TnP and AHR-CYP1A1 Signaling Crosstalk in an Injury-Induced Zebrafish Inflammation Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
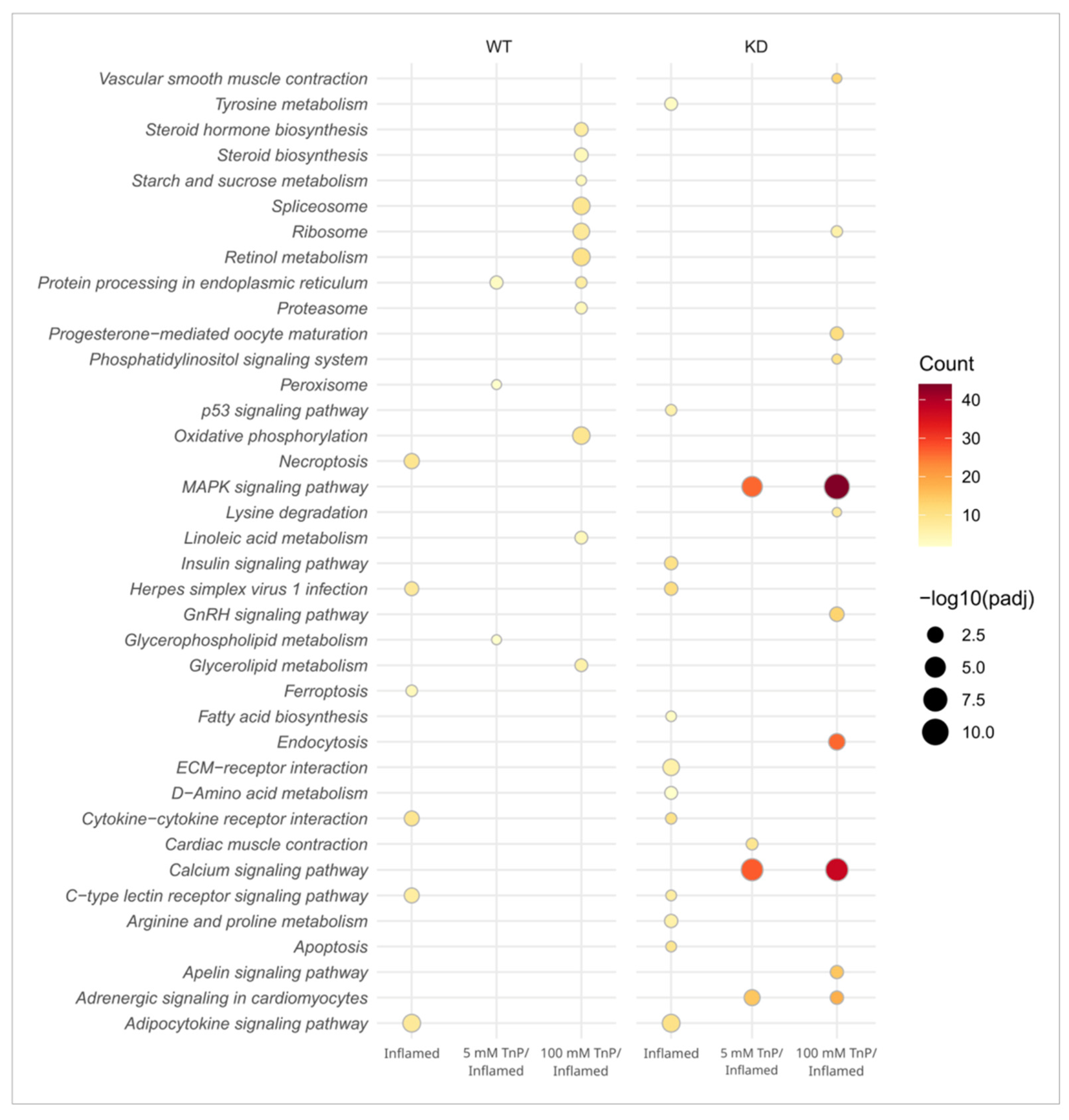
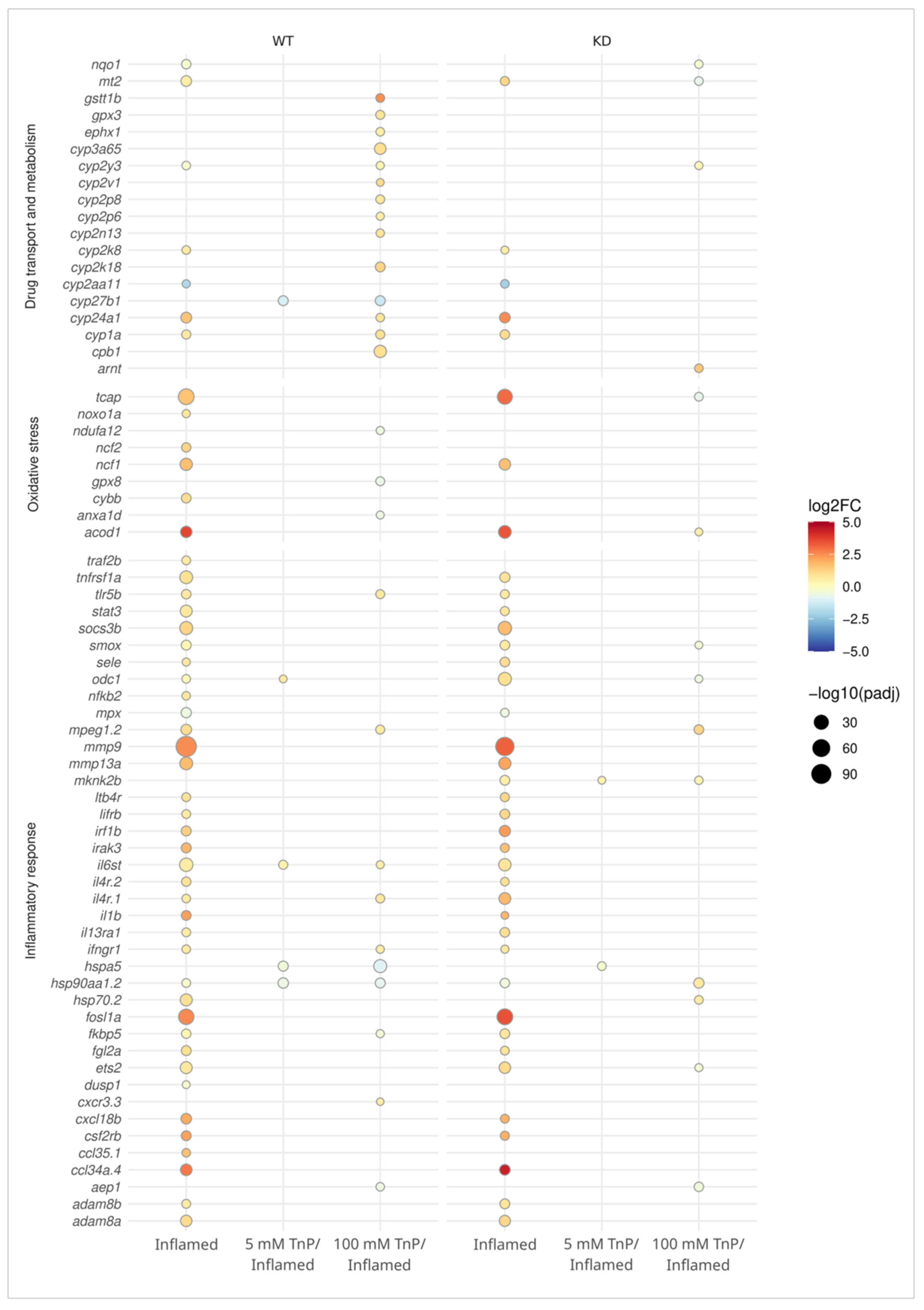
2. Results and Discussion
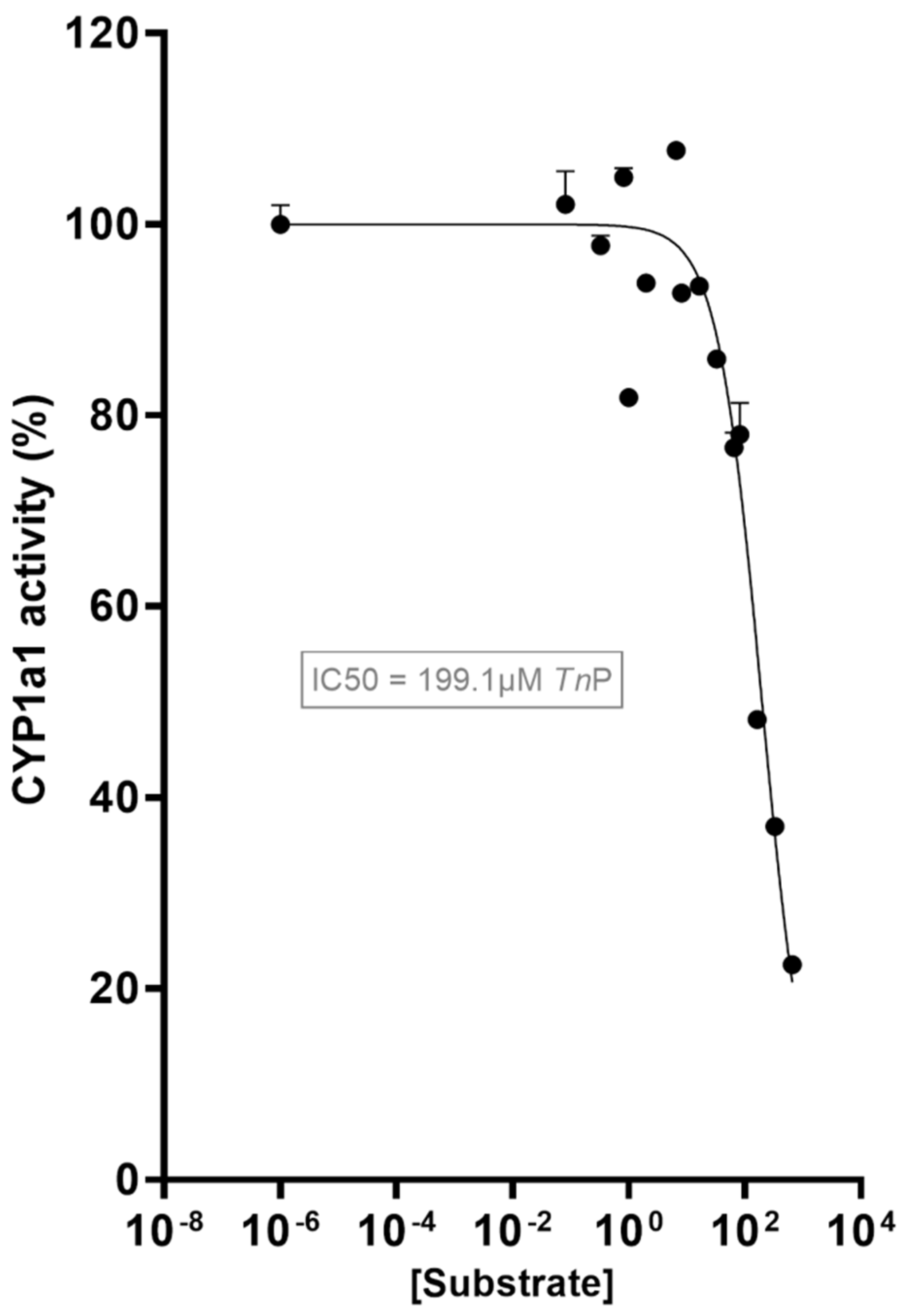
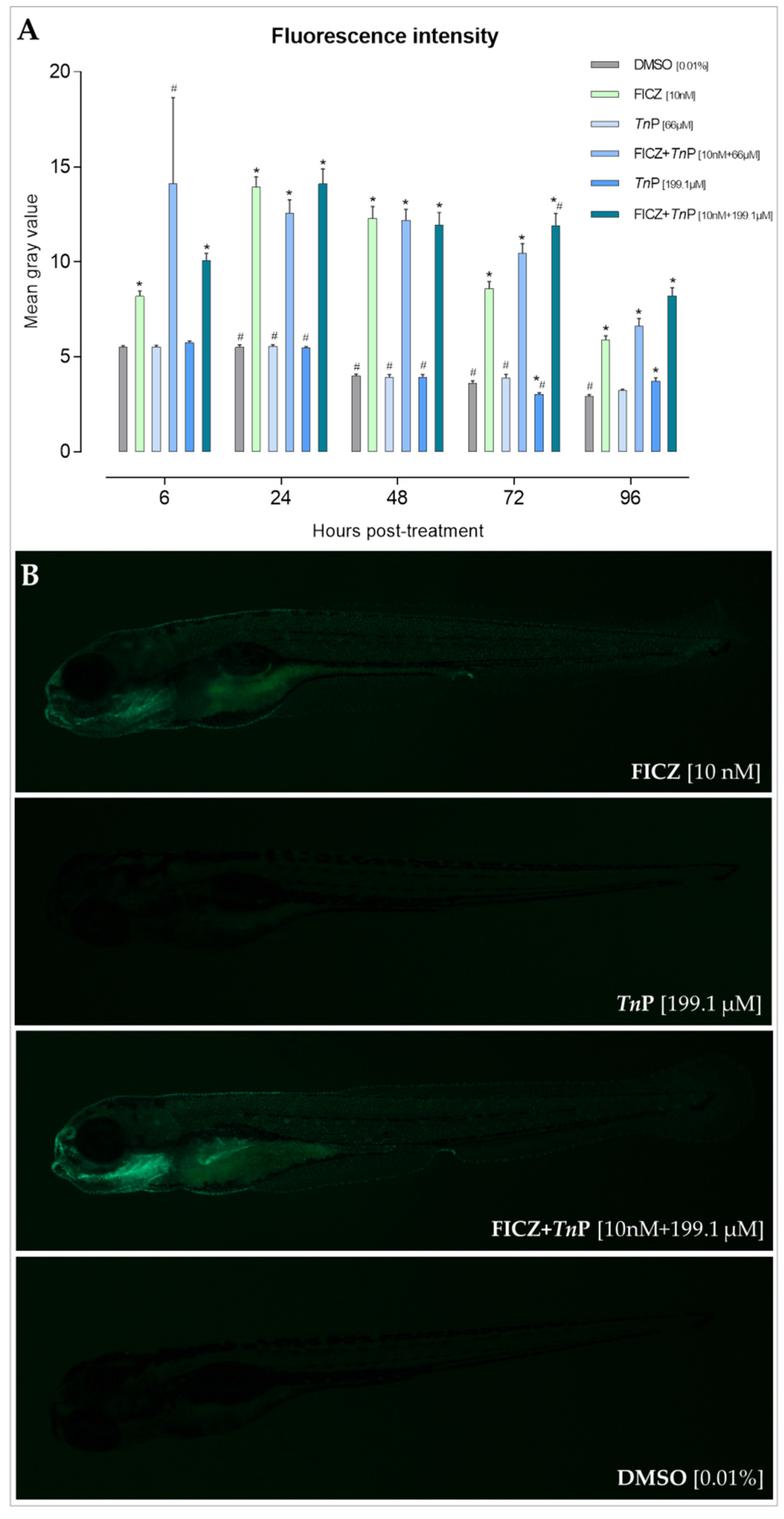
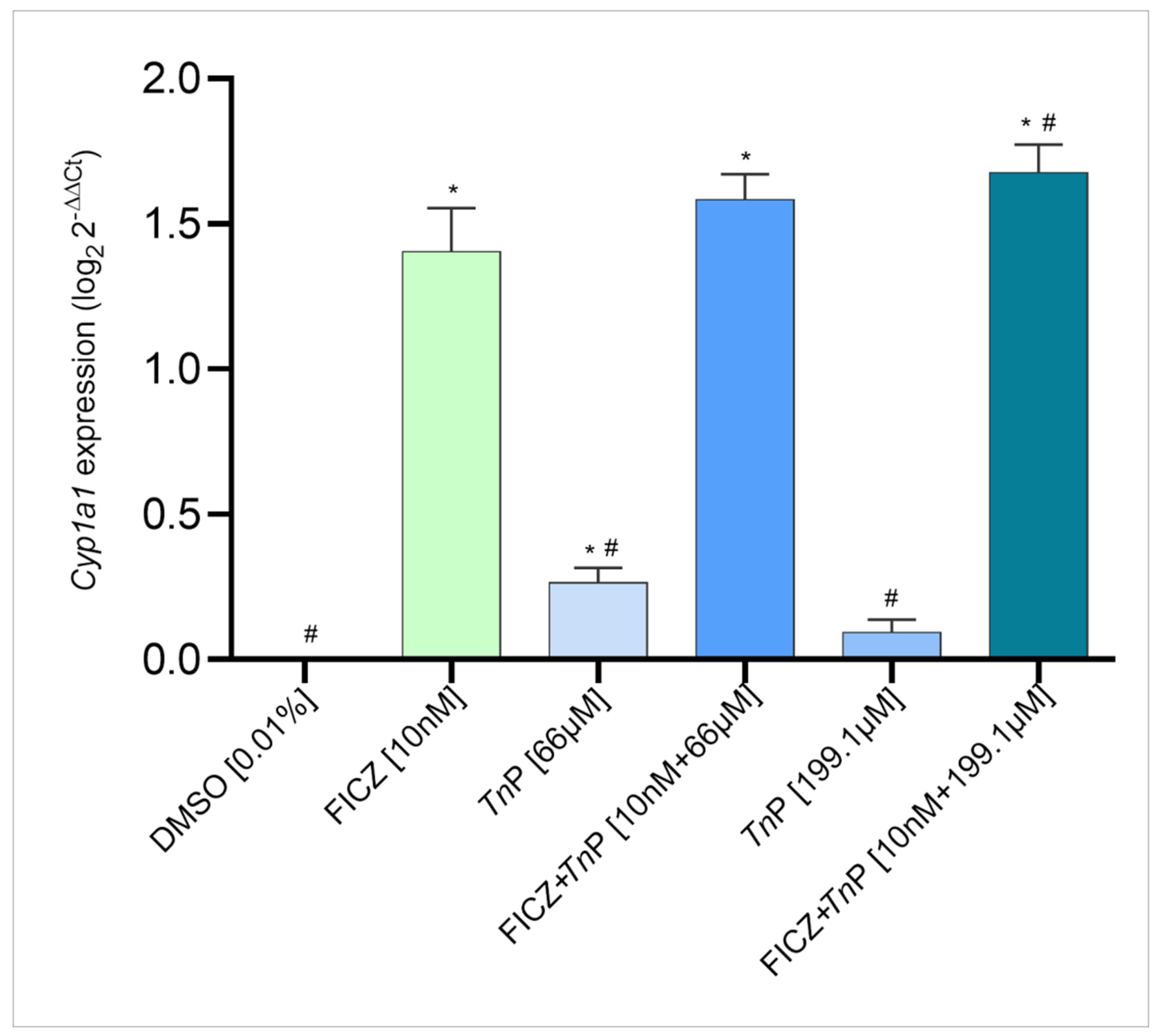
2.1. TnP Disrupts the AHR-CYP Signaling Pathway
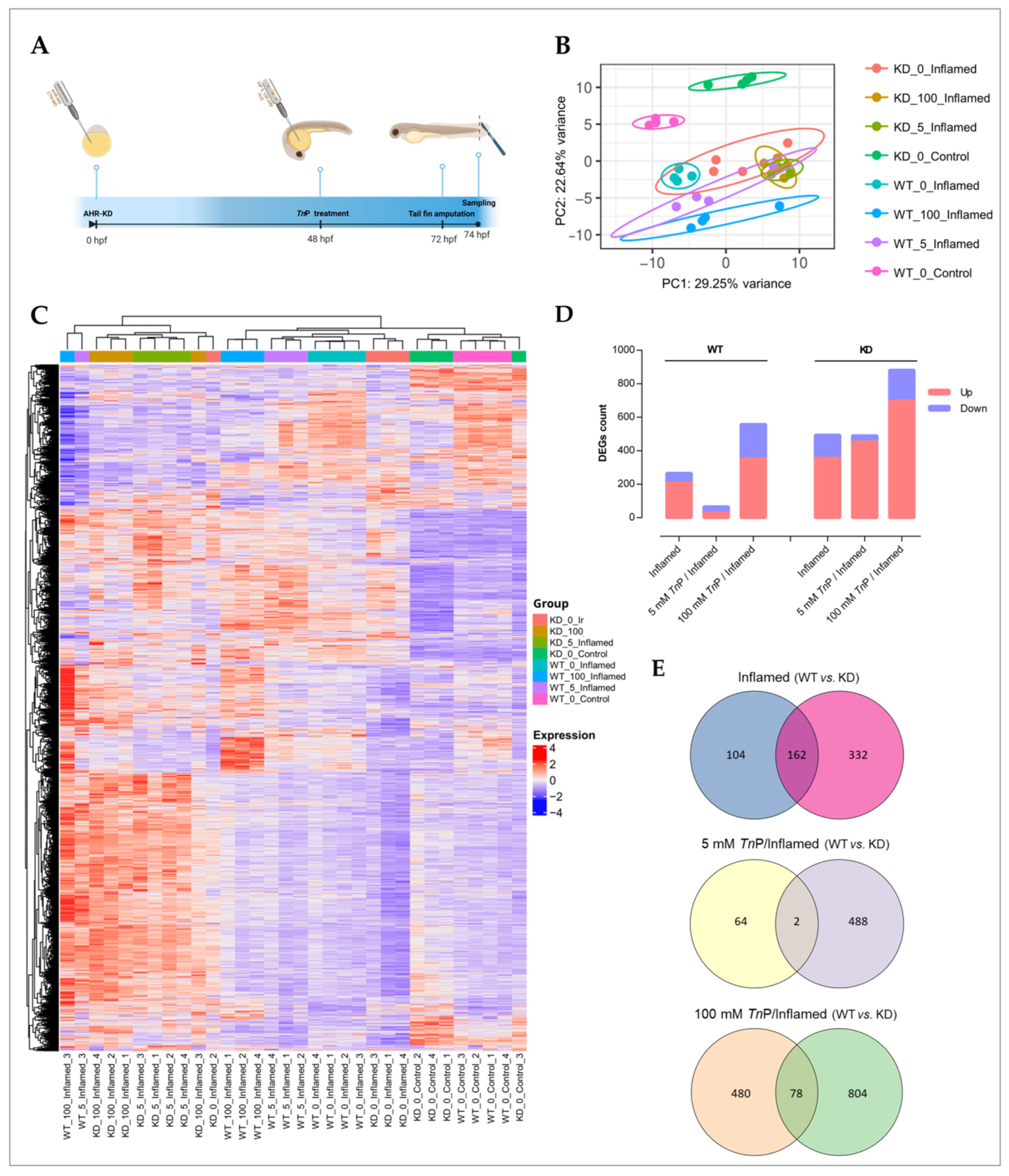
2.2. The Role of AHR in the Therapeutic Effect of TnP
2.3. Comparisons between Zebrafish and Human CYP1A1 and TnP-CYP1A1 Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
3.2. CYP1A1 Activity In Vitro Inhibition Assay by TnP
3.3. Zebrafish Maintenance and Cyp1a Reporter Experiments
3.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
3.5. Experimental Settings for Transcriptome Analysis
3.5.1. Ahr2 Knockdown, TnP Treatment, and Inflammation Model
3.5.2. RNA Quantification and Library Preparation
3.5.3. Clustering and Sequencing
3.6. Data Analysis
3.6.1. Quality Control and Trimming
3.6.2. Reads Mapping, Quantification of Mapped Transcripts, Gene Expression Matrix, and Transcript Annotation
3.6.3. Reads Grouping
3.6.4. Differential Expression and Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
3.7. In Silico Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Favreau, P.; Stöcklin, R. Marine snail venoms: Use and trends in receptor and channel neuropharmacology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Peinado, C.; Defaus, S.; Andreu, D. Hitchhiking with Nature: Snake Venom Peptides to Fight Cancer and Superbugs. Toxins 2020, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lopes-Ferreira, M.V.A.; Lima, C.; Pimenta, D.C.; Conceição, K.; Demasi, M.; Portaro, F.C.V. Monica Valdyrce dos Anjos Lopes Ferreira, Cristália Produtos Químicos Farmacêuticos Ltda, Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP). Peptídeos Cíclicos Antiinflamatórios e Antialérgicos. Patent PI0703175 PI0602885-3A2, 25 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Komegae, E.N.; Souza, T.A.; Grund, L.Z.; Lima, C.; Lopes-Ferreira, M. Multiple functional therapeutic effects of TnP: A small stable synthetic peptide derived from fish venom in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.; Falcão, M.A.P.; Pinto, F.J.; Bernardo, J.T.G.; Lopes-Ferreira, M. The Anti-Inflammatory Peptide TnP Is a Candidate Molecule for Asthma Treatment. Cells 2023, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nebert, D.W.; Karp, C.L. Endogenous functions of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR): Intersection of cytochrome P450 1 (CYP1)-metabolized eicosanoids and AHR biology. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 36061–36065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mimura, J.; Ema, M.; Sogawa, K.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. Identification of a novel mechanism of regulation of Ah (dioxin) receptor function. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Quintana, F.J.; Basso, A.S.; Iglesias, A.H.; Korn, T.; Farez, M.F.; Bettelli, E.; Caccamo, M.; Oukka, M.; Weiner, H.L. Control of T(reg) and T(H)17 cell differentiation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature 2008, 453, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, E.A.; Mezrich, J.D.; Bradfield, C.A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: A perspective on potential roles in the immune system. Immunology 2009, 127, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marlowe, J.L.; Puga, A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor, cell cycle regulation, toxicity, and tumorigenesis. J. Cell Biochem. 2005, 96, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dhfyan, A.; Alhoshani, A.; Korashy, H.M. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/cytochrome P450 1A1 pathway mediates breast cancer stem cells expansion through PTEN inhibition and β-Catenin and Akt activation. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 14, Erratum in Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, H.; Nishioka, K.; Nakajima, S.; Kim, S.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Fukasawa, M.; Kamisuki, S.; Sugawara, F.; Ohtani, N.; et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-cytochrome P450 1A1 pathway controls lipid accumulation and enhances the permissiveness for hepatitis C virus assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 19559–19571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shankar, P.; Dasgupta, S.; Hahn, M.E.; Tanguay, R.L. A Review of the Functional Roles of the Zebrafish Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptors. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 178, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rannug, A.; Rannug, U. The tryptophan derivative 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole, FICZ, a dynamic mediator of endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling, balances cell growth and differentiation. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2018, 48, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wincent, E.; Bengtsson, J.; Mohammadi Bardbori, A.; Alsberg, T.; Luecke, S.; Rannug, U.; Rannug, A. Inhibition of cytochrome P4501-dependent clearance of the endogenous agonist FICZ as a mechanism for activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4479–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xie, Y.; Meijer, A.H.; Schaaf, M.J.M. Modeling Inflammation in Zebrafish for the Development of Anti-inflammatory Drugs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 620984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hahn, M.E.; Karchner, S.I.; Merson, R.R. Diversity as Opportunity: Insights from 600 Million Years of AHR Evolution. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souder, J.P.; Gorelick, D.A. ahr2, But Not ahr1a or ahr1b, Is Required for Craniofacial and Fin Development and TCDD-dependent Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 170, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nguyen, L.P.; Bradfield, C.A. The search for endogenous activators of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.R.; Miao, H.; Deng, D.Q.; Vaziri, N.D.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.Y. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolism mediates renal fibrosis by aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling activation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, A.S.; Holloman, B.L.; Wilson, K.; Miranda, K.; Dopkins, N.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M. AhR Activation Leads to Attenuation of Murine Autoimmune Hepatitis: Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals Unique Immune Cell Phenotypes and Gene Expression Changes in the Liver. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 899609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stockinger, B.; Shah, K.; Wincent, E. AHR in the intestinal microenvironment: Safeguarding barrier function. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rendic, S.; Guengerich, F.P. Survey of Human Oxidoreductases and Cytochrome P450 Enzymes Involved in the Metabolism of Xenobiotic and Natural Chemicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bhutani, P.; Joshi, G.; Raja, N.; Bachhav, N.; Rajanna, P.K.; Bhutani, H.; Paul, A.T.; Kumar, R.U.S. FDA Approved Drugs from 2015–June 2020: A Perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2339–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstone, J.V.; McArthur, A.G.; Kubota, A.; Zanette, J.; Parente, T.; Jönsson, M.E.; Nelson, D.R.; Stegeman, J.J. Identification and developmental expression of the full complement of Cytochrome P450 genes in Zebrafish. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stegeman, J.J.; Behrendt, L.; Woodin, B.R.; Kubota, A.; Lemaire, B.; Pompon, D.; Goldstone, J.V.; Urban, P. Functional characterization of zebrafish cytochrome P450 1 family proteins expressed in yeast. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 2340–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wincent, E.; Kubota, A.; Timme-Laragy, A.; Jönsson, M.E.; Hahn, M.E.; Stegeman, J.J. Biological effects of 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) in vivo are enhanced by loss of CYP1A function in an Ahr2-dependent manner. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 110–111, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, T.P.; Puga, A.; Shertzer, H.G. Induction of cellular oxidative stress by aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2002, 141, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothhammer, V.; Quintana, F.J. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: An environmental sensor integrating immune responses in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Klapczynski, A.; Kuch, N.; Arpino, F.; Simon-Keller, K.; De La Torre, C.; Sticht, C.; van Abeelen, F.A.; Oversluizen, G.; Gretz, N. Gene expression profiling reveals aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a possible target for photobiomodulation when using blue light. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dere, E.; Lee, A.W.; Burgoon, L.D.; Zacharewski, T.R. Differences in TCDD-elicited gene expression profiles in human HepG2, mouse Hepa1c1c7 and rat H4IIE hepatoma cells. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishanova, A.Y.; Perepechaeva, M.L. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Oxidative Stress as a Double Agent and Its Biological and Therapeutic Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kyoreva, M.; Li, Y.; Hoosenally, M.; Hardman-Smart, J.; Morrison, K.; Tosi, I.; Tolaini, M.; Barinaga, G.; Stockinger, B.; Mrowietz, U.; et al. CYP1A1 Enzymatic Activity Influences Skin Inflammation Via Regulation of the AHR Pathway. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1553–1563.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiering, C.; Wincent, E.; Metidji, A.; Iseppon, A.; Li, Y.; Potocnik, A.J.; Omenetti, S.; Henderson, C.J.; Wolf, C.R.; Nebert, D.W.; et al. Feedback control of AHR signalling regulates intestinal immunity. Nature 2017, 542, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shah, K.; Maradana, M.R.; Joaquina Delàs, M.; Metidji, A.; Graelmann, F.; Llorian, M.; Chakravarty, P.; Li, Y.; Tolaini, M.; Shapiro, M.; et al. Cell-intrinsic Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor signalling is required for the resolution of injury-induced colonic stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asnani, A.; Zheng, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.H.; Vohra, A.; Chi, A.; Cornella-Taracido, I.; Wang, H.; Johns, D.G.; et al. Highly potent visnagin derivatives inhibit Cyp1 and prevent doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e96753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, P.Y.; Kutchukian, P.; Anand, R.; Imbriglio, J.; Andrews, C.; Padilla, H.; Vohra, A.; Lane, S.; Parker, D.L.; Cornella Taracido, I.; et al. Cyp1 Inhibition Prevents Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy in a Zebrafish Heart-Failure Model. Chembiochem 2020, 21, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, F.; Tsubota, M.; Kawabata, A. Involvement of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels in Inflammation and Inflammatory Pain. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.; Axtell, R.; Mitra, A.; Miranda, M.; Lock, C.; Tsien, R.W.; Steinman, L. Inhibitory role for GABA in autoimmune inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2580–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, J.J.N.; Behn, J.; Chong, C.S.; Zhong, G.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Fan, H.; Loo, L.H. Structure-based virtual screening of CYP1A1 inhibitors: Towards rapid tier-one assessment of potential developmental toxicants. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 3031–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Denisov, I.G.; Makris, T.M.; Sligar, S.G.; Schlichting, I. Structure and chemistry of cytochrome P450. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2253–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenaan, C.; Zhang, H.; Shea, E.V.; Hollenberg, P.F. Uncovering the role of hydrophobic residues in cytochrome P450-cytochrome P450 reductase interactions. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 3957–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Im, S.C.; Waskell, L. The interaction of microsomal cytochrome P450 2B4 with its redox partners, cytochrome P450 reductase and cytochrome b5. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 507, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grover, A.K. Use of allosteric targets in the discovery of safer drugs. Med. Princ. Pract. 2013, 22, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Modell, A.E.; Blosser, S.L.; Arora, P.S. Systematic Targeting of Protein-Protein Interactions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wincent, E.; Le Bihanic, F.; Dreij, K. Induction and inhibition of human cytochrome P4501 by oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol. Res. (Camb.) 2016, 5, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Williams, D.R.; Kim, M.K.; Jung, Y.D.; Teraoka, H.; Park, H.C.; Choy, H.E.; et al. Cyp1a reporter zebrafish reveals target tissues for dioxin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 134–135, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brox, S.; Seiwert, B.; Küster, E.; Reemtsma, T. Toxicokinetics of Polar Chemicals in Zebrafish Embryo (Danio rerio): Influence of Physicochemical Properties and of Biological Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10264–10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Soneson, C.; Hickey, P.F.; Johnson, L.K.; Pierce, N.T.; Shepherd, L.; Morgan, M.; Patro, R. Tximeta: Reference sequence checksums for provenance identification in RNA-seq. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainer, J.; Gatto, L.; Weichenberger, C.X. ensembldb: An R package to create and use Ensembl-based annotation resources. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3151–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M. org.Dr.eg.db: Genome Wide Annotation for Zebrafish, R Package Version 3.8.2; Bioconductor: Boston, MA, USA, 2019.
- Witten, D. Classification and clustering of sequencing data using a Poisson model. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2011, 5, 2493–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, F.; Binder, H. pcaExplorer: An R/Bioconductor package for interacting with RNA-seq principal components. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, H.; Tuknait, A.; Chaudhary, K.; Singh, B.; Kumaran, S.; Raghava, G.P. PEPstrMOD: Structure prediction of peptides containing natural, non-natural and modified residues. Biol. Direct 2015, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuki, S. pyMSAviz: MSA Visualization Python Package for Sequence Analysis. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/moshi4/pyMSAviz (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, O.; Stützle, T.; Exner, T.E. Empirical scoring functions for advanced protein-ligand docking with PLANTS. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOVIA. Dassault Systèmes, Discovery Studio 2021, v. 21.1.0.20298; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Disner, G.R.; Fernandes, T.A.d.M.; Nishiyama-Jr, M.Y.; Lima, C.; Wincent, E.; Lopes-Ferreira, M. TnP and AHR-CYP1A1 Signaling Crosstalk in an Injury-Induced Zebrafish Inflammation Model. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091155
Disner GR, Fernandes TAdM, Nishiyama-Jr MY, Lima C, Wincent E, Lopes-Ferreira M. TnP and AHR-CYP1A1 Signaling Crosstalk in an Injury-Induced Zebrafish Inflammation Model. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091155
Chicago/Turabian StyleDisner, Geonildo Rodrigo, Thales Alves de Melo Fernandes, Milton Yutaka Nishiyama-Jr, Carla Lima, Emma Wincent, and Monica Lopes-Ferreira. 2024. "TnP and AHR-CYP1A1 Signaling Crosstalk in an Injury-Induced Zebrafish Inflammation Model" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091155
APA StyleDisner, G. R., Fernandes, T. A. d. M., Nishiyama-Jr, M. Y., Lima, C., Wincent, E., & Lopes-Ferreira, M. (2024). TnP and AHR-CYP1A1 Signaling Crosstalk in an Injury-Induced Zebrafish Inflammation Model. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091155









