Evaluation of Prediction Models for the Capping and Breaking Force of Tablets Using Machine Learning Tools in Wet Granulation Commercial-Scale Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Data Preparation
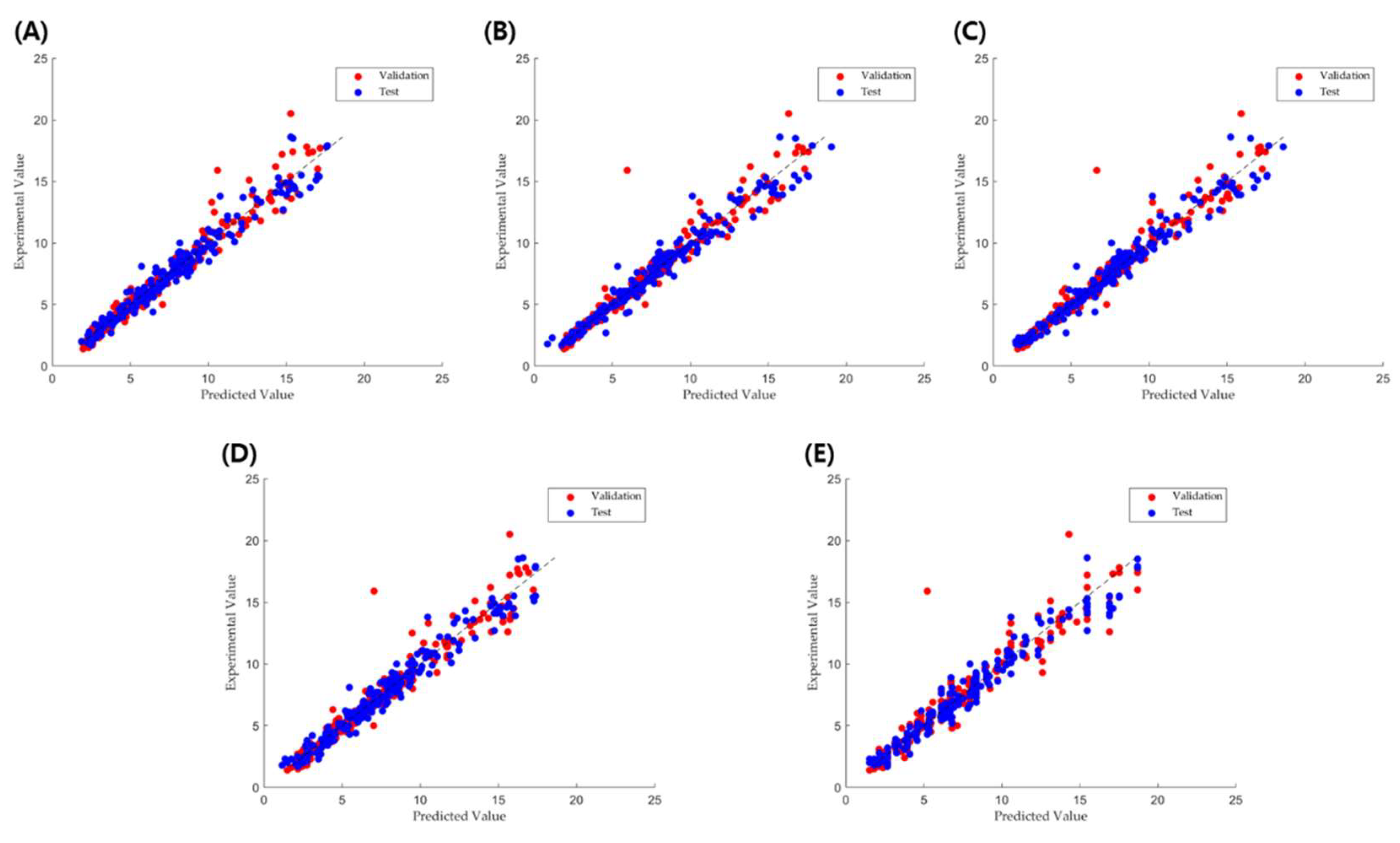
2.2. TBF Prediction
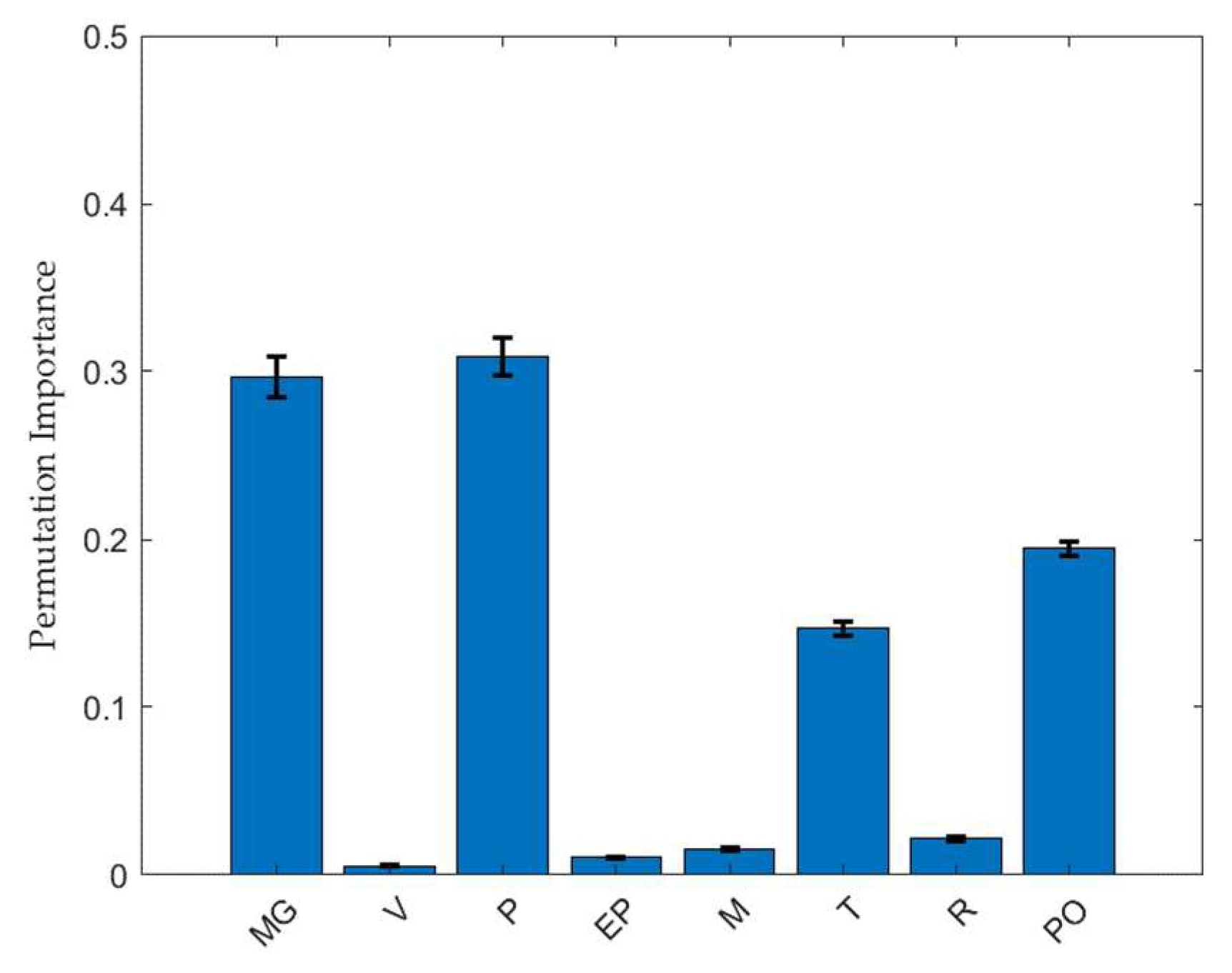
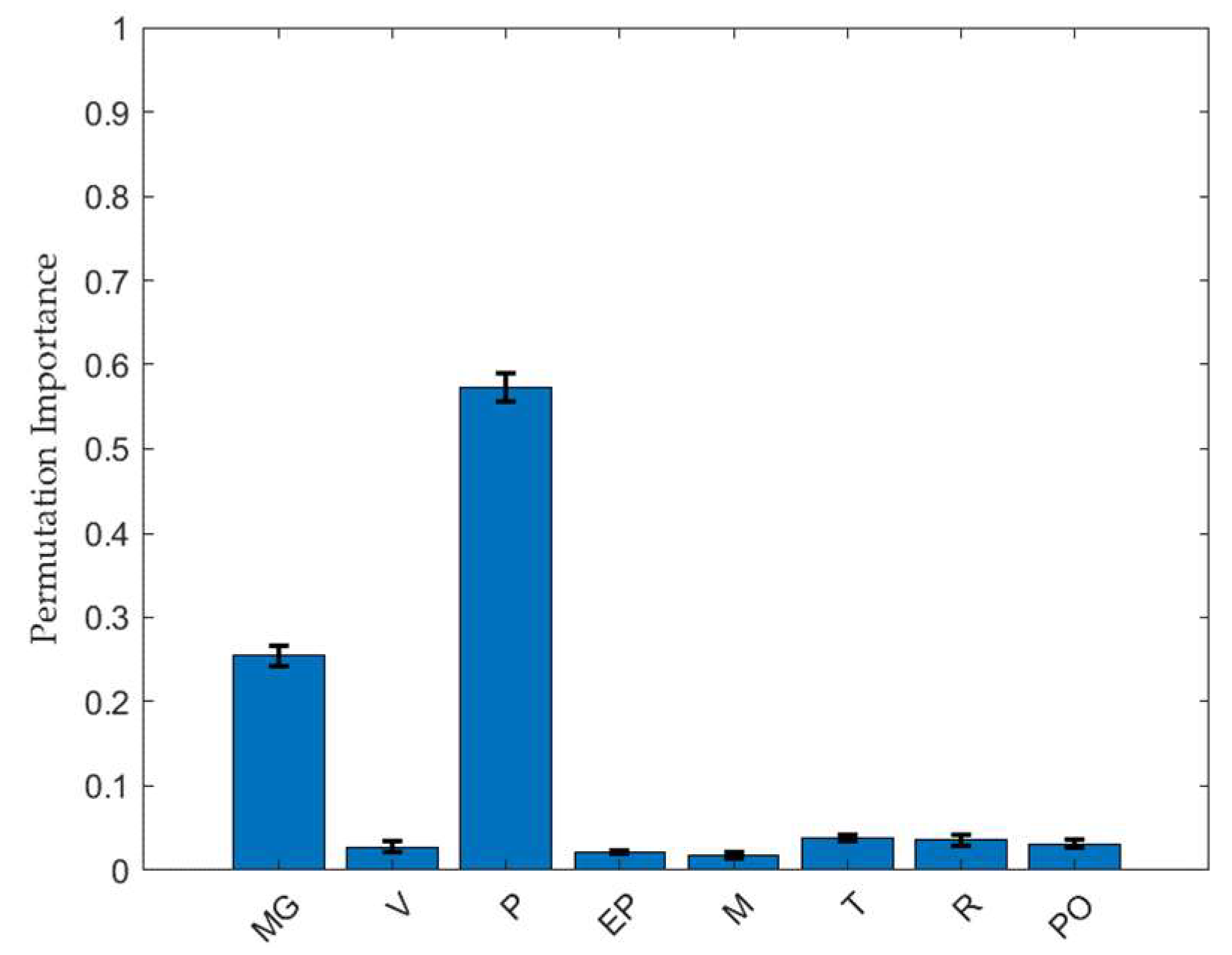
2.3. Feature Importance Analysis of the Factors Affecting the TBF
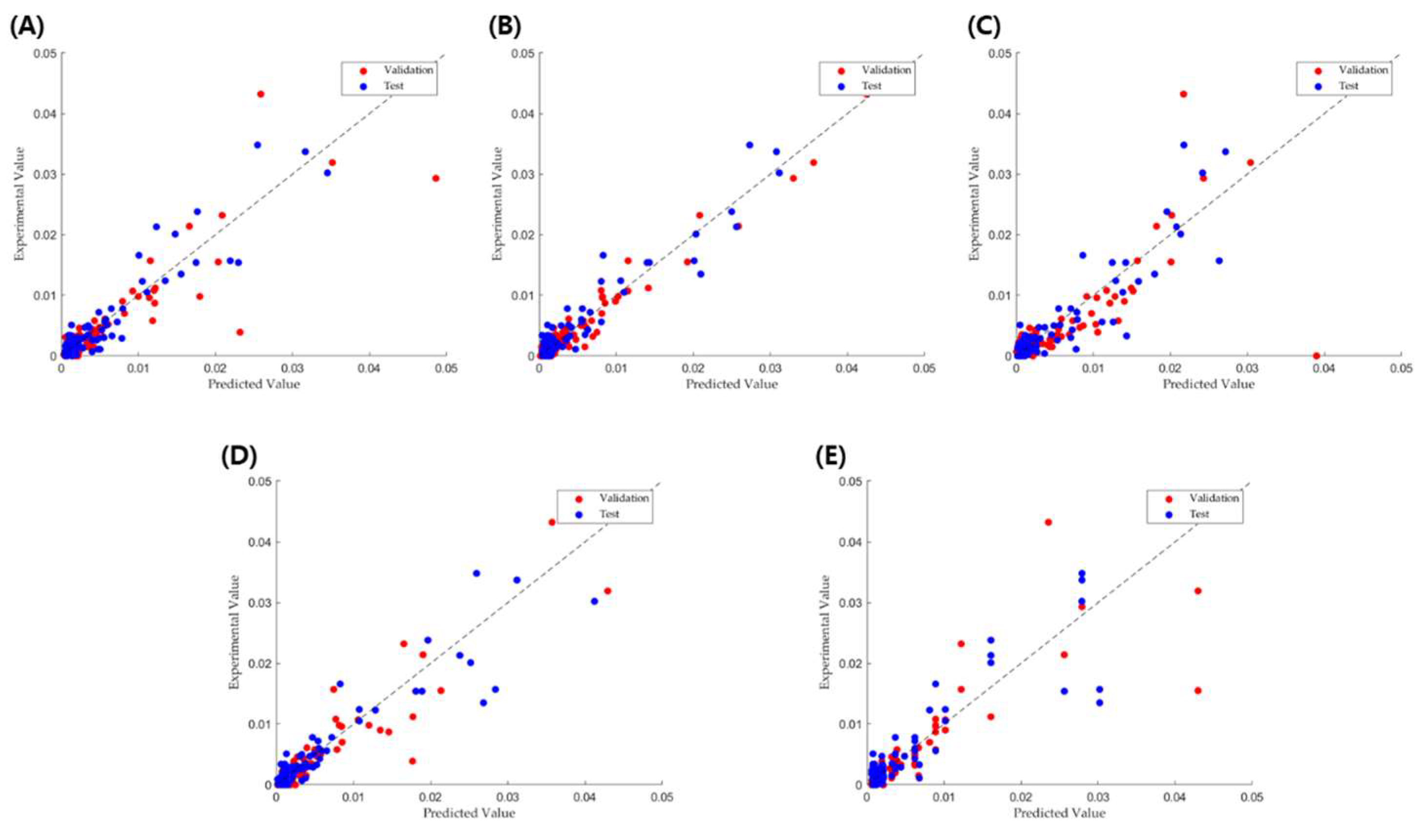
2.4. Friability Prediction
2.5. Feature Importance Analysis of the Factors Affecting Friability
2.6. Tablet Capping Occurrence Prediction
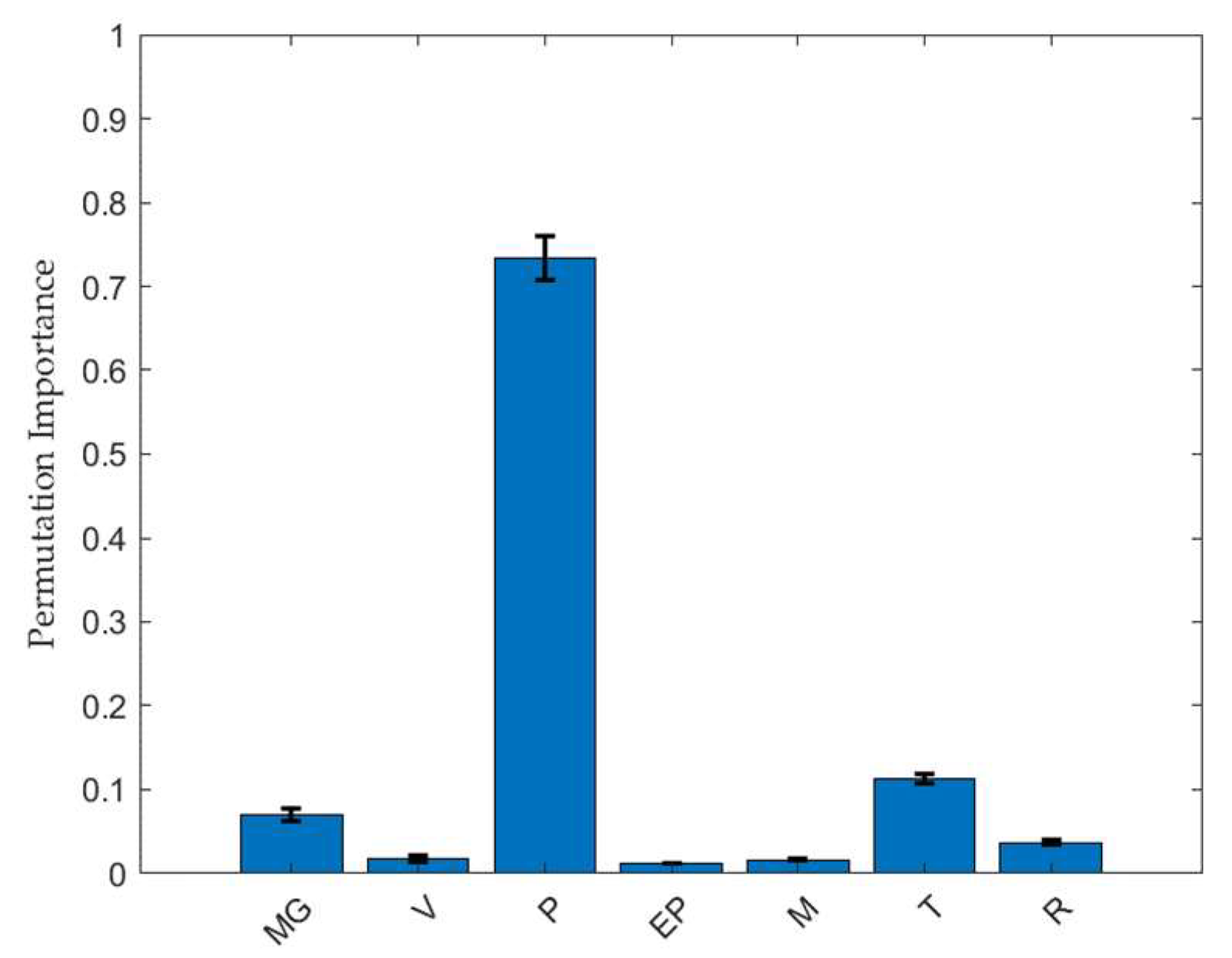
2.7. Feature Importance Analysis for the Factors Affecting Capping Occurrence
2.8. Strength and Limitations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. MF-Loaded Granule Using the Wet Granulation Method and Tablet Preparation
3.3. Porosity of the MF-Loaded Tablets
3.4. Compaction Breaking Force Required to Break the MF-Loaded Tablets
3.5. Friability Test
3.6. Machine Learning Techniques
3.7. Evaluation of the Results
3.8. Relative Importance of Each Input Variable
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akseli, I.; Xie, J.; Schultz, L.; Ladyzhynsky, N.; Bramante, T.; He, X.; Deanne, R.; Horspool, K.R.; Schwabe, R. A practical framework toward prediction of breaking force and disintegration of tablet formulations using machine learning tools. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki-Lohiluoma, E.; Säkkinen, N.; Palomäki, M.; Winberg, O.; Ta, H.X.; Heikkinen, T.; Kiljunen, E.; Kauppinen, A. Use of machine learning in prediction of granule particle size distribution and tablet tensile strength in commercial pharmaceutical manufacturing. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, C.; Alderborn, G.; Duberg, M.; Karehill, P.G. Bonding surface area and bonding mechanism-two important factors fir the understanding of powder comparability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1993, 19, 2143–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H. Comprehensive Study on Compression Pressure to Improve Tablet Defects in Multi-Layer Tablets. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Pharmacy, Graduate School of Dankook University, Cheonan, Republic of Korea, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, T.; Dave, V.S.; Cetinkaya, C. Early detection and assessment of invisible cracks in compressed oral solid dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Ouyang, D. Predicting oral disintegrating tablet formulations by neural network techniques. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Oishi, T.; Shirotori, K.; Marumo, Y.; Kosugi, A.; Kumada, S.; Hirai, D.; Takayama, K.; Onuki, Y. Modeling of quantitative relationships between physicochemical properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients and tensile strength of tablets using a boosted tree. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnikrishnan, S.; Donovan, J.; Macpherson, R.; Tormey, D. Machine learning for automated quality evaluation in pharmaceutical manufacturing of emulsions. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 15, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Kittikunakorn, N.; Sorman, B.; Xi, H.; Chen, A.; Marsh, M.; Mongeau, A.; Piché, N.; Williams, R.O., III; Skomski, D. Application of deep learning convolutional neural networks for internal tablet defect detection: High accuracy, throughput, and adaptability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Rangel, E.; Inzucchi, S.E. Metformin: Clinical use in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millen, N.; Kovačević, A.; Djuriš, J.; Ibrić, S. Machine learning modeling of wet granulation scale-up using particle size distribution characterization parameters. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 15, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Baranwal, Y.; Tseng, Y.C. An insight into predictive parameters of tablet capping by machine learning and multivariate tools. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Koizumi, K.; Zama, Y.; Kiriyama, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsumoto, M. New compressed tablet rapidly disintegrating in saliva in the mouth using crystalline cellulose and a disintegrant. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1308–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bi, Y.; Sunada, H.; Yonezawa, Y.; Danjo, K.; Otsuka, A.; Iida, K. Preparation and evaluation of a compressed tablet rapidly disintegrating in the oral cavity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, P.; Joiris, E.; Martelli, S. Particle interaction of lubricated or unlubricated binary mixtures according to their particle size and densification mechanism. Farmaco 2004, 59, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Han, S.H.; Oh, J.S.; Seo, D.W.; Kang, M.J. Evaluation of the ejection pressure for tracking internal cracks during compaction in bilayer tablet formulations using experimental and finite element methods. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tye, C.K.; Sun, C.C.; Amidon, G.E. Evaluation of the effects of tableting speed on the relationships between compaction pressure, tablet tensile strength, and tablet solid fraction. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gams, M.; Horvat, M.; Ožek, M.; Luštrek, M.; Gradišek, A. Integrating artificial and human intelligence into tablet production process. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowhan, Z.T.; Yang, I.C.; Amaro, A.A.; Chi, L.H. Effect of Moisture and Crushing Strength on Tablet Friability and In Vitro Dissolution. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomane, K.S.; More, P.K.; Raghavendra, G.; Bansal, A.K. Molecular Understanding of the Compaction Behavior of Indomethacin Polymorphs. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, D.H.; Park, H.; Ha, E.S.; Kim, H.H.; Jang, S.W.; Kim, M.S. Optimization of Bilayer Tablet Manufacturing Process for Fixed-Dose Combination of Sustained-Release High-Dose Drug and Immediate-Release Low-Dose Drug Based on Quality by Design (QbD). Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kook, J.H.; Seo, D.W.; Kang, M.J. The Effect of Compression Pressure on the First-Layer Surface Roughness and Delamination of Metformin and Evogliptin Bilayer and Trilayer Tablets. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USP Standard No. 1217; Tablet Breaking Force. The United States Pharmacopeial Convention: North Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-4DC4CB4A-5FB0-4F87-8F72-45582BEAC6E9_2_en-US?source=Quick%20Search&highlight=tablet%20breaking%20force (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Park, K. A Review of Computational Drug Repurposing. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 27, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, M.C.; Castelfranco, A.M.; Roncalli, V.; Lenz, P.H.; Hartline, D.K. t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE): A Tool for Eco-Physiological Transcriptomic Analysis. Mar. Genom. 2020, 51, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Ali, Z.A.; Wong, B.M. Harnessing semi-supervised machine learning to automatically predict bioactivities of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 10, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Marumo, Y.; Kumada, S.; Okada, K.; Onuki, Y. Application of Machine Learning to a Material Library for Modeling of Relationships Between Material Properties and Tablet Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrić, M.; Horner, D.; Chen, L.; Brustad, N.; Schoos, A.M.M.; Lasky-Su, J.; Chawes, B.; Rasmussen, M.A. Vertical Metabolome Transfer from Mother to Child: An Explainable Machine Learning Method for Detecting Metabolomic Heritability. Metabolites 2024, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Yoo, S. InterDILI: Interpretable Prediction of Drug-Induced Liver Injury Through Permutation Feature Importance and Attention Mechanism. J. Cheminform. 2024, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Function | Ingredient | |
|---|---|---|
| Active pharmaceutical ingredient | MF | 500 |
| Binder | Polyvinylpyrrolidone | 20 |
| Lubricant | Mg stearate | 3.6–12.3 |
| Controlled release excipient | Carbomer 934P | 10 |
| Controlled release excipient | HPMC2208 | 50 |
| Controlled release excipient | Methacrylic acid copolymer | 20 |
| Objective Variable | Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBF | RF | 0.959 | 0.780 | 0.561 |
| GPR | 0.959 | 0.890 | 0.541 | |
| SVM | 0.958 | 0.798 | 0.530 | |
| BT | 0.959 | 0.787 | 0.595 | |
| DT | 0.954 | 0.863 | 0.609 | |
| Friability | RF | 0.919 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| GPR | 0.949 | 0.002 | 0.001 | |
| SVM | 0.764 | 0.004 | 0.002 | |
| BT | 0.917 | 0.003 | 0.001 | |
| DT | 0.822 | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | RF | DT | SVM | BT | kNN |
| TP | 21 | 21 | 16 | 27 | 20 |
| TN | 210 | 207 | 217 | 201 | 212 |
| FP | 3 | 7 | 2 | 7 | 5 |
| FN | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Accuracy (%) | 97.06 | 95.80 | 97.90 | 95.80 | 97.48 |
| Misclassification (%) | 2.94 | 4.20 | 2.10 | 4.20 | 2.52 |
| No. of samples | 238 | 238 | 238 | 238 | 238 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.H.; Han, S.H.; Seo, D.-W.; Kang, M.J. Evaluation of Prediction Models for the Capping and Breaking Force of Tablets Using Machine Learning Tools in Wet Granulation Commercial-Scale Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010023
Kim SH, Han SH, Seo D-W, Kang MJ. Evaluation of Prediction Models for the Capping and Breaking Force of Tablets Using Machine Learning Tools in Wet Granulation Commercial-Scale Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sun Ho, Su Hyeon Han, Dong-Wan Seo, and Myung Joo Kang. 2025. "Evaluation of Prediction Models for the Capping and Breaking Force of Tablets Using Machine Learning Tools in Wet Granulation Commercial-Scale Pharmaceutical Manufacturing" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010023
APA StyleKim, S. H., Han, S. H., Seo, D.-W., & Kang, M. J. (2025). Evaluation of Prediction Models for the Capping and Breaking Force of Tablets Using Machine Learning Tools in Wet Granulation Commercial-Scale Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. Pharmaceuticals, 18(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010023






