YM155 Inhibition of Survivin Enhances Carboplatin Efficacy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
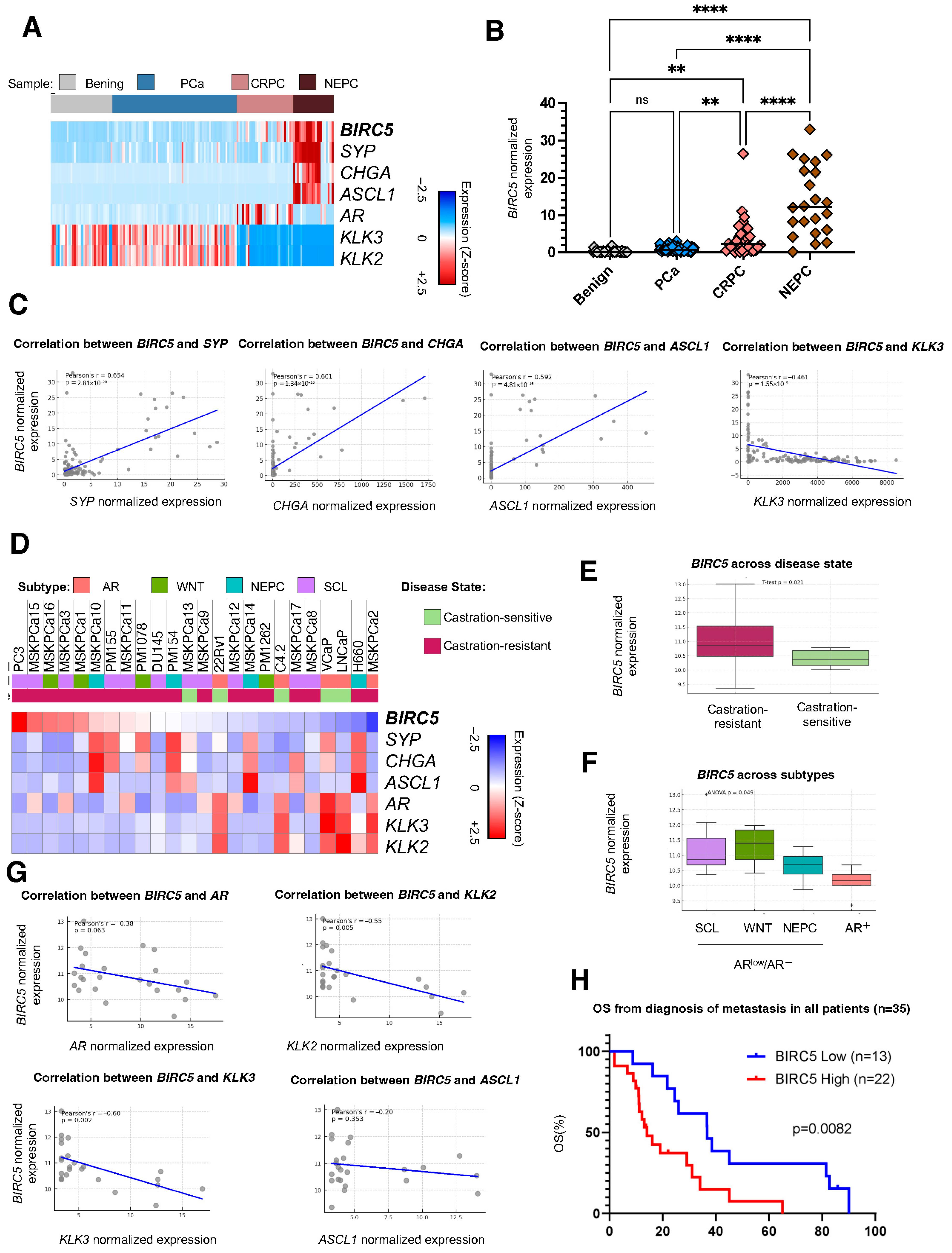
2.1. Survivin Is Overexpressed in mCRPC and NEPC and Correlates with Shorter OS
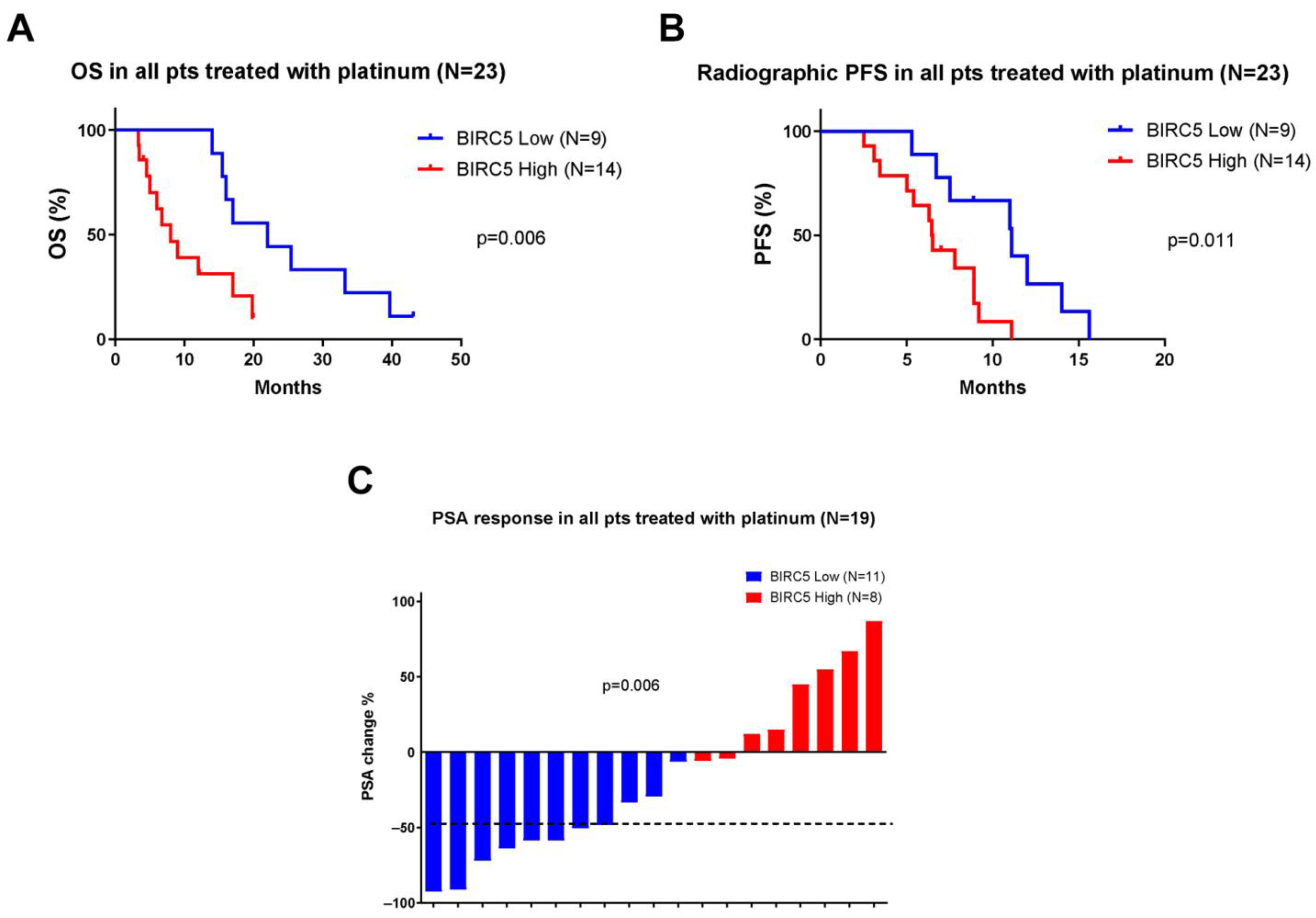
2.2. Survivin Overexpression Is Associated with Response and Outcomes in Platinum-Treated Patients
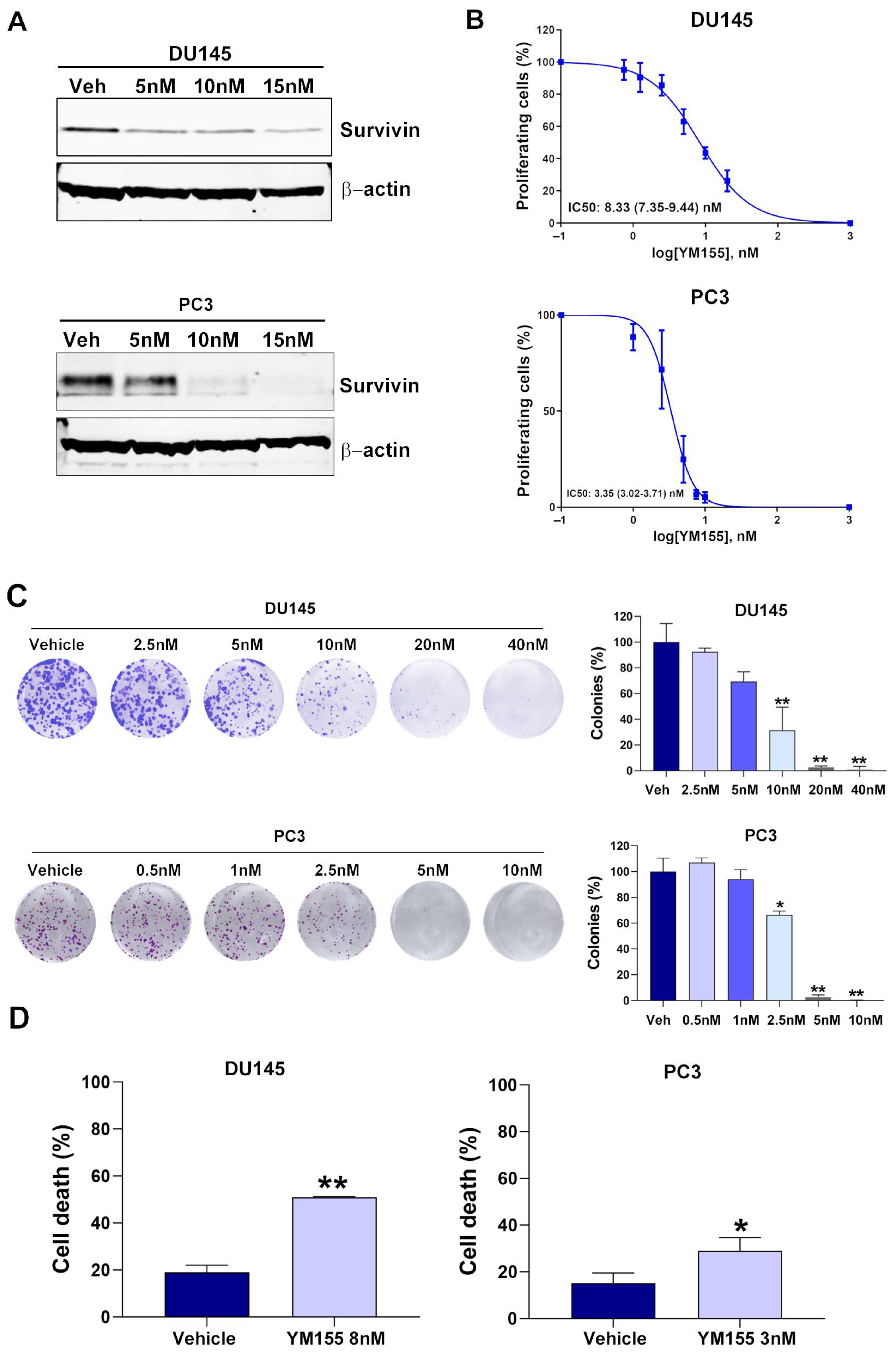
2.3. YM155 Inhibition of Survivin Decreases Cell Proliferation and Induces Cell Death in mCRPC Cell Lines
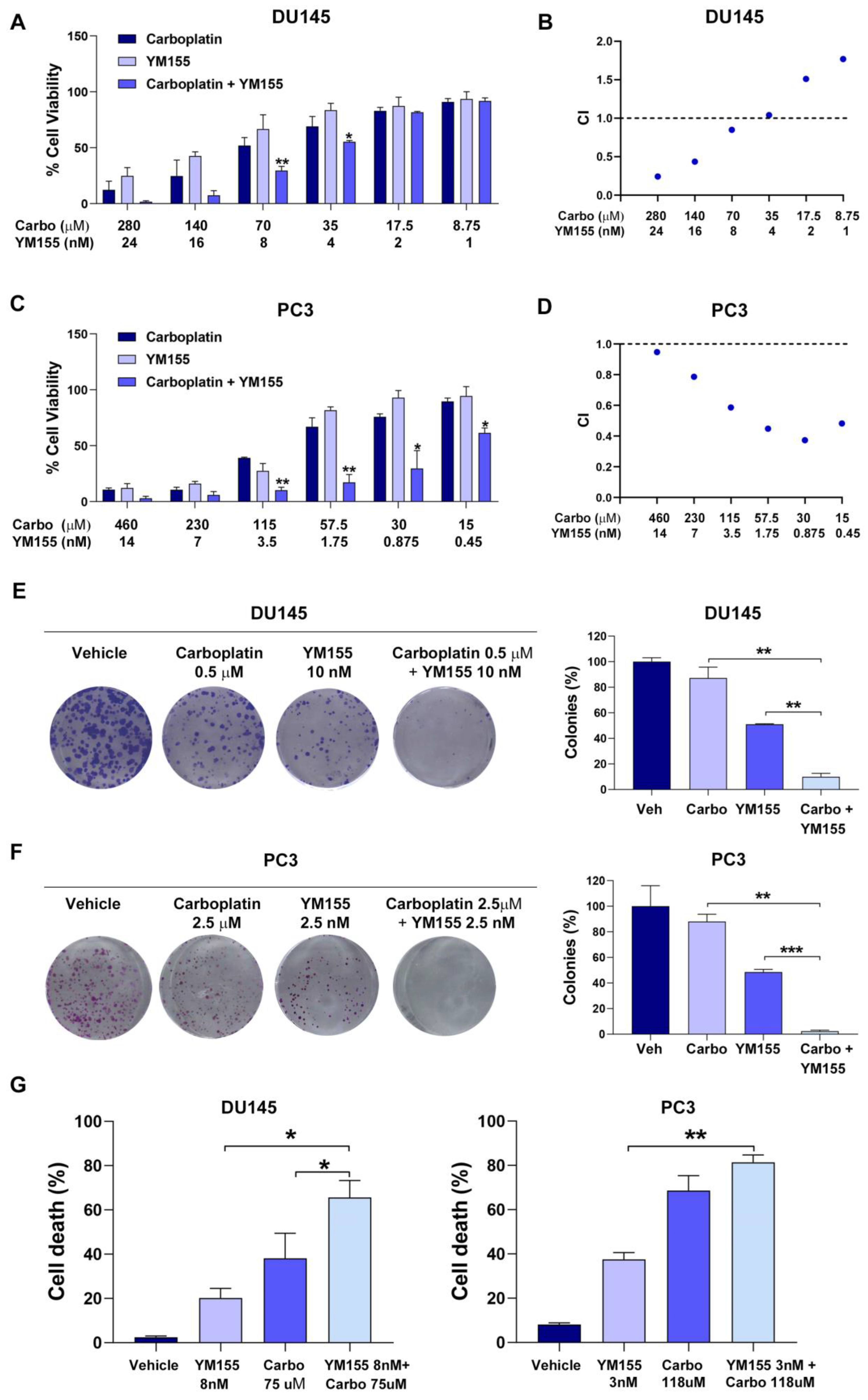
2.4. YM155 Inhibition of Survivin Synergistically Sensitizes mCRPC Cells to Carboplatin Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Computational Analysis of Human PC Data
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Drugs
4.4. MTT Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Cytotoxicity of Drug Combinations
4.6. Colony Formation Assay
4.7. Western Blot Assay
4.8. Cell Death Assay
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| AVPC | aggressive variant PC |
| BIRC5 | Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 5 (gene encoding survivin) |
| CI | Combination index |
| NEPC | Neuroendocrine prostate cancer |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PSA | Prostate-specific antigen |
| mCRPC | Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer |
| rPFS | Radiographic progression-free survival |
References
- Sandhu, S.; Moore, C.M.; Chiong, E.; Beltran, H.; Bristow, R.G.; Williams, S.G. Prostate cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceder, Y.; Bjartell, A.; Culig, Z.; Rubin, M.A.; Tomlins, S.; Visakorpi, T. The Molecular Evolution of Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2016, 2, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posdzich, P.; Darr, C.; Hilser, T.; Wahl, M.; Herrmann, K.; Hadaschik, B.; Grunwald, V. Metastatic Prostate Cancer-A Review of Current Treatment Options and Promising New Approaches. Cancers 2023, 15, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, A.M.; Harzstark, A.L.; Corn, P.G.; Wen, S.; Araujo, J.C.; Tu, S.M.; Pagliaro, L.C.; Kim, J.; Millikan, R.E.; Ryan, C.; et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy for variant castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corn, P.G.; Heath, E.I.; Zurita, A.; Ramesh, N.; Xiao, L.; Sei, E.; Li-Ning-Tapia, E.; Tu, S.M.; Subudhi, S.K.; Wang, J.; et al. Cabazitaxel plus carboplatin for the treatment of men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancers: A randomised, open-label, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Trougakos, I.P.; Erin, N.; Papageorgis, P. Apoptosis Deregulation and the Development of Cancer Multi-Drug Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mita, A.C.; Mita, M.M.; Nawrocki, S.T.; Giles, F.J. Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target for cancer therapeutics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5000–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffaroni, N.; Daidone, M.G. Survivin expression and resistance to anticancer treatments: Perspectives for new therapeutic interventions. Drug Resist. Updates 2002, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, D.C. Survivin and apoptosis control. Adv. Cancer Res. 2003, 88, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, G.; Adida, C.; Altieri, D.C. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, D.C. The molecular basis and potential role of survivin in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennati, M.; Folini, M.; Zaffaroni, N. Targeting survivin in cancer therapy: Fulfilled promises and open questions. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodel, F.; Hoffmann, J.; Distel, L.; Herrmann, M.; Noisternig, T.; Papadopoulos, T.; Sauer, R.; Rodel, C. Survivin as a radioresistance factor, and prognostic and therapeutic target for radiotherapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4881–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adida, C.; Haioun, C.; Gaulard, P.; Lepage, E.; Morel, P.; Briere, J.; Dombret, H.; Reyes, F.; Diebold, J.; Gisselbrecht, C.; et al. Prognostic significance of survivin expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2000, 96, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrandina, G.; Legge, F.; Martinelli, E.; Ranelletti, F.O.; Zannoni, G.F.; Lauriola, L.; Gessi, M.; Gallotta, V.; Scambia, G. Survivin expression in ovarian cancer and its correlation with clinico-pathological, surgical and apoptosis-related parameters. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Lotan, Y.; Saboorian, H.; Khoddami, S.M.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Slawin, K.M.; Ashfaq, R. Survivin expression is associated with features of biologically aggressive prostate carcinoma. Cancer 2004, 100, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, T.; Okamoto, I.; Takezawa, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Nakahara, T.; Kita, A.; Koutoku, H.; Sasamata, M.; Hatashita, E.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Marked anti-tumour activity of the combination of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, and platinum-based drugs. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Niederkorn, J.Y.; Neelam, S.; Alizadeh, H. Downregulation of survivin expression enhances sensitivity of cultured uveal melanoma cells to cisplatin treatment. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Long, Y.; Miao, Y.; Su, M.; Zhang, Q.; Han, H.; Hao, X. Knockdown of survivin expression by siRNAs enhances chemosensitivity of prostate cancer cells and attenuates its tumorigenicity. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2009, 41, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, Z.H. Cisplatin: Mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7265–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeniuk, M.S.; Gupta, R.T.; Healy, P.; McNamara, M.; Ramalingam, S.; Harrison, M.; George, D.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Armstrong, A.J. Platinum sensitivity in metastatic prostate cancer: Does histology matter? Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018, 21, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.; Omlin, A.; Higano, C.; Sweeney, C.; Martinez Chanza, N.; Mehra, N.; Kuppen, M.C.P.; Beltran, H.; Conteduca, V.; Vargas Pivato de Almeida, D.; et al. Activity of Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Patients With Advanced Prostate Cancer With and Without DNA Repair Gene Aberrations. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2021692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.M.; O’Donovan, N.; Duffy, M.J. Survivin: A new target for anti-cancer therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Ling, X.; Haller, A.; Nakahara, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Kita, A.; Koutoku, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Brattain, M.G.; Li, F. Suppression of survivin promoter activity by YM155 involves disruption of Sp1-DNA interaction in the survivin core promoter. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 3, 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, A.; Jia, D.; Bhatt, V.; Akel, M.; Roberge, J.; Guo, J.Y.; Langenfeld, J. Ym155 localizes to the mitochondria leading to mitochondria dysfunction and activation of AMPK that inhibits BMP signaling in lung cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, T.; Kita, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Mori, M.; Amino, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Tominaga, F.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kinoyama, I.; Matsuhisa, A.; et al. YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, induces regression of established human hormone-refractory prostate tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8014–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, A.; Nakahara, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Nakano, K.; Nakata, M.; Mori, M.; Kaneko, N.; Koutoku, H.; Izumisawa, N.; Sasamata, M. Antitumor effects of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, against human aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Nakahara, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kita, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Kiyonaga, F.; Kaneko, N.; Sasamata, M. Antitumor activity of YM155, a selective small-molecule survivin suppressant, alone and in combination with docetaxel in human malignant melanoma models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5423–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kita, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Kinoyama, I.; Matsuhisa, A.; Nakano, K.; Shishido, T.; Koutoku, H.; et al. YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, enhances taxane-induced apoptosis and tumor regression in a human Calu 6 lung cancer xenograft model. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2011, 22, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyao, T.; Koike, H.; Sekine, Y.; Ohtsu, A.; Oka, D.; Suzuki, K. YM155 Reverses Cabazitaxel Resistance in Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer by Reducing Survivin Expression. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 5091–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Thomas, A.; Rajan, A.; Chun, G.; Lopez-Chavez, A.; Szabo, E.; Spencer, S.; Carter, C.A.; Guha, U.; Khozin, S.; et al. A phase I/II study of sepantronium bromide (YM155, survivin suppressor) with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2601–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.X.; Liu, Y.; Mo, Z.M.; Luo, R.J.; Chen, W.K. Exploring BIRC family genes as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in prostate cancer. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H.; Prandi, D.; Mosquera, J.M.; Benelli, M.; Puca, L.; Cyrta, J.; Marotz, C.; Giannopoulou, E.; Chakravarthi, B.V.; Varambally, S.; et al. Divergent clonal evolution of castration-resistant neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H.; Rickman, D.S.; Park, K.; Chae, S.S.; Sboner, A.; MacDonald, T.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sheikh, K.L.; Terry, S.; Tagawa, S.T.; et al. Molecular characterization of neuroendocrine prostate cancer and identification of new drug targets. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Xu, D.; Wang, S.; Wong, C.K.; Martinez-Fundichely, A.; Lee, C.J.; Cohen, S.; Park, J.; Hill, C.E.; Eng, K.; et al. Chromatin profiles classify castration-resistant prostate cancers suggesting therapeutic targets. Science 2022, 376, eabe1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conteduca, V.; Ku, S.Y.; Puca, L.; Slade, M.; Fernandez, L.; Hess, J.; Bareja, R.; Vlachostergios, P.J.; Sigouros, M.; Mosquera, J.M.; et al. SLFN11 Expression in Advanced Prostate Cancer and Response to Platinum-based Chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, R.P.; Weinberger, P.M.; Copland, J.A.; Mahdavian, E.; Xu, Q. YM155 Induces DNA Damage and Cell Death in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells by Inhibiting DNA Topoisomerase IIalpha at the ATP-Binding Site. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, A.; Hennig, D.; Schafer, C.; Wirth, M.; Marx, C.; Heinzel, T.; Schneider, G.; Kramer, O.H. Survivin and YM155: How faithful is the liaison? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Diao, X.; Huang, S. Induction of autophagy-dependent apoptosis by the survivin suppressant YM155 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2011, 302, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielpour, D.; Gao, Z.; Zmina, P.M.; Shankar, E.; Shultes, B.C.; Jobava, R.; Welford, S.M.; Hatzoglou, M. Early Cellular Responses of Prostate Carcinoma Cells to Sepantronium Bromide (YM155) Involve Suppression of mTORC1 by AMPK. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Quinn, D.I.; Ferrari, A.; Ahmann, F.; Giaccone, G.; Drake, T.; Keating, A.; de Bono, J.S. A phase II study of YM155, a novel small-molecule suppressor of survivin, in castration-resistant taxane-pretreated prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, Y.; Kaibara, A.; Takada, A.; Nishimura, T.; Katashima, M.; Sawamoto, T. Population pharmacokinetic modeling of sepantronium bromide (YM155), a small molecule survivin suppressant, in patients with non-small cell lung cancer, hormone refractory prostate cancer, or unresectable stage III or IV melanoma. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abida, W.; Cyrta, J.; Heller, G.; Prandi, D.; Armenia, J.; Coleman, I.; Cieslik, M.; Benelli, M.; Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; et al. Genomic correlates of clinical outcome in advanced prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11428–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranyutanon, S.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Dasgupta, S.; Pai, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P. Cellular and Molecular Progression of Prostate Cancer: Models for Basic and Preclinical Research. Cancers 2020, 12, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz de Porras, V.; Wang, X.C.; Palomero, L.; Marin-Aguilera, M.; Sole-Blanch, C.; Indacochea, A.; Jimenez, N.; Bystrup, S.; Bakht, M.; Conteduca, V.; et al. Taxane-induced Attenuation of the CXCR2/BCL-2 Axis Sensitizes Prostate Cancer to Platinum-based Treatment. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcon, C.; Martin, F.; Prada, E.; Mora, J.; Soriano, A.; Guillen, G.; Gallego, S.; Roma, J.; Samitier, J.; Villanueva, A.; et al. MEK and MCL-1 sequential inhibition synergize to enhance rhabdomyosarcoma treatment. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz de Porras, V.; Bakht, M.K.; Fernandez-Saorín, M.; Alcon, C.; Palomero, L.; Francisco-Rodon, J.; Figols, M.; Montero, J.; Conteduca, V.; Beltran, H.; et al. YM155 Inhibition of Survivin Enhances Carboplatin Efficacy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111752
Ruiz de Porras V, Bakht MK, Fernandez-Saorín M, Alcon C, Palomero L, Francisco-Rodon J, Figols M, Montero J, Conteduca V, Beltran H, et al. YM155 Inhibition of Survivin Enhances Carboplatin Efficacy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111752
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz de Porras, Vicenç, Martin K. Bakht, Maria Fernandez-Saorín, Clara Alcon, Luis Palomero, Júlia Francisco-Rodon, Mariona Figols, Joan Montero, Vincenza Conteduca, Himisha Beltran, and et al. 2025. "YM155 Inhibition of Survivin Enhances Carboplatin Efficacy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111752
APA StyleRuiz de Porras, V., Bakht, M. K., Fernandez-Saorín, M., Alcon, C., Palomero, L., Francisco-Rodon, J., Figols, M., Montero, J., Conteduca, V., Beltran, H., & Font, A. (2025). YM155 Inhibition of Survivin Enhances Carboplatin Efficacy in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111752










