Multi-Omics and Experimental Insights into the Protective Effects of Sesquiterpenoid Lactones from Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. in Acute Lung Injury: Regulation of PI3K-Akt and MAPK-NF-κB Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Composition in SLEL Through UPLC-Q/TOF/MSn
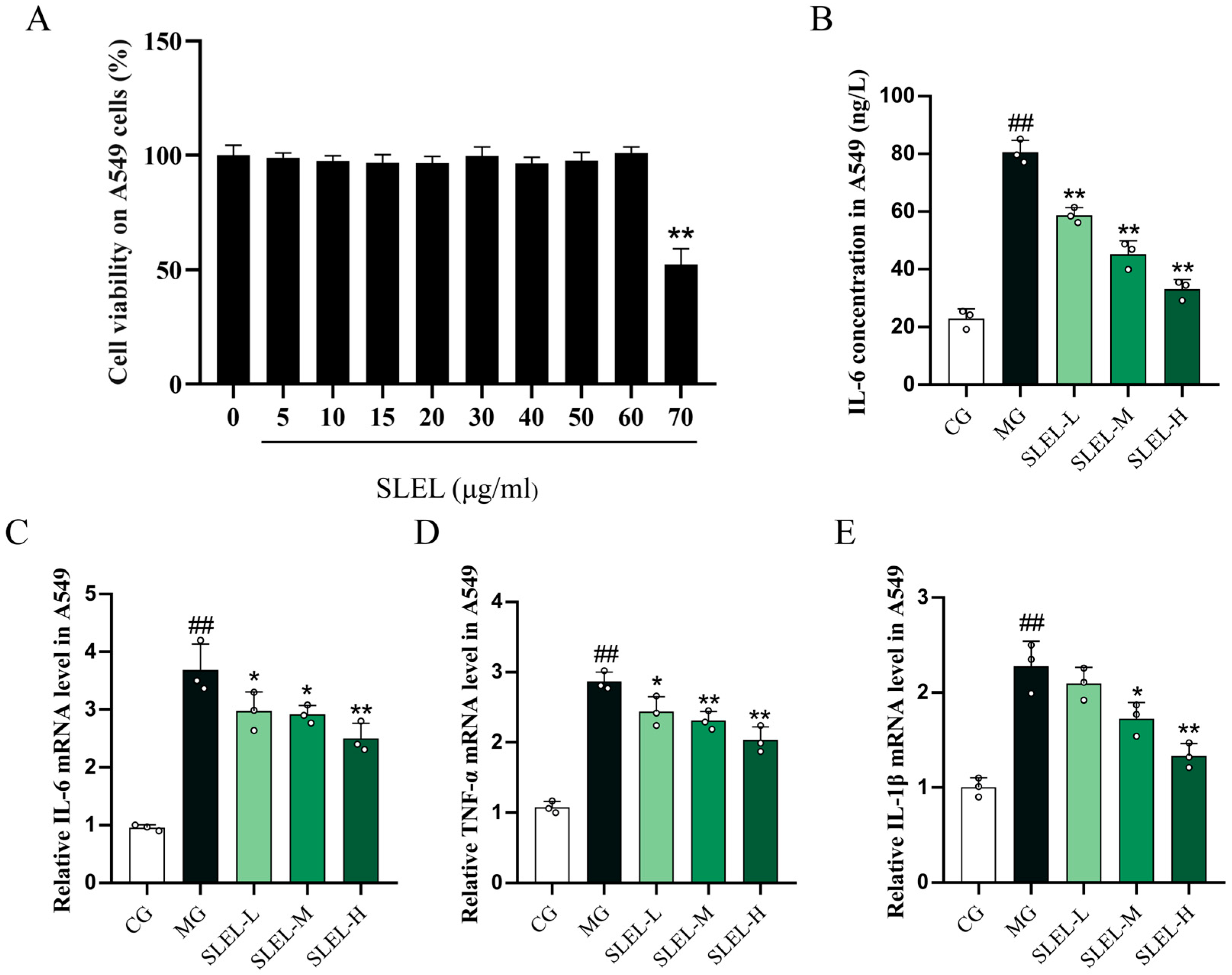
2.2. SLEL Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Cascade in Macrophages via Cytokine Suppression
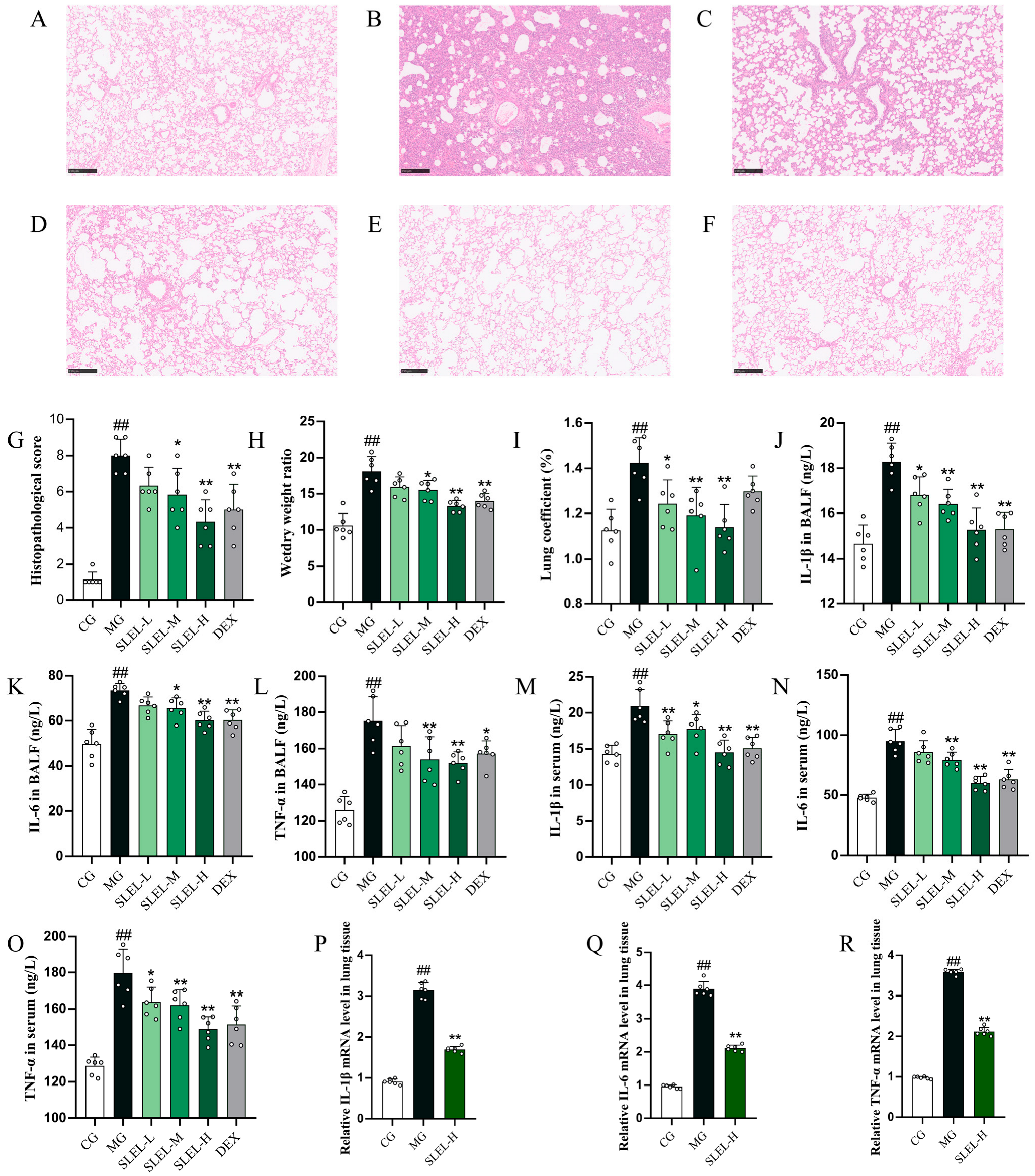
2.3. SLEL Decreased the Inflammation in ALI Rats
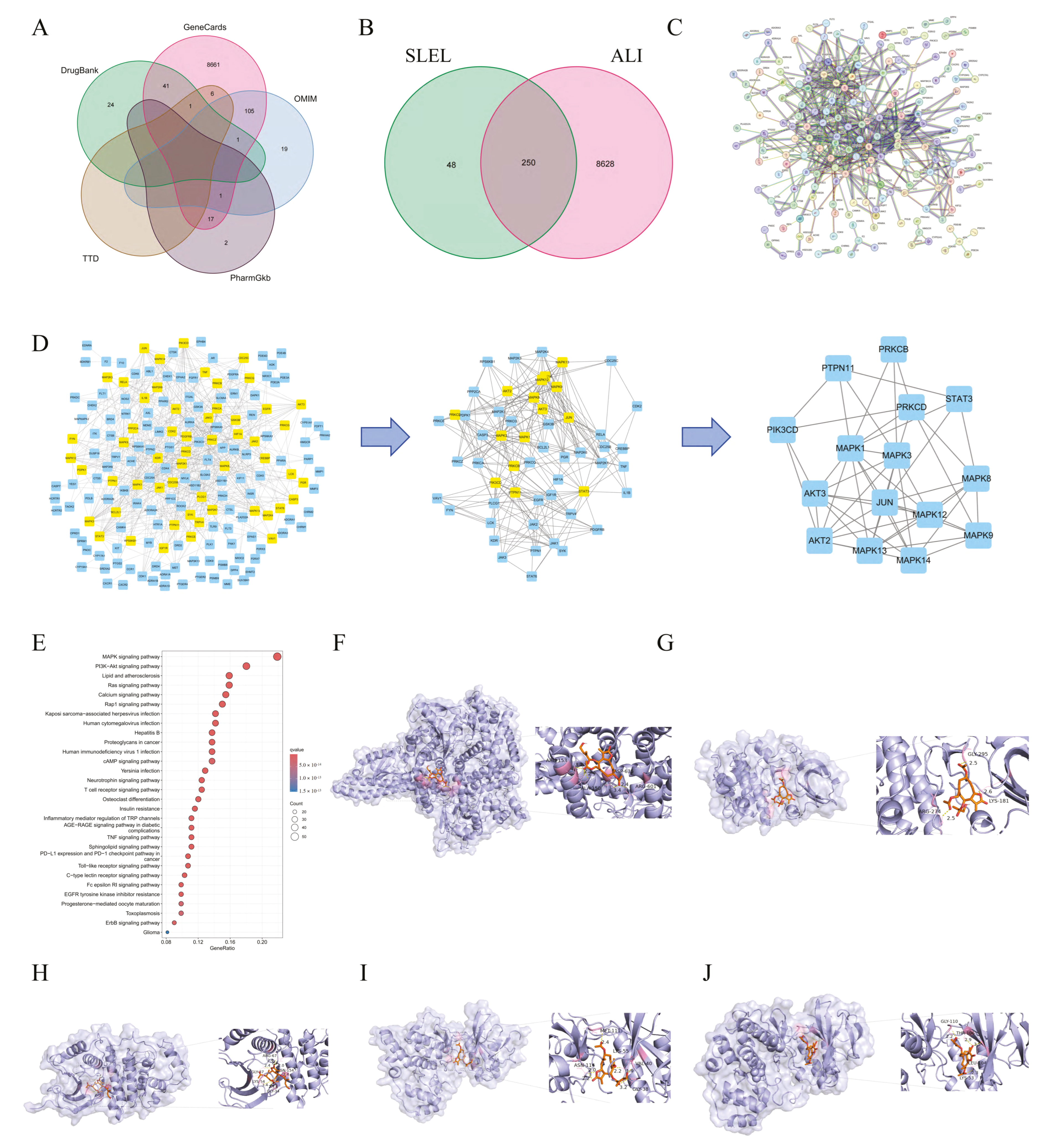
2.4. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Elucidate SLEL’s Anti-ALI Mechanisms
2.5. Transcriptomics Unravels SLEL’s Anti-ALI Pathway Modulation
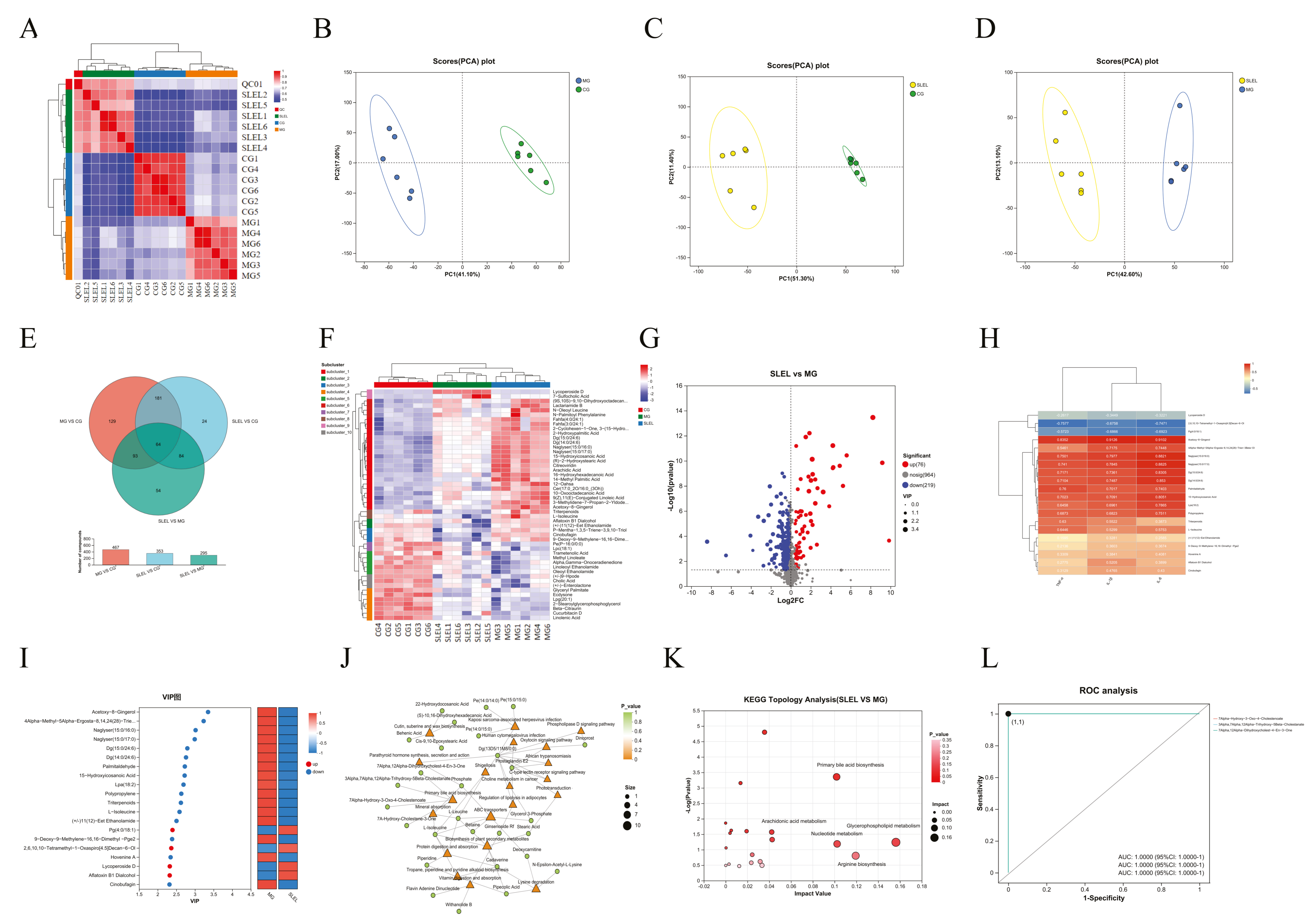
2.6. Metabolomics Decodes SLEL’s Bile Acid-Mediated Anti-ALI Mechanism
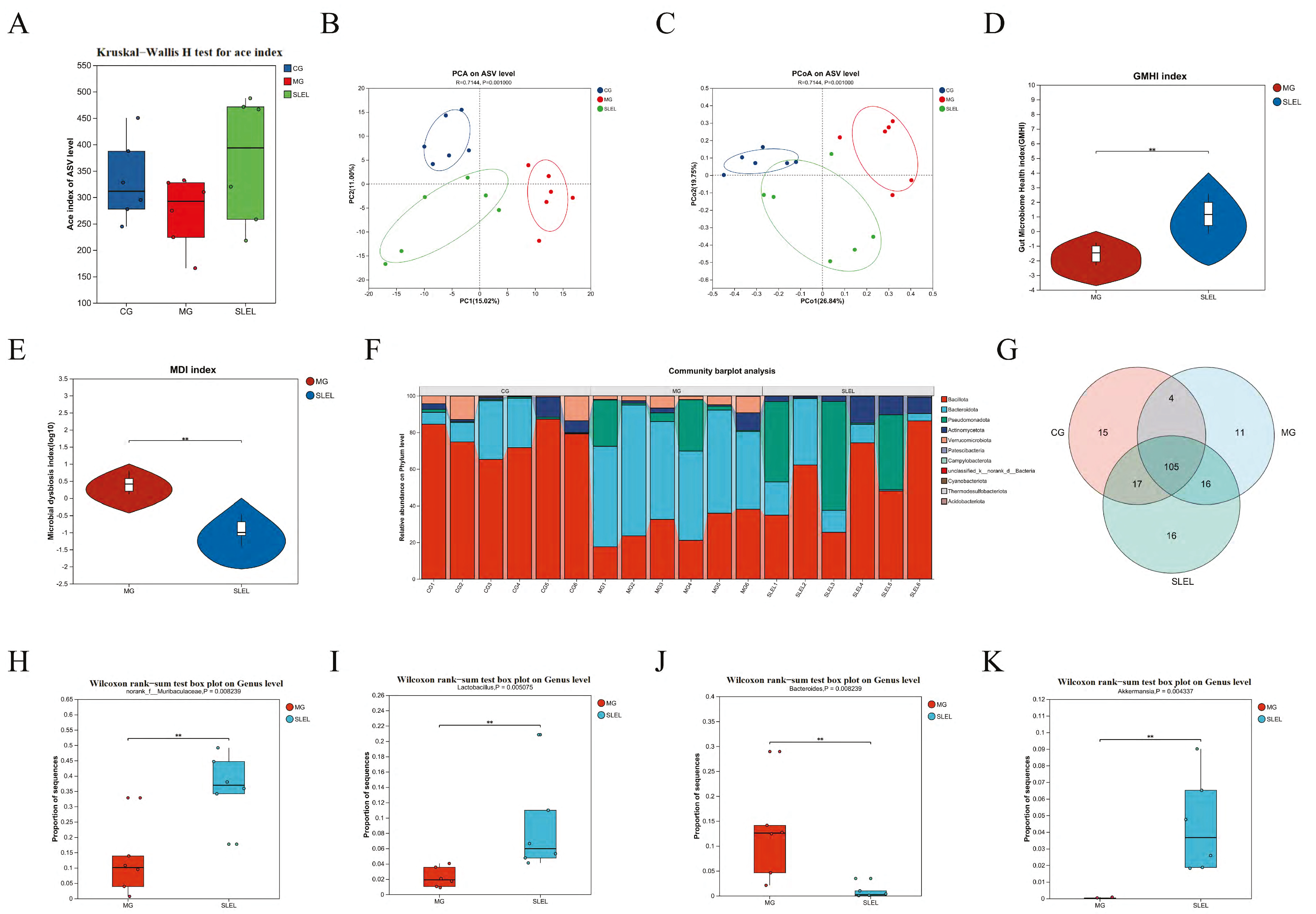
2.7. 16S rRNA Analysis of SLEL’s Impact on Gut Microbiota in ALI
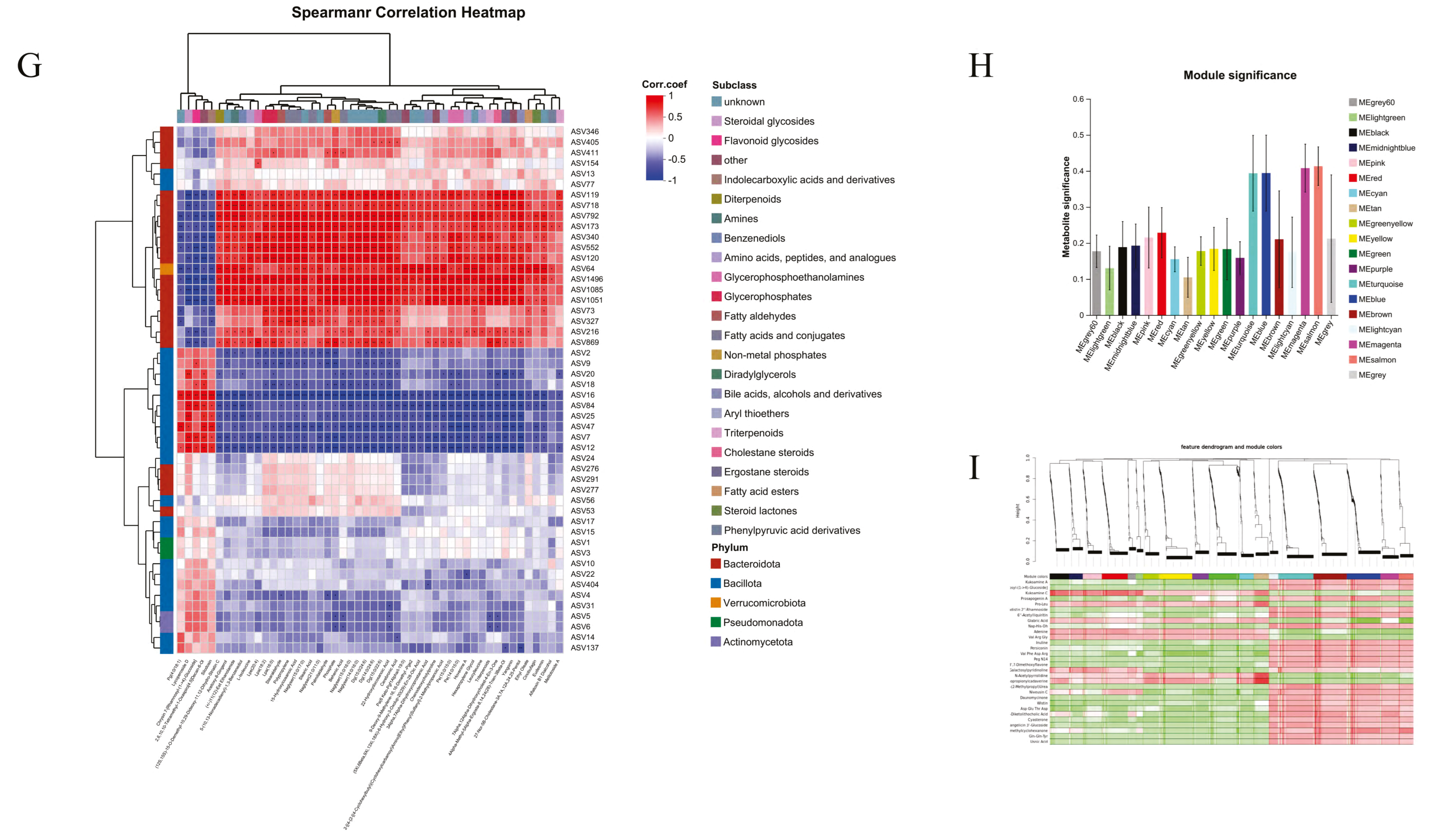
2.8. Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals SLEL’s Anti-ALI Mechanisms
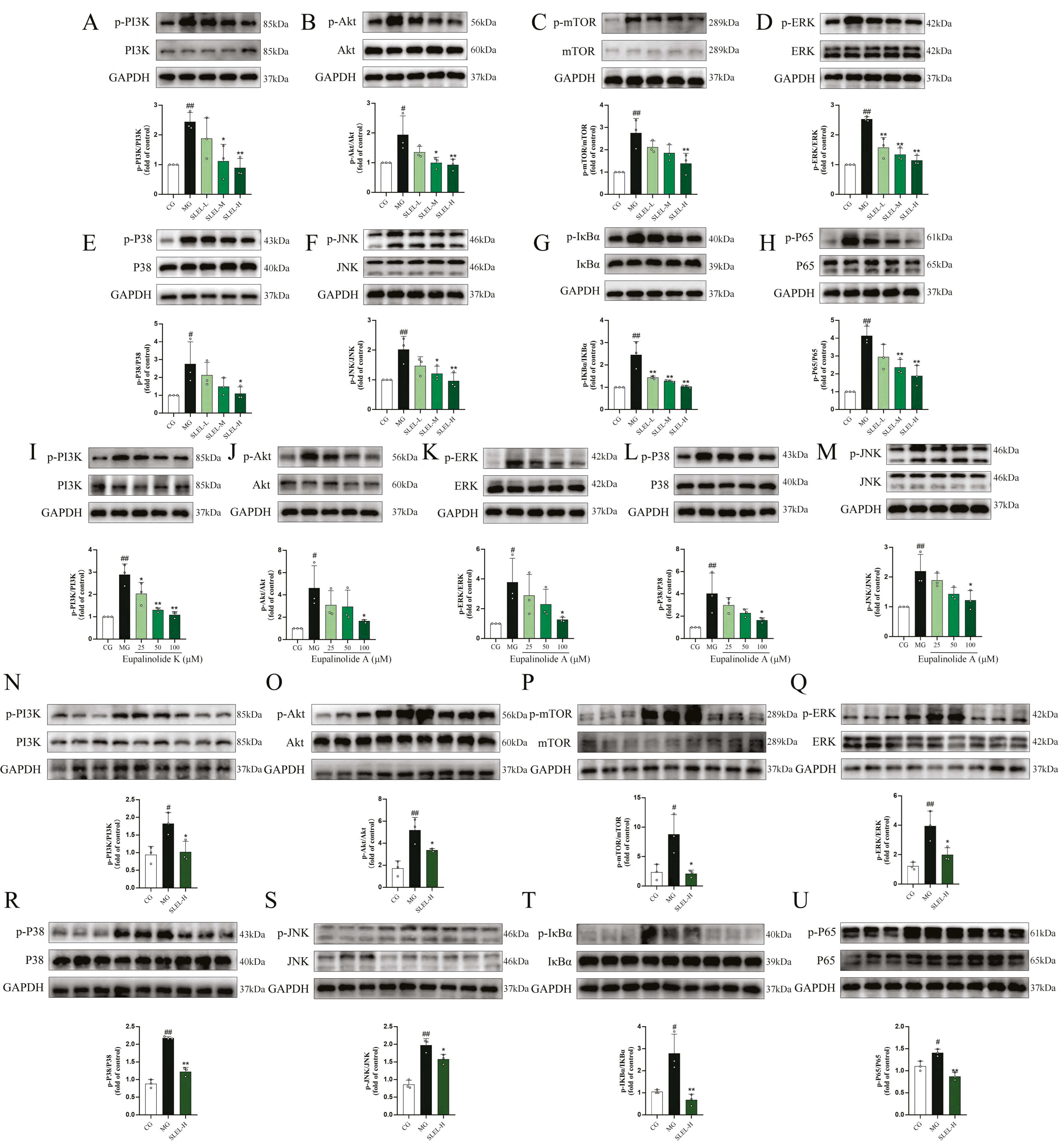
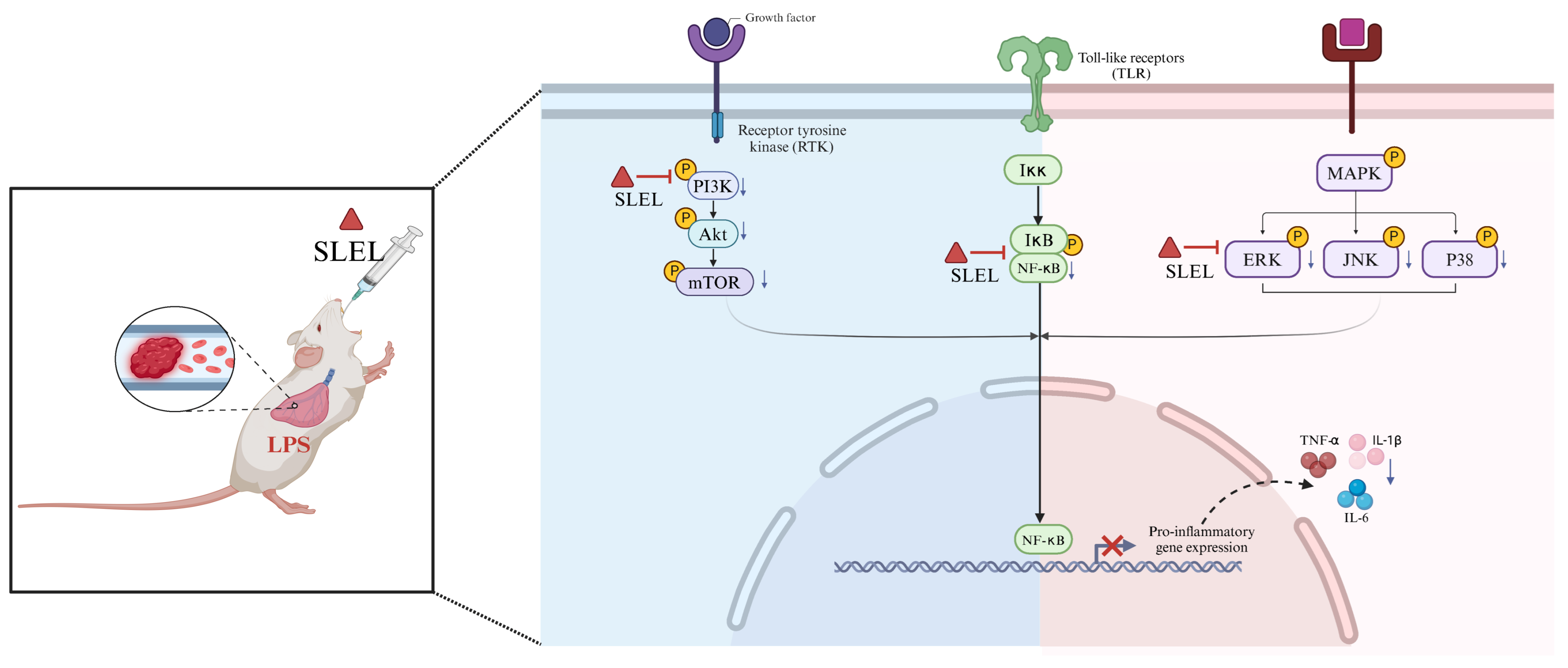
2.9. SLEL Attenuates Inflammation via Dual Suppression of PI3K-Akt and MAPK-NF-κB Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALI | Acute lung injury |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic acid assay |
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit-8 |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ERK | Extracellular regulated protein kinases |
| Go | Gene ontology |
| GSEA | Gene set enrichment analysis |
| IκBα | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B alpha |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PMA | Phorbol myristate acetate |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute |
| SLEL | Sesquiterpenoid lactones of Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese medicine |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| UPLC-QTOF-MS | Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| VIP | Variable importance in projection |
| WGCNA | Weighted gene co-expression network analysis |
References
- Mowery, N.T.; Terzian, W.T.H.; Nelson, A.C. Acute lung injury. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2020, 57, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.T.; Chambers, R.C.; Liu, K.D. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, G.F.; Gatto, L.A.; Habashi, N.M. Impact of mechanical ventilation on the pathophysiology of progressive acute lung injury. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, R.D.; Vaquera, K.; George, T.J. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support for Vaping-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 110, e193–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, J.E.; Matthay, M.A. Clinical review: Early treatment of acute lung injury—Paradigm shift toward prevention and treatment prior to respiratory failure. Crit. Care. 2012, 16, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, K.L.; Stecenko, A.A. Gene therapy for acute lung injury. Intensive Care Med. 2000, 26, S119–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liao, X.; Gao, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, W. Potential pharmaceuticals targeting neuroimmune interactions in treating acute lung injury. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushianthan, A.; Grocott, M.P.; Postle, A.D.; Cusack, R. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury. Postgrad. Med. J. 2011, 87, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Lai, F.; Wang, Y.; Lou, C. Traditional Applications, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Activities of Eupatorium lindleyanum DC.: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 8, 577124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, F.F.; Basting, R.T.; de Freitas, A.S.; Dias Rabelo, L.D.S.; Nonato, F.R.; Zafred, R.R.T.; Sousa, I.M.O.; Queiroz, N.C.A.; Napimoga, J.T.C.; de Carvalho, J.E.; et al. Artemisinin and deoxyartemisinin isolated from Artemisia annua L. promote distinct antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects in an animal model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Chu, C.; Qin, J.J.; Guan, X. Research progress on antitumor mechanisms and molecular targets of Inula sesquiterpene lactones. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, C.; Xue, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, G.; Shan, C.; Ding, N.; Peng, G.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y. Comprehensive Comparison of Three Different Medicinal Parts of Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. Using the RRLC-Q-TOF-MS-Based Metabolic Profile and In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules 2024, 29, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, H.; Xue, Y.; Xianqin, L. Yemazhui (Herba Eupatorii Lindleyani) ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury modulation of the toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa-B/nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 protein signaling pathway and intestinal flora in rats. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 44, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, C.J.; Huang, Y.L.; Huang, W.C.; Yeh, K.W.; Huang, T.Y.; Lin, C.F. Water extract of Helminthostachys zeylanica attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by modulating NF-κB and MAPK pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.C.; Ma, X.G. Effects of TNF-α proliferation and apoptosis of alveolar type II epithelial cells in rats. Acta Med. Univ. Sci. Technol. Huazhong 2020, 49, 673–676. [Google Scholar]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Qi, C.; Feng, F.; Wang, Y.; Di, T.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; et al. Combining network pharmacology, RNA-seq, and metabolomics strategies to reveal the mechanism of Cimicifugae Rhizoma—Smilax glabra Roxb herb pair for the treatment of psoriasis. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Han, P.; Fu, J.; Yu, H.; Xu, H.; Hu, J.C.; Lu, J.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Bu, M.M.; et al. Gut microbiota-based metabolites of Xiaoyao Pills (a typical Traditional Chinese medicine) ameliorate depression by inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase levels in brain. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 313, 116555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Pang, Z. Luteolin inhibits inflammation and M1 macrophage polarization in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced acute pneumonia through suppressing EGFR/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB and EGFR/ERK/AP-1 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2025, 141, 156663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.M. MAP kinase activation in macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, W.; Wu, H. Essential oil from Cinnamomum cassia Presl bark regulates macrophage polarization and ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. Exploring the lung-gut direction of the gut-lung axis in patients with ARDS. Crit. Care. 2024, 28, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ruan, Q. Kukoamine A protects mice against osteoarthritis by inhibiting chondrocyte inflammation and ferroptosis via SIRT1/GPX4 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H. The maca protein ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by modulating the gut microbiota and production of SCFAs. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10329–10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Liu, Y.P.; Dai, J.W.; Bai, Y.; Hu, X.; Azhar, M.; Huang, X.J. The preventive effect and mechanism of Tibetan medicine Aconitum tanguticum (Maxim.) Stapf on acute lung injury. Chin. Med. 2025, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chimenti, L.; Camprubí-Rimblas, M.; Guillamat-Prats, R.; Gomez, M.N.; Tijero, J.; Blanch, L.; Artigas, A. Nebulized Heparin Attenuates Pulmonary Coagulopathy and Inflammation through Alveolar Macrophages in a Rat Model of Acute Lung Injury. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, M.; Chen, X.; Chang, D.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Song, J.; et al. Phytochemical determination and mechanistic investigation of Polygala tenuifolia root (Yuanzhi) extract for bronchitis: UPLC-MS/MS analysis, network pharmacology and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 333, 118418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhou, K.; Liu, C.; Yao, L.; Cao, W.; Luo, X. Multi-Omics and Experimental Insights into the Protective Effects of Sesquiterpenoid Lactones from Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. in Acute Lung Injury: Regulation of PI3K-Akt and MAPK-NF-κB Pathways. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101523
Luo C, Yang Y, Xia L, Zhou K, Liu C, Yao L, Cao W, Luo X. Multi-Omics and Experimental Insights into the Protective Effects of Sesquiterpenoid Lactones from Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. in Acute Lung Injury: Regulation of PI3K-Akt and MAPK-NF-κB Pathways. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101523
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Chen, Yan Yang, Lian Xia, Keyun Zhou, Chuanxin Liu, Ling Yao, Weiguo Cao, and Xianqin Luo. 2025. "Multi-Omics and Experimental Insights into the Protective Effects of Sesquiterpenoid Lactones from Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. in Acute Lung Injury: Regulation of PI3K-Akt and MAPK-NF-κB Pathways" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101523
APA StyleLuo, C., Yang, Y., Xia, L., Zhou, K., Liu, C., Yao, L., Cao, W., & Luo, X. (2025). Multi-Omics and Experimental Insights into the Protective Effects of Sesquiterpenoid Lactones from Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. in Acute Lung Injury: Regulation of PI3K-Akt and MAPK-NF-κB Pathways. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101523





