Approved and Commercialized Antidiabetic Medicines (Excluding Insulin) in Seven European Countries—A Cross-Sectional Comparison
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General Attributes of the Range of Antidiabetic Medicines
2.2. Observations
2.3. Active Substances (INNs)
2.4. Brand Names
2.5. Type of Medicine
2.6. Pharmaceutical Forms
2.7. Strengths
2.8. Marketing Authorization Holder
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source
4.2. Data Collection and National Context
- A10BA (biguanides);
- A10BB (sulfonylurea);
- A10BD (oral fixed combinations);
- A10F (alpha-glucosidase inhibitors);
- A10BG (thiazolidinediones, TDZ);
- A10BH (dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, DPP-4i);
- A10J (glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues, GLP-1 receptor agonists, GLP-1 RA);
- A10K (sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors);
- A10X (other blood glucose-lowering drugs, excluding insulins).
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cousin, E.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Ong, K.L.; Vos, T.; Abbafati, C.; Haque, S. Diabetes mortality and trends before 25 years of age: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Cai, X.; Guan, Q.; Ou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lin, X. Burden of type 1 and type 2 diabetes and high fasting plasma glucose in Europe, 1990–2019: A comprehensive analysis from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1307432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, A.; Handelsman, Y.; Heile, M.; Shannon, M. Burden of Illness in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2018, 24, S5–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W. Global trends in burden of type 2 diabetes attributable to physical inactivity across 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1343002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Lombardo, F.; Maggini, M.; Gruden, G.; Bruno, G. Temporal Trend in Hospitalizations for Acute Diabetic Complications: A Nationwide Study, Italy, 2001–2010. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Manley, S.E.; Cull, C.A.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuring, T.; Archangelidi, O.; Suhrcke, M. The Economic Costs of Type 2 Diabetes: A Global Systematic Review. PharmacoEconomics 2015, 33, 811–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat, K.; Dhamani, K.; Gul, R.; Froelicher, E.S. The effectiveness of patient-centered care vs. Usual care in type 2 diabetes self-management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public. Health 2022, 10, 994766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonde, L.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Reddy, S.S.; McGill, J.B.; Berga, S.L.; Bush, M.; Chandrasekaran, S.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Einhorn, D.; Galindo, R.J.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Developing a Diabetes Mellitus Comprehensive Care Plan-2022 Update. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 923–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menditto, E.; Orlando, V.; De Rosa, G.; Minghetti, P.; Musazzi, U.M.; Cahir, C.; Kurczewska-Michalak, M.; Kardas, P.; Costa, E.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; et al. Patient Centric Pharmaceutical Drug Product Design—The Impact on Medication Adherence. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buse, J.B.; Diamant, M.; Ferrannini, E.; Nauck, M.; Peters, A.L.; Tsapas, A.; Wender, R.; Matthews, D.R. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2015: A Patient-Centered Approach: Update to a Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2014, 38, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Quality of Care: A Process for Making Strategic Choices in Health Systems; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Medicine Agency. Marketing Authorisation. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/marketing-authorisation (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 31 March 2004 Laying down Union Procedures for the Authorisation and Supervision of Medicinal Products for Human Use and Establishing a European Medicines Agency. 2004. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2004/726/oj (accessed on 21 October 2023).
- Bade, C.; Olsacher, A.; Boehme, P.; Truebel, H.; Fehring, L. Reasons for supply side driven drug shortages—A mixed-methods study on first-level, higher-level, and root causes from the perspective of marketing authorization holders. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2023, 19, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HMA/EMA Task Force on Availability of Authorised Medicines for Human and Veterinary Use (TFAAM) Terms of Reference. 2022. Available online: https://www.hma.eu/fileadmin/dateien/HMA_joint/00-_About_HMA/03-Working_Groups/TF_Availability/2022_09_HMA-EMA_TF_Availability_ToR.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- European Commission. A Pharmaceutical Strategy for Europe. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/human-use/strategy_en. (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- European Commission. Introducing HERA, the European Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Authority, the Next Step towards Completing the European Health Union, Brussel. 2021. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:52021DC0576 (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Regulation (EU) 2022/123 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 January 2022 on a Reinforced Role for the European Medicines Agency in Crisis Preparedness and Management for Medicinal Products and Medical Devices. 2022. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32022R0123 (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- European Commission. Reform of the EU Pharmaceutical Legislation. Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/medicinal-products/pharmaceutical-strategy-europe/reform-eu-pharmaceutical-legislation_en (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Overbeek, J.A.; Heintjes, E.M.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Blin, P.; Lassalle, R.; Hall, G.C.; Lapi, F.; Bianchini, E.; Hammar, N.; Bezemer, I.D.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Patterns Across Europe: A Population-based Multi-database Study. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantalone, K.M.; Hobbs, T.M.; Wells, B.J.; Kong, S.X.; Kattan, M.W.; Bouchard, J.; Yu, C.; Sakurada, B.; Milinovich, A.; Weng, W.; et al. Clinical characteristics, complications, comorbidities and treatment patterns among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a large integrated health system. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2015, 3, e000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, R.; Kato, H.; Kisanuki, K.; Oh, A.; Hiroi, S.; Onishi, Y.; Guelfucci, F.; Shimasaki, Y. Treatment patterns, persistence and adherence rates in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan: A claims-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.M.; Martins, S.O.; Raposo, J. Consumption of antidiabetic medicines in Portugal: Results of a temporal data analysis of a thirteen-year study (2005–2017). BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, J.A.; Cánovas, G.; Durán, A. Factors Associated with Adherence to Clinical Practice Guidelines for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results of a Spanish Delphi Consensus. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 9970859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardetko, N.; Nabergoj Makovec, U.; Locatelli, I.; Janez, A.; Kos, M. Uptake of new antidiabetic medicines in 11 European countries. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) and CRA, The Root Cause of Unavailability and Delay to Innovative Medicines. 2023. Available online: https://www.efpia.eu/media/677292/cra-efpia-root-causes-unavailability-delay-080423-final.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Leopold, C.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K.; Vogler, S.; de Joncheere, K.; Laing, R.O.; Leufkens, H.G.M. Is Europe still heading to a common price level for on-patent medicines? An exploratory study among 15 Western European countries. Health Policy 2013, 112, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, P.; Vandoros, S. Pharmaceutical price comparisons across the European Union and relative affordability in Cyprus. Health Policy Technol. 2016, 5, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blind, E.; Janssen, H.; Dunder, K.; de Graeff, P.A. The European Medicines Agency’s approval of new medicines for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA, Zynquista. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/zynquista (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Alhindi, Y.; Avery, A. The efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide for glycaemic management in adults with type 2 diabetes compared to subcutaneous semaglutide, placebo, and other GLP-1 RA comparators: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2022, 28, 100944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A.; Keam, S.J. Sotagliflozin: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA, Public statement, Zynquista Withdrawal of the marketing authorisation in the European Union, 19 May 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/public-statement/public-statement-zynquista-withdrawal-marketing-authorisation-european-union_en.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araszkiewicz, A.; Bandurska-Stankiewicz, E.; Borys, S.; Budzyński, A.; Cyganek, K.; Cypryk, K.; Czech, A.; Czupryniak, L.; Drzewoski, J.; Dzida, G.; et al. Guidelines on the management of patients with diabetes. A position of Diabetes Poland. Curr. Top. Diabetes 2022, 2, 1–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecki, M.T.; Klupa, T.; Bociąga-Jasik, M.; Kowalska, I.; Gumprecht, J.; Strojek, K.; Zozulińska-Ziółkiewicz, D.; Czupryniak, L.; Hohendorff, J.; Kania, M. Guidelines of the Diabetes Poland on the therapeutic management and glycemic monitoring in diabetic patients in the COVID-19 pandemic and other viral pandemics. Curr. Top. Diabetes 2022, 2, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwczyński, A.; Brzozowska, M.; Jacyna, A.; Iltchev, P.; Iwańczuk, T.; Wierzba, W.; Marczak, M.; Orlewska, K.; Szymański, P.; Orlewska, E. Drug-class-specific changes in the volume and cost of antidiabetic medications in Poland between 2012 and 2015. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchi, R.; Sugiyama, T.; Goto, A.; Imai, K.; Ihana-Sugiyama, N.; Ohsugi, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T.; Ueki, K. Retrospective nationwide study on the trends in first-line antidiabetic medication for patients with type 2 diabetes in Japan. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grytsai, O.; Myrgorodska, I.; Rocchi, S.; Ronco, C.; Benhida, R. Biguanides drugs: Past success stories and promising future for drug discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piragine, E.; Petri, D.; Martelli, A.; Calderone, V.; Lucenteforte, E. Adherence to Oral Antidiabetic Drugs in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokicka, D.; Wróbel, M.; Szymborska-Kajanek, A.; Bożek, A.; Strojek, K. Assessment of compliance to self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetic patients and level of implementation of Polish Diabetes Association Recommendation for general practitioners. Clin. Diabetol. 2018, 7, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juste, A.M.; Miguel, A.G.; Plou, B.P.; Rubio, F.G.; Pascual-Salcedo, M.M.A.; Menditto, E.; Torres, A.P. Adherence to treatment of hypertension, hypercholesterolaemia and diabetes in an elderly population of a Spanish cohort. Med. Clin. 2019, 153, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Romano, D.; Maffioli, P. Effects of metformin extended release compared to immediate release formula on glycemic control and glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2017, 11, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, P.; Li, S. Long-Acting Metformin Vs. Metformin Immediate Release in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 669814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.; Chaar, B.B.; Vera, N.; Pillai, A.S.; Lim, J.S.; Bero, L.; Moles, R.J. Medicine shortages in Fiji: A qualitative exploration of stakeholders’ views. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, A.; Goebel, R.; Ganso, M.; Zagermann-Muncke, P.; Schulz, M. Drug shortages may compromise patient safety: Results of a survey of the reference pharmacies of the Drug Commission of German Pharmacists. Health Policy 2018, 122, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongh, T.; Becker, D.; Boulestreau, M.; Davé, A.; Dijkstal, F.; King, R.; Petrosova, L.; Varnai, P.; Vis, C.; Spit, W.; et al. Future-Proofing Pharmaceutical Legislation—Study on Medicine Shortages—Final Report (Revised); Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation Drug Agency. Drug Shortages. Root Causes and Potential Solutions. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/131130/download?attachment (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Biogaran. Available online: https://biogaran.com/en/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Laboratoire Arrow. Available online: https://www.laboratoire-arrow.com/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Laboratoire EG LABO. Available online: https://www.eglabo.fr/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Polpharma Zakłady Farmaceutyczne. Available online: https://polpharma.pl/ (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Arena Group. Available online: https://arenagroup.com/ (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Zentiva. Available online: https://www.zentiva.com/ (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Galenika. Available online: https://galenika.rs/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Market Research Future. Available online: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/diabetes-drug-market-1160 (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Shrestha, S.S.; Zhang, P.; Hora, I.; Geiss, S.L.; Luman, T.E.; Gregg, W.E. Factors Contributing to Increases in Diabetes-Related Preventable Hospitalization Costs among U.S. Adults During 2001–2014. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Vemer, P.; Zhu, J.; Postma, M.J.; Chen, W. Economic Burden in Chinese Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using Electronic Insurance Claims Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices of Romania. Medicinal Product Index. Available online: https://nomenclator.anm.ro/medicamente (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Bulgarian Drug Agency. Register of Pharmaceutical Products. Available online: https://www.bda.bg/en/registers/register-of-pharmaceutical-products (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Medicines and Medical Devices Agency of Serbia (Alims). Human Medicines. Available online: https://www.alims.gov.rs/english/medicinal-products/search-for-human-medicines/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- State Institute for Drug Control. Medicinal Product Database. Available online: https://www.sukl.cz/vyhledavani-v-databazi-leku (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products. Register of Medicinal Products. Available online: https://www.urpl.gov.pl/pl/produkty-lecznicze/zagadnienia-rejestracyjne/rejestr-produkt%C3%B3w-leczniczych (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- The Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS). AEMPS online drug information center—CIMA. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/publico/lista.html (accessed on 6 February 2022).
- The National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM). Directory of Pharmaceutical Specialties. Available online: http://agence-prd.ansm.sante.fr/php/ecodex/index.php#result (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- The Ministry of Health and Prevention. Public Drug Database. Available online: https://base-donnees-publique.medicaments.gouv.fr/index.php (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- The Ministry of Health. Nomenclátor de Facturación. Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/en/profesionales/nomenclator.do (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- National Council on Prices and Reimbursement of Medicinal Products. Available online: https://www.ncpr.bg/en/ (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Ministry of Health, National Public Catalog of Maximum Prices of Medicines for Human Use. Available online: https://ms.ro/en/ministry/structure/directia-politica-medicamentului-si-a-dispozitivelor-medicale/preturi-medicamente (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Decision on the highest prices of drugs for use in human medicine, which are subject to prescription. Official Gazette of the Republic of Serbia No. 48/2021-8, 90/2021-3, 92/2021-12 (corr), 125/2021-42, 18/2022-65, 67/2022-75, 107/2022-8, 141/2022-178.
- Ministry of Health Annex to the announcement of the Minister of Health 2022, Poland. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/zdrowie/obwieszczenia-ministra-zdrowia-lista-lekow-refundowanych (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. ATC/DDD Index. Available online: https://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/ (accessed on 10 April 2022).
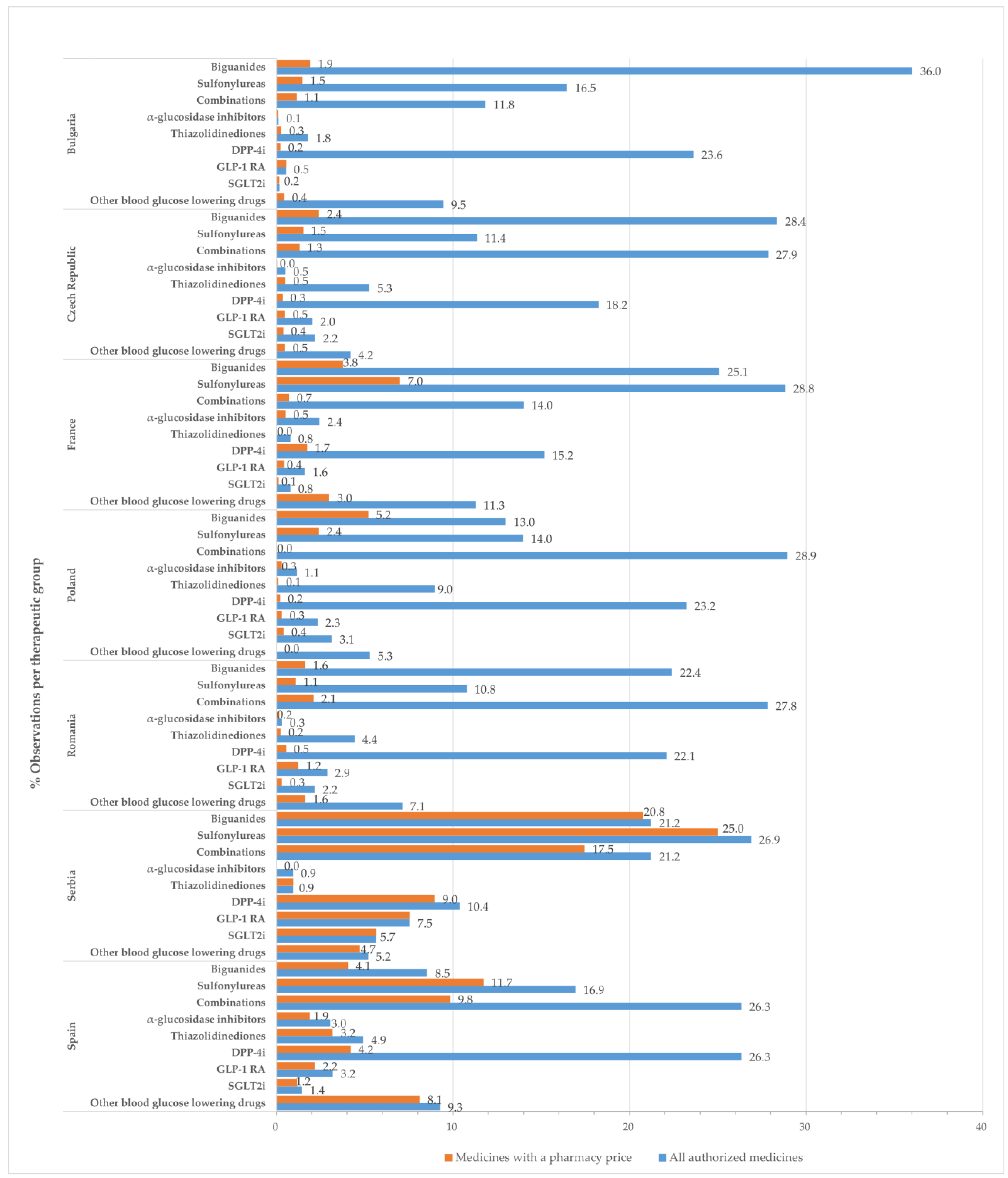
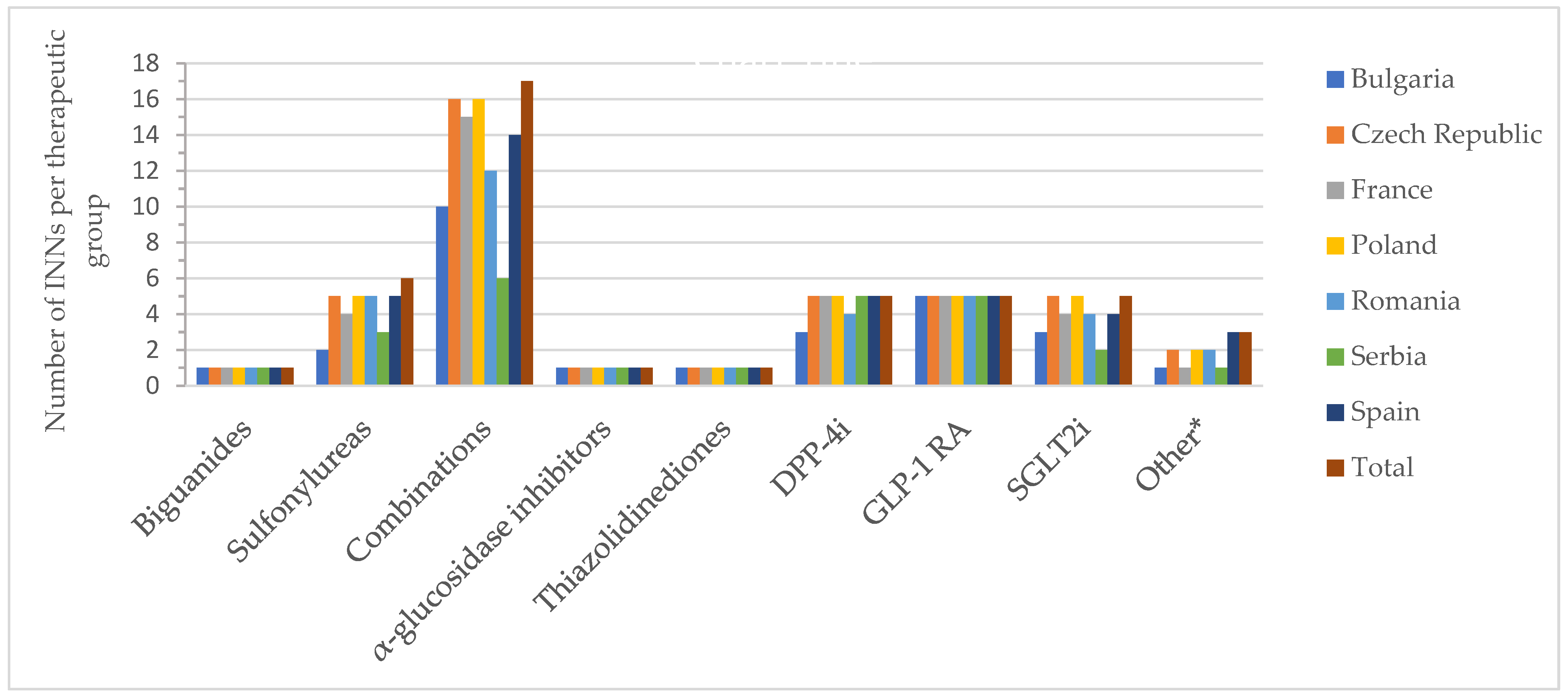
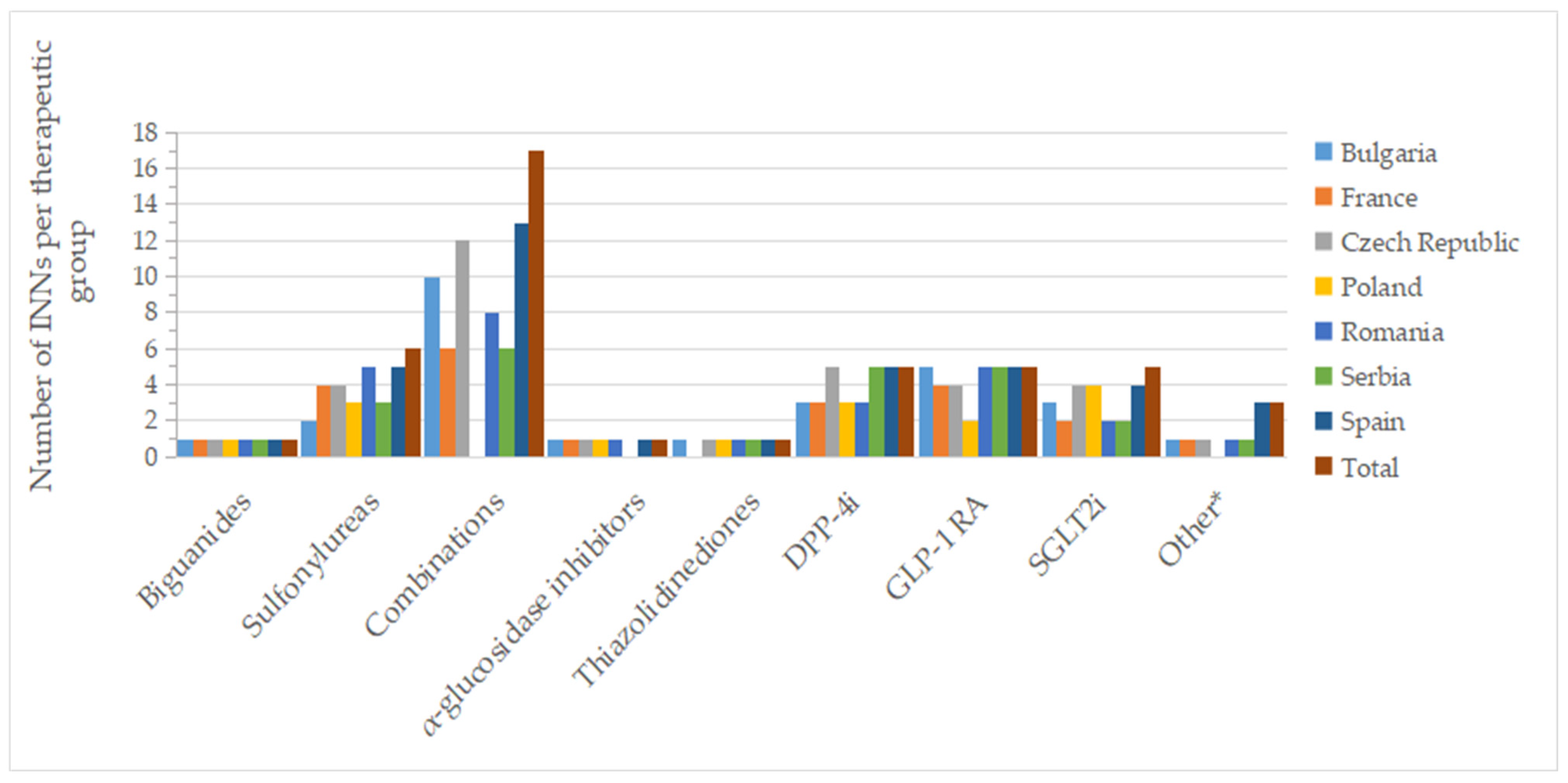
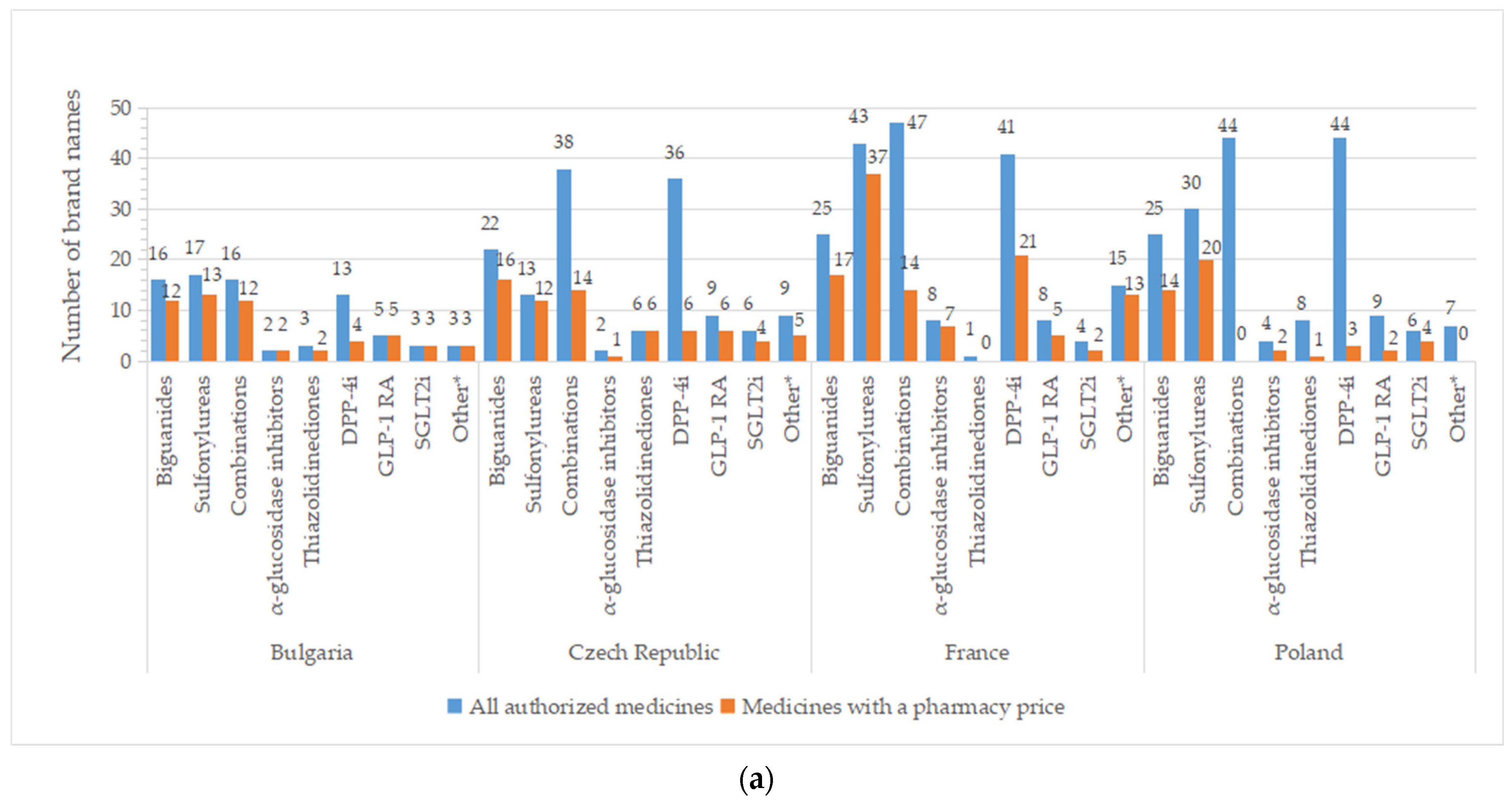

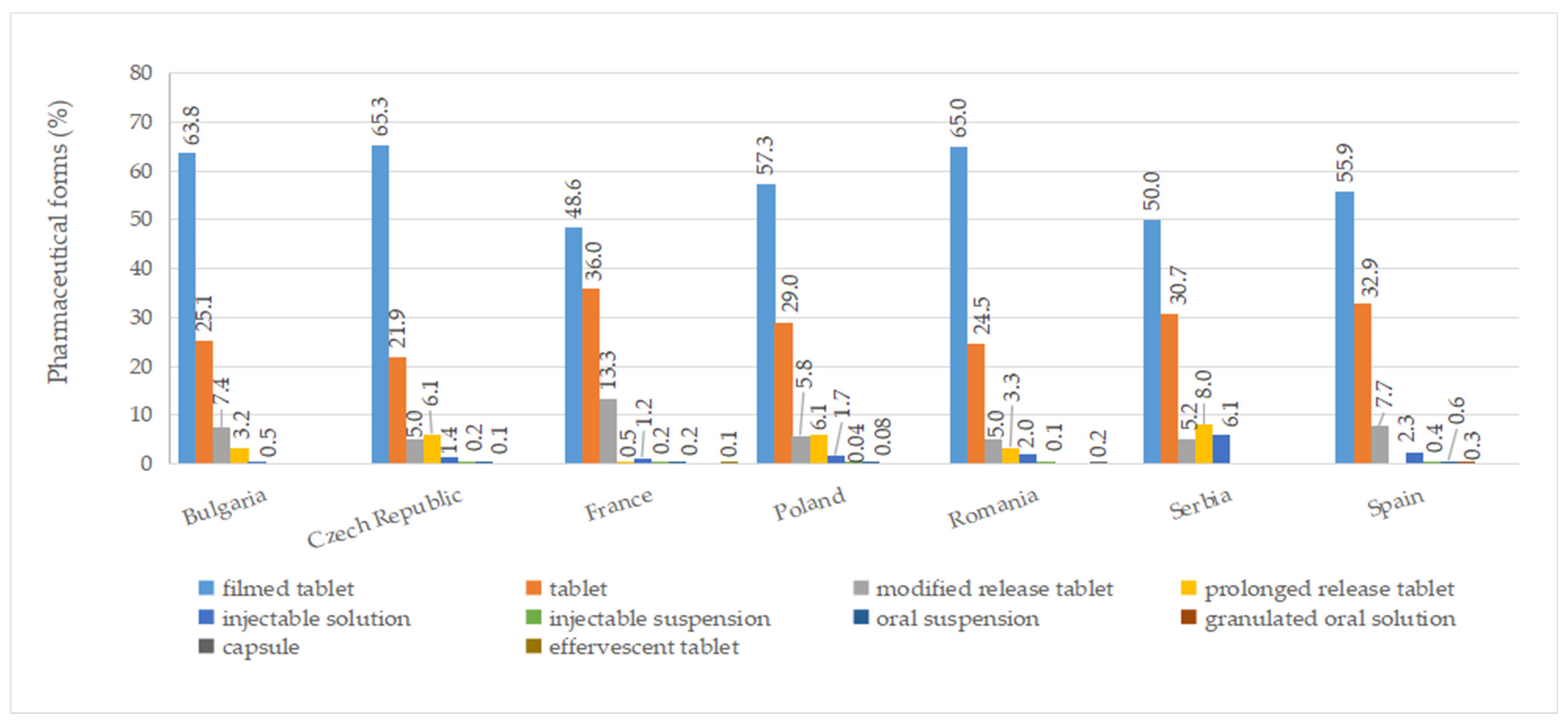
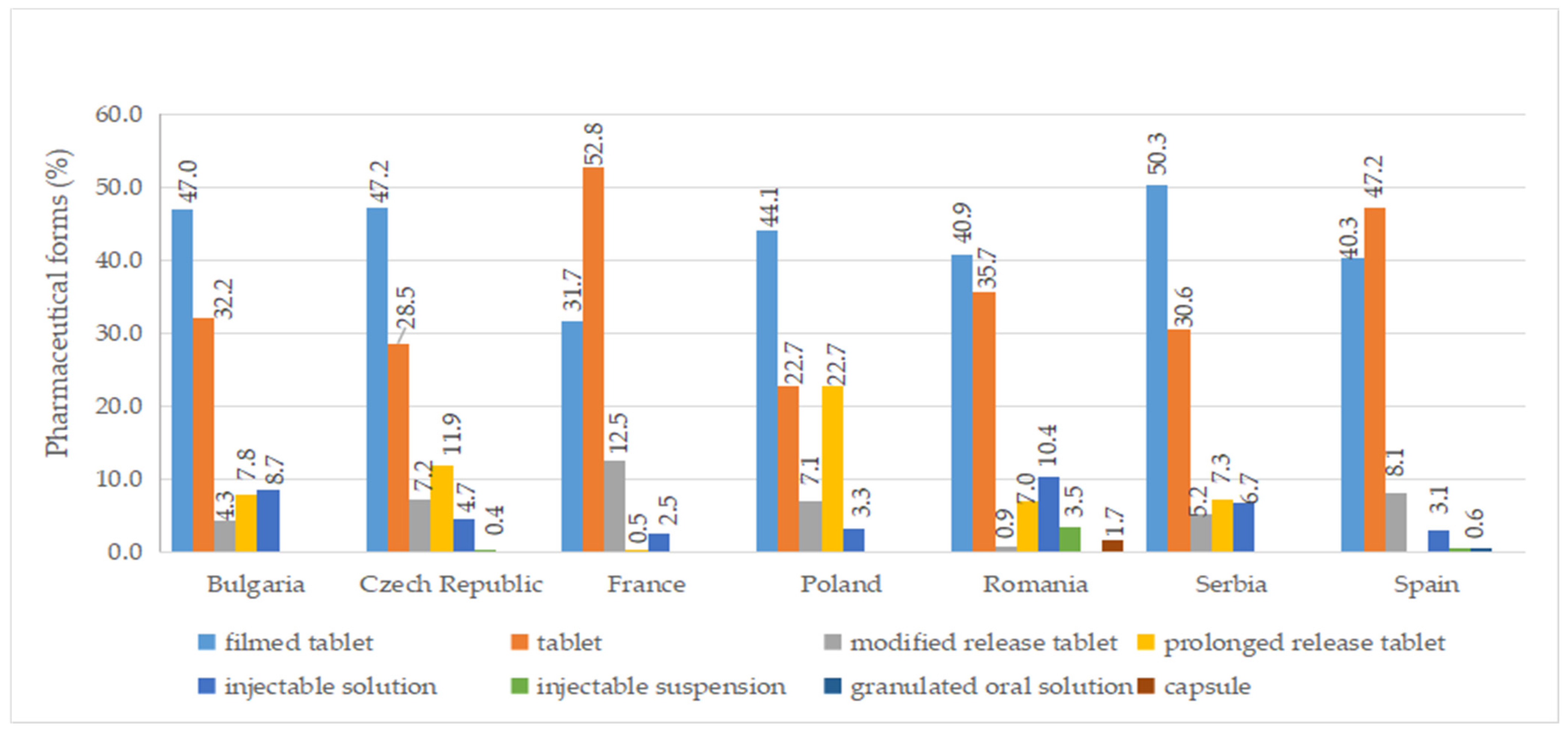


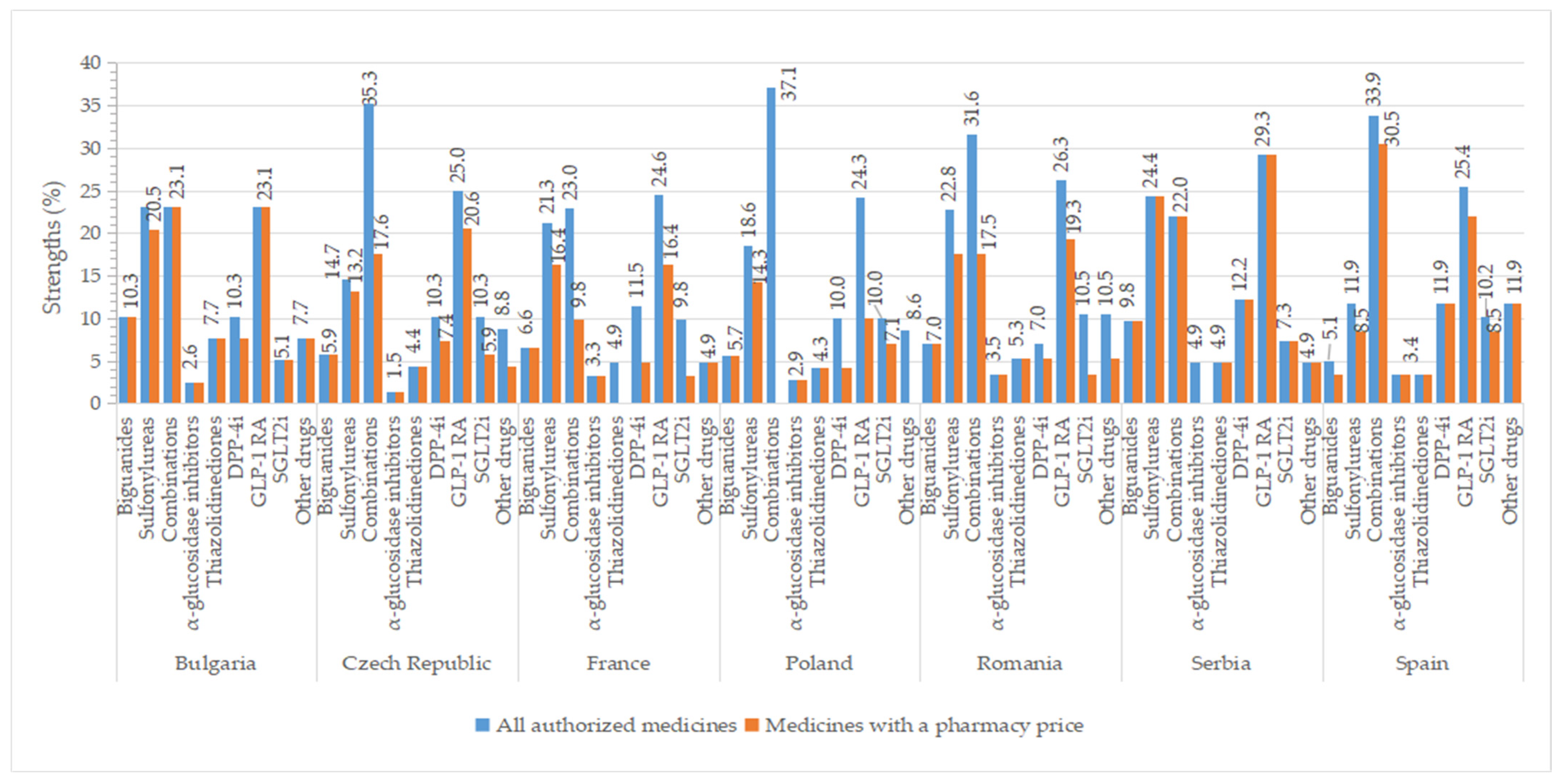
| Country | Number of Observations (%) | Number of Brand Names (%) | Number of INNs * (%) | Number of Strengths (%) | Number of Pharmaceutical Forms (%) | Number of MAHs ** (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulgaria | 115 (6.2%) | 56 (71.8%) | 27 (100.0%) | 34 (87.2%) | 5 (100.0%) | 25 (73.5%) |
| Czech Republic | 235 (7.5%) | 70 (49.6%) | 33 (80.5%) | 46 (67.6%) | 6 (85.7%) | 29 (69.0%) |
| France | 439 (17.3%) | 116 (60.4%) | 22 (59.5%) | 34 (55.7%) | 5 (62.5%) | 30 (62.5%) |
| Poland | 211 (8.9%) | 46 (26.0%) | 15 (36.6%) | 27 (38.6%) | 5 (71.4%) | 30 (50.0%) |
| Romania | 115 (8.9%) | 49 (58.3%) | 27 (77.1%) | 44 (77.2%) | 7 (100.0%) | 21 (65.6%) |
| Serbia *** | 193 (91.0%) | 49 (90.7%) | 24 (96.0%) | 41 (100.0%) | 5 (100.0%) | 23 (95.8%) |
| Spain | 320 (46.3%) | 123 (57.7%) | 38 (97.4%) | 51 (86.4%) | 6 (85.7%) | 45 (70.3%) |
| Therapeutic Group | Number of Brand Names/INN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ATC Code) | Bulgaria | Czech Republic | France | Poland | Romania | Serbia | Spain |
| Biguanides (A10BA) | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 |
| Sulfonylureas (A10BB) | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | ≥1 | >1 | >1 |
| Combinations (A10BD) | ≥1 | ≥1 | >1 | N/A | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 |
| α-glucosidase inhibitors (A10BF) | >1 | 1 | >1 | >1 | 1 | N/A | >1 |
| Thiazolidinediones (A10BG) | >1 | >1 | N/A | 1 | 1 | 1 | >1 |
| DPP-4i (A10BH) | ≥1 | ≥1 | >1 | 1 | >1 | ≥1 | >1 |
| GLP-1 RA (A10BJ) | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 |
| SGLT2i (A10BK) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Other blood glucose-lowering drugs, | >1 | >1 | >1 | N/A | >1 | >1 | ≥1 |
| excluding insulin (A10X) | |||||||
| Therapeutic Group | Innovator Medicine Name/INN | Generic Medicine Name/INN | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ATC Code) | B | CZ | F | P | R | SB | SP | B | CZ | F | P | R | SB | SP |
| Biguanides (A10BA) | >1 | >1 | 1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | 1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 |
| Sulfonylureas (A10BB) | 1 | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≤1 | 1 | ≥1 | >1 | >1 * | ≥1 | ≥1 * | ≥1 * | >1 * | <1 ** |
| Combinations (A10BD) | ≤1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | <1 ** | ≥1 | ≥1 * | >1 * | >1 * | >1 * | ≥1 * | ≤1 ** | ≤1 ** |
| α-glucosidase inhibitors (A10BF) | 1 | N/A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | N/A | N/A | >1 |
| Thiazolidinediones (A10BG) | N/A | 1 | 1 | >1 | 1 | N/A | 1 | >1 | >1 | N/A | >1 | >1 | 1 | >1 |
| DPP-4i (A10BH) | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | 1 | ≥1 | >1 * | >1 * | ≥1 * | >1 * | >1 * | <1 ** | >1 * |
| GLP-1 RA (A10BJ) | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| SGLT2i (A10BK) | 1 | ≥1 | 1 | ≥1 | 1 | 1 | ≥1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Other blood glucose-lowering drugs, | N/A | ≥1 | 1 | ≥1 | ≤1 | N/A | ≥1 | >1 | >1 * | >1 | >1 | >1 * | >1 | <1 ** |
| excluding insulin (A10X) | ||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Group | Innovator Medicine Name/INN | Generic Medicine Name/INN | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ATC Code) | B | CZ | F | P | R | SB | SP | B | CZ | F | P | R | SB | SP |
| Biguanides (A10BA) | >1 | >1 | 1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | 1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 |
| Sulfonylureas (A10BB) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | 1 | 1 | >1 | >1 * | >1 * | ≥1 * | ≥1 * | ≤1 ** | >1 ** |
| Combinations (A10BD) | ≤1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | N/A | ≥1 | ≤1 | ≥1 | ≤1 ** | N/A | <1 ** | N/A | ≥1 * | ≤1 ** | ≤1 ** |
| α-glucosidase inhibitors (A10BF) | 1 | N/A | 1 | 1 | 1 | N/A | 1 | 1 | 1 | >1 | 1 | N/A | N/A | >1 |
| Thiazolidinediones (A10BG) | N/A | 1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1 | >1 | >1 | N/A | 1 | 1 | 1 | >1 |
| DPP-4i (A10BH) | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≤1 | 1 | ≤1 | ≥1 | ≤1 | N/A | >1 * | ≤1 | <1 ** | ≤1 ** | N/A |
| GLP-1 RA (A10BJ) | 1 | ≥1 | >1 | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| SGLT2i (A10BK) | 1 | ≥1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ≥1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Other blood glucose-lowering drugs, | N/A | 1 | 1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ≥1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | N/A | >1 | >1 | <1 ** |
| excluding insulin (A10X) | ||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Group | Number of Strengths/INN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ATC Code) | Bulgaria | Czech Republic | France | Poland | Romania | Serbia | Spain |
| Biguanides (A10BA) | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 |
| Sulfonylureas (A10BB) | >1 | ≥1 | >1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 |
| Combinations (A10BD) | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | N/A | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 |
| α-glucosidase inhibitors (A10BF) | 1 | 1 | >1 | >1 | >1 | N/A | >1 |
| Thiazolidinediones (A10BG) | >1 | >1 | N/A | >1 | >1 | >1 | >1 |
| DPP-4i (A10BH) | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 |
| GLP-1 RA (A10J) | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | >1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 |
| SGLT2i (A10K) | 1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | ≥1 | >1 | ≥1 |
| Other blood glucose-lowering drugs, excluding insulins (A10X) | >1 | >1 | >1 | N/A | >1 | >1 | >1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atănăsoie, A.-M.; Ancuceanu, R.V.; Krajnović, D.; Waszyk-Nowaczyk, M.; Skotnicki, M.; Tondowska, D.; Petrova, G.; Niculae, A.M.; Tăerel, A.-E. Approved and Commercialized Antidiabetic Medicines (Excluding Insulin) in Seven European Countries—A Cross-Sectional Comparison. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060793
Atănăsoie A-M, Ancuceanu RV, Krajnović D, Waszyk-Nowaczyk M, Skotnicki M, Tondowska D, Petrova G, Niculae AM, Tăerel A-E. Approved and Commercialized Antidiabetic Medicines (Excluding Insulin) in Seven European Countries—A Cross-Sectional Comparison. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(6):793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060793
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtănăsoie, Ana-Maria, Robert Viorel Ancuceanu, Dušanka Krajnović, Magdalena Waszyk-Nowaczyk, Marcin Skotnicki, Dorota Tondowska, Guenka Petrova, Andrei Marian Niculae, and Adriana-Elena Tăerel. 2024. "Approved and Commercialized Antidiabetic Medicines (Excluding Insulin) in Seven European Countries—A Cross-Sectional Comparison" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 6: 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060793
APA StyleAtănăsoie, A.-M., Ancuceanu, R. V., Krajnović, D., Waszyk-Nowaczyk, M., Skotnicki, M., Tondowska, D., Petrova, G., Niculae, A. M., & Tăerel, A.-E. (2024). Approved and Commercialized Antidiabetic Medicines (Excluding Insulin) in Seven European Countries—A Cross-Sectional Comparison. Pharmaceuticals, 17(6), 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060793










