Spinorphin Molecules as Opportunities for Incorporation into Spinorphin@AuNPs Conjugate Systems for Potential Sustained Targeted Delivery to the Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Spectral Characterization
2.3. Analyses by Circular Dichroism
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5. SEM-EDS Analysis
Determination of Zeta Potential
2.6. Anticonvulsant Activity
3. Materials and Methods
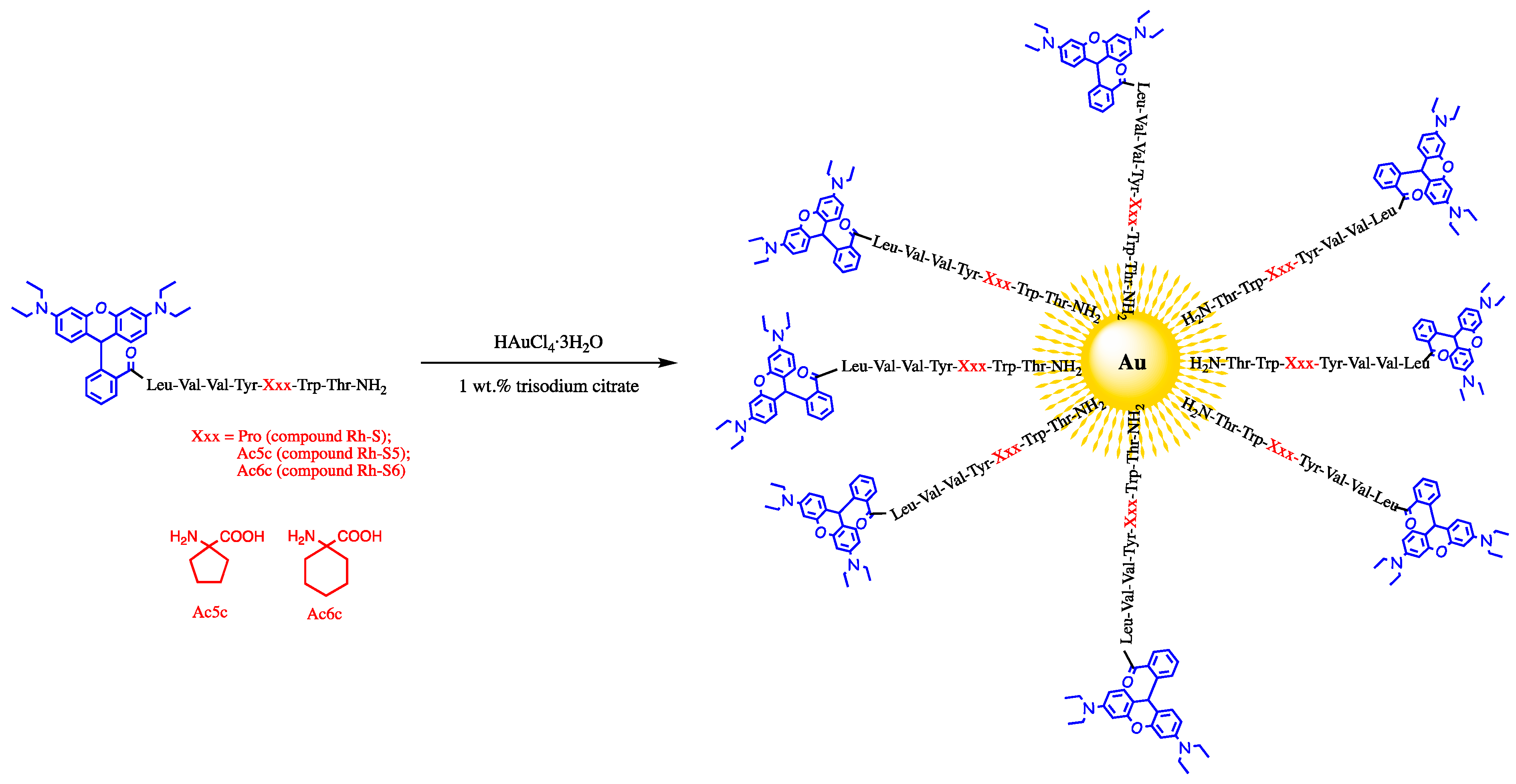
3.1. Preparation of Nanopeptide Systems of the Type Rh-S (Spinorphin Derivatives)@AuNPs
3.1.1. Synthesis of AuNPs
3.1.2. Synthesis of Spinorphin@AuNP Conjugates
3.2. Zeta Potential
3.3. Spectral Measurement
3.4. Analyses for Determining the Structural Morphology of Spinorphin@AuNP Conjugates
3.5. Biological Analysis
3.5.1. Pharmacology
- Animals
- Drugs and dosage
3.5.2. Tests for Anticonvulsant Activity Determination
- 6-Hz seizure test
- Maximal electroshock test (MES test)
3.5.3. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfram, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Y.; Shen, J.; Gentile, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Nie, G.; Chen, C.; Shen, H.; et al. Safety of nanoparticles in medicine. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Birla, S.; Yadav, A.; Santos, C.A. Strategic role of selected noble metal nanoparticles in medicine. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 696–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.F.; Sun, Y.L.; Yeh, F.Y.; Tseng, I.H.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.S. Detection of chymase activity using a specific peptide probe conjugated onto gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29013–29021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, R.R.; Julius, A.; Suman, T.Y.; Mohanavel, V.; Karthick, A.; Pazhanimuthu, C.; Samrot, A.V.; Muhibbullah, M. Role of nanoparticles in biodegradation and their importance in environmental and biomedical applications. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 6090846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, S.D.; Kwon, Y.M.; Omidi, Y.; Speth, R.C. Nanoparticle approaches for the renin-angiotensin system. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.; Wong, N.K. Nanotechnology and its use in imaging and drug delivery. Biomed. Rep. 2021, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, H.; Huo, Q. Gold nanoparticle-enabled biological and chemical detection and analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2849–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.A.; Gil, P.R.; Zhang, F.; Zanella, M.; Parak, W.J. Biological applications of gold nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1896–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Han, G.; De, M.; Kim, C.K.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in delivery applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyanage, P.Y.; Hettiarachchi, S.D.; Zhou, Y.; Ouhtit, A.; Seven, E.S.; Oztan, C.Y.; Celik, E.; Leblanc, R.M. Nanoparticle-mediated targeted drug delivery for breast cancer treatment. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Ghasemi, A.; Zangabad, P.S.; Rahighi, R.; Basri, S.M.M.; Mirshekari, H.; Amiri, M.; Pishabad, Z.S.; Aslani, A.; Bozorgomid, M.; et al. Smart micro/nanoparticles in stimulus-responsive drug/gene delivery systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1457–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, S.M.D.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Moin, A.; Hussain, T.; Kamal, M.A.; Sonbol, H.; Khafagy, E.-S. Antibiotic-loaded gold nanoparticles: A nano-arsenal against ESBL producer-resistant pathogens. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, P.P.; Rai, A.; Baruah, P.K. Recent advances in the development of antibiotics-coated gold nanoparticles to combat antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic peptides: Current applications and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.S. Therapeutic proteins. Ther. Proteins Methods Protoc. 2012, 899, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudlarz, A.; Szemraj, J. Nanoparticles as carriers of proteins, peptides and other therapeutic molecules. Open Life Sci. 2018, 13, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavolta, L.; Cabral, F.R. Peptides: Important tools for the treatment of central nervous system disorders. Neuropeptides 2011, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.; Kim, H.; Lee, E.; Lee, M. Self-assembly of T-shaped aromatic amphiphiles into stimulus-responsive nanofibers. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6807. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.H.; Kirshenbaum, K. Photoresponsive peptoid oligomers bearing azobenzene side chains. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 2516–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boturyn, D.; Coll, J.-L.; Garanger, E.; Favrot, M.-C.; Dumy, P. Template assembled cyclopeptides as multimeric system for integrin targeting and endocytosis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5730–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, T.; Niemeier, N.; Afonin, S.; Ulrich, A.S.; Krug, H.F.; Braese, S. Peptoidic amino-and guanidinium-carrier systems: Targeted drug delivery into the cell cytosol or the nucleus. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, S.; Araya, E.; Fiedler, J.L.; Arias, J.I.; Adura, C.; Albericio, F.; Giralt, E.; Arias, J.L.; Fernández, M.S.; Kogan, M.J. Improving the brain delivery of gold nanoparticles by conjugation with an mphipathic peptide. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, L.; Hu, G.; Chen, J.; Cun, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; He, Q.; Gao, H. Biomaterials Tumor microenvironment sensitive doxorubicin delivery and release to glioma using angiopep-2 decorated gold nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2015, 37, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Zavala, F.; Arriagada, H.; Hassan, N.; Velasco, C.; Riveros, A.; Álvarez, A.R.; Minniti, A.N.; Rojas-Silva, X.; Muñoz, L.L.; Vasquez, R.; et al. Peptide multifunctionalized gold nanorods decrease toxicity of β-amyloid peptide in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCully, M.; Sanchez-Navarro, M.; Teixido, M.; Giralt, E. Peptide mediated brain delivery of nano-and submicroparticles: A synergistic approach. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevozhay, D.; Kańska, U.; Budzyńska, R.; Boratyński, J. Current status of research on conjugates and related drug delivery systems in the treatment of cancer and other diseases. Postep. Hig. I Med. Dosw. 2007, 61, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Wu, J.; Shi, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanotechnology for protein delivery: Overview and perspectives. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishya, R.; Khurana, V.; Patel, S.; Mitra, A.K. Long-term delivery of protein therapeutics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinsmaa, Y.; Yoshikawa, M. Release of Hemorphin-5 from Human Hemoglobin by Pancreatic Elastase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Todorov, P.; Georgieva, S.; Tchekalarova, J.; Subaer, S.; Peneva, P.; Hartati, H. Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Investigation of New N-Modified Spinorphin Analogs. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Carpinone, P.L.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Demokritou, P.; Moudgil, B.M. Synthesis of precision gold nanoparticles using Turkevich method. KONA Powder Part. J. 2020, 37, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; No, Y.H.; Sluyter, R.; Konstantinov, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.H. Peptide nanoparticle conjugates as a theranostic platform. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 500, 215530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.A. Interpretation of α-synuclein UV absorption spectra in the peptide bond and the aromatic regions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 212, 112022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, P.; Georgieva, S.; Peneva, P.; Nikolov, S.; Rangelov, M.; Todorova, N.; Pechlivanova, D.; Tchekalarova, J. Synthesis, molecular docking, electrochemical and fluorimetric analysis of new caffeic and cinnamic acid-conjugated hemorphin derivatives designed as potential anticonvulsant and antinociceptive agents. Bioorganic Chem. 2024, 143, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornander, L.H.; Feng, B.; Beke-Somfai, T.; Nordén, B. UV transition moments of tyrosine. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2014, 118, 9247–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashchuk, V.M.; Kudrya, V.Y.; Levchenko, S.M.; Tkachuk, Z.Y.; Hovorun, D.M.; Mel’Nik, V.I.; Vorob’Yov, V.P.; Klishevich, G.V. Optical response of the polynucleotides-proteins interaction. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 535, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adochitei, A.; Drochioiu, G. Rapid characterization of peptide secondary structure by FT-IR spectroscopy. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2011, 56, 783–791. [Google Scholar]
- Olmedo, I.; Araya, E.; Sanz, F.; Medina, E.; Arbiol, J.; Toledo, P.; Alvarez-Lueje, A.; Giralt, E.; Kogan, M.J. How changes in the sequence of the peptide CLPFFD-NH2 can modify the conjugation and stability of gold nanoparticles and their affinity for β-amyloid fibrils. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.B. Biological spectroscopy: By ID Campbell and RA Dwek. pp 404. Addison-Wesley, Wokingham, UK. 1984. £ 37.95 and £ 14.95 (softback). ISBN 0-8053-1847-X and 0-8053-1849-6. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 1985, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Smyth, H.D.C. Smart Magnetically Responsive Hydrogel Nanoparticles Prepared by a Novel Aerosol-Assisted Method for Biomedical and Drug Delivery Applications. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 910539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghamirzaei, M.; Khiabani, M.S.; Hamishehkar, H.; Mokarram, R.R.; Amjadi, M. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) from Chinese lettuce (CL) leave extract (Brassica rapa var. pekinensis). Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, N.; Astruc, D. State of the art in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 638–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.H.; Saqer, A.M.A.; Assirey, E.; Naqvi, A.; Okasha, R.M. Successful green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a Corchorus olitorius extract and their antiproliferative effect in cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciaro, B.; Moros, M.; Rivera-Fernández, S.; Bellelli, A.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Mangoni, M.L. Gold-nanoparticles coated with the antimicrobial peptide esculentin-1a(1-21)NH2 as a reliable strategy for antipseudomonal drugs. Acta Biomater. 2017, 47, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, V.; Pilakka-Kanthikeel, S.; Atluri, V.S.; Ding, H.; Arias, A.Y.; Jayant, R.D.; Kaushik, A.; Nair, M. Therapeutical neurotargeting via magnetic nanocarrier: Implications to opiate-induced neuropathogenesis and neuroAIDS. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Hikiba, S.; Yamashita, K.; Muto, M.; Okochi, M. Array-based functional peptide screening and characterization of gold nanoparticle synthesis. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, N.; Mehrnejad, F.; Vaezi, Z.; Sedghi, M.; Asghari, S.M.; Naderi-Manesh, H. Encapsulation of an endostatin peptide in liposomes: Stability, release, and cytotoxicity study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.P., Jr.; Focken, T.; Karimi Tari, P.; Dube, C.; Goodchild, S.J.; Andrez, J.C.; Bankar, G.; Burford, K.; Chang, E.; Chowdhury, S.; et al. The contribution of NaV1.6 to the efficacy of voltage-gated sodium channel inhibitors in wild type and NaV1.6 gain-of-function (GOF) mouse seizure control. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 3993–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






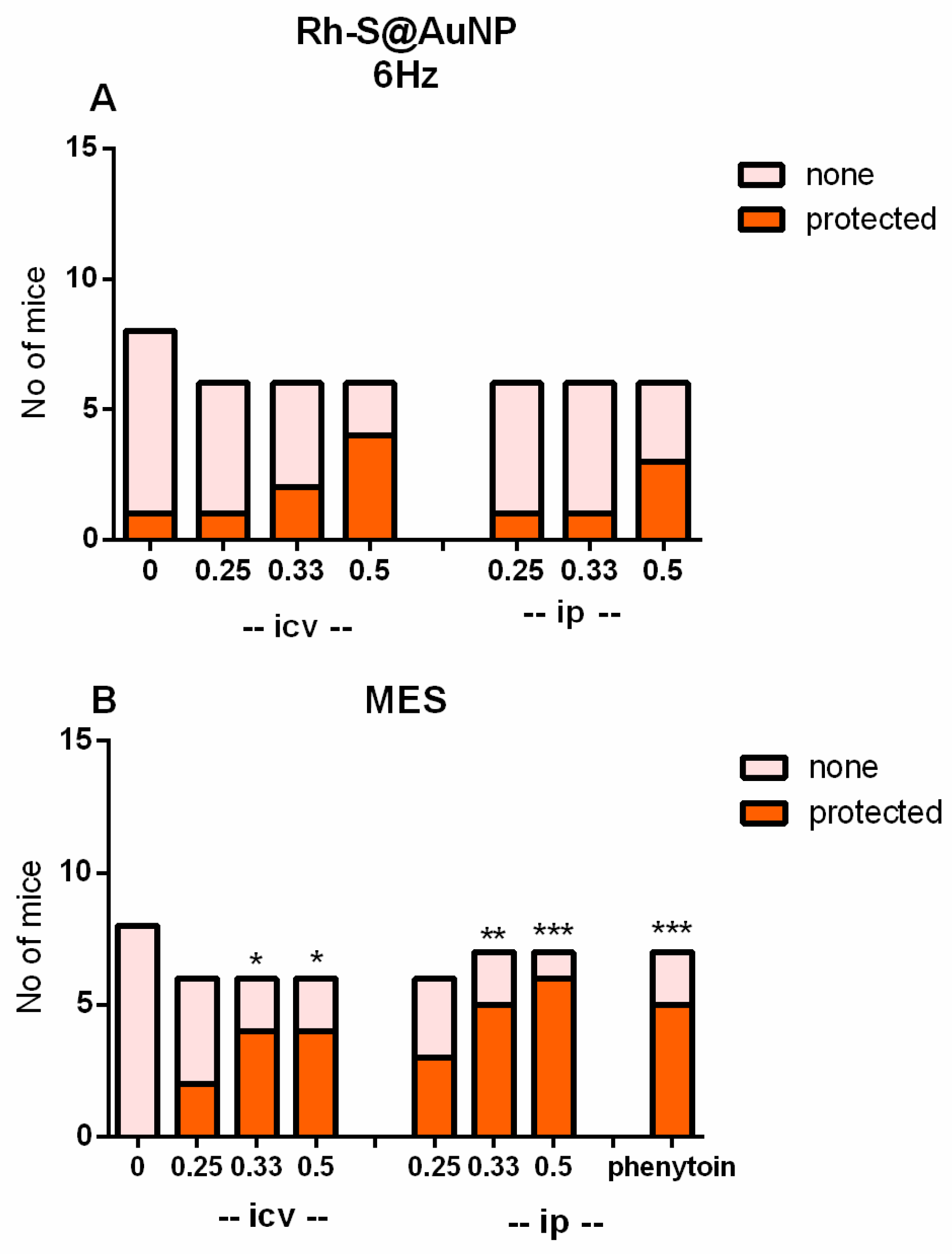


| Compound | % Protection | % Mortality |
|---|---|---|
| control | 0 | 70 |
| Rh-S | ||
| 0.25 mg/kg | 0 | 67 |
| 0.33 mg/kg | 0 | 67 |
| 0.5 mg/kg | 0 | 67 |
| Rh-S@AuNP | ||
| 0.25 mg/kg | 50% | 33 |
| 0.33 mg/kg | 71% | 0 |
| 0.5 mg/kg | 86% | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgieva, S.; Todorov, P.; Tchekalarova, J. Spinorphin Molecules as Opportunities for Incorporation into Spinorphin@AuNPs Conjugate Systems for Potential Sustained Targeted Delivery to the Brain. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010053
Georgieva S, Todorov P, Tchekalarova J. Spinorphin Molecules as Opportunities for Incorporation into Spinorphin@AuNPs Conjugate Systems for Potential Sustained Targeted Delivery to the Brain. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgieva, Stela, Petar Todorov, and Jana Tchekalarova. 2025. "Spinorphin Molecules as Opportunities for Incorporation into Spinorphin@AuNPs Conjugate Systems for Potential Sustained Targeted Delivery to the Brain" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010053
APA StyleGeorgieva, S., Todorov, P., & Tchekalarova, J. (2025). Spinorphin Molecules as Opportunities for Incorporation into Spinorphin@AuNPs Conjugate Systems for Potential Sustained Targeted Delivery to the Brain. Pharmaceuticals, 18(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010053








