Study on the Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Gintonin in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Its Relationship with TRPV1, TRPV4, and NaV1.5
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
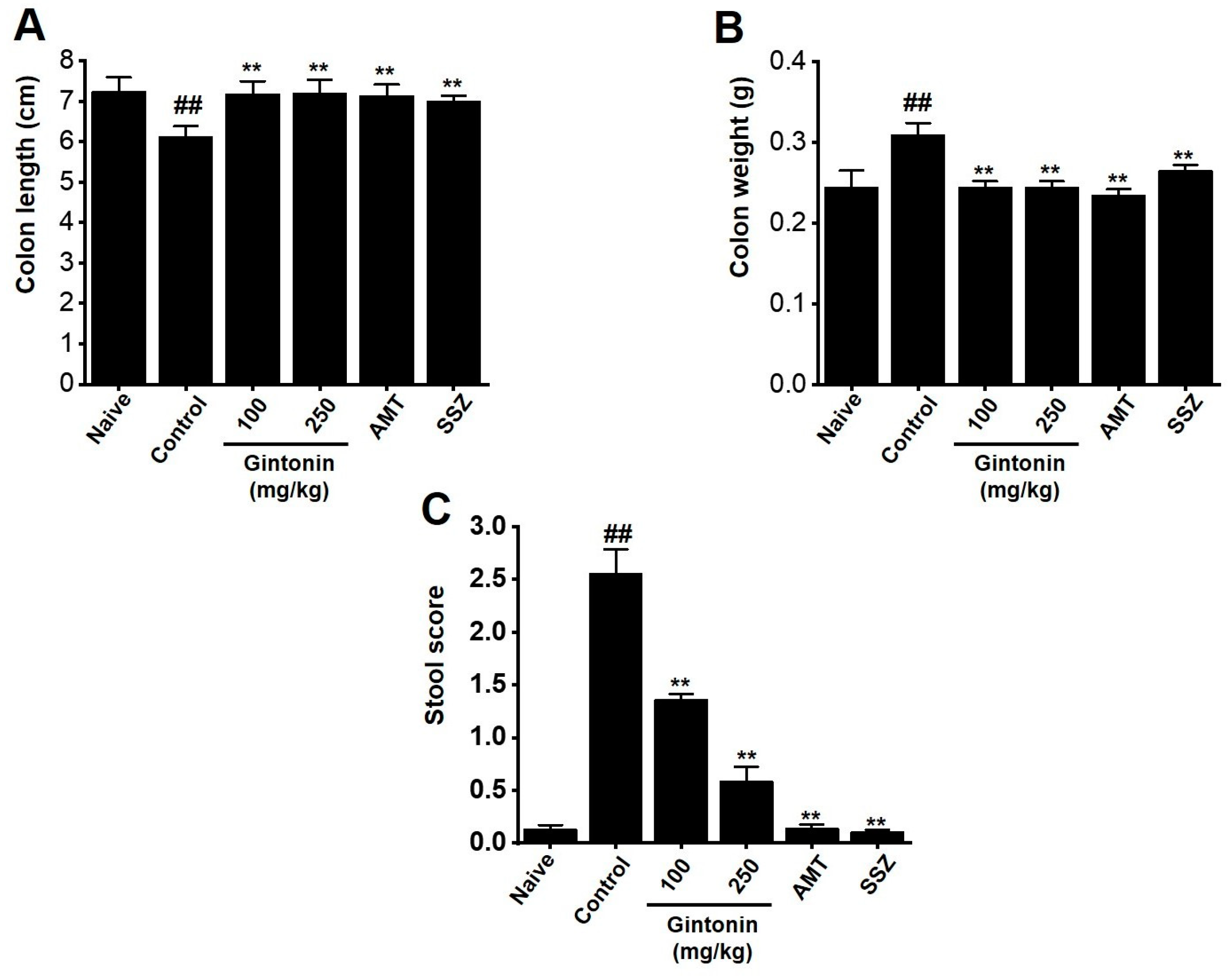
2.1. Subsection Effects of Gintonin on Colon and Stool Changes in the Zymosan-Inducd Murine Model
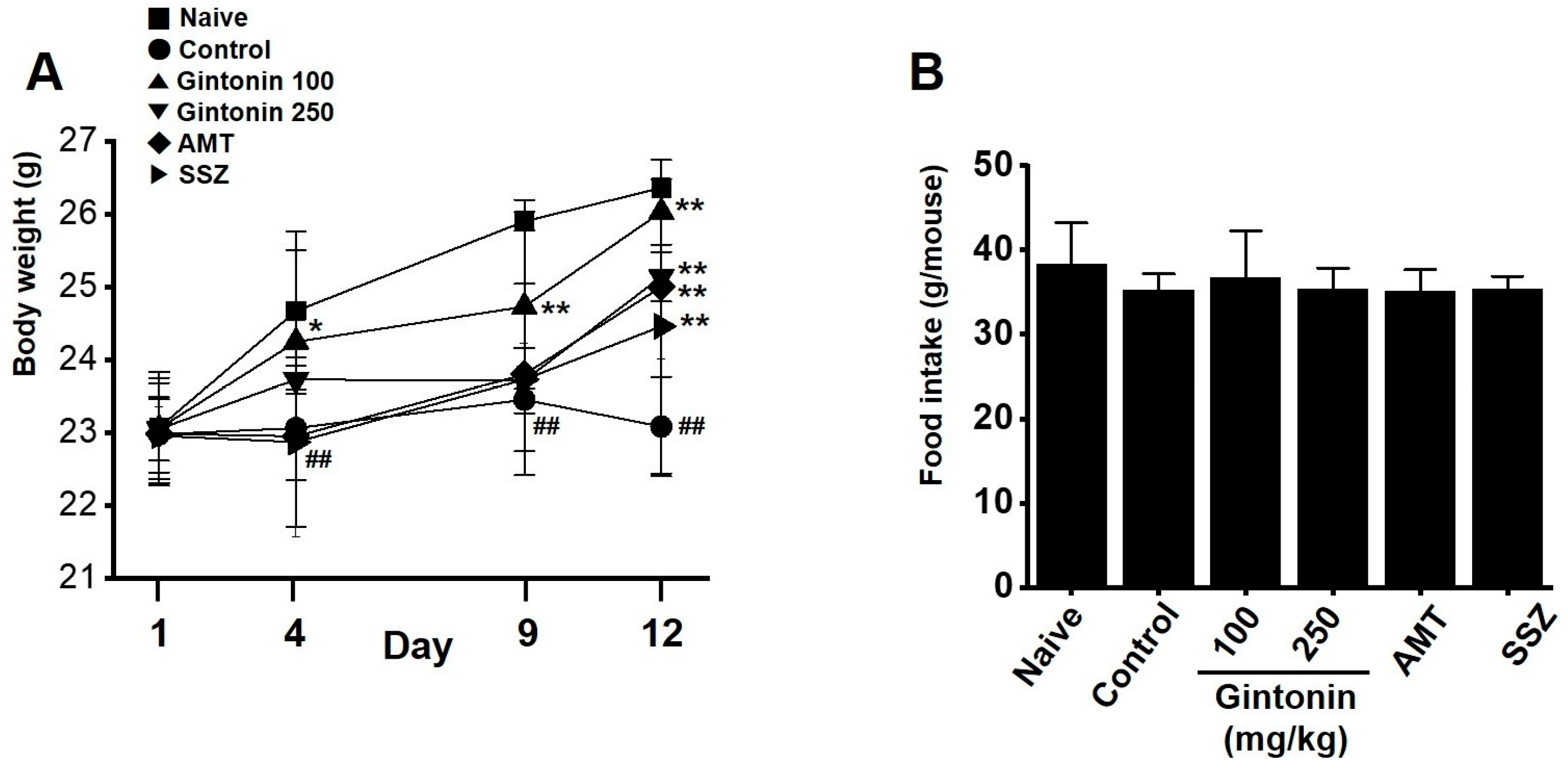
2.2. Effects of Gintonin on Body Weight and Food Intake Changes in the Zymosan-Induced Murine Model
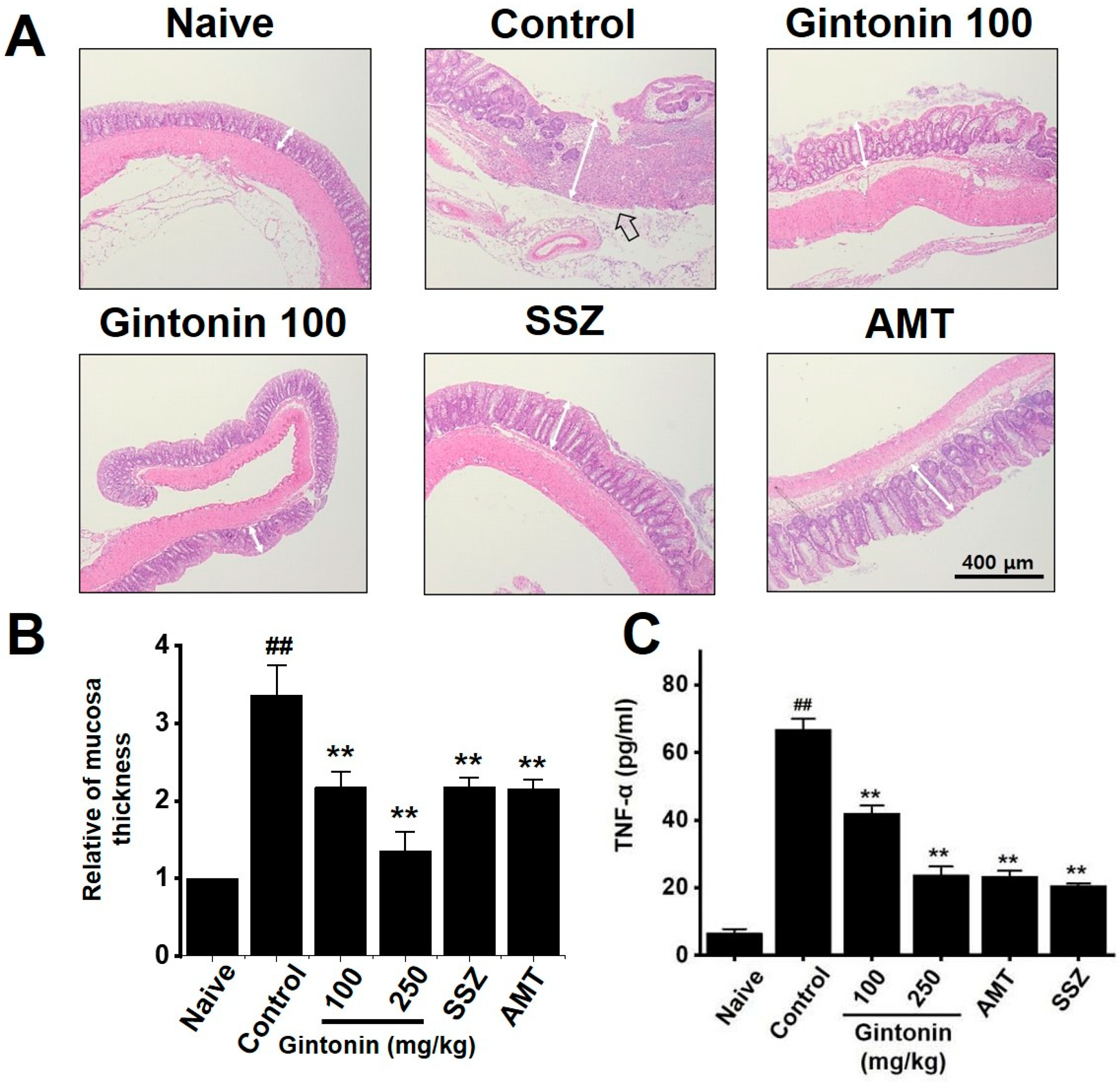
2.3. Effects of Gintonin on Zymosan-Induced Colitis
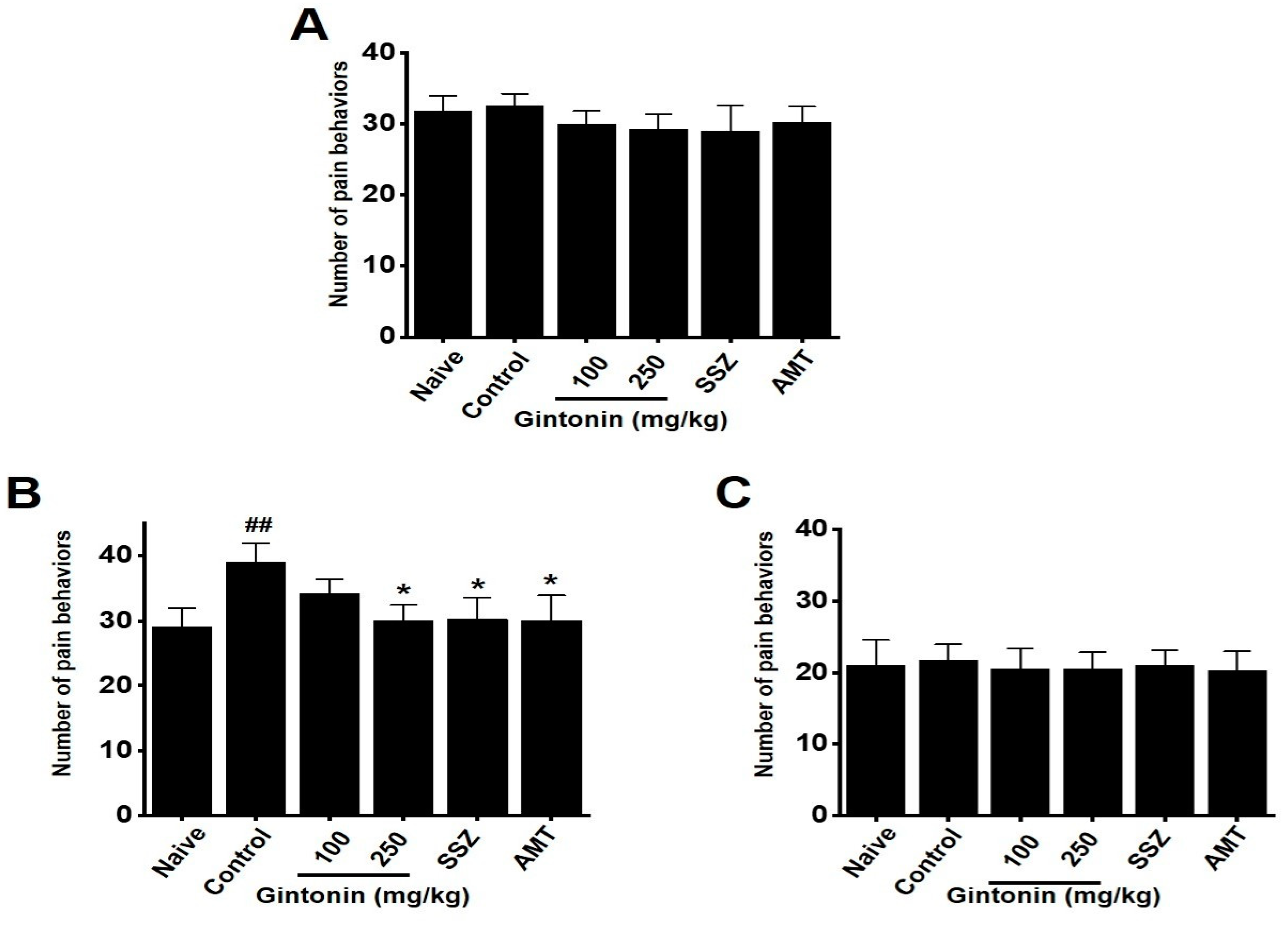
2.4. Effects of Gintonin on Pain-Related Behaviors
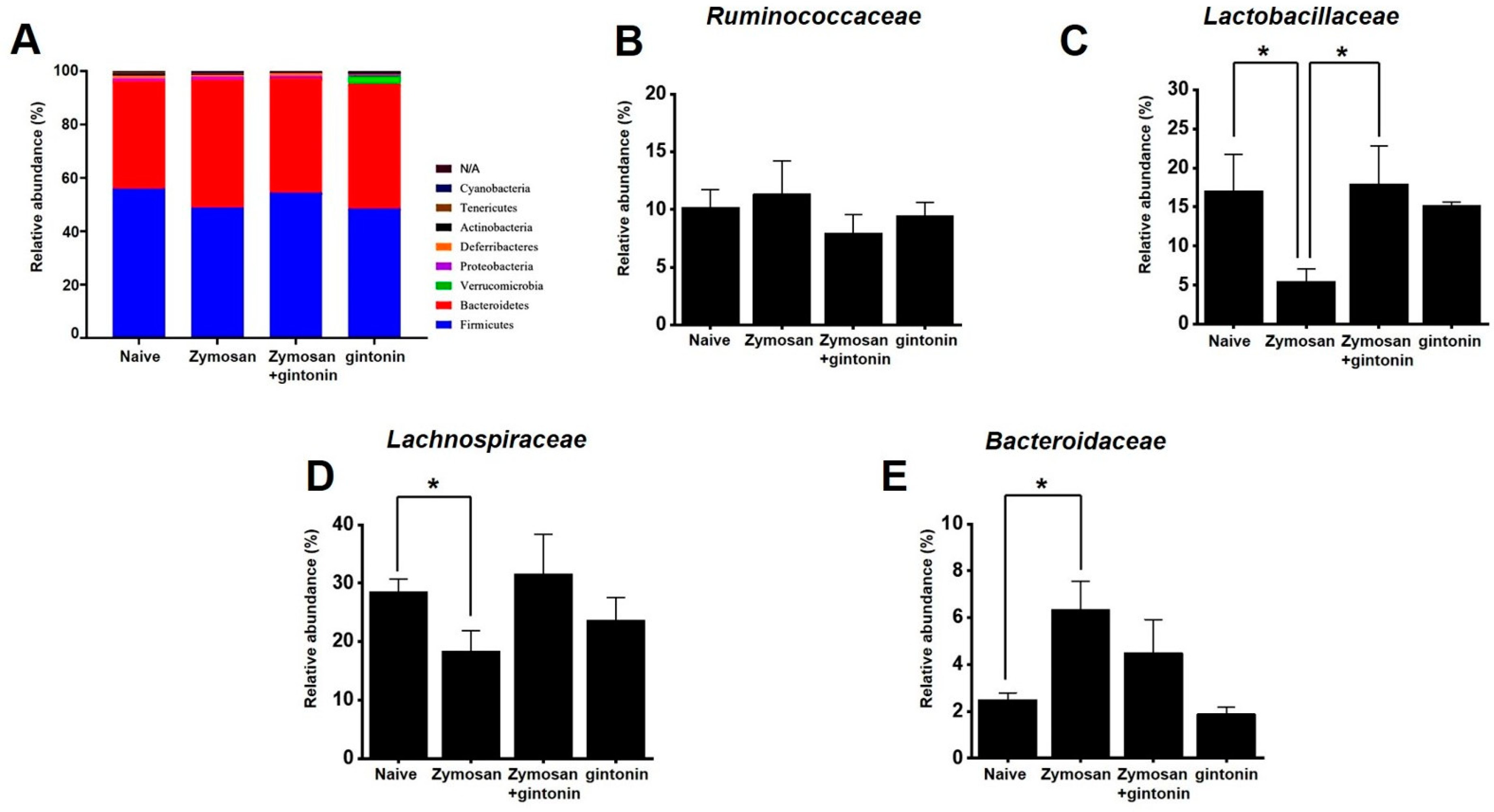
2.5. Effect of Gintonin on the Composition of Fecal Microorganisms
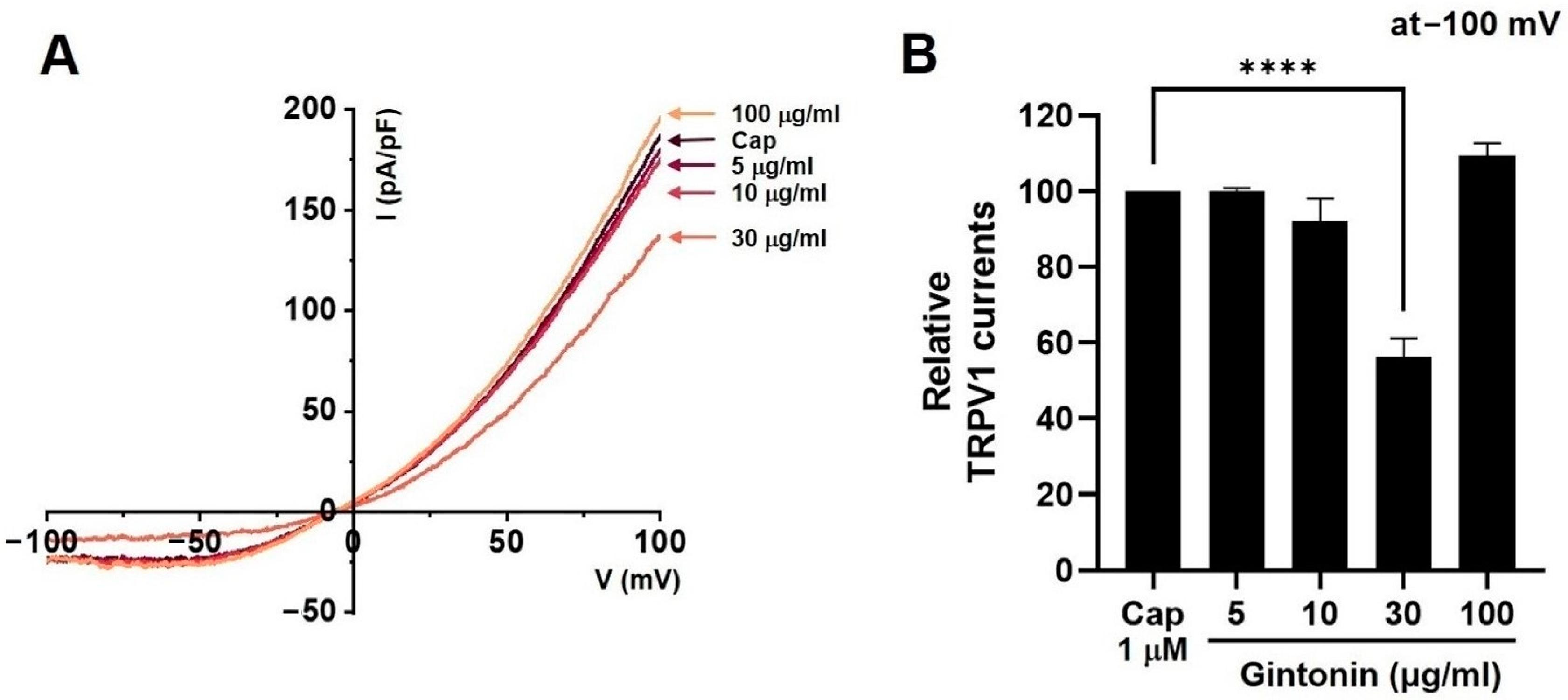
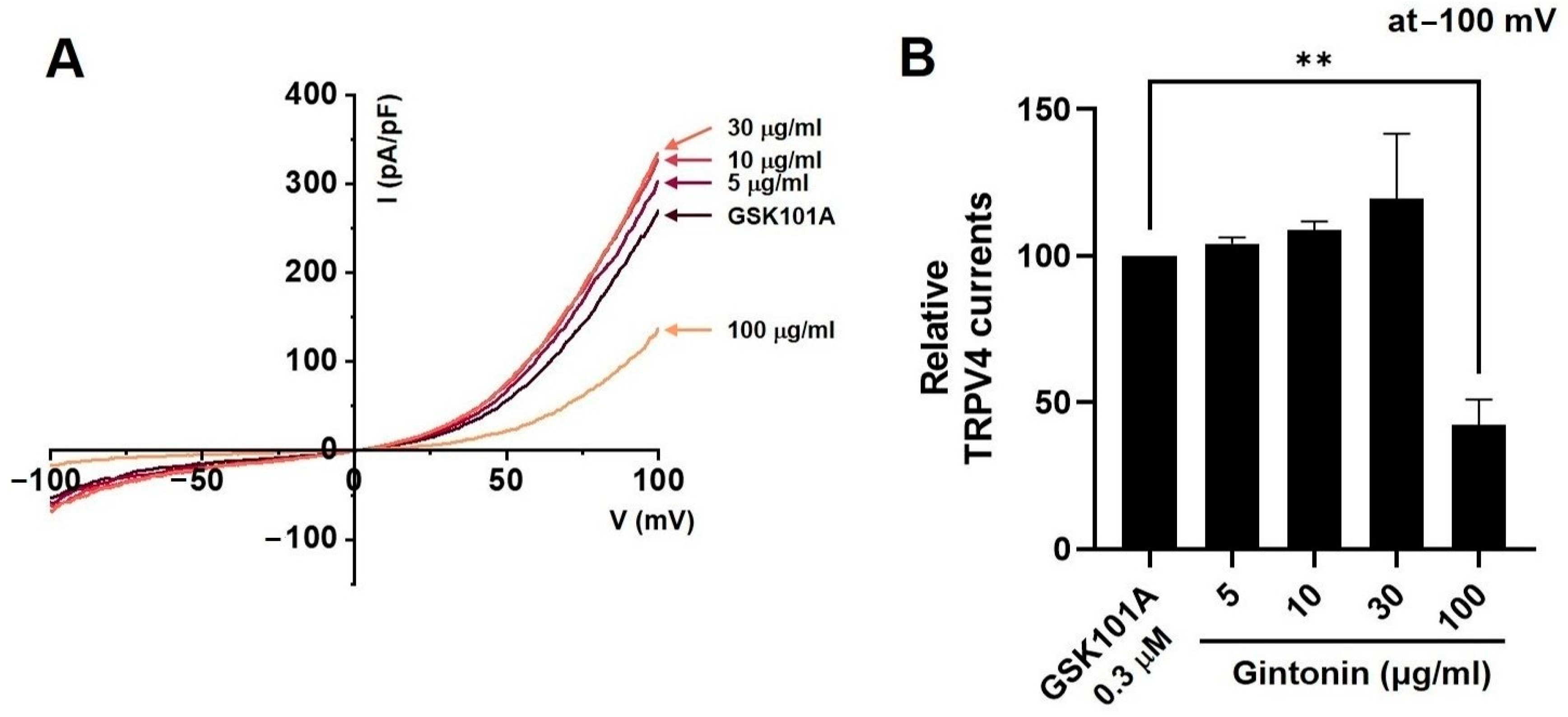
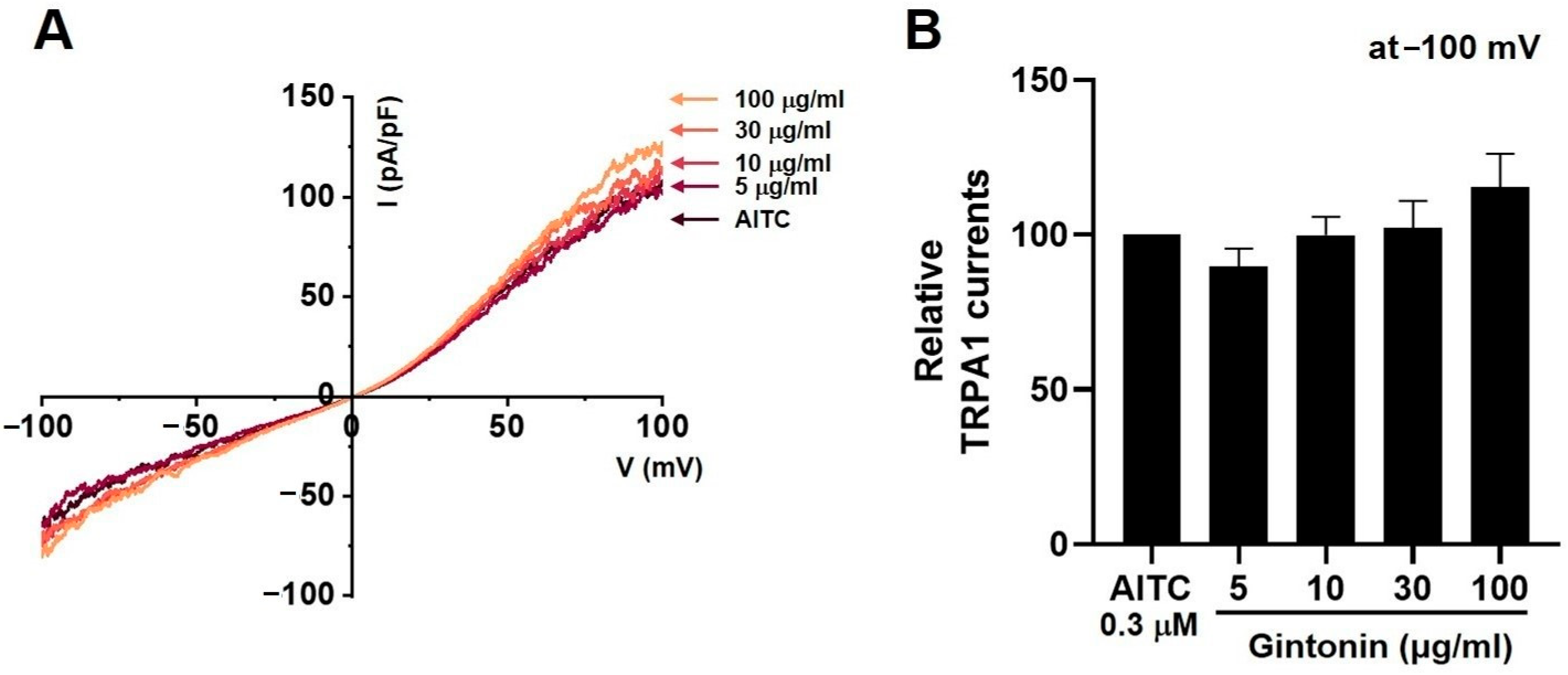
2.6. Effects of Gintonin on TRPV1, TRPV4, and TRPA1 Channel Currents
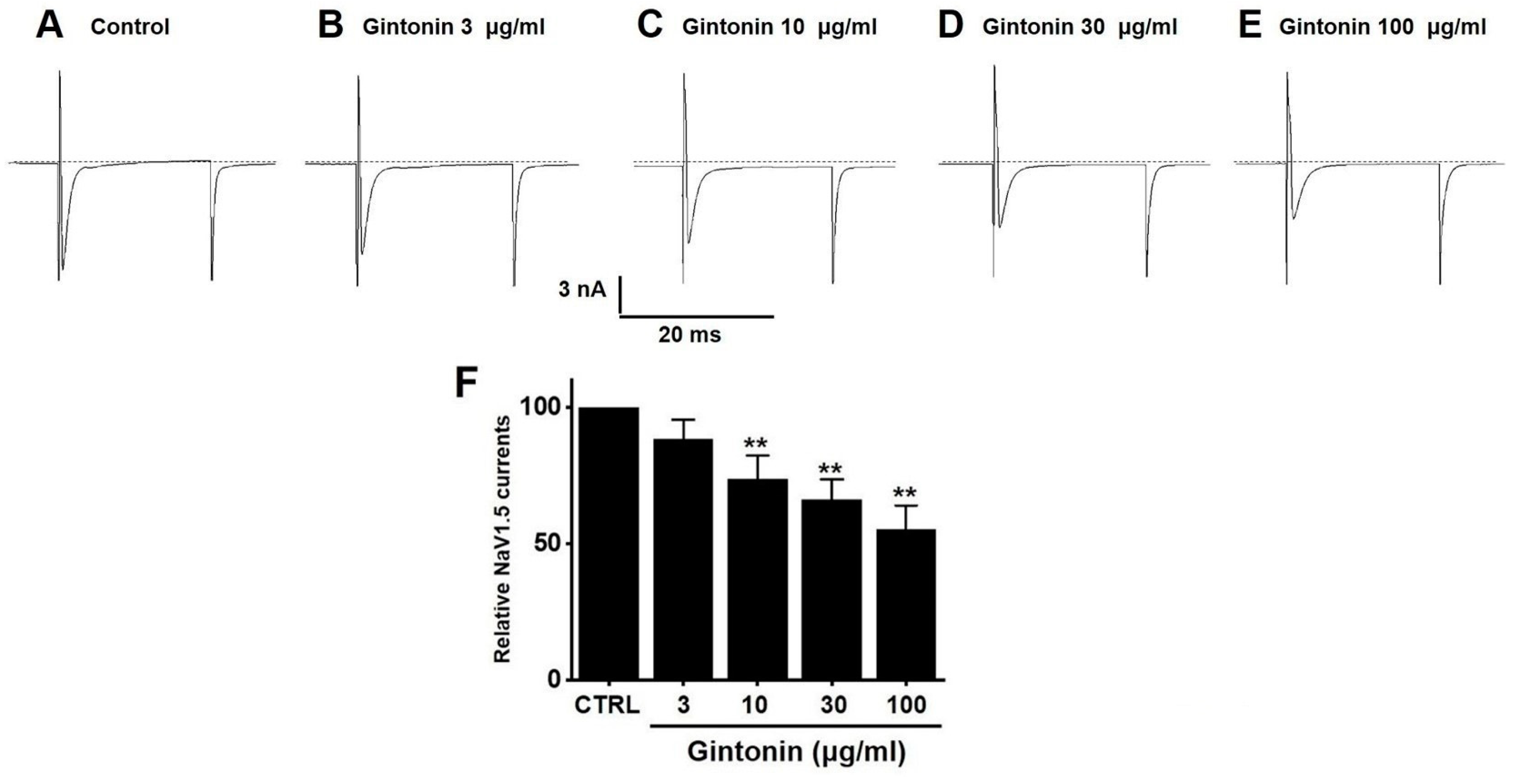
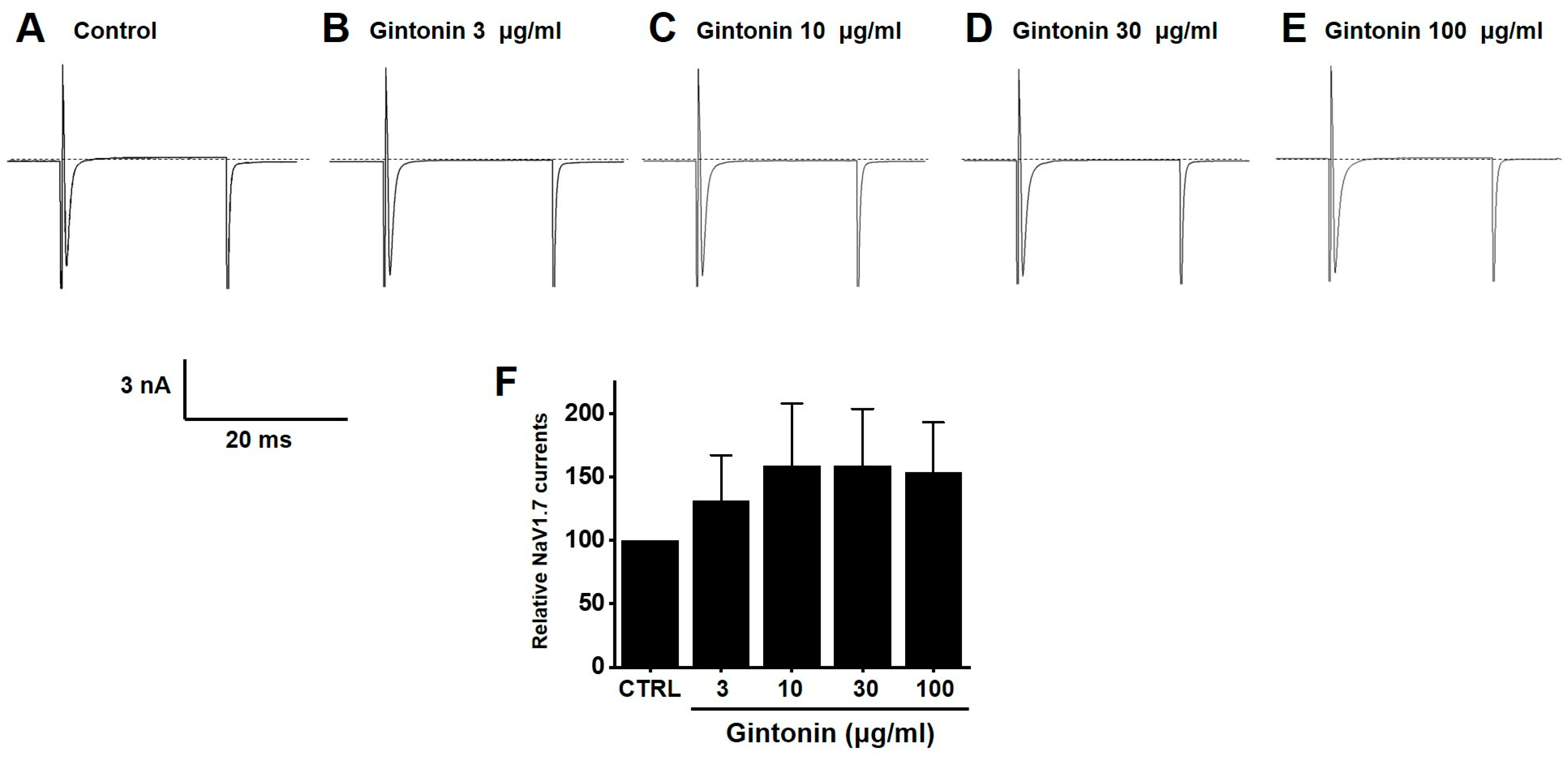
2.7. Effects of Gintonin on NaV1.5 and NaV1.7 Channel Currents
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Gintonin Preparation
4.2. Animal Experiments
4.3. Change in the Colon by Zymosan
4.4. Changes in Body Weight and Food Intake
4.5. Identifying Histological Characteristics
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Measurement
4.7. Measuring of Pain-Related Behavioral Changes
4.8. Microbiota Analysis
4.9. Electrophysiology
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hung, T.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Lee, H.F. Update in diagnosis and management of irritable bowel syndrome. Tzu. Chi. Med. J. 2023, 35, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enck, P.; Aziz, Q.; Barbara, G.; Farmer, A.D.; Fukudo, S.; Mayer, E.A.; Niesler, B.; Quigley, E.M.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Schemann, M.; et al. Irritable bowel syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2016, 2, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, P.; Parr, H.; Barberio, B.; Black, C.J.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome according to Rome III or IV criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeeshan, M.H.; Vakkalagadda, N.P.; Sree, G.S.; Anne, K.K.; Devi, S.; Parkash, O.; Fawwad, S.B.U.; Haider, S.M.W.; Mumtaz, H.; Hasan, M. Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: Prevalence and risk factors. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 81, 104408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.Y.; Wang, F.Y.; Lv, M.; Ma, X.X.; Tang, X.D.; Lv, L. Irritable bowel syndrome: Epidemiology, overlap disorders, pathophysiology and treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 4120–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Li, Z.; Toner, B.B.; Diamant, N.E.; Creed, F.H.; Thompson, D.; Read, N.W.; Babbs, C.; Barreiro, M.; Bank, L.; et al. Functional bowel disorders. A multicenter comparison of health status and development of illness severity index. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1995, 40, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.R.; Kwon, M.J.; Choi, W.G.; Kim, S.C.; Park, J.W.; Nam, J.H.; Kim, B.J. The traditional herbal medicines mixture, Banhasasim-tang, relieves the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome via modulation of TRPA1, NaV1.5 and NaV1.7 channels. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 312, 116499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S. Current status of diagnosis and treatment of irritable bowel syndrome in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2023, 38, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramythiotis, D.; Karlafti, E.; Didagelos, M.; Fafouti, M.; Veroplidou, K.; Protopapas, A.A.; Kaiafa, G.; Netta, S.; Michalopoulos, A.; Savopoulos, C. Post-COVID-19 and irritable bowel syndrome: A literature review. Medicina 2023, 59, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yang, L.; Ren, J.; Lang, N. Exploring the pathways of drug repurposing and Panax ginseng treatment mechanisms in chronic heart failure: A disease module analysis perspective. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.C.; Hwang, S.H.; Nah, S.Y. Bioactive lipids in gintonin-enriched fraction from ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Shin, E.J.; Shin, T.J.; Lee, B.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, S.H.; Jang, C.G.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Gintonin, a ginseng-derived lysophosphatidic acid receptor ligand, attenuates Alzheimer’s disease-related neuropathies: Involvement of non-amyloidogenic processing. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 31, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Shin, E.J.; Lee, B.H.; Choi, S.H.; Jung, S.W.; Cho, I.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Han, J.S.; Chung, C.H.; et al. Oral Administration of Gintonin Attenuates Cholinergic Impairments by Scopolamine, Amyloid-β Protein, and Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Nam, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Joo, M.; Ha, T.S.; Weon, K.Y.; Choi, S.; Jun, J.Y.; Park, E.J.; Wie, J.; et al. Characteristics of gintonin-mediated membrane depolarization of pacemaker activity in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 873–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.S.; Kwon, T.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, R.; Bae, C.S.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Cho, I.H.; Nah, S.Y. Gintonin alleviates HCl/Ethanol- and indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, V.; Pickens, D.; Gautam, S.; Kessler, R.; Mertz, H. Amitriptyline reduces rectal pain related activation of the anterior cingulate cortex in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2005, 54, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabit, C.E.; Holbrook, M.; Shenouda, S.M.; Dohadwala, M.M.; Widlansky, M.E.; Frame, A.A.; Kim, B.H.; Duess, M.A.; Kluge, M.A.; Levit, A.; et al. Effect of sulfasalazine on inflammation and endothelial function in patients with established coronary artery disease. Vasc. Med. 2012, 17, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kader, L.; Willits, A.; Meriano, S.; Christianson, J.A.; La, J.H.; Feng, B.; Knight, B.; Kosova, G.; Deberry, J.; Coates, M.; et al. Identification of arginine-vasopressin receptor 1a (Avpr1a/AVPR1A) as a novel candidate gene for chronic visceral pain sheds light on the potential role of enteric neurons in the development of visceral hypersensitivity. J. Pain. 2024, 25, 104572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Chun, E.; Choi, J.J.; Shin, Y.; Kho, Y.T.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, T.W.; Shin, E.; et al. Administration of wasabia koreana ameliorates irritable bowel syndrome-like symptoms in a zymosan-induced mouse model. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ruwe, D.; Saffari, R.; Kravchenko, M.; Zhang, W. Effects of TRPV1 activation by capsaicin and endogenous N-arachidonoyl taurine on synaptic transmission in the prefrontal cortex. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Jaimes, J.; Collins, D.; Edgar, T.; Walters, E.T.; Roger, G.; O’Neil, R.G. Determinants of TRPV4 activity following selective activation by small molecule agonist GSK1016790A. PLoS ONE 2011, 2, e16713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandor, Z.; Dekany, A.; Kelemen, D.; Bencsik, T.; Papp, R.; Bartho, L. The TRPA1 activator allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) contracts human jejunal muscle: Pharmacological analysis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 119, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Sung, I.K. Strategy to Manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2014, 86, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.G.; Park, K.S.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.M.; Park, C.H.; Lee, K.J.; Park, H.J.; Rhee, J.C. Guidelines for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 57, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shepherd, S.J.; Lomer, M.C.; Gibson, P.R. Short-chain carbohydrates and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Yung, Y.C.; Chen, A.; Chun, J. Lysophosphatidic acid signalling in development. Development 2015, 142, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S. Therapeutic response prediction of fecal microbiota transplantation for patients with irritable bowel syndrome: In terms of gut microbiota. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 80, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, P.; Núñez, P.; Quera, R.; Bay, C. Gastrointestinal microbiome, what is behind faecal microbiota transplantation? New Microbes New Infect. 2021, 42, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enck, P.; Mazurak, N. Dysbiosis in functional bowel disorders. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 72, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salhy, M.; Hausken, T.; Hatlebakk, J.G. Current status of fecal microbiota transplantation for irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Wang, G.; Lu, W.; Narbad, A.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. Evidence from comparative genomic analyses indicating that Lactobacillus-mediated irritable bowel syndrome alleviation is mediated by conjugated linoleic acid synthesis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Kim, N.; Yoon, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, S.I.; Park, J.H.; Lee, D.H. Compositional and functional changes in the gut microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Lam, E.F.; Lam, T.T.; Chan, Y.; Law, W.; Tse, P.C.; Kamm, M.A.; Sung, J.J.; Chan, F.K.; Wu, J.C. Effect of probiotic bacteria on the intestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durbán, A.; Abellán, J.J.; Jiménez-Hernández, N.; Salgado, P.; Ponce, M.; Ponce, J.; Garrigues, V.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A. Structural alterations of faecal and mucosa-associated bacterial communities in irritable bowel syndrome. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2012, 4, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, L.; Wang, B. TRP channels in inflammatory bowel disease: Potential therapeutic targets. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 203, 115195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyder, A.; Mazzone, A.; Strege, P.R.; Tester, D.J.; Saito, Y.A.; Bernard, C.E.; Enders, F.T.; Ek, W.E.; Schmidt, P.T.; Dlugosz, A.; et al. Loss-of-function of the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.5 (channelopathies) in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, I.M.; Christianson, J.A. Ion channels, ion channel receptors, and visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Castro, J.; Blomster, L.V.; Agwa, A.J.; Maddern, J.; Schober, G.; Herzig, V.; Chow, C.Y.; Cardoso, F.C.; Demétrio De Souza França, P.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.7 alleviates chronic visceral pain in a rodent model of irritable bowel syndrome. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1362–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, M.; Jarmuż, A.; Wasilewski, A.; Sałaga, M.; Fichna, J. Role of transient receptor potential channels in intestinal inflammation and visceral pain: Novel targets in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Le Berre, C. Newer biologic and small-molecule therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, H.A.; Chen, A.; Kravatz, N.L.; Chavan, S.S.; Chang, E.H. Involvement of neural transient receptor potential channels in peripheral inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P. TRP channels in the digestive system. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Liefferinge, E.; Van Noten, N.; Degroote, J.; Vrolix, G.; Van Poucke, M.; Peelman, L.; Van Ginneken, C.; Roura, E.; Michiels, J. Expression of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in the gut of the peri-weaning pig is strongly dependent on age and intestinal site. Animals 2020, 10, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo Maurino, J.J.; Fonseca-Camarillo, G.; Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Barreto-Zuñiga, R.; Benítez, B.M.; Granados, J.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K. TRPV subfamily (TRPV2, TRPV3, TRPV4, TRPV5, and TRPV6) gene and protein expression in patients with ulcerative colitis. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 2906845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, S.M.; Page, A.J.; Hughes, P.A.; Adam, B.; Liebregts, T.; Cooper, N.J.; Holtmann, G.; Liedtke, W.; Blackshaw, L.A. Selective role for TRPV4 ion channels in visceral sensory pathways. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aldebert, E.; Cenac, N.; Rousset, P.; Martin, L.; Rolland, C.; Chapman, K.; Selves, J.; Alric, L.; Vinel, J.P.; Vergnolle, N. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 activated inflammatory signals by intestinal epithelial cells and colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, T.; Mitsuyama, K.; Yamasaki, H.; Mori, A.; Yoshimura, T.; Araki, T.; Morita, M.; Tsuruta, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Kuwaki, K.; et al. Gene expression of transient receptor potential channels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of inflammatory bowel disease patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meents, J.E.; Ciotu, C.I.; Fischer, M.J.M. TRPA1: A molecular view. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 121, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, J.; Szitter, I.; Kemeny, A.; Perkecz, A.; Kereskai, L.; Pohóczky, K.; Vincze, A.; Gódi, S.; Szabó, I.; Szolcsányi, J.; et al. Upregulation of the transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 ion channel in the inflamed human and mouse colon and its protective roles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Alliger, K.; Weidinger, C.; Yerinde, C.; Wirtz, S.; Becker, C.; Engel, M.A. Functional role of transient receptor potential channels in immune cells and epithelia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, D.; Ye, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Wan, J. The TRPA1 channel in the cardiovascular system: Promising features and challenges. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, L.M.; Strege, P.R.; Rusinova, R.; Andersen, O.S.; Farrugia, G.; Beyder, A. Capsaicin as an amphipathic modulator of Na(V)1.5 mechanosensitivity. Channels 2022, 16, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strege, P.R.; Mazzone, A.; Kraichely, R.E.; Sha, L.; Holm, A.N.; Ou, Y.; Lim, I.; Gibbons, S.J.; Sarr, M.G.; Farrugia, G. Species dependent expression of intestinal smooth muscle mechanosensitive sodium channels. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2007, 19, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.J.; Cormier, R.T.; Scott, P.M. Role of ion channels in gastrointestinal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5732–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strege, P.R.; Ou, Y.; Sha, L.; Rich, A.; Gibbons, S.J.; Szurszewski, J.H.; Sarr, M.G.; Farrugia, G. Sodium current in human intestinal interstitial cells of Cajal. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G1111–G1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, G.R., 3rd; Ackerman, M.J.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Thapa, P.; Farrugia, G. Gastrointestinal symptoms in families of patients with an SCN5A-encoded cardiac channelopathy: Evidence of an intestinal channelopathy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, K.; Rougier, J.S.; Ogrodnik, J.; Abriel, H. Electrophysiological properties of mouse and epitope-tagged human cardiac sodium channel Na v1.5 expressed in HEK293 cells. F1000Research 2013, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, N.E.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, R.M.; Rhim, H.; Kim, H.C.; Han, M.; Lee, E.H.; Park, J.; Kim, J.N.; et al. Gintonin facilitates brain delivery of donepezil, a therapeutic drug for Alzheimer disease, through lysophosphatidic acid 1/3 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, J.M.A.; Martinez-Caro, L.; Garcia-Nicas, E.; Cervero, F. A new model of visceral pain and referred hyperalgesia in the mouse. Pain 2001, 92, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, R.; Inui, R.; Akamatsu, Y.; Goto, M.; Doi, H.; Matsuoka, S. Illumina iSeq 100 and MiSeq exhibit similar performance in freshwater fish environmental DNA metabarcoding. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, N.-R.; Ko, S.-J.; Nam, J.-H.; Choi, W.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Nah, S.-Y.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, B.-J. Study on the Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Gintonin in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Its Relationship with TRPV1, TRPV4, and NaV1.5. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091170
Choi N-R, Ko S-J, Nam J-H, Choi W-G, Lee J-H, Nah S-Y, Park J-W, Kim B-J. Study on the Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Gintonin in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Its Relationship with TRPV1, TRPV4, and NaV1.5. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091170
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Na-Ri, Seok-Jae Ko, Joo-Hyun Nam, Woo-Gyun Choi, Jong-Hwan Lee, Seung-Yeol Nah, Jae-Woo Park, and Byung-Joo Kim. 2024. "Study on the Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Gintonin in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Its Relationship with TRPV1, TRPV4, and NaV1.5" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091170
APA StyleChoi, N.-R., Ko, S.-J., Nam, J.-H., Choi, W.-G., Lee, J.-H., Nah, S.-Y., Park, J.-W., & Kim, B.-J. (2024). Study on the Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms of Gintonin in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Its Relationship with TRPV1, TRPV4, and NaV1.5. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091170







