Dual-Algorithm Integration Framework Reveals Qing-Wei-Zhi-Tong’s Dual Mechanisms in Chronic Gastritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Active Compounds in QWZT
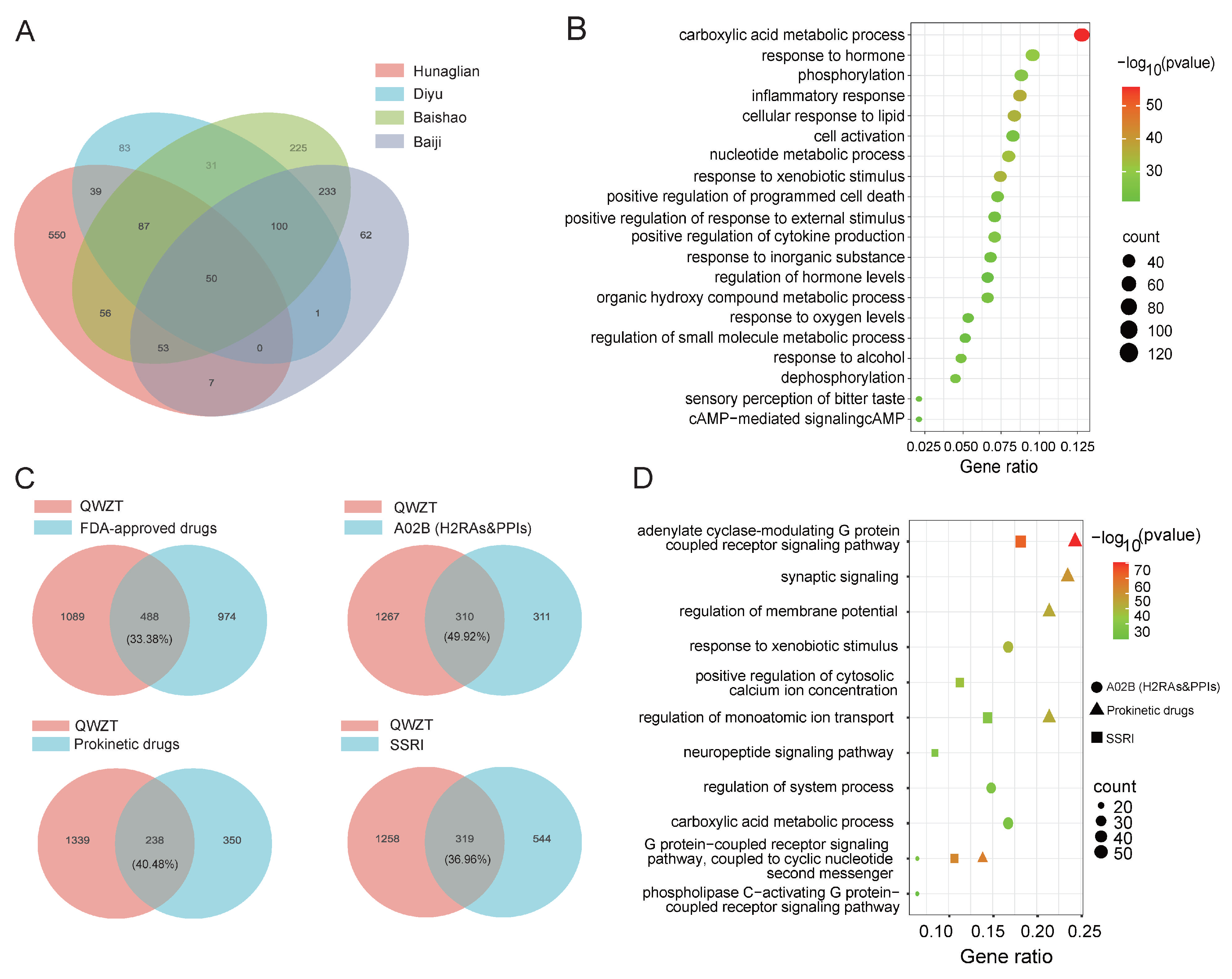
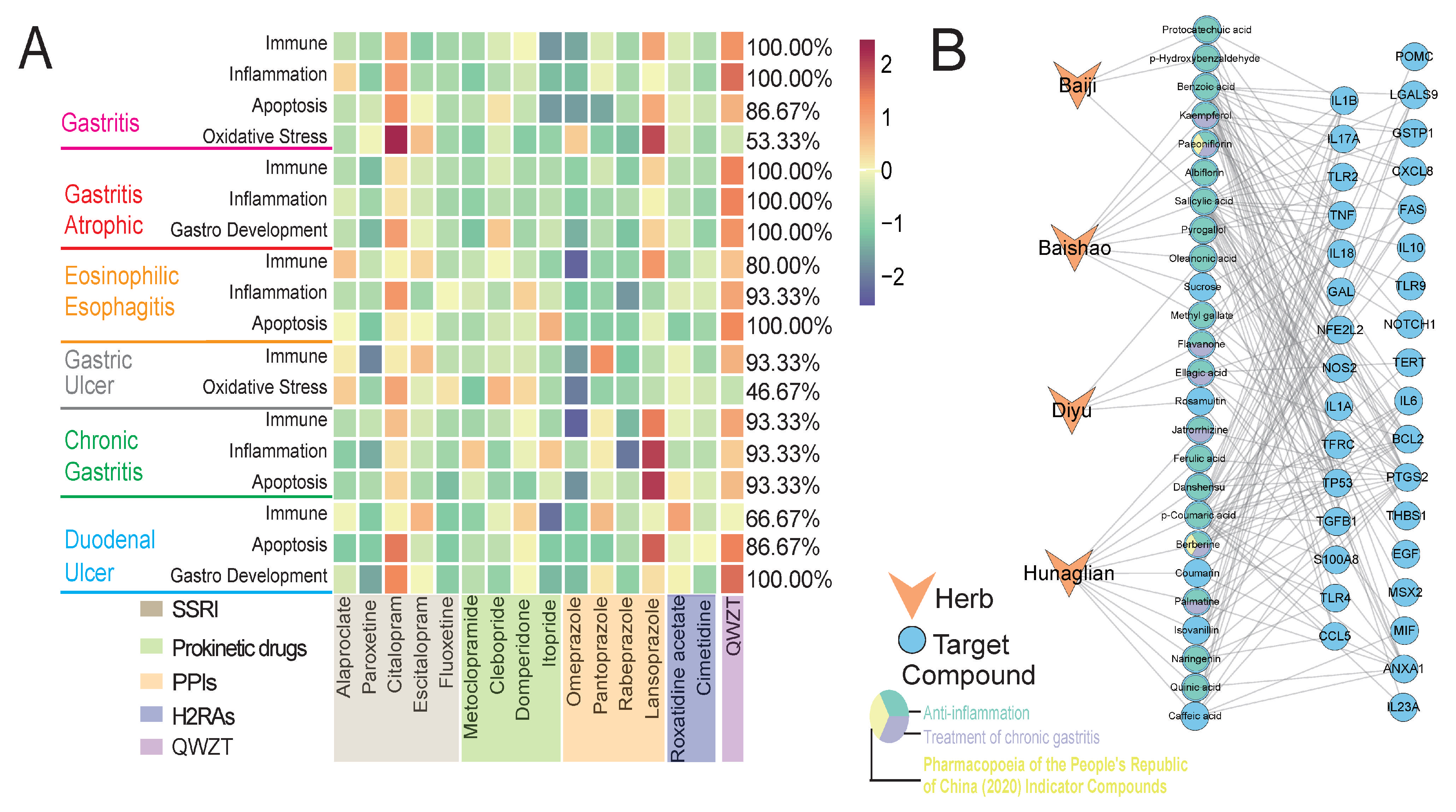
2.2. Comparison of Potential Targets and Associated Biological Processes for QWZT Compounds and FDA-Approved Drugs
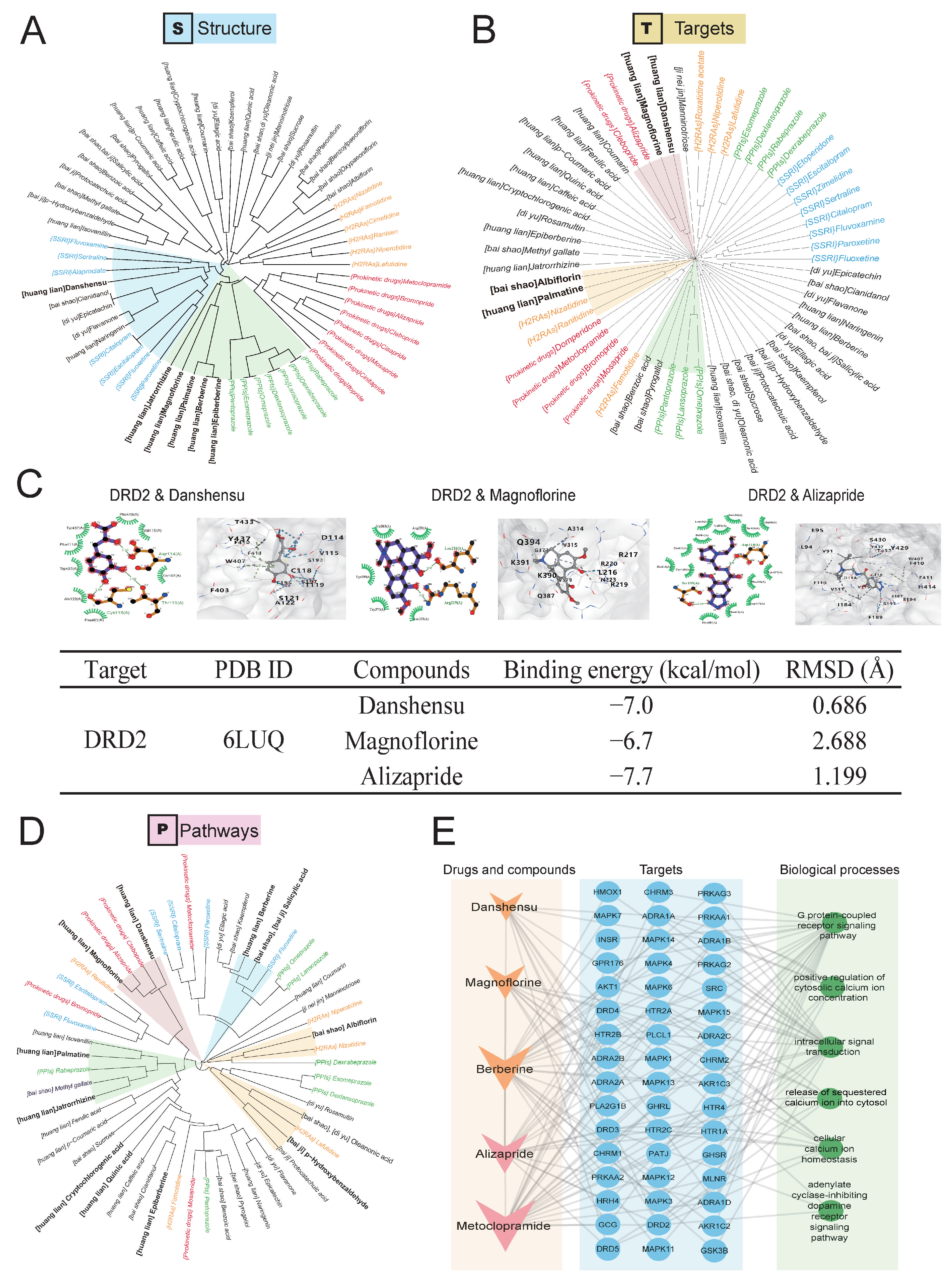
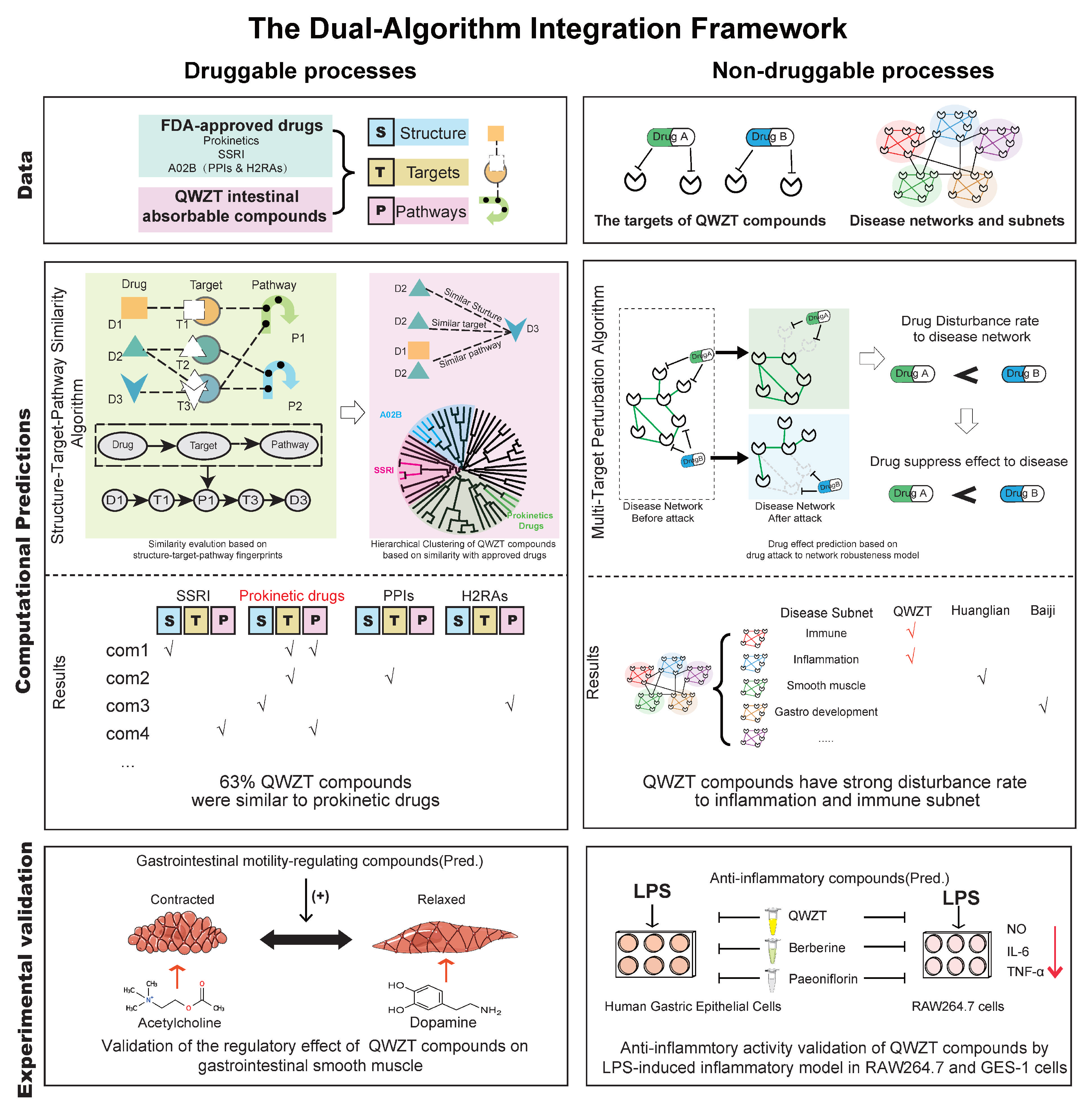
2.3. Predicting Activity of QWZT Compounds Based on Structure, Target, and Pathway Similarity to FDA-Approved Drugs
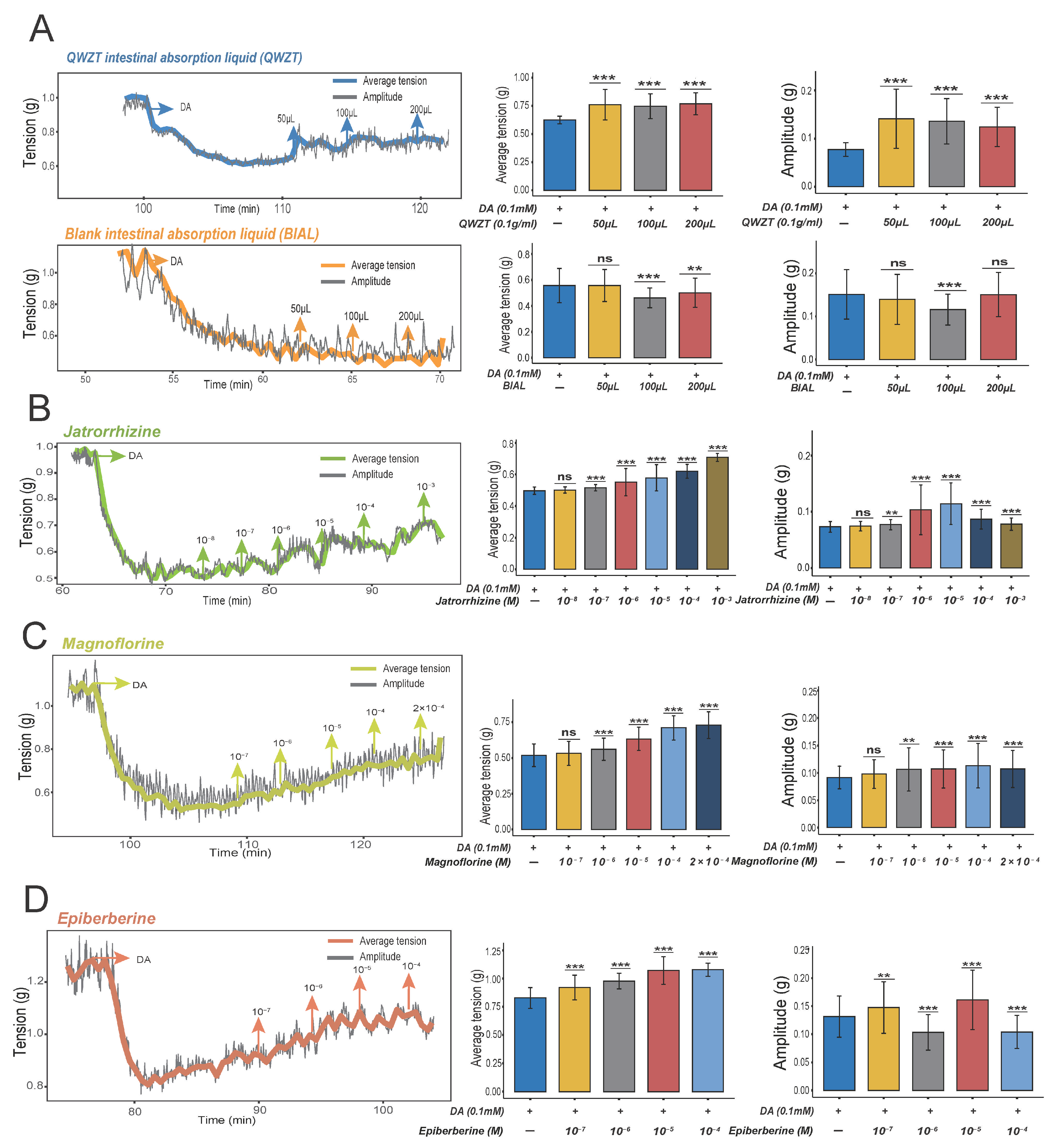
2.4. Prediction and Validation of the Potential Regulatory Effects of QWZT Compounds with Similarities to FDA-Approved Drugs on Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle
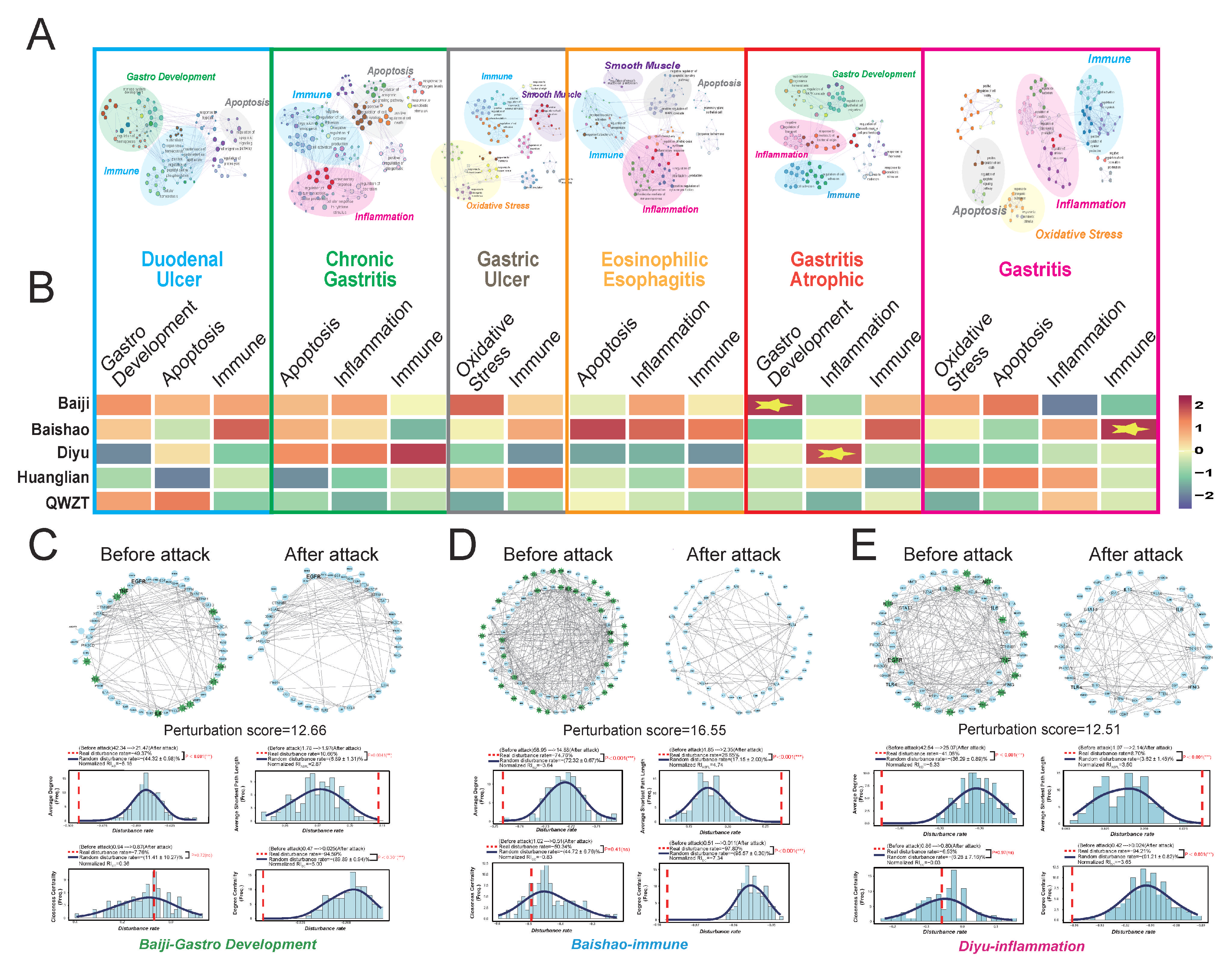
2.5. QWZT-Driven Multi-Target Network Perturbation of Undruggable Pathology in Gastritis-Related Diseases
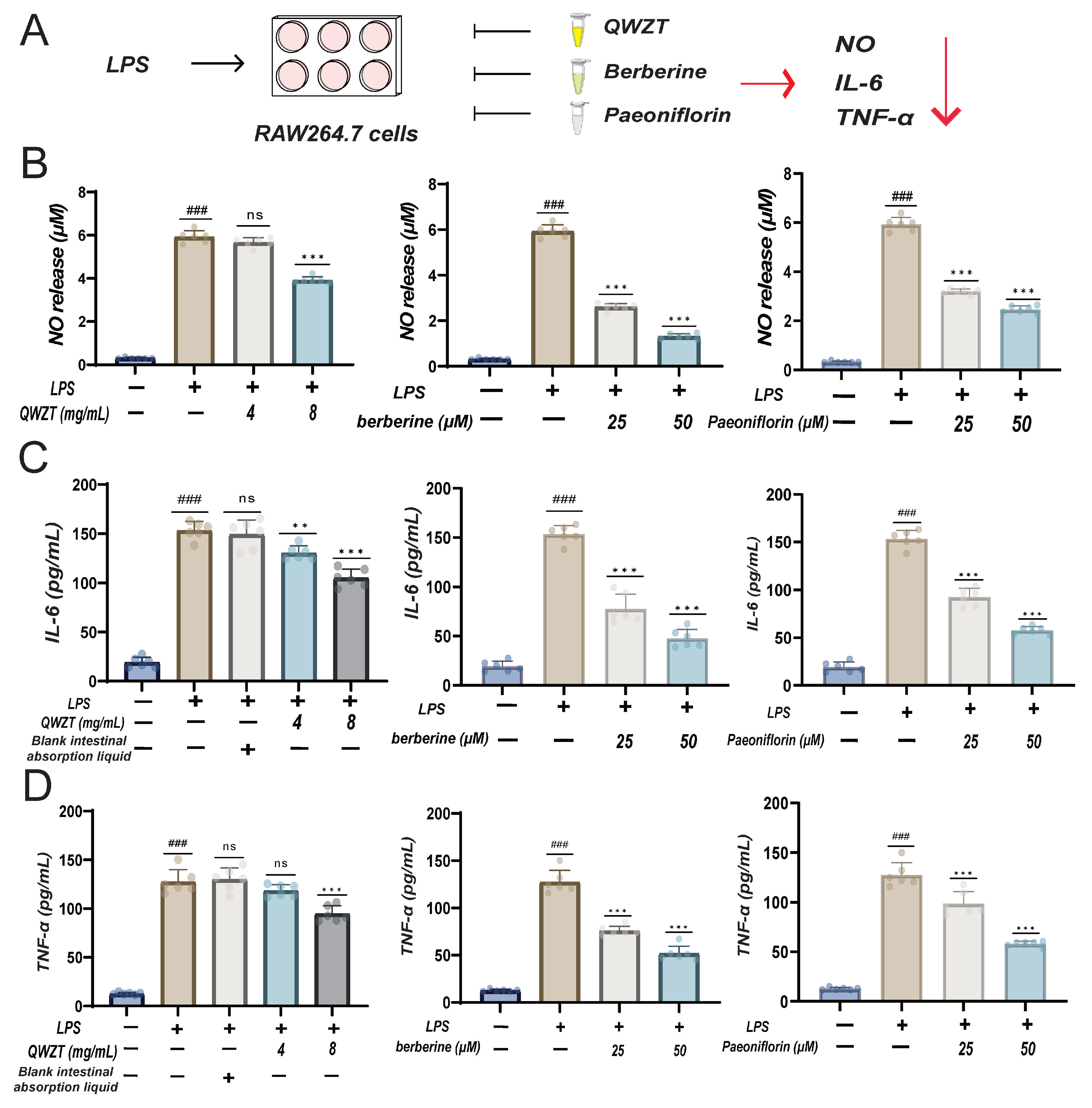
2.6. Discovery and Validation of QWZT and Its Specific Compounds Activities on Undruggable Process
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation and Identification of Intestinal Absorption Fluid of QWZT
4.1.1. Preparation of the QWZT Everted Gut Sac Liquid
4.1.2. Identification of Intestinal Absorbable Compounds of QWZT by UPLC-MS
4.2. Prediction and Functional Enrichments of Targets in Intestinal Absorbable Compounds and FDA-Approved Drugs
4.2.1. Targets Prediction of Intestinal Absorbable Compounds
4.2.2. Targets Prediction of FDA-Approved Drugs
4.2.3. GO Biological Process Enrichment Analysis of Drug Targets
4.3. Structure–Target–Pathway Similarity Algorithm
4.3.1. Drug Similarity Evaluation Based on Meta Path Searching in “Compound-Target-Pathway” Heterogeneous Network
4.3.2. Molecular Docking
4.3.3. Construction of Drug–Compound–Target–Biological Process and Similar Compound–Drug Network
4.4. Experiments on the Regulatory Effects of Drugs on Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle
4.4.1. Animals
4.4.2. Instruments and Reagents
4.4.3. Description of the Isolated Intestinal Diastolic Assay
4.5. Drug Disturbance on the Robustness of the Disease Network
4.5.1. Construction of the PPI Network and Functional Subnetworks of Six Gastritis-Related Diseases
4.5.2. Multi-Target Perturbation Algorithm
4.6. Analysis of the Impact of QWZT and Its Herbs on Undruggable Pathology in Gastritis-Related Diseases
4.6.1. Construction of the Network Before and After Drug Perturbation
4.6.2. Permutation Test of Real and Random Networks
4.7. Discovery Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity of QWZT Compounds
4.8. LPS-Induced Inflammatory Model in RAW264.7 Cells
4.8.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.8.2. Solution Preparation
4.8.3. Nitric Oxide (NO) Measurement
4.8.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.9. LPS-Induced Inflammatory Model in GES-1 Cells
4.9.1. GES-1 Cell Culture and Treatment
4.9.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.9.3. Evaluation of Toxicity of Drugs in GES-1 Cells
4.9.4. Evaluation of Drug Effects
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | average degree |
| ASPL | average shortest path length |
| BP | biological process |
| CG | chronic gastritis |
| CC | closeness centrality |
| DC | degree centrality |
| DRD2 | dopamine receptor D2 |
| GES-1 | Human Gastric Epithelial Cells |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| H2RAs | H2 receptor antagonists |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MOA | mechanisms of action |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| PPIs | proton pump inhibitors |
| QWZT | Qing-Wei-Zhi-Tong micro-pills |
| SSRIs | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| TCM-NP | traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| UPLC-MS | Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
References
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, N.; Lv, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y. Protective Effect of Ultraviolet C Irradiation on the Gastric Mucosa of Rats with Chronic Gastritis Induced by Physicochemical Stimulations. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5189797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Du, Y.Q.; Liu, W.Z.; Ren, J.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Lv, N.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Lv, B.; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Consensus on Chronic Gastritis (2017, Shanghai). J. Dig. Dis. 2018, 19, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Z.S.; Zou, D.W.; Wu, R.P.; Yao, Y.Z.; Jin, Z.D.; Ye, P.; Li, S.D.; Zhang, W.J.; Du, Y.Q.; et al. Alarm Features and Age for Predicting Upper Gastrointestinal Malignancy in Chinese Patients with Dyspepsia with High Background Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Upper Gastrointestinal Malignancy: An Endoscopic Database Review of 102 665 Patients from 1996 to 2006. Gut 2010, 59, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P. Kyoto Global Consensus Report on Helicobacter pylori Gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, J.; Talley, N.J.; Camilleri, M.; Holtmann, G.; Hu, P.; Malagelada, J.-R.; Stanghellini, V. Functional Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1466–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.-M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori Infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Howden, C.W.; Moss, S.F. ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 212–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallone, C.A.; Chiba, N.; Van Zanten, S.V.; Fischbach, L.; Gisbert, J.P.; Hunt, R.H.; Jones, N.L.; Render, C.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Moayyedi, P.; et al. The Toronto Consensus for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Adults. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 51–69.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.-M.; Jiang, X.-T.; Chen, C.-C.; Luo, J.-C.; Bair, M.-J.; Chen, P.-Y.; Chou, C.-K.; Fang, Y.-J.; Chen, M.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; et al. Second-Line Levofloxacin-Based Quadruple Therapy versus Bismuth-Based Quadruple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication and Long-Term Changes to the Gut Microbiota and Antibiotic Resistome: A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y. Clinical observation on the efficacy of Qingwei Zhitong micro-pills combined with other medications in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori. Chin. J. Basic Med. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 24, 1435–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, H.; An, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, F. Integration of Gut Microbiome and Serum Metabolome Revealed the Effect of Qing-Wei-Zhi-Tong Micro-Pills on Gastric Ulcer in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Traditional Chinese medicine combined with standard triple therapy for chronic non-atrophic gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori and its mechanism of action. J. Jilin Univ. 2016, 42, 789–792. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhou, J.; Hu, Z.; Ji, G.; Xie, J.; Wu, D. The Effects of Jatrorrhizine on Contractile Responses of Rat Ileum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 663, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Yao, S. Jatrorrhizine Attenuates Inflammatory Response in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastritis by Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Arch. Microbiol. 2025, 207, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Dou, D.; Tao, X.; Kang, T. Berberine Depresses Contraction of Smooth Muscle via Inhibiting Myosin Light-Chain Kinase. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Wei, S.; Zou, W.; Zhao, Y. Elucidation of the Mechanism of Berberine against Gastric Mucosa Injury in a Rat Model with Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Based on a Combined Strategy of Multi-Omics and Molecular Biology. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 15, 1499753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xie, X.; Tang, Q.; Huang, T.; Tang, X.; Jiao, B.; Wang, R.; Zhu, X.; Ye, X.; Ma, H.; et al. Epiberberine Inhibits Helicobacter pylori and Reduces Host Apoptosis and Inflammatory Damage by Down-Regulating Urease Expression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 117046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Bao, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Wu, S.; Wen, J.; Yang, T.; Wei, S.; et al. Palmatine Ameliorates Helicobacter pylori-Induced Chronic Atrophic Gastritis by Inhibiting MMP-10 through ADAM17/EGFR. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 882, 173267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenberg, A.; Lash, R.H.; Genta, R.M. A National Study of Helicobactor Pylori Infection in Gastric Biopsy Specimens. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1894–1901.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, W.L.; Coss, E.; Rugge, M.; Genta, R.M. Autoimmune Atrophic Gastritis—Pathogenesis, Pathology and Management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.-H.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.-L.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Q.-Q.; Wang, X.-J. Chinmedomics: A Powerful Approach Integrating Metabolomics with Serum Pharmacochemistry to Evaluate the Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Engineering 2019, 5, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B. Traditional Chinese Medicine Network Pharmacology: Theory, Methodology and Application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, S. Network Pharmacology: Towards the Artificial Intelligence-Based Precision Traditional Chinese Medicine. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 25, bbad518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network Pharmacology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Kang, J.; Guo, W.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Du, X.; et al. Network Pharmacology to Unveil the Mechanism of Moluodan in the Treatment of Chronic Atrophic Gastritis. Phytomedicine 2022, 95, 153837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, W.; Su, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, H. Prediction of Drug Positioning for Quan-Du-Zhong Capsules Against Hypertensive Nephropathy Based on the Robustness of Disease Network. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Li, D.; Yang, H. Construction of a prediction analysis platform for the anti-COVID-19 effect of traditional Chinese medicine and analysis of potential effects of commonly used herbal medicines. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 45, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Tang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wei, J.; Tang, S.; Wu, H.; Yang, H. Exploration of the Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine by AI Approach Using Unsupervised Machine Learning for Cellular Functional Similarity of Compounds in Heterogeneous Networks, XiaoErFuPi Granules as an Example. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, R.; Ng, K. Effects of Differently Processed Tea on the Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2024, 29, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.S.; Bhuju, R.; Martinez, E.; Basta, M.; Deyab, A.; Mansour, C.; Tejada, D.; Deshpande, V.; Elias, S.; Nagesh, V.K. The Gut Microbiome’s Impact on the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Gastric Cancer—An Updated Literature Review. Cancers 2025, 17, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, R.; Gou, H.; Lau, H.C.H.; Yu, J. Stomach Microbiota in Gastric Cancer Development and Clinical Implications. Gut 2024, 73, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-L.; Lu, C.-C.; Lai, W.-F.; Wu, T.-S.; Lu, J.-J.; Chen, Y.-M.; Tzeng, C.-M.; Liu, H.-T.; Wei, H.; Lai, H.-C. Role of Gut Microbiota in Identification of Novel TCM-Derived Active Metabolites. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z. Chronic Gastritis Rat Model and Role of Inducing Factors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek, B.E.; Yuksel, M.; Cumbul, A.; Ercan, F.; Cabadak, H.; Aydin, B.; Alican, I. The Effect of Metformin on Ethanol- and IndomethacinInduced Gastric Ulcers in Rats. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 33, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Liang, R.; Yang, H. BNC Protects H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts from H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injury through ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Al-Jenoobi, F.I.; Al-mohizea, A.M. Everted Gut Sac Model as a Tool in Pharmaceutical Research: Limitations and Applications. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Diao, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; et al. BATMAN-TCM: A Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular mechANism of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burclaff, J.; Willet, S.G.; Sáenz, J.B.; Mills, J.C. Proliferation and Differentiation of Gastric Mucous Neck and Chief Cells During Homeostasis and Injury-Induced Metaplasia. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 598–609.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Narayan, R.; Corsello, S.M.; Peck, D.D.; Natoli, T.E.; Lu, X.; Gould, J.; Davis, J.F.; Tubelli, A.A.; Asiedu, J.K.; et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles. Cell 2017, 171, 1437–1452.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.; Ozkirimli, E.; Özgür, A. A Comparative Study of SMILES-Based Compound Similarity Functions for Drug-Target Interaction Prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, N. Functionality Pattern Matching as an Efficient Complementary Structure/Reaction Search Tool: An Open-Source Approach. Molecules 2010, 15, 5079–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape Provides a Biologist-Oriented Resource for the Analysis of Systems-Level Datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; Viteri, G.; Gong, C.; Lorente, P.; Fabregat, A.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Cook, J.; Gillespie, M.; Haw, R.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D498–D503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open Chemical Toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Han, J.; Yan, X.; Yu, P.S.; Wu, T. PathSim: Meta Path-Based Top-K Similarity Search in Heterogeneous Information Networks. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2011, 4, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jiang, C.; Xi, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, N.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, H. Investigation of Pharmacological Mechanism of Natural Product Using Pathway Fingerprints Similarity Based on “Drug-Target-Pathway” Heterogenous Network. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.-X.; Cao, Y. CB-Dock2: Improved Protein–Ligand Blind Docking by Integrating Cavity Detection, Docking and Homologous Template Fitting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W159–W164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Bravo, À.; Queralt-Rosinach, N.; Gutiérrez-Sacristán, A.; Deu-Pons, J.; Centeno, E.; García-García, J.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. DisGeNET: A Comprehensive Platform Integrating Information on Human Disease-Associated Genes and Variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D833–D839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Morris, J.H.; Cook, H.; Kuhn, M.; Wyder, S.; Simonovic, M.; Santos, A.; Doncheva, N.T.; Roth, A.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING Database in 2017: Quality-Controlled Protein–Protein Association Networks, Made Broadly Accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D362–D368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Guo, F. Exploration of the Specific Pathology of HXMM Tablet Against Retinal Injury Based on Drug Attack Model to Network Robustness. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 826535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassano, S.N.; Bassett, D.S. Topological Distortion and Reorganized Modular Structure of Gut Microbial Co-Occurrence Networks in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Z.; Lin, S.; Fan, Z.; Yang, Z.-C.; Gong, Y.; Qin, T.; Yu, R.; He, Y. Efficacy and Potential Mechanisms of Jatrorrhizine on MNNG-Induced Chronic Atrophic Gastritis in Rats Based on Serological Metabolomics and Molecular Docking. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, L.; Washington, M.K.; Chaturvedi, R.; Israel, D.A.; Cao, H.; Wang, B.; et al. Berberine Promotes Recovery of Colitis and Inhibits Inflammatory Responses in Colonic Macrophages and Epithelial Cells in DSS-Treated Mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G504–G514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cai, Y.; Guan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, W.; Guan, X. Quinic Acid Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Neuroinflammation by Inhibiting DR3/IKK/NF-κB Signaling via Gut Microbial Tryptophan Metabolites. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2374608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.; Hu, C.; Huo, Y. Palmatine Alleviates Inflammation and Modulates Ferroptosis against Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Chen, L.; Fu, K.; Shi, D.; Ma, X.; Yang, N.; Chen, X.; Cheng, S.; Lu, J.; et al. Danshensu Enhances Autophagy and Reduces Inflammation by Downregulating TNF-α to Inhibit the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Ischemic Flaps. Phytomedicine 2025, 137, 156378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermis, A.; Aritici Colak, G.; Acikel-Elmas, M.; Arbak, S.; Kolgazi, M. Ferulic Acid Treats Gastric Ulcer via Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Life 2023, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Rho, H.S.; Choi, K. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a P-Coumaric Acid and Kojic Acid Derivative in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophage Cells. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2019, 24, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, K.; Zheng, J. Naringenin Attenuates Inflammation and Apoptosis of Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB Pathway. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinniah, A.; Yazid, S.; Flower, R.J. From NSAIDs to Glucocorticoids and Beyond. Cells 2021, 10, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giner-Larza, E.M.; Máñez, S.; Recio, M.C.; Giner, R.M.; Prieto, J.M.; Cerdá-Nicolás, M.; Ríos, J.L. Oleanonic Acid, a 3-Oxotriterpene from Pistacia, Inhibits Leukotriene Synthesis and Has Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 428, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, L.; Huang, L.; Liang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Zhou, B. Pyrogallol Enhances Therapeutic Effect of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells against LPS-Mediated Inflammation and Lung Injury via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 191, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, L.B.; Seito, L.N.; Manchope, M.F.; Verri, W.A.; Cunha, T.M.; Henriques, M.G.; Rosas, E.C. Methyl Gallate Attenuates Inflammation Induced by Toll-like Receptor Ligands by Inhibiting MAPK and NF-κb Signaling Pathways. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Ren, C.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Yao, R.; Yu, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Leng, Y.; et al. Pharmacologically Significant Constituents Collectively Responsible for Anti-Sepsis Action of XueBiJing, a Chinese Herb-Based Intravenous Formulation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jia, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhong, S.; You, J.; Zou, T. Benzoic Acid as a Dietary Supplement Mitigates Inflammation and Intestinal Injury in Acute Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli -Infected Mice without Adverse Effects in Healthy Mice. Food Funct. 2025, 16, 3195–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.P.; Malar, D.S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Sureda, A.; Xiao, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Daglia, M. Kaempferol and Inflammation: From Chemistry to Medicine. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guan, G.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Duan, X.; Xu, X. P-Hydroxy Benzaldehyde, a Phenolic Compound from Nostoc Commune, Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis against Oxidative Stress via the Nrf2/HO-1/NQO-1/NF-κB/AP-1 Pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Du, Y.; Chen, G.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kang, M.; Zhu, S.; Wang, D. Protocatechuic Acid Attenuates Inflammation in Macrophage-like Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in ApoE−/− Mice. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.Y.; Fatemi, I.; Kalantari, H.; Mombeini, M.A.; Mehrzadi, S.; Goudarzi, M. Ellagic Acid Prevents Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Histopathological Alterations in Acrylamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Wistar Rats. J. Diet. Suppl. 2020, 17, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustos-Salgado, P.; Andrade-Carrera, B.; Domínguez-Villegas, V.; Díaz-Garrido, N.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Badía, J.; Baldomà, L.; Mallandrich, M.; Calpena-Campmany, A.; Garduño-Ramírez, M.L. Screening Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavanones Solutions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Yang, T.; Wen, J.; Wei, S.; Jing, M.; Zou, W.; Zhao, Y. Berberine Attenuates Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Induced by MNNG and Its Potential Mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 644638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Liang, N.; Li, J.; Ding, W.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z. Plant-Derived Extracts or Compounds for Helicobacter-Associated Gastritis: A Systematic Review of Their Anti-Helicobacter Activity and Anti-Inflammatory Effect in Animal Experiments. Chin. Med. 2025, 20, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xu, J.-G.; He, X.-Y.; Lin, X.-H. Paeoniflorin Exhibits Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity by Regulating Macrophage Activity. World Chin. J. Dig. 2023, 31, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.G.; Sung, G.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.H.; Ha, V.T.; Kim, H.G.; Yi, Y.; et al. Kaempferol, a Dietary Flavonoid, Ameliorates Acute Inflammatory and Nociceptive Symptoms in Gastritis, Pancreatitis, and Abdominal Pain. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, T.; Tashima, K.; Umeda, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Takeeda, M.; Takata, K.; Takeuchi, K. Effect of Ellagic Acid on Gastric Damage Induced in Ischemic Rat Stomachs Following Ammonia or Reperfusion. Life Sci. 2002, 70, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Woo, H.J.; Yang, J.Y.; Kim, J.-B.; Kim, S.-H. Hesperetin Inhibits Expression of Virulence Factors and Growth of Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
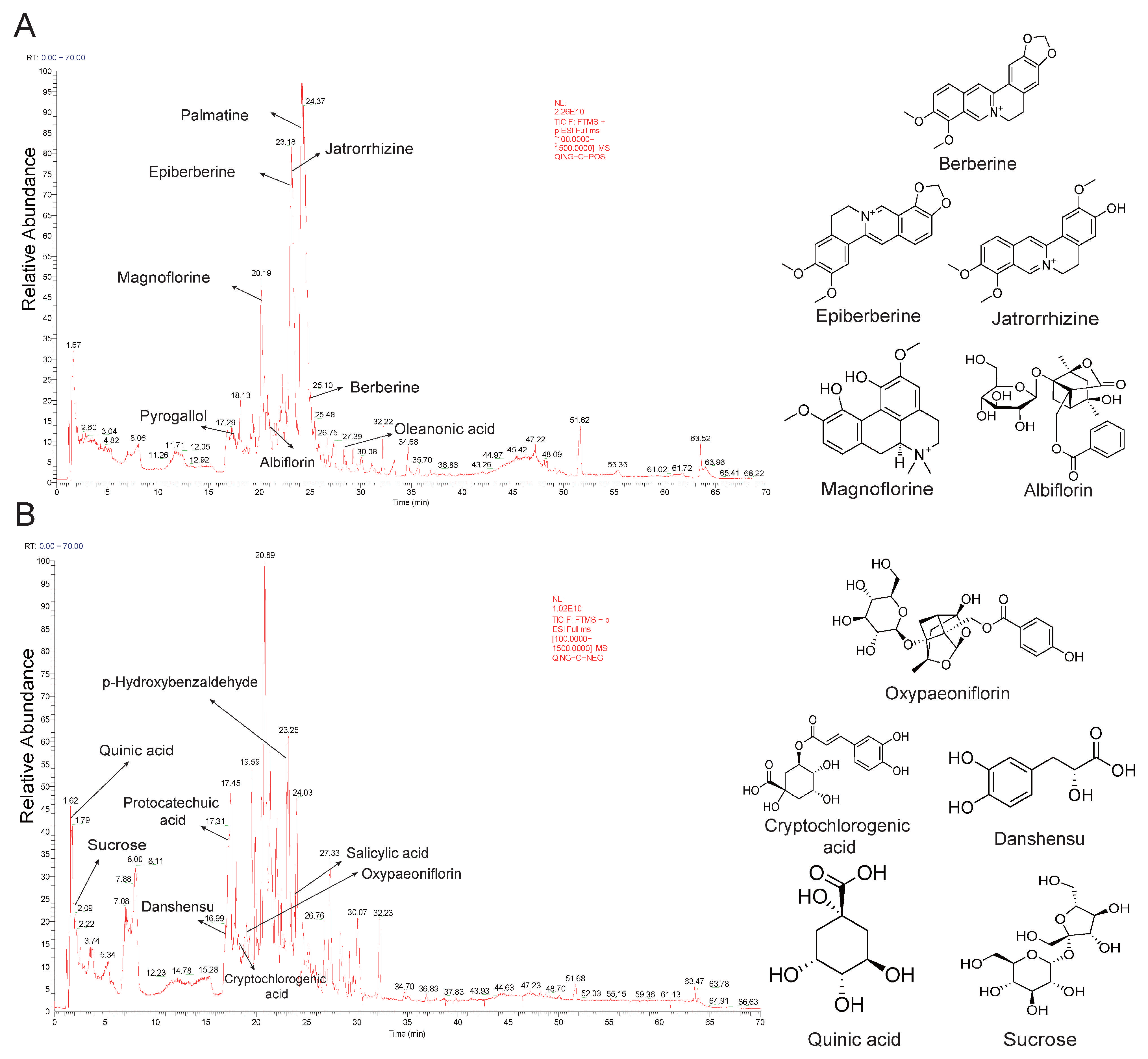


| Compound | Source | Formula | RT (min) | Precursor Ion | Peak Area | Maximum Peak Area Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Detected m/z | Expected m/z | Error (ppm) | ||||||
| Magnoflorine | HL | C20H23NO4 | 20.20 | [M + H]+ | 342.1696 | 342.1701 | −1.4 | 1.67 × 1011 | 23.06% |
| Jatrorrhizine | HL | C20H19NO4 | 23.38 | [M + H]+ | 338.1382 | 338.1386 | −1.2 | 1.23 × 1011 | 16.93% |
| Berberine | HL | C20H17NO4 | 25.04 | [M + H]+ | 336.1229 | 336.1232 | −1.1 | 8.19 × 1010 | 11.29% |
| Epiberberine | HL | C20H17NO4 | 23.13 | [M + H]+ | 336.1226 | 336.1232 | −1.9 | 6.82 × 1010 | 9.40% |
| Sucrose | BS | C12H22O11 | 2.08 | [M+Cl]− | 377.0852 | 377.0846 | 1.5 | 4.51 × 109 | 2.72% |
| Quinic acid | HL | C7H12O6 | 1.62 | [M − H]− | 191.0559 | 191.0553 | 2.8 | 4.42 × 109 | 2.66% |
| Albiflorin | BS | C23H28O11 | 20.51 | [M + H]+ | 481.1701 | 481.1706 | −1.0 | 1.92 × 1010 | 2.64% |
| Palmatine | HL | C21H21NO4 | 24.08 | [M + H]+ | 352.1539 | 352.1546 | −2.0 | 1.75 × 1010 | 2.42% |
| Danshensu | HL | C9H10O5 | 16.93 | [M − H − H2O]− | 179.0348 | 179.0342 | 3.4 | 3.77 × 109 | 2.27% |
| Cryptochlorogenic acid | HL | C16H18O9 | 18.22 | [M − H]− | 353.0873 | 353.0869 | 1.3 | 2.87 × 109 | 1.73% |
| Oxypaeoniflorin | BS | C23H28O12 | 19.16 | [M − H]− | 495.1503 | 495.1498 | 1.1 | 2.34 × 109 | 1.41% |
| p-Hydroxybenzaldehyde | BJ | C7H6O2 | 23.21 | [M − H]− | 121.0291 | 121.0285 | 4.3 | 1.96 × 109 | 1.18% |
| Salicylic acid | BS, BJ | C7H6O3 | 23.80 | [M − H]− | 137.0241 | 137.0236 | 3.2 | 1.70 × 109 | 1.03% |
| Oleanonic acid | BS, DY | C30H46O3 | 28.36 | [M + H]+ | 455.3518 | 455.3523 | −1.2 | 6.07 × 109 | 0.84% |
| Pyrogallol | BS | C6H6O3 | 17.43 | [M + H]+ | 127.0390 | 127.0394 | −3.7 | 3.37 × 109 | 0.46% |
| Protocatechuic acid | BJ | C7H6O4 | 17.02 | [M − H]− | 153.0191 | 153.0185 | 3.5 | 7.51 × 108 | 0.45% |
| Methyl gallate | BS | C8H8O5 | 19.28 | [M − H]− | 183.0296 | 183.0291 | 2.8 | 7.36 × 108 | 0.44% |
| Paeoniflorin | BS | C23H28O11 | 20.92 | [M + H]+ | 498.1969 | 498.1973 | −0.8 | 3.04 × 109 | 0.42% |
| Benzoylpaeoniflorin | BS | C30H32O12 | 26.75 | [M + H]+ | 602.2231 | 602.2232 | −0.3 | 2.81 × 109 | 0.39% |
| Epicatechin | DY | C15H14O6 | 19.36 | [M − H]− | 289.0714 | 289.0709 | 1.8 | 5.46 × 108 | 0.33% |
| Ellagic acid | DY | C14H6O8 | 21.94 | [M − H]− | 300.9985 | 300.9980 | 1.7 | 4.15 × 108 | 0.25% |
| Caffeic acid | HL | C9H8O4 | 17.16 | [M − H]− | 179.0347 | 179.0342 | 2.5 | 4.04 × 108 | 0.24% |
| Manninotriose | JNJ | C18H32O16 | 2.58 | [M − H]− | 503.1612 | 503.1608 | 0.8 | 2.85 × 108 | 0.17% |
| Ferulic acid | HL | C10H10O4 | 20.74 | [M + H]+ | 195.0651 | 195.0657 | −2.7 | 8.62 × 108 | 0.12% |
| p-Coumaric acid | HL | C9H8O3 | 18.47 | [M − H]− | 163.0399 | 163.0394 | 3.3 | 1.49 × 108 | 0.09% |
| Benzoic acid | BS | C7H6O2 | 20.34 | [M + H]+ | 123.0438 | 123.0444 | −4.2 | 3.81 × 108 | 0.05% |
| Isovanillin | HL | C8H8O3 | 21.47 | [M + H]+ | 153.0546 | 153.0551 | −3.1 | 3.78 × 108 | 0.05% |
| Cianidanol | BS | C15H14O6 | 20.25 | [M − H]− | 289.0714 | 289.0709 | 1.7 | 4.2 × 107 | 0.03% |
| Kaempferol | BS | C15H10O6 | 28.04 | [M − H]− | 285.0402 | 285.0396 | 1.9 | 2.60 × 107 | 0.02% |
| Rosamultin | DY | C36H58O10 | 27.65 | [M − H]− | 685.3722 | 685.3717 | 0.8 | 2.43 × 107 | 0.01% |
| Coumarin | HL | C9H6O2 | 20.67 | [M + H]+ | 147.0440 | 147.0445 | −3.8 | 8.76 × 107 | 0.01% |
| Flavanone | DY | C15H12O2 | 24.01 | [M + H]+ | 225.0907 | 225.0912 | −2.4 | 6.17 × 107 | 0.01% |
| Naringenin | HL | C15H12O5 | 23.95 | [M + H]+ | 273.0754 | 273.0760 | −2.2 | 5.44 × 107 | 0.01% |
| Compound | Maximum Peak Area Ratio | Regulation of Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle | Treatment of Chronic Gastritis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnoflorine | 23.06% | — | — |
| Jatrorrhizine | 16.93% | Increase the contractions of ileum longitudinal muscles [14] | Suppress the inflammation and colonization of H. pylori in CAG rats [15] |
| Berberine | 11.29% | Inhibit the contractility of isolated gastric intestine smooth muscle [16] | Improve CAG via alleviating inflammation response [17] |
| Epiberberine | 9.40% | — | Reduce gastric inflammation caused by H. pylori infection [18] |
| Palmatine | 2.42% | — | Alleviate the histological damage of gastric mucosa and inflammatory response [19] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cai, R.; Xu, H.; Guo, F. Dual-Algorithm Integration Framework Reveals Qing-Wei-Zhi-Tong’s Dual Mechanisms in Chronic Gastritis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111743
Shu Z, Huang Y, Xi Y, Zhang B, Cai R, Xu H, Guo F. Dual-Algorithm Integration Framework Reveals Qing-Wei-Zhi-Tong’s Dual Mechanisms in Chronic Gastritis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111743
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Zhijie, Ying Huang, Yujie Xi, Bo Zhang, Rui Cai, He Xu, and Feifei Guo. 2025. "Dual-Algorithm Integration Framework Reveals Qing-Wei-Zhi-Tong’s Dual Mechanisms in Chronic Gastritis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111743
APA StyleShu, Z., Huang, Y., Xi, Y., Zhang, B., Cai, R., Xu, H., & Guo, F. (2025). Dual-Algorithm Integration Framework Reveals Qing-Wei-Zhi-Tong’s Dual Mechanisms in Chronic Gastritis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111743






