Exploring the Mechanism of Topical Application of Clematis Florida in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis through Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Main Compounds in CF Extract
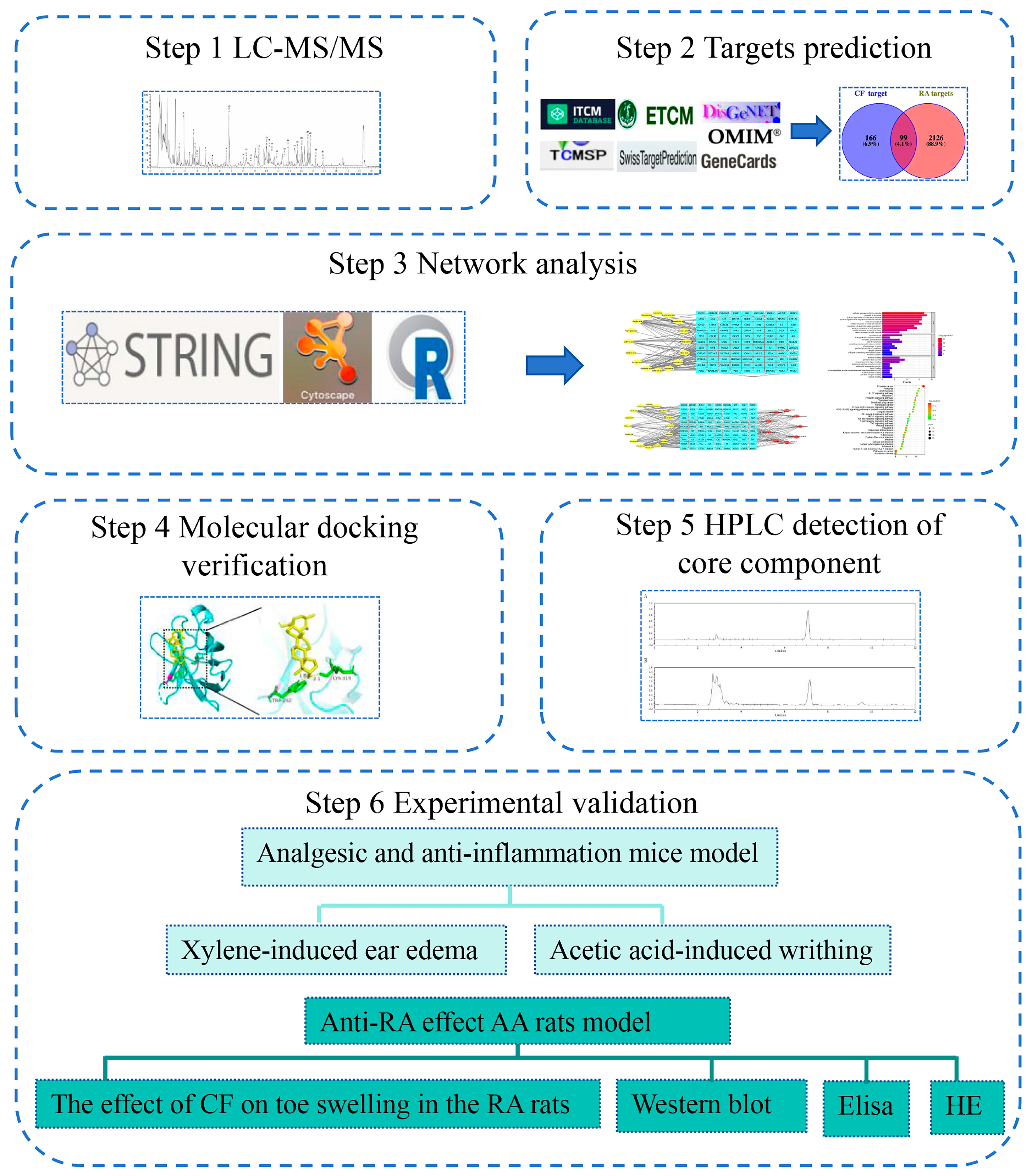
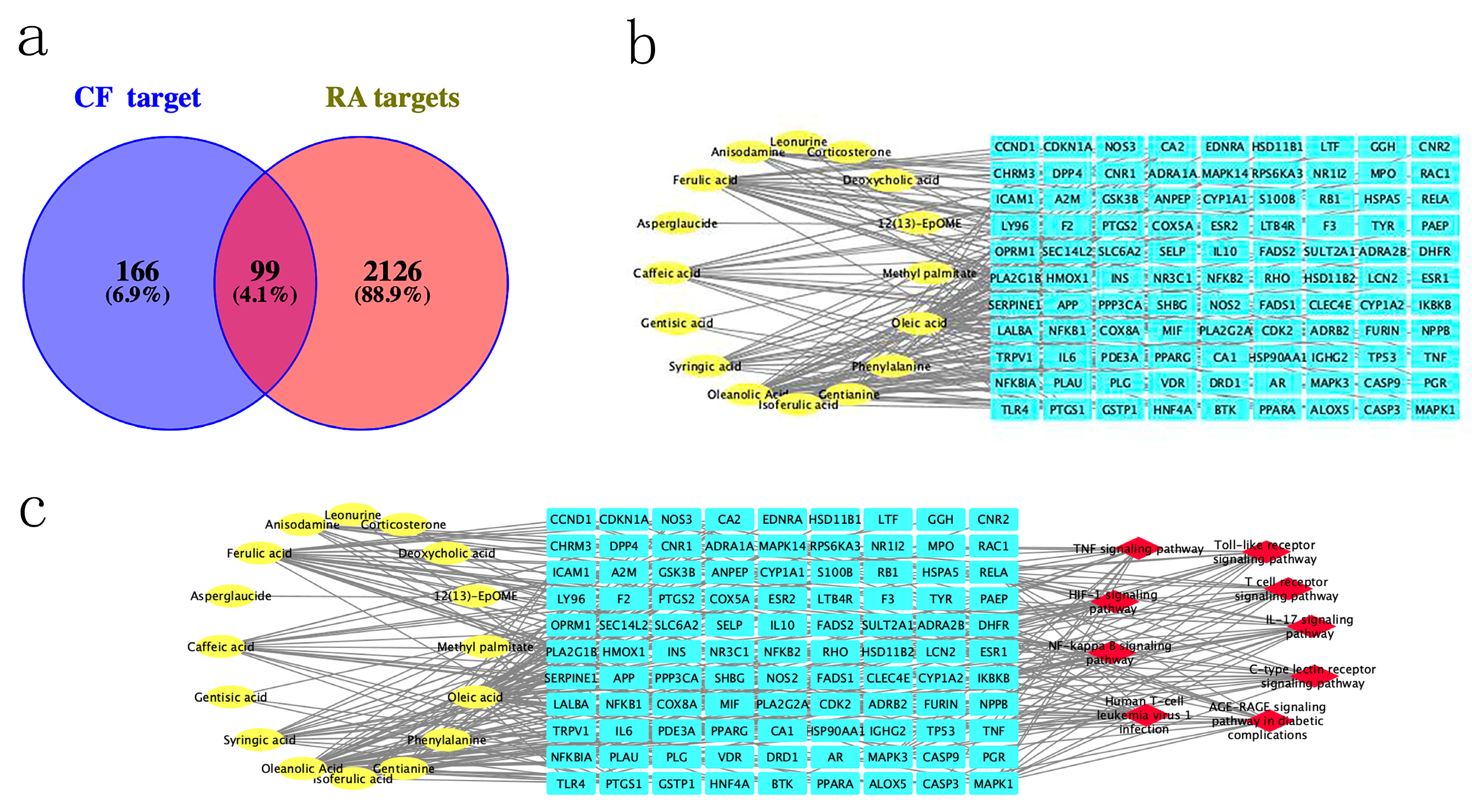
2.2. Construction of CT Network and Screening Core Compounds in CF
2.3. Screening of Main Targets
2.4. GO Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Construction of CPS Network and Screening of Core Targets
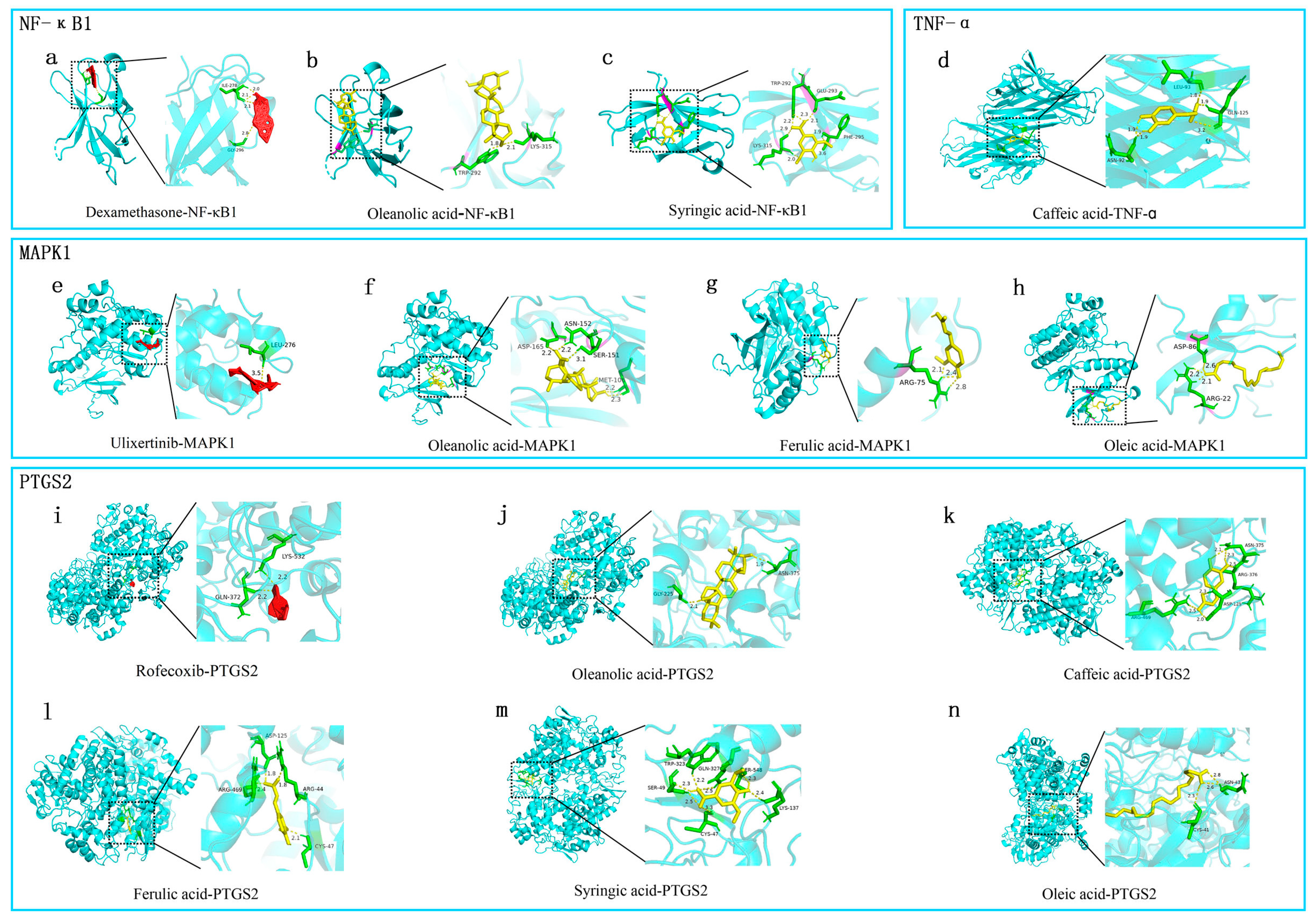
2.6. Molecular Docking Effectiveness
2.7. HPLC Measurement of Quality Control Substance Oleanolic Acid Content
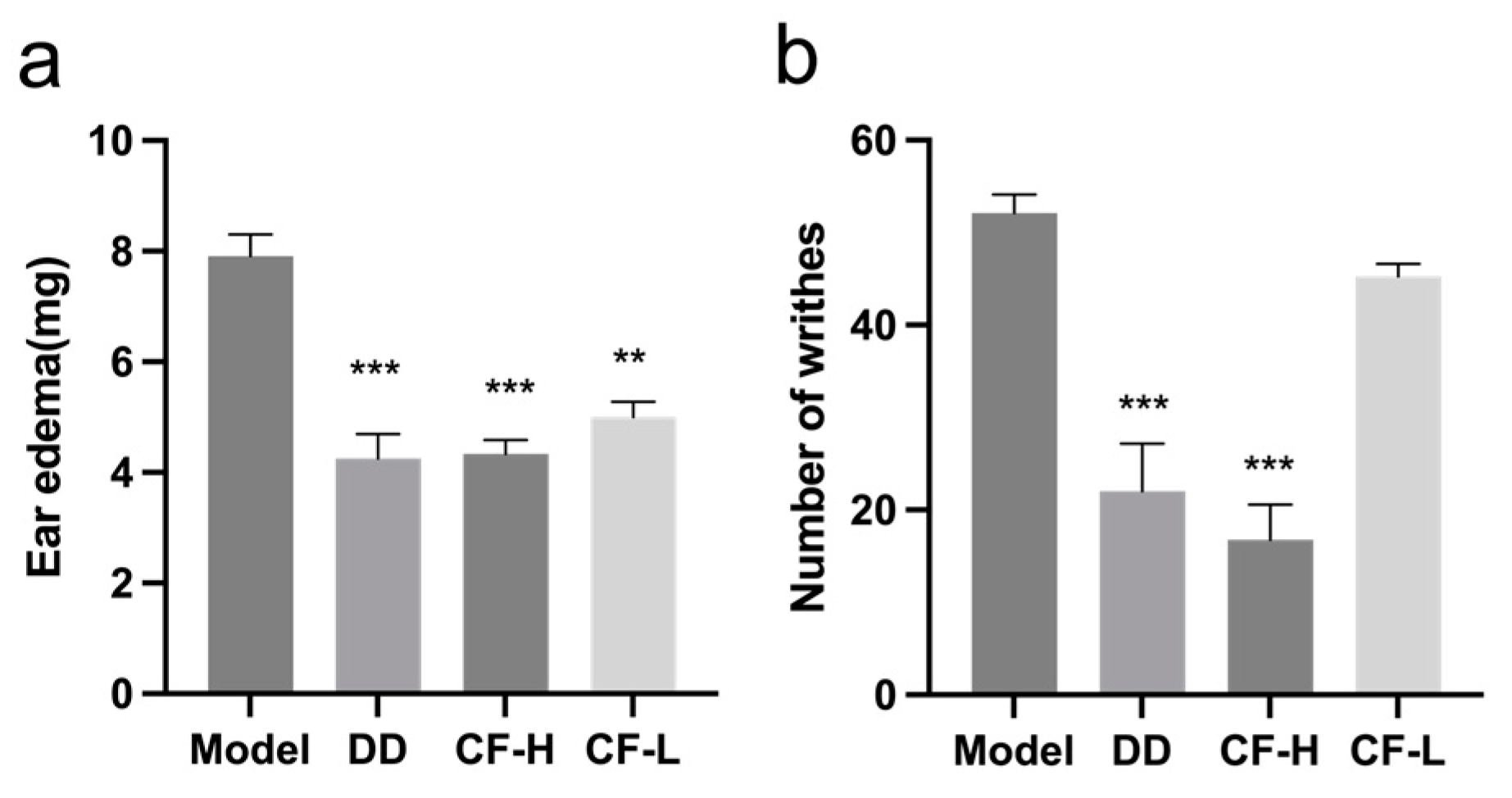
2.8. CF Alleviated Xylene-Induced Mouse Ear Edema
2.9. CF Showed Analgesic Activity in Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Model
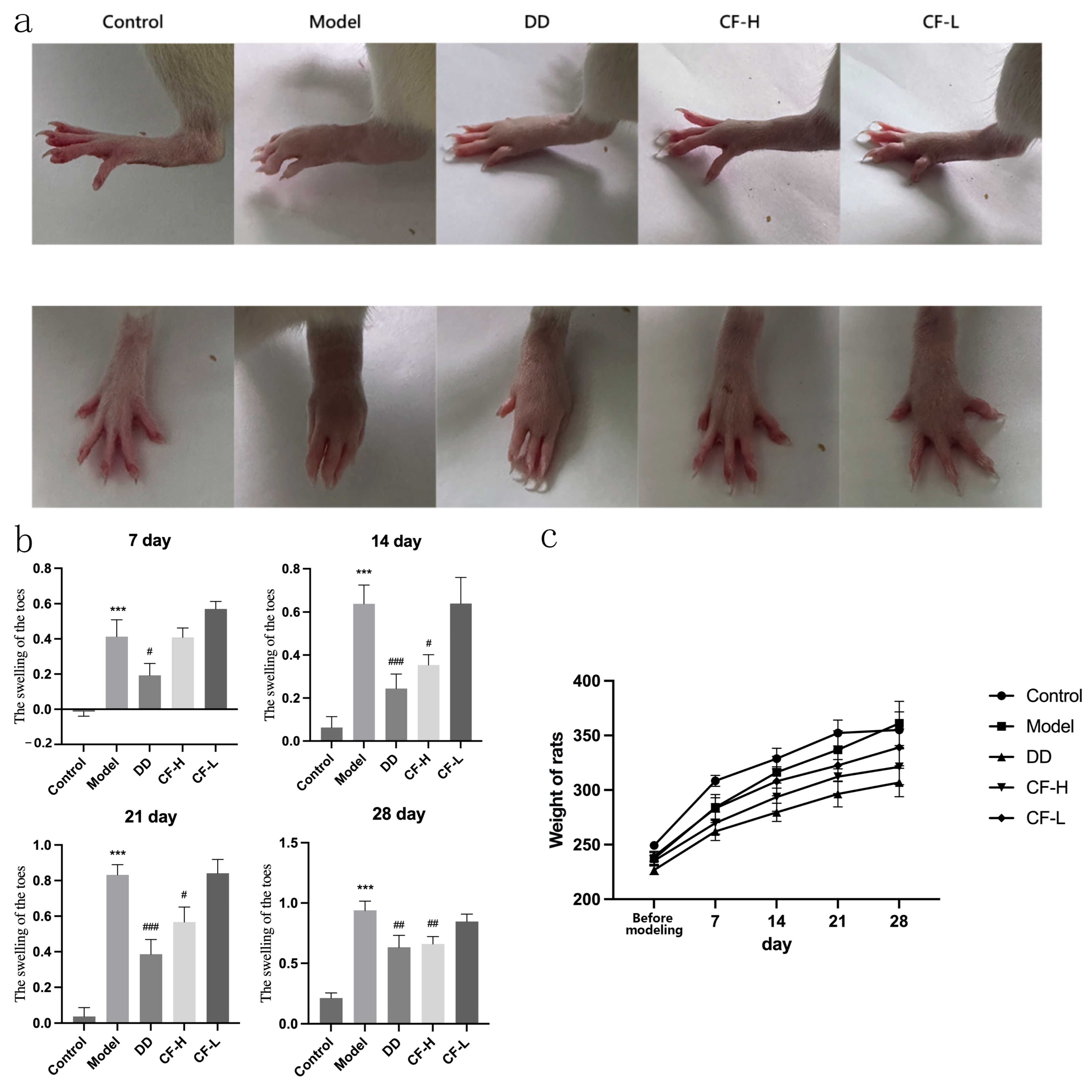
2.10. CF Alleviated the Severity of Arthritis in Rats
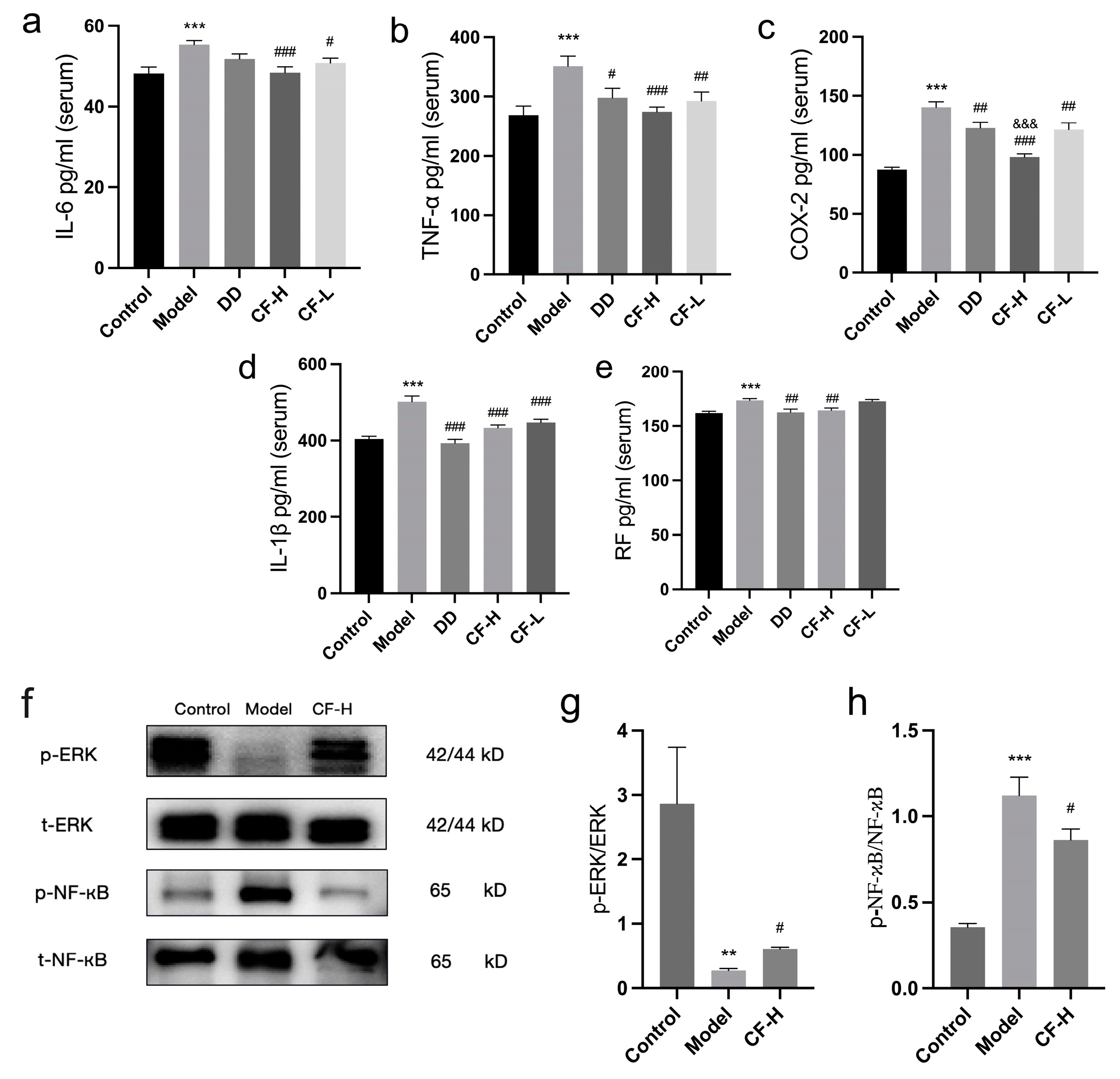
2.11. Effects of CF Extracts on Serum IL-6, COX-2, TNF-α, IL-1β, and RF in RA Rats
2.12. Protein Expression of p-ERK, ERK, p-NF-κB and NF-κB in Rats
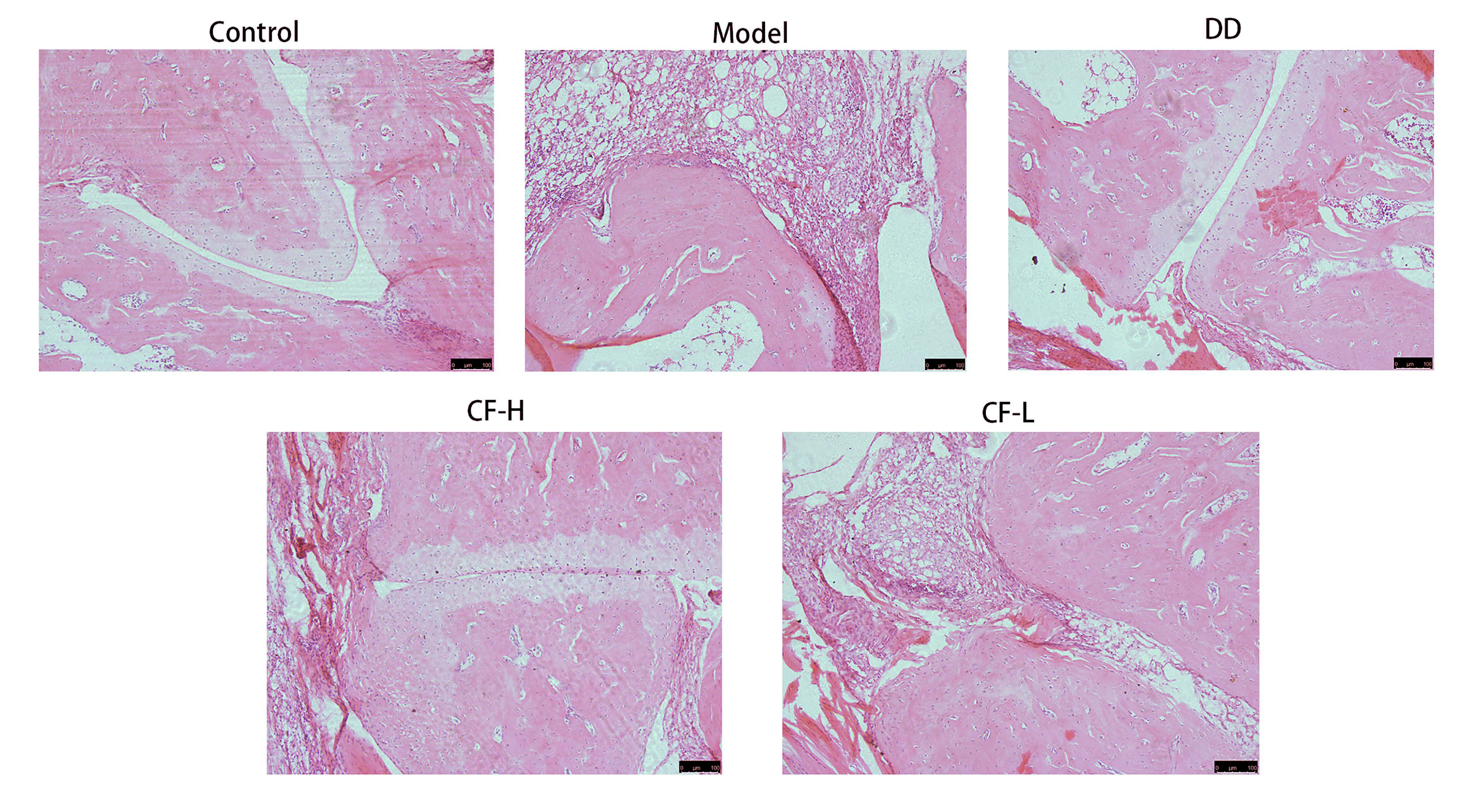
2.13. Histological Analysis of Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.1.1. Sample Preparation
4.1.2. Instruments and Analytical Conditions
4.1.3. Screening of Main Compounds of CF
4.2. Network Pharmacology Analysis
4.2.1. Candidate Therapeutic Targets of CF Screening
4.2.2. Construction of RA-Related Target Database
4.2.3. Intersection between Main Compounds and Disease Targets
4.2.4. Construction of CT Network
4.2.5. CPS Network Construction and Core Target Acquisition
4.2.6. GO Enrichment Analysis
4.2.7. Molecular Docking
4.3. Quality Control of CF Extract
4.3.1. Sample and Standard Solution Preparation
4.3.2. Instruments and Analytical Conditions
4.4. Experimental Validation
4.4.1. Animals
4.4.2. Preparation of the CF Extract
4.4.3. Xylene-Induced Mouse Ear Edema
4.4.4. Acetic Acid-Induced Abdominal Writhing Response
4.4.5. AA Model Preparation
4.4.6. Experimental Grouping and Drug Administration
4.4.7. Detecting the Degree of Toe Swelling in Rats
4.4.8. Determination of Serum Inflammatory Factor
4.4.9. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
4.4.10. Western Blotting
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Jadhav, K.; Vaghasiya, K.; Ray, E.; Shukla, R.; Verma, R.K. New Generation Smart Drug Delivery Systems for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 984–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, A.K.; Sahoo, A.; Dwivedi, K.; Singh, R.; Kumar, V. Potential Therapeutic Application of Biophenols-Plants Secondary Metabolites in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8900–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.; Wilson, A.G.; Barton, A. DNA Methylation as a Marker of Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Delft, M.A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J. An Overview of Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Chen, G.; Huang, G. Synthesis and Biological Activities of Chemical Drugs for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Top Curr. Chem. 2019, 377, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anita, C.; Munira, M.; Mural, Q.; Shaily, L. Topical Nanocarriers for Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, C.; Yang, F.; Zhu, F.; Hua, D. Effect of External Use of Qingluo San on Clinical Efficacy in Patients with Acute Gouty Arthritis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Dong, R.; Yan, Y.; Wu, J.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J.; Shen, C.; Han, J.; Shen, T. Preliminary Study on Formulation Process Optimization and Pharmacody-Namics of She Medicine Clematis Florida Var. Plena Cream. Strait Pharm. J. 2023, 35, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.-H.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Fang, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Jiang, Y.-Y. Uses, Chemical Compositions, Pharmacological Activities and Toxicology of Clematidis Radix et Rhizome—A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.-N.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Zhang, H.-T.; Ma, X.-H.; Shen, J.-H.; Li, P.; Zhong, T.-H.; Zhang, Y.-H. The in Vitro and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Triterpene Saponins from Clematis Florida. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 6180–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.-R.; Li, Y.-N.; He, S.-L.; Chen, Q.-S.; Xu, X.-Y. Cytotoxic Activities of Total Saponins from Plena Clematis on Human Tumor Cell Lines In Vitro. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 24, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network Pharmacology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Network Pharmacology, a Promising Approach to Reveal the Pharmacology Mechanism of Chinese Medicine Formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Liao, J.; Chen, Q.; Lu, X.; Fan, X. Network Pharmacology Approaches for Research of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2023, 21, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, L.C.; Shao, D.; Meng, C.; Perros, F.; Garfield, B.E.; Zhu, J.; Montani, D.; Dorfmuller, P.; Humbert, M.; Adcock, I.M.; et al. Dexamethasone Induces Apoptosis in Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.J.; Infante, J.R.; Janku, F.; Wong, D.J.L.; Sosman, J.A.; Keedy, V.; Patel, M.R.; Shapiro, G.I.; Mier, J.W.; Tolcher, A.W.; et al. First-in-Class ERK1/2 Inhibitor Ulixertinib (BVD-523) in Patients with MAPK Mutant Advanced Solid Tumors: Results of a Phase I Dose-Escalation and Expansion Study. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkey, C.J. COX-1 and COX-2 Inhibitors. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2001, 15, 801–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.M.; Ramos-Romero, S.; Perona, J.S. Oleanolic Acid: Extraction, Characterization and Biological Activity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.-H.; Ma, X.-H.; Zeng, X.-M.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Cai, Y.-M.; Zhang, H.-T.; Lin, X.-Y.; Feng, S.-B.; Zhong, T.-H.; Zhang, Y.-H. A New Indole-Type Alkaloid from the Roots of Clematis Florida Var. Plena. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa-María, C.; López-Enríquez, S.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Geniz, I.; Reyes-Quiroz, M.E.; Moreno, M.; Palomares, F.; Sobrino, F.; Alba, G. Update on Anti-Inflammatory Molecular Mechanisms Induced by Oleic Acid. Nutrients 2023, 15, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Ashraf, G.M.; Sheikh, K.; Khan, A.; Ali, S.; Ansari, M.M.; Adnan, M.; Pasupuleti, V.R.; Hassan, M.I. Potential Therapeutic Implications of Caffeic Acid in Cancer Signaling: Past, Present, and Future. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 845871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwuma, C.I.; Matsabisa, M.G.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Erukainure, O.L.; Chabalala, M.H.; Islam, M.S. Medicinal Plants with Concomitant Anti-Diabetic and Anti-Hypertensive Effects as Potential Sources of Dual Acting Therapies against Diabetes and Hypertension: A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, T.; Whalin, J.G.; Richards, M.P.; Alayash, A.I. Caffeic Acid: An Antioxidant with Novel Antisickling Properties. FEBS Open Bio. 2021, 11, 3293–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikry, E.M.; Gad, A.M.; Eid, A.H.; Arab, H.H. Caffeic Acid and Ellagic Acid Ameliorate Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats via Targeting Inflammatory Signals, Chitinase-3-like Protein-1 and Angiogenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamine, Y.; Lyoussi, B.; Miguel, M.G.; Anjos, O.; Estevinho, L.; Alaiz, M.; Girón-Calle, J.; Martín, J.; Vioque, J. Physicochemical Characteristics and Antiproliferative and Antioxidant Activities of Moroccan Zantaz Honey Rich in Methyl Syringate. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liang, Y. Chemoprotective Effect of Syringic Acid on Cyclophosphamide Induced Ovarian Damage via Inflammatory Pathway. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xiao, H.; Luo, M.; Meng, J.; Zhong, L.; Wu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, F.; Xie, J. Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Effects of Pimpinella Candolleana on Ulcerative Colitis in Rats: A Comprehensive Study of Quality, Chemical Composition, and Molecular Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1328977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Wen, Z.-H.; Su, S.-X.; Chen, Y.-P.; Liu, W.-C.; Guo, S.-Q.; Li, X.-F.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Xu, N.-B.; et al. Elucidating the Synergistic Effect of Multiple Chinese Herbal Prescriptions in the Treatment of Post-Stroke Neurological Damage. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 784242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jia, J. Natural COX-2 Inhibitors as Promising Anti-Inflammatory Agents: An Update. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 3622–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamer, P. Osteoarthritis Pain and Its Treatment. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2000, 12, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Bansal, Y.; Kumar, R.; Bansal, G. A Panoramic Review of IL-6: Structure, Pathophysiological Roles and Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanamee, É.S.; Faustman, D.L. The Benefits of Clustering in TNF Receptor Superfamily Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1225704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marahleh, A.; Kitaura, H.; Ohori, F.; Kishikawa, A.; Ogawa, S.; Shen, W.-R.; Qi, J.; Noguchi, T.; Nara, Y.; Mizoguchi, I. TNF-α Directly Enhances Osteocyte RANKL Expression and Promotes Osteoclast Formation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, R.-S.; Shi, Z.; Li, J.-Q. Nuclear Factor-κB in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Qian, P.; Guo, Y.; Gu, L.; Jurat, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, D. Myrtenal and β-Caryophyllene Oxide Screened from Liquidambaris Fructus Suppress NLRP3 Inflammasome Components in Rheumatoid Arthritis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, F.; Cai, M.; Ding, D. The Protective Effect of Gentisic Acid on Rheumatoid Arthritis via the RAF/ERK Signaling Pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Ni, J.; Fang, Y.S.; Li, T.; Tan, H.F.; Zhang, Q.S. Effects of Curcumin on Apoptosis and Proliferation of Inflammatory Chondrocytes Induced by Lipopolysaccharide. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2018, 22, 5157–5162. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Gu, J.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Tu, J.; Zhang, D.; Sun, W.; Kong, X. Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Suppresses Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis via P38 MAPK Signaling in Rat Visceral Preadipocytes. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 948–956. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, L.; Wei, T.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, Z. Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Activates ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt Signalling Pathways and Promotes the Proliferation of Human Amnion-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Prolif. 2017, 50, e12383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.-J.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.-S.; Tian, J.; Yu, D.-J.; Li, H.-Z.; Zhang, F.-J. OPN Inhibits Autophagy through CD44, Integrin and the MAPK Pathway in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 919366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; He, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Su, X.; Yan, S.; Su, W.; et al. A Novel Drug Combination of Mangiferin and Cinnamic Acid Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting TLR4/NFκB/NLRP3 Activation-Induced Pyroptosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 912933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Shi, L.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Zhu, L.; Xia, T.-S.; Ding, Q. A Hederagenin Saponin Isolated from Clematis Ganpiniana Induces Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells via the Mitochondrial Pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Cheng, T.-F.; Jia, Y.-R.; Li, P.; Li, F. Anti-Rheumatoid Arthritis Effects of Traditional Chinese Herb Couple in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 205, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Jie, H.; Han, J.; He, Z.; Hu, J. Experimental Study on the Acute Toxicity of the Decoction of the Clematis Florida Var. Plena, D.Don. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharmacy 2017, 26, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, C.; Hu, J. Study on the Toxicity of Ethanolic Extracts from Clematis Florida Thunb. Var. Plena DE. Don Ointment by Skin Administration. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2020, 10, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, R.; Calpena, A.C.; Mallandrich, M.; Clares, B. Enhancing Topical Analgesic Administration: Review and Prospect for Transdermal and Transbuccal Drug Delivery Systems. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2867–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission, N.P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; ISBN 978-7-5214-1574-2. [Google Scholar]

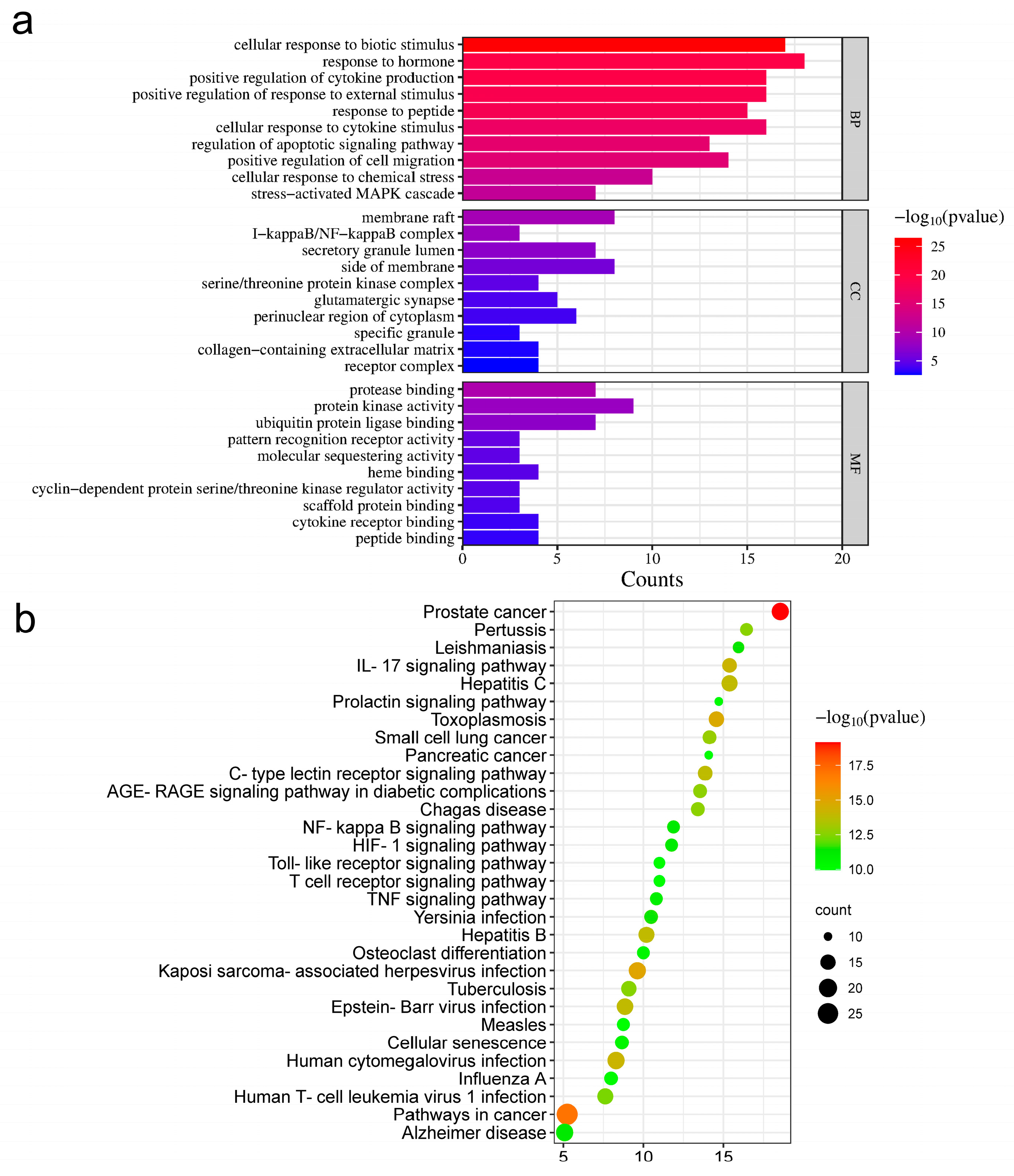

| Pathway | Target | FDR Values |
|---|---|---|
| IL-17 signaling pathway | LCN2, GSK3B, IL6, NF-κB1, TNF, PTGS2, CASP3, HSP90AA1, MAKP1, IKBKB, MAPK3, MAPK14, NF-κBIA, RELA | 7.20 × 10−15 |
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | NF-κB1, IKBKB, NF-κBIA, RELA, PTGS2, PPP3CA, MAPK14, MAPK3, MAPK1, TNF, IL6, IL10, NF-κB2, CLEC4E | 1.61 × 10−14 |
| AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | ICAM1, NOS3, F3, TNF, IL6, NF-κB1, SERPINE1, MAPK3, CASP3, RELA, MAPK1, CCND1, MAPK14 | 2.09 × 10−13 |
| Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection | CDK2, RB1, CCND1, CDKN1A, MAPK3, PPP3CA, TP53, NFKBIA, NF-κB1, TNF, MAPK1, RELA, IL6, IKBKB, NF-κB2, ICAM1 | 4.24 × 10−13 |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | PLAU, ICAM1, PTGS2, RELA, TNF, NF-κB1, NF-κB2, IKBKB, TLR4, NF-κBIA, LY96, BTK | 5.96 × 10−12 |
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | NOS2, NOS3, NF-κB1, INS, CDKN1A, SERPINE1, HMOX1, TLR4, MAPK3, MAPK1, RELA, IL6 | 6.31 × 10−12 |
| TNF signaling pathway | TNF, IL6, RELA, NF-κB1, CASP3, IKBKB, PTGS2, MAPK1, MAPK3, ICAM1, MAPK14, NF-κBIA | 1.51 × 10−11 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | TNF, NF-κB1, LY96, TLR4, RELA, MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK14, IL6, IKBKB, NF-κBIA | 9.63 × 10−11 |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | IL10, IKBKB, TNF, NF-κB1, NF-κBIA, GSK3B, MAPK14, RELA, MAPK1, MAPK3, PPP3CA | 9.63 × 10−11 |
| Target | Full Name of Target | Target Alias | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTGS2 | 2Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 | COX-2 | 15 |
| MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | ERK2 | 11 |
| NFκB1 | Nuclear factor kappa-B | P50 | 11 |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | TNF-alpha | 11 |
| RELA | V-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A | NFκB P65 | 11 |
| MAPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | ERK1 | 9 |
| PTGS1 | Prostaglandin–endoperoxide synthase 1 | COX-1 | 9 |
| IL6 | Interleukin 6 | HGF | 9 |
| NFκBIA | NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha antibody | IKBA | 8 |
| IKBKB | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta | IKK2 | 8 |
| MAPK14 | Recombinant human mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 | CSPS | 8 |
| ADRB2 | beta-2 adrenergic receptor | ADRB2R | 8 |
| Target | Degree | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| TNF | 251 | 1/552 |
| NFκB1 | 169 | 13/552 |
| PTGS2 | 127 | 40/552 |
| RELA | 105 | 59/552 |
| MAPK1 | 73 | 108/552 |
| Target | PDB ID | Compound | Affinity/(kcal·mol−1) | Grid Center | Grid Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF-κB1 | 1U36 | Dexamethasone | −9.17 | (50.11, 22.21, 3.56) | (90, 78, 66) |
| 1U36 | Oleanolic acid | −6.6 | (50.11, 22.21, 3.56) | (90, 78, 66) | |
| 1U36 | Syringic acid | −3.87 | (50.11, 22.21, 3.56) | (90, 78, 66) | |
| MAPK1 | 4S31 | Ulixertinib | −7.17 | (−3.24, 7.31, 46.47) | (98, 76, 106) |
| 4S31 | Oleanolic acid | −8.14 | (−3.24, 7.31, 46.47) | (98, 76, 106) | |
| 4S31 | Ferulic acid | −4.57 | (−3.24, 7.31, 46.47) | (98, 76, 106) | |
| 4S31 | Oleic acid | −3.15 | (−3.24, 7.31, 46.47) | (98, 76, 106) | |
| PTGTS2 | 5F19 | Rofecoxib | −7.08 | (22.29, 44.99, 39.17) | (62, 62, 84) |
| 5F19 | Oleanolic Acid | −10.31 | (22.29, 44.99, 39.17) | (62, 62, 84) | |
| 5F19 | Caffeic acid | −5.83 | (22.29, 44.99, 39.17) | (62, 62, 84) | |
| 5F19 | Syringic acid | −5.6 | (22.29, 44.99, 39.17) | (62, 62, 84) | |
| 5F19 | Oleic acid | −5.27 | (22.29, 44.99, 39.17) | (62, 62, 84) | |
| 5F19 | Ferulic acid | −5.2 | (22.29, 44.99, 39.17) | (62, 62, 84) | |
| TNF-α | 2AZ5 | Caffeic acid | −5.37 | (−13.12, 69.19, 26.69) | (54, 52, 62) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, T.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, G.; Han, J. Exploring the Mechanism of Topical Application of Clematis Florida in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis through Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070914
Lei T, Jiang C, Zhao L, Zhang J, Xiao Q, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhou C, Wang G, Han J. Exploring the Mechanism of Topical Application of Clematis Florida in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis through Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070914
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Ting, Chang Jiang, Li Zhao, Jizhou Zhang, Qing Xiao, Yanhong Chen, Jie Zhang, Chunquan Zhou, Gong Wang, and Jing Han. 2024. "Exploring the Mechanism of Topical Application of Clematis Florida in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis through Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070914
APA StyleLei, T., Jiang, C., Zhao, L., Zhang, J., Xiao, Q., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., Zhou, C., Wang, G., & Han, J. (2024). Exploring the Mechanism of Topical Application of Clematis Florida in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis through Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070914






