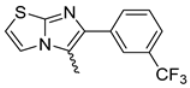
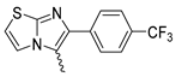
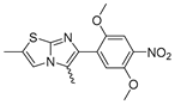
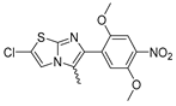
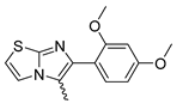
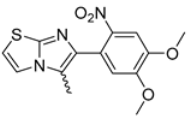
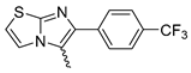
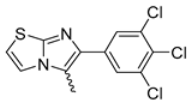
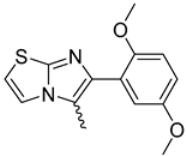
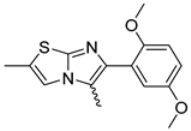
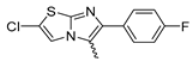
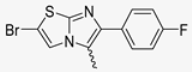
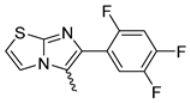
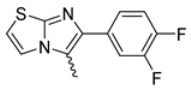
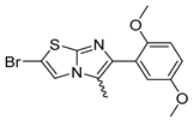
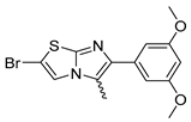
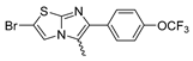
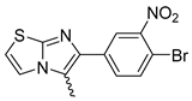
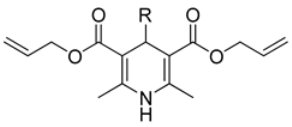
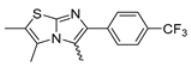
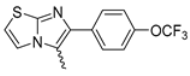
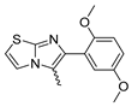
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study investigates the pharmacological potential of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives, functionalized with an imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole scaffold, as selective modulators of intestinal motility. Given their structural similarity to both L-type calcium channel blockers and spasmolytics such as Otilonium Bromide (OB), we explored their repurposing for the treatment of gut motility disorders. Methods: A focused library of 83 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives was screened for spasmolytic activity on potassium (80 mM)-induced depolarization in isolated guinea pig ileal and colonic tissues. Compounds showing pharmacodynamic profiles similar to OB and nifedipine were further evaluated for their effects on the spontaneous contractility of longitudinal and circular smooth muscle layers. Additional functional assays assessed intestinal transit, visceral nociception, and mixing/fragmentation efficiency. Microbiota safety was preliminarily tested on mixed cultures of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species. Results: Compounds 62 and 65 selectively relaxed intestinal smooth muscle, primarily targeting the longitudinal layer without affecting vascular contractility. Ex vivo testing highlights that compounds 62 and 65 could both modulate gut transit and mixing without causing functional constipation or pain. Microbiota analyses showed no detrimental effects on “good” bacterial species Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus spp. Conclusions: The favorable gastrointestinal and microbiological profiles of compounds 62 and 65, combined with their structural versatility, support their potential repurposing for functional bowel disorders. Their selective activity suggests a promising role in therapies targeting intestinal motility while preserving microbiota homeostasis, supporting the need for extended pharmacological characterization.
1. Introduction
L-type calcium channels represent key therapeutic targets in numerous pathologies in which they are directly or indirectly involved. The 1,4-dihydropyridine scaffold has proven particularly effective, leading over time to the synthesis and commercialization of numerous compounds based on this scaffold, which have played a central role in the management of various cardiovascular diseases [1,2,3]. Owing to its chemical versatility, it is considered a privileged structure for potential applications In the prevention of several central nervous system (CNS) and intestinal disorders [4,5], as demonstrated by extensive research focused on both the synthesis of new derivatives and the growing understanding of the unique properties of L-type calcium channels across different tissues. Well-known derivatives such as Nifedipine (NIF) and Amlodipine are widely used in the treatment of hypertension.
Despite their high efficacy on L-type calcium channels in cardiovascular smooth muscle [6], these drugs are not effective for controlling intestinal motility disorders. These conditions are associated with various chronic, multifactorial gastrointestinal diseases [7] and require the use of multiple drug classes tailored to disease severity [8], combined with appropriate dietary management, as outlined in the Rome IV criteria [9]. Among these, Otilonium Bromide (OB) is widely used as it directly relaxes the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract by blocking L-type calcium channels, thus reducing muscle contractions and relieving abdominal cramping and pain. Its local spasmolytic action, proven clinical efficacy, and favorable tolerability profile [10] make it a reference compound in the treatment of functional bowel disorders. Beyond direct L-type calcium channel blockade, intestinal motility can also be regulated through alternative receptor pathways involving calcium-dependent signaling. For example, scopolamine blocks muscarinic (at low doses) and nicotinic (at high doses) receptors in the gastrointestinal tract and ganglia, respectively, but due to poor systemic absorption, its action is mainly localized in the intestine [11]. Opioid σ receptor agonists like loperamide have limited use due to poor selectivity and the risk of inducing gallbladder atony [12]. Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channels, which are overexpressed in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), regulate transmembrane cation flow according to electrochemical gradients, causing increased intracellular Ca2+ and Na+ and subsequent depolarization [13]. Histamine H1-receptors located on TRPV1-expressing nerves amplify intestinal dysmotility [14], and H1-antagonists such as ebastine can prevent histamine-induced sensitization of TRPV1 [15]. All the above-mentioned receptors involved in the regulation of intestinal motility depend on calcium influx for activation. This highlights the potential of calcium channel blockers, which limit intracellular calcium entry, thereby reducing contractile activity and indirectly modulating the function of calcium-dependent membrane receptors [16]. Our research group has long focused on the structure–activity relationships of NIF analogues bearing variably substituted imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole moieties at position 4, aiming to develop compounds selective for specific cardiovascular parameters while considering off-target effects on intestinal smooth muscle [17,18,19,20].
Our previous work has demonstrated that the imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole group, variably decorated and combined with different ester substitutions at carbons 3 and 5 of the 1,4-dihydropyridine ring, can selectively modulate cardiovascular parameters, exhibit neuroprotective effects, and unexpectedly control intestinal smooth muscle activity. Notably, the 1,4-dihydropyridine scaffold substituted at position 4 with various imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole groups exhibits high efficacy and potency on gastrointestinal but not vascular smooth muscle [18], making it a compelling candidate for the development of new selective analogues.
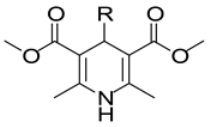
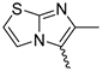
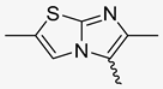
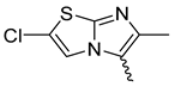
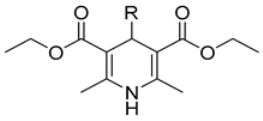
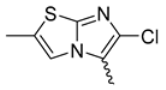
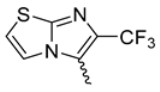
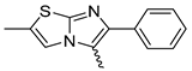
In this study, we adopted a drug repurposing strategy to investigate a small chemical library of 83 compounds, originally designed for unrelated therapeutic targets, as potential modulators of intestinal motility. NIF was tested as a structural analogue of the synthesized compounds, given the shared 1,4-DHP core, while Otilonium Bromide (OB) served as a functional analogue (Figure 1). Although NIF is not clinically used to treat intestinal motility disorders and may even impair motility by inducing constipation [21], its inclusion allowed us to compare structural activity and selectivity profiles toward intestinal versus cardiovascular smooth muscle.
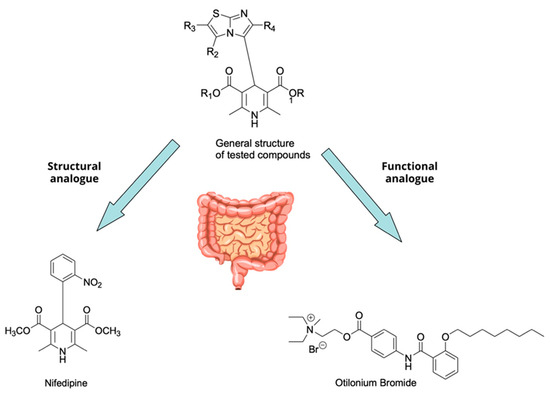
Figure 1.
Rational of 4-Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-1,4-DHPs repurposing compounds.
Specifically, we evaluated their effects on the contractility of longitudinal smooth muscle from rat ileum depolarized with 80 mM potassium. The most promising candidates (2, 10, 31, 43, 62, 65), which did not display significant cardiovascular activity, were further characterized for their effects on potassium-depolarized smooth muscle from the colon, as well as on circular smooth muscle from both the ileum and colon.
Spontaneous intestinal contractility plays a crucial role in the digestive process, contributing to peristaltic movements that regulate the speed of bolus transit, mixing, and fragmentation [22,23]. These coordinated activities ensure that the luminal content comes into close contact with the intestinal mucosa, thereby directly influencing nutrient absorption. This function involves both the longitudinal and circular layers of the smooth muscle tissue. Given this physiological relevance, two compounds exhibiting pharmacodynamic profiles comparable to those of the reference functional analogue were selected for further investigation into spontaneous contractility.
Furthermore, their potential impact on selected populations of gut microbiota was preliminarily tested on mixed cultures of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species, supporting their relevance as lead candidates for future therapeutic applications in gastrointestinal disorders.
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
4-Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-1,4-DHPs used in this study were synthesized as previously reported. In particular, compounds 1, 8, 18 (1, 8, 18) [24], 2–7, 9–10, 12–16, 19–20, 22–24, 26–39 [17], 11, 17, 21, 53–57, 80–82 [18], 25, 59–79, 83 [19], and 41–52, 58 [20].
Briefly, the synthesis (Scheme 1) was accomplished by means of the well-known Hantzsch reaction [25]: onepot condensation of the appropriate β-ketoester, methylacetatoacetate or ethylacetoacetate or allylacetoacetate with the opportune aldehydes in a solution of aqueous ammonia and propan-2-ol.
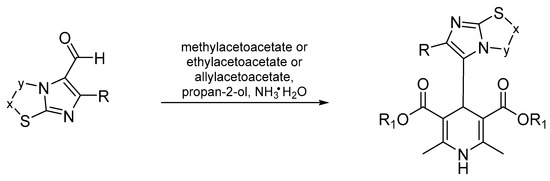
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of 4-Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-1,4-DHPs.
2.2. Spasmolitic Activity on K+-Depolarized Guinea Pig Ileum Longitudinal Smooth Muscle
Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 summarize the spasmolytic activity of the compounds on longitudinal smooth muscle from guinea pig ileum, grouped according to the esterification at positions 3 and 5 of the 1,4-dihydropyridine core. For comparison, the tables also include previously and newly reported data on cardiovascular parameters, namely negative inotropic effects on guinea pig left atrium paced at 1 Hz, negative chronotropic effects on spontaneously beating right atrium, and spasmolytic effects on K+-depolarized vascular smooth muscle [17,18,19,20]. For compounds not previously characterized for cardiovascular effects, intrinsic activity and potency are reported only if the intrinsic activity exceeded 50%.

Table 1.
Relaxant activity of methyl esters compounds on K+-depolarized guinea pig ileum longitudinal smooth muscle vs. cardiovascular parameters.

Table 2.
Relaxant activity of ethyl esters compounds on K+-depolarized guinea pig ileum longitudinal smooth muscle vs. cardiovascular parameters.

Table 3.
Relaxant activity of allyl esters compounds on K+-depolarized guinea pig ileum longitudinal smooth muscle vs. cardiovascular parameters.
Results showed that NIF exerted spasmolytic effects on ileal smooth muscle comparable to those observed on vascular smooth muscle. It possesses high potency on cardiovascular parameters, with a selectivity index of approximately 173-fold for vascular smooth muscle over negative inotropic activity, and about 26-fold over negative chronotropic activity. Conversely, OB demonstrated 230-fold lower potency on ileal longitudinal smooth muscle compared to its inotropic activity and showed no significant effects on chronotropy or vascular smooth muscle contraction.
2.2.1. Methyl Esters
A total of 52 methyl esters were evaluated (Table 1). Among them, 2, 10, 31, and 43 exhibited negligible activity on cardiovascular parameters while showing selective spasmolytic effects on K+-depolarized longitudinal ileal smooth muscle. The most potent was 10 [EC50 = 0.095 µM (95% CI: 0.072–0.13)], followed by 31, which was sixfold less potent [EC50 = 0.55 µM (95% CI: 0.43–0.69)], then 43 [EC50 = 0.96 µM (95% CI: 0.74–1.06)], and 2, which was approximately 93 times less potent [EC50 = 8.83 µM (95% CI: 5.53–10.41)].
All other methyl esters exhibited spasmolytic activity on ileum together with variable cardiovascular effects. Notably, only 21 displayed some activity on vascular smooth muscle and had a fivefold higher potency on ileum [EC50 = 0.0033 µM (95% CI: 0.0025–0.0042)] compared to vascular smooth muscle [EC50 = 0.016 µM (95% CI: 0.012–0.025)], and a 706-fold selectivity over inotropic effects [EC50 = 2.33 µM (95% CI: 1.90–2.66)].
Compounds showing negative chronotropic effects in addition to ileal spasmolytic activity included 30, 35, 42, and 44–50. Among these, 44, 45, and 50 displayed comparable potencies on both parameters. The remaining compounds were more potent on ileum than on chronotropy, with selectivity indices ranging from 8-fold (42) to 251-fold (30) and up to 461-fold (48). On the other hand, compounds exhibiting negative inotropic effects included C1, 3–8, 15, 17, 23, 26, and 32–34, and 52. Notably, 8 showed equal potency on both parameters. Compounds 1 and 17 were selective for ileum, being 2-fold and 26-fold more potent, respectively, on intestinal smooth muscle than on inotropic activity. All other compounds in this group were more potent as negative inotropes, with varying selectivity. Compound 26 exhibited the highest selectivity for inotropic effects (approximately 281-fold).
The remaining 22 compounds (9, 11–14, 16, 18–20, 22, 24, 25, 27–29, 36–41, and 51) displayed spasmolytic activity accompanied by negative inotropic and/or chronotropic effects, with variable intrinsic activity and potency. Among them, only 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 22, and 24 were more potent on the ileum than on cardiac parameters. The most selective was 22, which was 46- and 134-fold more potent on the ileum than on inotropic and chronotropic responses, respectively. Compound 16 showed the highest ileal potency [EC50 = 0.036 µM (95% CI: 0.028–0.046)], with 9-fold and 104-fold selectivity over inotropic and chronotropic effects, respectively. Also noteworthy was 19, which exhibited high potency on the ileum [EC50 = 0.083 µM (95% CI: 0.066–0.10)] and showed 23- and 16-fold selectivity for ileal over inotropic and chronotropic parameters, respectively.
Compounds 12, 28, and 29 showed comparable potency across all three functional endpoints. The remaining compounds were either more potent on cardiovascular response or, as in the case of 11, exhibited similar activity on both ileal and inotropic effects.
2.2.2. Ethyl Esters
The small chemical library includes 27 ethyl ester derivatives (Table 2). Among these, only compounds 62 and 65 demonstrated selectivity for spasmolytic activity on guinea pig ileal longitudinal smooth muscle, with no significant cardiovascular effects. Both showed high intrinsic activity, exceeding 90%: 92 ± 1.4 at 10 µM for 62 and 97 ± 0.9 at 5 µM for 65. Their potency followed a similar trend, with 65 being approximately three times more potent than 62. As spasmolytics, both compounds were less powerful than NIF (by approximately 413- and 1280-fold, respectively), but more potent than OB (by 14- and 4-fold, respectively). All ethyl esters lacked activity on vascular smooth muscle, except for 66, whose potency on the ileum was approximately twofold lower than its negative inotropic effect, yet four- and seventeen fold higher than its negative inotropic and chronotropic effects, respectively.
Compounds 53, 54, 68, 70, 71, 73, 74, and 78 exhibited both spasmolytic activity on ileal smooth muscle and negative inotropic effects. Among them, compounds 53, 54, 68, and 70 were selective for the spasmolytic effect on longitudinal ileum (by 2-, 76-, 42-, and 3-fold, respectively), while compounds 71, 73, 74, and 78 were selective for negative inotropic activity (by 2-, 10-, 3-, and 10-fold, respectively). Compounds 55, 63, and 75 showed both spasmolytic and negative chronotropic effects. Among them, 55 was 29-fold more potent as a spasmolytic, 63 exhibited 71-fold selectivity for negative chronotropy, and 75 displayed no significant difference in potency between the two activities.
The other ethyl esters exhibited both negative inotropic and chronotropic effects. Of these, 56–58, 60, 69, and 79 were more potent on the ileal smooth muscle than on the cardiac parameters. Notably, 79 showed a 1154-fold selectivity for the spasmolytic effect over the negative inotropic effect, but only a fourfold over negative chronotropy. Compound 67 showed comparable potency between the spasmolytic and negative inotropic effects, while 61 showed no significant difference between spasmolytic and negative chronotropic activity. Finally, the remaining, 59, 64, 72, 76, and 77, were less potent on ileal smooth muscle than on one or both cardiac parameters.
2.2.3. Allyl Esters
All the allyl ester derivatives (Table 3) tested were devoid of spasmolytic activity on vascular smooth muscle. Compounds 80, 81, and 83 exhibited both negative inotropic and chronotropic effects, whereas 82 showed only a negative inotropic effect. Concerning spasmolytic potency on guinea pig longitudinal ileal smooth muscle, 81 was the most potent, with an IC50 of 0.0053 µM (95% CI: 0.0038–0.0073), and it demonstrated marked selectivity over cardiac effects, 138-fold relative to negative inotropy and 372-fold relative to negative chronotropy. The remaining compounds were either non-selective or less potent on ileal smooth muscle than on cardiac parameters. Exceptions were 80 and 83, which displayed higher spasmolytic potency compared to their negative chronotropic effects, by 20- and 2-fold, respectively.
2.2.4. Comparative Considerations
A comparison among methyl, ethyl, and allyl esters highlights marked differences in pharmacological profiles in terms of both potency and selectivity for smooth muscle subtypes (see Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3). Methyl esters, despite a wide variability in structure, included several compounds with high spasmolytic potency on intestinal smooth muscle and limited cardiovascular involvement, suggesting a favorable selectivity profile for peripheral smooth muscle. Ethyl esters, while generally less potent than methyl analogues, featured two derivatives, 62 and 65, that exhibited excellent selectivity for intestinal smooth muscle with negligible cardiovascular effects, underscoring their potential as gut-selective spasmolytics. Allyl esters showed the highest potencies among the series (notably 81), yet their cardiovascular involvement was more pronounced, with fewer compounds achieving functional selectivity. Overall, these findings suggest that specific structural modifications at positions 3 and 5 of the 1,4-dihydropyridine core markedly influence the balance between intestinal and cardiovascular activity, and that selected methyl and ethyl esters may offer promising templates for the development of functionally selective smooth muscle relaxants with reduced cardiac side effects
Additionally, the comparison of compounds with the same substituent at position 4 but different esterification—methyl (26), ethyl (58), and allyl (82)—confirms that the combination of ester and substituent at position 4 modulates the activity profile.
We selected only those compounds that did not show significant cardiovascular effects in our experimental models. This narrow selection was necessary because, at this stage, we lack data on the bioavailability of the tested molecules. As a result, even compounds with potent and selective intestinal activity, but with concurrent cardiovascular action, were excluded from further characterization in this initial study.
2.3. Spasmolytic Activity on K+-Depolarized Guinea Pig Colon Longitudinal Smooth Muscle
The compounds with selective spasmolytic activity for the ileum longitudinal smooth muscle and without significant cardiovascular effects (2, 10, 31, 43, 62, and 65), were studied on guinea pig colon longitudinal smooth muscle K+ depolarized (80 mM). The data are presented in Table 4, along with those of NIF and OB. NIF exhibited high intrinsic activity (94 ± 1.6), reaching its maximum effect at 0.01 μM, whereas OB achieved maximal intrinsic activity (90 ± 2.3) at 50 μM. In terms of potency, NIF was approximately 1805-fold more potent than OB [IC50 = 0.0019 μM (95% CI: 0.0015–0.0024) and 3.43 μM (95% CI: 2.65–4.44), respectively].

Table 4.
Spasmolytic activity of selected compounds on K+-depolarized guinea pig longitudinal colon smooth muscle.
As expected, all selected compounds displayed spasmolytic activity on guinea pig longitudinal colonic smooth muscle. Among them, 65 was the most potent [IC50 = 0.049 μM (95% CI: 0.035–0.068)], being only 25-fold less potent than nifedipine and approximately 70-fold more potent than OB. C10 showed a potency not significantly different from that of OB, while 2 and 31 demonstrated comparable potencies. Compounds 43 and 62 were 2-fold and 35-fold less potent than nifedipine, but 34-fold and 2-fold more potent than OB, respectively.
2.4. Spasmolitic Activity on K+-Depolarized Guinea Pig Ileum and Colon Circular Smooth Muscle
The selected compounds, along with the reference drugs NIF and OB, were evaluated on circular smooth muscle of guinea pig ileum and colon under identical experimental conditions. The data are summarized in Table 5. OB showed no significant effects on the circular muscle of either the ileum or the colon. In contrast, NIF was active on the circular smooth muscle of both tissues, exhibiting a 393-fold higher potency for the ileum. Only 62 and 65 displayed a profile similar to the reference drug, showing no notable activity on the circular smooth muscle of the ileum and colon. Compound 2 demonstrated selective activity on the circular smooth muscle of the ileum, with no significant effect on the colon circular muscle. Compound 43 exhibited a profile comparable to that of the structural analogue NIF, acting on the circular smooth muscle of both intestinal segments, with a 38-fold selectivity for the ileum. In contrast, 10 and 31 were more potent on the circular smooth muscle of the colon, with selectivity of 2.2 and 1.6 times, respectively.

Table 5.
Spasmolytic activity of selected compounds on K+-depolarized guinea pig circular ileum and colon smooth muscle.
2.5. Activity on Spontaneous Guinea Pig Ileum and Colon Smooth Muscle
Based on the spasmolytic activity data against 80 mM potassium-induced contraction, 62 and 65 were selected to investigate their effects on the spontaneous contractility of longitudinal and circular smooth muscle from guinea pig ileum and colon. Concentration–response curves were performed, and parameters such as muscle tone and peristaltic wave frequency were monitored. NIF and OB were studied in parallel under identical conditions.
2.5.1. Ileum
Longitudinal smooth muscle. Figure 2 shows SC, MCA, BSMA, and PSD of spontaneous ileum longitudinal basal contractility. NIF showed minimal and concentration-independent effects on muscle tone. In contrast, OB induced a concentration-dependent reduction in longitudinal muscle tone, with a maximal decrease of approximately 70% at 5 μM. Compound 65 caused a slight tone reduction at concentrations ≥0.5 μM, while compound 62 reduced tone starting at 0.5 μM, reaching a maximum effect of approximately 50% at 5 μM. Regarding peristaltic wave frequency, OB decreased high-frequency (HF) and medium-frequency (MF) waves in a concentration-dependent manner; low-frequency (LF) waves were reduced by 80% at concentrations ≥5 μM. NIF, 65, and 62 reduced LF waves starting at 1 μM, while MF and HF waves remained stable or showed only minor reductions.
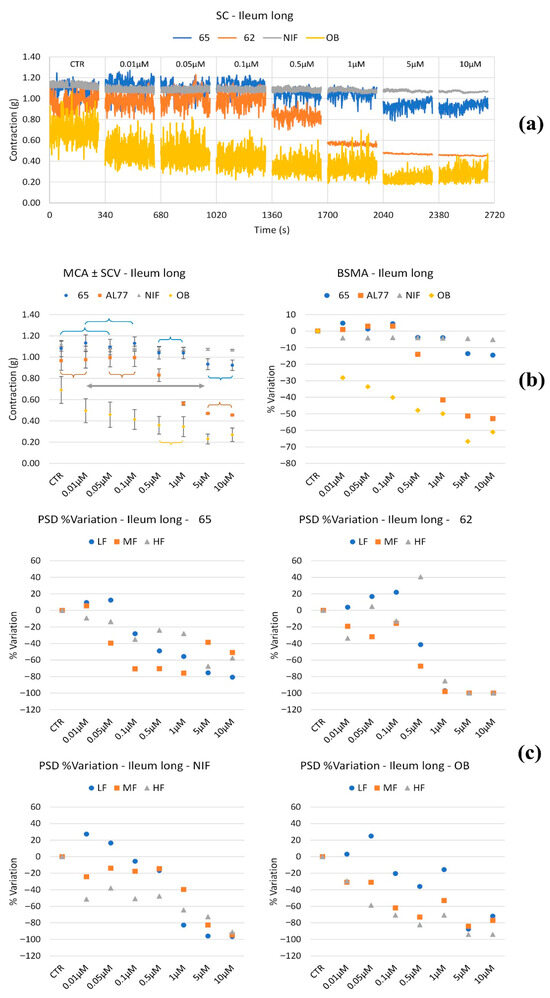
Figure 2.
Experimental original recording of the concentration–response curve of 62, 65, NIF (Nifedipine), and OB (Otilonium Bromide), on spontaneous ileum longitudinal basal contractility. (a) Spontaneous Contraction (SC) signals for each concentration; (b) Mean Contraction Amplitude (MCA) and Spontaneous Contraction Variability (SCV). Not significant differences between MCAs at different concentrations are reported in the graph; all the comparisons not reported are to be considered significant (p < 0.05); the grey arrow highlights the not significant differences between all the tones for NIF for all concentrations between 0.01 μM and 10μM; (c) absolute powers (PSD) of the different bands of interest (LF: [0.0,0.2[ Hz; MF: [0.2,0.6[ Hz; HF: [0.6,1.0] Hz) and PSD% variations for the control phase.
Circular smooth muscle. All compounds tested (Figure 3), including the reference drugs, induced a mild reduction in muscle tone starting at 0.05 μM. Regarding peristaltic wave frequencies, NIF, 65, and 62 showed minimal or no effect on low-frequency (LF), medium-frequency (MF), and high-frequency (HF) waves. In contrast, OB caused an increase in LF waves, peaking at 10 μM, while MF and HF waves increased at all tested concentrations but decreased by approximately 50% at 10 μM.
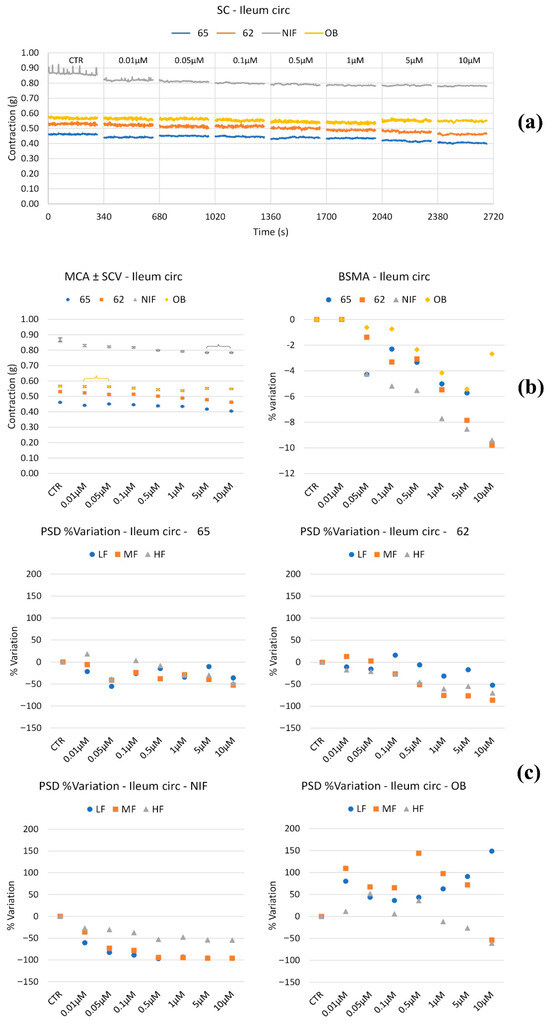
Figure 3.
Experimental original recording of the concentration–response curve of 62, 65, NIF (Nifedipine), and OB (Otilonium Bromide) on spontaneous ileum circular basal contractility. (a) Spontaneous Contraction (SC) signals for each concentration; (b) Mean Contraction Amplitude (MCA) and Spontaneous Contraction Variability (SCV). Not significant differences between MCAs at different concentrations are reported in the graph; all the comparisons not reported are to be considered significant (p < 0.05); (c) absolute powers (PSD) of the different bands of interest (LF: [0.0,0.2[ Hz; MF: [0.2,0.6[ Hz; HF: [0.6,1.0] Hz) and PSD% variations with respect to the control phase.
2.5.2. Colon
Longitudinal smooth muscle. Figure 4 shows the parameters of interest of spontaneous longitudinal colon basal contractility. NIF caused a mild reduction in muscle tone at low concentrations, whereas OB reduced tone by approximately 20%, but only at concentrations above 5 μM. In contrast, compounds 62 and 65 induced a concentration-dependent tone reduction starting at low concentrations, reaching maximal decreases of –60% for 62 at 5 μM and –50% for 65 at 10 μM.
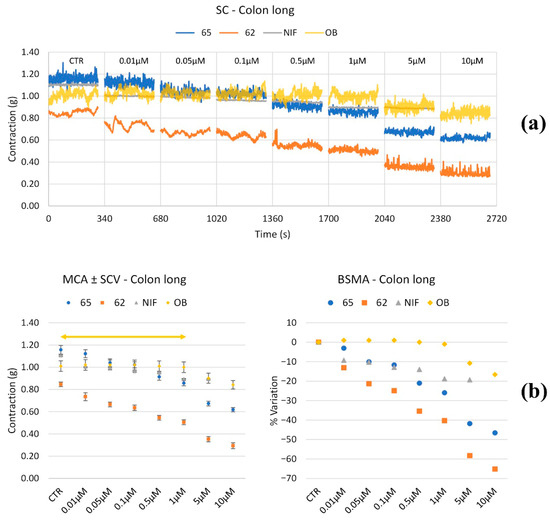
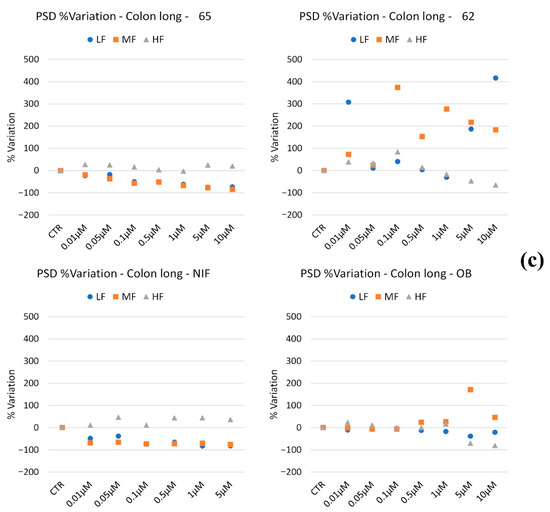
Figure 4.
Experimental original recording of the concentration–response curve of 65, 62, NIF (Nifedipine), and OB (Otilonium Bromide) on spontaneous longitudinal colon basal contractility. (a) Spontaneous Contraction (SC) signals for each concentration; (b) Mean Contraction Amplitude (MCA) and Spontaneous Contraction Variability (SCV). Not significant differences between MCAs at different concentrations are reported in the graph; all the comparisons not reported are to be considered significant (p < 0.05); the yellow arrow highlights the not significant differences between all the tones for OB for all concentrations up to 1.0 μM; (c) absolute powers (PSD) of the different bands of interest (LF: [0.0,0.2[ Hz; MF: [0.2,0.6[ Hz; HF: [0.6,1.0] Hz) and PSD% variations with respect to the control phase.
Regarding peristaltic wave frequencies, 65 mildly reduced LF and MF waves in a concentration-dependent manner, while HF waves remained stable across all concentrations. Compound 62 exhibited variable effects depending on concentration: LF waves increased by 300% at 0.1 μM, returned to control levels at intermediate concentrations, and rose again up to 400% at concentrations ≥5 μM. MF waves peaked with a 400% increase at intermediate concentrations. HF waves increased up to 0.1 μM and then progressively declined.
NIF decreased LF and MF waves, with HF waves remaining constant. OB maintained stable LF and HF waves, with decreases at high concentrations, while MF waves increased by approximately 200% only at 5 μM.
Circular smooth muscle. OB exhibited no significant effect on muscle tone. NIF and 65 caused a slight reduction in tone across all tested concentrations. Conversely, 62 induced a mild increase in tone, peaking at +15% at 0.1 μM (Figure 5).
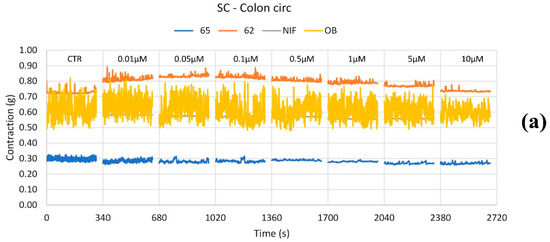
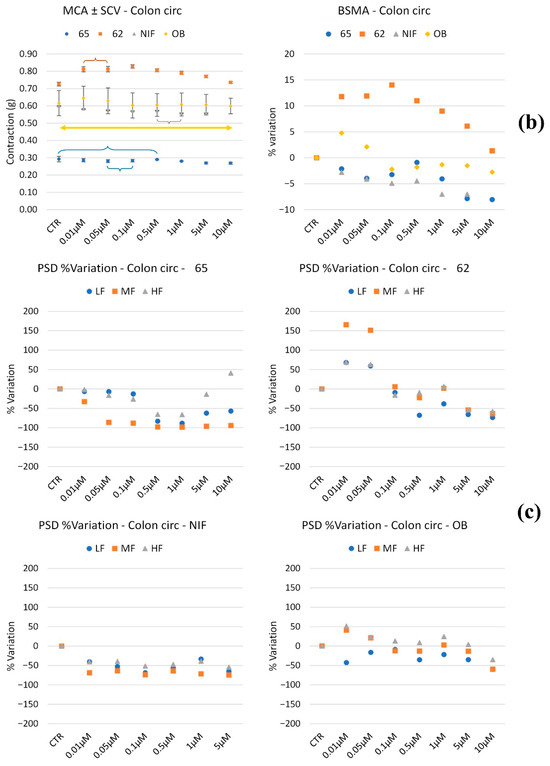
Figure 5.
Experimental original recording of the concentration–response curve of 62, 65, NIF (Nifedipine), and OB (Otilonium Bromide) on spontaneous circular colon basal contractility. (a) Spontaneous Contraction (SC) signals for each concentration; (b) Mean Contraction Amplitude (MCA) and Spontaneous Contraction Variability (SCV). Not significant differences between MCAs at different concentrations are reported in the graph; all the comparisons not reported are to be considered significant (p < 0.05); the yellow arrow highlights the not significant differences between all the tones for OB for all the concentrations; (c) absolute powers (PSD) of the different bands of interest (LF: [0.0,0.2[ Hz; MF: [0.2,0.6[ Hz; HF: [0.6,1.0] Hz) and PSD% variations with respect to the control phase.
Regarding peristaltic wave frequencies, 62 increased all frequency bands up to 0.05 μM, followed by a subsequent decrease at higher concentrations. Compound 65 reduced LF, MF, and HF waves at all concentrations, except for a slight increase in HF waves at 10 μM. NIF induced a mild decrease across all frequency bands, while OB maintained frequencies within ±50% of baseline values, showing no significant changes.
2.6. Effect vs. Mixed Cultures of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus Species
Microbiota safety was preliminarily tested on cultures of beneficial gut bacteria to ensure that the compounds do not disrupt microbial communities essential for intestinal health and overall homeostasis. No growth inhibition was observed on any agar plate for 62 and 65 (see Figure 6), showing that 62 and 65 do not affect the viability of beneficial gut bacteria at the concentrations tested.
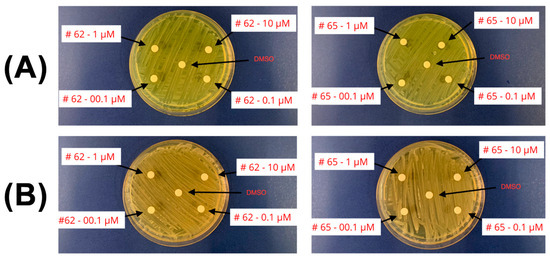
Figure 6.
Agar plates showing no growth inhibition. (A) Bifidobacteria. (B) Lactobacilli. Concentrations of 62 and 65 are detailed.
3. Discussion
Our research group has extensively investigated 1,4-dihydropyridines (DHPs) modified at position 4 by replacing the ortho-nitrobenzene moiety with diversely substituted imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole systems [17,19,20,24]. This structural modification has generated compounds with distinct pharmacological profiles, influencing cardiac parameters [17,24] and exhibiting neuroprotective properties [19,20], with potential therapeutic applications extending to cystic fibrosis [18]. These multifaceted activities arise from both the substitution pattern on the imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole core and the esterification at positions 2 and 6 of the 1,4-DHP scaffold. The 1,4-DHP nucleus is a versatile scaffold extensively utilized for the synthesis of compounds targeting multiple biological pathways across different therapeutic areas [27,28].
Within a library of 83 compounds, most displayed selective cardiovascular activities. However, a subset exhibited pronounced spasmolytic effects on potassium-induced contractions of the longitudinal smooth muscle of guinea pig ileum, with potency comparable to or surpassing that of NIF, a structural reference compound well characterized for its activity on smooth muscle tissue.
Moreover, several compounds demonstrated neuroprotective effects [19,20], suggesting a potential mechanistic link between peripheral modulation of intestinal smooth muscle and beneficial CNS effects. Given the recognized role of the CNS in gastrointestinal motility and the pathophysiology of motility disorders [29], these findings open promising avenues for future therapeutic development of 1,4-DHP derivatives.
Motivated by these observations, we hypothesized a possible repositioning of 1,4-DHPs bearing 4-substituted imidazo[2,1-b]thiazoles for the treatment of disorders associated with altered intestinal motility. We undertook a detailed investigation into the structure–activity relationship governing motility control, considering the Roma IV criteria that identify calcium channels as pertinent targets for motility regulation [30]. Many 1,4-DHPs exert potency on intestinal smooth muscle calcium channels comparable to or exceeding that on vascular smooth muscle channels. However, their clinical utility in this context is limited by poor selectivity and the predominant use of 1,4-DHPs as antihypertensive agents, where their pronounced tropism for non-vascular intestinal smooth muscle is considered an adverse side effect. Similar limitations apply to their use in neurological disorders, restricting the exploitation of the 1,4-DHP core’s full therapeutic potential.
This repositioning concept is supported by the fundamental role of intracellular Ca2+ concentration in intestinal smooth muscle contraction, regulated chiefly by calcium influx via voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), as evidenced by potassium-induced depolarization, and by receptor-mediated pathways indirectly modulating intracellular calcium to amplify phasic contractions [31].
Both pathways culminate in rapid contractions followed by plateau phases representing tonic and phasic components, respectively, with the tonic phase being highly sensitive to VDCC modulators [32].
Among the evaluated compounds, many exhibited high potency and selectivity for spasmolytic effects on ileal smooth muscle while retaining their cardiovascular activity. Remarkably, six compounds, four methyl esters (2, 10, 31, 43) and two ethyl esters (62, 65), were devoid of cardiovascular effects and selectively targeted the longitudinal smooth muscle of the ileum. Compounds 2 and 10 differ solely by their R substituent (CH3 vs. CF3), with the electron-withdrawing CF3 group significantly enhancing intrinsic activity and potency by approximately 93-fold. Compounds 31, bearing a trimethoxyphenyl moiety, and 43, featuring a para-pyridine substituent, showed comparable activity and potency profiles. The ethyl esters 62 and 65, each containing halogen substituents, exhibited similar potency to their methyl ester counterparts. Notably, none of the allyl esters demonstrated selective spasmolytic activity on the longitudinal smooth muscle (Table 3).
While NIF showed high potency on both cardiovascular parameters and guinea pig longitudinal ileum muscle, OB exhibited more pronounced negative inotropic effects in our experimental models than effects on potassium-depolarized longitudinal ileum and colon muscles. OB, a quaternary ammonium compound with negligible systemic absorption, with no cardiovascular side effects, is widely used for intestinal motility disorders [33]. Included in the Roma IV criteria as a motility-modulating drug [34], OB served as a functional reference to evaluate the new compounds’ activity profiles.
The six inactive compounds for cardiovascular parameters (2, 10, 31, 43, 62, and 65) were further investigated on longitudinal colon muscle and circular ileum and colon muscles, with OB and NIF as controls. OB acted exclusively on induced motility of longitudinal muscle without significant effects on circular muscle, whereas NIF exhibited spasmolytic effects on both longitudinal and circular muscle components. As shown in Figure 7, only the two ethyl esters displayed a profile similar to OB. The remaining compounds affected both longitudinal and circular muscles, similar to NIF. Compound 43 replicated NIF’s selectivity, while 31 and 10 were more potent spasmolytics on circular colon muscle. C2 selectively modulated circular ileum muscle contraction.
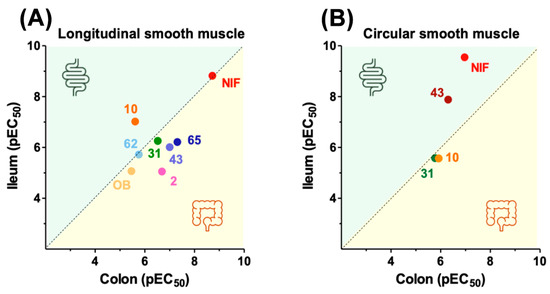
Figure 7.
Effect of selected compounds on the ileum and colon: longitudinal smooth muscle (A); circular smooth muscle (B).
The characterization of compounds exhibiting a potassium depolarization activity profile similar to the functional analogue (62 and 65) was extended to evaluate their effects on the spontaneous contractility of longitudinal and circular smooth muscle from the ileum and colon. Table 6 and Table 7 summarize the effects produced by individual compounds at single concentrations alongside the structural reference compound (NIF) and the functional reference (OB).

Table 6.
Effects on the ileum of the different compounds on transit speed, pain, mixing, fragmentation, and tones.

Table 7.
Effects on the colon of the different compounds on transit speed, pain, mixing, fragmentation, and tones.
In the ileum (Table 6), both 62 and 65 decrease muscle tone, inducing relaxation of both longitudinal and circular smooth muscle layers starting from a concentration of 0.5 µM. They reduce transit time at concentrations above 1 µM and may exert mild antinociceptive effects [35] while preserving mixing and fragmentation functions. These combined effects result in the modulation of intestinal transit without complete inhibition. The functional reference compound OB exerts a more pronounced relaxation on longitudinal muscle and mildly promotes fragmentation and mixing.
Both 62 and 65 exert relaxing effects on ileal smooth muscle, slowing bolus transit and promoting nutrient absorption, with more pronounced effects observed at concentrations ≥1 μM.
In the colon segments (Table 7), 62, 65, and NIF showed variable effects on the tone of the longitudinal smooth muscle, with 62 and 65 being more effective at lower concentrations. Both 65 and NIF induced relaxation of the circular muscle layer, whereas 62 elicited a contractile response. In contrast, OB had no significant effect on either muscle layer. Compound 65 decreased transit time without inducing nociceptive responses and reduced both mixing and fragmentation efficiency of the luminal content. Compound 62 exhibited a concentration-dependent and non-linear profile. At low concentrations, it increased transit, mixing, and fragmentation, while at intermediate concentrations, it maintained normal transit without affecting fragmentation or mixing. At high frequencies, transit was increased again, without enhancement of fragmentation or mixing at all concentrations tested; high-frequency activity was linked to discomfort or pain increase. Finally, both NIF and OB preserved normal transit velocity and nociceptive thresholds, showing only mild effects on mixing and fragmentation dynamics.
Compound 62 exerts its effects primarily on the relaxation of longitudinal smooth muscle, with no significant impact or slightly negative effects on other parameters. Compound 65 relaxes both the longitudinal and circular muscle layers, slightly reducing the mixing process, while simultaneously slowing transit, thereby promoting water absorption and fecal formation.
It is now well established that intestinal health and overall well-being are closely linked to the integrity of the gut microbiota [36]. Therefore, any therapeutic strategy should aim to preserve this microbial ecosystem. Among the most beneficial microorganisms, Bifidobacterium spp. [37] and Lactobacillus spp. play a key role in restoring eubiosis and supporting both intestinal [38,39] and brain health [40]. Probiotic supplementation is commonly employed to reestablish these beneficial populations. For example, in the context of ischemic stroke, inflammation can serve as a reparative process for neural tissue, but it also carries neurotoxic risk [41]. Gut microbiota composition has been shown to influence post-stroke inflammatory responses, suggesting that selective antimicrobial modulation could promote host-beneficial microbial communities.
Many natural and synthetic substances are able to modulate the microbiota, profoundly involving the gut–brain axis (GBA) [42,43].
The 1,4-dihydropyridine scaffold, when appropriately functionalized, possesses intrinsic antibacterial properties [44,45,46]. Notably, even amlodipine has been reported to restore intestinal barrier integrity and support gut microbial diversity in hypertensive mice with NAFLD [46], underscoring the importance of preserving commensal bacteria. Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli ferment dietary fibers in the colon, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), namely acetate, propionate, and butyrate. SCFAs have numerous protective effects on gut health: they enhance mucus production, protect against inflammation, and modulate neuroinflammation by inhibiting key enzymatic pathways implicated in Alzheimer’s disease [47].
The imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole core, a key feature in the molecules under investigation, displays selective antimicrobial properties without disrupting endogenous urovaginal microbiota [48]. Based on this background, 62 and 65 were preliminarily tested on bifidobacteria and lactobacilli spp. present in the composition of formulations currently used in clinical settings to support both intestinal and neurological well-being. The Bifidobacterium included equal amounts of B. infantis, which contributes to immune system development and fortifies the intestinal barrier [49]; B. longum, known for its anti-inflammatory effects [50]; B. bifidum [51]; B. brevis; and B. lactis [52]. On the other hand, the Lactobacillus blend consisted of L. rhamnosus, which modulates inflammation [53] and is important and connected to gut and brain homeostasis [54]; L. fermentum, which mitigates DSS-induced colitis via immune modulation and microbiota shifts [55]; L. acidophilus, shown to attenuate inflammation and restore gut barrier function in obesity models [56]; L. plantarum, associated with reduced anxiety, depression, and insomnia by modulating GBA activity [57]; and L. salivarius, which protects intestinal integrity and counters chemotherapy-induced mucositis [58].
This experimental setup was designed to assess the effect of the compounds not on isolated bacterial strains but on synergistic microbial communities relevant to host homeostasis and therapeutic applications.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis
The synthesis of the compounds studied is described. Please see above for details and references. All solvents and reagents were supplied by Aldrich Chemical Company Ltd. (Gillingham, UK) and were used as supplied, or were prepared according to the literature.
4.2. Gut In Vitro Tissues Activities
Male guinea pigs (200–400 g) obtained from Charles River (Calco, Como, Italy) were used. The animals were housed according to the ECC Council Directive regarding the protection of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes (Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council) and the WMA Statement on Animal Use in Biomedical Research. All procedures followed the guidelines of the animal care and use committee of the University of Bologna (Bologna, Italy). The ethical committee authorization was reported and numbered as “Protocol 2DBFE.N.YEV” by the Comitato Etico Scientifico for Animal Research Protocols and approved by the Ministry of Health in December 2023. The animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the organ (ileum and proximal colon) required was set up rapidly under a suitable resting tension in 15 mL organ bath containing an appropriate physiological salt solution (PSS) consistently warmed (see below) and buffered to pH 7.4 by saturation with 95% O2–5% CO2 gas. Gut strip preparations were used to examine the spontaneously and K+-induced contractility of the compounds (0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50, and 100 μM), first dissolved in DMSO and then diluted with PSS according to Mattioli et al. [59]. According to this procedure, the concentration of DMSO in the bath solution never exceeded 0.3%, a concentration which did not produce appreciable effects. During the generation of cumulative concentration–response curves, the next higher concentration of the compounds was added only after the preparation reached a steady state.
Guinea pig ileum. The terminal portion of ileum (3–4 cm near the ileo-caecal junction) was cleaned, and segments 2–3 cm long were set up under 1 g tension at 37 °C in organ baths containing Tyrode solution of the following composition (mM): NaCl, 118; KCl, 4.75; CaCl2, 2.54; MgSO4·7H2O, 1.20; KH2PO4·2H2O, 1.19; NaHCO3 25; glucose 11. The two segments obtained (2–3 cm) were set up under 1 g tension in the longitudinal direction along the intestinal wall. Tissue was allowed to equilibrate for at least 30 min, during which time the bathing solution was changed every 10 min. The circular musculature was studied with a similar procedure.
Guinea pig proximal colon. Starting approximately 1 cm distal from the caecocolonic junction, two segments of about 1 cm of the guinea pig proximal colon were obtained. The proximal colon was cleaned by rinsing it with a De Jalon solution of the following composition (mM): NaCl, 155; KCl, 5.6; CaCl2, 0.5; NaHCO3, 6.0; glucose, 2.8. The mesenteric tissue was then removed. The two segments of longitudinal or circular smooth muscle were suspended in organ baths containing gassed warm de Jalon solution under a load of 1 g, maintained at 37 °C.
4.2.1. Potassium-Induced Spasmolytic Activity
The experiments were carried out using a height K+ concentration as previously described [60]. Briefly, after the equilibration period, ileum strips (longitudinal or circular) were contracted by washing in PSS containing 80 mM KCl (equimolar substitution of K+ for Na+). When the contraction reached a plateau (about 30 min), cumulative concentration curves of compounds were constructed. Contractions were recorded using a displacement transducer (FT. 03, Grass Instruments, Quincy, MA, USA) using Power Lab software (7 Pro software; AD Instruments Pty Ltd., Castle Hill, Australia).
4.2.2. Spontaneous Contraction
For the ileum and proximal colon, the tracing graphs of spontaneous contractions of longitudinal or circular ileum and colon smooth muscle were continuously recorded with LabChart Software (7 Pro software; AD Instruments, Bella Vista, New South Wales, Australia) as previously described [59,61]. After the equilibration period (approximately 30 to 45 min, depending on the tissue), cumulative concentration curves of the compounds were constructed using NIF and OB as positive controls. A 5-min stationary interval of the Spontaneous Contraction (SC) recording was selected at the final stage of each concentration. For each interval, the following parameters were extracted and calculated: the Mean Contraction Amplitude (MCA), evaluated as the mean force value (g); the standard deviations of the force values over the period, as an index of the Spontaneous Contraction Variability (SCV); the Basal Spontaneous Motor Activity (BSMA), as the percentage (%) variation of each mean force value (g) concerning the control period.
The spontaneous contractions were investigated in the frequency domain through a standard FFT analysis and a subsequent Power Spectral Density (PSD) plot. The absolute powers of the following frequency bands of interest, low [0.0,0.2[ Hz (LF), medium [0.2,0.6[ Hz (MF), and high [0.6,1.0] Hz (HF) [59], were then calculated. The PSD percentage (%) variations for each band of interest concerning the control were estimated.
All calculations were performed during the post-processing phase. To avoid errors due to the presence of artifacts, the period of analysis was chosen by a skilled operator.
4.2.3. Cardiovascular Activity
Heart. The methods related to the study of inotropic and chronotropic effects evaluated separately on guinea pig left atria driven at 1 Hz and on spontaneously beating right atria, respectively, have been previously described [62].
Aorta. As previously described [62], the thoracic aorta was prepared and used precontracted with 80 mM K+ (see above) to evaluate its spasmolytic activity.
4.2.4. Data Analysis
For the spasmolytic activity on K+-depolarized gut strips, data were analyzed using Student’s t-test and are presented as mean ± S.E.M. [26]. Since the drugs were added cumulatively, the difference between the control and the experimental values at each concentration was tested for a p value < 0.05. The potency of drugs, defined as IC50, was evaluated from log concentration–response curves (Probit analysis using Litchfield and Wilcoxon [26] or GraphPad Prism® software (Prism 5.0) [63,64]) in the appropriate pharmacological preparations.
For changes in spontaneous contractility, all the calculations were performed in a post-processing phase with LabChart software. To avoid errors due to the presence of artifacts, the period of analysis was selected by a skilled operator.
4.3. Activity vs. Probiotics
The effectiveness of 62 and 65 against bacteria was evaluated. Compounds 62 and 65 at growing concentrations (0.01, 0.1, 1, and 5 μM) were tested in vitro against lactobacilli (Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 7469, IVD Microbiologicals: https://www.microbiologics.com) and bifidobacteria (Bifidobacterium breve ATCC 15700, Microbiologicals: https://www.microbiologics.com). The Petri plates used were Rogosa Agar (Liofilchem cod. 10039: https://www.liofilchem.com, acceded on 5 May 2025) for lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium agar (Liofilchem cod. 10458: https://www.liofilchem.com, acceded on 5 May 2025) for bifidobacteria. Incubation times and conditions are detailed in the Instruction for Use (IFU) of the manufacturer. Every test was performed in triplicate, spotting 4 μL, and using DMSO as both the blank and diluent.
5. Conclusions
The present study highlights the potential of selected 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives, particularly 62 and 65 bearing an imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole scaffold, as promising candidates for the treatment of intestinal motility disorders and for irritable bowel syndrome (Figure 8). These compounds demonstrated selective spasmolytic activity on the gastrointestinal smooth muscle, especially the longitudinal layer of the ileum and colon, while lacking significant cardiovascular effects. Their pharmacodynamic profile partially overlaps with that of OB, a well-known drug indicated in Roma IV criteria for gut motility disorders.
Figure 8.
Outlook of conclusion remarks and perspectives.
Moreover, both 62 and 65 showed a favorable impact on spontaneous contractility and did not impair key physiological processes such as propulsion, mixing, or fragmentation at therapeutic concentrations, especially for 62, both at the ileum and colon levels. Preliminary microbiological assessments further revealed no detrimental effects on key intestinal probiotics such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus spp., suggesting compatibility with improvements on gut microbiota health, exerting a key role in GBA regulation and inflammatory conditions. In addition, the increase in SCFAs such as butyrate is an essential consideration in GBA regulation and inflammatory conditions. It is known that these bacterial populations increase significantly if the patient follows a diet rich in prebiotic fibers [65], making possible a possible co-administration to amplify the intestinal and systemic effects.
These considerations are supported by recent studies that have demonstrated how the administration of an aqueous probiotic suspension promotes the colonization and growth of probiotic strains in the colon, leading to increased lactate levels, promoting enhanced SCFA production, particularly butyrate [66].
Lastly, previous studies have reported weak pro-apoptotic activity of diethyl 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives carrying an indole moiety at position 4 in colon cancer cell lines [67], underscoring the importance of further characterizing our newly identified compounds not only in the context of intestinal motility modulation but also for their potential anticancer properties. This multidimensional profile supports the proposed repurposing strategy and warrants further investigation into the mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications of these compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.B. and L.B.M.; methodology, I.C. and L.B.M.; software, L.B.M., L.C., and I.C.; validation, L.B.M., L.C., and I.C.; formal analysis, L.C. and L.B.M.; investigation, L.C., A.L. (Alessandra Locatelli), A.L. (Alberto Leoni), A.S., C.M., and L.B.M.; resources, R.B.; data curation, L.C., I.C., A.L. (Alessandra Locatelli), A.S., and L.B.M.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C., R.B., and L.B.M.; writing—review and editing, R.B. and M.F.; visualization, M.F. and E.C.; supervision, I.C., R.B., and M.M.; project administration, R.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Research of the University of Bologna (Bologna, Italy) (protocol code 2DBFE.N.YEV and approved by the Ministry of Health in 1 December 2023). All procedures followed the guidelines of the animal care and use committee of the University of Bologna (Bologna, Italy) according to the ECC Council Directive regarding protecting animals for experimental and other scientific purposes (Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council) and the WMA Statement on Animal Use in Biomedical Research.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data presented in this study is contained within the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BSMA | Basal Spontaneous Motor Activity |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DHP | Dihydropyridine |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| GBA | Gut–Brain Axis |
| HF | High-Frequency |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| LF | Low Frequency |
| MCA | Mean Contraction Amplitude |
| MF | Medium Frequency |
| OB | Otilonium Bromide |
| PSS | Physiological Salt Solution |
| PSD | Power Spectral Density |
| SC | Spontaneous Contraction |
| SCV | Spontaneous Contraction Variability |
| VDCC | Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channel |
References
- Ioan, P.; Carosati, E.; Micucci, M.; Cruciani, G.; Broccatelli, F.; Zhorov, B.S.; Chiarini, A.; Budriesi, R. 1,4-Dihydropyridine Scaffold in Medicinal Chemistry, the Story so Far and Perspectives (Part 1): Action in Ion Channels and GPCRs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4901–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Sharma, M.; Singh, R.K. Designing 1,4-Dihydropyridines-Based Multitarget Therapeutics: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2025, 25, 2325–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carosati, E.; Ioan, P.; Micucci, M.; Broccatelli, F.; Cruciani, G.; Zhorov, B.S.; Chiarini, A.; Budriesi, R. 1,4-Dihydropyridine Scaffold in Medicinal Chemistry, the Story so Far and Perspectives (Part 2): Action in Other Targets and Antitargets. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4306–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyder, A.; Farrugia, G. Targeting Ion Channels for the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2012, 5, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnegger-Brauns, M.J.; Huber, I.G.; Koschak, A.; Wild, C.; Obermair, G.J.; Einzinger, U.; Hoda, J.-C.; Sartori, S.B.; Striessnig, J. Expression and 1,4-Dihydropyridine-Binding Properties of Brain L-Type Calcium Channel Isoforms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triggle, D.J. 1,4-Dihydropyridines as Calcium Channel Ligands and Privileged Structures. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2003, 23, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Johnson, A.C.; Grundy, D. Gastrointestinal Physiology and Function. In Gastrointestinal Pharmacology; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2017; Volume 239, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayuk, G.S.; Gyawali, C.P. Functional Dyspepsia: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Drugs 2020, 80, 1319–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: History, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features and Rome IV. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1262–1279.E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traini, C.; Idrizaj, E.; Garella, R.; Faussone-Pellegrini, M.-S.; Baccari, M.C.; Vannucchi, M.G. Otilonium Bromide Treatment Prevents Nitrergic Functional and Morphological Changes Caused by Chronic Stress in the Distal Colon of a Rat IBS Model. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6988–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytgat, G.N. Hyoscine Butylbromide: A Review of Its Use in the Treatment of Abdominal Cramping and Pain. Drugs 2007, 67, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzio, L. Factors Affecting Gallbladder Motility: Drugs. Dig. Liver Dis. 2003, 35, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, M.; Berumen, A.; Peters, S.; Wei, T.; Breen-Lyles, M.; Harmsen, W.S.; Busciglio, I.; Burton, D.; Vazquez Roque, M.; DeVault, K.R.; et al. Intestinal Chemosensitivity in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Associates with Small Intestinal TRPV Channel Expression. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, M.M.; Balemans, D.; Van Wanrooy, S.; Dooley, J.; Cibert-Goton, V.; Alpizar, Y.A.; Valdez-Morales, E.E.; Nasser, Y.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Vanbrabant, W.; et al. Histamine Receptor H1-Mediated Sensitization of TRPV1 Mediates Visceral Hypersensitivity and Symptoms in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 875–887.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Boeckxstaens, G. Dietary and Pharmacological Treatment of Abdominal Pain in IBS. Gut 2017, 66, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankratov, Y.; Lalo, U. Calcium Permeability of Ligand-Gated Ca2+ Channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 739, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budriesi, R.; Ioan, P.; Locatelli, A.; Cosconati, S.; Leoni, A.; Ugenti, M.P.; Andreani, A.; Di Toro, R.; Bedini, A.; Spampinato, S.; et al. Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole System: A Scaffold Endowing Dihydropyridines with Selective Cardiodepressant Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budriesi, R.; Ioan, P.; Leoni, A.; Pedemonte, N.; Locatelli, A.; Micucci, M.; Chiarini, A.; Galietta, L.J.V. Cystic Fibrosis: A New Target for 4-Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-1,4-dihydropyridines. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3885–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, A.; Frosini, M.; Locatelli, A.; Micucci, M.; Carotenuto, C.; Durante, M.; Cosconati, S.; Budriesi, R. 4-Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-1,4-DHPs and Neuroprotection: Preliminary Study in Hits Searching. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 169, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, A.; Cosconati, S.; Micucci, M.; Leoni, A.; Marinelli, L.; Bedini, A.; Ioan, P.; Spampinato, S.M.; Novellino, E.; Chiarini, A.; et al. Ligand Based Approach to L-Type Calcium Channel by Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-1,4-dihydropyridines: From Heart Activity to Brain Affinity. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3866–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toal, C.B.; Meredith, P.A.; Elliott, H.L. Long-Acting Dihydropyridine Calcium-Channel Blockers and Sympathetic Nervous System Activity in Hypertension: A Literature Review Comparing Amlodipine and Nifedipine GITS. Blood Press. 2012, 21, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruth, S.; Qi, X. Digestive System: System Recent Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-83968-390-9. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, K.S.; Thavamani, A. Physiology, Peristalsis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Andreani, A.; Leoni, A.; Rambaldi, M.; Locatelli, A.; Bossa, R.; Galatulas, I.; Chiericozzi, M.; Bissoli, M. Dihydropyridines Bearing an Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole System. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 32, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.P. Hantzsch’s Pyridine Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1949, 71, 4003–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallarida, R.J.; Murray, R.B. Manual of Pharmacologic Calculations with Computer Programs, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Swanson, T.M.; Pryde, D.C.; Scheuer, T.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structural Basis for Inhibition of a Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channel by Ca2+ Antagonist Drugs. Nature 2016, 537, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fátima Silva Lago, A.; de Benedicto, D.F.; da Silva, L.; Thomasi, S.S. 1,4-Dihydropyridine Derivatives: An Overview of Synthesis Conditions and Biological Tests. Curr. Org. Chem. 2023, 27, 1567–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, K.N.; Travagli, R.A. Central nervous system control of gastrointestinal motility and secretion and modulation of gastrointestinal functions. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 1339–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Palsson, O.S.; Whitehead, W.E.; van Tilburg, M.A.L.; Chang, L.; Chey, W.; Crowell, M.D.; Keefer, L.; Lembo, A.J.; Parkman, H.P.; Rao, S.S.; et al. Rome IV Diagnostic Questionnaires and Tables for Investigators and Clinicians. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, W.A.; Furness, J.B. The Enteric Nervous System and Regulation of Intestinal Motility. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999, 61, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, K.M.; Koh, S.D.; Ro, S.; Ward, S.M. Regulation of Gastrointestinal Motility--Insights from Smooth Muscle Biology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, S. Quaternary Ammonium Derivatives as Spasmolytics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 3561–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Van den Houte, K.; Besard, L.; Tack, C.; Arts, J.; Caenepeel, P.; Piessevaux, H.; Vandenberghe, A.; Matthys, C.; Biesiekierski, J.; et al. Diet or Medication in Primary Care Patients with IBS: The DOMINO Study—A Randomised Trial Supported by the Belgian Health Care Knowledge Centre (KCE Trials Programme) and the Rome Foundation Research Institute. Gut 2022, 71, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Chung, G.; Kim, S.K. Phytochemical-Based Therapeutics from Traditional Eastern Medicine: Analgesic Effects and Ion Channel Modulation. Front. Pain Res. 2025, 6, 1537154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodmann, T.; Endo, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Vinderola, G.; Kneifel, W.; de Vos, W.M.; Salminen, S.; Gómez-Gallego, C. Safety of Novel Microbes for Human Consumption: Practical Examples of Assessment in the European Union. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Yao, G.; Yang, Z.; Huang, T.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhang, H. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis Uncovers Metabolic Variability of Four Bifidobacterial Strains for Probiotic Development. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1522036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, V.; Westermann, C.; Riedel, C.U. Bifidobacteria-Host Interactions—An Update on Colonisation Factors. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 960826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, J.; Smidt, H.; Rijkers, G.T.; de Vos, W.M. Intestinal Microbiota in Human Health and Disease: The Impact of Probiotics. Genes. Nutr. 2011, 6, 209–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyei-Baffour, V.O.; Vijaya, A.K.; Burokas, A.; Daliri, E.B.-M. Psychobiotics and the Gut-Brain Axis: Advances in Metabolite Quantification and Their Implications for Mental Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-García, A.; Fernández-Ochoa, Á.; Cádiz-Gurrea, M.d.l.L.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A. Neuroprotective Effects of Agri-Food By-Products Rich in Phenolic Compounds. Nutrients 2023, 15, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Shi, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, J. From Microbial Homeostasis to Systemic Pathogenesis: A Narrative Review on Gut Flora’s Role in Neuropsychiatric, Metabolic, and Cancer Disorders. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 8851–8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarda, L.; Mattioli, L.B.; Corazza, I.; Marzetti, C.; Budriesi, R. Targeting the Gut-Brain Axis with Plant-Derived Essential Oils: Phytocannabinoids and Beyond. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.A.S.; Silva, J.B.A.; Silva, N.B.S.; Félix, P.C.A.; Dos Santos, D.A.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Martins, C.H.G.; Magalhães, L.G.; Crotti, A.E.M. Antibacterial and Antileishmanial Activity of 1,4-Dihydropyridine Derivatives. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, 22, e202401300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.R.; Idhayadhulla, A.; Nasser, A.J.A.; Selvin, J. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of a New Series 1,4-Dihydropyridine Derivatives. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2011, 76, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, D.; Qian, M.; Liu, J.; Pan, C.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Wang, L. Amlodipine, an Anti-Hypertensive Drug, Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Gut Microbiota. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 2054–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.-H.; Xie, R.-Y.; Liu, X.-L.; Chen, S.; Tang, H.-D. Mechanisms of Short-Chain Fatty Acids Derived from Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigi, R.; Vitali, B.; Prata, C.; Palomino, R.A.N.; Graziadio, A.; Locatelli, A.; Rambaldi, M.; Leoni, A. Investigation on the Effects of Antimicrobial Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole Derivatives on the Genitourinary Microflora. Med. Chem. 2018, 14, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosheva, M.; Tokodi, I.; Krasnow, A.; Pedersen, H.K.; Lukjancenko, O.; Eklund, A.C.; Grathwohl, D.; Sprenger, N.; Berger, B.; Cercamondi, C.I.; et al. Infant Formula With a Specific Blend of Five Human Milk Oligosaccharides Drives the Gut Microbiota Development and Improves Gut Maturation Markers: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 920362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. Bifidobacterium Longum: Protection against Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 8030297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-S.; Cha, L.; Sim, M.; Jung, S.; Chun, W.Y.; Baik, H.W.; Shin, D.-M. Probiotic Supplementation Improves Cognitive Function and Mood with Changes in Gut Microbiota in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Trial. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabous, A.; Stellavato, A.; Cimini, D.; Vassallo, V.; D’Agostino, M.; Schiraldi, C. A Probiotic Multi-Strain Mixture Combined with Hydroxyectoine Improves Intestinal Barrier Function by Alleviating Inflammation in Lipopolysaccharide Stimulated Differentiated Caco-2 Cells. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 11578–11589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, T.; Gong, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, Z.; et al. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Gut Microbiota and Attenuate Inflammatory in DSS-Induced Colitis Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Guan, K.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Q. PYY-Mediated Appetite Control and Obesity Alleviation through Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Driven Gut-Brain Axis Modulation by Lacticaseibacillus Rhamnosus HF01 Isolated from Qula. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 7960–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.J.; Kim, W.-K.; Han, D.H.; Lee, K.; Ko, G. Lactobacillus Fermentum Species Ameliorate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis by Regulating the Immune Response and Altering Gut Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Tian, H.; Xue, Y.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. Lactobacillus Acidophilus Ameliorates Obesity in Mice through Modulation of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Intestinal Permeability. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 175, 106020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, Z. Editorial: Innate Immunity and Cross-Talk with Microflora in the Regulation of Immune Recognition and Polarization during Immune-Related Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1335238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dang, G.; Hao, W.; Li, A.; Zhang, H.; Guan, S.; Ma, T. Dietary Supplementation of Compound Probiotics Improves Intestinal Health by Modulated Microbiota and Its SCFA Products as Alternatives to In-Feed Antibiotics. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 17, 1969–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, L.B.; Budriesi, R.; Camarda, L.; Nardi, E.; Rossi, P.L.; Bondioli, L.; Corazza, I. Biomechanical Characterization of Spontaneous and Induced Motility in Small Animals’ Gastrointestinal Tissue for Human Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Purposes. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, L.B.; Frosini, M.; Amoroso, R.; Maccallini, C.; Chiano, E.; Aldini, R.; Urso, F.; Corazza, I.; Micucci, M.; Budriesi, R. Olea Europea L. Leaves and Hibiscus Sabdariffa L. Petals Extracts: Herbal Mix from Cardiovascular Network Target to Gut Motility Dysfunction Application. Nutrients 2022, 14, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panaro, M.A.; Budriesi, R.; Calvello, R.; Cianciulli, A.; Mattioli, L.B.; Corazza, I.; Rotondo, N.P.; Porro, C.; Lamonaca, A.; Ferraro, V.; et al. Lentil Waste Extracts for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Symptoms Control: Anti-Inflammatory and Spasmolytic Effects. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, L.B.; Corazza, I.; Budriesi, R.; Hrelia, S.; Malaguti, M.; Caliceti, C.; Amoroso, R.; Maccallini, C.; Crupi, P.; Clodoveo, M.L.; et al. From Waste to Health: Olive Mill Wastewater for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motulsky, H.J. Prism 5.0 Statistics Guide; GraphPad Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 31, 39–42. Available online: https://cdn.graphpad.com/faq/2/file/Prism_v5_Statistics_Guide.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Motulsky, H.; Christopoulos, A. Fitting Models to Biological Data Using Linear and Nonlinear Regression: A Practical Guide to Curve Fitting; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-19-517179-2. [Google Scholar]
- So, D.; Whelan, K.; Rossi, M.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.; Kelly, J.T.; Shanahan, E.R.; Staudacher, H.M.; Campbell, K.L. Dietary Fiber Intervention on Gut Microbiota Composition in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 965–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak-Kopeć, P.; Śliżewska, K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids by Human Intestinal Microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Lee, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Koh, D.; Lim, Y. Synthetic Diethyl 2,6-Dimethyl-1,4-Dihydropyridine-3,5-Dicarboxylates Induce Apoptosis. Med. Chem. 2018, 14, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).