Mechanism Study of Xiaoyao San against Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis-Related Liver Fibrosis Based on a Combined Strategy of Transcriptome Analysis and Network Pharmacology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
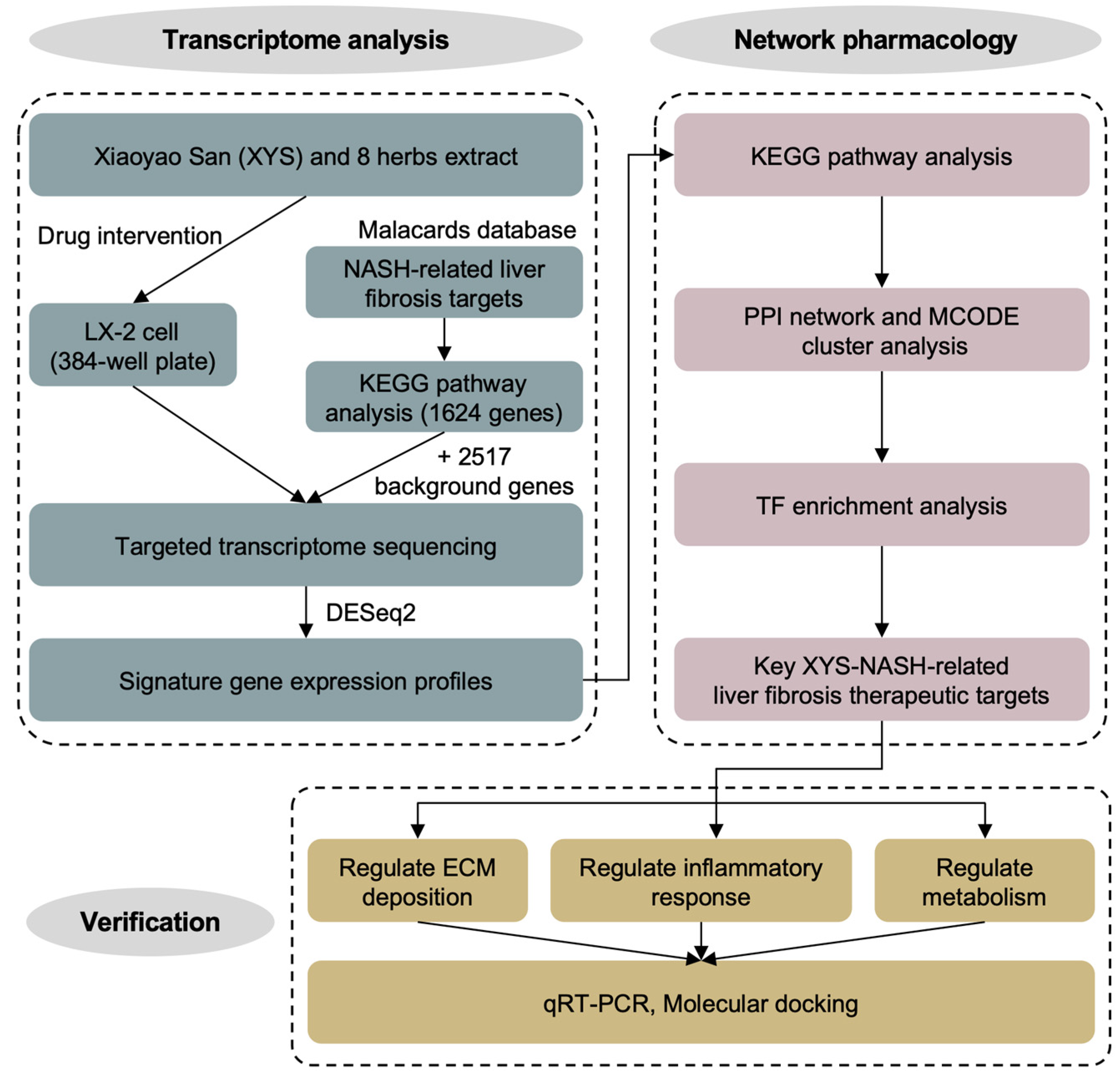
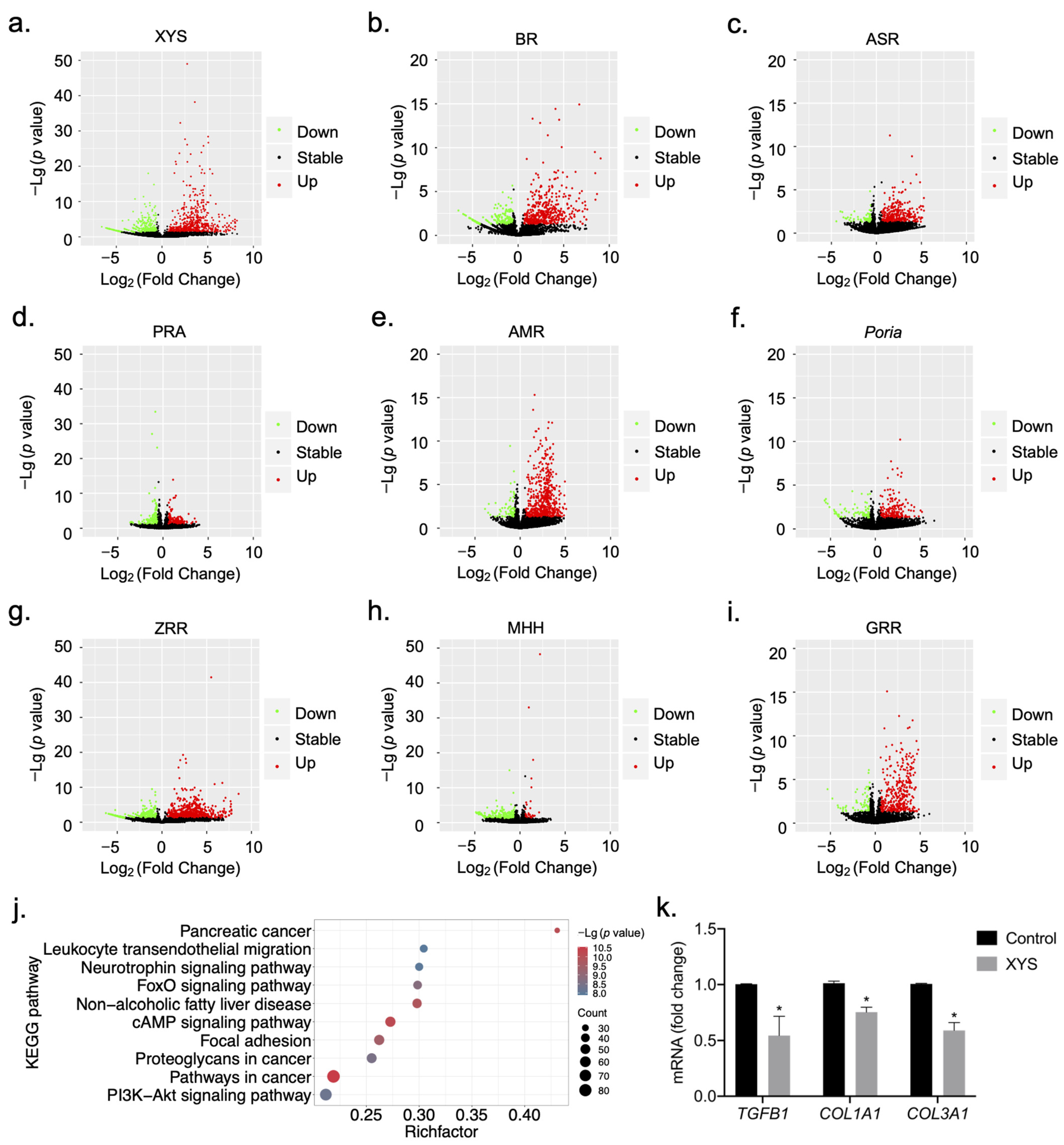
2.1. Construction of Signature Gene Expression Profiles for the Response to Treatment with XYS and Its Constituent Herbs
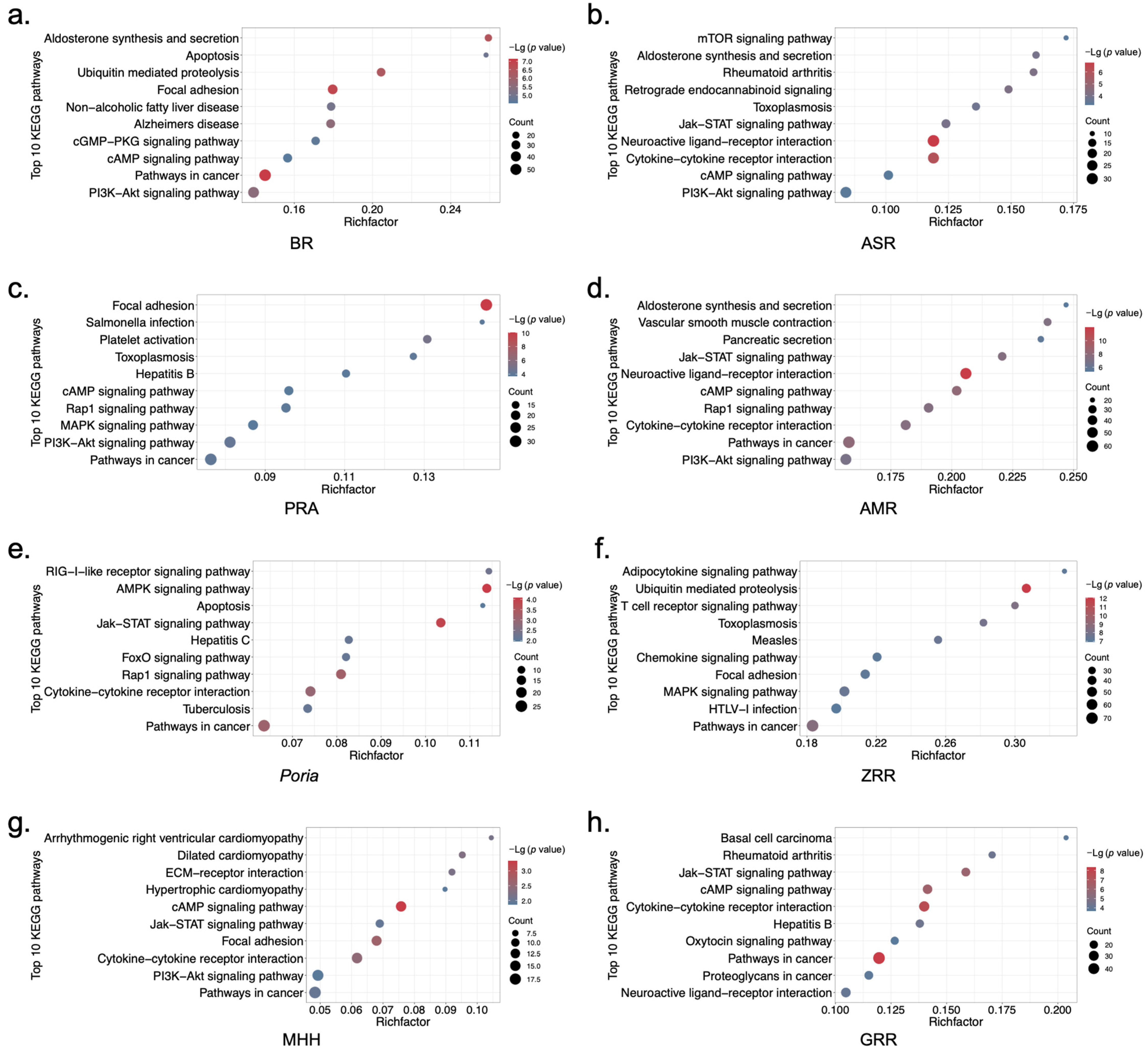
2.2. Biological Functional Analysis of XYS and Its Constituent Herbs
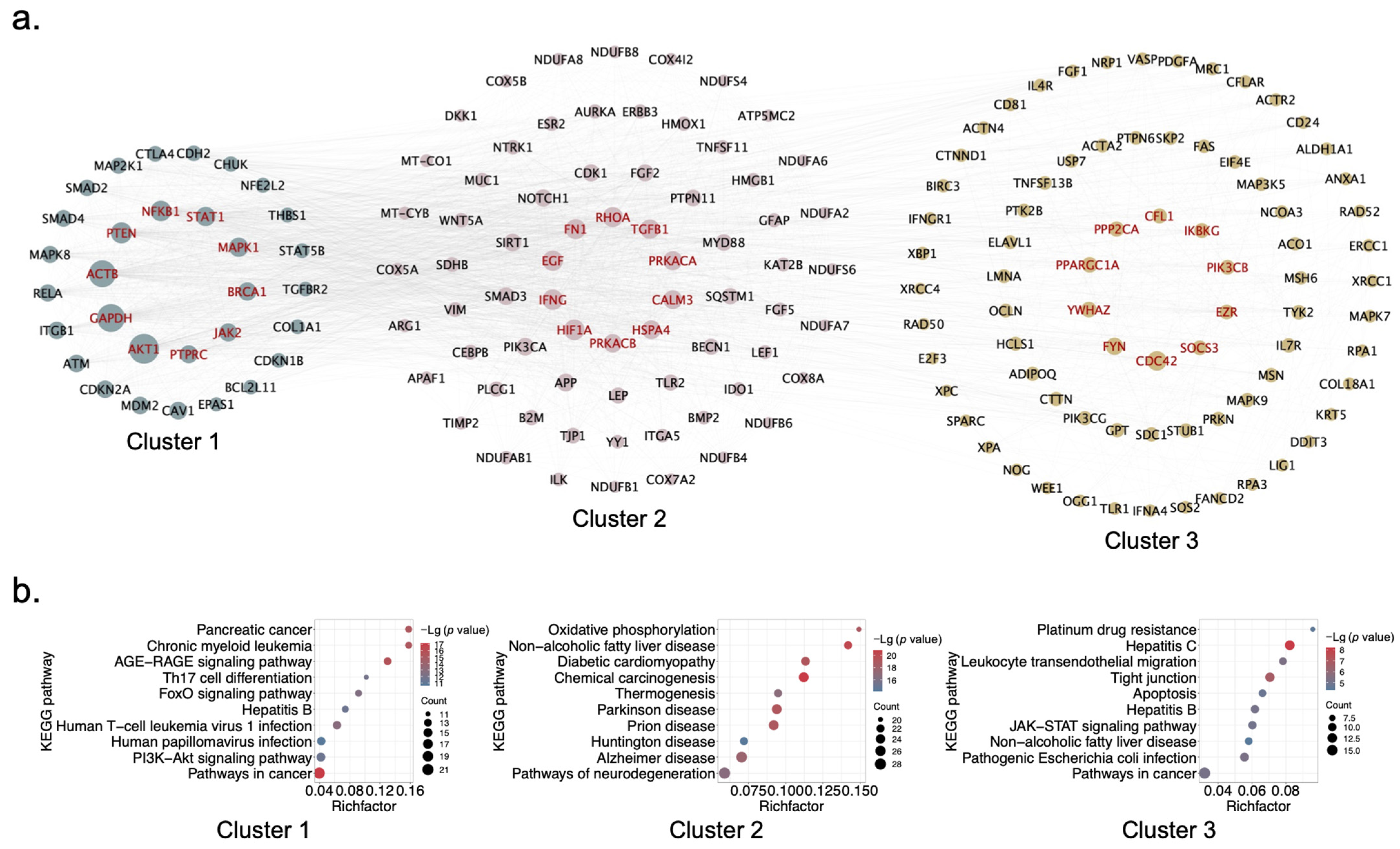
2.3. Identification of Hub Genes and Clusters of XYS via PPI Network Analysis
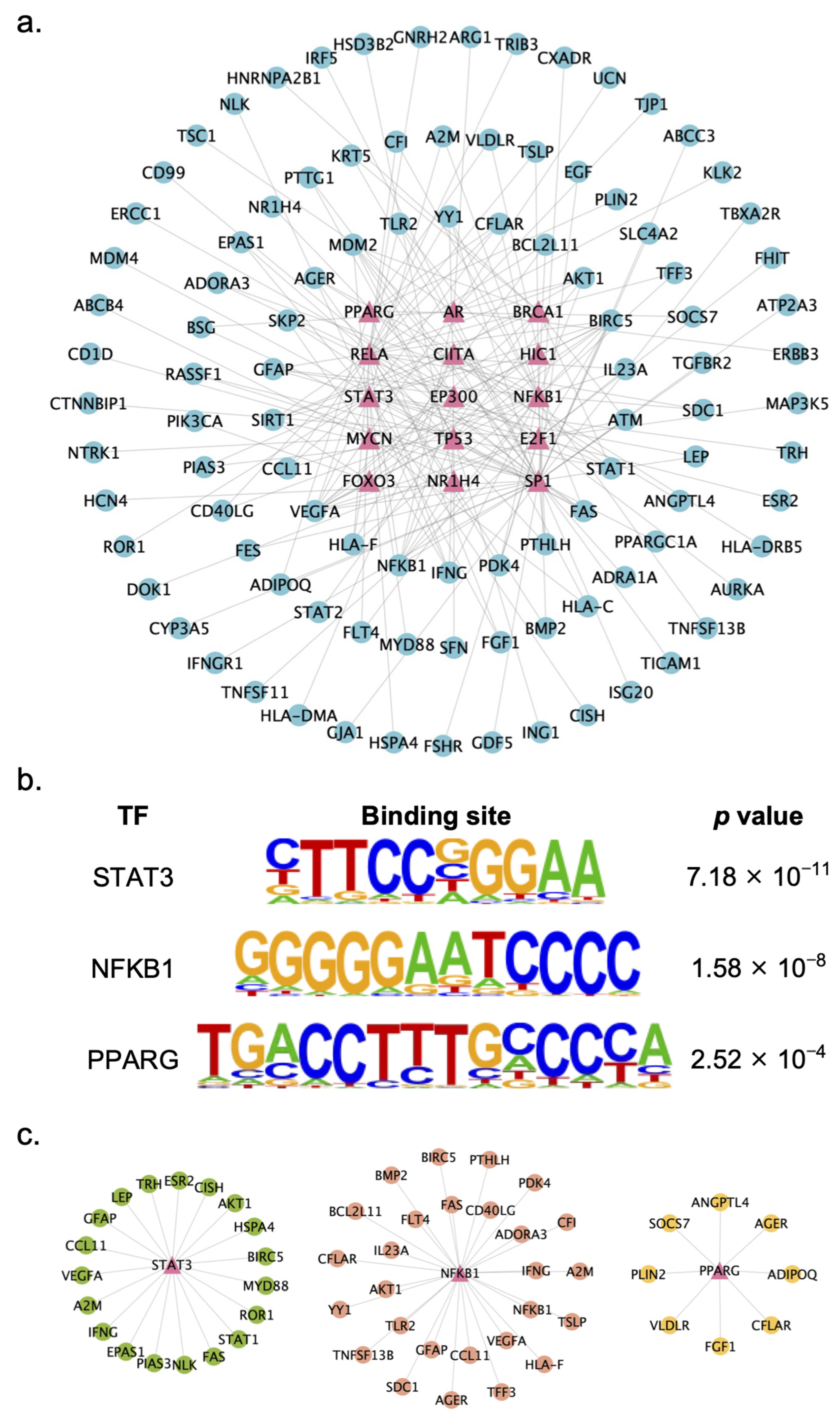
2.4. Identification of Key TFs Regulated by XYS
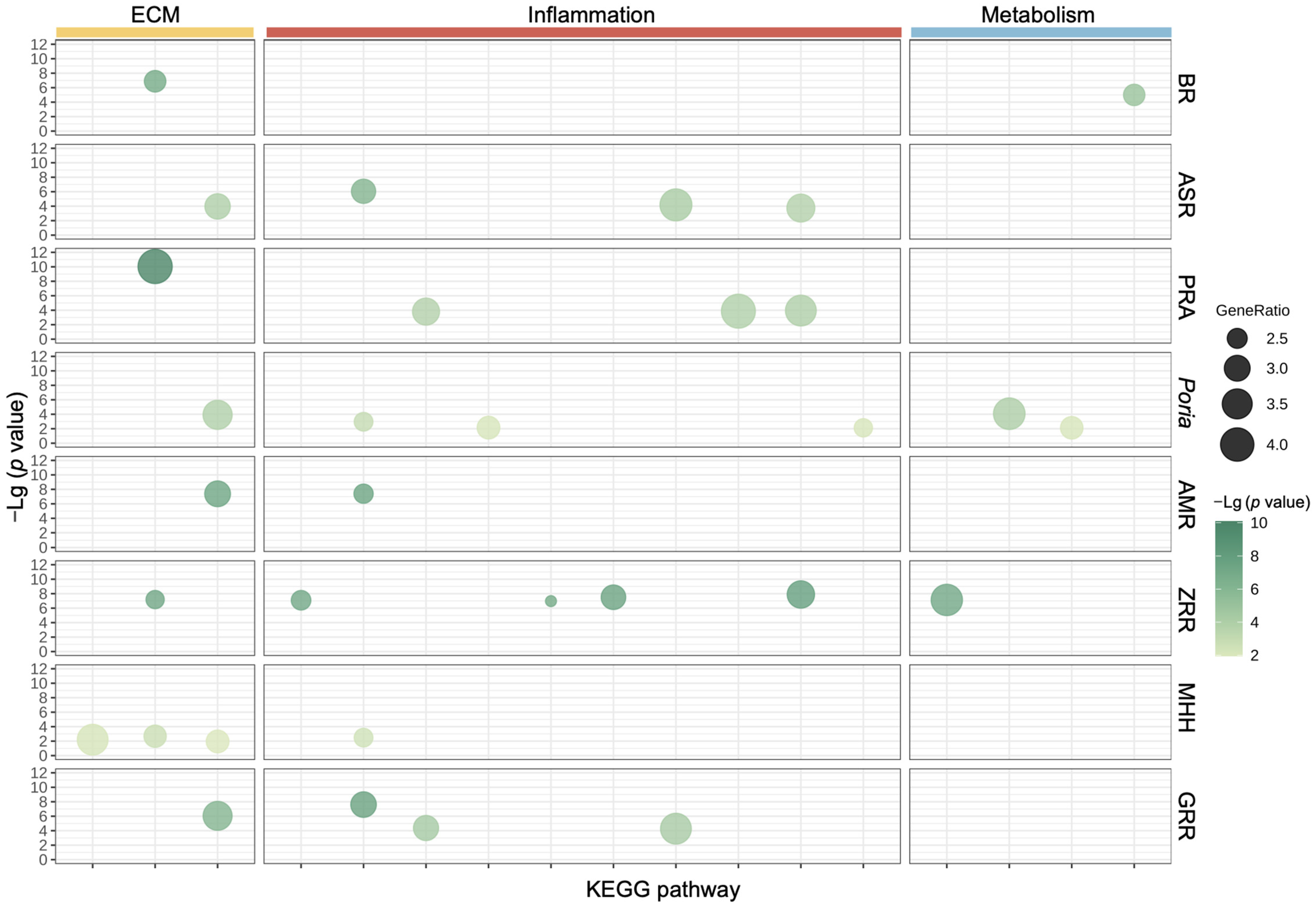
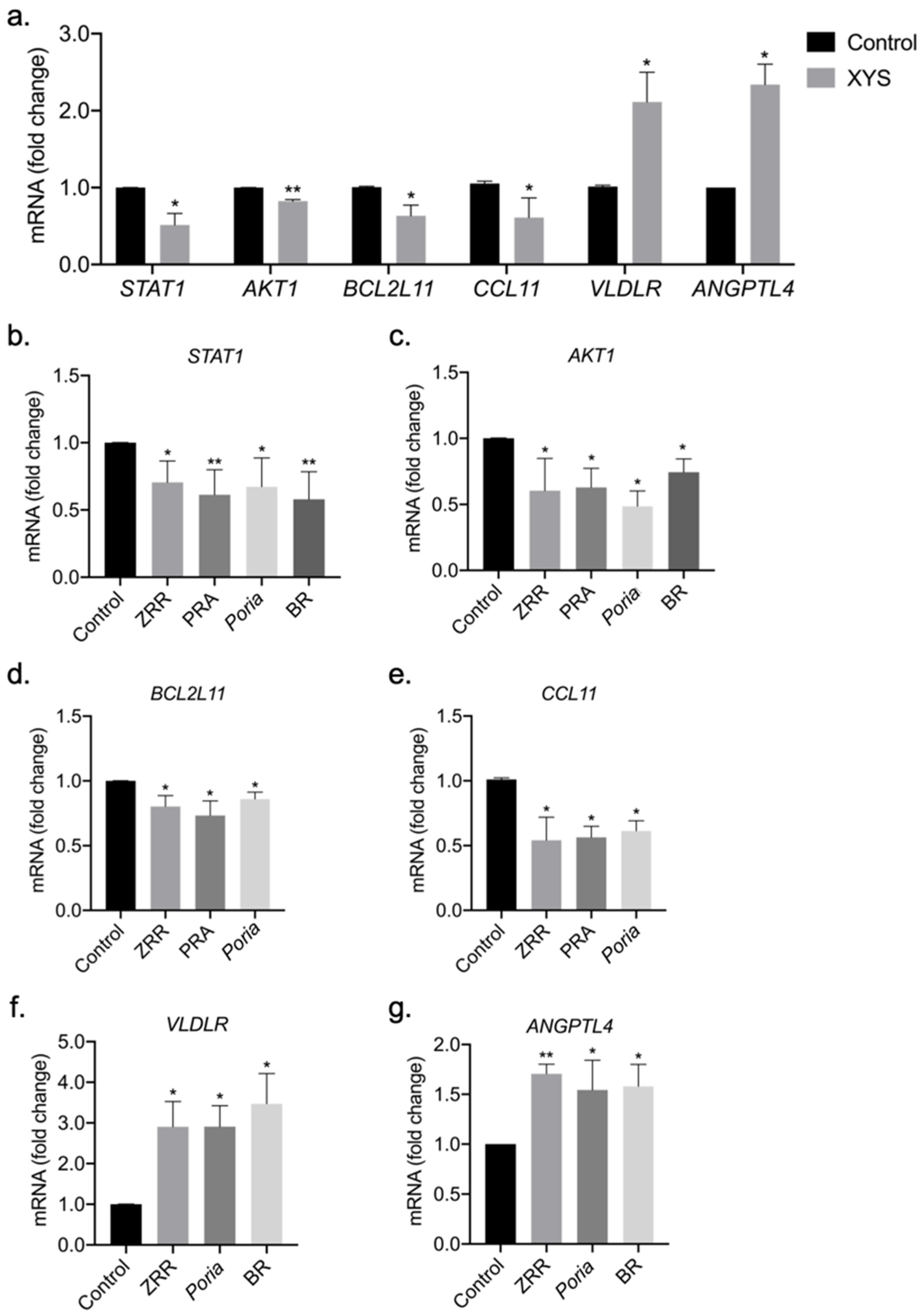
2.5. Validation of Potential Therapeutic Targets of XYS and Its Eight Constituent Herbs
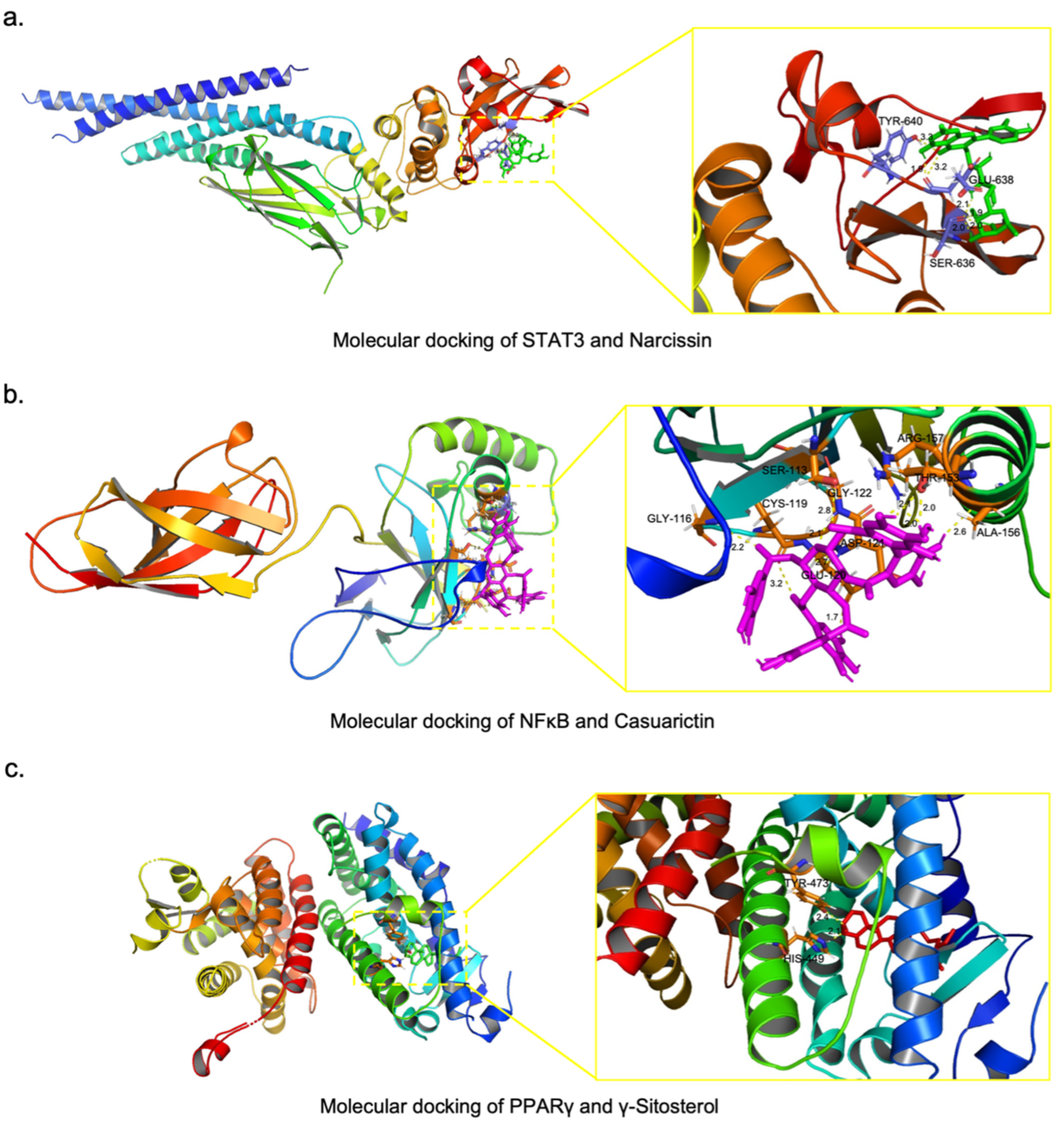
2.6. Screening of Potential Active Compounds in XYS That Inhibit NASH-Related Liver Fibrosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Design of the Study
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Extraction of XYS and Its Constituent Herbs
4.4. HTS2
4.5. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.6. Construction of the Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
4.7. Construction of the Gene–Transcription Factor (TF) Regulatory Interaction Network
4.8. Cell Viability Assay
4.9. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.10. Molecular Docking
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parola, M.; Pinzani, M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 65, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Poulsen, K.L.; Wu, L.J.; Liu, S.; Miyata, T.; Song, Q.L.; Wei, Q.D.; Zhao, C.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Yang, J.B. Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH). Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivella, J.P.; Martin, P.; Carrion, A.F. Novel targeted therapies for the management of liver fibrosis. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2020, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkorakis, M.; Boutari, C.; Hill, M.A.; Kotsis, V.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Resmetirom, the first approved drug for the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: Trials, opportunities, and challenges. Metabolism 2024, 154, 155835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.T.; Xie, Y.; Gong, S.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yu, H.; Zhou, T.R.; Huang, F.R.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.H.; Huang, R.L.; et al. Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.J.; Schuppan, D. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for fibrotic liver disease: Hope and hype. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.H.; Fu, S.L.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, D.J.; Chen, Q. Modified xiaoyao san combined with chemotherapy for breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1050337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.L.; Zeng, P.G.H.; Wang, X.H.; Mo, X.W.; Ma, Q.Y.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, N.J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Xue, Z.; Huang, J.Q.; et al. Xiaoyao pills, a Chinese patent medicine, treats mild and moderate depression: A randomized clinical trial combined with DNA methylation analysis. Phytomedicine 2024, 130, 155660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.Q.; Tang, J.M.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, S.D. Treatment of HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B by xiaoyao powder combined with interferon-α: A clinical observation. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2014, 34, 666–670. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Yang, J.; Ma, W.; Li, C.; An, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Q. Xiaoyao powder in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 288, 114999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wei, M.; Hong, G.; Qi, T.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yi, Y. Xiaoyao san attenuates hepatic steatosis through estrogen receptor α pathway in ovariectomized ApoE-/- mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 82, 114612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, R.; Cai, F.F.; Zhou, W.J.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.L.; Su, S.B. Xiaoyaosan decoction alleviated rat liver fibrosis via the TGFβ/SMAD and AKT/FoxO3 signaling pathways based on network pharmacology analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 264, 113021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Revelo, X.; Malhi, H. Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An overview. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Tabas, I.; Pajvani, U.B. Mechanisms of fibrosis development in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, N.; Nativ, N.; Stelzer, G.; Twik, M.; Guan-Golan, Y.; Stein, T.I.; Bahir, I.; Belinky, F.; Morrey, C.P.; Safran, M.; et al. MalaCards: An integrated compendium for diseases and their annotation. Database 2013, 2013, bat018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, G.D.; Hogue, C.W. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics 2003, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qi, Y.F.; Yu, Y.R. STAT3, A key regulator in liver fibrosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 21, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.A.; Xiao, W.A.; Long, J.F.; Zhang, H.M. The STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 suppresses fibrogenesis and angiogenesis in liver fibrosis. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 1600–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-κB in the liver--linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Galicia-Moreno, M.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; Meza-Rios, A.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. PPARs as metabolic sensors and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, F.Y.; Fan, X.; Lin, C.; Hao, Y.W.; Wei, H.D.; Lin, W.R.; Jiang, Y.; He, F.C. Quantitative proteomic analysis on activated hepatic stellate cells reversion reveal STAT1 as a key regulator between liver fibrosis and recovery. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, G.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Deng, M.H.; Yuan, F.C.; Gong, J.P. TIM-4 interference in kupffer cells against CCl4-induced liver fibrosis by mediating AKT1/mitophagy signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsumi, T.; Singh, R.; Sabharwal, L.; Bando, H.; Meng, J.; Arima, Y.; Yamada, M.; Harada, M.; Jiang, J.J.; Kamimura, D.; et al. Inflammation amplifier, a new paradigm in cancer biology. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.W.; Ting, Y.W.; Yong, Y.K.; Tan, H.Y.; Barathan, M.; Riazalhosseini, B.; Bee, C.J.; Tee, K.K.; Larsson, M.; Velu, V.; et al. Chronic inflammation involves CCL11 and IL-13 to facilitate the development of liver cirrhosis and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2021, 81, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espirito Santo, S.M.; Rensen, P.C.; Goudriaan, J.R.; Bensadoun, A.; Bovenschen, N.; Voshol, P.J.; Havekes, L.M.; van Vlijmen, B.J. Triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism in unique VLDL receptor, LDL receptor, and LRP triple-deficient mice. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teratani, T.; Tomita, K.; Wada, A.; Sugihara, N.; Higashiyama, M.; Inaba, K.; Horiuchi, K.; Hanawa, Y.; Nishii, S.; Mizoguchi, A.; et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 4 deficiency augments liver fibrosis in liver diseases such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice through enhanced free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate cells. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Cao, S.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Corke, H.; Beta, T.; Li, H.B. Bioactive compounds and bioactivities of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Foods 2019, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Wei, W. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of paeoniflorin and total glucosides of paeony. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 207, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.F.; Li, S.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Shen, J.Y.; Ding, Y.J.; Chen, T.; Ma, L.; Liu, J.F.; Lai, Y.X.; Chen, B.; et al. Bioactive triterpenoid compounds of Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf in the treatment of diabetic ulcers via regulating the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 325, 117812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.Z.; Cao, Z.; Tickner, J.; Qiu, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, C.Y.; Dong, S.W.; Xu, J.K. Poria cocos polysaccharide attenuates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NFATc1 activity and phosphorylation of ERK and STAT3. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 647, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.S.; Wang, K.; Mam, K.; Bao, L.; Liu, H.W. An insoluble polysaccharide from the sclerotium of Poria cocos improves hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice via modulation of gut microbiota. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.C.; Yang, R.; Ma, Y.S.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, Y. A systematic review of the active saikosaponins and extracts isolated from Radix Bupleuri and their applications. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 620–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wang, H.Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.Q.; Peng, K.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, P.X.; Qu, P. Saikosaponin-a attenuates oxidized LDL uptake and prompts cholesterol efflux in THP-1 Cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 67, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aasr, M.; Kabbash, A.; El-Seoud, K.A.A.; Al-Madboly, L.A.; Ikeda, T. Antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities of flavonol glycosides isolated from Atriplex halimus L. herb. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 8, 1159. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, C.F.B.; Ferreira, M.J.P.; Belchor, M.N.; Costa, C.R.C.; Novaes, D.P.; Dos Santos Junior, A.B.; Tamayose, C.I.; Pinho, M.V.T.; de Oliveira, M.A.; Toyama, M.H. Evaluation of the inhibitory potential of casuarictin, an ellagitannin isolated from white mangrove (Laguncularia racemosa) leaves, on snake venom secretory phospholipase A2. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Sangiovanni, E.; Vrhovsek, U.; Piazza, S.; Colombo, E.; Gasperotti, M.; Mattivi, F.; De Fabiani, E.; Dell’Agli, M. Strawberry tannins inhibit IL-8 secretion in a cell model of gastric inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, R.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Ignacimuthu, S. Antidiabetic activity of γ-sitosterol isolated from Lippia nodiflora L. in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 667, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, S.Y.; Gupta, H.; Ganesan, R.; Priya Sharma, S.; Won, S.M.; Jeong, J.J.; Kim, D.J.; et al. The juxtaposition of Ilex cornuta fruit and gut microbiota against alcoholic liver disease based on the integrated pharmacology via metabolomics. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Song, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.J.; Suk, K.T. The unfolded features on the synchronized fashion of gut microbiota and Drynaria rhizome against obesity via integrated pharmacology. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Qiu, J.S.; Fu, X.D. RASL-seq for massively parallel and quantitative analysis of gene expression. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2012, 98, 4.13.1–4.13.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.L.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023, protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Cho, J.W.; Lee, S.; Yun, A.; Kim, H.; Bae, D.; Yang, S.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, E.; et al. TRRUST v2, an expanded reference database of human and mouse transcriptional regulatory interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D380–D386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S.; Benner, C.; Spann, N.; Bertolino, E.; Lin, Y.C.; Laslo, P.; Cheng, J.X.; Murre, C.; Singh, H.; Glass, C.K. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.L.; Li, P.; Wang, J.N.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.H.; Huang, C.; Li, P.D.; Guo, Z.H.; Tao, W.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.M.; Chen, T.; Lv, C.Y.; Tang, S.H.; Zhang, X.B.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhou, R.R.; et al. ETCM: An encyclopaedia of traditional Chinese medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D976–D982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xie, D.L.; Yu, Y.R.; Liu, H.L.; Shi, Y.; Shi, T.L.; Wen, C.P. TCMID 2.0, a comprehensive resource for TCM. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 6, D1117–D1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.Y.; Zheng, G.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, Z.K.; Mao, T.T.; Gao, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Ji, X.J.; Yu, J.Y.; et al. HIT 2.0, an enhanced platform for herbal ingredients’ targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1238–D1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pinyin Name | Latin Name | Number of DEGs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up- Regulated | Down- Regulated | Total | ||
| XYS | \ | 574 | 342 | 916 |
| Chai Hu | Bupleuri Radix | 428 | 170 | 598 |
| Dang Gui | Angelicae Sinensis Radix | 311 | 53 | 364 |
| Bai Shao | Paeoniae Radix Alba | 184 | 119 | 303 |
| Bai Zhu | Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma | 558 | 69 | 627 |
| Fu Ling | Poria | 182 | 77 | 259 |
| Sheng Jiang | Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens | 515 | 250 | 765 |
| Bo He | Menthae Haplocalycis Herba | 31 | 180 | 211 |
| Zhi Gan Cao | Glycyrrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma Praeparata Cum Melle | 342 | 69 | 411 |
| Source Herb | Chemical Name | CAS No. | Binding Energy (Kcal·moL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| \ | Positive control | \ | −7.79 |
| BR | Narcissin | 604-80-8 | −13.53 |
| BR | Rutin | 153-18-4 | −10.67 |
| BR | Saikosaponin B | 58558-08-0 | −10.49 |
| BR | Saikosaponin A | 20736-09-8 | −10.48 |
| BR | Stigmasterol glucoside | 19716-26-8 | −10.19 |
| PRA | 1,2,4,6-Tetragalloylglucose | 84297-49-4 | −12.06 |
| PRA | Tellimagrandin II | 81571-72-4 | −12.04 |
| PRA | Tellimagrandin I | 79786-08-6 | −11.61 |
| PRA | 1,2,6-Tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose | 79886-49-0 | −11.55 |
| PRA | 1,2,3-Tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose | 84415-91-8 | −11.51 |
| ZRR | Theaflavin 3,3′-digallate | 30462-35-2 | −10.81 |
| ZRR | Geraniin | 60976-49-0 | −10.45 |
| ZRR | Eudesobovatol A | 125196-77-2 | −9.42 |
| ZRR | Isoginkgetin | 548-19-6 | −8.74 |
| Source Herb | Chemical Name | CAS No. | Binding Energy (Kcal·moL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| \ | Positive control | \ | −6.15 |
| PRA | Casuarictin | 79786-00-8 | −12.64 |
| PRA | Eugeniin | 58970-75-5 | −10.97 |
| PRA | 1,2,6-Trigalloylglucose | 79886-49-0 | −10.85 |
| PRA | Peonidin-3,5-O-di-beta-glucopyranoside | 47851-83-2 | −10.66 |
| PRA | 1,2,3-Tri-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose | 84415-91-8 | −10.61 |
| ZRR | Geraniin | 60976-49-0 | −12.03 |
| ZRR | Theaflavin 3,3′-digallate | 30462-35-2 | −10.71 |
| ZRR | Rutin | 153-18-4 | −10.63 |
| ZRR | Eudesobovatol A | 125196-77-2 | −9.30 |
| ZRR | Isoginkgetin | 548-19-6 | −8.76 |
| Poria | 25-hydroxy-3-epidehydrotumulosic acid | 167775-55-5 | −7.91 |
| Poria | 3-Epidehydrotumulosic acid | 167775-54-4 | −7.87 |
| Poria | Avicularin | 572-30-5 | −7.47 |
| Poria | Dehydrotumulosic acid | 6754-16-1 | −7.42 |
| Poria | Tumulosic acid | 508-24-7 | −7.35 |
| Source Herb | Chemical Name | CAS No. | Binding Energy (Kcal·moL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| \ | Positive control | \ | −7.84 |
| BR | γ-Sitosterol | 83-47-6 | −9.60 |
| BR | Poriferasterol | 481-16-3 | −9.51 |
| BR | Baicalin | 21967-41-9 | −8.61 |
| BR | Cubebin | 18423-69-3 | −8.09 |
| Poria | Turanose | 547-25-1 | −9.45 |
| Poria | Methyl dehydroabietate | 1235-74-1 | −8.12 |
| ZRR | γ-Sitosterol | 83-47-6 | −9.60 |
| ZRR | β-Sitosterol | 83-46-5 | −9.26 |
| ZRR | Gingerenone B | 128700-98-1 | −8.67 |
| ZRR | Dihydrocurcumin | 76474-56-1 | −8.57 |
| ZRR | Gingerenone A | 128700-97-0 | −8.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, D.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Huang, W.; Hao, M.; Xie, L. Mechanism Study of Xiaoyao San against Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis-Related Liver Fibrosis Based on a Combined Strategy of Transcriptome Analysis and Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091128
Yan D, Zhang X, Ma C, Huang W, Hao M, Xie L. Mechanism Study of Xiaoyao San against Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis-Related Liver Fibrosis Based on a Combined Strategy of Transcriptome Analysis and Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091128
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Di, Xiaoling Zhang, Chengmei Ma, Wenting Huang, Mimi Hao, and Lan Xie. 2024. "Mechanism Study of Xiaoyao San against Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis-Related Liver Fibrosis Based on a Combined Strategy of Transcriptome Analysis and Network Pharmacology" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091128
APA StyleYan, D., Zhang, X., Ma, C., Huang, W., Hao, M., & Xie, L. (2024). Mechanism Study of Xiaoyao San against Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis-Related Liver Fibrosis Based on a Combined Strategy of Transcriptome Analysis and Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091128






