Novel Dual 5-HT7 Antagonists and Sodium Channel Inhibitors as Potential Therapeutic Agents with Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Activities
Abstract
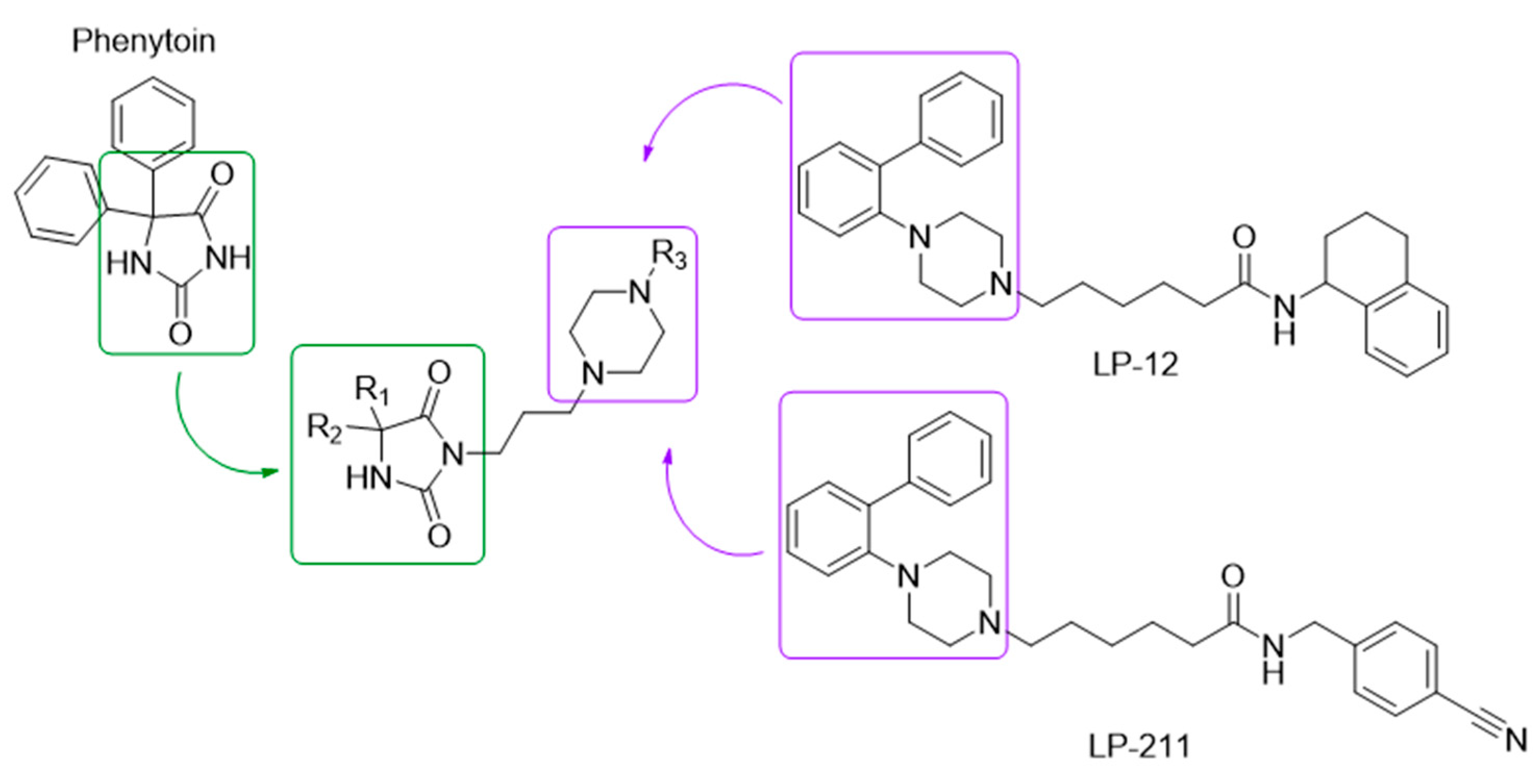
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
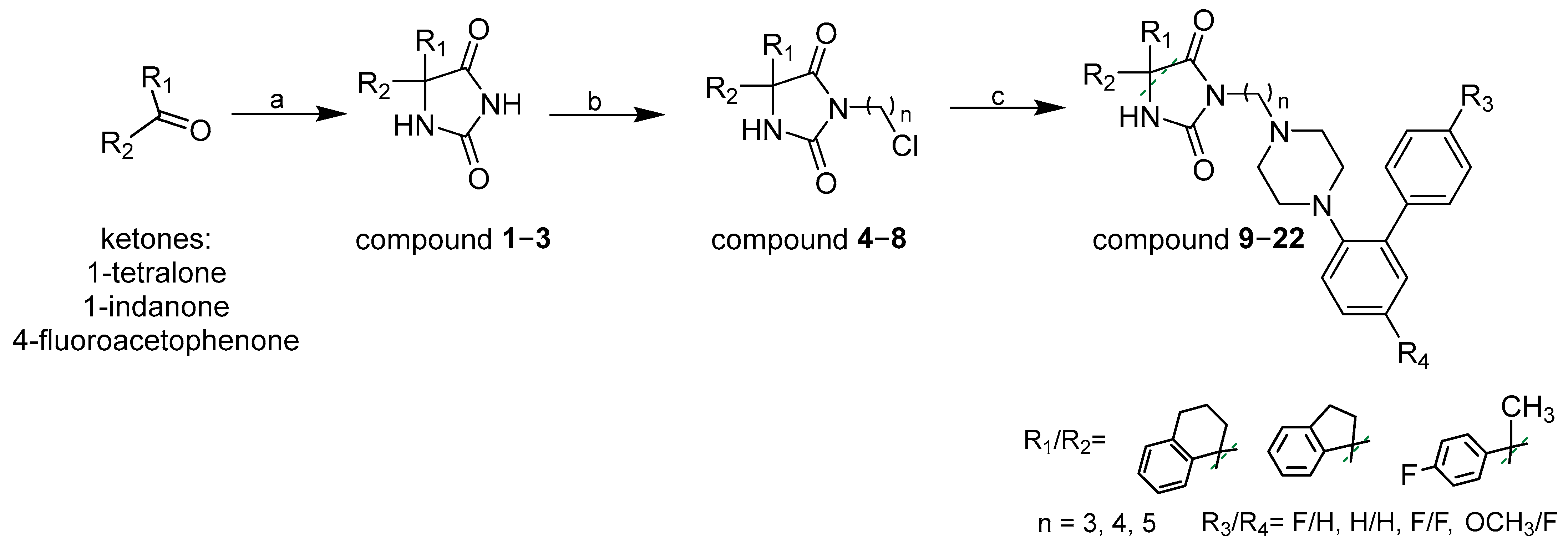
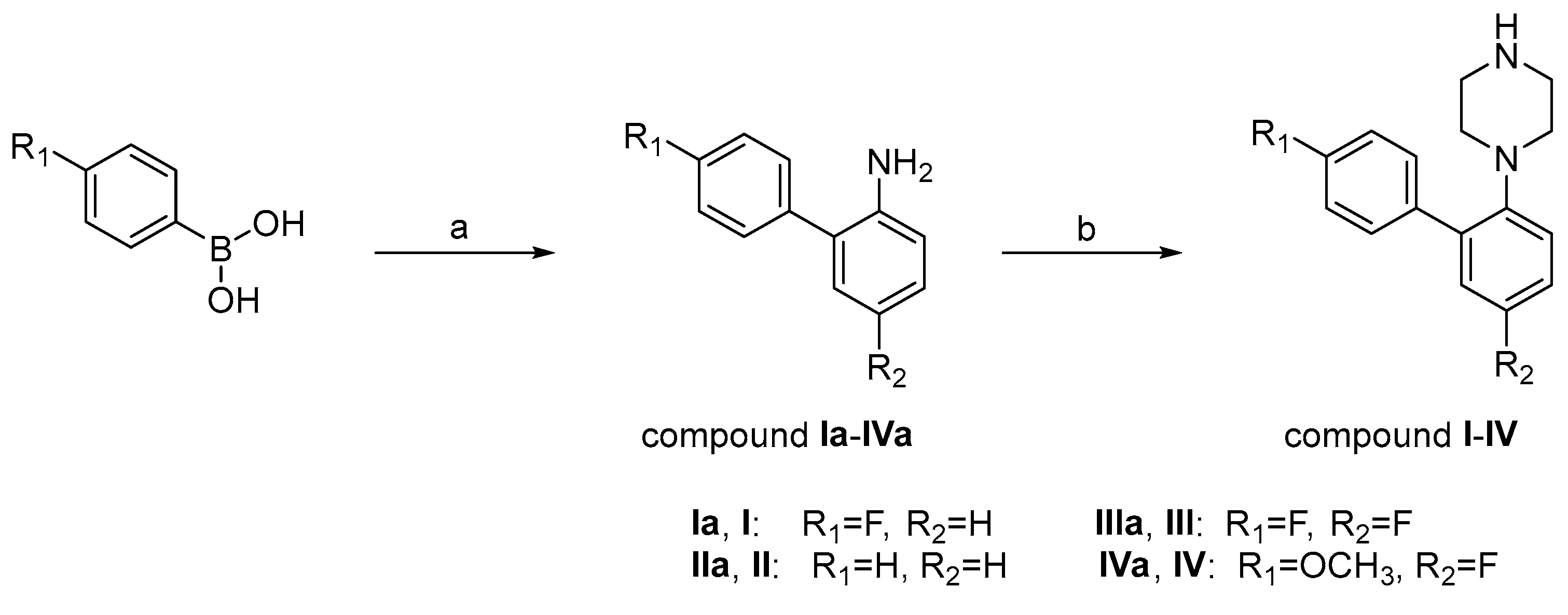
2.1. Chemistry
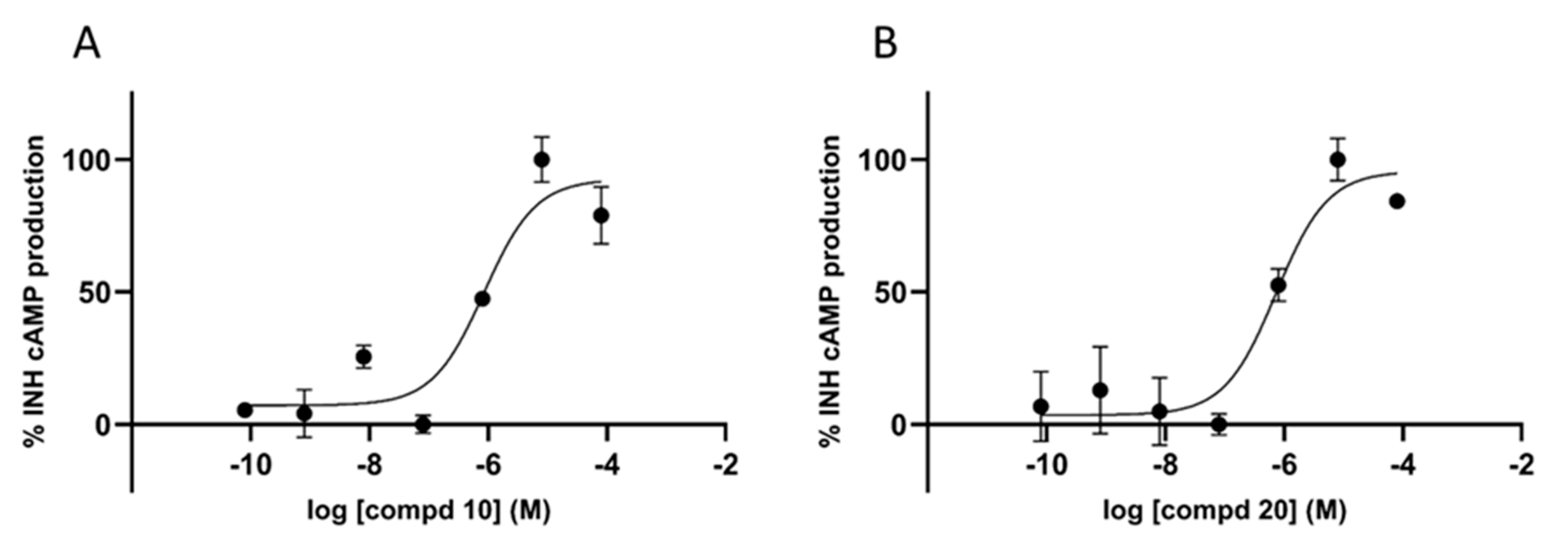
2.2. In Vitro Binding Affinity and Functional Profile for 5-HT7R and Sodium Channels
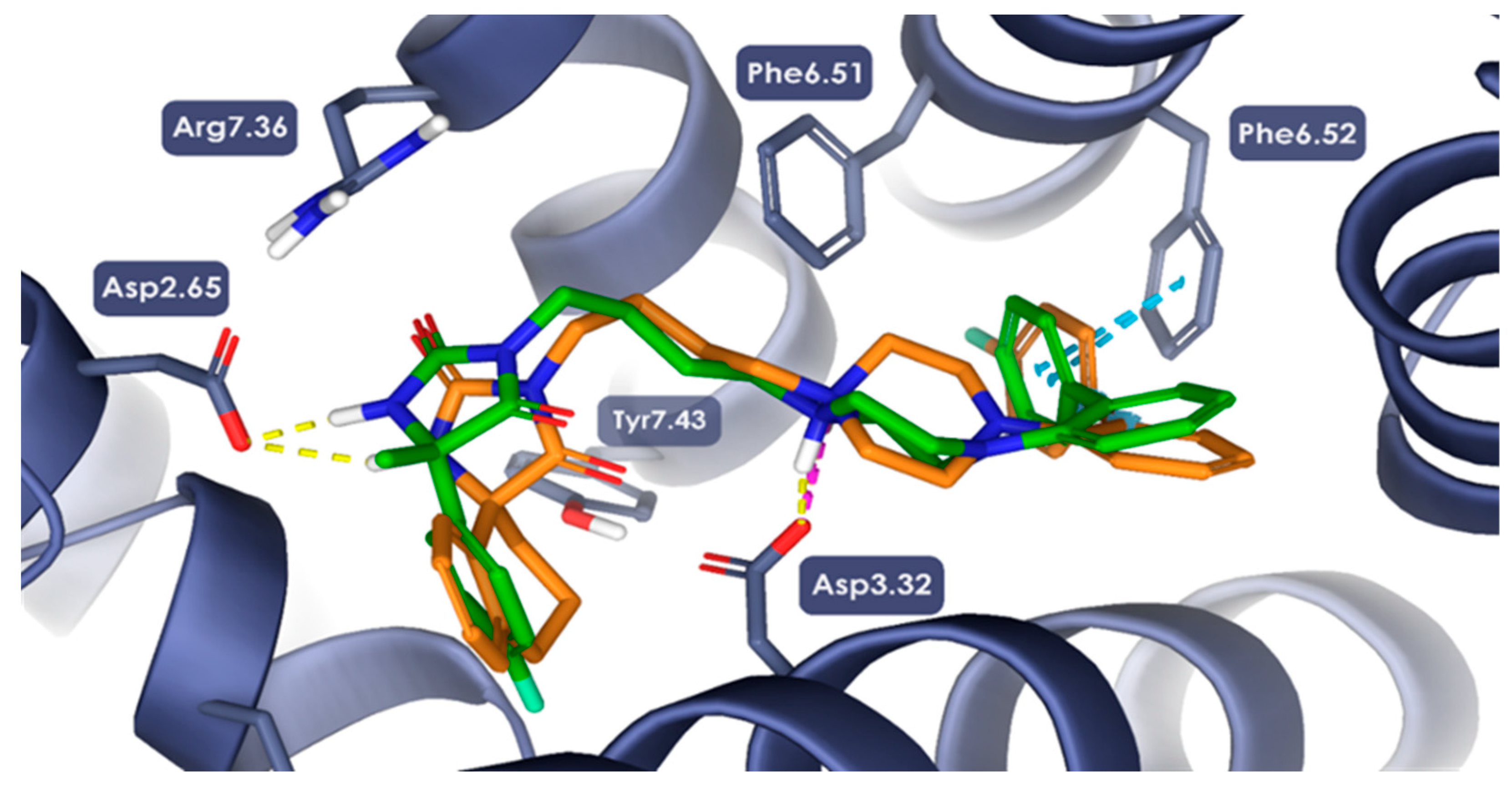
2.3. Molecular Modeling Studies
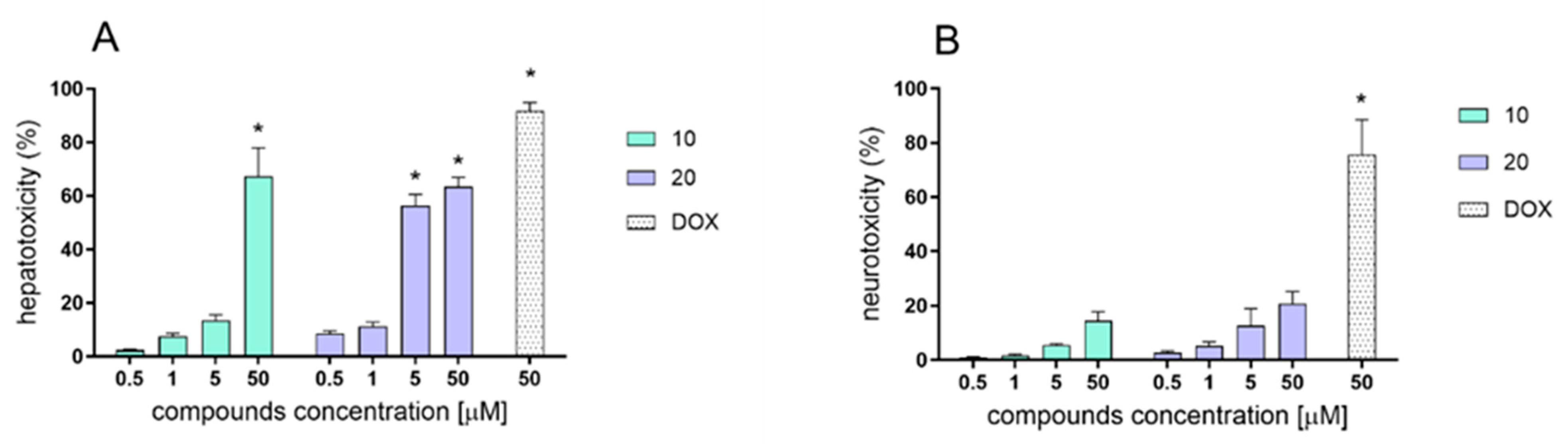
2.4. In Vitro Evaluation of Hepato- and Neurotoxicity Activity
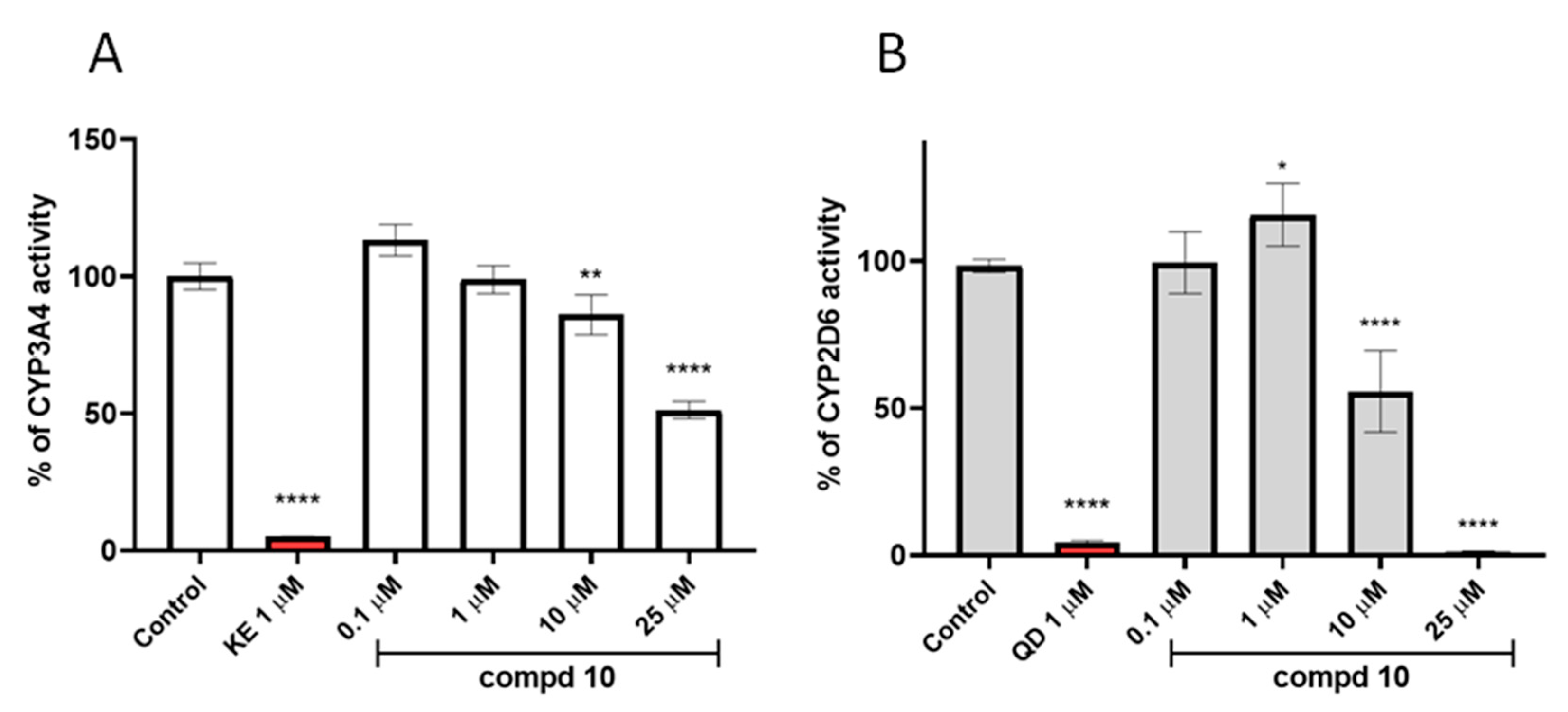
2.5. In Vitro ADME Studies
2.6. In Vivo Pharmacology
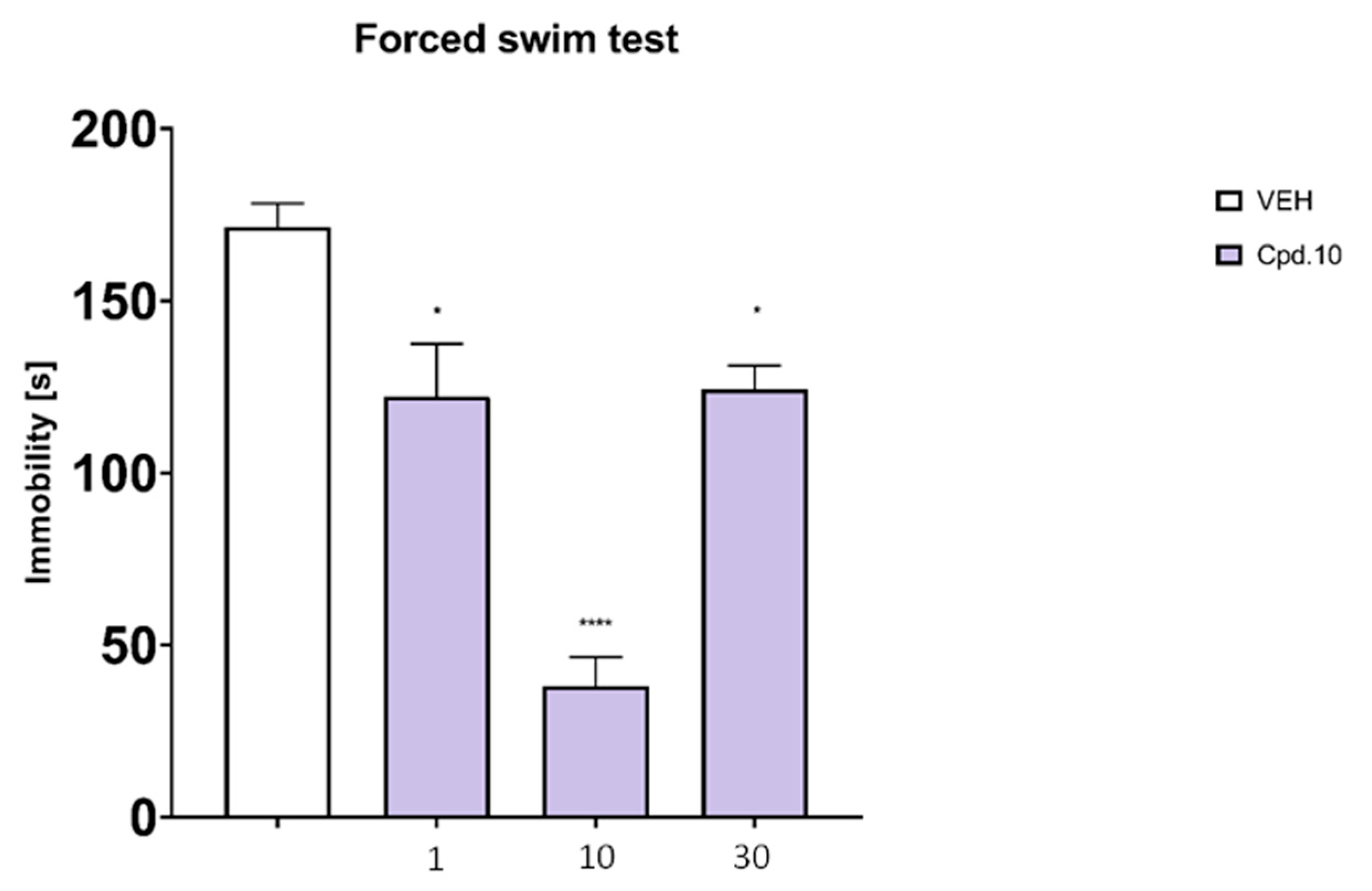
2.6.1. Forced Swim Test
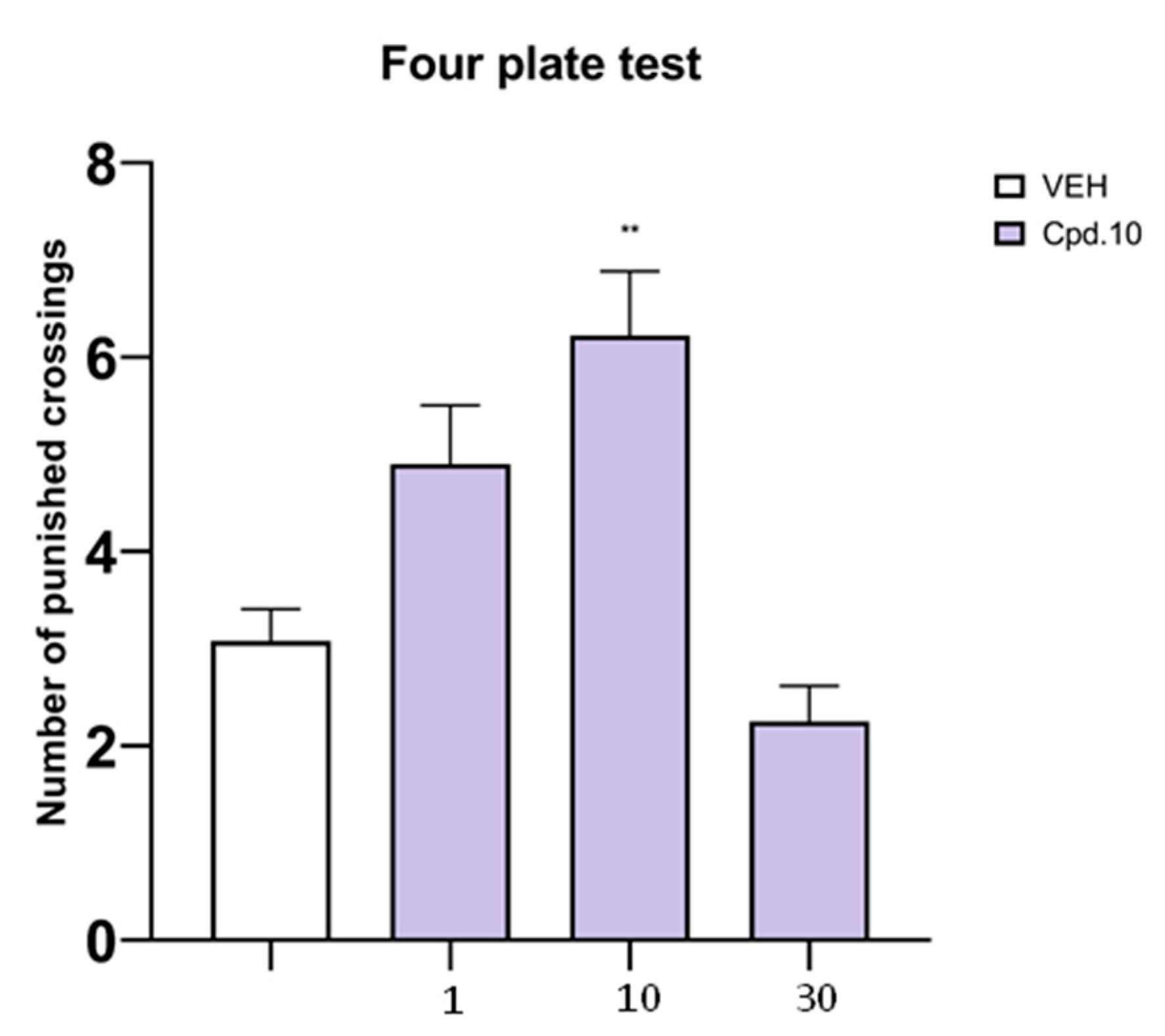
2.6.2. Four-Plate Test
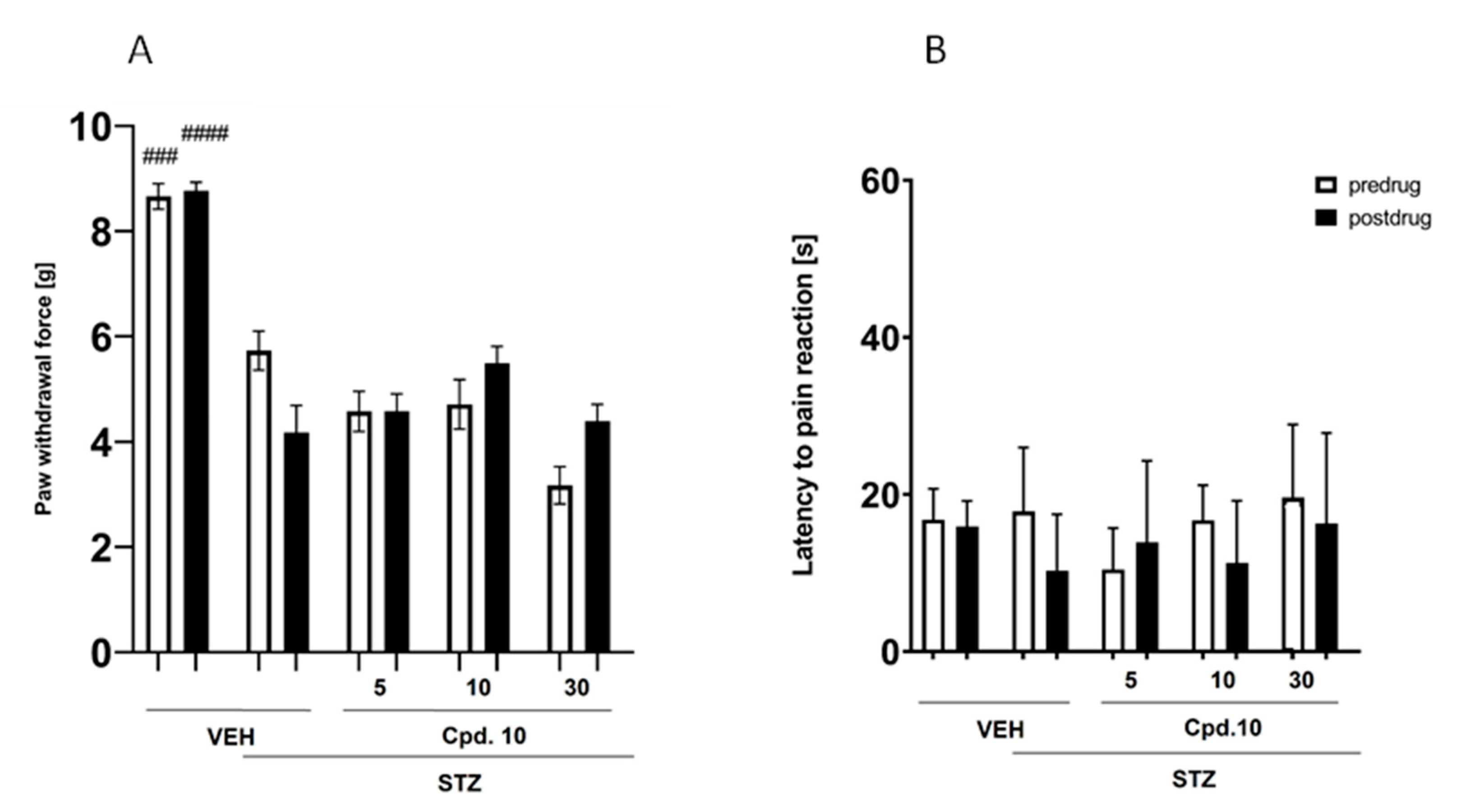
2.6.3. STZ Model of Painful Peripheral Neuropathy
Effect on Blood Glucose Level
Effect on Mechanical Nociceptive Threshold (Von Frey Test)
Effect on Thermal (Heat) Nociceptive Threshold (Hot Plat Test)
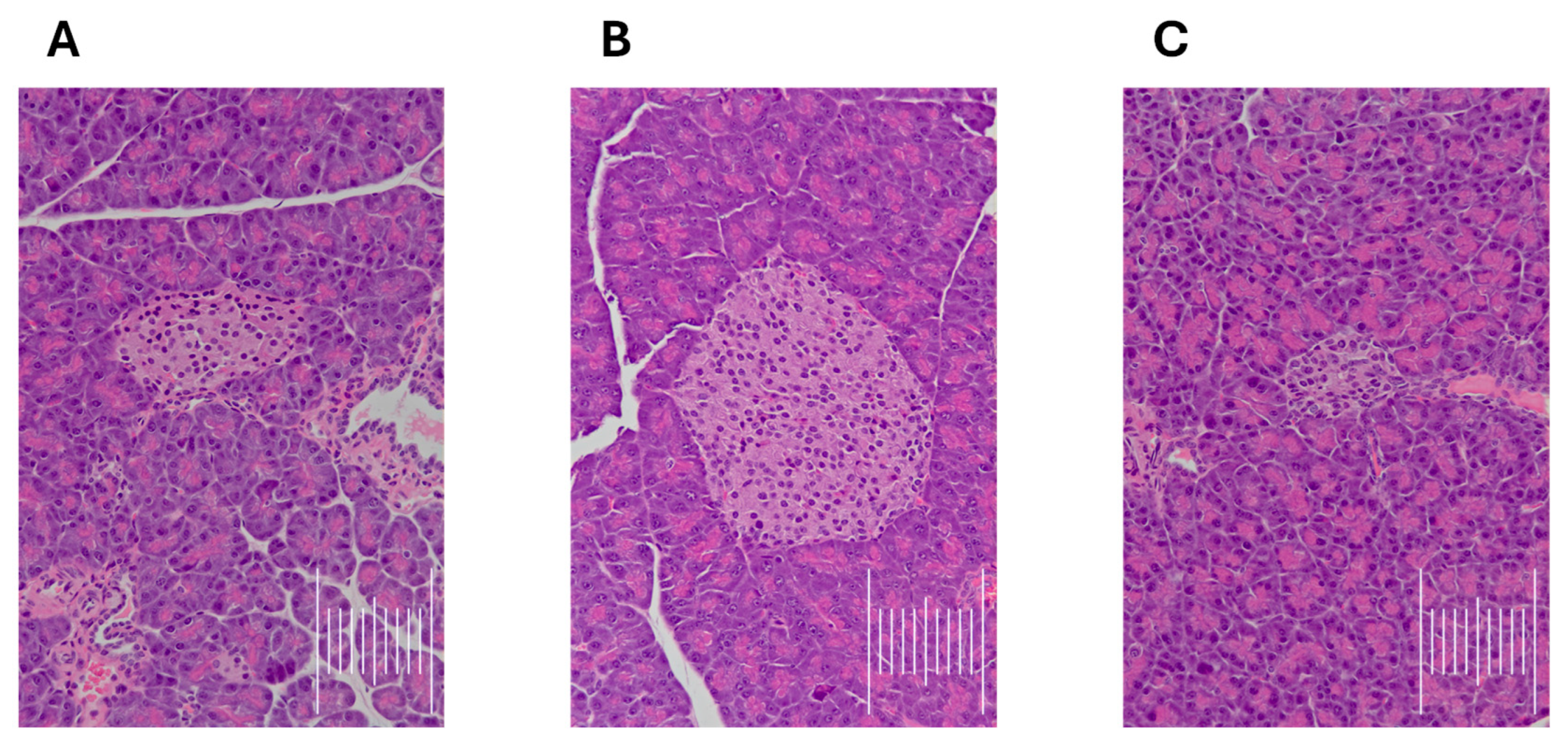
Effect on Pancreatic Cell Architecture and Sciatic Nerve Structure
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of 1-(4′,5-Difluoro-[1,1′-Biphenyl]-2-yl)Piperazine (Compound III)
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Final Compounds (9–22)
- 1-(5-(4-(4′-Fluoro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)pentyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (compound 9).
- 1-(4-(4-(4′-Fluoro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (compound 10).
- 1-(3-(4-(4′-Fluoro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)propyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (compound 11).
- 1-(4-(4-([1,1′-Biphenyl]-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (compound 12).
- 1-(4-(4-(4′,5-Difluorobiphen-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (compound 13).
- 1-(4-(4-(5-Fluoro-4′-methoxybiphen-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (compound 14).
- 1-(4-(4-(4′-Fluoro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-2′,3′-dihydrospiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-indene]-2,5-dione (compound 15).
- 1-(4-(4-([1,1′-Biphenyl]-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-2′,3′-dihydrospiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-indene]-2,5-dione (compound 16).
- 1-(4-(4-(4′,5-Difluorobiphen-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-2′,3′-dihydrospiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-indene]-2,5-dione (compound 17).
- 1-(4-(4-(5-Fluoro-4′-methoxybiphen-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-2′,3′-dihydrospiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-indene]-2,5-dione (compound 18).
- 3-(4-(4-(4′-Fluoro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (compound 19).
- 3-(4-(4-([1,1′-Biphenyl]-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (compound 20).
- 3-(4-(4-(4′,5-Difluorobiphen-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (compound 21).
- 3-(4-(4-(5-Fluoro-4′-methoxybiphen-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)- 5-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (compound 22).
3.2. Functional and Radioligand Binding Assay
3.2.1. Radioligand Binding Assay
3.2.2. Functional Assay for 5-HT7R
3.3. Molecular Modeling Studies
3.4. Cytotoxicity Analysis
3.5. In Vitro ADMET Studies
3.6. Pharmacology In Vivo
3.6.1. Animals and Housing Conditions
3.6.2. Drugs and Dose Selection for the In Vivo Tests
3.6.3. Behavioral Tests
Forced Swim Test (Assessment of Antidepressant-Like Activity)
Four-Plate Test (Assessment of Anxiolytic-Like Activity)
STZ-Induced Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Model (Assessment of Antiallodynic and Antihyperalgesic Activities)
- Induction of Neuropathy—STZ Model (Diabetic Neuropathy Model)
- Effect on the Mechanical Nociceptive Threshold (Von Frey Test)
- Effect on the Heat Nociceptive Threshold (Hot Plate Test)
- Effect on Pancreatic Cell Architecture and Sciatic Nerve Structure
3.6.4. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roughan, W.H.; Campos, A.I.; García-Marín, L.M.; Cuéllar-Partida, G.; Lupton, M.K.; Hickie, I.B.; Medland, S.E.; Wray, N.R.; Byrne, E.M.; Ngo, T.T.; et al. Comorbid Chronic Pain and Depression: Shared Risk Factors and Differential Antidepressant Effectiveness. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 643609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, M.J.; Robinson, R.L.; Katon, W.; Kroenke, K. Depression and Pain Comorbidity: A Literature Review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 2433–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla-Jaime, H.; Sánchez-Salcedo, J.A.; Estevez-Cabrera, M.M.; Molina-Jiménez, T.; Cortes-Altamirano, J.L.; Alfaro-Rodríguez, A. Depression and Pain: Use of Antidepressants. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 20, 384–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, K.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Therapeutic Potential and Limitation of Serotonin Type 7 Receptor Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santello, M.; Bisco, A.; Nevian, N.E.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Nevian, T. The brain-penetrant 5-HT7 receptor agonist LP-211 reduces the sensory and affective components of neuropathic pain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 106, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Wen, S.; Xiao, Z. Antihyperalgesic effect of 5-HT7 receptor activation on the midbrain periaqueductal gray in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 127, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkaya, K.; Akgün, Ö.M.; Senel, B.; Öncel Torun, Z.; Seyrek, M.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Dogrul, A. Selective 5-HT7 receptor agonists LP 44 and LP 211 elicit an analgesic effect on formalin-induced orofacial pain in mice. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2016, 24, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, C.; Lo Russo, S.L.M.; Lacivita, E.; Frank, A.; Alleva, E.; Stark, H.; Saso, L.; Leopoldo, M.; Adriani, W. Prior Activation of 5-HT7 Receptors Modulates the Conditioned Place Preference with Methylphenidate. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 426033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Du, C.X.; Tan, H.H.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.B.; Zhang, J.; Niu, X.L.; Liu, J. Activation and blockade of serotonin7 receptors in the prelimbic cortex regulate depressive-like behaviors in a 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson’s disease rat model. Neuroscience 2015, 311, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, N.C.; Parker, S.A.J.; Hilton, E.J.; Seliman, Y.; Tidgewell, K.J.; Kolber, B.J. Cyanobacterial extract with serotonin receptor subtype 7 (5-HT7R) affinity modulates depression and anxiety-like behavior in mice. Synapse 2018, 72, e22059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldo, M.; Lacivita, E.; Contino, M.; Colabufo, N.A.; Berardi, F.; Perrone, R. Structure-activity relationship study on N-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-4-aryl-1-piperazinehexanamides, a class of 5-HT7 receptor agents. 2. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 4214–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.; Hornbach, A.; Smith, J.E.; Garbaccio, N.C.; Keller, N.; Lemke, J.; Foppiani, J.A.; Gavlasova, D.; Lee, T.C.; Buckley, M.C.; et al. Efficacy of Sodium Channel-Selective Analgesics in Postoperative, Neuralgia, and Neuropathy-Related Pain Management: A Systematic Review and Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunze, H.C.R. The effectiveness of anticonvulsants in psychiatric disorders. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 10, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegazza, M.; Curia, G.; Biagini, G.; Ragsdale, D.S.; Avoli, M. Voltage-gated sodium channels as therapeutic targets in epilepsy and other neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prica, C.; Hascoet, M.; Bourin, M. Antidepressant-like effect of lamotrigine is reversed by veratrine: A possible role of sodium channels in bipolar depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 191, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, E. Lamotrigine: A depression mood stabiliser. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 14, S89–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiroz, R.B.; De Carvalho, F.L.; Da Fonsêca, D.V.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Salgado, P.R.R.; Paulo, L.L.; De Queiroz, A.B.M.; De Morais Pordeus, L.C.; De Souza, S.A.; Da Silva Souza, H.D.; et al. Antinociceptive Effect of Hydantoin 3-Phenyl-5-(4-ethylphenyl)-imidazolidine-2,4-dione in Mice. Molecules 2015, 20, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselink, J.M.K.; Stahl, S.M. Phenytoin in Bipolar Depression: An Old Chapter, but Not Yet Properly Evaluated. J. Mood Disord. Ther. 2019, 1, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishory, A.; Winokur, M.; Bersudsky, Y. Prophylactic effect of phenytoin in bipolar disorder: A controlled study. Bipolar Disord. 2003, 5, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czopek, A.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Bucki, A.; Byrtus, H.; Pawłowski, M.; Kazek, G.; Bojarski, A.J.; Piaskowska, A.; Kalinowska-Tłücik, J.; Partyka, A.; et al. Novel spirohydantoin derivative as a potent multireceptor-active antipsychotic and antidepressant agent. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3436–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czopek, A.; Zagorska, A.; Kolaczkowski, M.; Bucki, A.; Gryzlo, B.; Rychtyk, J.; Pawlowsk, M.; Siwek, A.; Satala, G.; Bojarski, A.; et al. New Spirohydanoin Derivatives—Synthesis, Pharmacological Evaluation, and Molecular Modeling Study. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Jaromin, A.; Czopek, A.; Parapini, S.; Basilico, N.; Misiak, E.; Gubernator, J.; Zagórska, A. Synthesis and antiplasmodial activity of novel bioinspired imidazolidinedione derivatives. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczor, A.; Szemerédi, N.; Kucwaj-Brysz, K.; Dąbrowska, M.; Starek, M.; Latacz, G.; Spengler, G.; Handzlik, J. Computer-Aided Search for 5-Arylideneimidazolone Anticancer Agents Able to Overcome ABCB1-Based Multidrug Resistance. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 2386–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, V.M.; Bharucha, D.B.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Dorian, P.; Kowey, P.R. Results of a curtailed randomized controlled trial, evaluating the efficacy and safety of azimilide in patients with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: The SHIELD-2 trial. Am. Heart J. 2017, 185, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Saad, F.; Chowdhury, S.; Oudard, S.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Graff, J.N.; Olmos, D.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide Treatment and Metastasis-free Survival in Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. (Ed.) Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 3123–3126. [Google Scholar]
- Miyaura, N.; Suzuki, A. Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions of Organoboron Compounds. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacivita, E.; Podlewska, S.; Speranza, L.; Niso, M.; Satała, G.; Perrone, R.; Perrone-Capano, C.; Bojarski, A.J.; Leopoldo, M. Structural modifications of the serotonin 5-HT7 receptor agonist N-(4-cyanophenylmethyl)-4-(2-biphenyl)-1-piperazinehexanamide (LP-211) to improve in vitro microsomal stability: A case study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 120, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacivita, E.; Patarnello, D.; Stroth, N.; Caroli, A.; Niso, M.; Contino, M.; De Giorgio, P.; Di Pilato, P.; Colabufo, N.A.; Berardi, F.; et al. Investigations on the 1-(2-biphenyl)piperazine motif: Identification of new potent and selective ligands for the serotonin 7 (5-HT 7) receptor with agonist or antagonist action in vitro or ex vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6375–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, P.B.; Leopoldo, M.; Caccia, S.; Sarkisyan, G.; Fracasso, C.; Martelli, G.; Lacivita, E.; Berardi, F.; Perrone, R. LP-211 is a brain penetrant selective agonist for the serotonin 5-HT7 receptor. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 481, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modica, M.N.; Lacivita, E.; Intagliata, S.; Salerno, L.; Romeo, G.; Pittalà, V.; Leopoldo, M. Structure-Activity Relationships and Therapeutic Potentials of 5-HT7 Receptor Ligands: An Update. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8475–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołaczkowski, M.; Nowak, M.; Pawłowski, M.; Bojarski, A.J. Receptor-based pharmacophores for serotonin 5-HT7R antagonists—Implications to selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6732–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, R.A.; Sallander, J.; Benhamú, B.; Porras, E.; Campillo, M.; Pardo, L.; López-Rodríguez, M.L. Synthesis of new serotonin 5-HT7 receptor ligands. Determinants of 5-ht7/5-ht1a receptor selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2384–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, N.; Li, T.Y.; Young, A.H.; Stokes, P.R.A. The 5-HT7 receptor system as a treatment target for mood and anxiety disorders: A systematic review. J. Psychopharmacol. 2023, 37, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytka, K.; Partyka, A.; Jastrzębska-Więsek, M.; Siwek, A.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; Mordyl, B.; Kazek, G.; Rapacz, A.; Olczyk, A.; Gałuszka, A.; et al. Antidepressant- and Anxiolytic-Like Effects of New Dual 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 Antagonists in Animal Models. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, J.R.; Calabreso, J.R.; Goodwin, G.M. Lamotrigine for treatment of bipolar depression: Independent meta-analysis and meta-regression of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Br. J. Psychiatry 2009, 194, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, N.; Doly, S.; Courteix, C. Diabetic Neuropathic Pain and Serotonin: What Is New in the Last 15 Years? Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulugol, A.; Oltulu, C.; Gunduz, O.; Citak, C.; Carrara, R.; Shaqaqi, M.R.; Sanchez, A.M.; Dogrul, A. 5-HT7 receptor activation attenuates thermal hyperalgesia in streptozocin-induced diabetic mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, S.; Marrison, S.T.; Haley, S. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Prevention and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2024, 109, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.; Shakarwal, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Jaju, B.P. Effect of mianserin on blood glucose level in rabbits. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1993, 37, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Hisaoka-Nakashima, K.; Morioka, N. Blockade of receptor for advanced glycation end-products with azeliragon ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathy. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 163, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, H.; Yonemochi, N.; Ardianto, C.; Yang, L.; Kamei, J. Pregabalin increases food intake through dopaminergic systems in the hypothalamus. Brain Res. 2018, 1701, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crucitti, A.; Zhang, Q.; Nilsson, M.; Brecht, S.; Yang, C.R.; Wernicke, J. Duloxetine treatment and glycemic controls in patients with diagnoses other than diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: A meta-analysis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung-Chi, C.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (KI) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.B. 3H-batrachotoxinin-A benzoate binding to voltage-sensitive sodium channels: Inhibition by the channel blockers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. J. Neurosci. 1986, 6, 2064–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wuyun, Q.; Freddolino, P.L.; Zhang, Y. Integrating deep learning, threading alignments, and a multi-MSA strategy for high-quality protein monomer and complex structure prediction in CASP15. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2023, 91, 1684–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałat, K.; Gawlik, K.; Witalis, J.; Pawlica-Gosiewska, D.; Filipek, B.; Solnica, B.; Więckowski, K.; Malawska, B. Evaluation of antinociceptive and antioxidant properties of 3-[4-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-dihydrofuran-2-one in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2013, 386, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Anton, G.; Blavet, N.; Jalfre, M. Behavioural despair in rats: A new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1978, 47, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourin, M.; Masse, F.; Dailly, E.; Hascoët, M. Anxiolytic-like effect of milnacipran in the four-plate test in mice: Mechanism of action. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 81, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
| Compd | R1/R2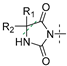 | n | R3/R4 | 5-HT7 Ki [nM] ± SD | Na+ Channel (Site 2): % Inhibition of Control Specific Binding 100/10/1 [µM] * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 |  | 5 | F/H | 6 ± 1 | 55.6/-/- |
| 10 |  | 4 | F/H | 8 ± 2 | 107.2/99.3/88.6 |
| 11 |  | 3 | F/H | 46 ± 11 | 83.6/-/- |
| 12 |  | 4 | H/H | 14 ± 2 | -/-/- |
| 13 |  | 4 | F/F | 81 ± 18 | -/-/- |
| 14 |  | 4 | F/OCH3 | 143 ± 23 | -/-/- |
| 15 |  | 4 | F/H | 17 ± 3 | -/-/- |
| 16 |  | 4 | H/H | 12 ± 2 | -/-/- |
| 17 |  | 4 | F/F | 46 ± 11 | -/-/- |
| 18 |  | 4 | F/OCH3 | 47 ± 7 | -/-/- |
| 19 | 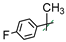 | 4 | F/H | 34 ± 5 | -/-/- |
| 20 | 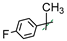 | 4 | H/H | 5 ± 1 | -/97.8/83.0 |
| 21 | 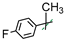 | 4 | F/F | 131 ± 12 | -/-/- |
| 22 |  | 4 | F/OCH3 | 65 ± 4 | -/-/- |
| LP-211 ** | - | - | - | 15 ± 1 | -/-/- |
| PHE *** | - | - | - | - | 53.9/-/- |
| Compd/Drug | Molecular Mass (m/z) | % Remaining | Molecular Mass of the Metabolite (m/z) | Metabolic Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 527.31 | 50.18 | 543.33 (M1) 257.18 (M2) 543.33 (M3) 559.30 (M4) 273.15 (M5) | hydroxylation decomposition hydroxylation dihydroxylation decomposition |
| Verapamil | 455.31 | 30.80% | 441.35 (M1) 291.32 (M2) 165.09 (M3) 441.29 (M4) 427.33 (M5) 277.26 (M6) | demethylation defragmentation defragmentation demethylation didemethylation defragmentation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czopek, A.; Koczurkiewicz-Adamczyk, P.; Wójcik-Pszczoła, K.; Kornas, D.; Sitko, W.; Bucki, A.; Sapa, M.; Kamiński, K.; Satała, G.; Duszyńska, B.; et al. Novel Dual 5-HT7 Antagonists and Sodium Channel Inhibitors as Potential Therapeutic Agents with Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Activities. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101485
Czopek A, Koczurkiewicz-Adamczyk P, Wójcik-Pszczoła K, Kornas D, Sitko W, Bucki A, Sapa M, Kamiński K, Satała G, Duszyńska B, et al. Novel Dual 5-HT7 Antagonists and Sodium Channel Inhibitors as Potential Therapeutic Agents with Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Activities. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101485
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzopek, Anna, Paulina Koczurkiewicz-Adamczyk, Katarzyna Wójcik-Pszczoła, Daria Kornas, Wojciech Sitko, Adam Bucki, Michał Sapa, Krzysztof Kamiński, Grzegorz Satała, Beata Duszyńska, and et al. 2025. "Novel Dual 5-HT7 Antagonists and Sodium Channel Inhibitors as Potential Therapeutic Agents with Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Activities" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101485
APA StyleCzopek, A., Koczurkiewicz-Adamczyk, P., Wójcik-Pszczoła, K., Kornas, D., Sitko, W., Bucki, A., Sapa, M., Kamiński, K., Satała, G., Duszyńska, B., Bojarski, A. J., Latacz, G., Czopek, J., Szpor, J., Dryja, P., & Sałat, K. (2025). Novel Dual 5-HT7 Antagonists and Sodium Channel Inhibitors as Potential Therapeutic Agents with Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Activities. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101485








