Identification and Integrative Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds Isolated from Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. by Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Extract and Fractions
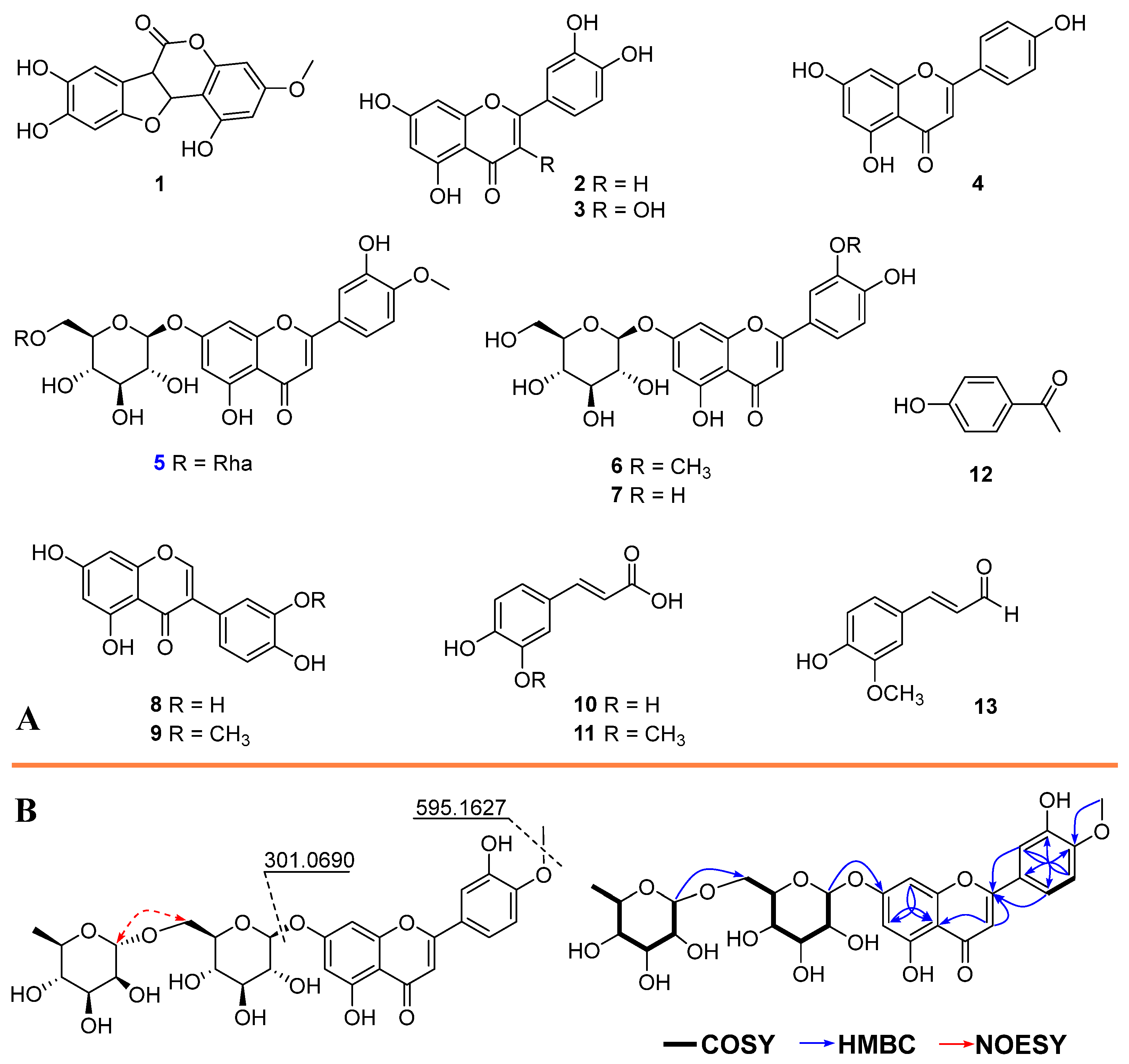
2.2. Separation and Identification of Compounds from the Most Active Fraction
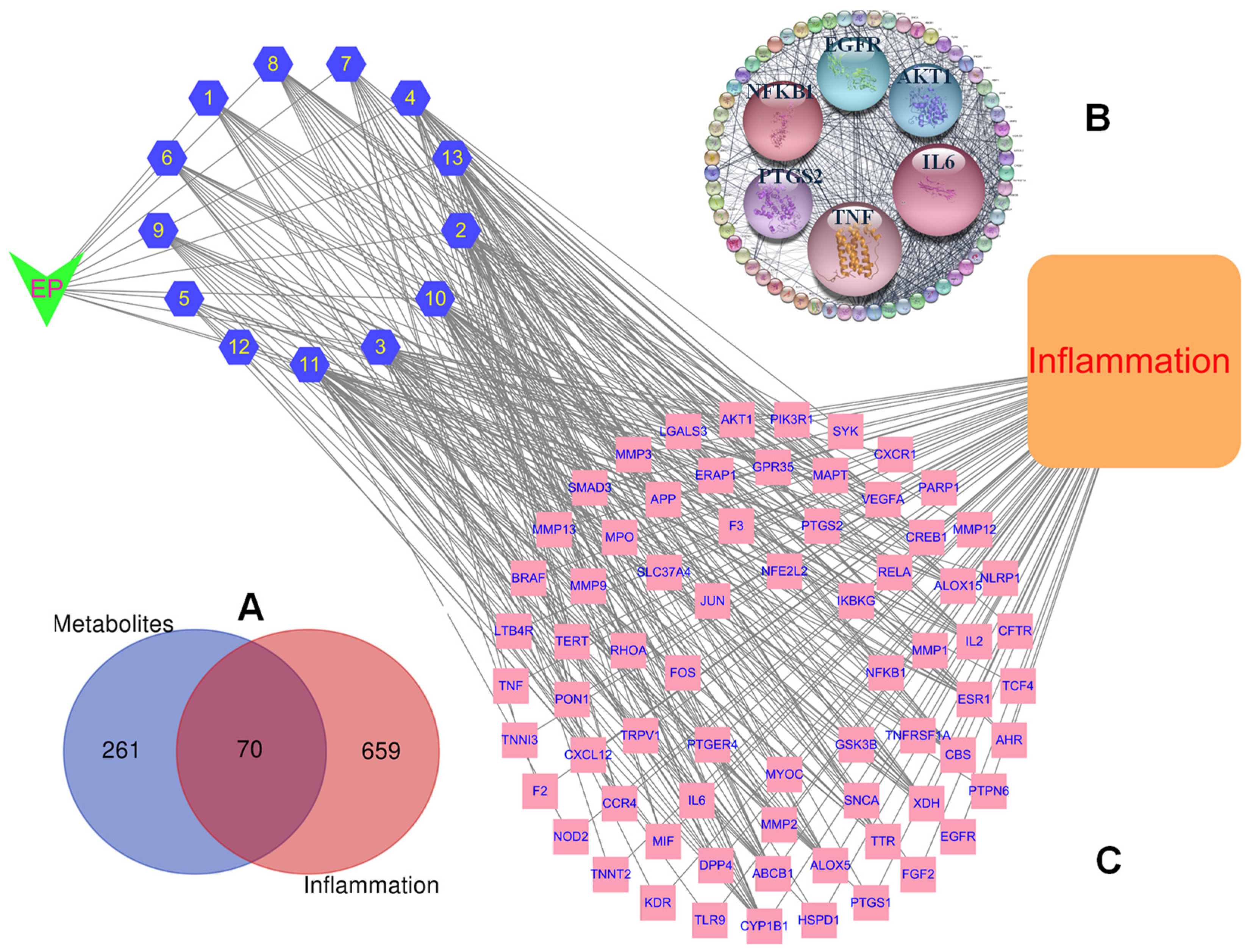
2.3. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Isolated Compounds of E. prostrata
2.3.1. Construction of the PPI Network and Core Targets
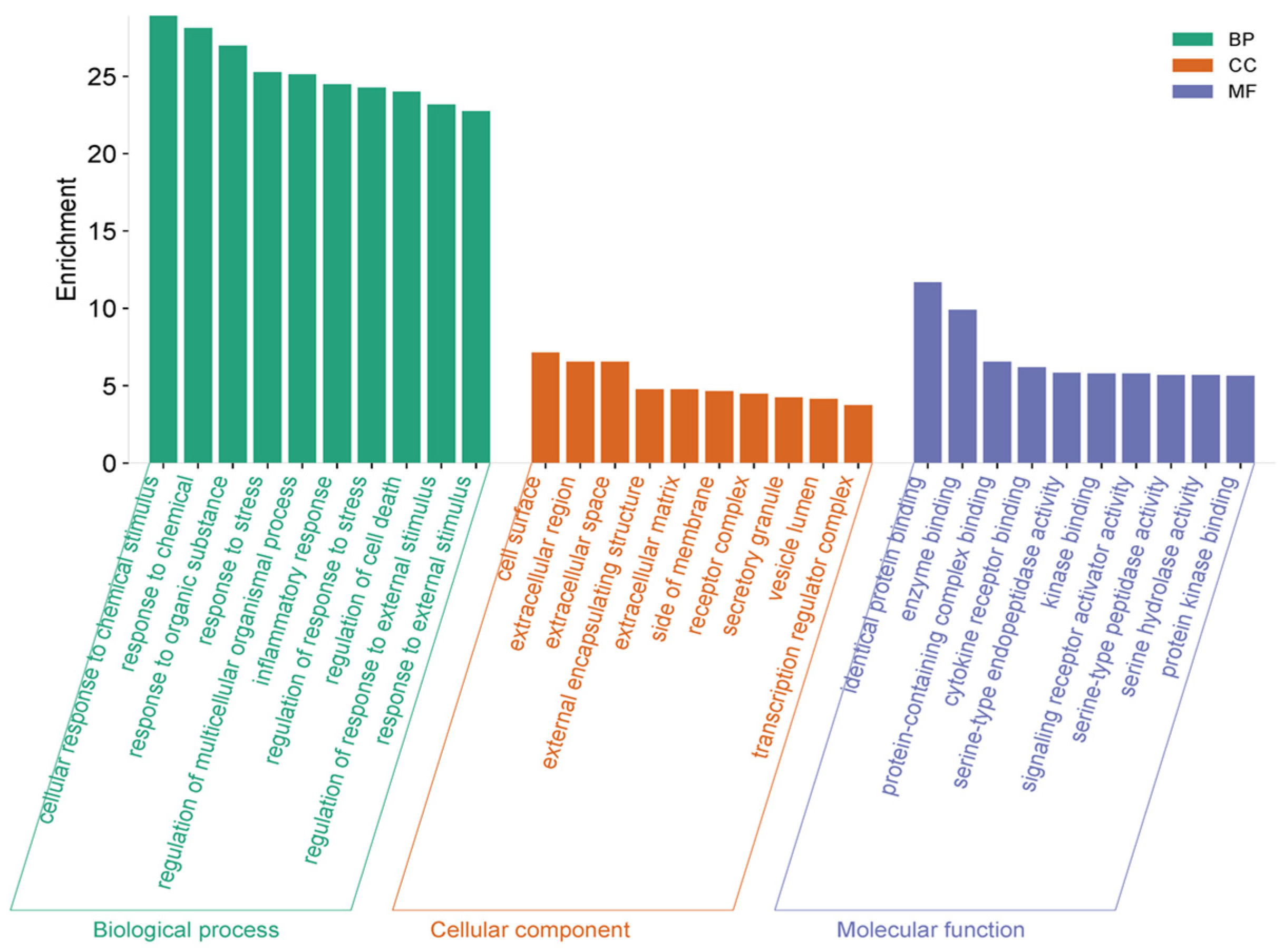
2.3.2. Enriched Gene Ontology (GO) Clusters
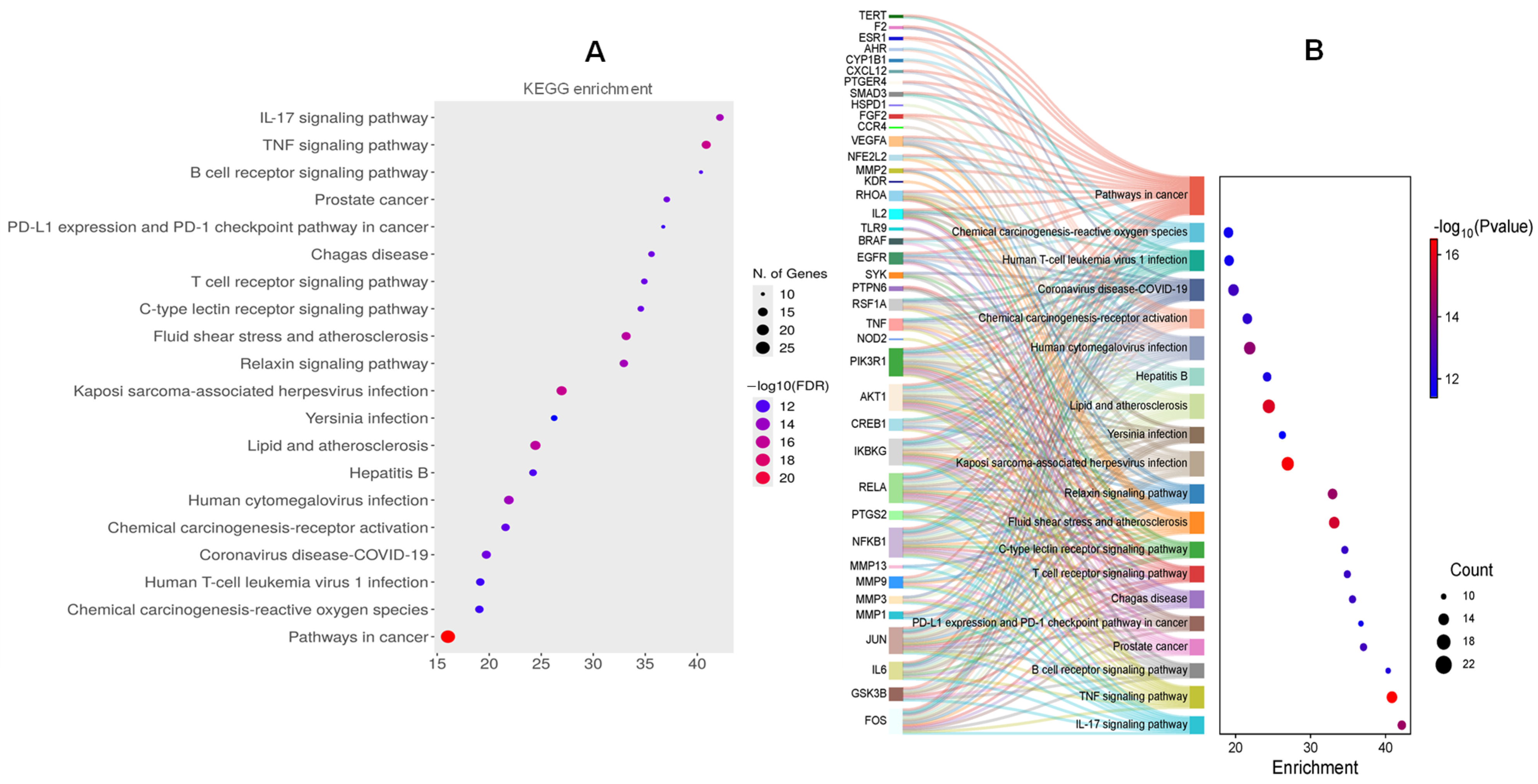
2.3.3. Prediction of Potential Therapeutic Targets by the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Enrichment
2.4. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Isolated Compounds (1–13) In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Separation of Compounds
4.2. Network Pharmacology
4.2.1. Compound and Inflammation-Related Target Prediction
4.2.2. Protein–Protein Interaction Network and Topological Analysis
4.2.3. Gene Ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathways
4.3. Prediction of Binding Affinities of Compounds and Target Proteins
4.4. Bioassays
4.4.1. Cell Culture and Toxicity
4.4.2. ELISA Assays
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, L.; Zhai, Y.-Y.; Xu, J.; Yao, W.-F.; Cao, Y.-D.; Cheng, F.-F.; Bao, B.-H.; Zhang, L. A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 245, 112109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.D.; Nguyen, D.H.; Ma, E.S.; Lee, J.H.; Min, B.S.; Choi, J.S.; Woo, M.H. PTP1B inhibitory and anti-inflammatory properties of constituents from Eclipta prostrata L. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.-M.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Zhong, X.-K.; Jiang, J.-G. Eclipta prostrata L. phytochemicals: Isolation, structure elucidation, and their antitumor activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4016–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, Y.S.; Seong, E.S.; Kim, M.J. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. extract and isolated compounds. Molecules 2023, 28, 7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewtrakul, S.; Subhadhirasakul, S.; Cheenpracha, S.; Karalai, C. HIV-1 protease and HIV-1 integrase inhibitory substances from Eclipta prostrata. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.L.R.; Wilairatana, P.; Silva, L.R.; Moreira, P.S.; Vilar Barbosa, N.M.M.; da Silva, P.R.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; de Menezes, I.R.A.; Felipe, C.F.B. Biochemical aspects of the inflammatory process: A narrative review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.; Barreda, D.R. Acute inflammation in tissue healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, J.D.; Vucic, D. The balance of TNF mediated pathways regulates inflammatory cell death signaling in healthy and diseased tissues. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Vázquez, E.; Cobo-Vuilleumier, N.; López-Noriega, L.; Lorenzo, P.I.; Gauthier, B.R. The PTGS2/COX2-PGE2 signaling cascade in inflammation: Pro or anti? A case study with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 4157–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, A.; Fernández-Hernando, C.; Cirino, G.; Sessa, W.C. Akt1 is critical for acute inflammation and histamine-mediated vascular leakage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14552–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, T.; Perkins, N.D.; Wilson, C.L. NFKB1: A suppressor of inflammation, ageing and cancer. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.; Ahmed, B.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Anwar, F.; Verma, A. Deconvoluting the dual hypoglycemic effect of wedelolactone isolated from Wedelia calendulacea: Investigation via experimental validation and molecular docking. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 18180–18196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, M.; Shafiq, S.; Ullah, H.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F. Isolation of quercetin and mandelic acid from Aesculus indica fruit and their biological activities. BMC Biochem. 2018, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaffo, C.M.N.; Tchangna, R.S.V.; Mbaveng, A.T.; Kamga, J.; Harvey, F.M.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Bochet, C.G.; Kuete, V. Botanicals from the leaves of Acacia sieberiana had better cytotoxic effects than isolated phytochemicals towards MDR cancer cells lines. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jin, C.H. Inhibitory activity of flavonoids, chrysoeriol and luteolin-7-O-glucopyranoside, on soluble epoxide hydrolase from Capsicum chinense. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.-P.; Xi, F.-M.; Chen, W.-S.; Lu, W.-Q.; Wu, Z.-J. Chemical constituents of Eclipta prostrata. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2021, 57, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Le, D.D.; Zhao, B.T.; Ma, E.S.; Min, B.S.; Woo, M.H. Antioxidant compounds isolated from the roots of Phlomis umbrosa Turcz. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2018, 24, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewtrakul, S.; Subhadhirasakul, S.; Tansakul, P.; Cheenpracha, S.; Karalai, C. Antiinflammatory constituents from Eclipta prostrata using RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanatidou, A.I.; Dedoussis, G.V. Construction and analysis of protein-protein interaction network of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 131, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.-H.; Liu, M.; Ren, J.-X.; Ouyang, D.-W. Structural Characterization of Chemical Compounds Based on Their Fragmentation Rules in Sophorae fructus by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. Pharm. Front. 2022, 04, e162–e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W.; Xie, J.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Cui, M. Combining network pharmacology, machine learning, molecular docking and molecular dynamic to explore the mechanism of Chufeng Qingpi decoction in treating schistosomiasis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1453529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Dong, H.; Bai, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; et al. LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF-κB, STAT3 or AP-1 activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5484–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.-H.; Park, T.; Kang, M.-G.; Park, D. Anti-inflammatory activity and ROS regulation effect of sinapaldehyde in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Molecules 2020, 25, 4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, M.; Ruiz-Carmona, S.; Barril, X. An investigation of structural stability in protein-ligand complexes reveals the balance between order and disorder. Commun. Chem. 2019, 2, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, K.; Ashraf, S.; Jabeen, A.; Saeed, M.; Nur-e-Alam, M.; Ahmed, S.; Al-Rehaily, A.J.; Ul-Haq, Z. Identification of potential TNF-α inhibitors: From in silico to in vitro studies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, X.; Xu, H.; Wu, W.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, M.; Hou, Y.; Bai, G. A natural AKT inhibitor swertiamarin targets AKT-PH domain, inhibits downstream signaling, and alleviates inflammation. FEBS J. 2020, 287, e15112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, M.H.; Atif, H.M.; Eladl, M.A.; Elaidy, S.M.; Helaly, A.M.N.; Hisham, F.A.; Farag, N.E.; Osman, N.M.S.; Ibrahiem, A.T.; Khella, H.W.Z.; et al. Betanin improves motor function and alleviates experimental Parkinsonism via downregulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway: Molecular docking and biological investigations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.W.; Nag, S.; Stany, B.K.; Mishra, S.; Naidu, R. Identification of SRC, AKT1 and MAPK3 as therapeutic targets of apigenin and luteolin in colorectal and colon carcinoma through network pharmacology. Food Biosci. 2025, 67, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, V.; Khan, M.I.; Jamal, Q.M.; Alzahrani, F.A.; Albiheyri, R. Computational molecular docking and simulation-based assessment of anti-inflammatory properties of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis Linn phytochemicals. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, J.; Li, X.; Guo, N. Simultaneous extraction, identification and quantification of phenolic compounds in Eclipta prostrata using microwave-assisted extraction combined with HPLC–DAD–ESI–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.K.; Wang, S.-L.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Phan, T.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, T.T.; Nguyen, A.D.; Nguyen, V.B.; Doan, M.D. Assessment of the chemical profile and potential medical effects of a flavonoid-rich extract of Eclipta prostrata L. collected in the central highlands of Vietnam. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansakaow, S.; Tragoolpua, Y. Antioxidant activity, phenolic compound content and phytochemical constituents of Eclipta prostrata (Linn.) Linn. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2014, 41, 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhan, X.-M.; Zhao, S.-B.; Xu, X.-L.; Jiang, J.-G.; Zhu, W. Comparison of the regulatory effects of flavonoids and saponins from Eclipta prostrate on insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.R. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, M.; Duan, W.; Choi, H.; Eun, S.-Y.; Madireddi, S.; Mehta, A. TNF superfamily in inflammatory disease: Translating basic insights. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, T.; Janadri, S. Anti-inflammatory effect of wedelolactone on DSS induced colitis in rats: IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2023, 14, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagas, M.D.S.S.; Behrens, M.D.; Moragas-Tellis, C.J.; Penedo, G.X.M.; Silva, A.R.; Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque, C.F. Flavonols and flavones as potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial compounds. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 9966750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as potential anti-inflammatory molecules: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Nakamura, K.; Tago, K.; Mashino, T.; Kasahara, T. Anti-inflammatory activity of structurally related flavonoids, apigenin, luteolin and fisetin. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yue, J.; Cui, Y.; Feng, J.; He, Q.; Liang, J.; You, W.; Shi, H.; Sun, W.; Yi, Q. Wedelolactone alleviates inflammation and cartilage degeneration by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.-M.; Wang, L.; Yang, D.; Li, C.; Pang, S.-T.; Li, X.-H.; Li, R.; Yang, B.; Lian, Y.-P.; Ma, L.; et al. Wedelolactone alleviates doxorubicin-induced inflammation and oxidative stress damage of podocytes by IκK/IκB/NF-κB pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ni, Y.; Ning, X.; Zhang, H. Wedelolactone ameliorates synovial inflammation and cardiac complications in a murine model of collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2022, 60, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, K.S.; Asaruddin, M.R.B.; Bhawani, S.A. Pharmacophore study, molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation of virgin coconut oil derivatives as anti-inflammatory agent against COX-2. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Fraction | IL-6 (μg/mL) | TNF-α (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Ext. | 55.68 ± 1.05 | 66.18 ± 3.16 |
| H | 71.00 ± 3.38 | 78.22 ± 4.87 |
| E | 43.24 ± 0.83 | 45.97 ± 2.01 |
| W | 82.02 ± 2.81 | 95.37 ± 1.96 |
| Dexa. | 1.85 ± 0.06 | 2.55 ± 0.08 |
| Compound | IL-6 | TNF | AKT1 | NFKB1 | EGFR | PTGS2 | Average Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −4.51 | −5.01 | −4.85 | −5.96 | −6.23 | −5.89 | −5.41 |
| 2 | −4.65 | −5.63 | −5.17 | −6.50 | −8.01 | −7.80 | −6.29 |
| 3 | −4.91 | −6.20 | −5.03 | −6.20 | −7.91 | −6.87 | −6.19 |
| 4 | −4.25 | −5.65 | −4.42 | −5.89 | −6.77 | −7.03 | −5.73 |
| 5 | −3.45 | −5.47 | −3.41 | −3.44 | −2.13 | −4.87 | −4.27 |
| 6 | −4.40 | −5.20 | −4.37 | −5.54 | −5.59 | −4.49 | −4.96 |
| 7 | −4.37 | −4.96 | −4.09 | −5.16 | −4.91 | −5.02 | −4.75 |
| 8 | −4.39 | −4.59 | −4.75 | −5.44 | −6.84 | −5.44 | −5.24 |
| 9 | −4.32 | −4.33 | −4.43 | −6.38 | −6.29 | −5.96 | −5.29 |
| 10 | −4.58 | −4.35 | −3.44 | −5.82 | −5.25 | −5.49 | −4.82 |
| 11 | −3.48 | −4.72 | −3.51 | −5.83 | −5.13 | −6.40 | −4.85 |
| 12 | −4.41 | −4.37 | −3.73 | −4.99 | −5.30 | −5.56 | −4.81 |
| 13 | −4.34 | −4.62 | −3.55 | −5.76 | −5.02 | −5.92 | −4.87 |
| Compound | IL-6 (μM) | TNF (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.66 ± 0.54 | 22.12 ± 1.18 |
| 2 | 13.24 ± 0.73 | 2.56 ± 0.08 |
| 3 | 9.89 ± 0.80 | 6.18 ± 0.03 |
| 4 | 25.45 ± 1.26 | 8.01 ± 0.11 |
| 5 | 88.71 ± 3.42 | 75.43 ± 2.60 |
| 6 | 95.26 ± 3.60 | 23.07 ± 0.84 |
| 7 | 80.56 ± 2.53 | 73.49 ± 4.04 |
| 8 | 17.45 ± 1.30 | 64.75 ± 3.07 |
| 9 | 37.86 ± 1.09 | 12.30 ± 1.06 |
| 10 | 79.91 ± 4.18 | 98.52 ± 2.17 |
| 11 | 32.55 ± 0.98 | 38.76 ± 1.29 |
| 12 | 36.28 ± 2.51 | 44.37 ± 1.04 |
| 13 | 23.81 ± 0.45 | 52.67 ± 2.19 |
| Dexa. | 3.62 ± 0.05 | 2.20 ± 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Anh, C.; Linh, N.N.; Phan, P. Identification and Integrative Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds Isolated from Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. by Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111653
Van Anh C, Linh NN, Phan P. Identification and Integrative Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds Isolated from Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. by Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111653
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Anh, Cao, Nguyen Ngoc Linh, and Phuochien Phan. 2025. "Identification and Integrative Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds Isolated from Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. by Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Evaluation" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111653
APA StyleVan Anh, C., Linh, N. N., & Phan, P. (2025). Identification and Integrative Discovery of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds Isolated from Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. by Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111653






