The Development and Characterization of Layered Pellets Containing a Combination of Amorphized Amlodipine Besylate and Hydrochlorothiazide Using a High-Shear Granulator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
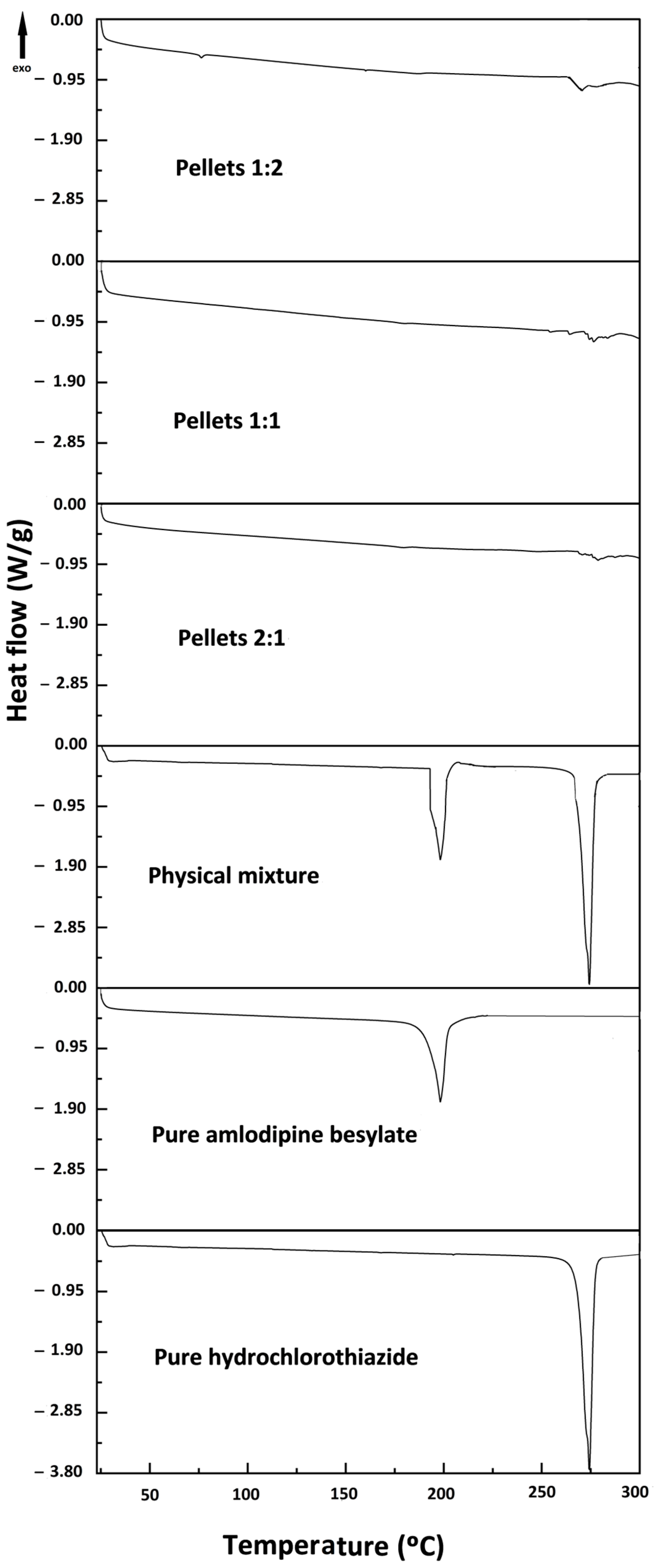
2.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
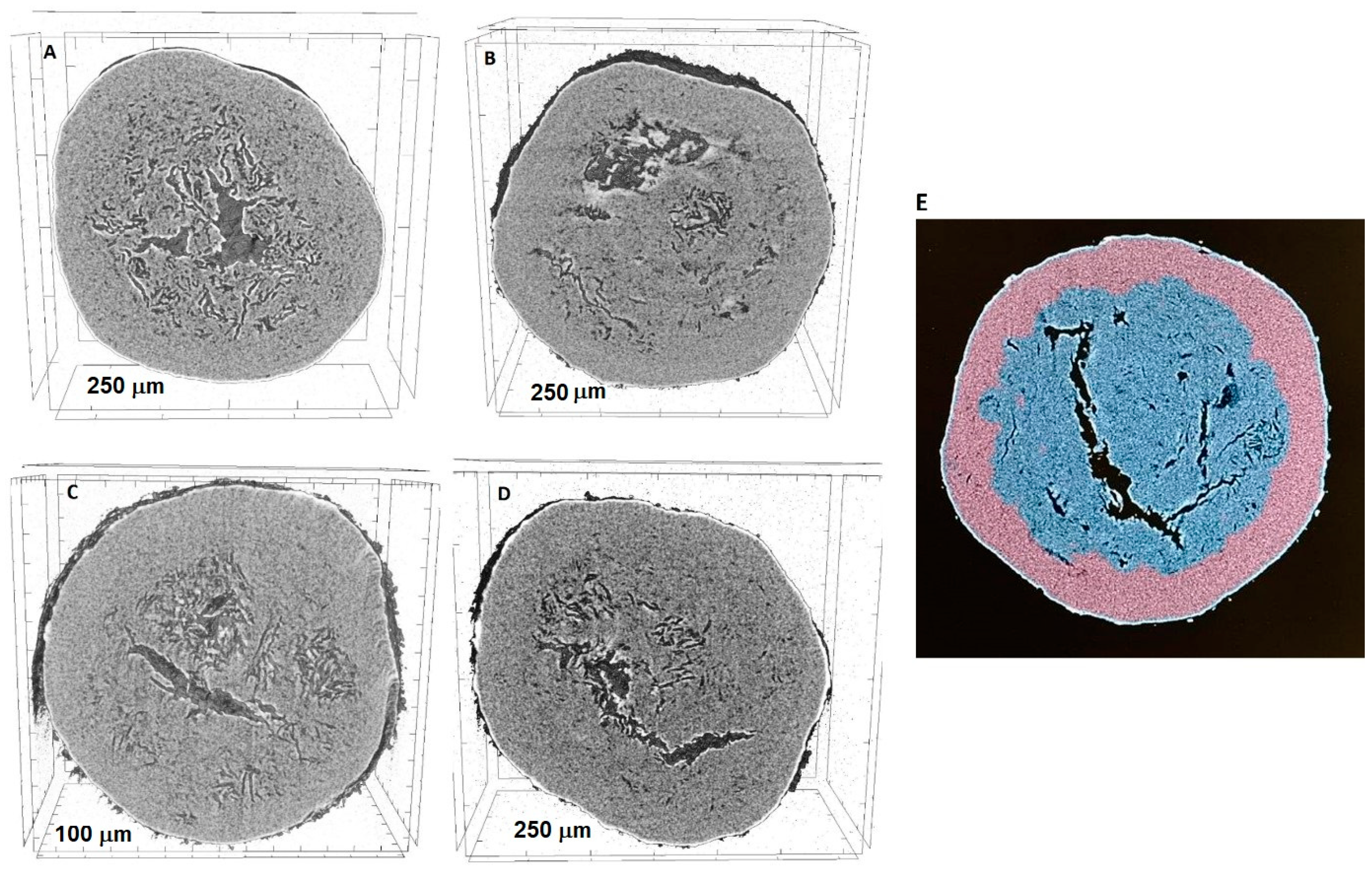
2.3. Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) Measurements
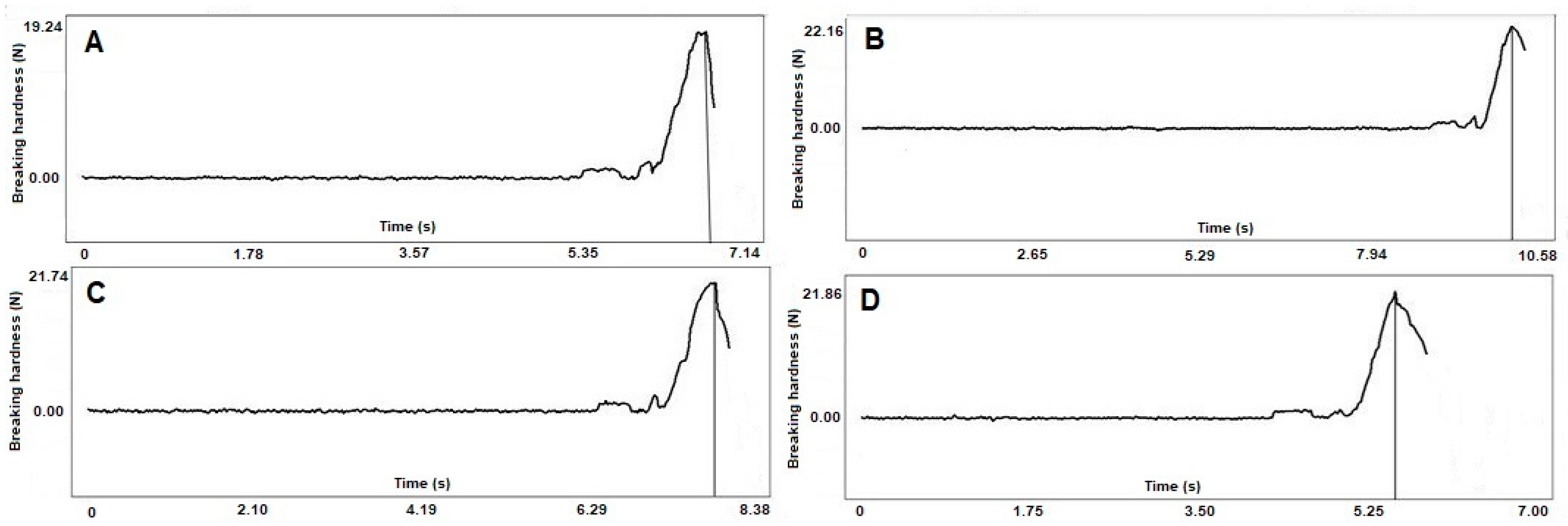
2.4. Hardness and Mechanical Properties
2.5. Dissolution Test
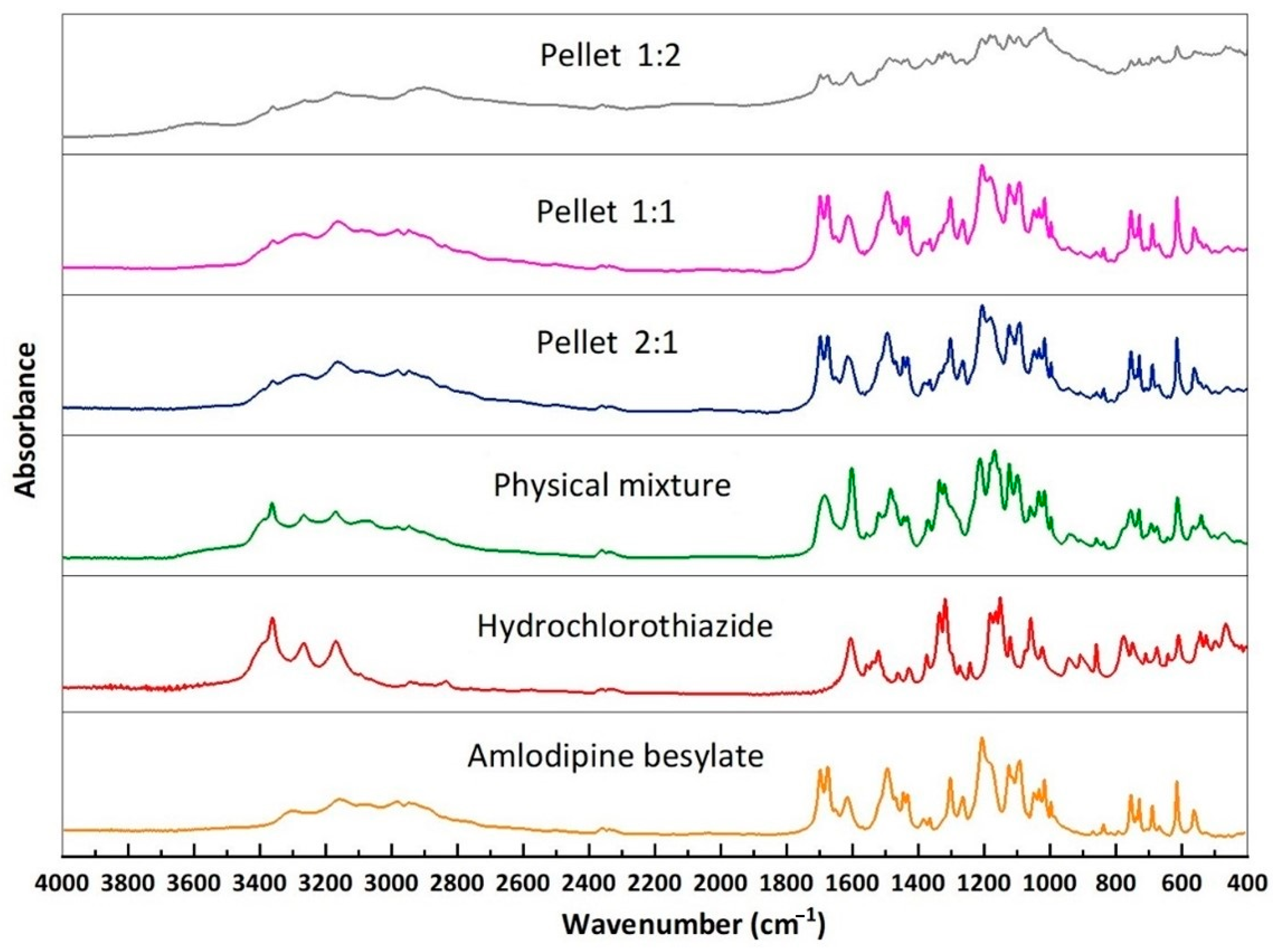
2.6. FTIR
2.7. Stability Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Co-Amorphous Preparation
3.3. Characterization of Layered Pellets
3.3.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.3.2. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
3.3.3. Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) Measurements
3.3.4. Hardness and Mechanical Properties
3.3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.3.6. Dissolution Test
3.3.7. Stability Study
3.3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kondo, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Miura, S.; Niwa, T. Solventless Granulation and Spheronization of Indomethacin Crystals Using a Mechanical Powder Processor: Effects of Mechanically Induced Amorphization on Particle Formation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 154, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Rades, T. Solventless Amorphization and Pelletization Using a High Shear Granulator. Part I.; Feasibility Study Using Indomethacin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 181, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Grohganz, H.; Löbmann, K.; Rades, T.; Hempel, N.-J. Co-Amorphous Drug Formulations in Numbers: Recent Advances in Co-Amorphous Drug Formulations with Focus on Co-Formability, Molar Ratio, Preparation Methods, Physical Stability, In Vitro and In Vivo Performance, and New Formulation Strategies. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Mata, S.; Niwa, T. Solventless-Mixing Particle Coating Using a High Shear Mixer for Preparing Coated Pellets Using Dry Methyl Methacrylate and Diethylaminoethyl Methacrylate Copolymer Latex. Adv. Powder Technol. 2025, 36, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svarcová, M.; Vetchý, D. Pellets preparation by the drug layering technique in a rotary processor. Ceska Slov. Farm. 2007, 56, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Kato, M.; Niwa, T. Solventless-Mixing Layering Using a High Shear Mixer for Preparing Drug Pellets: A Feasibility Study Using Acetaminophen. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 3624–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cal, K.; Mikolaszek, B.; Hess, T.; Papaioannou, M.; Lenik, J.; Ciosek-Skibińska, P.; Wall, H.; Paszkowska, J.; Romanova, S.; Garbacz, G.; et al. The Use of Calcium Phosphate-Based Starter Pellets for the Preparation of Sprinkle IR MUPS Formulation of Rosuvastatin Calcium. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Kido, K.; Niwa, T. Spheronization Mechanism of Pharmaceutical Material Crystals Processed by Extremely High Shearing Force Using a Mechanical Powder Processor. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 107, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kállai-Szabó, N.; Lengyel, M.; Farkas, D.; Barna, Á.T.; Fleck, C.; Basa, B.; Antal, I. Review on Starter Pellets: Inert and Functional Cores. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, J.; Mladenovic, A.; Djuris, J.; Ibric, S. Evaluation of Powder, Solution and Suspension Layering for the Preparation of Enteric Coated Pellets. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 85, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Fernandes, J.; Shaikh, F.; Patel, V. Quality Aspects in the Development of Pelletized Dosage Forms. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyire, A.; Mohammed, A.R. Multiparticulate Systems for Paediatric Drug Delivery. In Multiparticulate Drug Delivery: Formulation, Processing and Manufacturing; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 213–236. ISBN 978-1-4939-7012-4. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Martins, I.C.B.; Rades, T. Recent Advances in Co-Former Screening and Formation Prediction of Multicomponent Solid Forms of Low Molecular Weight Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, L.I.; Grohganz, H.; Palmelund, H.; Löbmann, K.; Rades, T.; Musa, O.M.; Steed, J.W. Predictive Identification of Co-Formers in Co-Amorphous Systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 157, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiman, A.; Higashi, K.; Ueda, K.; Moribe, K. Effect of Drug-Coformer Interactions on Drug Dissolution from a Coamorphous in Mesoporous Silica. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 600, 120492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Song, J.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Tian, B.; He, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, Q. Co-Amorphization of Atorvastatin by Lisinopril as a Co-Former for Solubility Improvement. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhao, P.; Bao, R.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Tang, X.; He, Z.; Fu, Q. Stoichiometric-Dependent Physical Stability of Atorvastatin-Lisinopril Co-Amorphous in Stress Testing. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 139, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, M.; McArdle, P.; Erxleben, A. Dual-Drug Amorphous Formulation of Gliclazide. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koradia, V.; Lopez de Diego, H.; Frydenvang, K.; Ringkjøbing-Elema, M.; Müllertz, A.; Bond, A.D.; Rantanen, J. Solid Forms of Amlodipine Besylate: Physicochemical, Structural, and Thermodynamic Characterization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 5279–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussan, K.P.S.; Thayyil, M.S.; Deshpande, S.K.; Jinitha, T.V.; Manoj, K.; Ngai, K.L. Molecular Dynamics, Physical and Thermal Stability of Neat Amorphous Amlodipine Besylate and in Binary Mixture. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 119, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkhani, R.; Kara, F.E.; Rietveld, I.; Kalfat, R.; Galai, H. The Physical Stability of Co-Amorphous Candesartan-Amlodipine. Chem. Afr. 2025, 8, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanphui, P.; Devi, V.K.; Clara, D.; Malviya, N.; Ganguly, S.; Desiraju, G.R. Cocrystals of Hydrochlorothiazide: Solubility and Diffusion/Permeability Enhancements through Drug–Coformer Interactions. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Duong, T.V.; Phan, D.T. Development and Validation of HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Amlodipine Besylate, Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide in Combined Tablets. MedPharmRes 2023, 7, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, M.A.S.; Souza Dos Santos, R.A.; Sinisterra, R.D. Pharmaceutical Composition of Hydrochlorothiazide:β-Cyclo-Dextrin: Preparation by Three Different Methods, Physico-Chemical Characterization and in Vivo Diuretic Activity Evaluation. Molecules 2011, 16, 4482–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruponen, M.; Rusanen, H.; Laitinen, R. Dissolution and Permeability Properties of Co-Amorphous Formulations of Hydrochlorothiazide. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, X.; Shen, S.; Chen, Q.; Song, S.; Gu, C.; Wang, C. Improved in Vitro and in Vivo Properties of Telmisartan in the Co-Amorphous System with Hydrochlorothiazide: A Potential Drug-Drug Interaction Mechanism Prediction. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 161, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinuddin, S.M.; Ruan, S.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Shi, Q.; Cai, B.; Cai, T. Facile Formation of Co-Amorphous Atenolol and Hydrochlorothiazide Mixtures via Cryogenic-Milling: Enhanced Physical Stability, Dissolution and Pharmacokinetic Profile. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myślińska, M.; Stocker, M.W.; Ferguson, S.; Healy, A.M. A Comparison of Spray-Drying and Co-Precipitation for the Generation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions (ASDs) of Hydrochlorothiazide and Simvastatin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 2097–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysant, S.G.; Chrysant, C.; Trus, J.; Hitchcock, A. Antihypertensive Effectiveness of Amlodipine in Combination with Hydrochlorothiazide. Am. J. Hypertens. 1989, 2, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Party, P.; Bartos, C.; Farkas, Á.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Ambrus, R. Formulation and In Vitro and In Silico Characterization of “Nano-in-Micro” Dry Powder Inhalers Containing Meloxicam. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Party, P.; Soliman, L.; Nagy, A.; Farkas, Á.; Ambrus, R. Optimization, In Vitro, and In Silico Characterization of Theophylline Inhalable Powder Using Raffinose-Amino Acid Combination as Fine Co-Spray-Dried Carriers. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.; Moghadam, T.T.; Ranjbar, B. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Techniques: Applications in Biology and Nanoscience. J. Biomol. Tech. 2010, 21, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maremanda, V.D.; Maertin, D.; Bitar, M.; Pandey, A. Wurster Technology-Assisted Step-by-Step Engineering of Multi-Layered Pellets (Sprinkles): Microscopy, Micro-CT, and e-Tongue-Based Analysis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristó, K.; Csík, E.; Sebők, D.; Kukovecz, Á.; Sovány, T.; Regdon, G.; Csóka, I.; Penke, B.; Pintye-Hódi, K. Effects of the Controlled Temperature in the Production of High-Shear Granulated Protein-Containing Granules. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sántha, K.; Kállai-Szabó, N.; Fülöp, V.; Jakab, G.; Gordon, P.; Kállai-Szabó, B.; Balogh, E.; Antal, I. Comparative Evaluation of Pellet Cushioning Agents by Various Imaging Techniques and Dissolution Studies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 22, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdhani, R.; Bhatt, S.; Amin, P. Review on pelletization: Dry powder layering of pellets using tangential spray rotor processor/insert. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2024, 17, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Ma, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, W. A Drug-Drug Co-Amorphous System for Highly Improved Solubility of Breviscapine: An Experimental and Computational Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xiong, X.; Suo, Z.; Hou, Q.; Gan, N.; Tang, P.; Ding, X.; Li, H. Co-Amorphous Palbociclib-Organic Acid Systems with Increased Dissolution Rate, Enhanced Physical Stability and Equivalent Biosafety. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 3946–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelquader, M.M.; Essa, E.A.; El Maghraby, G.M. Inhibition of Co-Crystallization of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Hydrochlorothiazide for Enhanced Dissolution Rate in Their Fixed Dose Combination. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapourani, A.; Valkanioti, V.; Kontogiannopoulos, K.N.; Barmpalexis, P. Determination of the Physical State of a Drug in Amorphous Solid Dispersions Using Artificial Neural Networks and ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. X 2020, 2, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
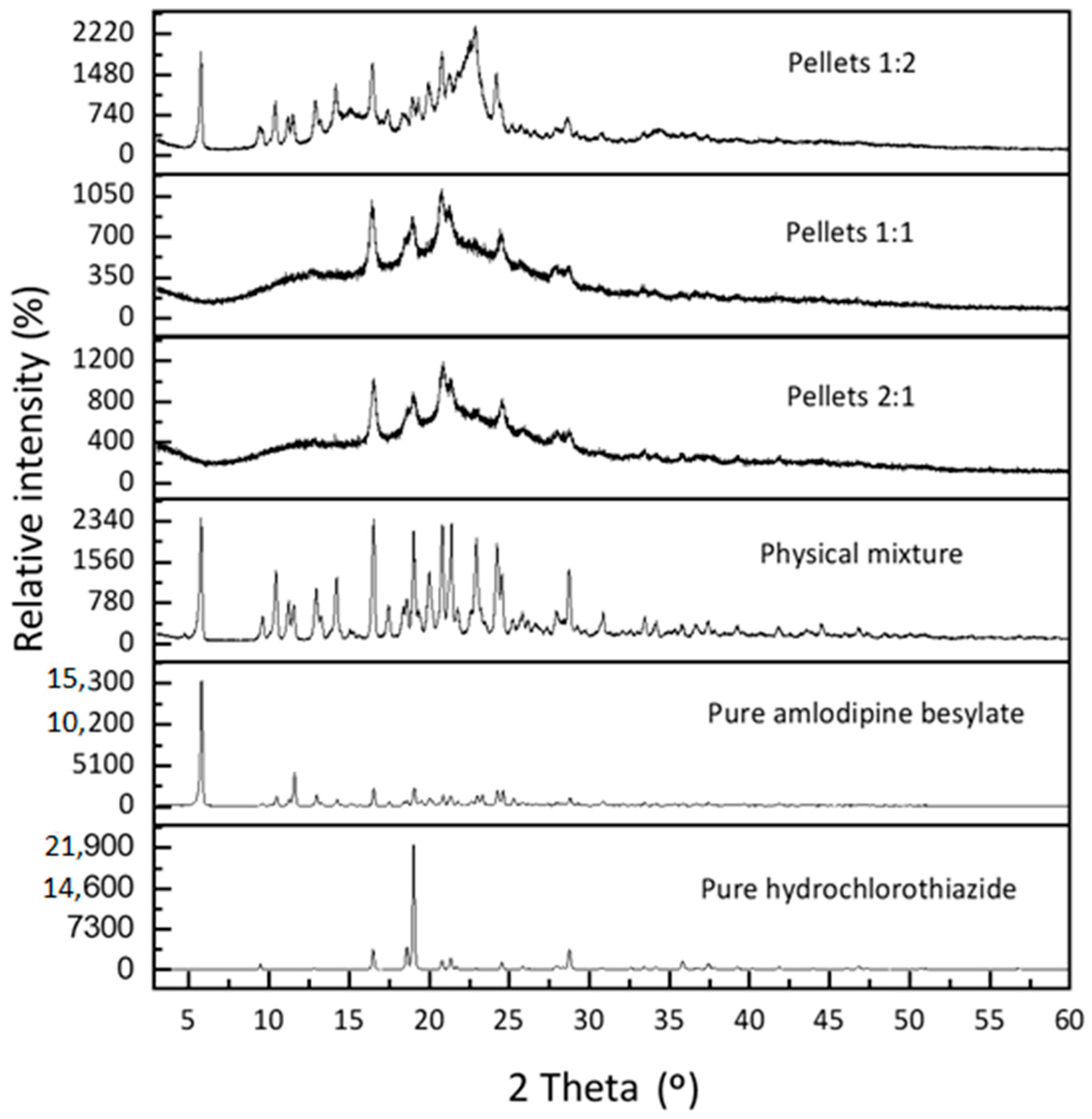

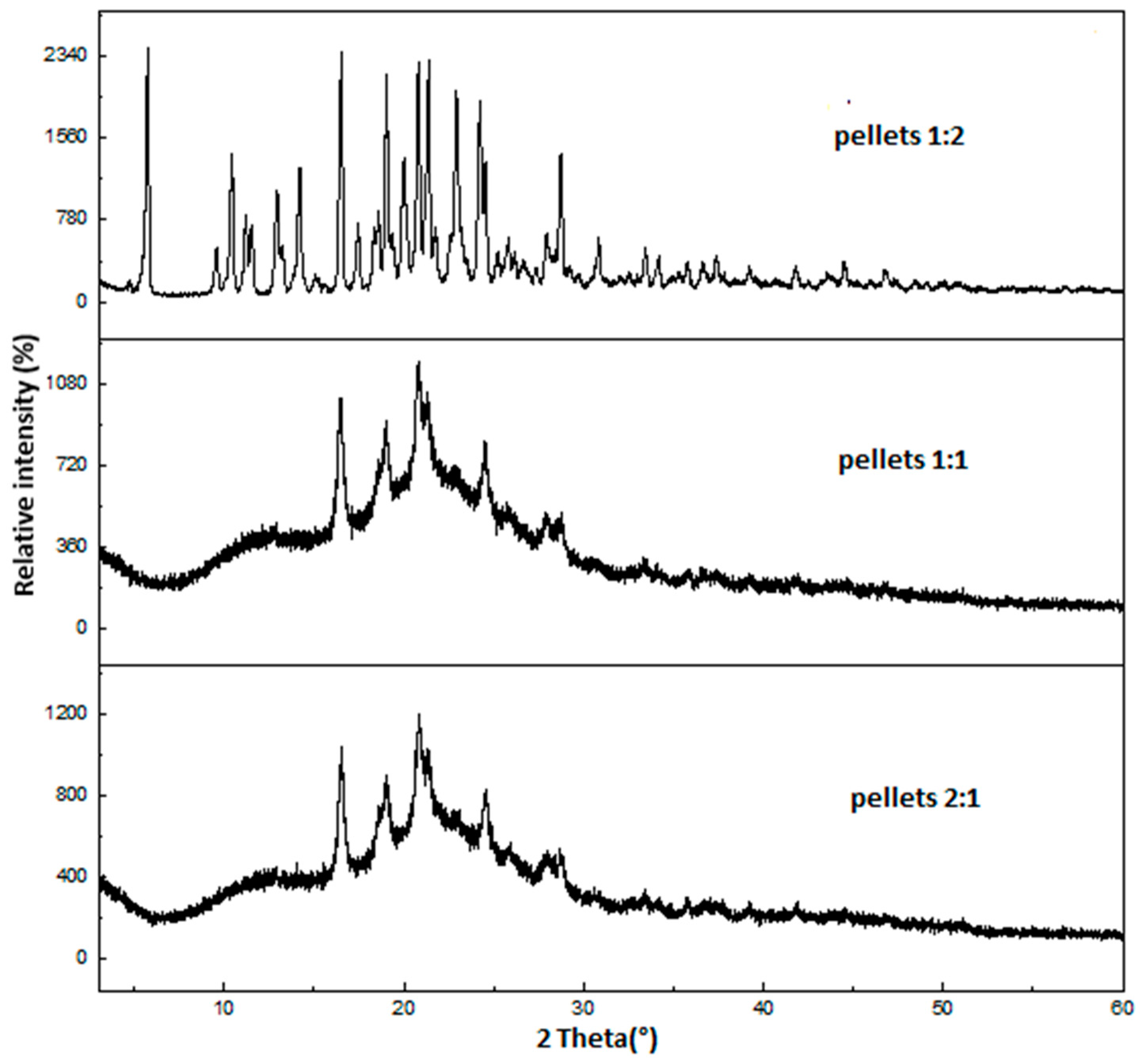
| Samples | Crystallinity Index (%) |
|---|---|
| pure amlodipine besylate | 88.0 |
| pure hydrochlorothiazide | 92.5 |
| physical mixture | 90.2 |
| 1:1 pellet | 33.0 |
| 2:1 pellet | 26.8 |
| 1:2 pellet | 53.6 |
| Samples | Diameter (mm) | Breaking Hardness (N) |
|---|---|---|
| Pure cellet | 1.159 ± 0.042 | 19.871 ± 2.801 |
| 2:1 pellet | 1.282 ± 0.017 | 21.607 ± 3.072 |
| 1:1 pellet | 1.335 ± 0.013 | 21.470 ± 3.220 |
| 1:2 pellet | 1.314 ± 0.074 | 21.820 ± 3.511 |
| Samples | Crystallinity Index (%) at T0 | Crystallinity Index (%) After Stability Test |
|---|---|---|
| 1:1 pellet | 33.0 | 34.0 |
| 2:1 pellet | 26.8 | 29.1 |
| 1:2 pellet | 53.6 | 79.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoud, A.A.K.; Ludasi, K.; Dobó, D.G.; Sebők, D.; Kukovecz, Á.; Hornok, V.; Sajdik, K.; Szabó, T.; Sovány, T.; Regdon, G., Jr.; et al. The Development and Characterization of Layered Pellets Containing a Combination of Amorphized Amlodipine Besylate and Hydrochlorothiazide Using a High-Shear Granulator. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101496
Mahmoud AAK, Ludasi K, Dobó DG, Sebők D, Kukovecz Á, Hornok V, Sajdik K, Szabó T, Sovány T, Regdon G Jr., et al. The Development and Characterization of Layered Pellets Containing a Combination of Amorphized Amlodipine Besylate and Hydrochlorothiazide Using a High-Shear Granulator. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101496
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoud, Azza A. K., Krisztina Ludasi, Dorina Gabriella Dobó, Dániel Sebők, Ákos Kukovecz, Viktória Hornok, Kadosa Sajdik, Tamás Szabó, Tamás Sovány, Géza Regdon, Jr., and et al. 2025. "The Development and Characterization of Layered Pellets Containing a Combination of Amorphized Amlodipine Besylate and Hydrochlorothiazide Using a High-Shear Granulator" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101496
APA StyleMahmoud, A. A. K., Ludasi, K., Dobó, D. G., Sebők, D., Kukovecz, Á., Hornok, V., Sajdik, K., Szabó, T., Sovány, T., Regdon, G., Jr., & Kristó, K. (2025). The Development and Characterization of Layered Pellets Containing a Combination of Amorphized Amlodipine Besylate and Hydrochlorothiazide Using a High-Shear Granulator. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101496










