Rat Sympathetic Neuron Calcium Channels Are Insensitive to Gabapentin
Abstract
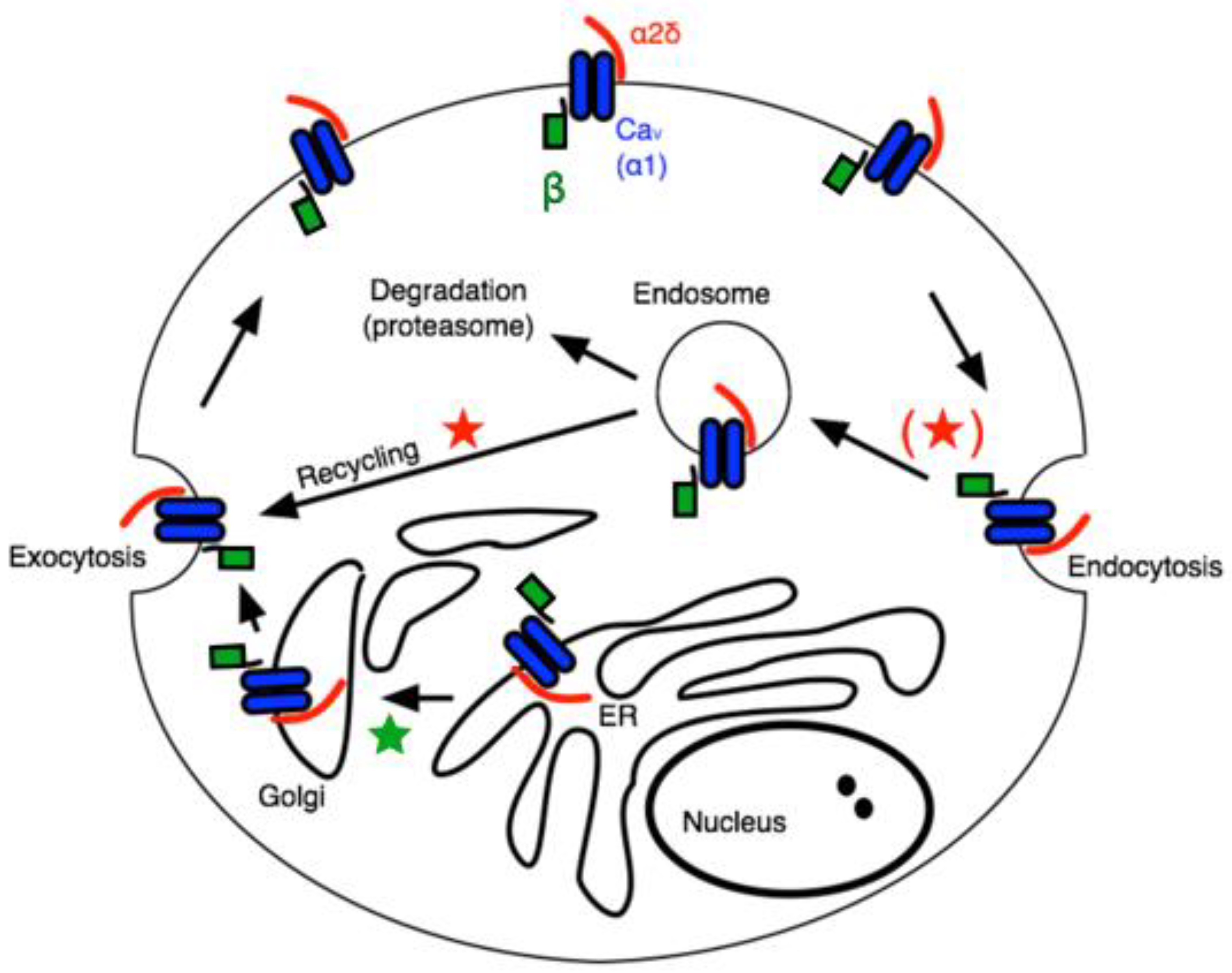
1. Introduction
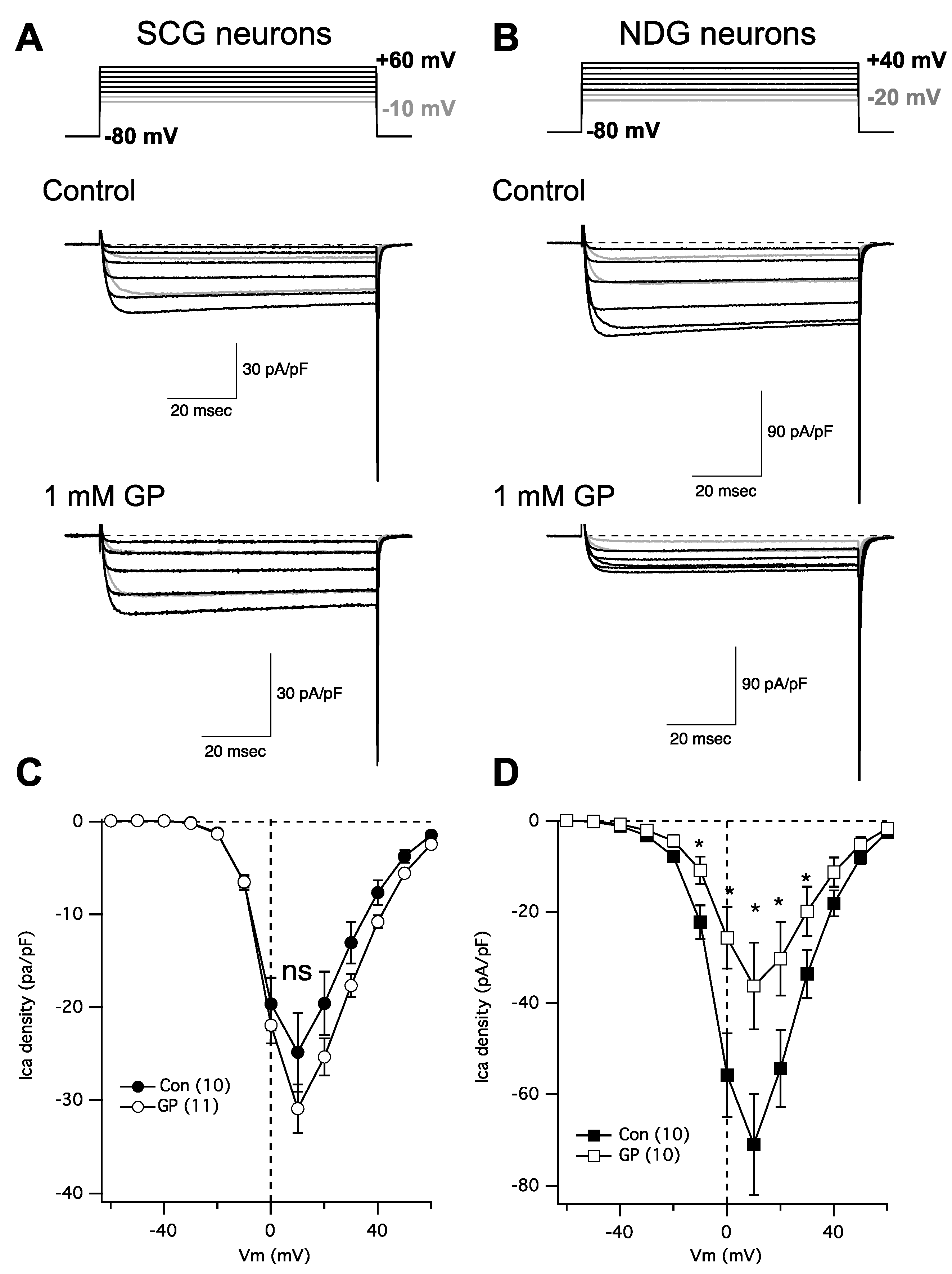
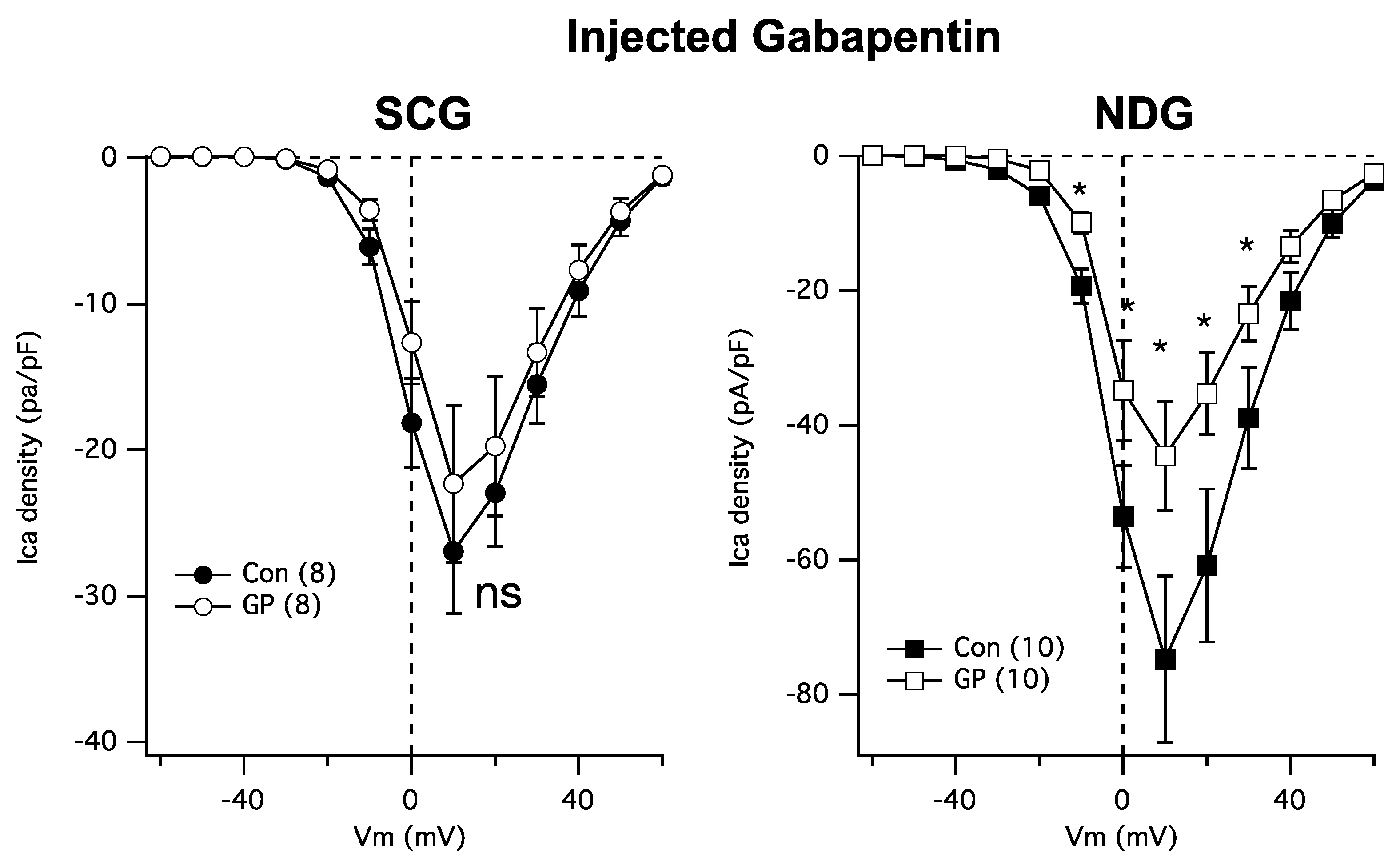
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Isolation and Culture
4.2. Electrophysiology
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shanthanna, H.; Gilron, I.; Rajarathinam, M.; AlAmri, R.; Kamath, S.; Thabane, L.; Devereaux, P.J.; Bhandari, M. Benefits and safety of gabapentinoids in chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, E.E.; Sandilands, E.A.; Webb, D.J. Gabapentin and pregabalin: Do the benefits outweigh the harms? J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2017, 47, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, N.S.; Brown, J.P.; Dissanayake, V.U.; Offord, J.; Thurlow, R.; Woodruff, G.N. The novel anticonvulsant drug, gabapentin (Neurontin), binds to the alpha2delta subunit of a calcium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5768–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, D.J.; Donovan, C.M.; Meder, W.P.; Whetzel, S.Z. Preferential action of gabapentin and pregabalin at P/Q-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels: Inhibition of K+-evoked [3H]-norepinephrine release from rat neocortical slices. Synapse 2002, 45, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Chen, S.R.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.D.; Sirrieh, R.E.; MacLean, D.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.H.; Jayaraman, V.; et al. The alpha2delta-1-NMDA Receptor Complex Is Critically Involved in Neuropathic Pain Development and Gabapentin Therapeutic Actions. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2307–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, R.D.; McDavid, S.M.; Brindley, R.L.; Jewell, M.L.; Currie, K.P. Gabapentin inhibits catecholamine release from adrenal chromaffin cells. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, M.; Itoh, Y.; Wada, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Fujita, T. Gabapentin blocks L-type and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels involved in depolarization-stimulated nitric oxide synthase activity in primary cultures of neurons from mouse cerebral cortex. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.J.; McClelland, D.; Herd, M.B.; Sutton, K.G.; Hall, M.D.; Lee, K.; Pinnock, R.D.; Scott, R.H. Gabapentin-mediated inhibition of voltage-activated Ca2+ channel currents in cultured sensory neurones is dependent on culture conditions and channel subunit expression. Neuropharmacology 2002, 42, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alden, K.J.; Garcia, J. Differential effect of gabapentin on neuronal and muscle calcium currents. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 727–735. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.G.; Barrett, C.F.; Groth, R.D.; Safa, P.; Tsien, R.W. CaMKII locally encodes L-type channel activity to signal to nuclear CREB in excitation-transcription coupling. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Groth, R.D.; Wheeler, D.G.; Barrett, C.F.; Tsien, R.W. Excitation-transcription coupling in sympathetic neurons and the molecular mechanism of its initiation. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 70, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Yan, C.; Lu, S.; Dong, M.; Yan, N. Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 complex. Science 2015, 350, aad2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolphin, A.C. Calcium channel auxiliary alpha2delta and beta subunits: Trafficking and one step beyond. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolphin, A.C. Voltage-gated calcium channels and their auxiliary subunits: Physiology and pathophysiology and pharmacology. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5369–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, J.S.; Ferron, L.; Kadurin, I.; Pratt, W.S.; Dolphin, A.C. Functional exofacially tagged N-type calcium channels elucidate the interaction with auxiliary alpha2delta-1 subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8979–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canti, C.; Davies, A.; Berrow, N.S.; Butcher, A.J.; Page, K.M.; Dolphin, A.C. Evidence for two concentration-dependent processes for beta-subunit effects on alpha1B calcium channels. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opatowsky, Y.; Chomsky-Hecht, O.; Kang, M.G.; Campbell, K.P.; Hirsch, J.A. The voltage-dependent calcium channel beta subunit contains two stable interacting domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52323–52332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadurin, I.; Alvarez-Laviada, A.; Ng, S.F.; Walker-Gray, R.; D’Arco, M.; Fadel, M.G.; Pratt, W.S.; Dolphin, A.C. Calcium currents are enhanced by alpha2delta-1 lacking its membrane anchor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 33554–33566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Van-Minh, A.; Dolphin, A.C. The alpha2delta ligand gabapentin inhibits the Rab11-dependent recycling of the calcium channel subunit alpha2delta-2. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 12856–12867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.B.; Kammermeier, P.J. CaV2 channel subtype expression in rat sympathetic neurons is selectively regulated by alpha2delta subunits. Channels 2017, 11, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hendrich, J.; Van Minh, A.T.; Heblich, F.; Nieto-Rostro, M.; Watschinger, K.; Striessnig, J.; Wratten, J.; Davies, A.; Dolphin, A.C. Pharmacological disruption of calcium channel trafficking by the alpha2delta ligand gabapentin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3628–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.R.; Schofield, G.G.; Weight, F.F. Na+ and Ca2+ currents of acutely isolated adult rat nodose ganglion cells. J. Neurophysiol. 1986, 55, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapio, M.R.; Vazquez, F.A.; Loydpierson, A.J.; Maric, D.; Kim, J.J.; LaPaglia, D.M.; Puhl, H.L.; Lu, V.B.; Ikeda, S.R.; Mannes, A.J.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Dorsal Root, Nodose and Sympathetic Ganglia for the Development of New Analgesics. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 615362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, V.B.; Williams, D.J.; Won, Y.J.; Ikeda, S.R. Intranuclear microinjection of DNA into dissociated adult mammalian neurons. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 10, e1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scott, M.B.; Kammermeier, P.J. Rat Sympathetic Neuron Calcium Channels Are Insensitive to Gabapentin. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091237
Scott MB, Kammermeier PJ. Rat Sympathetic Neuron Calcium Channels Are Insensitive to Gabapentin. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091237
Chicago/Turabian StyleScott, Mallory B., and Paul J. Kammermeier. 2024. "Rat Sympathetic Neuron Calcium Channels Are Insensitive to Gabapentin" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091237
APA StyleScott, M. B., & Kammermeier, P. J. (2024). Rat Sympathetic Neuron Calcium Channels Are Insensitive to Gabapentin. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091237







