Daphnetin Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain via Regulation of Microglial Responses and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in the Spinal Cord
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
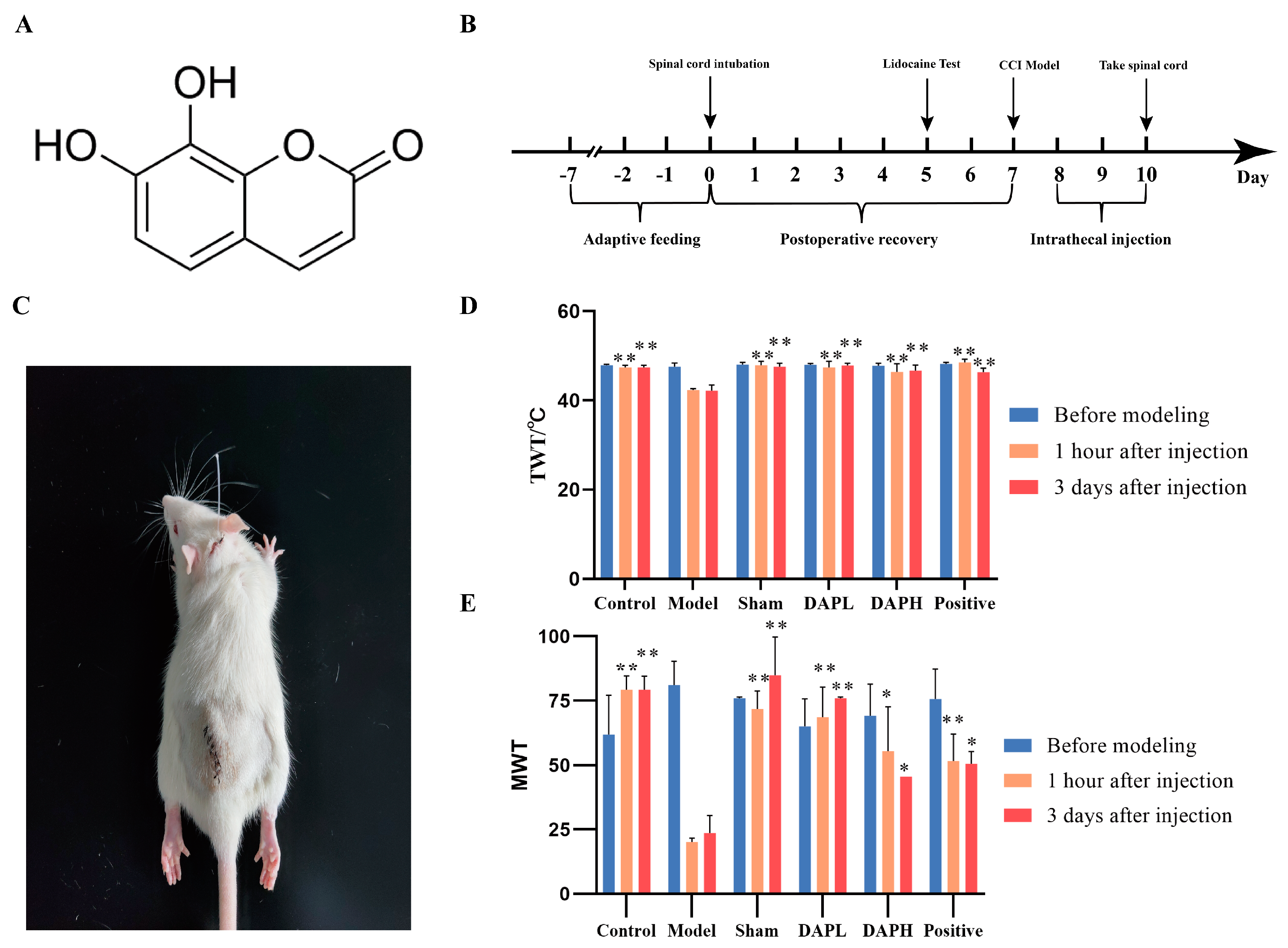
2.1. DAP Improved NP in CCI Rats
2.2. DAP Inhibited the Activation of Microglia and the Expression of Inflammatory Factors in the Spinal Cords of CCI Rats
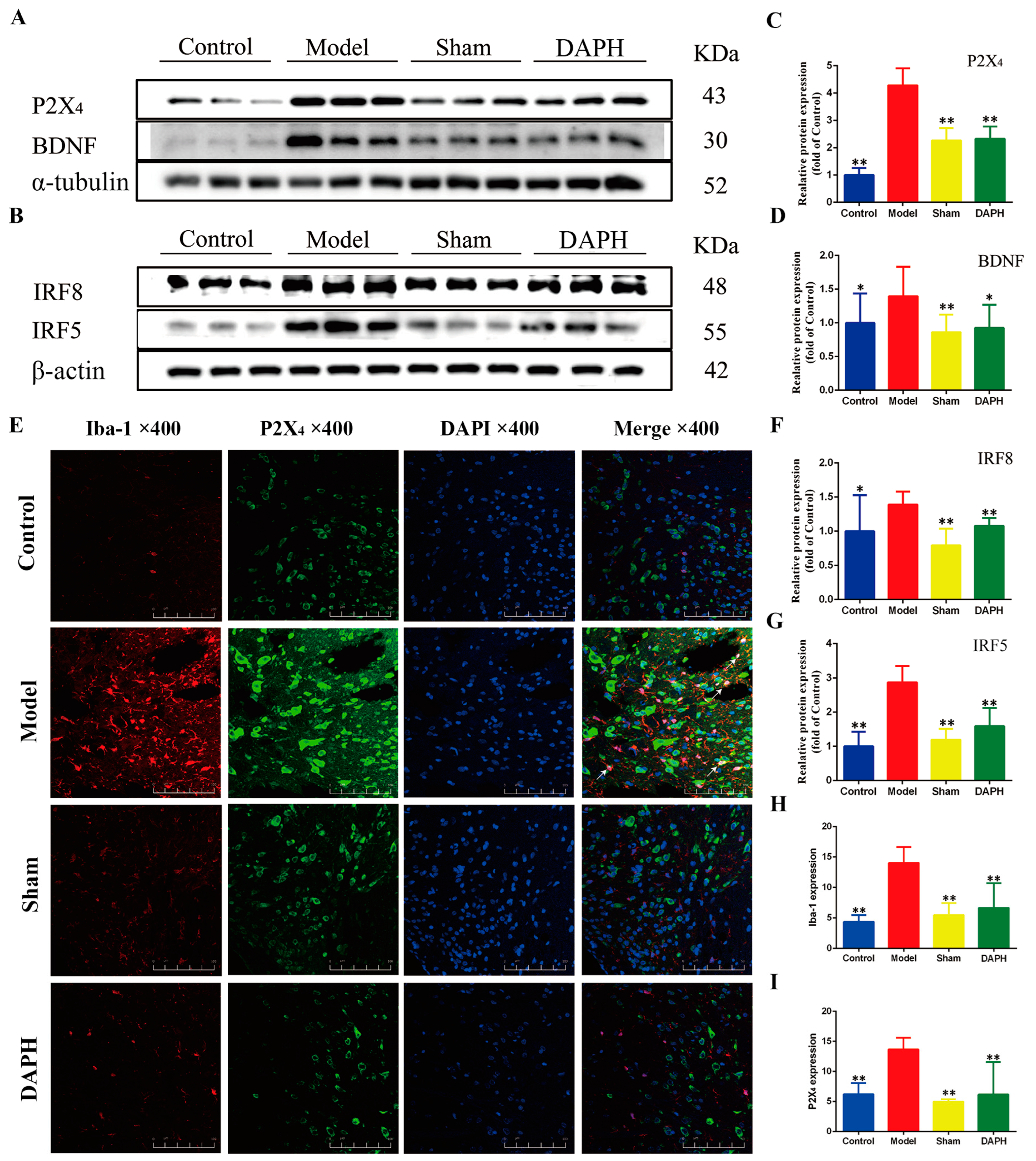
2.3. DAP Regulated P2X4 Receptors in Spinal Microglia of CCI Rats by Interfering with IRF8 Protein
2.4. DAP Inhibited the Activation of the MAPK Pathway in Spinal Microglia of CCI Rats by Interfering with P2X4 Receptors
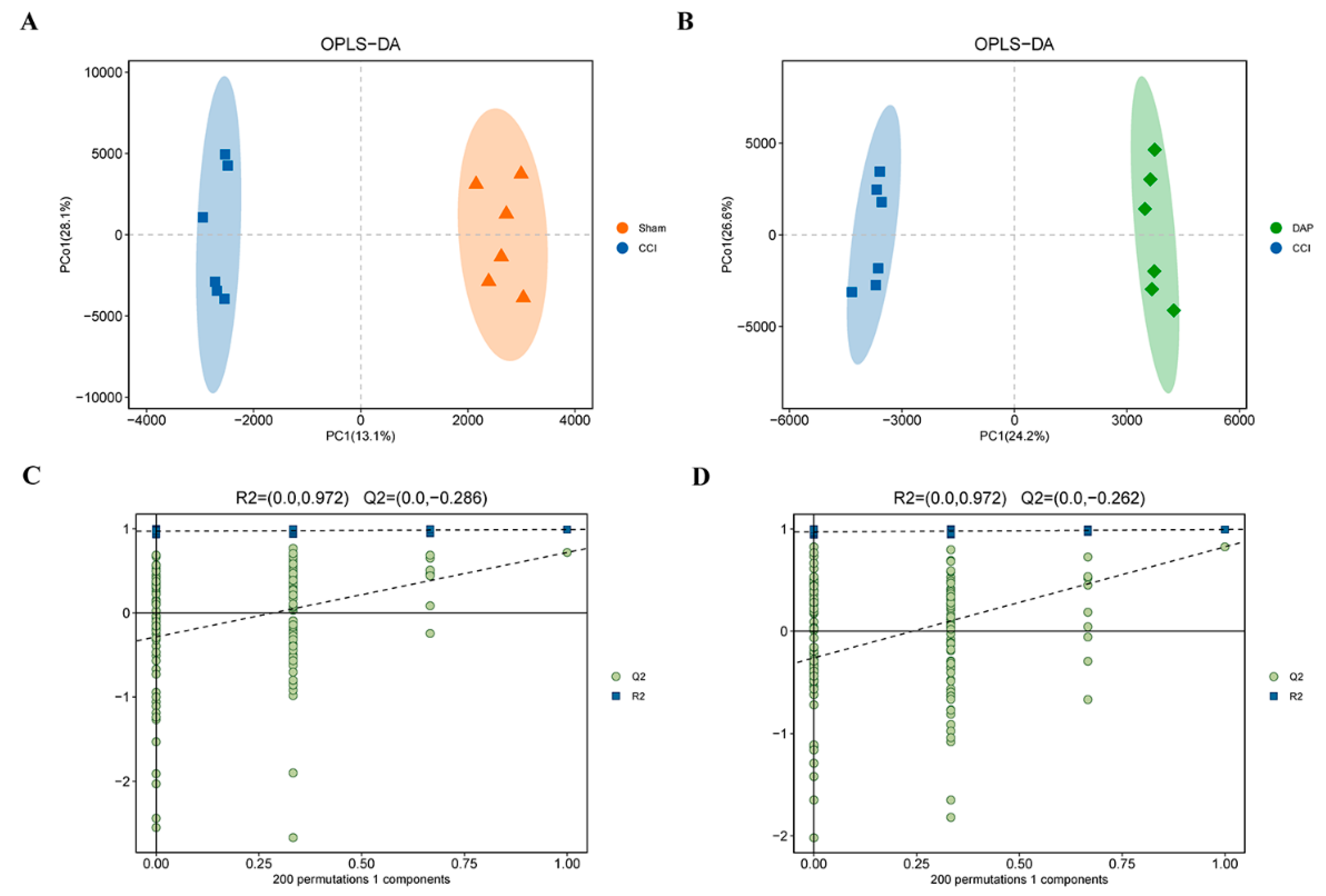
2.5. DAP Induced Changes in Spinal Cord Proteomics Profile in CCI Rats
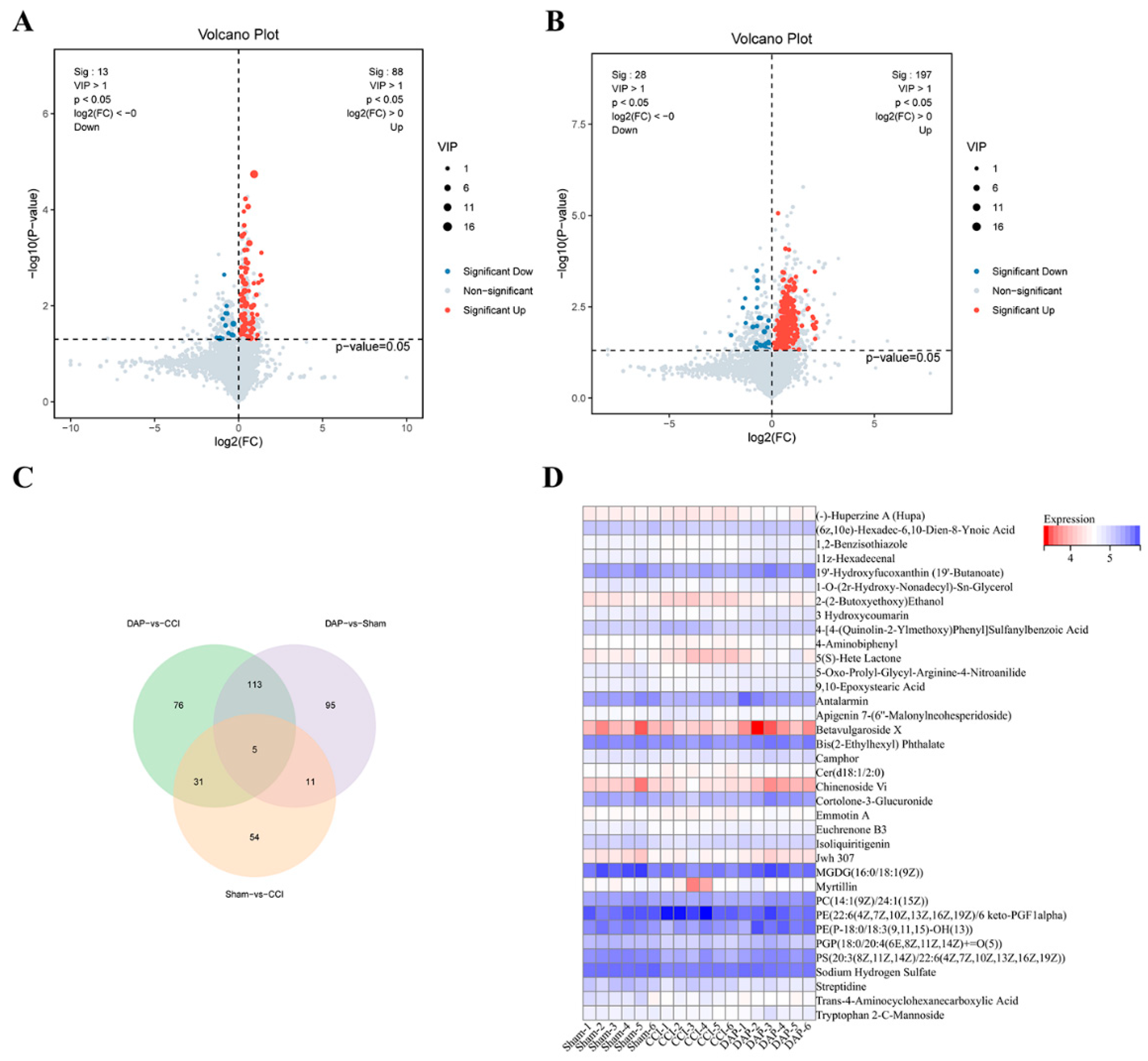
2.6. DAP Induced Changes in Spinal Cord Metabolomics Profile in CCI Rats
2.7. Association Analysis of DEPs and DEMs between the DAP and CCI Groups
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Establishment of Model and Drug Administration
4.3. Behavioral Tests
4.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.5. Proteomics Analysis
4.6. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhassira, D.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Attal, N.; Laurent, B.; Touboul, C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 2008, 136, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhassira, D. Neuropathic pain: Definition, assessment and epidemiology. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Gao, Y.J. Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Chamessian, A.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Pain Regulation by Non-neuronal Cells and Inflammation. Science 2016, 354, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Tsuda, M.; Koizumi, S. ATP- and adenosine-mediated signaling in the central nervous system: Chronic pain and microglia: Involvement of the atp receptor P2X4. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 94, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, W.J.; Zhu, Z.M.; Liu, Z.X. The role of P2X4 receptor in neuropathic pain and its pharmacological properties. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Kang, Y.-H.; Mao, Y.; Wang, H.-H.; Ge, W.-H.; Shi, L.-Y. Anti-inflammatory and protective properties of daphnetin in endotoxin-induced lung injury. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12315–12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, H.; Ying, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, D.; Ge, W.; Shi, L. Daphnetin attenuates microglial activation and proinflammatory factor production via multiple signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, B.; Liu, X.; Han, Q.; Ge, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shi, L. Daphnetin Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis through Regulating Heme Oxygenase-1. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Shan, J.; Di, L.; Jiang, L.; Xu, H. Therapeutic effects of daphnetin on adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Nie, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Ye, F.; Shi, L.; Lv, Z.; Xie, J.; et al. Daphnetin inhibits spinal glial activation via Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB signaling pathway and attenuates CFA-induced inflammatory pain. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 98, 107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Effects of daphnetin on neuropathic pain in rats induced by chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve and its mechanism. J. Guangxi Med. Univ. 2022, 39, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Liang, W.; Zhang, M.; Cui, S.; Huang, X.; Ou, W.; Huang, R.; Gao, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, S. Daphnetin Improves Neuropathic Pain by Inhibiting the Expression of Chemokines and Inflammatory Factors in the Spinal Cord and Interfering with Glial Cell Polarization. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Alam, A.; Chen, Q.; Eusman, M.A.; Pal, A.; Eguchi, S.; Wu, L.; Ma, D. The role of microglia in the pathobiology of neuropathic pain development: What do we know? Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qadri, Y.J.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.-R. Microglia in Pain: Detrimental and Protective Roles in Pathogenesis and Resolution of Pain. Neuron 2018, 100, 1292–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcangio, M. Role of the immune system in neuropathic pain. Scand. J. Pain. 2019, 20, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.W.; Cheng, K.I.; Chen, J.Y.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Yeh, J.-L.; Hsu, J.-H.; Dai, Z.-K.; Wu, B.-N. Loganin prevents chronic constriction injury-provoked neuropathic pain by reducing TNF-alpha/IL-1beta-mediated NF-kappaB activation and schwann cell demyelination. Phytomedicine 2020, 67, 153166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinho, P.; Madeira, D.; Dias, L.; Simões, A.P.; Cunha, R.A.; Canas, P.M. Purinergic signaling orchestrating neuron-glia communication. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, L.P.; Ase, A.R.; Boué-Grabot, E.; Séguéla, P. P2X4 receptor channels form large noncytolytic pores in resting and activated microglia. Glia 2012, 60, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Tsuda, M.; Yoshinaga, R.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Ozato, K.; Tamura, T.; Inoue, K. IRF8 is a critical transcription factor for transforming microglia into a reactive phenotype. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Iwamoto, S.; Yoshinaga, R.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Nishiyama, A.; Mak, T.W.; Tamura, T.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K. Transcription factor IRF5 drives P2X4R+-reactive microglia gating neuropathic pain. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, T.; Beggs, S.; Wan, X.; Salter, M.W. P2X4-receptor-mediated synthesis and release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in microglia is dependent on calcium and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3518–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, K.; Tsuda, M. Role of microglia and P2X4 receptors in chronic pain. Pain. Rep. 2021, 6, E864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Zhu, X.; Huang, F.; He, H.; Fan, W. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and pain. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Boehm, J.; Lee, J.C. p38 MAP kinases: Key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.; Huang, R.; Gao, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, S. Traditional Chinese medicine use in neuropathic pain: Targeting glial cell-mediated neuroinflammation. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2023, 9, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, J.L.; Jiang, J.; Felix, J.S.; Bray, J.K.; da Silva, L.; Gharaibeh, R.Z.; McMahon, L.R.; Schmittgen, T.D. Alterations in mouse spinal cord and sciatic nerve microRNAs after the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 731, 135029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, S.R. Surgical animal models of neuropathic pain: Pros and Cons. Int. J. Neurosci. 2015, 125, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, H.; DeLeo, J.A.; Colburn, R.W.; Weinstein, J.N. Spinal glial activation and cytokine expression after lumbar root injury in the rat. Spine 2000, 25, 1206–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthos, D.N.; Sandkühler, J. Neurogenic neuroinflammation: Inflammatory CNS reactions in response to neuronal activity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iht, H.; Mtv, C.; Wkk, W.; Liu, X. Spinal microglia-neuron interactions in chronic pain. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 1575–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda, M.; Shigemoto-Mogami, Y.; Koizumi, S.; Salter, M.W.; Inoue, K. P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 2003, 424, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapplebeck, J.C.S.; Dalgarno, R.; Tu, Y.; Moriarty, O.; Beggs, S.; Kwok, C.H.T.; Halievski, K.; Assi, S.; Mogil, J.S.; Trang, T.; et al. Microglial P2X4R-evoked pain hypersensitivity is sexually dimorphic in rats. Pain. 2018, 159, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorge, R.E.; Mapplebeck, J.C.; Rosen, S.; Beggs, S.; Taves, S.; Alexander, J.K.; Martin, L.J.; Austin, J.-S.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Chen, D.; et al. Different immune cells mediate mechanical pain hypersensitivity in male and female mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorge, R.E.; Totsch, S.K. Sex Differences in Pain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert, D.; Duveau, A.; Carracedo, S.; Linck, N.; Langla, A.; Muramatsu, R.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Rassendren, F.; Grutter, T.; Fossat, P.; et al. Microglial P2X4 receptors are essential for spinal neurons hyperexcitability and tactile allodynia in male and female neuropathic mice. Iscience 2023, 26, 108110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, L.W.; Yeung, S.C.; Cheung, C.W. Enriched Environment and Effects on Neuropathic Pain: Experimental Findings and Mechanisms. Pain. Pract. 2018, 18, 1068–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Sasaki, A.; Nakata, E.; Kohno, K.; Masuda, T.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Imai, T.; Kuraishi, Y.; Tsuda, M.; et al. A novel P2X4 receptor-selective antagonist produces anti-allodynic effect in a mouse model of herpetic pain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Tsuda, M. Microglia-neuron interactions in the models of neuropathic pain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 169, 113614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Tsuda, M. Microglia in neuropathic pain: Cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic receptors and pain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1717–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Berta, T.; Nedergaard, M. Glia and pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain. 2013, 154 (Suppl. 1), S10–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.S.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Suter, M.R. P38 mapk, microglial signaling, and neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain. 2007, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Chen, D.; Lin, F.; Chen, M.; Yu, H.; Hou, L.; Li, C. Role of interleukin-4, the chemokine CCL3 and its receptor CCR5 in neuropathic pain. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 77, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrini, F.; De Koninck, Y. Microglia control neuronal network excitability via BDNF signalling. Neural Plast. 2013, 2013, 429815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, B.U.; Kummer, K.K.; Leitner, M.G.; Kress, M. Chloride—The Underrated Ion in Nociceptors. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.A. BDNF in neuropathic pain; the culprit that cannot be apprehended. Neuroscience 2024, 543, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Gómez, P.; Garcia-Serrano, A.; Visioli, F.; Fontecha, J. relevance of dietary glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids to human health. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2015, 101, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eros, G.; Ibrahim, S.; Siebert, N.; Boros, M.; Vollmar, B. Oral phosphatidylcholine pretreatment alleviates the signs of experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Ning, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Supraphysiologic doses of 17β-estradiol aggravate depression-like behaviors in ovariectomized mice possibly via regulating microglial responses and brain glycerophospholipid metabolism. J. Neuroinflammation 2023, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Hernández, Y.; Lara-Ramírez, E.E.; Salgado-Bustamante, M.; López, J.A.; Oropeza-Valdez, J.J.; Jaime-Sánchez, E.; Castañeda-Delgado, J.E.; Magaña-Aquino, M.; Murgu, M.; Enciso-Moreno, J.A. Glycerophospholipid Metabolism Alterations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Tuberculosis Comorbidity. Arch. Med. Res. 2019, 50, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, Y.; Horikawa, M.; Sato, S.; Eto, F.; Hanada, M.; Banno, T.; Arima, H.; Ushirozako, H.; Yamada, T.; Xu, D.; et al. Lysophosphatidic acid precursor levels decrease and an arachidonic acid-containing phosphatidylcholine level increases in the dorsal root ganglion of mice after peripheral nerve injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 698, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Nagai, J.; Chun, J.; Ueda, H. An LPA species (18:1 LPA) plays key roles in the self-amplification of spinal LPA production in the peripheral neuropathic pain model. Mol. Pain. 2013, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindblom, R.P.; Berg, A.; Ström, M.; Aeinehband, S.; Dominguez, C.A.; Al Nimer, F.; Abdelmagid, N.; Heinig, M.; Zelano, J.; Harnesk, K.; et al. Complement receptor 2 is up regulated in the spinal cord following nerve root injury and modulates the spinal cord response. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Uchida, H.; Nagai, J.; Inoue, M.; Aoki, J.; Ueda, H. Evidence for de novo synthesis of lysophosphatidic acid in the spinal cord through phospholipase A2 and autotaxin in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 333, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y. Trps and pain. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Du, L.; Liu, S.; Lan, Z.; Zang, K.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, P.L.; et al. A TRPV4-dependent neuroimmune axis in the spinal cord promotes neuropathic pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e161507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Meng, H.Y.; Liu, S.M.; Lan, Z.; Zang, K.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, P.L.; et al. Identification of key metabolic changes during liver fibrosis progression in rats using a urine and serum metabolomics approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, L.; Gao, R.; Yao, M.; Qu, X.; Sun, G.; Fu, Q.; Hu, C.; Han, G. Ferroptosis: A new regulatory mechanism in neuropathic pain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1206851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Zecca, L.; Hong, J.S. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: Uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, X.; Jiang, W.; Li, W.; Zhu, S.; Liao, C.; Zou, L.; Ding, R.; Chen, J. Advanced oxidation protein products induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Størkson, R.V.; Kjørsvik, A.; Tjølsen, A.; Hole, K. Lumbar catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1996, 65, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.J.; Xie, Y.K. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 1988, 33, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, W.J. Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1980, 20, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, C.; Liu, T.; Abdul, M.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, J.-L. Pellino1 regulates neuropathic pain as well as microglial activation through the regulation of MAPK/NF-κB signaling in the spinal cord. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, M.; Gao, J.; Huang, R.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; et al. Daphnetin Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain via Regulation of Microglial Responses and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in the Spinal Cord. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060789
Liang W, Zhang T, Zhang M, Gao J, Huang R, Huang X, Chen J, Cheng L, Zhang L, Huang Z, et al. Daphnetin Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain via Regulation of Microglial Responses and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in the Spinal Cord. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(6):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060789
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Wulin, Tianrui Zhang, Mingqian Zhang, Jiahui Gao, Rikang Huang, Xiyan Huang, Jianhua Chen, Lu Cheng, Liyuan Zhang, Zhishan Huang, and et al. 2024. "Daphnetin Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain via Regulation of Microglial Responses and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in the Spinal Cord" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 6: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060789
APA StyleLiang, W., Zhang, T., Zhang, M., Gao, J., Huang, R., Huang, X., Chen, J., Cheng, L., Zhang, L., Huang, Z., Tan, Q., Jia, Z., & Zhang, S. (2024). Daphnetin Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain via Regulation of Microglial Responses and Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in the Spinal Cord. Pharmaceuticals, 17(6), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060789






