The GLP-1 Analog Liraglutide Reduces Fever Through Sex-Dependent Neuroinflammatory Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
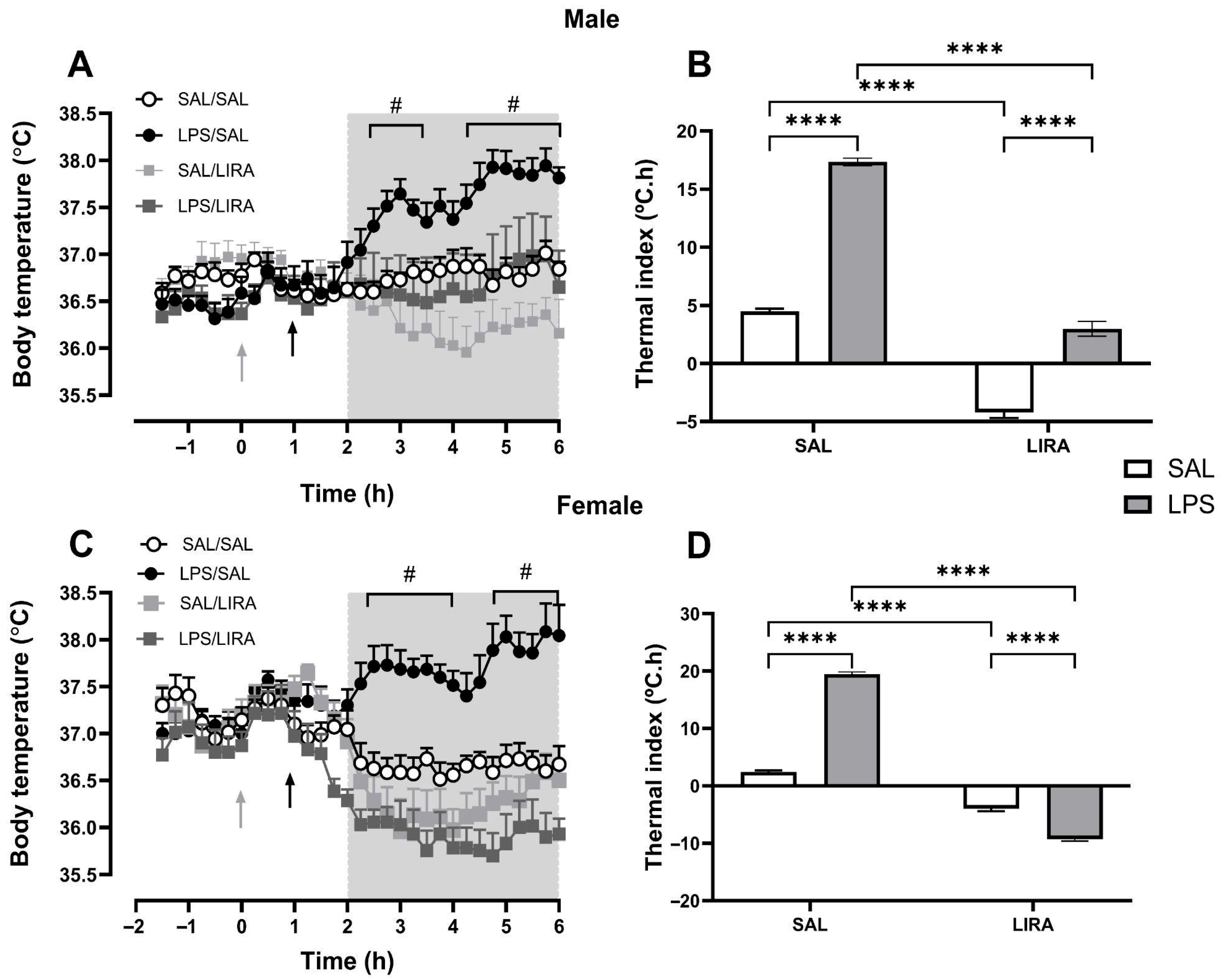
2.1. LIRA Reduces Body Temperature in Both Euthermic and Febrile Rats
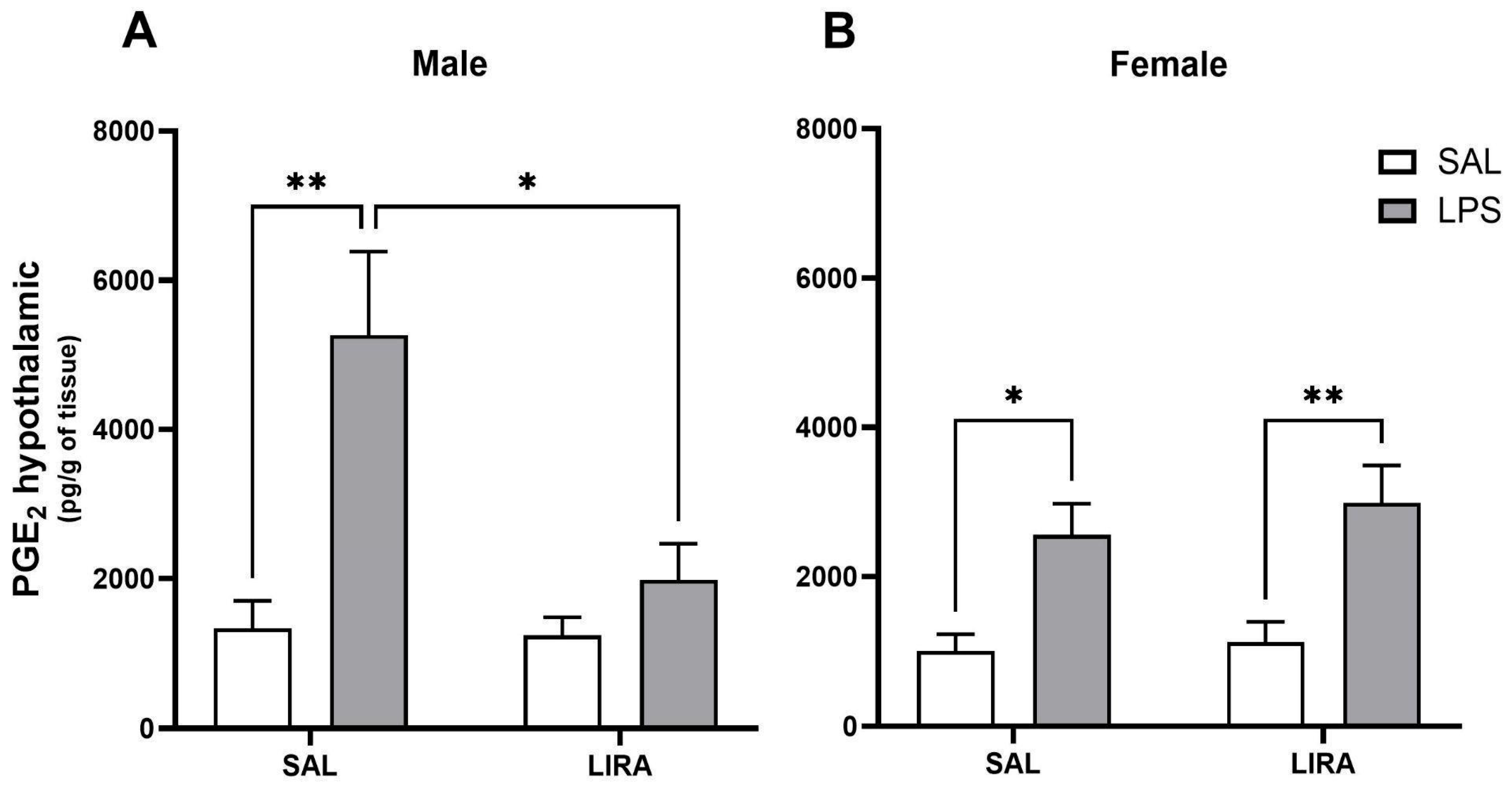
2.2. Effect of Post-Treatment with LIRA on Hypothalamic PGE2 Production
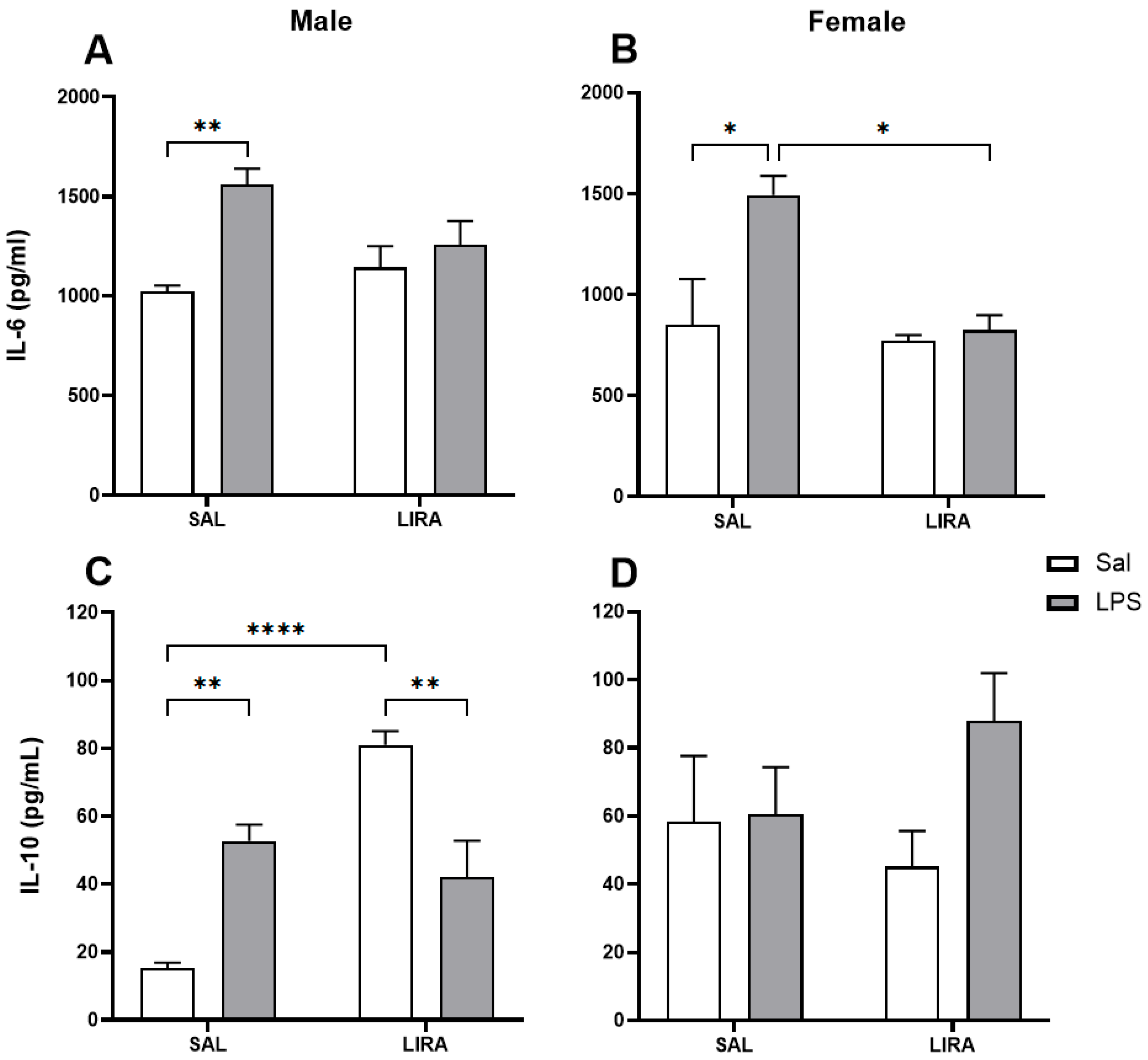
2.3. Effect of Post-Treatment with LIRA on Circulating IL-6 and IL-10 Levels
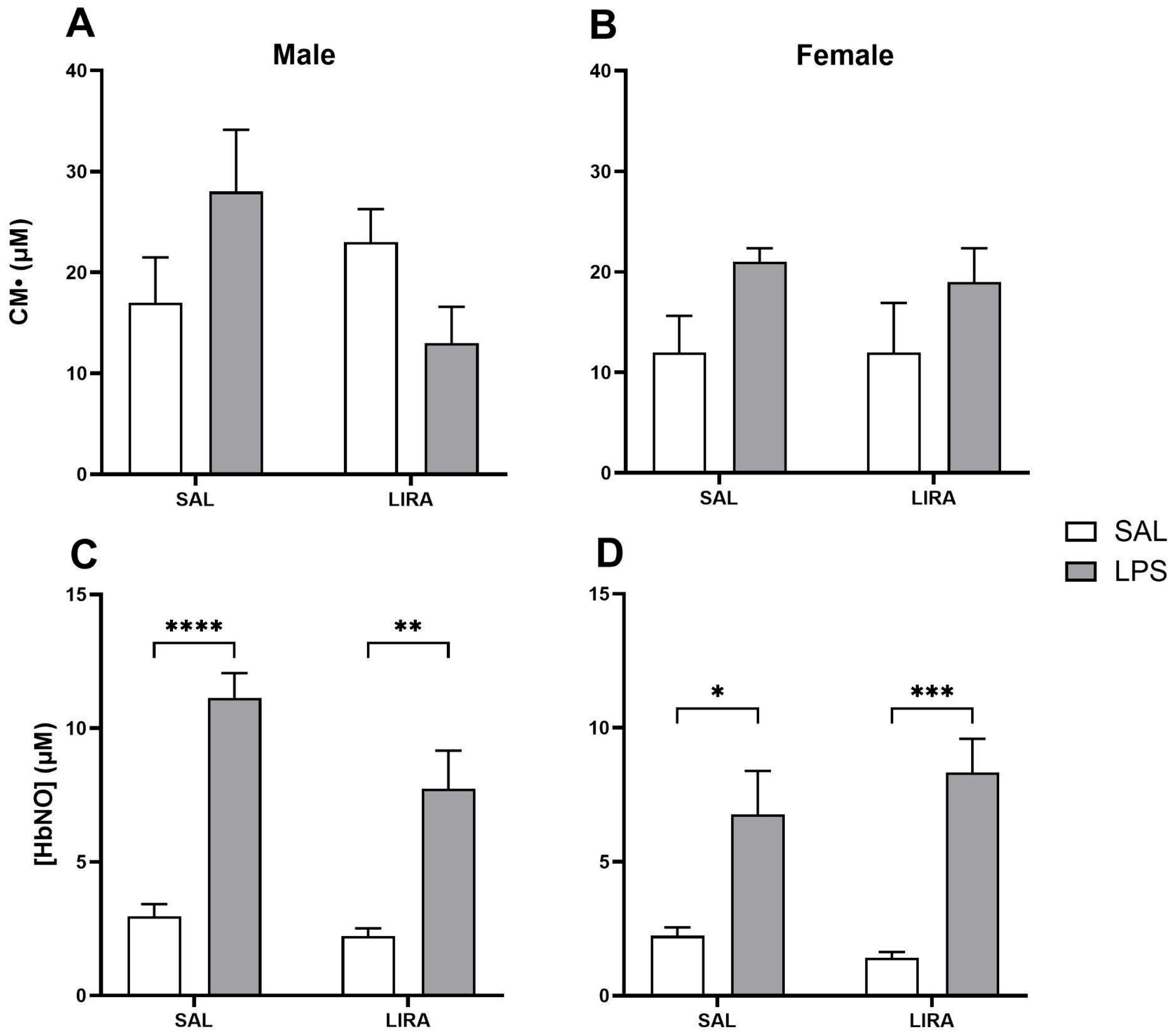
2.4. Effect of LIRA on ROS and HbNO Production
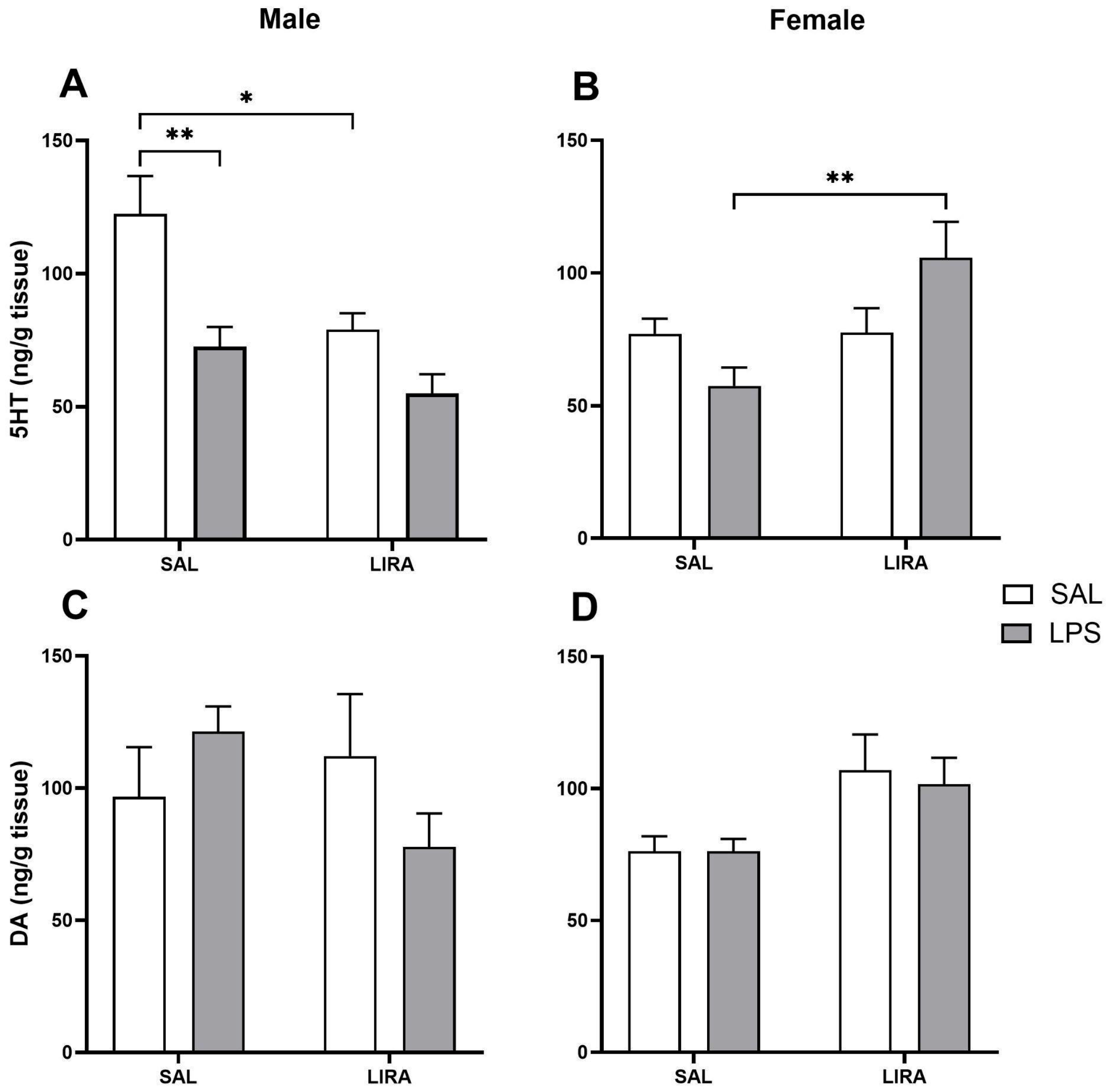
2.5. Changes in 5-HT and DA Levels in the Hypothalamus by LIRA
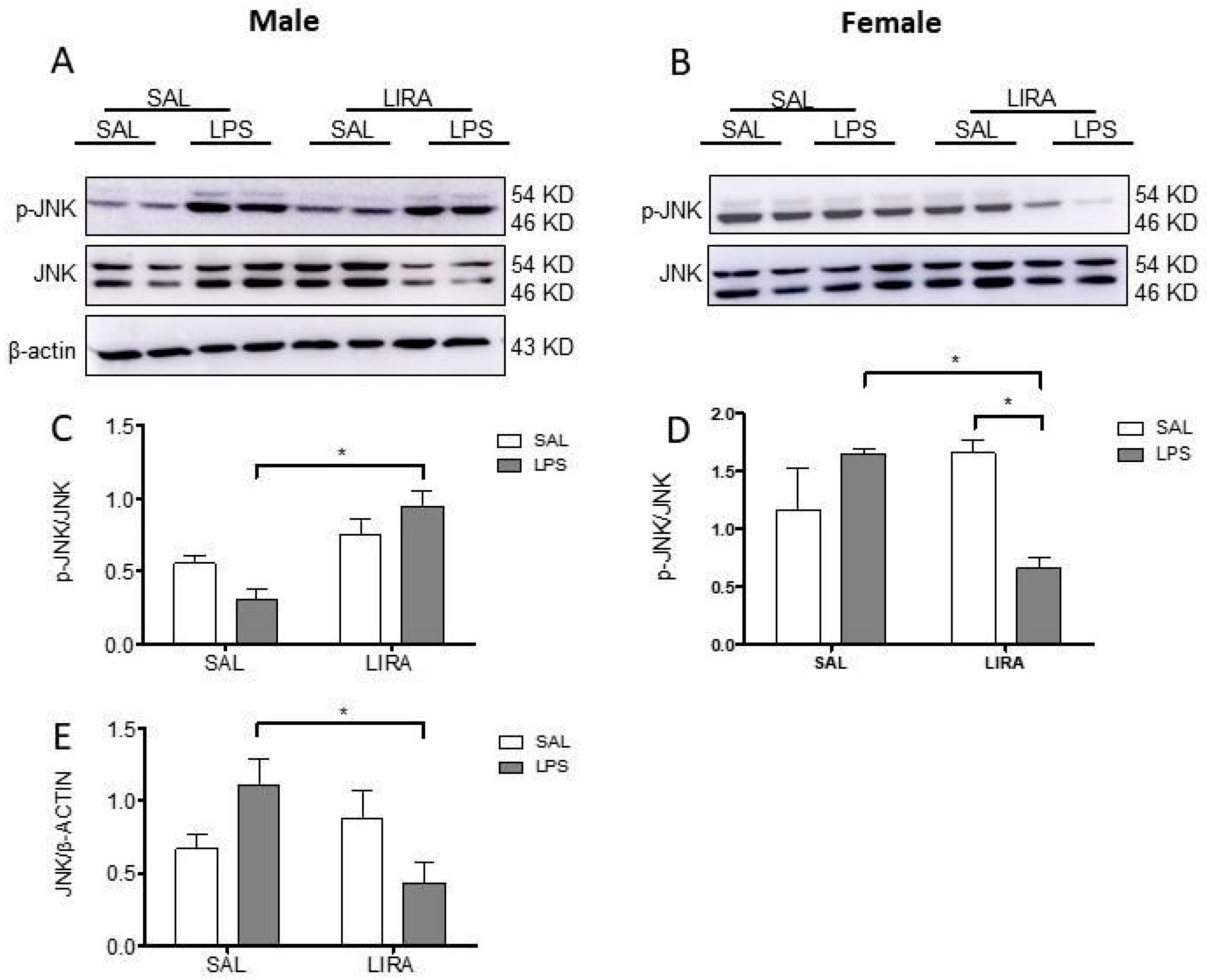
2.6. Sex-Specific Modulation of Hypothalamic JNK Signaling by LIRA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
4.3. Temperature Datalogger Implantation and Core Temperature Measurements
4.4. Experimental Design
4.5. Quantification of Hypothalamic PGE2 by ELISA
4.6. Measurement of IL-6 and IL-10 Levels in Serum
4.7. Quantification of ROS and HbNO by EPR Spectroscopy
4.8. Neurotransmitter Measurement by HPLC
4.9. Western Blotting for Detection of JNK and Phospho-JNK
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide |
| CM• | 3-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine-1-oxyl |
| CMH | 1-hydroxy-3-methoxycarbonyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylpyrrolidine |
| CP• | 3-carboxy-proxyl nitroxide |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DA | Dopamine |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EP3 | Prostaglandin E2 receptor 3 |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| ESA | Electrochemical detector brand (Coulochem III) |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 |
| GLP-1R | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 receptor |
| HbNO | Nitrosylated Hemoglobin |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| i.p. | Intraperitoneal |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LIRA | Liraglutide |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation Assay buffer |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SAL | Saline |
| SDS/PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| TBS-T | Tris-Buffered Saline with Tween 20 |
| TGFβ1 | Transforming Growth Factor beta 1 |
References
- Dinarello, C.A.; Cannon, J.G.; Wolff, S.M. New Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Fever. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.F.; Nakamura, K. Central neural pathways for thermoregulation. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.S.; Repasky, E.A.; Fisher, D.T. Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: The immune system feels the heat. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, E.A.; Johnson, C.D. Recent advances in thermoregulation. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2015, 39, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, A.; Engblom, D. Neural Mechanisms of Inflammation-Induced Fever. Neuroscientist 2018, 24, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.C.; van Mil, S.; Murray, E.; Mallet, J.F.; Matar, C.; Ismail, N. Age and sex differences in immune response following LPS treatment in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 58, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanovich, R.; Ketko, I.; Charkoudian, N. Sex Differences in Human Thermoregulation: Relevance for 2020 and Beyond. Physiology 2020, 35, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, L.C.M.; Cruz Jv Maba, I.K.; Zampronio, A.R. Fever Induced by Zymosan A and Polyinosinic-Polycytidylic Acid in Female Rats: Influence of Sex Hormones and the Participation of Endothelin-1. Inflammation 2021, 44, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, F.C.; Siboza, F.; Fuller, A. Temperature regulation in women: Effects of the menstrual cycle. Temperature 2020, 7, 226–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, H.O.; Radulski, D.R.; Wilhelms, D.B.; Stojakovic, A.; Brito, L.M.O.; Engblom, D.; Franco, C.R.C.; Zampronio, A.R. Female Sex Hormones Influence the Febrile Response Induced by Lipopolysaccharide, Cytokines and Prostaglandins but not by Interleukin-1β in Rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, Q.J.; Chen, X.; Mouihate, A.; Martin, S. Vasopressin-Induced Antipyresis: Sex- and Experience-Dependent Febrile Responses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 856, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurot, C.; Martin, C.; Sudre, L.; Breton, J.; Bougault, C.; Rattenbach, R.; Bismuth, K.; Jacques, C.; Berenbaum, F. Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist, exerts analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-degradative actions in osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.L.; Wang, Z.M.; Xu, C.; Che, F.-H.; Hu, X.-F.; Cao, R.; Xie, Y.-N.; Qiu, Y.; Shi, H.-B.; Liu, B.; et al. Liraglutide Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Modulating Macrophage Polarization. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaman, L.; Comer, J. Antagonism of central glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced fever. Auton. Neurosci. 2000, 85, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.A.; Amatnecks, J.A.; de Oliveira Guaita, G.; Stern, C.A.J.; Branco, L.G.S.; Zampronio, A.R. Sexual dimorphism of hypothalamic serotonin release during systemic inflammation: Role of endothelin-1. J. Neuroimmunol. 2024, 394, 578427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.M.; Murr, A.S.; Cooper, R.L. The rodent estrous cycle: Characterization of vaginal cytology and its utility in toxicological studies. Birth Defects Res. Part B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 80, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mert, I.; Cetinkaya, A.; Gurler, M.; Gurler, M.; Turel, C.A.; Celik, H.; Torun, I.E.; Turel, I. Anti-inflammatory potential of liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, in rats with peripheral acute inflammation. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sélley, E.; Molnár, G.A.; Kun, S.; Szijártó, I.A.; Laczy, B.; Kovács, T.; Fülöp, F.; Wittmann, I. Complex vasoactivity of liraglutide. Contribution of three gasotransmitters. Artery Res. 2015, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangshaab, M.; Gutierrez, A.; Huynh, K.D.; Knudsen, J.S.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Petersen, A.G.; Rungby, J.; Gejl, M.; Simonsen, U. Different mechanisms involved in liraglutide and glucagon-like peptide-1 vasodilatation in rat mesenteric small arteries. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baris, E.; Portakal, H.S.; Aslan, A.; Firtina Karagonlar, Z.; Tosun, M. Liraglutide modulates cyclooxygenase and α7 acetylcholine receptors: In vitro and in silico insights into its anti-inflammatory role in LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 16229–16239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xie, T.; Guo, X.; Wu, D.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist exendin-4 mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.; de Souza, G.E.P. Fever induction pathways: Evidence from responses to systemic or local cytokine formation. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2001, 34, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Gatti, S.; Toniatti, C.; Poli, V.; Bartfai, T. Interleukin (IL)-6 gene expression in the central nervous system is necessary for fever response to lipopolysaccharide or IL-1 beta: A study on IL-6-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, W.; Kluger, M.J.; Soszynski, D.; Conn, C.A.; Rudolph, K.; Leon, L.R.; Zheng, H. IL-6 and IL-1β in Fever: Studies Using Cytokine-Deficient (Knockout) Mice. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 856, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; McLean, B.A.; Baggio, L.L.; Koehler, J.A.; Hammoud, R.; Rittig, N.; Yabut, J.M.; Seeley, R.J.; Brown, T.J.; Drucker, D.J. Central glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor activation inhibits Toll-like receptor agonist-induced inflammation. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 130–143.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Overgaard, R.v.; Jacobsen, L.v.; Jensen, C.B.; Le Roux, C.W. Exposure–response analyses of liraglutide 3.0 mg for weight management. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, F.; Zou, Q.; Pu, Y. GLP-1R agonist liraglutide attenuates pain hypersensitivity by stimulating IL-10 release in a nitroglycerin-induced chronic migraine mouse model. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 812, 137397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz-Chaves, Y.; Toba, L.; Fandiño, J.; González-Matías, L.C.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Mallo, F. The GLP-1 analog, liraglutide prevents the increase of proinflammatory mediators in the hippocampus of male rat pups submitted to maternal perinatal food restriction. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Ping, F.; Li, Y. Liraglutide Attenuates Hepatic Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Inoguchi, T.; Sonoda, N.; Hendarto, H.; Makimura, H.; Sasaki, S.; Yokomizo, H.; Fujimura, Y.; Miura, D.; Takayanagi, R. GLP-1 analog liraglutide protects against cardiac steatosis, oxidative stress and apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Atherosclerosis 2015, 240, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, A.; Oyama JIchi Komoda, H.; Komoda, H.; Asaka, M.; Komatsu, A.; Sakuma, M.; Kodama, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kotooka, N.; Hirase, T.; et al. The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces TNF-α-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.R.B.; Firmino, M.; Jorge, J.S.; Ferreira, M.L.O.; Rodovalho, T.M.; Weis, S.N.; Souza, G.E.P.; Morais, P.C.; Sousa, M.V.; Souza, P.E.N.; et al. Increase of reactive oxygen species in different tissues during lipopolysaccharide-induced fever and antipyresis: An electron paramagnetic resonance study. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikalov, S.; Fink, B. ESR Techniques for the Detection of Nitric Oxide In Vivo and in Tissues. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 396, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, D.P.; Kent, S.; McKinley, M.J.; Mathai, M.L. Suppression of endotoxin-induced fever in near-term pregnant rats is mediated by brain nitric oxide. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R2174–R2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, R.N.; Ravanelli, M.I.; Batalhao, M.E.; Carnio, E.C.; Branco, L.G.S. Propyretic role of the locus coeruleus nitric oxide pathway. Exp. Physiol. 2010, 95, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.A.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; McCann, S.M.; Branco, L.G.S. Antipyretic role of the NO-cGMP pathway in the anteroventral preoptic region of the rat brain. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 282, R584–R593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmstädter, J.; Keppeler, K.; Aust, F.; Küster, L.; Frenis, K.; Filippou, K.; Vujacic-Mirski, K.; Tsohataridis, S.; Kalinovic, S.; Kröller-Schön, S.; et al. GLP-1 Analog Liraglutide Improves Vascular Function in Polymicrobial Sepsis by Reduction of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammoh, O.; Qnais, E.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Hatahet, T.; Alqudah, A. Metabolic resilience: Liraglutide’s potential in alleviating depressive symptoms. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.J.; Henderson, J.A.; Abell, C.W.; Bethea, C.L. Effects of Ovarian Steroids and Raloxifene on Proteins that Synthesize, Transport, and Degrade Serotonin in the Raphe Region of Macaques. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 2035–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiroi, R.; Neumaier, J.F. Estrogen decreases 5-HT1B autoreceptor mRNA in selective subregion of rat dorsal raphe nucleus: Inverse association between gene expression and anxiety behavior in the open field. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, C.M.D.; Rodrigues-Santos, C.; Fernández, R.A.R.; Carolino, R.O.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Anselmo-Franci, J.A.; Branco, L.G. Central serotonin attenuates LPS-induced systemic inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonogaki, K.; Kaji, T. The GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Liraglutide Decreases Primary Bile Acids and Serotonin in the Colon Independently of Feeding in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, S.; Kurobe-Takashima, Y.; Kuriki, D.; Susaki, K.; Otsuka, K.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Abe, K.; Kobayashi, S. Phosphatidylcholine suppresses inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated MG6 microglial cells by inhibiting NF-κB/JNK/p38 MAPK signaling. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0328206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchenthaler, I.; Lane, M.; Shughrue, P. Distribution of pre-pro-glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor messenger RNAs in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 403, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, H.O.; Reis, R.C.; Bini, I.; Wilhelms, D.; Engblom, D.; Gil da Costa, R.M.; Brito, L.O.; Nascimento, M.D.D.S.; de Andrade, M.S.; Zampronio, A.R.; et al. NK1 receptor mediates cerebral cellular and extracellular morphological changes during the LPS-induced febrile response. Brain Res. 2024, 1842, 149107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.J. Thermal biology of the laboratory rat. Physiol. Behav. 1990, 47, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.J.; de Melo Soares, D.; Martins, J.M.; Machado, R.d.R.; Sorgi, C.A.; Faccioli, L.H.; de Melo, M.C.C.; Malvar, D.D.C.; Souza, G.E.P. Febrile response induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) in rats: Involvement of prostaglandin E2 and cytokines. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 201, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.G.; Barbiero, J.K.; Ariza, D.; Dombrowski, P.A.; Sabioni, P.; Bortolanza, M.; Da Cunha, C.; Vital, M.A.B.F.; Lima, M.M.S. Behavioral, Neurochemical and Histological Alterations Promoted by Bilateral Intranigral Rotenone Administration: A New Approach for an Old Neurotoxin. Neurotox. Res. 2012, 21, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Sousa, G.L.S.; da Cruz, E.K.M.; de Aguiar, S.C.R.; Nascimento, A.P.L.d.; Gomes, B.R.B.; Londe, A.B.R.; Gonçalves, L.J.F.; Royer, C.; Costa, R.A.; Zampronio, A.R.; et al. The GLP-1 Analog Liraglutide Reduces Fever Through Sex-Dependent Neuroinflammatory Modulation. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111738
de Sousa GLS, da Cruz EKM, de Aguiar SCR, Nascimento APLd, Gomes BRB, Londe ABR, Gonçalves LJF, Royer C, Costa RA, Zampronio AR, et al. The GLP-1 Analog Liraglutide Reduces Fever Through Sex-Dependent Neuroinflammatory Modulation. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111738
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Sousa, Gabriela L. Soares, Ester K. Martins da Cruz, Sara C. Rojas de Aguiar, Ana P. Lima do Nascimento, Bruna R. Bezerra Gomes, Anna B. Rodrigues Londe, Luana J. Faria Gonçalves, Carine Royer, Regina Azevedo Costa, Aleksander Roberto Zampronio, and et al. 2025. "The GLP-1 Analog Liraglutide Reduces Fever Through Sex-Dependent Neuroinflammatory Modulation" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111738
APA Stylede Sousa, G. L. S., da Cruz, E. K. M., de Aguiar, S. C. R., Nascimento, A. P. L. d., Gomes, B. R. B., Londe, A. B. R., Gonçalves, L. J. F., Royer, C., Costa, R. A., Zampronio, A. R., de Souza, P. E. N., & Veiga-Souza, F. H. (2025). The GLP-1 Analog Liraglutide Reduces Fever Through Sex-Dependent Neuroinflammatory Modulation. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111738






