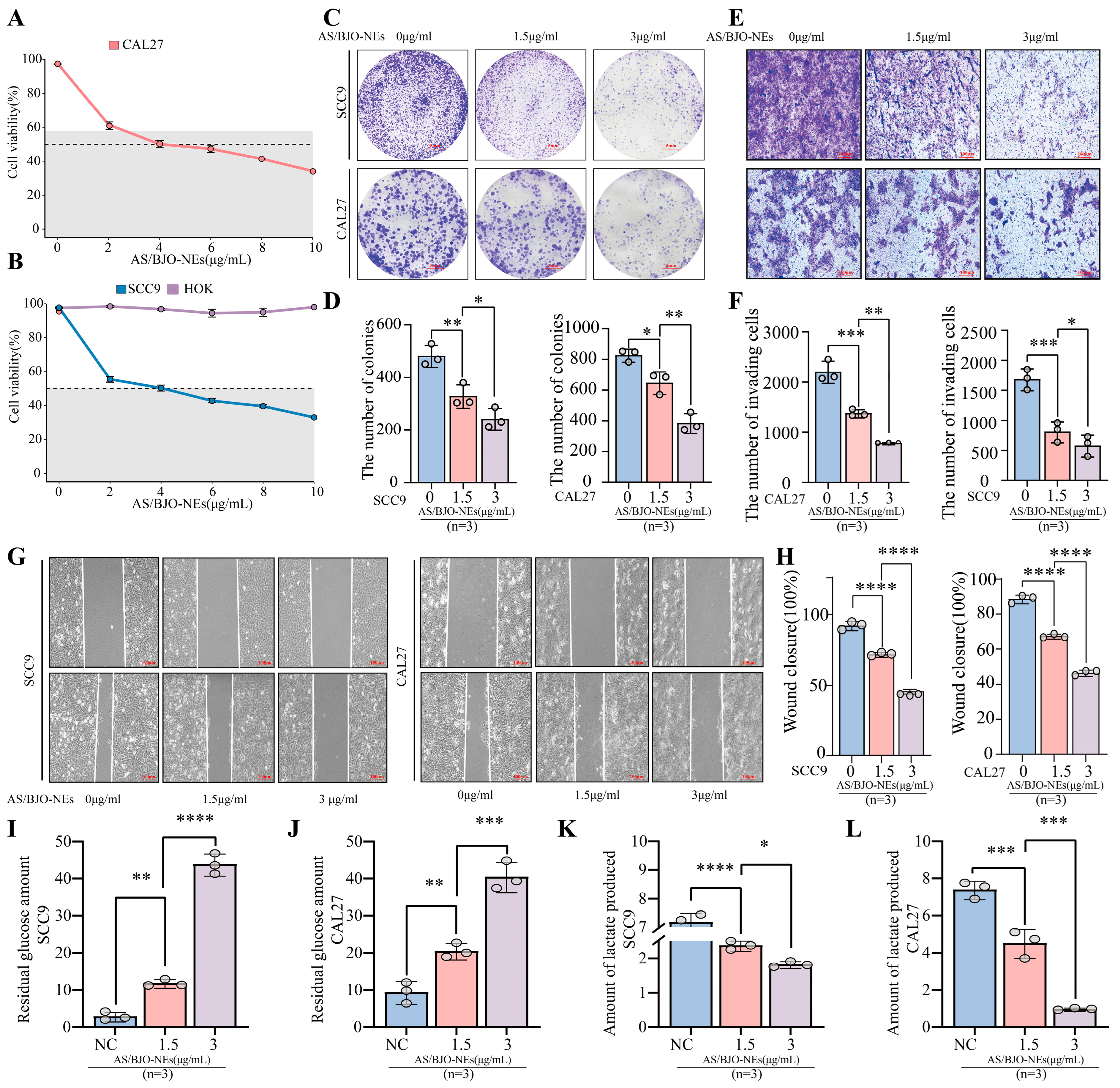
2.8. AS/BJO-NEs Inhibit OSCC Proliferation Invasion Metastasis and Glycolytic Metabolism
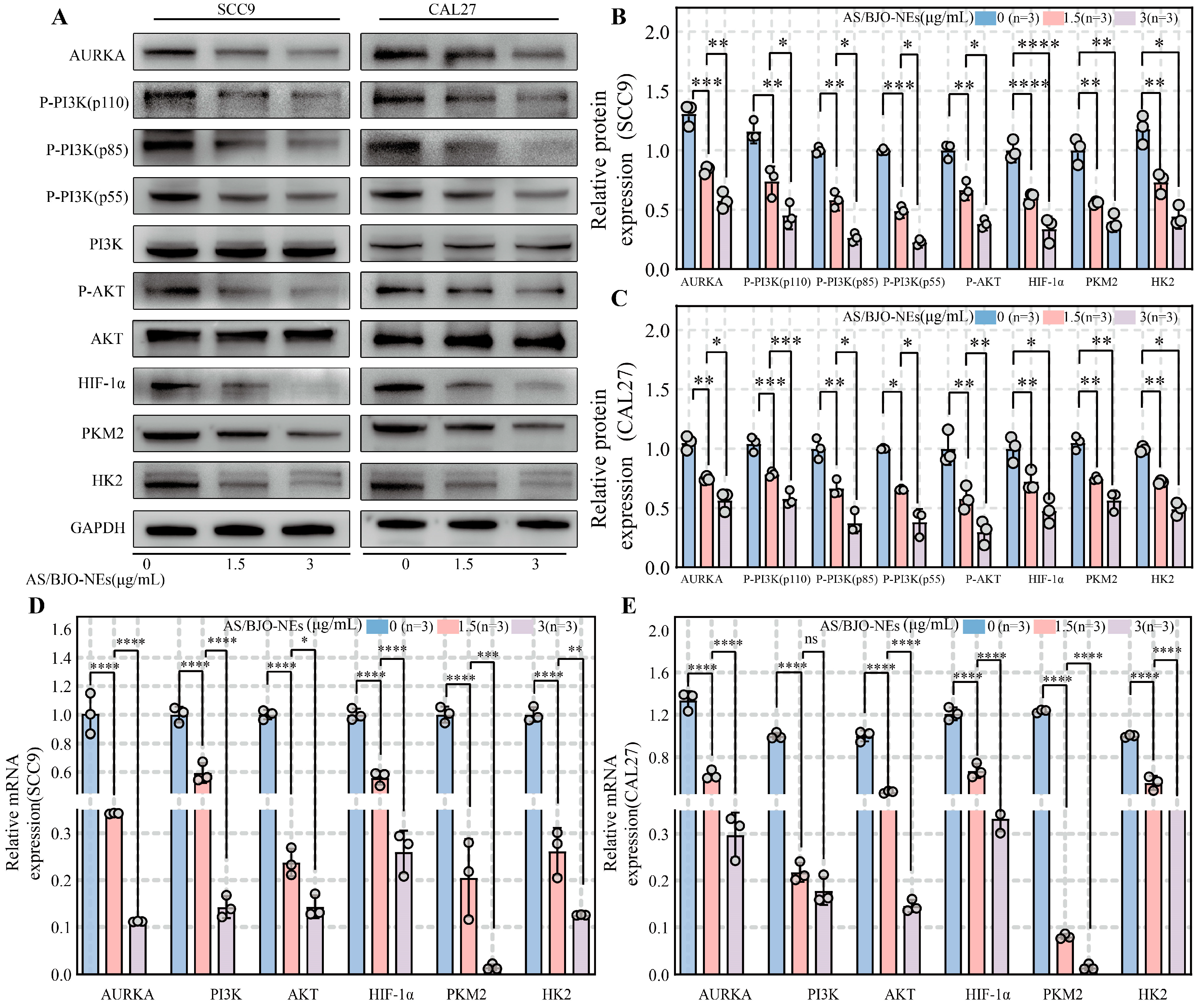
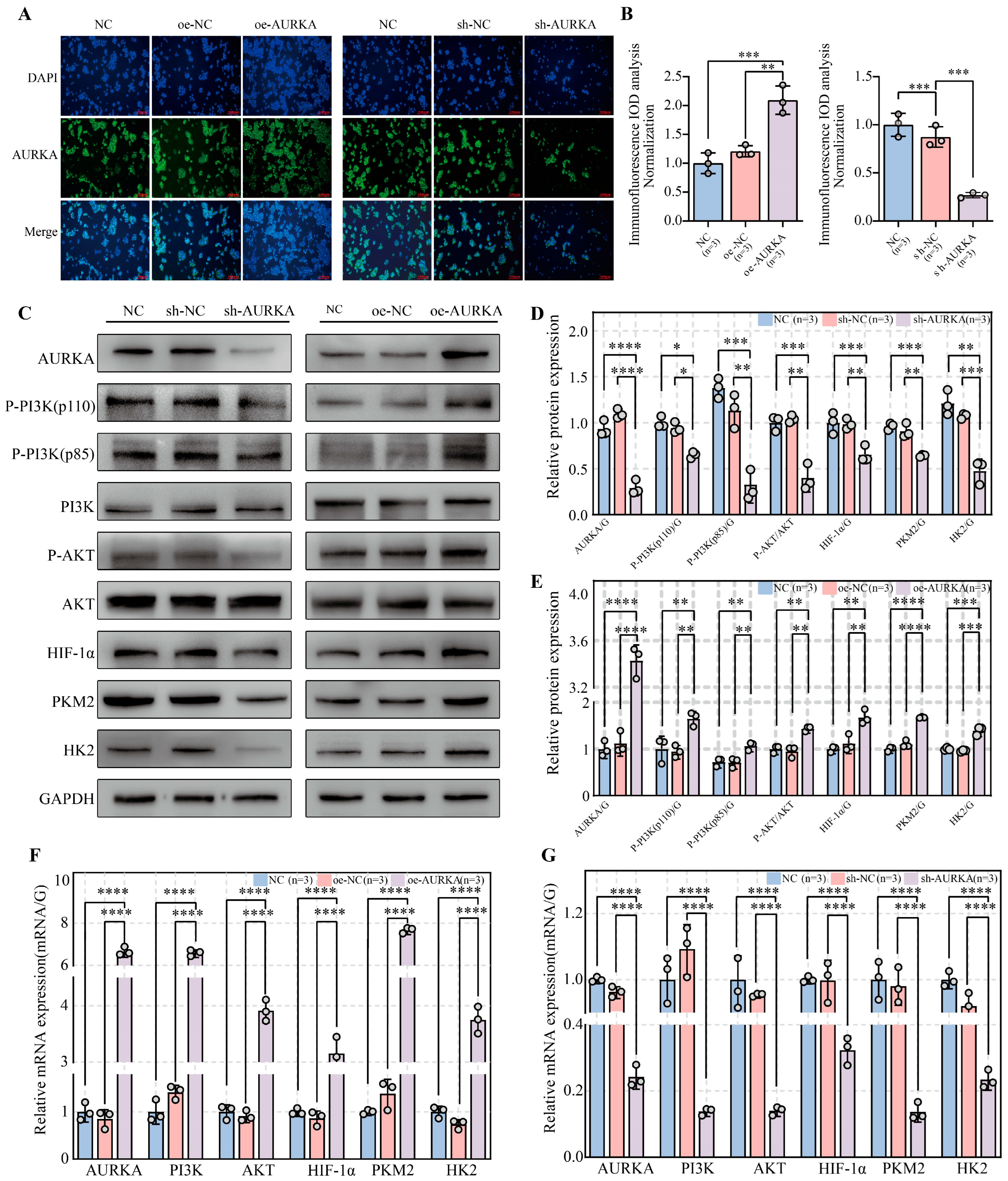
2.9. AS/BJO-NEs Downregulate AURKA and the PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α Pathway While Inhibiting Glycolysis-Related Enzyme Expression in OSCC
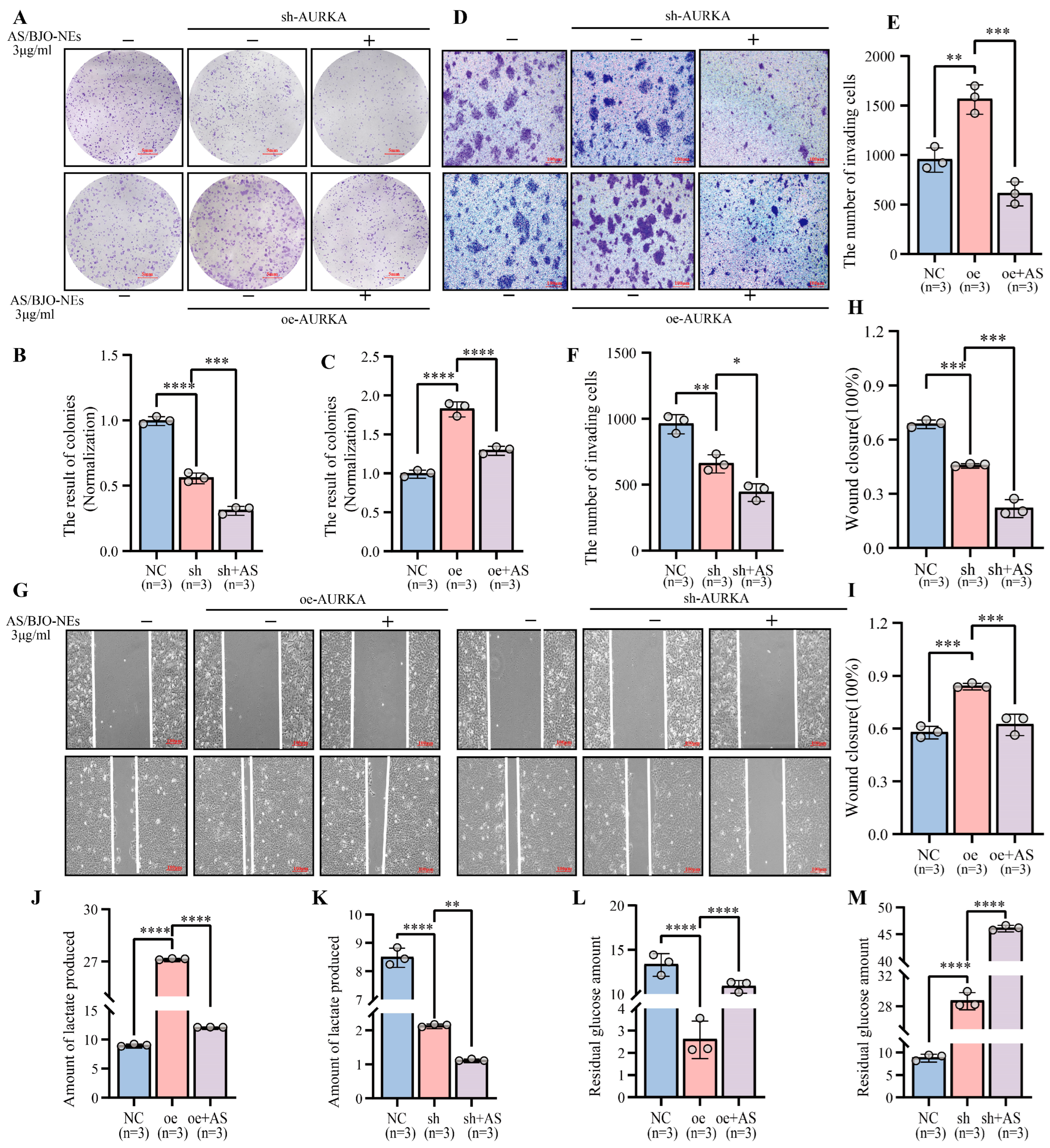
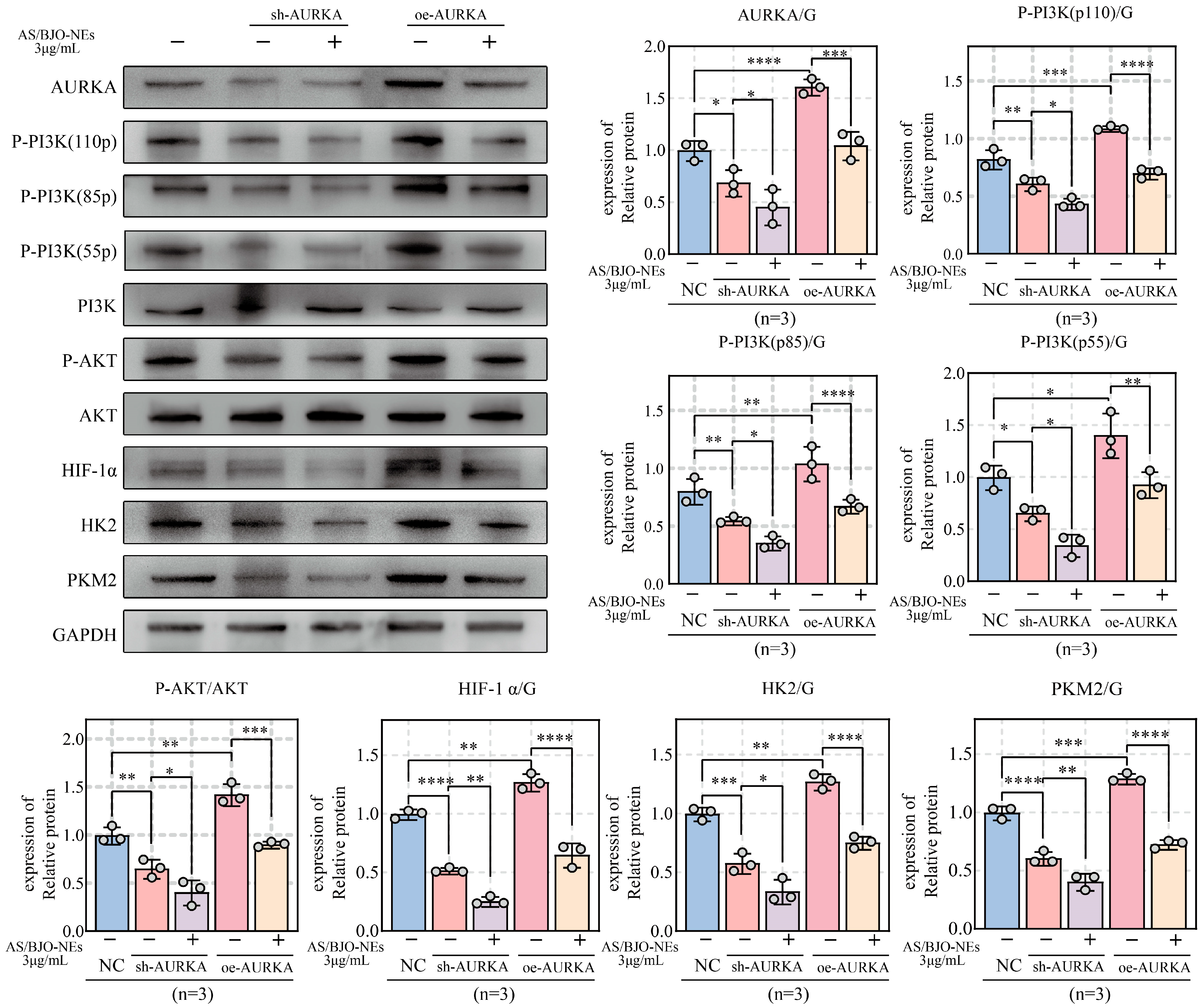
2.10. AS/BJO-NEs Suppress OSCC Proliferation, Invasion, Metastasis, and Glycolytic Activity by Targeting the AURKA/PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α Signaling Pathway
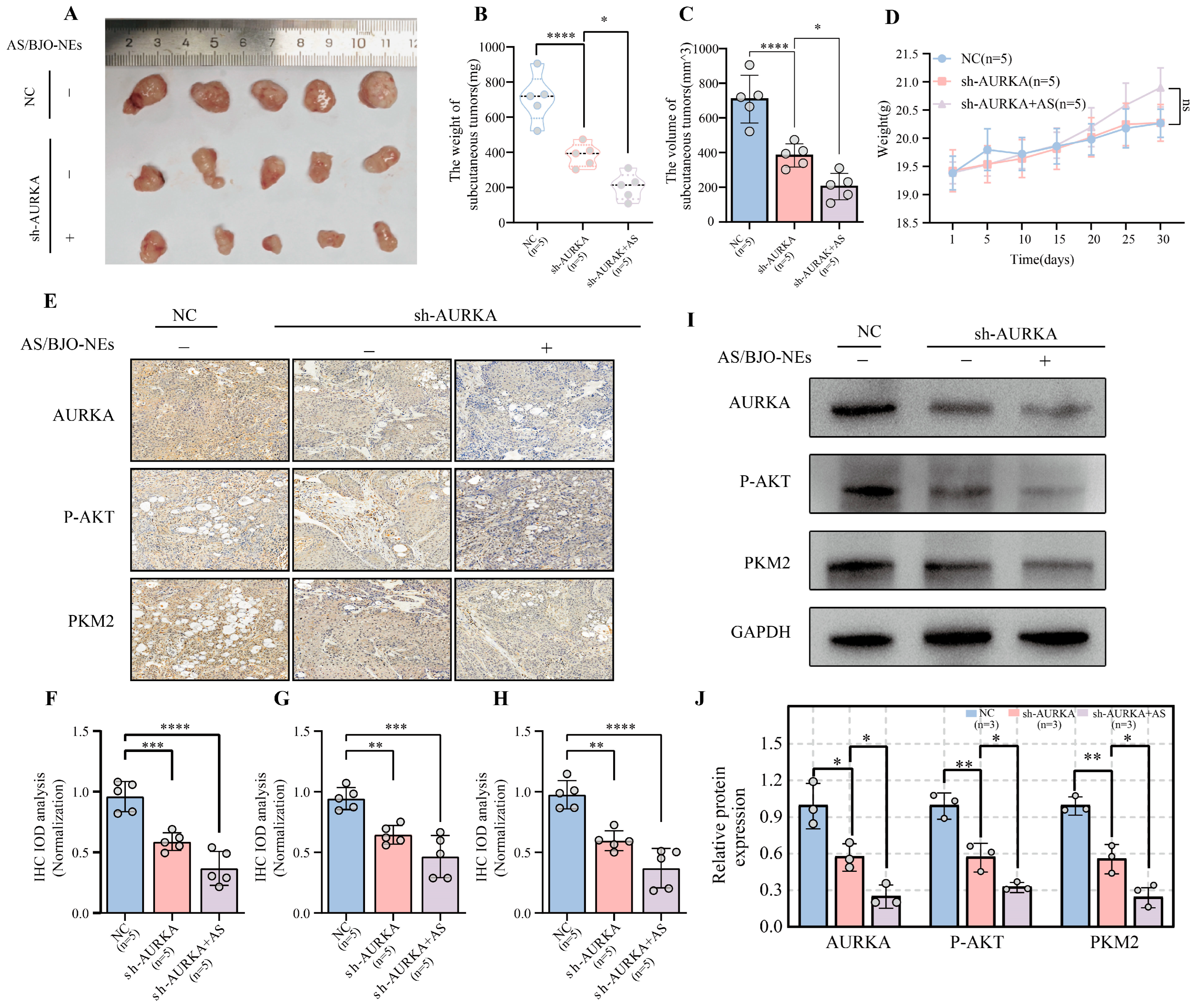
2.11. In Vivo Experimental Validation of AS/BJO-NEs Downregulates AURKA and Inhibits OSCC Proliferation and Glycolysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Network Pharmacological Analysis of AS/BJO-NEs Against OSCC
4.2. Obtain Transcriptome and Single-Cell Transcriptome Data
4.3. Construction of a Machine Learning Prognostic Risk Model Related to OSCC Glycolysis
4.4. Unsupervised Cluster Analysis Based on Machine Learning Model Genes
4.5. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
4.6. Function Enrichment Analysis
4.7. Immune Infiltration and TIDE Analysis
4.8. Drug Sensitivity Analysis
4.9. Molecular Docking
4.10. The Composition and Preparation of AS/BJO-NEs
4.11. UPLC/MS Spectrum
4.12. Cell Culture and Manipulation
4.13. Establish AURKA Knockdown/Overexpression Cell Lines
4.14. Cell Counting Kit-8 Assay and Colony Formation
4.15. Cell Scratch Test
4.16. Transwell Invasion Assay
4.17. Western Blot
4.18. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.19. Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
4.20. Glycolytic Metabolite Assays
4.21. Animal Experiments
4.22. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
4.23. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| AS-IV | Astragaloside-IV |
| BJO | Brucea javanica oil |
| AS/BJO-NEs | Astragaloside–Brucea Javanica Oil nanoemulsion |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| WGCNA | Weighted gene co-expression network analysis |
| GSEA | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| GSVA | Gene Set Variation Analysis |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| HOK | Human oral mucosal keratinocytes |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| GHGs | Glycolytic hub genes |
| GRGs | glycolysis-related genes |
| HK | Hexokinase |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate Kinase M2 |
| OB | Oral bioavailability |
| TME | Tumor immune microenvironment |
| DL | Drug-likeness |
| P-AKT | Phospho-AKT |
| Phospho-PI3K | P-PI3K |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| IFA | Immunofluorescence assay |
| IHC | Immunohistochemical |
| CCK8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 assay |
References
- Vadovics, M.; Ho, J.; Igaz, N.; Alföldi, R.; Rakk, D.; Veres, É.; Szücs, B.; Horváth, M.; Tóth, R.; Szücs, A.; et al. Candida albicans Enhances the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro and In Vivo. mBio 2021, 13, e0314421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Cheng, B.; Xie, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Circadian Clock Gene Bmal1 Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Increases Paclitaxel Sensitivity in Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinn, S.B.; Myers, J.N. Oral Cavity Carcinoma: Current Management, Controversies, and Future Directions. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3269–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeesan, D.; Sathasivam, K.V.; Fuloria, N.K.; Balakrishnan, V.; Khor, G.H.; Ravichandran, M.; Solyappan, M.; Fuloria, S.; Gupta, G.; Ahlawat, A.; et al. Comprehensive insights into oral squamous cell carcinoma: Diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapeutic advances. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 261, 155489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, F.A.; da Silva Bittencourt, L.; Barbosa, S.; Diel, L.F.; Bernardi, L.; Matte, C.; Lamers, M.L. Energy Metabolic Profile in Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Preliminary Landscape of Warburg Effect in Oral Cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2025, 64, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kende, P.; Mathur, Y.; Varte, V.; Tayal, S.; Patyal, N.; Landge, J. The efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy as compared to upfront surgery for the management of oral squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 53, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. Invasion and Metastasis Inhibition of Lung Cancer by Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Review. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. 2025, 31, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; He, Y.; Ming, L.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, H. Anti-tumor Effect and Mechanism of Active Ingredients from Yin-nourishing Chinese Herbs: A Review. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2025, 31, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, S.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.; Hu, Q. Evaluation of efficacy, safety and underlying mechanism on Traditional Chinese medicine as synergistic agents for cancer immunotherapy: A preclinical systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 338 Pt 1, 119035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Gao, L.; Du, G.; Qin, X. Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: A research review on the pharmacological effects. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 87, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Li, Z.; Jia, R.-X.; Bao, X.; Wang, W.; Song, S. Research progress on antitumor mechanism of astragaloside IV. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 54, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Lu, F. Astragaloside IV inhibits cell viability and glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating KAT2A-mediated succinylation of PGAM1. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Xie, L.; Gong, F.; Zhang, S.; Xi, T. Efficacy and safety of Chinese medicine injections in combination with docetaxel and cisplatin for non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1277284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Cao, L.; Wu, J.; Lu, T.; Li, S.; Li, J. Efficacy and Safety of Brucea javanica Oil Emulsion Injection in the Treatment of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 784164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.; Fang, Z.; Shao, Y.; Wang, W. Brucea javanica oil inhibits tongue squamous cell invasion and metastasis by regulating miR-138-EZH2 pathway. J. Stomatol. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Li, M.; Zhan, J.; Jiang, L.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Ma, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wang, W. Brucea javanica oil inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of oral squamous carcinoma by regulated the MTFR2 pathway. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1477293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseema, A.; Kovooru, L.; Behera, A.K.; Kumar, K.P.P.; Srivastava, P. A critical review of synthesis procedures, applications and future potential of nanoemulsions. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 287, 102318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.; Sharma, P.; Murtaza, M.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaglan, S. Fabrication, characterization, and interventions of protein, polysaccharide and lipid-based nanoemulsions in food and nutraceutical delivery applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Ding, W.Y.; Huang, Q.Y.; Lv, T.; Zeng, Y.; Feng, J. Application Advantages of Nanoemulsion in Field of Traditional Chinese Medicine Preparation: A Review. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2021, 27, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.K.; Lim, Z.Y.; Jeon, W.Y.; Cho, N.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jackman, J.A. Medicinal Activities and Nanomedicine Delivery Strategies for Brucea javanica Oil and Its Molecular Components. Molecules 2020, 25, 5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Abulaiti, A.; Maimaiti, A.; Abulaiti, Z.; Fan, G.; Aili, Y.; Ji, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Integrated machine learning survival framework develops a prognostic model based on inter-crosstalk definition of mitochondrial function and cell death patterns in a large multicenter cohort for lower-grade glioma. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, F.; Asif, M.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Qasim, M.; Tahir Ul Qamar, M. Machine learning for synergistic network pharmacology: A comprehensive overview. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, C.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Y.; Zeng, B.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; et al. Identification of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs with the significance in prognosis and immunotherapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 171, 108198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagaev, A.; Kotlov, N.; Nomie, K.; Svekolkin, V.; Gafurov, A.; Isaeva, O.; Osokin, N.; Kozlov, I.; Frenkel, F.; Gancharova, O.; et al. Conserved pan-cancer microenvironment subtypes predict response to immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 845–865.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, H.; Ou, S.; Liang, T.; Zhou, J. The SNHG1-Centered ceRNA Network Regulates Cell Cycle and Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2022, 258, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, R.; Wu, Z.; Song, S.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, R. Deep learning-based predictive identification of neural stem cell differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, M.D.; Rocco, J.W.; Yom, S.S.; Haddad, R.I.; Saba, N.F. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in cancers of the lip, tongue and mouth. Oral Oncol. 2020, 102, 104551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-X.; Wang, B.; Yu, M. Research progress on antitumor mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine based on theory of “Fuzheng Quxie. Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 52, 5751–5757. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Shang, E.; Shu, C.; Kim, S.; Mela, A.; Humala, N.; Mahajan, A.; Yang, H.W.; Akman, H.O.; Quinzii, C.M.; et al. Aurora kinase A inhibition reverses the Warburg effect and elicits unique metabolic vulnerabilities in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Luo, J.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hu, S.; Shen, X.; Du, X.; Xiang, W. Alisertib impairs the stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting purine synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, C.; Bu, X.; Que, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J.; et al. ISL1 promoted tumorigenesis and EMT via Aurora kinase A-induced activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in neuroblastoma. Cell Death Disease 2021, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwed, A.; Kim, E.; Jacinto, E. Regulation and metabolic functions of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1371–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 mediates metabolic responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Su, J.; Chi, R.; Zhu, Q.; Lv, S.; Liang, W. Effect of amlodipine besylate combined with acupoint application of traditional Chinese medicine nursing on the treatment of renal failure and hypertension by the PI3K/AKT pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, W.; Wan, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, P.; Liu, X.S. Large-scale public data reuse to model immunotherapy response and resistance. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Kim, J.K.; Li, J.; Deng, P.; Zhang, W.; Krebsbach, P.H.; Wang, C.-Y. CD276 expression enables squamous cell carcinoma stem cells to evade immune surveillance. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1597–1613.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassn Mesrati, M.; Syafruddin, S.E.; Mohtar, M.A.; Syahir, A. CD44: A Multifunctional Mediator of Cancer Progression. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ren, X.; Galbo, P.M., Jr.; Moerdler, S.; Wang, H.; Sica, R.A.; Etemad-Gilbertson, B.; Shi, L.; Zhu, L.; Tang, X.; et al. KIR3DL3-HHLA2 is a human immunosuppressive pathway and a therapeutic target. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, K.; Butler, S.C.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Advances in LAG3 cancer immunotherapeutics. Trends Cancer 2025, 11, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, B.H. Role of Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. In Cancer Research: An Interdisciplinary Approach. Interdisciplinary Cancer Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc-Hotte, A.; Audiger, C.; Chabot-Roy, G.; Lombard-Vadnais, F.; Delisle, J.-S.; Peter, Y.-A.; Lesage, S. Immature and mature bone marrow-derived dendritic cells exhibit distinct intracellular mechanical properties. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberio, L.; Del Prete, A.; Schioppa, T.; Sozio, F.; Bosisio, D.; Sozzani, S. Chemokine and chemotactic signals in dendritic cell migration. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Melo, N.; Baumjohann, D. T follicular helper cells in cancer. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Craft, J. T Follicular Helper Cell Heterogeneity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 42, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmeyer, P.; Kling, A.; Schulz, X.; Perske, C.; Schliephake, H.; Hemmerlein, B. High mast cell density indicates a longer overall survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, F.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Gou, G.; Wen, M.; Luo, C.; Lu, X.; Hu, Y.; Du, Q.; et al. Mast cells: Key players in digestive system tumors and their interactions with immune cells. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Biehl, A.; Gadina, M.; Hasni, S.; Schwartz, D.M. JAK-STAT Signaling as a Target for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Current and Future Prospects. Drugs. Apr. 2017, 77, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhan, M.; Wang, H.; Gaur, U.; Little, P.J.; Xu, J.; Zheng, W. FOXO Signaling Pathways as Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liang, D.; Quan, X.; Gu, R.; Meng, Z.; Gan, H.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-H.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Wu, S.-J.; Wei, R.-A.; Sitholumusa, M.U.I.; Zhao, X.-P.; Liu, J.-Q.; Kai, G.-Y. Astragaloside IV alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating receptor C5aR1 and macrophage pyroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 162, 115176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Mai, L.; Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.; Su, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Lai, Z.; et al. Brucea javanica oil alleviates intestinal mucosal injury induced by chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluorouracil in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1136076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.T.; Mu, L.Q.; Dai, W.; Wang, C.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Xiang, D.X. Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of antitumor effect of Brucea javanica oil cationic nanoemulsions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2515–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Weng, S.; Guo, C.; Dang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. Machine learning-based integration develops an immune-derived lncRNA signature for improving outcomes in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Zhan, J.; Lai, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Shao, Y. Astragaloside–Brucea Javanica Oil Nanoemulsion Regulates Glycolysis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through AURKA-Mediated PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121783
Liu R, Zhan J, Lai Y, Ma Y, Wang W, Jiang L, Shao Y. Astragaloside–Brucea Javanica Oil Nanoemulsion Regulates Glycolysis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through AURKA-Mediated PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α Pathway. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(12):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121783
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Runqiang, Juan Zhan, Yihan Lai, Yujie Ma, Wei Wang, Lin Jiang, and Yisen Shao. 2025. "Astragaloside–Brucea Javanica Oil Nanoemulsion Regulates Glycolysis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through AURKA-Mediated PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α Pathway" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 12: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121783
APA StyleLiu, R., Zhan, J., Lai, Y., Ma, Y., Wang, W., Jiang, L., & Shao, Y. (2025). Astragaloside–Brucea Javanica Oil Nanoemulsion Regulates Glycolysis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through AURKA-Mediated PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α Pathway. Pharmaceuticals, 18(12), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18121783





