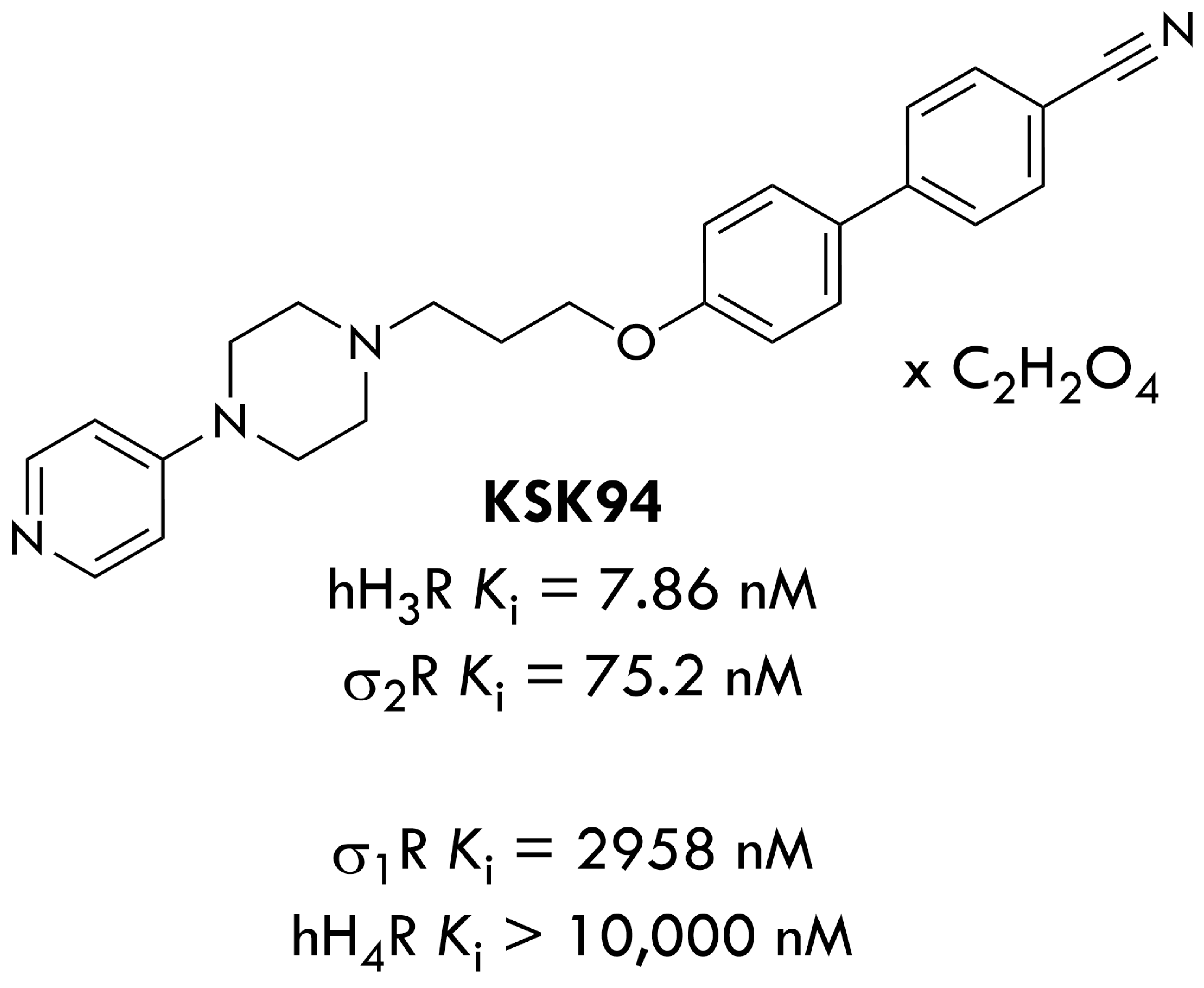
The Effect of KSK-94, a Dual Histamine H3 and Sigma-2 Receptor Ligand, on Adipose Tissue in a Rat Model of Developing Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
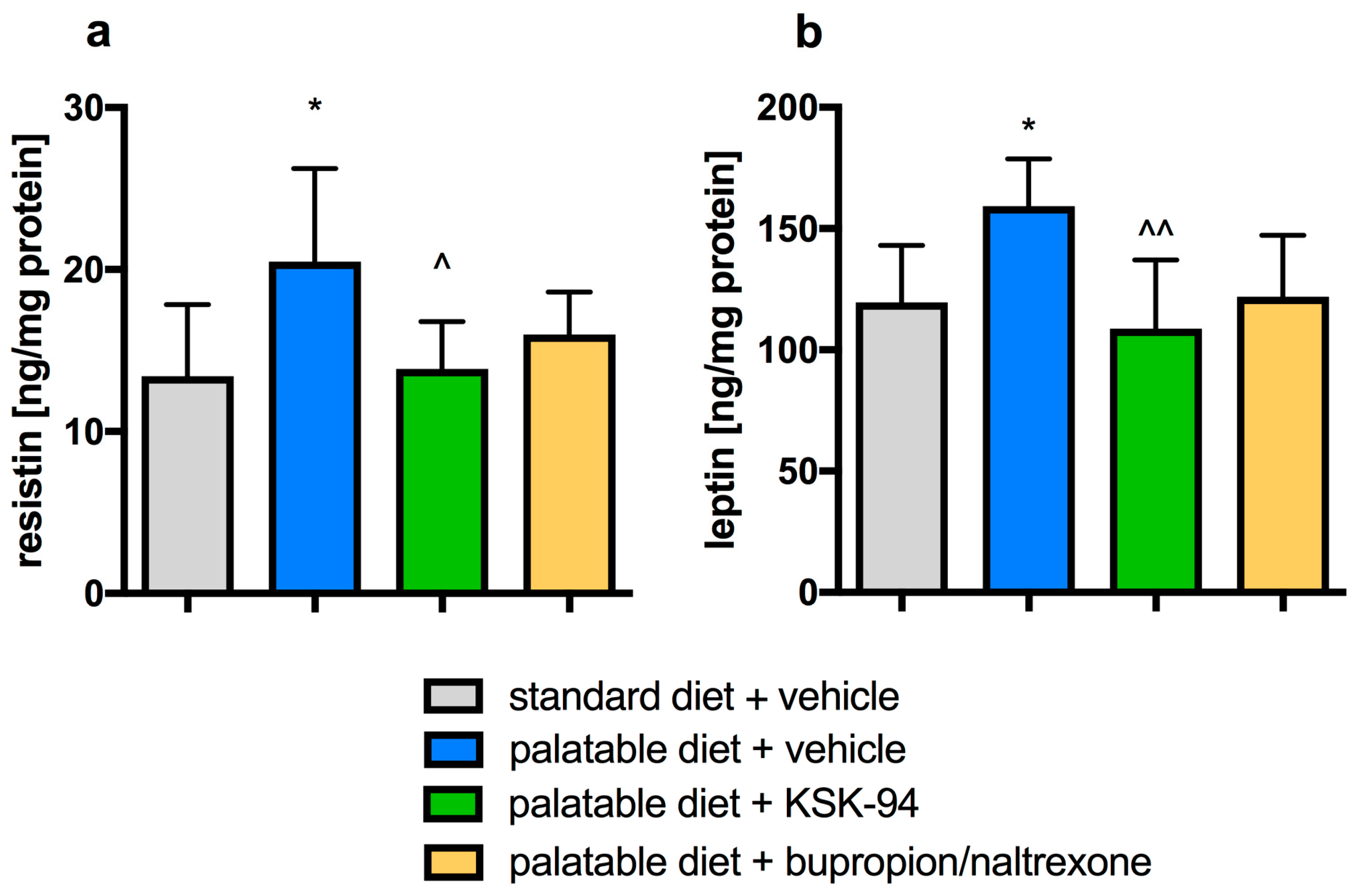
2.1. Assessment of the Development of Obesity and the Amount of Selected Hormones in Adipose Tissue
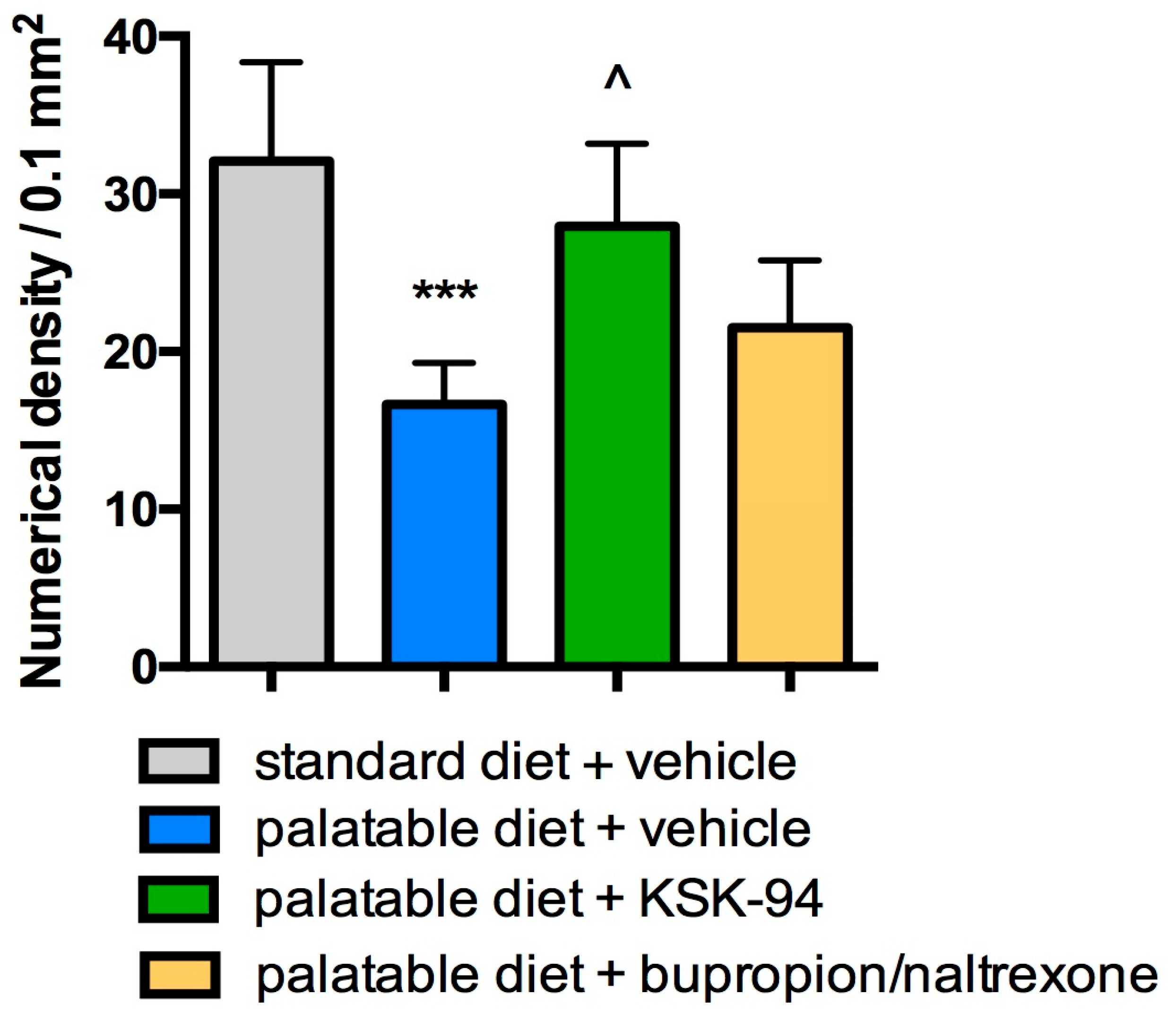
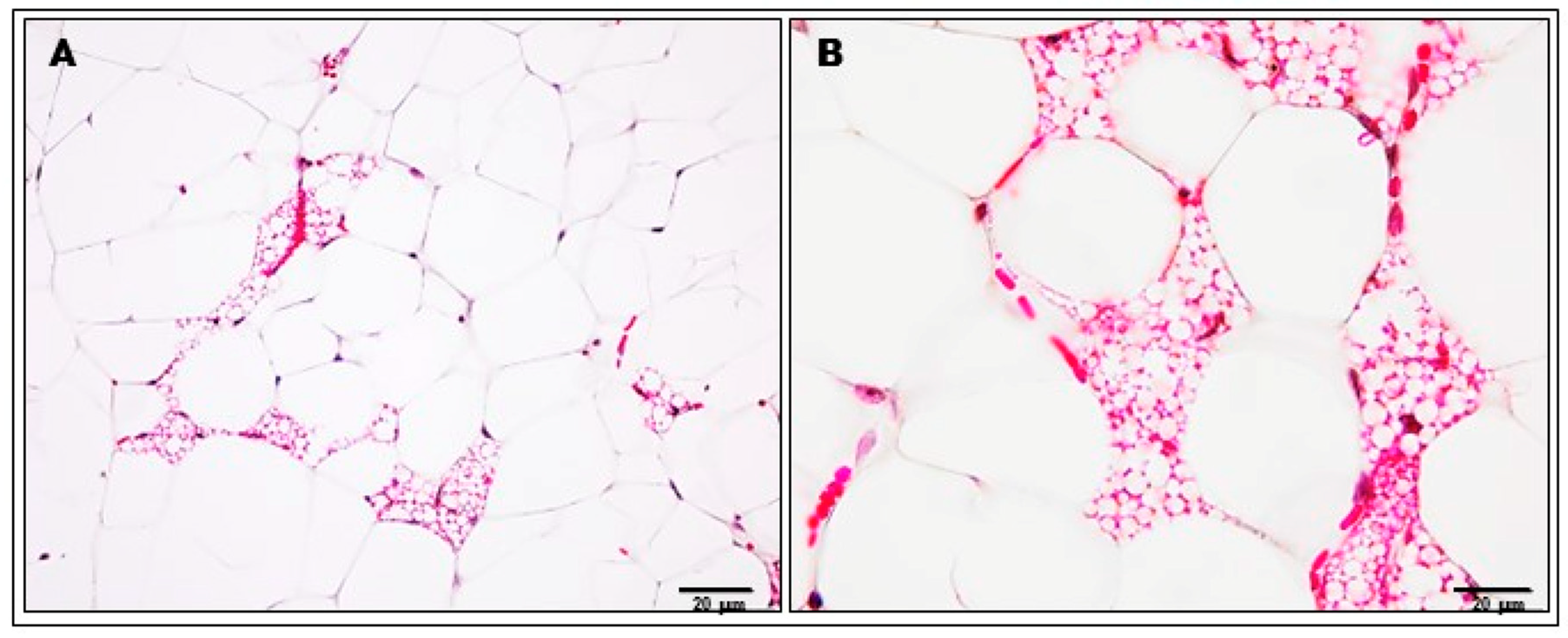
2.2. Analysis of Adipocytes, Inflammatory Cells and Capillary Congestion
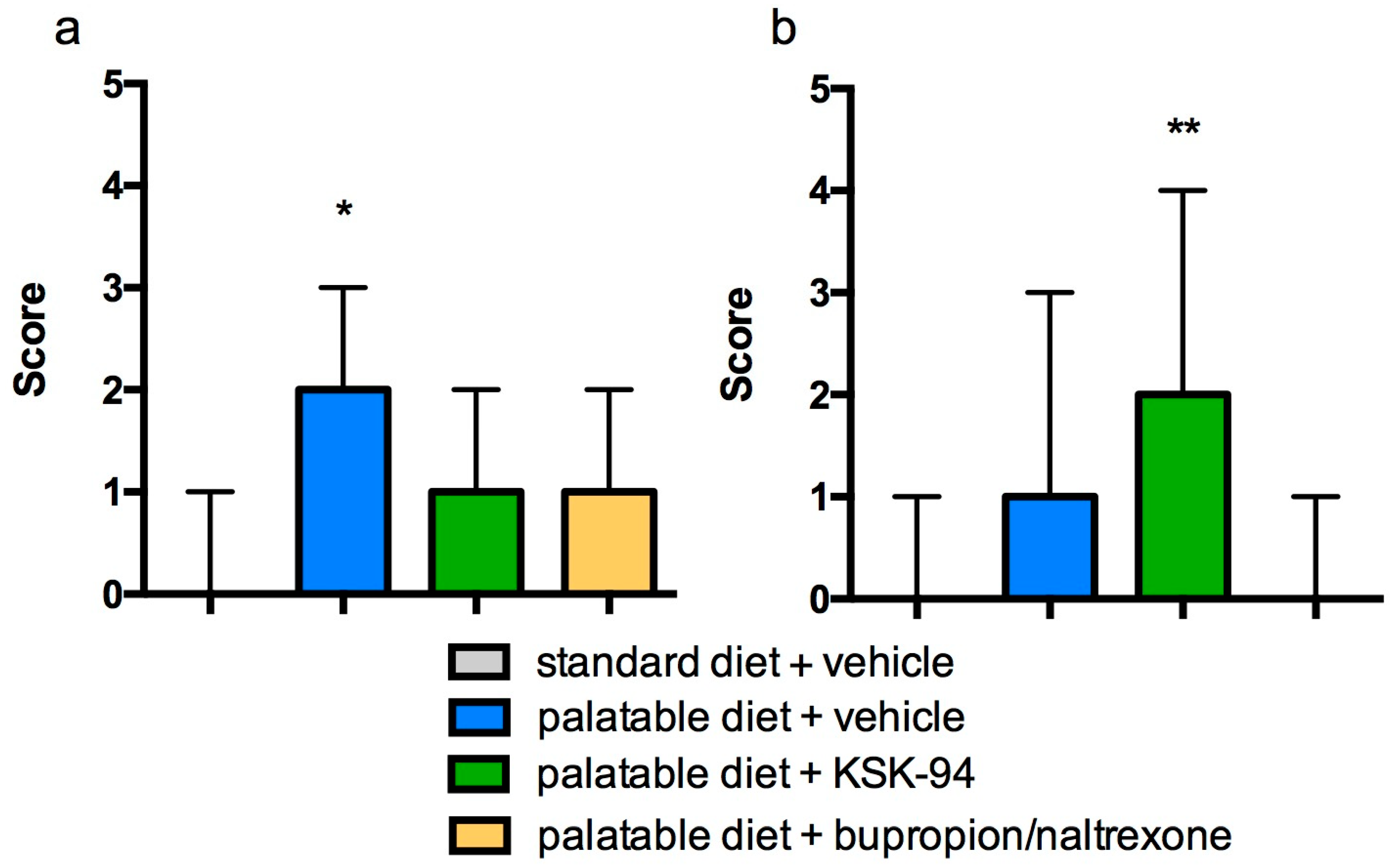
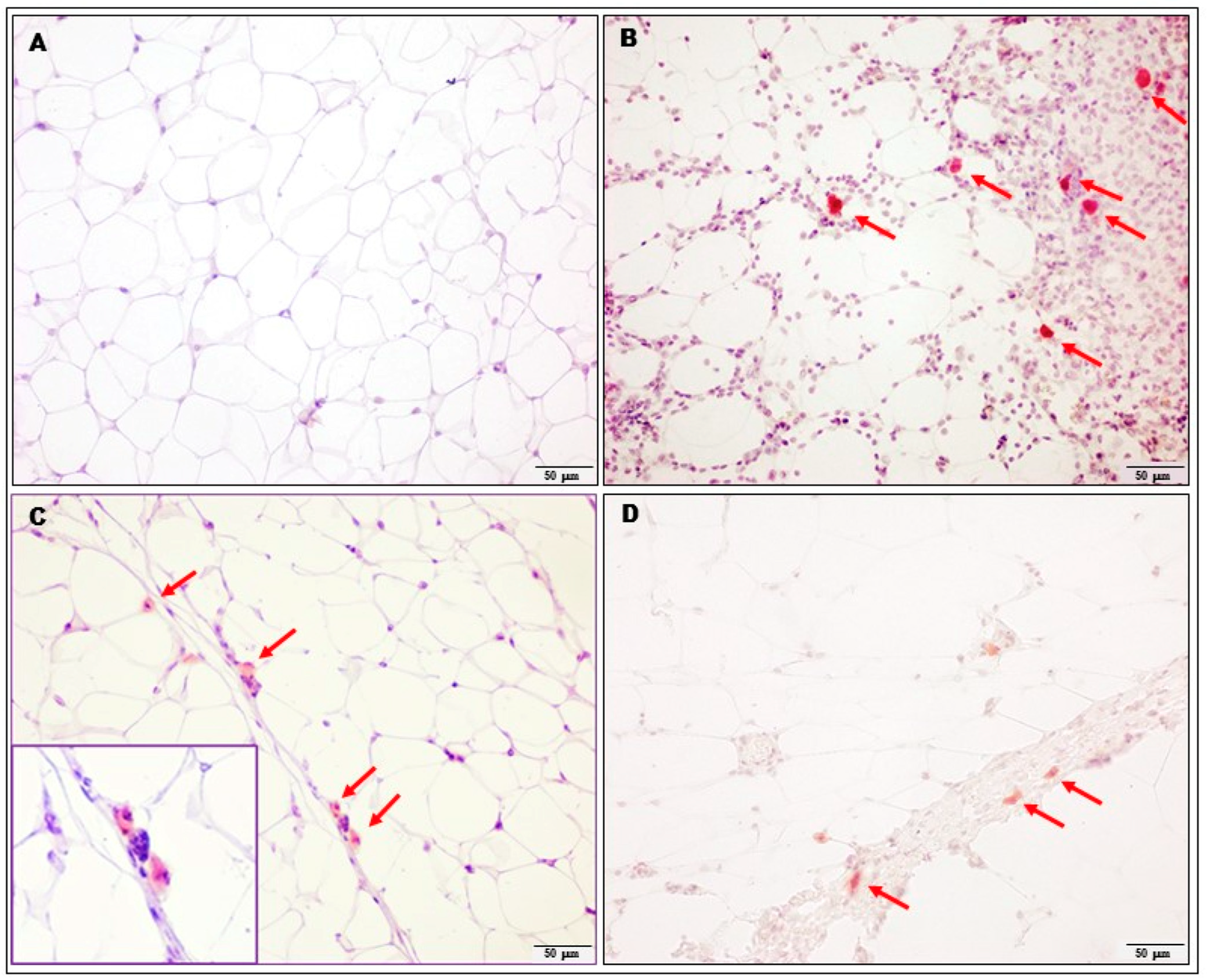
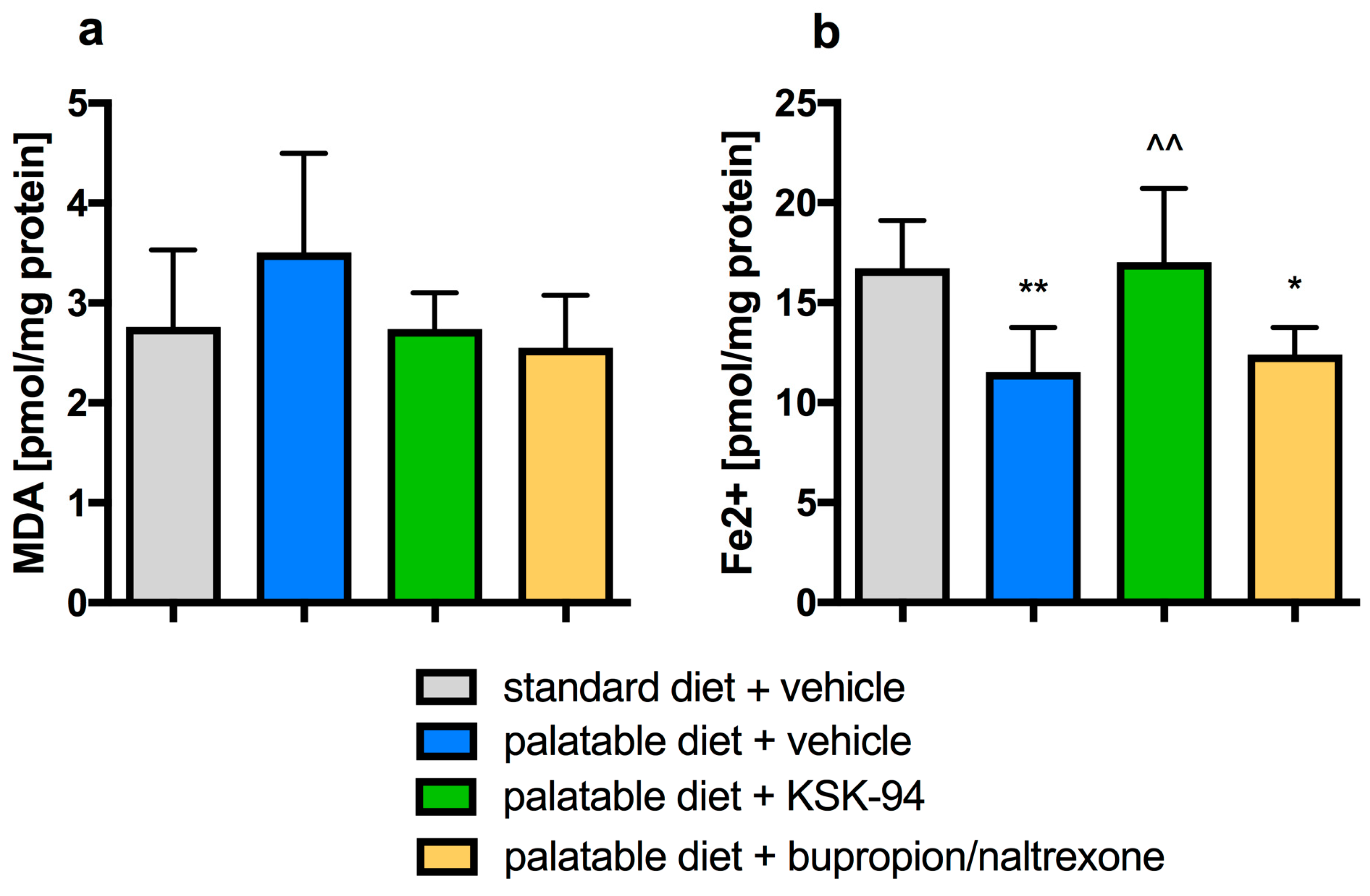
2.3. Evaluation of Inflammation in Adipose Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Chemicals
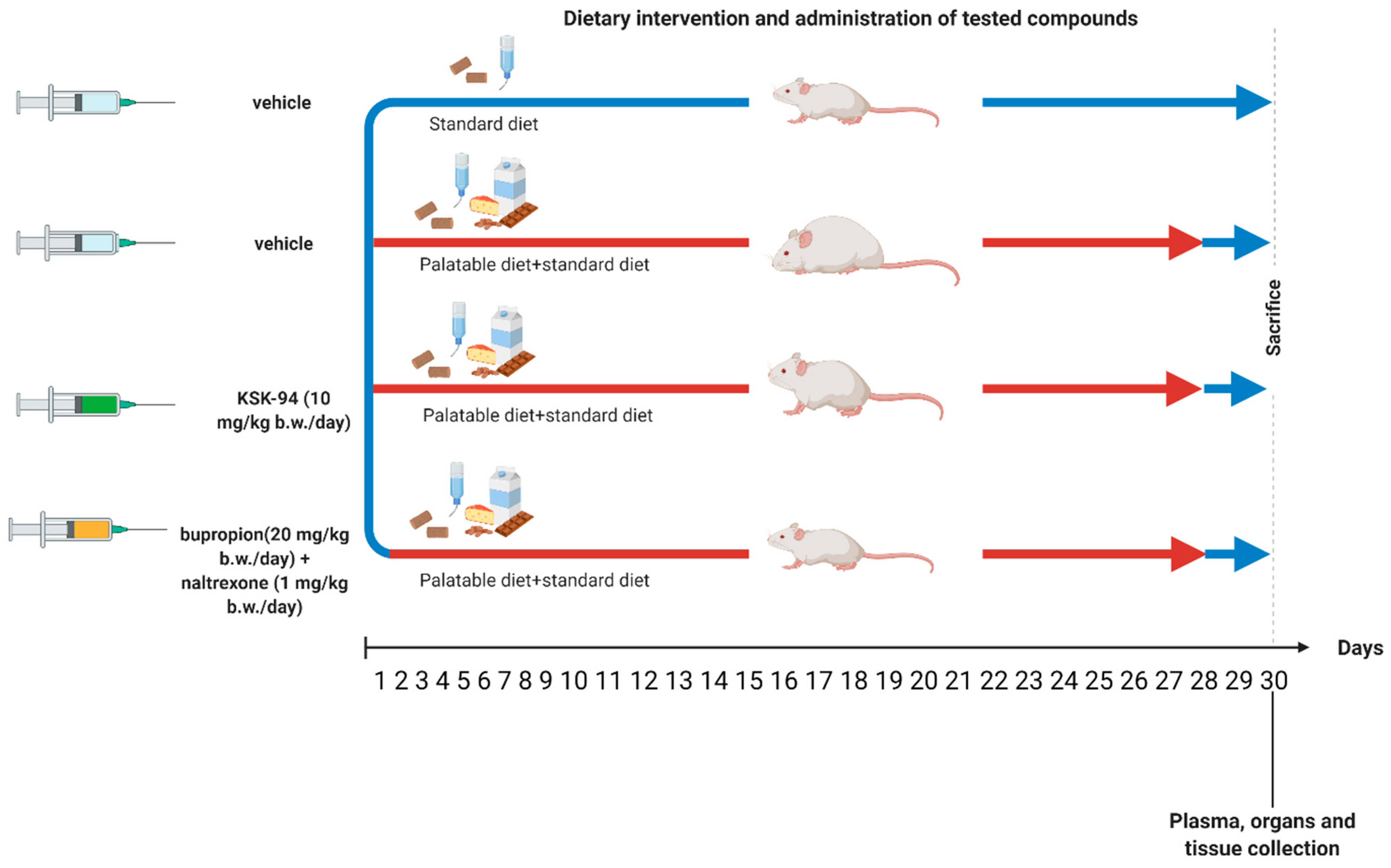
4.2. The Experimental Protocol
4.3. Histological Examination
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Preparation of Tissue Homogenates
4.6. Biochemical Assays
4.7. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation (Malondialdehyde Level)
4.8. Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catenacci, V.A.; Hill, J.O.; Wyatt, H.R. The obesity epidemic. Clin. Chest Med. 2009, 30, 415–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrup, A.; Toubro, S.; Raben, A.; Skov, A.R. The role of low-fat diet and fat substitutes in body weight management: What have we learned from clinical studies? J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1997, 97, S82–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparti, A.; Windhauser, M.M.; Champagne, C.M.; Bray, G.A. Effect of an acute reduction in carbohydrate intake on subsequent food intake in healthy men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, A.; Lavallde, N.; Almeras, N.; Allard, L.; Despres, J.-P.; Bouchard, C. Nutritional determinants of the increase in energy intake associated with a high-fat diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 1134–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.M.; Blundell, J.E. Effect of fat- and sucrose-containing foods on the size of eating episodes and energy intake in lean dietary restrained and unrestrained females: Potential for causing overconsumption. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 50, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishizuka, T.; Yamatodani, A. Integrative role of the histaminergic system in feeding and taste perception. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetti, F.; Furini, C.R.G.; Myskiw, J.D.C.; Provensi, G.; Passani, M.B.; Baldi, E.; Bucherelli, C.; Munari, L.; Izquierdo, I.; Blandina, P. Histamine in the basolateral amygdala promotes inhibitory avoidance learning independently of hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provensi, G.; Blandina, P.; Passani, M.B. The histaminergic system as a target for the prevention of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.R.; Kruse, A.C. The Molecular Function of sigma Receptors: Past, Present, and Future. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riad, A.; Zeng, C.; Weng, C.C.; Winters, H.; Xu, K.; Makvandi, M.; Metz, T.; Carlin, S.; Mach, R.H. Sigma-2 Receptor/TMEM97 and PGRMC-1 Increase the Rate of Internalization of LDL by LDL Receptor through the Formation of a Ternary Complex. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, B.; Kent, K.C.; Plutzky, J.; Guo, L.W. BRD2 regulation of sigma-2 receptor upon cholesterol deprivation. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 4, e201900540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Félix-Soriano, E.; Wright, K.R.; Shen, H.; Baer, L.A.; Stanford, K.I.; Guo, L.W. Differential Responses to Sigma-1 or Sigma-2 Receptor Ablation in Adiposity, Fat Oxidation, and Sexual Dimorphism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S.; Mitchell, G.; Barbatelli, G.; Murano, I.; Ceresi, E.; Faloia, E.; Wang, S.; Fortier, M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spalding, K.L.; Arner, E.; Westermark, P.O.; Bernard, S.; Buchholz, B.A.; Bergmann, O.; Blomqvist, L.; Hoffstedt, J.; Näslund, E.; Britton, T.; et al. Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature 2008, 453, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, G.H.; Bizzarri, A.; Venteclef, N.; Essers, Y.; Cleutjens, J.P.; Konings, E.; Jocken, J.W.; Cajlakovic, M.; Ribitsch, V.; Clément, K.; et al. Increased adipose tissue oxygen tension in obese compared with lean men is accompanied by insulin resistance, impaired adipose tissue capillarization, and inflammation. Circulation 2011, 124, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P. Hypoxia and adipose tissue function and dysfunction in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strissel, K.J.; DeFuria, J.; Shaul, M.E.; Bennett, G.; Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. T-cell recruitment and Th1 polarization in adipose tissue during diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice. Obesity 2010, 18, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Youm, Y.H.; Vandanmagsar, B.; Ravussin, A.; Gimble, J.M.; Greenway, F.; Stephens, J.M.; Mynatt, R.L.; Dixit, V.D. Obesity increases the production of proinflammatory mediators from adipose tissue T cells and compromises TCR repertoire diversity: Implications for systemic inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, A. The pathogenesis of obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 221–245. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mansoori, L.; Al-Jaber, H.; Prince, M.S.; Elrayess, M.A. Role of Inflammatory Cytokines, Growth Factors and Adipokines in Adipogenesis and Insulin Resistance. Inflammation 2022, 45, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáinz, N.; Barrenetxe, J.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Martínez, J.A. Leptin resistance and diet-induced obesity: Central and peripheral actions of leptin. Metabolism 2015, 64, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, L.K.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Henry, R.R.; Wittgrove, A.C.; Phillips, S.A. Adipose tissue depot and cell size dependency of adiponectin synthesis and secretion in human obesity. Adipocyte 2013, 2, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, J.H.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, leptin, and fatty acids in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis through adipose tissue crosstalk. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar, S.; Nogueiras, R.; Tung, L.Y.; Castañeda, T.R.; Vázquez, M.J.; Morris, A.; Williams, L.M.; Dickson, S.L.; Diéguez, C. Central administration of resistin promotes short-term satiety in rats. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 153, R1–R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, N.; Sallam, H.S.; Rizzo, M.; Nikolic, D.; Obradovic, M.; Bjelogrlic, P.; Isenovic, E.R. Resistin: An inflammatory cytokine. Role in cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 4961–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuryłowicz, A.; Puzianowska-Kuźnicka, M. Induction of Adipose Tissue Browning as a Strategy to Combat Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Dai, H.; Duan, Y.; An, Y.; Shi, L.; Lv, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, Q.; et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue: A novel therapeutic strategy for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mika, K.; Szafarz, M.; Bednarski, M.; Kuder, K.; Szczepańska, K.; Pociecha, K.; Pomierny, B.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Sapa, J.; Kotańska, M.; et al. Metabolic benefits of novel histamine H3 receptor ligands in the model of excessive eating: The im-portance of intrinsic activity and pharmacokinetic properties. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, K.; Szafarz, M.; Bednarski, M.; Latacz, G.; Sudoł, S.; Handzlik, J.; Pociecha, K.; Knutelska, J.; Nicosia, N.; Szczepańska, K.; et al. Histamine H3 receptor ligands-KSK-59 and KSK 73-reduce body weight gain in a rat model of excessive eating. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, K.; Szafarz, M.; Zadrożna, M.; Nowak, B.; Bednarski, M.; Szczepańska, K.; Pociecha, K.; Kubacka, M.; Nicosia, N.; Juda, I.; et al. KSK-74: Dual Histamine H3 and Sigma-2 Receptor Ligand with Anti-Obesity Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepańska, K.; Pockes, S.; Podlewska, S.; Höring, C.; Mika, K.; Latacz, G.; Bednarski, M.; Siwek, A.; Karcz, T.; Nagl, M.; et al. Structural modifications in the distal, regulatory region of histamine H3 receptor antagonists leading to the identification of a potent anti-obesity agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onakpoya, I.J.; Lee, J.J.; Mahtani, K.R.; Aronson, J.K.; Heneghan, C.J. Naltrexone–bupropion (Mysimba) in management of obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of unpublished clinical study reports. Br. J.Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 646–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-J.; Tomasi, D.; Volkow, N.D.; Wang, R.; Telang, F.; Caparelli, E.C.; Dunayevich, E. Effect of combined naltrexone and bupropion therapy on the brain’s reactivity to food cues. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Gavrilova, O.; Pack, S.; Jou, W.; Mullen, S.; Sumner, A.E.; Cushman, S.W.; Periwal, V. Hypertrophy and/or hyperplasia: Dynamics of adipose tissue growth. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, G.H.; Blaak, E.E. Adipose tissue dysfunction and impaired metabolic health in human obesity: A matter of oxygen. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerre-Millo, M. Adipose tissue hormones. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2002, 25, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Benencia, F. Inflammatory processes in obesity: Focus on endothelial dysfunction and the role of adipokines as inflammatory mediators. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 38, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, S.; Kant, R. An update on metabolic syndrome: Metabolic risk markers and adipokines in the development of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Apovian, C. Macrophage functions in lean and obese adipose tissue. Metabolism 2017, 72, 120–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensena, E.A.; Kniggea, U.; Warberga, J.; Kjæra, A. Histamine and the Regulation of Body Weight. Neuroendocrinology 2007, 86, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, N.; Han, S.P.; Fei, L.; Pan, X.Q.; Guo, M.; Chen, R.H.; Guo, X.R. Resistin-binding peptide antagonizes role of resistin on white adipose tissue. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, G. Insulin resistance and obesity: Resistin, a hormone secreted by adipose tissue. Nutr. Rev. 2004, 62, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asterholm, I.W.; Rutkowski, J.M.; Fujikawa, T.; Cho, Y.R.; Fukuda, M.; Tao, C.; Wang, Z.V.; Gupta, R.K.; Elmquist, J.K.; Scherer, P.E. Elevated resistin levels induce central leptin resistance and increased atherosclerotic progression in mice. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, C.M.; Bailey, S.T.; Bhat, S.; Brown, E.J.; Banerjee, R.R.; Wright, C.M.; Patel, H.R.; Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001, 409, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bostrom, P.; Sparks, L.M.; Ye, L.; Choi, J.H.; Giang, A.H.; Khandekar, M.; Virtanen, K.A.; Nuutila, P.; Schaart, G.; et al. Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human. Cell 2012, 150, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajimura, S.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Seale, P. Brown and Beige Fat: Physiological Roles beyond Heat Generation. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, K.; Ohyama, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Ogura, M.; Sato, A.; Hong, H.; Hosono, T.; Sharp, L.Z.; Scheel, D.W.; et al. Phosphoproteomics Identifies CK2 as a Negative Regulator of Beige Adipocyte Thermogenesis and Energy Expenditure. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.E.; Li, C.; Bian, H.; Smith, B.D.; Layne, M.D.; Farmer, S.R. Myocardin-related transcription factor A regulates conversion of progenitors to beige adipocytes. Cell 2015, 160, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, I.; Aprahamian, T.; Kikuchi, R.; Shimizu, A.; Papanicolaou, K.N.; MacLauchlan, S.; Maruyama, S.; Walsh, K. Vascular rarefaction mediates whitening of brown fat in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Kang, Q.; Yoneshiro, T.; Camporez, J.P.; Maki, H.; Homma, M.; Shinoda, K.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X.; Maretich, P.; et al. UCP1-independent signaling involving SERCA2b-mediated calcium cycling regulates beige fat thermogenesis and systemic glucose homeostasis. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchani, E.T.; Kazak, L.; Spiegelman, B.M. New advances in adaptive thermogenesis: UCP1 and beyond. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazak, L.; Chouchani, E.T.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Erickson, B.K.; Shinoda, K.; Cohen, P.; Vetrivelan, R.; Lu, G.Z.; Laznik-Bogoslavski, D.; Hasenfuss, S.C.; et al. A creatine-driven substrate cycle enhances energy expenditure and thermogenesis in beige fat. Cell 2015, 163, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotańska, M.; Śniecikowska, J.; Jastrzębska-Więsek, M.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Pytka, K. Metabolic and cardiovascular benefits and risks of EMD386088—A 5-HT6 receptor partial agonist and dopamine transporterinhibitor. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotańska, M.; Lustyk, K.; Bucki, A.; Marcinkowska, M.; Śniecikowska, J.; Kołaczkowski, M. Idalopirdine, a selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, reduces food intake and body weight in a model of excessive eating. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohshi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay of lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilska, A.; Dudek, M.; Iciek, M.; Kwiecień, I.; Sokołowska-Jezewicz, M.; Filipek, B.; Włodek, L. Biological actions of lipoic acid associated with sulfane sulfur metabolism. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, N.; Kwiecień, I.; Mazurek, J.; Mika, K.; Bednarski, M.; Miceli, N.; Ragusa, S.; Ekiert, H.; Maes, M.; Kotańska, M. Hydroalcoholic leaves extract of Isatis tinctoria L. via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects reduces stress-induced behavioral and cellular disorders in mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 3567879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotańska, M.; Wojtaszek, K.; Kubacka, M.; Bednarski, M.; Nicosia, N.; Wojnicki, M. The Influence of Caramel Carbon Quantum Dots and Caramel on Platelet Aggregation, Protein Glycation and Lipid Peroxidation. Antioxidants 2023, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group | Initial Body Weight (g) | Final Body Weight (g) | Visceral Fat Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| standard diet + vehicle | 187.8 ± 4.9 | 218.8 ± 7.5 | 4.2 ± 1.1 |
| palatable diet + vehicle | 190.8 ± 2.0 | 298.2 ± 19.7 *** | 8.9 ± 2.6 *** |
| palatable diet + KSK-94 | 193.4 ± 1.9 | 253.9 ± 10.6 ## | 2.6 ± 0.4 ### |
| palatable diet + bupropion/naltrexone | 192.9 ± 5.7 | 265.7 ± 17.1 ## | 4.2 ± 0.4 ### |
| Grade | Inflammatory Cells Infiltration | Capillary Congestion | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Minimal | Moderate | Severe | |
| standard diet + vehicle | 4 | 2 | - | - | 5 | 1 | - |
| palatable diet + vehicle | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| palatable diet+KSK-94 | 1 | 4 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 5 |
| palatable diet + bupropion/naltrexone | 1 | 3 | 2 | - | 4 | 2 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotańska, M.; Zadrożna, M.; Kubacka, M.; Mika, K.; Szczepańska, K.; Nowak, B.; Alesci, A.; Miller, A.; Lauriano, E.R.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. The Effect of KSK-94, a Dual Histamine H3 and Sigma-2 Receptor Ligand, on Adipose Tissue in a Rat Model of Developing Obesity. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070858
Kotańska M, Zadrożna M, Kubacka M, Mika K, Szczepańska K, Nowak B, Alesci A, Miller A, Lauriano ER, Kieć-Kononowicz K. The Effect of KSK-94, a Dual Histamine H3 and Sigma-2 Receptor Ligand, on Adipose Tissue in a Rat Model of Developing Obesity. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070858
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotańska, Magdalena, Monika Zadrożna, Monika Kubacka, Kamil Mika, Katarzyna Szczepańska, Barbara Nowak, Alessio Alesci, Anthea Miller, Eugenia Rita Lauriano, and Katarzyna Kieć-Kononowicz. 2024. "The Effect of KSK-94, a Dual Histamine H3 and Sigma-2 Receptor Ligand, on Adipose Tissue in a Rat Model of Developing Obesity" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070858
APA StyleKotańska, M., Zadrożna, M., Kubacka, M., Mika, K., Szczepańska, K., Nowak, B., Alesci, A., Miller, A., Lauriano, E. R., & Kieć-Kononowicz, K. (2024). The Effect of KSK-94, a Dual Histamine H3 and Sigma-2 Receptor Ligand, on Adipose Tissue in a Rat Model of Developing Obesity. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070858









