Structural Modification and Optimisation of Hyperoside Oriented to Inhibit TGF-β-Induced EMT Activity in Alveolar Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
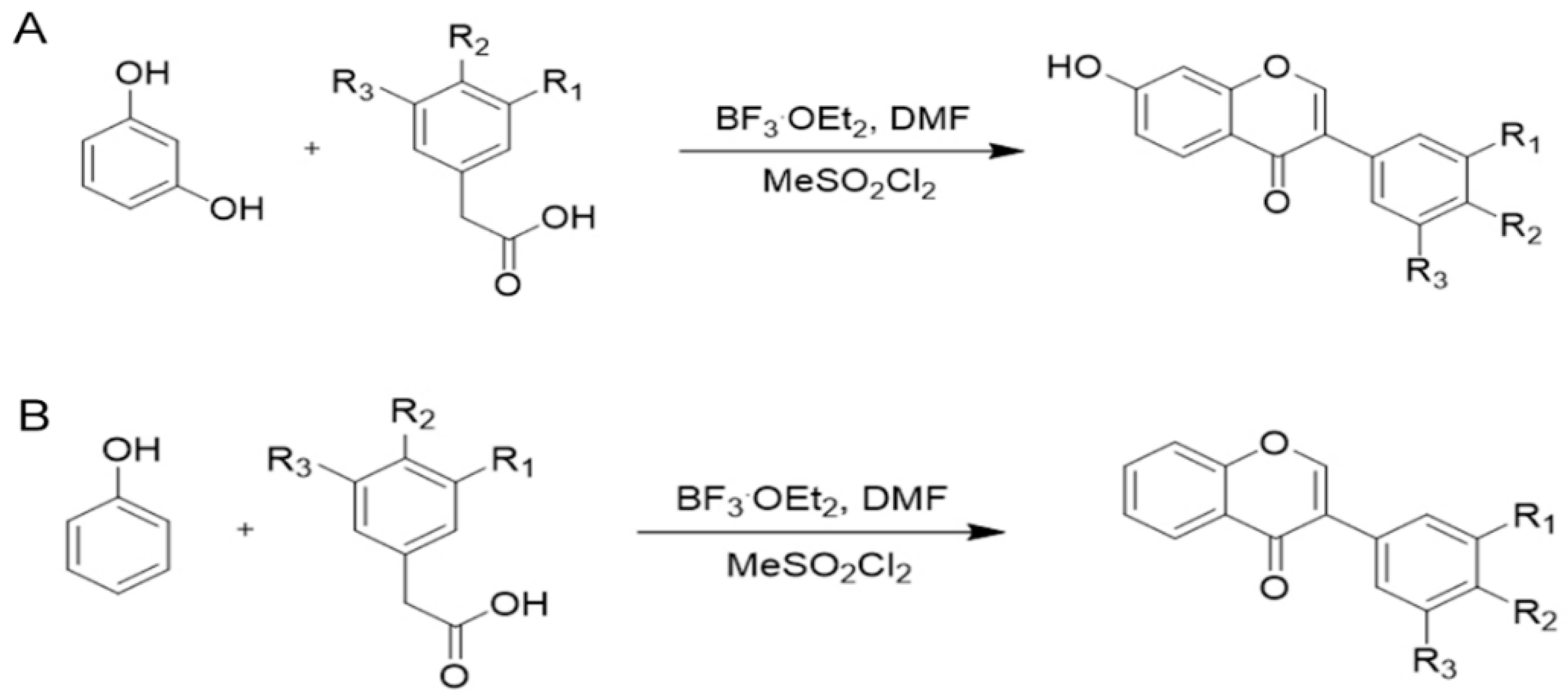
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. Effects of Hyperoside Derivatives on Cell Viability
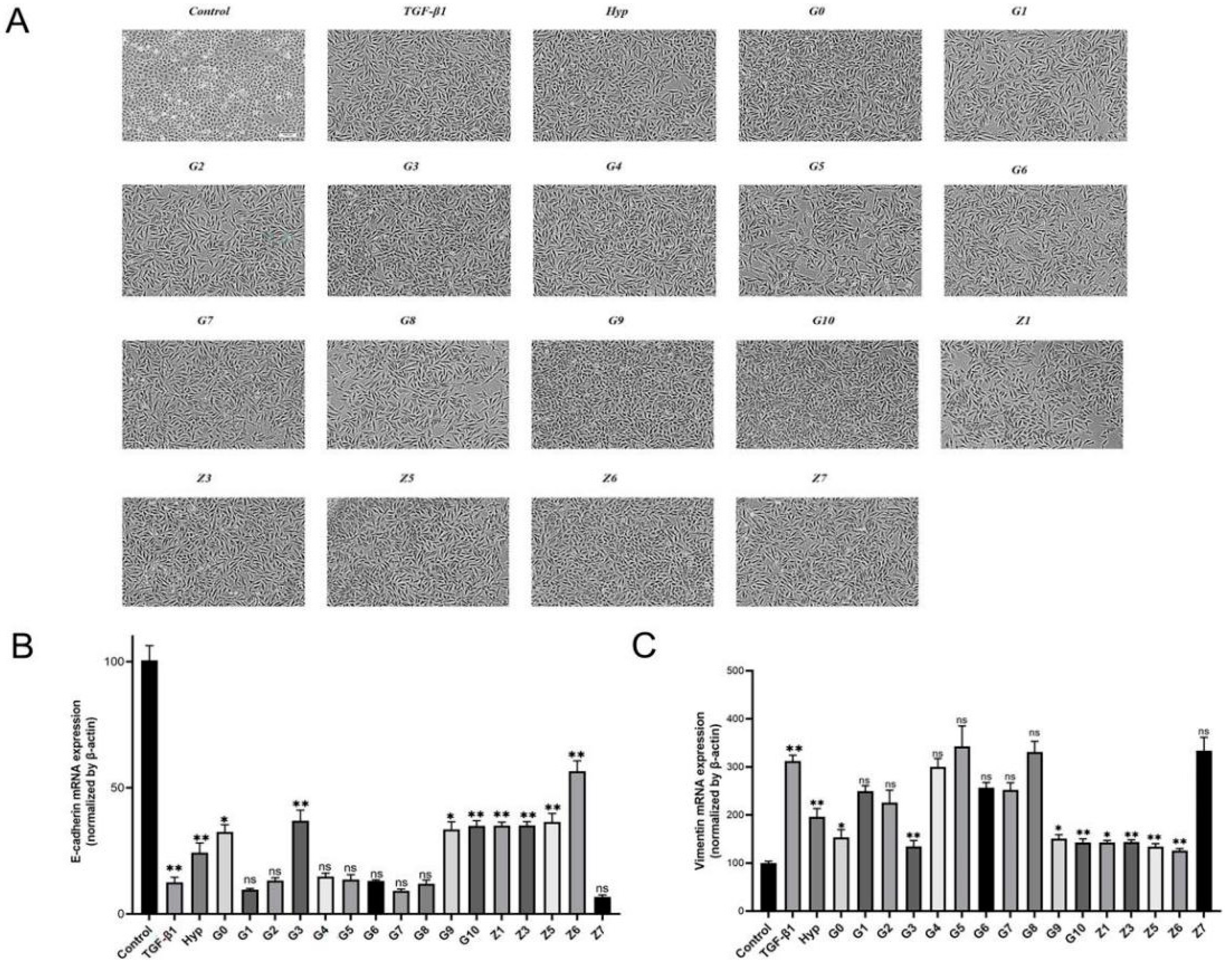
2.2.2. Preliminary Screening of Hyperoside and Its Derivatives with Anti-EMT Activity
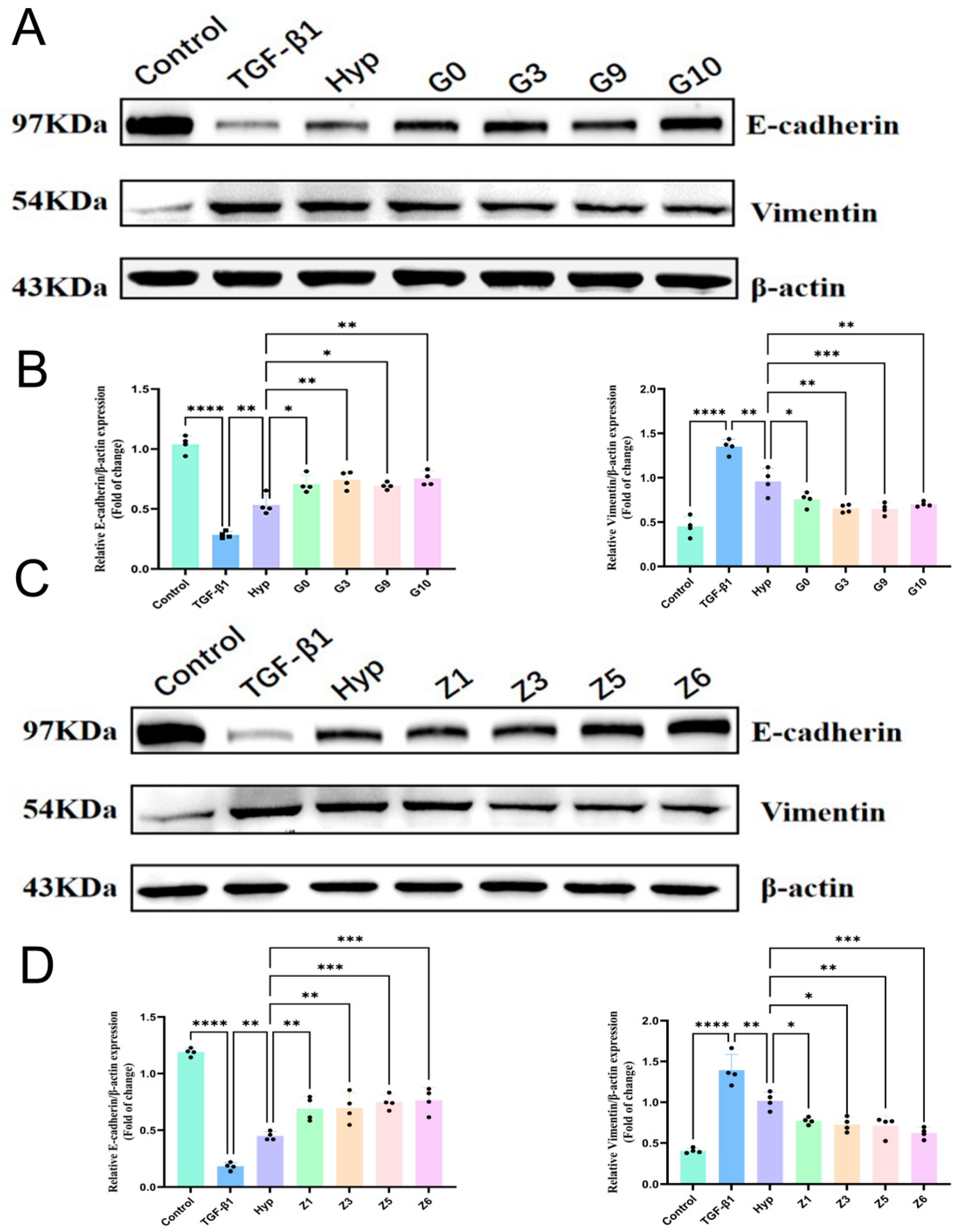
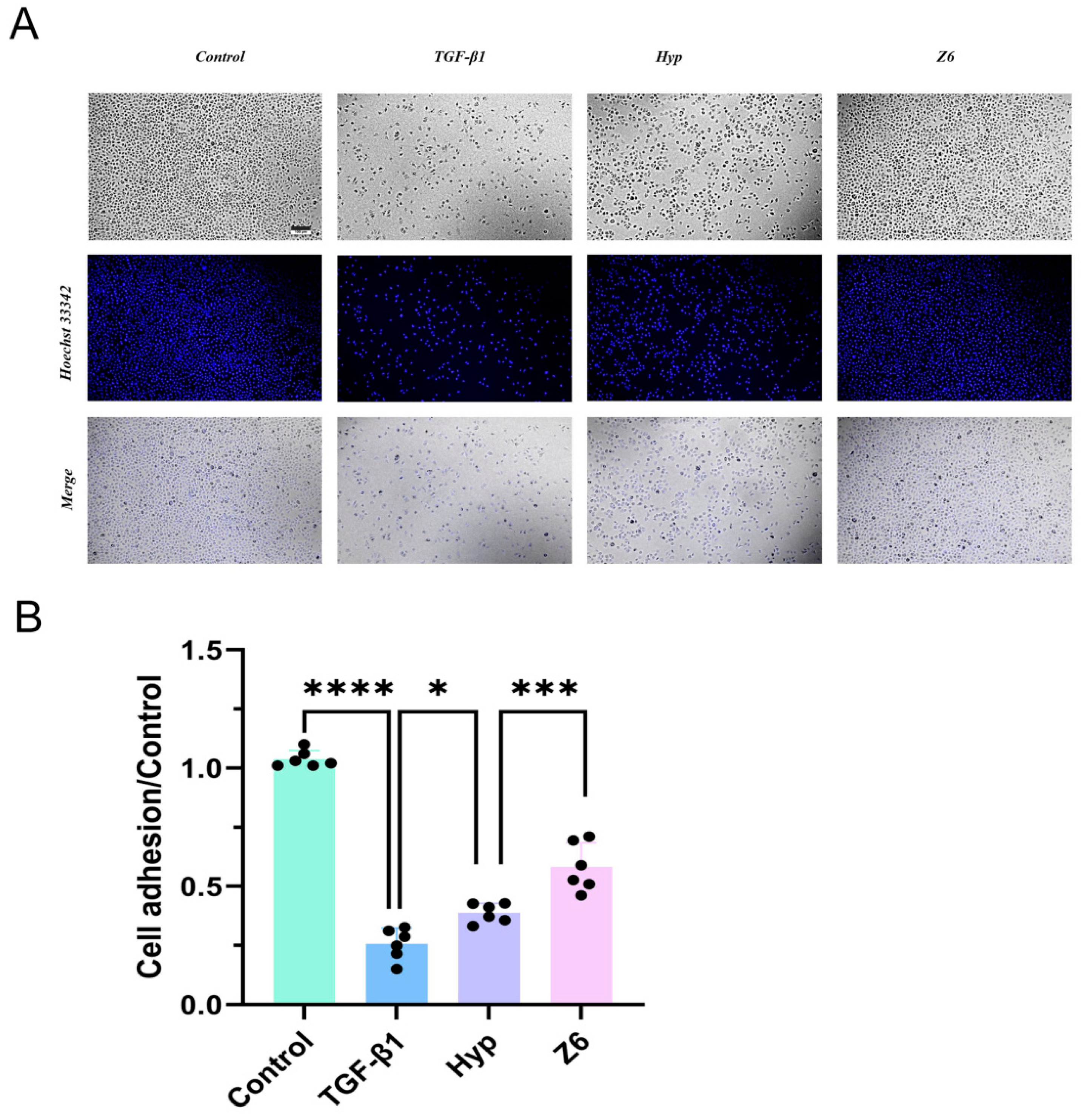
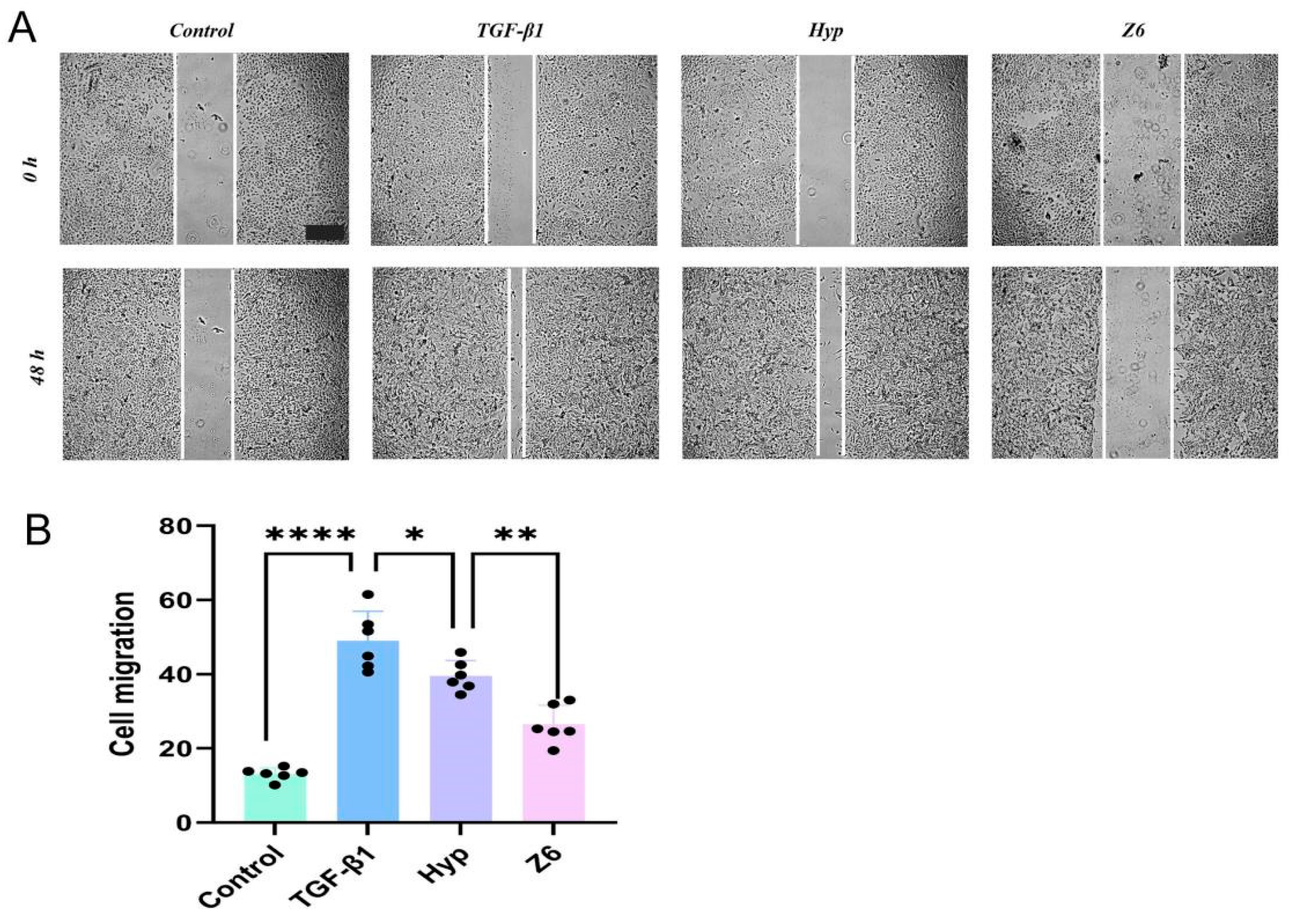
2.2.3. Validation of Hyperoside and Its Derivatives with Anti-EMT Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Methods
4.2. Synthesis
4.3. Cell Culture and Drug Configuration
4.3.1. Effect of Compounds on A549 Cell Activity by MTT Assay
4.3.2. qPCR Assay
4.3.3. Western Blot
4.3.4. Determination of Adhesion
4.3.5. Cell Migration
4.3.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, B.; Dai, L.; Cheng, X.; Meng, Z.; Yuan, L.; et al. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits TGF-β1-induced fibrogenesis through activating autophagy via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in MRC-5 cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2020, 52, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Yue, W.; Xu, K.; Cai, W.; Cui, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; He, J. Andrographolide attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-β1 in alveolar epithelial cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10501–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoz, D.F.; Lawson, W.E.; Blackwell, T.S. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A disorder of epithelial cell dysfunction. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 341, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, F.; Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, P.; Confalonieri, M. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: A Major Pathogenic Driver in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Medicina 2020, 56, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Chen, H.; Wu, H.; Tu, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C. Amiodarone induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549 cells via activation of TGF-β1. Drug. Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 43, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Sang, X.; You, X.; Wang, Y.; Paterson, I.C.; Hong, W.; Yang, X. Development of small molecule inhibitors targeting TGF-β ligand and receptor: Structures, mechanism, preclinical studies and clinical usage. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 191, 112154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, V. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Tumor Metastasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inui, N.; Sakai, S.; Kitagawa, M. Molecular Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis, with Focus on Pathways Related to TGF-β and the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.H.; Chen, D.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Feng, Y.L.; Cao, G.; Vaziri, N.D.; Zhao, Y.Y. New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 292, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, G.; Liang, Y.; Lu, F.; Zheng, R.; Zou, Q.; Hao, J. Inhibitory Effects of 3-Cyclopropylmethoxy-4-(difluoromethoxy) Benzoic Acid on TGF-beta1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation of In Vitro and Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Mohyeldin, R.H.; Bekhit, A.A.; Gomaa, W.; Zhao, Q.L.; Fathy, M. Vincamine Ameliorates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats; Targeting TGF-beta/MAPK/Snai1 Pathway. Molecules 2023, 28, 4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leask, A.; Abraham, D.J. TGF-beta signaling and the fibrotic response. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griggs, L.A.; Lemmon, C.A. Spatial Gradients of E-Cadherin and Fibronectin in TGF-beta1-Treated Epithelial Colonies Are Independent of Fibronectin Fibril Assembly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, V.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chikkaputtaiah, C.; Hazra, S.; Pal, M. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): A study from a structure, dynamics, and functional perspective. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14535–14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, F.; Volpe, M.C.; Confalonieri, M. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medicina 2019, 55, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Deng, J.; Tian, Y.J.; Liang, J.; Xie, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; He, X.; et al. Mangostanin Derivatives as Novel and Orally Active Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis with Improved Safety. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 13736–13751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Nepali, K.; Liou, J.P. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Current Status, Recent Progress, and Emerging Targets. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 527–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Aubert, J.D.; Mikulic, J.; Golshayan, D. Fibrogenic Disorders in Human Diseases: From Inflammation to Organ Dysfunction. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9811–9840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.E., Jr.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vats, A.; Chaturvedi, P. The Regenerative Power of Stem Cells: Treating Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis. Stem Cells Cloning 2023, 16, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, S.; Xia, W.; Sui, H.; Fu, X. Hyperoside: A Review of Its Structure, Synthesis, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity. Molecules 2022, 27, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Xiang, A.L.; Pang, H.B.; Liu, K.Q. Hyperoside protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation induced injury in cardiomyocytes by suppressing the Bnip3 expression. Gene 2017, 629, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.; Wang, L.; Jin, X.N.; Sui, H.J.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y. Hyperoside induces both autophagy and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tong, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Fan, H. Hyperoside Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Development in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 550955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Hu, W.; Bao, W.; Mao, L.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Wen, Y.; et al. Hyperoside suppresses BMP-7-dependent PI3K/AKT pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Cui, Q.; Su, W.; Zhang, D.; Pan, J.; Liu, X.; Pang, Z.; Zhu, Q. High-content screening of active components of Traditional Chinese Medicine inhibiting TGF-β-induced cell EMT. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.A.; Oster, C.G.; Mayer, M.M.; Avery, M.L.; Audus, K.L. Characterization of the A549 cell line as a type II pulmonary epithelial cell model for drug metabolism. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 243, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisatomi, K.; Mukae, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Ishimatsu, Y.; Kakugawa, T.; Hara, S.; Fujita, H.; Nakamichi, S.; Oku, H.; Urata, Y.; et al. Pirfenidone inhibits TGF-β1-induced over-expression of collagen type I and heat shock protein 47 in A549 cells. BMC Pulm. Med. 2012, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Chen, M.; Sun, T. Simvastatin attenuates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human alveolar epithelial cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 31, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, S.; Du, K.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Lu, J.; Niu, Y.; Tu, L.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Neocryptolepine Derivatives as Potential Anti-Gastric Cancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardullo, N.; Muccilli, V.; Pulvirenti, L.; Tringali, C. Natural Isoflavones and Semisynthetic Derivatives as Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitch, N.C. Isoflavonoids of the leguminosae. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 988–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D. 7-Hydroxyflavone Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Regulating Inflammation. Molecules 2022, 27, 5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmaoglu, S.; Algul, O.; Anıl, D.A.; Gobek, A.; Duran, G.G.; Ersan, R.H.; Duran, N. Synthesis and anti-proliferative activity of fluoro-substituted chalcones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3172–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, B.C.; Liebler, J.M.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Nicholson, A.G.; Crandall, E.D.; du Bois, R.M.; Borok, Z. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta1: Potential role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. Emt: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavert, N.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the invasive potential of tumors. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhitnyak, I.Y.; Rubtsova, S.N.; Litovka, N.I.; Gloushankova, N.A. Early Events in Actin Cytoskeleton Dynamics and E-Cadherin-Mediated Cell-Cell Adhesion during Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cells 2020, 9, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.; Guilford, P.; Thiery, J.P. Early events in cell adhesion and polarity during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4417–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Chatterjee, J. ROS and oncogenesis with special reference to EMT and stemness. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 99, 151073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzese, F.; Leone, A.; Rocco, M.; Carbone, C.; Piro, G.; Caraglia, M.; Di Gennaro, E.; Budillon, A. HDAC inhibitor vorinostat enhances the antitumor effect of gefitinib in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck by modulating ErbB receptor expression and reverting EMT. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2378–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 2011, 147, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guen, L.; Marchal, S.; Faure, S.; de Santa Barbara, P. Mesenchymal-epithelial interactions during digestive tract development and epithelial stem cell regeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3883–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D. Epithelial-endothelial transition and endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2022, 66, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, B.C.; Borok, Z. TGF-beta-induced EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L525–L534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Serial No. | Compounds | IC10 (mean ± SD, μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Hyp | 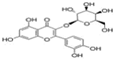 | 43.13 ± 0.6 |
| G0 | 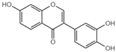 | 61.1 ± 4.4 |
| G1 | 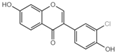 | 28.39 ± 3.2 |
| G2 | 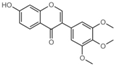 | 33.7 ± 4.2 |
| G3 | 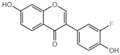 | 41.91 ± 2.5 |
| G4 | 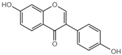 | 40.81 ± 2.6 |
| G5 | 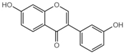 | 31.54 ± 0.4 |
| G6 | 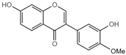 | 51.78 ± 3.2 |
| G7 | 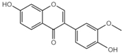 | 38.65 ± 0.6 |
| G8 | 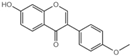 | 41.94 ± 0.4 |
| G9 | 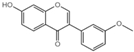 | 43.98 ± 2.8 |
| G10 | 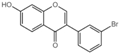 | 60.32 ± 0.3 |
| Z1 | 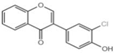 | 30.09 ± 1.0 |
| Z3 | 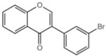 | 34.65 ± 0.8 |
| Z5 | 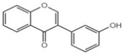 | 31.3 ± 4.3 |
| Z6 | 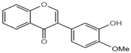 | 30.82 ± 0.4 |
| Z7 | 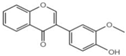 | 49.27 ± 0.5 |
| Target | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| E-cadherin | Forward | 5′-GAGTGCCAACTGGACCATTCAGTA-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CACAGTCACACACGCTGACCTCTA-3′ | |
| Vimentin | Forward | 5′-TGACATTGAGATTGCCACCTACAG-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-TCAACCGTCTTAATCAGAAGTGTCC-3′ | |
| β-actin | Forward | 5′-TGACGTGGACATCCGCAAAG-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CTGGAAGGTGGACAGCGAGG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Xu, M.; Liu, C.; Gong, K.; Yu, X.; Lu, K.; Zhu, J.; Guan, H.; Zhu, Q. Structural Modification and Optimisation of Hyperoside Oriented to Inhibit TGF-β-Induced EMT Activity in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050584
Gao Z, Xu M, Liu C, Gong K, Yu X, Lu K, Zhu J, Guan H, Zhu Q. Structural Modification and Optimisation of Hyperoside Oriented to Inhibit TGF-β-Induced EMT Activity in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(5):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050584
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ziye, Mengzhen Xu, Chuanguo Liu, Kai Gong, Xin Yu, Kaihui Lu, Jiang Zhu, Haixing Guan, and Qingjun Zhu. 2024. "Structural Modification and Optimisation of Hyperoside Oriented to Inhibit TGF-β-Induced EMT Activity in Alveolar Epithelial Cells" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 5: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050584
APA StyleGao, Z., Xu, M., Liu, C., Gong, K., Yu, X., Lu, K., Zhu, J., Guan, H., & Zhu, Q. (2024). Structural Modification and Optimisation of Hyperoside Oriented to Inhibit TGF-β-Induced EMT Activity in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 17(5), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17050584







