Box-Behnken Design-Based Optimization and Evaluation of Lipid-Based Nano Drug Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Bromocriptine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
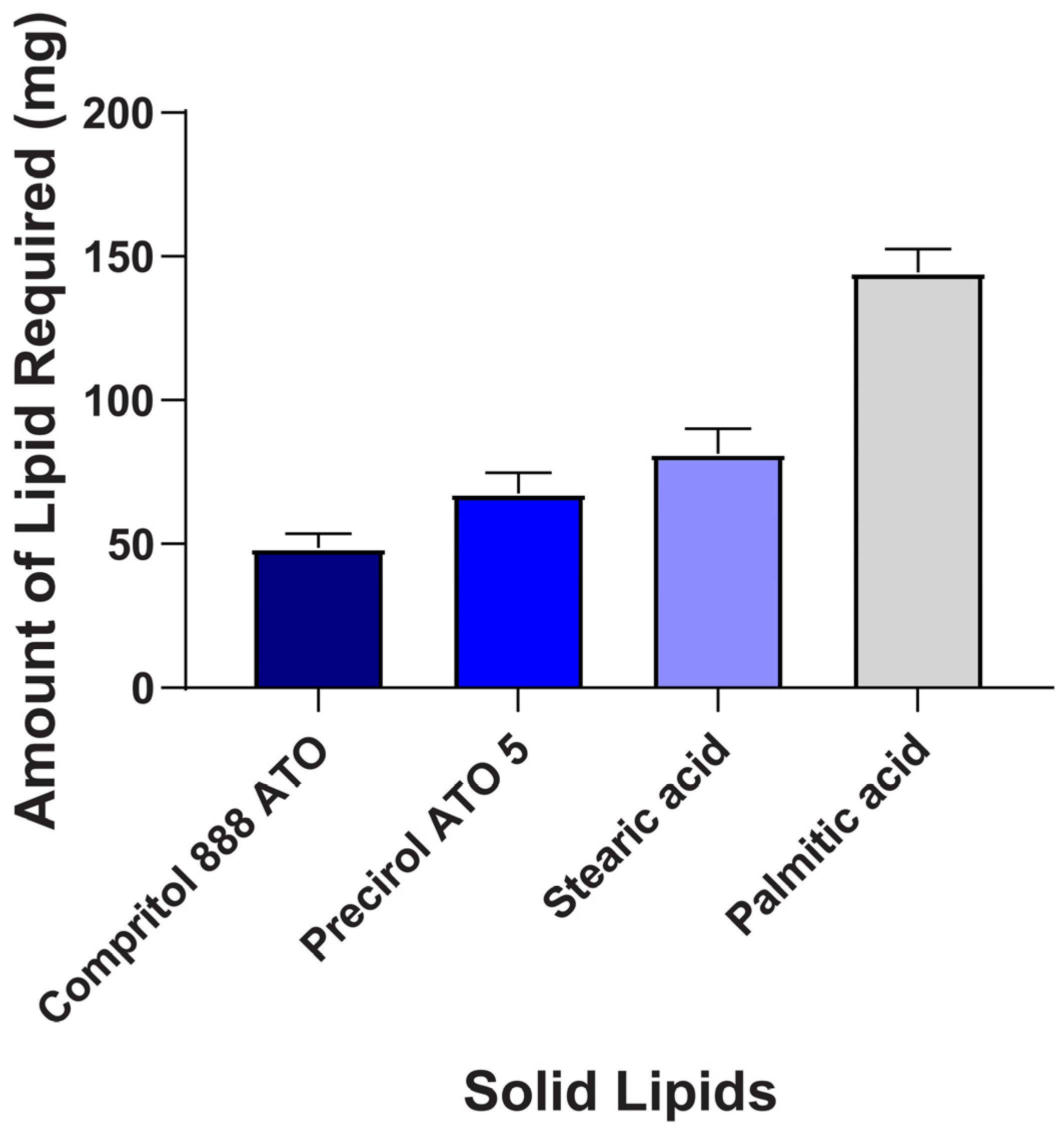
2.1. Screening of Lipids and Surfactant
2.2. Optimization of BCR-SLN and BCR-NLC
2.3. Influence of Independent Variables on Responses of BCR-SLN and BCR-NLC
2.3.1. Perturbation Graphs for Optimization of BCR-SLN and BCR-NLC
2.3.2. Response Surface Plots for Optimization of BCR-SLN
Effects of Variables on Responses
2.3.3. Response Surface Plots for Optimization of BCR-NLC
Effects of Variables on Responses
2.4. Optimization of Formulation
2.5. Evaluation of Optimized BCR-SLN and BCR-NLC Formulation
2.5.1. Particle Size, PDI, and Entrapment Efficiency
2.5.2. Microscopic Analysis by HR-TEM
2.5.3. DSC of Optimized Formulations
2.5.4. In Vitro Release Studies
2.6. Storage Stability Studies
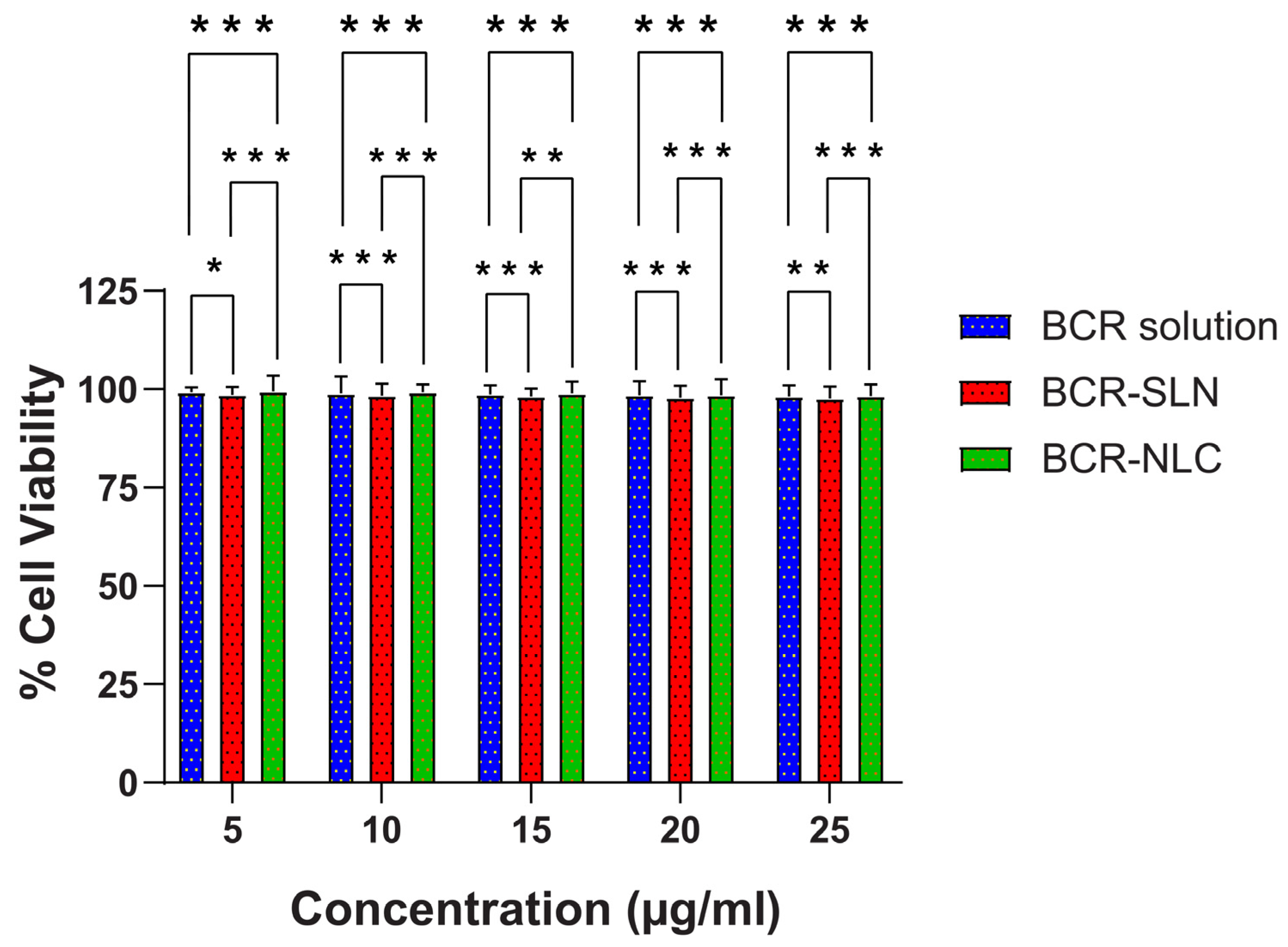
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies by MTT Assay
2.8. Pharmacokinetic and Brain Distribution Kinetic Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Screening of Solid Lipid and Liquid Lipid
3.2.1. Solubility Study
3.2.2. Partitioning Behaviour of Bromocriptine
3.2.3. Screening of Liquid Lipid
3.2.4. Effect of Solid Lipid: Liquid Lipid Ratio
3.3. Preparation of BCR-SLNs and NLCs
3.4. Optimization of SLNs and NLCs by Box Behnken Design
3.5. Characterization of Prepared Nanoparticles
3.5.1. Nanoparticle Size Analysis
3.5.2. Entrapment Efficiency
3.5.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HR-TEM) Analysis
3.5.4. Crystallinity Studies Using DSC
3.5.5. In Vitro Release Studies
3.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
3.7. Stability Study
3.8. In Vivo Studies
3.8.1. Experimental Animals and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic and Brain Distribution Kinetic Study of BCR-SLN and BCR-NLC
3.8.2. Analysis of BCR in Brain Samples
3.8.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Stefano, A.; Sozio, P.; Iannitelli, A.; Cerasa, L.S. New Drug Delivery Strategies for Improved Parkinson’s Disease Therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Gómez, G.; Cortés, H.; Magaña, J.J.; Leyva-García, N.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Florán, B. Nanoparticle Technology for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Surface Phenomena in Reaching the Brain. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. Blood–Brain Barrier Delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G.; Merlo, L.; Caffo, M. Innovative Brain Tumor Therapy; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Angolkar, M.; Paramshetti, S.; Halagali, P.; Jain, V.; Patil, A.B.; Somanna, P. Nanotechnological Advancements in the Brain Tumor Therapy: A Novel Approach. Ther. Deliv. 2022, 13, 531–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabathuler, R. Approaches to Transport Therapeutic Drugs across the Blood–Brain Barrier to Treat Brain Diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asha Spandana, K.M.; Bhaskaran, M.; Karri, V.N.; Natarajan, J. A Comprehensive Review of Nano Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of CNS Disorders. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.L.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Wu, X.Y.; Bendayan, R. Nanotechnology Applications for Improved Delivery of Antiretroviral Drugs to the Brain. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, I.P.; Bhandari, R.; Bhandari, S.; Kakkar, V. Potential of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles in Brain Targeting. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Boo, D.H.; No, H.; Kang, B.Y.; Kim, E.M.; Hwang, O.; Choi, H.J. Protective Effect of Bromocriptine against BH4-Induced Cath.a Cell Death Involving up-Regulation of Antioxidant Enzymes. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 451, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoort, P.; Thiery, M.; Baele, G.; Clement, D.; Dhont, M. Bromocriptine in an Injectable Retard Form for Puerperal Lactation Suppression: Comparison with Estandron Prolongatum. Obstet. Gynecol. 1987, 70, 866–869. [Google Scholar]
- Eleraky, E.N.; Omar, M.M.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Abou-Taleb, A.H. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers to Mediate Brain Delivery of Temazepam: Design and In Vivo Study. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kletzky, O.A.; Vermesh, M. Effectiveness of Vaginal Bromocriptine in Treating Women with Hyperprolactinemia. Fertil. Steril. 1989, 51, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdő, F.; Bors, L.A.; Farkas, D.; Bajza, Á.; Gizurarson, S. Evaluation of Intranasal Delivery Route of Drug Administration for Brain Targeting. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicinelli, E.; Cignarelli, M.; Petruzzi, D.; Matteo, G.; Rucria, C.; Schonauer, L.M. Nasal Spray Administration of Bromocriptine: Pharmacology and Effect on Serum Prolactin Level in Puerperal Women. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 1996, 10, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, B.; Tirumalesh, C.; Dinesh, S.; Narendar, D. Zotepine Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery: Development, Characterization, and in Vivo Pharmacokinetic Studies. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Gu, S.; Du, Y.; Shen, M.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers for Oral Delivery of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, G.; Gupta, V.; Kaur, R.; Thakur, K.; Malik, R.; Kumar, A.; Kaushal, N.; Katare, O.P.; Raza, K. Oral Delivery of Methylthioadenosine to the Brain Employing Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Pharmacokinetic, Behavioral, and Histopathological Evidences. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambhire, V.M. Enhanced Oral Delivery of Asenapine Maleate from Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Pharmacokinetic and Brain Distribution Evaluations. Asian J. Pharm. 2018, 12, 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Rehman, S.; Nabi, B.; Iqubal, A.; Nehal, N.; Fahmy, U.A.; Kotta, S.; Baboota, S.; Md, S.; Ali, J. Boosting the Brain Delivery of Atazanavir through Nanostructured Lipid Carrier-Based Approach for Mitigating NeuroAIDS. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Q.; Niu, J.; Guo, E.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Rao, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Neutrophil Membrane-Camouflaged Polyprodrug Nanomedicine for Inflammation Suppression in Ischemic Stroke Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2311803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Fantin, M.; Marti, M.; Drechsler, M.; Paccamiccio, L.; Mariani, P.; Sivieri, E.; Lain, F.; Menegatti, E.; Morari, M.; et al. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Delivery Systems for Bromocriptine. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intranasal Delivery of Bromocriptine Loaded Lipid Nano Carriers for Enhanced Brain Delivery in Parkinson’s Disease-MDS Abstracts. Available online: https://www.mdsabstracts.org/abstract/intranasal-delivery-of-bromocriptine-loaded-lipid-nano-carriers-for-enhanced-brain-delivery-in-parkinsons-disease/ (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Souto, E.B.; Mehnert, W.; Müller, R.H. Polymorphic Behaviour of Compritol®888 ATO as Bulk Lipid and as SLN and NLC. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.S.; Gahane, A.; Thakur, A.K. Deciphering the Mechanism and Structural Features of Polysorbate 80 during Adsorption on PLGA Nanoparticles by Attenuated Total Reflectance–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108545–108557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, K.; Afzal, S.M.; Surender, G.; Kishan, V. Tween 80 Containing Lipid Nanoemulsions for Delivery of Indinavir to Brain. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2013, 3, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, S.; Amin Nordin, S.; Abd Gani, S.S.; Shamsuddin, A.F.; Basri, M.; Bin Basri, H. Development of Nanoemulsion for Efficient Brain Parenteral Delivery of Cefuroxime: Designs, Characterizations, and Pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2571–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Z.; Yi, J.; Yang, X.; Hu, J.; Feng, X. Preparation and Drug Release Study of Novel Nanopharmaceuticals with Polysorbate 80 Surface Adsorption. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 4718045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirak, M.B.; Pezeshki, A. Effect of Surfactant Concentration on the Particle Size, Stability and Potential Zeta of Beta Carotene Nano Lipid Carrier. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 924–932. [Google Scholar]
- Vivek, K.; Reddy, H.; Murthy, R.S.R. Investigations of the Effect of the Lipid Matrix on Drug Entrapment, in Vitro Release, and Physical Stability of Olanzapine-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, V.; Bansal, K.; Verma, A.; Yadav, N.; Thakur, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Rosenholm, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Emerging Colloidal Nano Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zur Mühlen, A.; Schwarz, C.; Mehnert, W. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) for Controlled Drug Delivery–Drug Release and Release Mechanism. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.d.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano Based Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.-H.; Lee, B.-J.; Cho, C.-W. Mechanisms of Drug Release from Advanced Drug Formulations Such as Polymeric-Based Drug-Delivery Systems and Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Investig. 2017, 47, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Falconer, R.J.; Zhao, C.-X. Lipid Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Adv. Nanobiomed. Res. 2022, 2, 2100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Zhang, D.; Hao, L.; Li, C.; Qi, L.; Guo, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Design and Characterization of Amoitone B-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Controlled Drug Release. Drug Deliv. 2013, 20, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abousamra, M.M.; Mohsen, A.M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Tolnaftate: Design, Optimization and in-Vitro Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Uprit, S.; Kumar Sahu, R.; Roy, A.; Pare, A. Preparation and Characterization of Minoxidil Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Gel for Effective Treatment of Alopecia. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, I.; Yasir, M.; Verma, M.; Singh, A.P. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Groundbreaking Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, A.; Singh, I.; Pawar, P.; Grover, K. Design and Evaluation of Voriconazole Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Ophthalmic Application. J. Drug Deliv. 2016, 2016, 6590361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmaa Paarakh, M.; Ani Jose, P.; Setty, C.M.; Christoper, P. Release Kinetics–Concepts And Applications. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Novel Drug Delivery Systems: Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandita, D.; Ahuja, A.; Lather, V.; Benjamin, B.; Dutta, T.; Velpandian, T.; Khar, R.K. Development of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Enhancing the Oral Bioavailability of Paclitaxel. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilarasi, P.N.; Muthukumar, S.P.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Solid Lipid Nanoparticle Enhances Bioavailability of Hydroxycitric Acid Compared to a Microparticle Delivery System. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53784–53793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.-Y.; Li, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.-N.; Pan, W.-S.; Peng, J.-J.; Pan, Y.-S.; Tang, X. Preparation and Characterization of Vinpocetine Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) for Improved Oral Bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 394, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.T.; Barua, S.; Kim, H.; Hong, S.-C.; Yoo, S.-Y.; Jeon, H.; Cho, Y.; Gil, S.; Oh, K.; Lee, J. Absorption Study of Genistein Using Solid Lipid Microparticles and Nanoparticles: Control of Oral Bioavailability by Particle Sizes. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, P.; Mahjub, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Derakhshandeh, K.; Ghaleiha, A.; Mahboobian, M.M. Pharmacokinetics and Brain Distribution Studies of Perphenazine-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Shah, F.A.; Rana, I.; Ansari, M.M.; Din, F.u.; Rizvi, S.Z.H.; Aman, W.; Lee, G.-Y.; Lee, E.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; et al. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers-Mediated Brain Delivery of Carbamazepine for Improved in Vivo Anticonvulsant and Anxiolytic Activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 577, 119033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.; Date, A.; Joshi, M.; Patravale, V. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) of Tretinoin: Potential in Topical Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 345, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazuli, I.; Annu; Nabi, B.; Moolakkadath, T.; Alam, T.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Optimization of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Lurasidone Hydrochloride Using Box-Behnken Design for Brain Targeting: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3082–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkateswarlu, V.; Manjunath, K. Preparation, Characterization and in Vitro Release Kinetics of Clozapine Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalikwar, S.S.; Belgamwar, V.S.; Talele, V.R.; Surana, S.J.; Patil, M.U. Formulation and Evaluation of Nimodipine-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Delivered via Lymphatic Transport System. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 97, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Kumar, T.; Jain, V. Formulation Optimization of Erythromycin Solid Lipid Nanocarrier Using Response Surface Methodology. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 689391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aji Alex, M.R.; Chacko, A.J.; Jose, S.; Souto, E.B. Lopinavir Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) for Intestinal Lymphatic Targeting. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 42, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasya, G.; Aksu, B.; Badilli, U.; Onay-Besikci, A.; Tarimci, N. QbD Guided Early Pharmaceutical Development Study: Production of Lipid Nanoparticles by High Pressure Homogenization for Skin Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kesarla, R.; Chotai, N.; Misra, A.; Omri, A. Systematic Approach for the Formulation and Optimization of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles of Efavirenz by High Pressure Homogenization Using Design of Experiments for Brain Targeting and Enhanced Bioavailability. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5984014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.; Sood, S.; Gowthamarajan, K. Optimization of Artemether-Loaded NLC for Intranasal Delivery Using Central Composite Design. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teeranachaideekul, V.; Souto, E.B.; Junyaprasert, V.B.; Müller, R.H. Cetyl Palmitate-Based NLC for Topical Delivery of Coenzyme Q10–Development, Physicochemical Characterization and in Vitro Release Studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, D.; Spiess, E.; Paweletz, N.; Benke, R. A Procedure for Rupture-free Preparation of Confluently Grown Monolayer Cells for Scanning Electron Microscopy. J. Electron. Microsc. Tech. 1984, 1, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ng, W.K.; Kanaujia, P.; Kim, S.; Tan, R.B.H. Formulation Design, Preparation and Physicochemical Characterizations of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Containing a Hydrophobic Drug: Effects of Process Variables. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpugdee-Vollrath, M.; Ibold, Y.; Sriamornsak, P. Solid State Characterization of Trans Resveratrol Complexes with Different Cyclodextrins. J. Asian Assoc. Sch. Pharm. 2012, 1, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mircioiu, C.; Voicu, V.; Anuta, V.; Tudose, A.; Celia, C.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Sandulovici, R.; Mircioiu, I. Mathematical Modeling of Release Kinetics from Supramolecular Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Modeling and Comparison of Dissolution Profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansraj, G.P.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, P. Sumatriptan Succinate Loaded Chitosan Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhanced Anti-Migraine Potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jojo, G.M.; Kuppusamy, G.; De, A.; Karri, V.N. Formulation and Optimization of Intranasal Nanolipid Carriers of Pioglitazone for the Repurposing in Alzheimer’s Disease Using Box-Behnken Design. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sita, V.G.; Vavia, P. Bromocriptine Nanoemulsion-Loaded Transdermal Gel: Optimization Using Factorial Design, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Run | A | B | C | PS (U1) | PDI (U2) | EE (U3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg | % | RPM | nm | % | ||
| 1 | 250 | 2 | 5000 | 262.32 ± 12.31 | 0.364 ± 0.025 | 65.87 ± 1.10 |
| 2 | 300 | 2.5 | 5000 | 251.78 ± 10.28 | 0.289 ± 0.022 | 65.24 ± 0.96 |
| 3 | 250 | 1.5 | 7500 | 270.1 ± 12.02 | 0.387 ± 0.039 | 64.01±1.45 |
| 4 | 300 | 2 | 7500 | 257.78 ± 11.89 | 0.302 ± 0.042 | 67.91 ± 2.22 |
| 5 | 300 | 1.5 | 10,000 | 264.21 ± 8.12 | 0.341 ± 0.031 | 66.52 ± 1.56 |
| 6 | 350 | 1.5 | 7500 | 314.91 ± 10.58 | 0.514 ± 0.035 | 70.42 ± 0.87 |
| 7 | 350 | 2.5 | 7500 | 287.64 ± 11.26 | 0.398 ± 0.041 | 68.17 ± 1.34 |
| 8 | 300 | 2 | 7500 | 258.54 ± 9.44 | 0.297 ± 0.024 | 67.74 ± 1.89 |
| 9 | 350 | 2 | 10,000 | 290.21 ± 8.06 | 0.412 ± 0.032 | 72.01 ± 2.31 |
| 10 | 250 | 2.5 | 7500 | 228.54 ± 7.25 | 0.246 ± 0.018 | 66.27 ± 1.89 |
| 11 | 300 | 2.5 | 10,000 | 245.65 ± 11.21 | 0.321 ± 0.042 | 69.02 ± 3.45 |
| 12 | 250 | 2 | 10,000 | 224.16 ± 8.51 | 0.21 ± 0.016 | 71.12 ± 2.19 |
| 13 | 350 | 2 | 5000 | 292.24 ± 10.88 | 0.451 ± 0.019 | 72.01 ± 1.49 |
| 14 | 300 | 2 | 7500 | 256.12 ± 9.11 | 0.314 ± 0.030 | 68.34 ± 2.37 |
| 15 | 300 | 2 | 7500 | 256.64 ± 12.25 | 0.291 ± 0.025 | 68.21 ± 1.12 |
| 16 | 300 | 1.5 | 5000 | 305.24 ± 13.48 | 0.487 ± 0.031 | 66.34 ± 1.87 |
| 17 | 350 | 2 | 7500 | 257.01 ± 11.87 | 0.297 ± 0.015 | 68.01 ± 2.18 |
| R2 Value | Predicted R2 | Adjusted R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 0.9981 | 0.9747 | 0.9956 |
| U2 | 0.9885 | 0.8545 | 0.9737 |
| U3 | 0.9896 | 0.8726 | 0.9763 |
| Run | A | B | C | PS (V1) | PDI (V2) | EE (V3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (% w/v) | (rpm) | (nm) | (%) | |||
| 1 | 90:10 | 2.5 | 7500 | 259.6 ± 9.51 | 0.391 ± 0.040 | 75.87 ± 4.4 |
| 2 | 80:20 | 2 | 7500 | 226.8 ± 8.50 | 0.364 ± 0.022 | 77.65 ± 2.9 |
| 3 | 80:20 | 2.5 | 10,000 | 210.5 ± 6.55 | 0.245 ± 0.021 | 78.91 ± 3.1 |
| 4 | 70:30 | 2 | 10,000 | 196.5 ± 8.32 | 0.201 ± 0.018 | 84.02 ± 2.1 |
| 5 | 70:30 | 2.5 | 7500 | 205.2 ± 7.61 | 0.228 ± 0.032 | 82.81 ± 5.2 |
| 6 | 80:20 | 2 | 7500 | 228.01 ± 8.54 | 0.349 ± 0.025 | 77.54 ± 2.5 |
| 7 | 90:10 | 2 | 10,000 | 258.5 ± 5.87 | 0.411 ± 0.031 | 74.13 ± 3.5 |
| 8 | 80:20 | 1.5 | 10,000 | 243.54 ± 7.77 | 0.375 ± 0.035 | 76.54 ± 1.8 |
| 9 | 70:30 | 1.5 | 7500 | 236 ± 9.01 | 0.285 ± 0.021 | 80.61 ± 2.2 |
| 10 | 90:10 | 1.5 | 7500 | 272.5 ± 8.53 | 0.507 ± 0.067 | 72.16 ± 2.8 |
| 11 | 90:10 | 2 | 5000 | 260.1 ± 9.14 | 0.464 ± 0.051 | 75.01 ± 1.9 |
| 12 | 80:20 | 2 | 7500 | 228.4 ± 7.53 | 0.368 ± 0.026 | 77.49 ± 2.3 |
| 13 | 80:20 | 2.5 | 5000 | 246.3 ± 8.22 | 0.342 ± 0.031 | 79.01 ± 2.4 |
| 14 | 70:30 | 2 | 5000 | 229.54 ± 10.31 | 0.294 ± 0.026 | 81.02 ± 2.0 |
| 15 | 80:20 | 2 | 7500 | 228.7 ± 7.84 | 0.365 ± 0.023 | 77.68 ± 2.5 |
| 16 | 80:20 | 1.5 | 5000 | 245.21 ± 12.31 | 0.41 ± 0.040 | 74.96 ± 1.8 |
| 17 | 80:20 | 2 | 7500 | 229.5 ± 8.10 | 0.361 ± 0.024 | 77.65 ± 2.4 |
| R2 Value | Predicted R2 | Adjusted R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | 0.9966 | 0.9548 | 0.9923 |
| V2 | 0.9969 | 0.9804 | 0.9929 |
| V3 | 0.9991 | 0.9874 | 0.9978 |
| Zero-Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer-Peppas | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | R2 | R2 | n | |
| SLN | 0.7572 | 0.8322 | 0.9449 | 0.9516 | 0.54 |
| NLC | 0.6738 | 0.7792 | 0.9037 | 0.9238 | 0.55 |
| Formulation | Temp. | Parameters | Sample Interval (Months) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 6 | |||
| BCR SLN | 4 °C | PS (nm) | 219.21 ± 1.3 | 226.2 ± 7.6 | 232 ± 5.6 | 241.4 ± 6.1 |
| PDI | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.042 | 0.31 ± 0.038 | 0.42 ± 0.062 | ||
| EE (%) | 72.2 ± 1.20 | 67.78 ± 0.74 | 61.24 ± 0.48 | 56.87 ± 0.75 | ||
| 25 °C | PS (nm) | 219.21 ± 1.3 | 229.8 ± 2.9 | 236 ± 6.6 | 249.9 ± 6.4 | |
| PDI | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.043 | 0.31 ± 0.023 | 0.45 ± 0.087 | ||
| EE (%) | 71.12 ± 1.20 | 68.01 ± 0.81 | 65.21 ± 0.91 | 52.24 ± 1.68 | ||
| BCR NLC | 4 °C | PS (nm) | 182.87 ± 2.2 | 184.54 ± 3.3 | 186 ± 3.6 | 189.79 ± 4.9 |
| PDI | 0.16 ± 0.004 | 0.16 ± 0.43 | 0.18 ± 0.23 | 0.19 ± 0.87 | ||
| EE (%) | 83.57 ± 1.2 | 81.96 ± 0.89 | 80.58 ± 0.67 | 79.02 ± 0.47 | ||
| 25 °C | PS (nm) | 182.87 ± 2.2 | 184.7 ± 2.8 | 188.8 ± 4.8 | 191.2 ± 4.6 | |
| PDI | 0.16 ± 0.004 | 0.17 ± 0.15 | 0.18 ± 0.46 | 0.20 ± 0.44 | ||
| EE (%) | 83.57 ± 1.2 | 81.84 ± 0.87 | 79.04 ± 0.69 | 77.88 ± 0.24 | ||
| BCR Solution | BCR-SLN | BCR-NLC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRAIN | PLASMA | BRAIN | PLASMA | BRAIN | PLASMA | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1.66 ± 0.008 | 1.84 ± 0.01 | 15.69 ± 1.16 | 12.96 ± 0.29 | 18.49 ± 0.953 | 14.84 ± 0.29 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| T1/2 | 1.60 ± 0.16 | 2.17 ± 0.02 | 6.11 ± 0.49 | 5.79 ± 0.31 | 7.12 ± 0.16 | 6.87 ± 0.63 |
| Ke (h−1) | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.004 | 0.11 ± 0.009 | 0.12 ± 0.006 | 0.09 ± 0.002 | 0.10 ± 0.009 |
| AUC (ng h/mL) | 5.16 ± 0.28 | 6.50 ± 0.09 | 84.13 ± 5.98 | 69.83 ± 3.06 | 103.37 ± 3.57 | 80.28 ± 2.57 |
| AUC | 5.37 ± 0.35 | 7.14 ± 0.12 | 150.96 ± 11.3 | 121.67 ± 8.09 | 205.98 ± 5.41 | 156.59 ± 10.6 |
| Independent Variables | Levels Used | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Solid lipid concentration (mg) | 250 | 300 | 350 |
| Surfactant concentration (% w/v) | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| Homogenization Speed (rpm) | 5000 | 7500 | 10,000 |
| Dependent variables | |||
| PS (nm) (U1) | Minimum | ||
| PDI (U2) | Minimum | ||
| EE (%) (U3) | Maximum | ||
| Independent Variables | Levels Used | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Solid lipid: liquid lipid ratio | 70:30 | 80:20 | 90:10 |
| Surfactant concentration (% w/v) | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| Stirring speed (rpm) | 5000 | 7500 | 10,000 |
| Dependent variables | |||
| PS (nm) (V1) | Minimize | ||
| PDI (V2) | Maximum | ||
| EE (%) (V3) | Maximum | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
K M, A.S.; Angolkar, M.; Rahamathulla, M.; Thajudeen, K.Y.; Ahmed, M.M.; Farhana, S.A.; Shivanandappa, T.B.; Paramshetti, S.; Osmani, R.A.M.; Natarajan, J. Box-Behnken Design-Based Optimization and Evaluation of Lipid-Based Nano Drug Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Bromocriptine. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060720
K M AS, Angolkar M, Rahamathulla M, Thajudeen KY, Ahmed MM, Farhana SA, Shivanandappa TB, Paramshetti S, Osmani RAM, Natarajan J. Box-Behnken Design-Based Optimization and Evaluation of Lipid-Based Nano Drug Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Bromocriptine. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(6):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060720
Chicago/Turabian StyleK M, Asha Spandana, Mohit Angolkar, Mohamed Rahamathulla, Kamal Y. Thajudeen, Mohammed Muqtader Ahmed, Syeda Ayesha Farhana, Thippeswamy Boreddy Shivanandappa, Sharanya Paramshetti, Riyaz Ali M. Osmani, and Jawahar Natarajan. 2024. "Box-Behnken Design-Based Optimization and Evaluation of Lipid-Based Nano Drug Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Bromocriptine" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 6: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060720
APA StyleK M, A. S., Angolkar, M., Rahamathulla, M., Thajudeen, K. Y., Ahmed, M. M., Farhana, S. A., Shivanandappa, T. B., Paramshetti, S., Osmani, R. A. M., & Natarajan, J. (2024). Box-Behnken Design-Based Optimization and Evaluation of Lipid-Based Nano Drug Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Bromocriptine. Pharmaceuticals, 17(6), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060720







