Gefitinib-Induced Severe Dermatological Adverse Reactions: A Case Report and Pharmacogenetic Profile
Abstract
1. Introduction
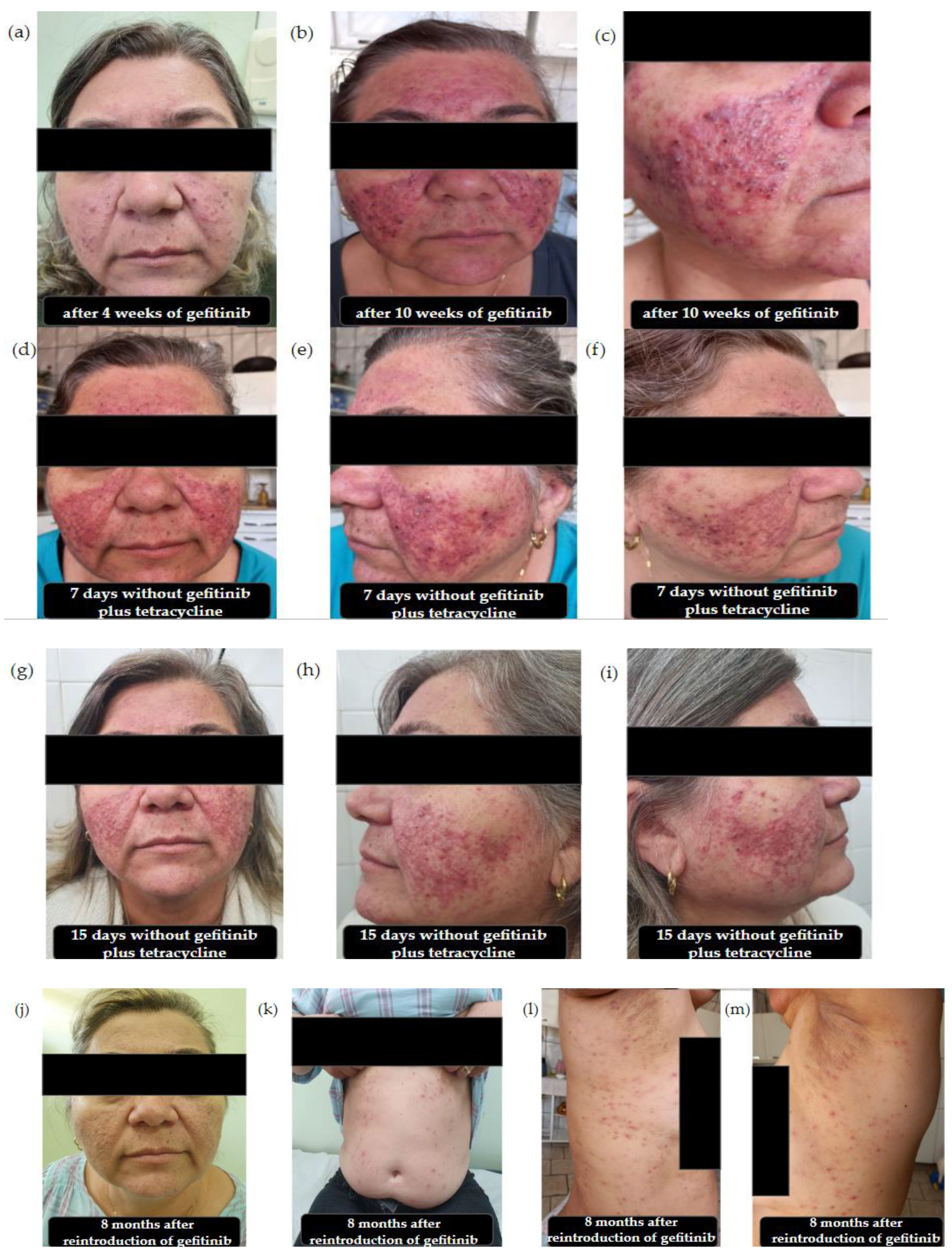
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, M.H.; Williams, G.A.; Sridhara, R.; Chen, G.; McGuinn, W.D.; Morse, D.; Abraham, S.; Rahman, A.; Liang, C.; Lostritto, R.; et al. United States Food and Drug Administration Drug Approval summary: Gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) tablets. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.; Yang, J.-J.; Lam, K.-C. Treating Patients with EGFR-Sensitizing Mutations: First Line or Second Line—Is There a Difference? J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, S.; Lulli, D.; Girolomoni, G. Epidermal growth factor receptor signalling in keratinocyte biology: Implications for skin toxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1189–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofheinz, R.-D.; Deplanque, G.; Komatsu, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ocvirk, J.; Racca, P.; Guenther, S.; Zhang, J.; Lacouture, M.E.; Jatoi, A. Recommendations for the Prophylactic Management of Skin Reactions Induced by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors in Patients with Solid Tumors. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fu, R.; Jiang, T.; Duan, D.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Ni, R.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Mechanism of Lethal Skin Toxicities Induced by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors and Related Treatment Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 804212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Acharjya, B. Adverse cutaneous drug reaction. Indian J. Dermatol. 2008, 53, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, W.J. Immune pathomechanism and classification of drug hypersensitivity. Allergy 2019, 74, 1457–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris, M.G.; Natale, R.B.; Herbst, R.S.; Lynch, T.J.; Prager, D.; Belani, C.P.; Schiller, J.H.; Kelly, K.; Spiridonidis, H.; Sandler, A.; et al. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized trial. JAMA 2003, 290, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, M.; Yano, S.; Giaccone, G.; Tamura, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Kudoh, S.; Rischin, D.; et al. Multi-Institutional Randomized Phase II Trial of Gefitinib for Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 41, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, M.; He, P.; Hidalgo, M.; Baker, S.D. Differential Metabolism of Gefitinib and Erlotinib by Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3731–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.; Kondo, M.; Horio, M.; Ando, M.; Saito, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Horio, Y.; Hasegawa, Y. Genetic polymorphisms of the adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporters (abcg2, abcb1) and gefitinib toxicity. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Qin, G.; Yao, C. Correlation between adverse events after drug treatment and the MDR1 C3435T polymorphism in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients in an Asian population: A meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 3522–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Guo, L.; Li, P.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, B.; Ren, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L. Determinants of gefitinib pharmacokinetics in healthy Chinese male subjects: A pharmacogenomic study of cytochrome p450 enzymes and transporters. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2020, 45, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliuca, S.; Gurnari, C.; Rubio, M.T.; Visconte, V.; Lenz, T.L. Individual HLA heterogeneity and its implications for cellular immune evasion in cancer and beyond. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 944872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S Department of Health and Human Services; National Institute of Health NCI; U.S Department of Health and Human Services. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE); Version 5.0. 2018. Available online: https://nciterms.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/pages/vocabulary.jsf?dictionary=CTCAE_v5&version=5.0 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Raehl, C.L.; Bond, C.A.; Woods, T.; Patry, R.A.; Sleeper, R.B. Individualized Drug Use Assessment in the Elderly. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2002, 22, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, R.; Weinman, J.; Hankins, M. The beliefs about medicines questionnaire: The development and evaluation of a new method for assessing the cognitive representation of medication. Psychol. Health 1999, 14, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, T.; Marques, A.; Geraldes, L.; Benrimoj, S.; Horne, R.; Fernandez-Llimos, F.; Salgado, T.; Marques, A.; Geraldes, L.; Benrimoj, S.; et al. Cross-cultural adaptation of the Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire into Portuguese. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2013, 131, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Ranade, A.; Venkataramanan, R.; Strom, S.; Chupka, J.; Ekins, S.; Schuetz, E.; Bachmann, K. A Comprehensive in Vitro and in Silico Analysis of Antibiotics That Activate Pregnane X Receptor and Induce CYP3A4 in Liver and Intestine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Lima, C.M.; Soares, H.P.; Raez, L.E.; Singal, R. EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control 2007, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, A.; Ready, N. Gefitinib therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2005, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cersosimo, R.J. Gefitinib: An adverse effects profile. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2006, 5, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; LoRusso, P.M.; Purdom, M.; Ward, D. Dermatologic Side Effects Associated with Gefitinib Therapy: Clinical Experience and Management. Clin. Lung Cancer 2003, 4, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunaga, N.; Tomizawa, Y.; Yanagitani, N.; Iijima, H.; Kaira, K.; Shimizu, K.; Tanaka, S.; Suga, T.; Hisada, T.; Ishizuka, T.; et al. Phase II prospective study of the efficacy of gefitinib for the treatment of stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations, irrespective of previous chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2007, 56, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piraccini, B.M.; Alessandrini, A. Drug-related nail disease. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, J.C.; Ghazarian, D.M.; Shaw, J.C. Scarring Alopecia Associated with Use of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor Gefitinib. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 1524–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, J.E.; Jones, B.F.; Lind, A.C.; Heffernan, M.P. Nonscarring inflammatory alopecia associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Q.; Sun, H.; Xue, D. A severe dermatologic adverse effect related with gefitinib: Case report and review of the literature. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2013, 9 (Suppl. S2), 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrazzi, A.; Russo, I.; Pasello, G.; Alaibac, M. Atypical skin reaction in a patient treated with gefitinib for advanced lung cancer: A case report and review of the literature. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Antona, C.; Savieo, J.L.; Lauschke, V.M.; Sangkuhl, K.; Drögemöller, B.I.; Wang, D.; van Schaik, R.H.N.; Gilep, A.A.; Peter, A.P.; Boone, E.C.; et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: CYP3A5. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 112, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Yu, X.; Xu, L.-M.; Mei, J.; Tian, M.-L.; Xu, M.; Jin, Q.-Y.; Ye, L.-B.; Yang, S.-X. Effect of genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of gefitinib in healthy Chinese volunteers. Xenobiotica 2024, 54, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, W.C.; Lam, D.C.L.; Ip, M.S.M.; Tam, T.C.C.; Ho, J.C.M. Association of genetic polymorphisms of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 with gefitinib-induced toxicities. Anticancer. Drugs 2022, 33, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckillop, D.; McCormick, A.D.; Millar, A.; Miles, G.S.; Phillips, P.J.; Hutchison, M. Cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism of gefitinib. Xenobiotica 2005, 35, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckillop, D.; Mccormick, A.D.; Miles, G.S.; Phillips, P.J.; Pickup, K.J.; Bushby, N.; Hutchison, M. In vitro metabolism of gefitinib in human liver microsomes. Xenobiotica 2004, 34, 983–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, E.; Umemura, S.; Nomura, S.; Kirita, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Yoh, K.; Niho, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; Tsuboi, M.; Ohe, Y.; et al. Impact of single nucleotide polymorphisms on severe hepatotoxicity induced by EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gow, J.M.; Hodges, L.M.; Chinn, L.W.; Kroetz, D.L. Substrate-Dependent Effects of Human ABCB1 Coding Polymorphisms. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, K.T.; Palkar, A.M.; Hong, A.L. Genetics of ABCB1 in Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fojo, A.T.; Ueda, K.S.D.J.; Slamon, D.J.; Poplack, D.G.; Gottesman, M.M.; Pastan, I. Expression of a multidrug-resistance gene in human tumors and tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, B.; Tulsyan, S.; Mittal, R. The effect of ABCB1 polymorphisms on the outcome of breast cancer treatment. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2016, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Haba, E.; García, M.I.; Cortejoso, L.; López-Lillo, C.; Barrueco, N.; García-Alfonso, P.; Alvarez, S.; Jiménez, J.L.; Martín, M.L.; Muñóz-Fernández, M.A.; et al. ABCB1 gene polymorphisms are associated with adverse reactions in fluoropyrimidine-treated colorectal cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics 2010, 11, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xin, S.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Determinants of Gefitinib toxicity in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A pharmacogenomic study of metabolic enzymes and transporters. Pharmacogenom. J. 2017, 17, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morau, M.V.; Seguin, C.S.; Visacri, M.B.; Pincinato, E.d.C.; Moriel, P. Genetic Variants in the ABCB1 and ABCG2 Gene Drug Transporters Involved in Gefitinib-Associated Adverse Reaction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Genes 2024, 15, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukal, S.; Guin, D.; Rawat, C.; Bora, S.; Mishra, M.K.; Sharma, P.; Paul, P.R.; Kanojia, N.; Grewal, G.K.; Kukreti, S.; et al. Multidrug efflux transporter ABCG2: Expression and regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6887–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusatis, G.; Gregorc, V.; Li, J.; Spreafico, A.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Verweij, J.; Ludovini, V.; Villa, E.; Hidalgo, M.; Sparreboom, A.; et al. Pharmacogenetics of ABCG2 and adverse reactions to gefitinib. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasaka, K.; Kaburagi, T.; Yasuda, S.; Ohmori, K.; Abe, K.; Sagara, H.; Ueda, Y.; Nagao, K.; Imura, J.; Imai, Y. Impact of functional ABCG2 polymorphisms on the adverse effects of gefitinib in Japanese patients with non–small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsey, A.J.; Cox, M.H.; Sarwat, S.; Kerr, I.D. The multidrug transporter ABCG2: Still more questions than answers. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.N.; Zhang, C.L.; He, H.R.; Pan, Z.Y.; Fan, D.; He, Y.L.; You, H.S.; Li, Y.J. Associations between ABCG2 gene polymorphisms and gefitinib toxicity in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncol. Targets. Ther. 2018, 11, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nofziger, C.; Turner, A.J.; Sangkuhl, K.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Agúndez, J.A.G.; Black, J.L.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Ruano, G.; Kennedy, M.A.; Phillips, M.S.; et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: CYP2D6. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 107, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, J.P.; Peter, A.P.; Shaman, J.A. Consequences of CYP2D6 Copy-Number Variation for Pharmacogenomics in Psychiatry. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzumura, T.; Kimura, T.; Kudoh, S.; Umekawa, K.; Nagata, M.; Kira, Y.; Nakai, T.; Matsuura, K.; Yoshimura, N.; Hirata, K. Reduced CYP2D6 Function Potentiates the Gefitinib-Induced Rash in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, ix79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowell, D.; Morris, L.G.T.; Grigg, C.M.; Weber, J.K.; Samstein, R.M.; Makarov, V.; Kuo, F.; Kendall, S.M.; Requena, D.; Riaz, N.; et al. Patient HLA class I genotype influences cancer response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Science 2018, 359, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Patient Genotype | Patient Phenotype |
|---|---|---|
| CYP2D6 | *1/*2 | normal metabolizer (CNV = 2) |
| CYP3A4 | *1/*2 | normal metabolizer |
| CYP3A5 | *3/*3 | poor metabolizer |
| ABCB1 | ||
| rs 1045642 (3435 A > C) | A/A | - |
| rs 1128503 (c.1236A > G) | G/G | - |
| rs 2032582 (2677 C > T/A) | C/C | - |
| ABCG2 | ||
| rs2231142 (c.421G > T) | G/T | - |
| rs2622604 (c.-20 + 614 T > C) | C/T | - |
| EGFR | ||
| rs2227983 (1562 G > A) | G/G | - |
| rs2293347 (c.2982 C > T) | C/C | - |
| HLA | ||
| A/B | Ref/Ref | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morau, M.V.; Seguin, C.S.; Perroud Junior, M.W.; Dagli-Hernandez, C.; Pincinato, E.d.C.; Moriel, P. Gefitinib-Induced Severe Dermatological Adverse Reactions: A Case Report and Pharmacogenetic Profile. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081040
Morau MV, Seguin CS, Perroud Junior MW, Dagli-Hernandez C, Pincinato EdC, Moriel P. Gefitinib-Induced Severe Dermatological Adverse Reactions: A Case Report and Pharmacogenetic Profile. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(8):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081040
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorau, Mariana Vieira, Cecilia Souto Seguin, Mauricio Wesley Perroud Junior, Carolina Dagli-Hernandez, Eder de Carvalho Pincinato, and Patricia Moriel. 2024. "Gefitinib-Induced Severe Dermatological Adverse Reactions: A Case Report and Pharmacogenetic Profile" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 8: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081040
APA StyleMorau, M. V., Seguin, C. S., Perroud Junior, M. W., Dagli-Hernandez, C., Pincinato, E. d. C., & Moriel, P. (2024). Gefitinib-Induced Severe Dermatological Adverse Reactions: A Case Report and Pharmacogenetic Profile. Pharmaceuticals, 17(8), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081040







