Abstract
The incidence of depression has been steadily rising in recent years, making it one of the most prevalent mental illnesses. As the pursuit of novel antidepressant drugs captivates the pharmaceutical field, the therapeutic efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been widely explored. Chaihu (Bupleurum) has been traditionally used for liver conditions such as hepatitis, liver inflammation, liver fibrosis, and liver cancer. It is believed to have hepatoprotective effects, promoting liver cell regeneration and protecting against liver damage. In addition, Bupleurum has also been used as a Jie Yu (depression-relieving) medicine in China, Japan, Republic of Korea, and other Asian countries for centuries. This review article aims to summarize the research conducted on the antidepressant properties and mechanisms of Bupleurum, as well as discuss the potential of TCM formulas containing Bupleurum. This review highlights various antidepressant ingredients isolated from Bupleurum, including saikosaponin A, saikosaponin D, rutin, puerarin, and quercetin, each with distinct mechanisms of action. Additionally, Chinese herb prescriptions and extracts containing Bupleurum, such as Chaihu Shugansan, Xiaoyaosan, and Sinisan, are also included due to their demonstrated antidepressant effects. This review reveals that these Bupleurum compounds exhibit antidepressant effects through the regulation of neurotransmitter mechanisms (such as 5-HT and DA), the NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) system, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and other intracellular signaling pathways. Collectively, this comprehensive review provides insights into the multiple applications of Bupleurum in the treatment of depression and highlights its potential as an alternative or complementary approach to traditional therapies. However, it is essential to consider the potential adverse effects and clinical restrictions of Bupleurum despite its promising potential. Further research is needed to elucidate its specific mechanisms of action and evaluate its effectiveness in human subjects.
1. Introduction
Depression is a prevalent and persistent mental disorder characterized by pervasive and persistent low mood, interest, and motivation, and even suicidal tendencies [1]. It imposes a significant socioeconomic burden, including increased healthcare spending and elevated suicide rates [2,3]. Despite numerous hypotheses regarding its pathogenesis, the precise etiology remains unclear, and accurate diagnostic and treatment modalities are lacking [4]. An important consideration in the selection of an antidepressant is its safety and tolerability. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are the three most commonly used classes of antidepressants in clinical practice. The common cardiovascular side-effects [5,6,7,8,9], gastrointestinal side-effects [10,11], hepatotoxicity [12,13], and sexual dysfunction [14,15,16] are reported. A considerable number of patients had delayed action time after taking the drug, showing resistance to the treatment [17,18]. Rapid antidepressant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonists such as ketamine have concerns about addiction, safety, and controllability [19,20,21]. Bupleurum has been used as a Jie Yu (depression-relieving) medicine [22] in China, Japan, Republic of Korea, and other Asian countries for centuries. However, there is a lack of further research and development on the antidepressant active substances in it, which may provide new ideas for the improvement in antidepressant drugs.
Bupleurum radix, also referred to as Chai Hu in China, is derived from the dried root of Bupleurum Chinese DC. Or Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. The Chinese pharmacopoeia describes Chai Hu as possessing a pungent, bitter, and slightly cold nature. It is said to have the functions of reducing fever, relieving liver stagnation, and elevating Yang Qi. More than 250 compounds have been isolated and identified from Bupleurum in recent years [23]. The main ones are triterpene saponins, essential oils, flavonoids, lignans, and polysaccharides [24,25,26]. Clinically, Chai Hu is often used to treat conditions such as colds, fever, chest and flank pain, irregular menstruation, uterine prolapse, and anal prolapse. In recent years, research on Bupleurum has primarily focused on its biological activities, including its anti-inflammatory [27,28], anticancer [29], antipyretic [30], antiviral [31], liver protection [32], and immune regulation properties [33]. Recent investigations have revealed that Bupleurum can improve depression-like behavior in mice and display antidepressant effects [34,35]. The meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of the bupleurum Chinese herbal formula in managing depression revealed that the bupleurum Chinese formula alone or given as integrative medicine with antidepressants reduced depression severity [36,37]. In this review, we provide a comprehensive summary of the pharmacological components of Bupleurum and the latest empirical evidence for its antidepressant effects. Additionally, we also list the antidepressant mechanisms of its related traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescriptions, which can provide new insights for the development of new clinical antidepressants with minimal side-effects.
2. The Pathological Underpinnings of Depression
The pathogenesis of depression remains a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, with numerous theories proposed to explain its underlying mechanisms. The widely accepted theories of the pathogenesis of depression include neuroimmunity, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrine factors, the monoamine hypothesis, and gut microbiology theory. These theories offer diverse perspectives on the biological, genetic, and environmental factors that contribute to the onset and progression of depression. By exploring the interplay between these theories, researchers may gain a more comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis of depression and develop more effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies (Figure 1).
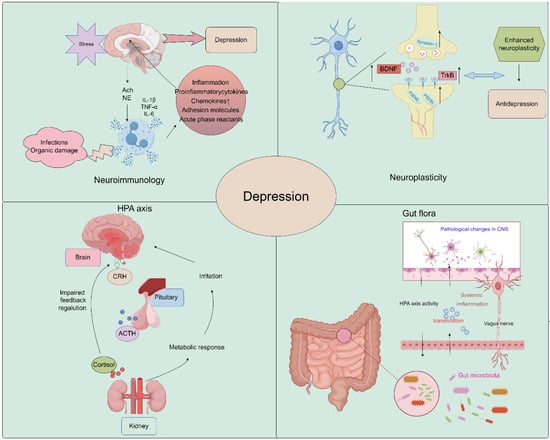
Figure 1.
Schematic image of pathological underpinnings of depression (by Figdraw).
2.1. Neuroplasticity
Growth and adaptation at the neuronal level, referred to as neuroplasticity, may be altered by inflammation and hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis dysfunction caused by environmental stress [38,39]. A major depressive disorder is associated with reduced neurogenesis processes controlled by regulatory proteins, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) [40,41]. Studies have demonstrated that Saikosaponin A, a triterpenoid saponin found in bupleurum, exerts significant upregulatory effects on the expression of p-CREB and BDNF, while it downregulates the expression of Bax and Caspase-3. It promotes the expression of Bcl-2, thereby preventing neuronal apoptosis and ameliorating depression-like behavior following cerebral ischemia [35]. Liu et al. demonstrated that Chaihu-Shugan-San, a traditional Chinese medicine formulation primarily composed of Chaihu, exerts antidepressant effects by enhancing synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus [42].
2.2. Neuroimmunology
In recent years, several new psychiatric studies have hypothesized that inflammatory processes are involved in the pathogenesis of major depressive disorder. A recent study showed that Interleukin-6 (IL-6) was downregulated in the CA1 hippocampus in two animal models of depression, chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and was upregulated by antidepressants. Conversely, IL-6 downregulation exacerbated neuronal abnormalities within the CA1 region and promoted the development of a depressive phenotype in rats [43]. In addition, Kynurenine (Kyn) is a pro-inflammatory metabolite in neuroimmune signaling networks that mediate depression-like behaviors. Intraperitoneal injection of Kyn activated the Nod-like receptor protein 2 (NLPR2) inflammasome in mouse hippocampal astrocytes, and NLRP2 knockdown in astrocytes abolished Kyn-induced depression-like behavior in mice [44]. Therefore, dysregulated innate immune responses can increase stress sensitivity and promote the development of depressive behaviors. These findings highlight the potential role of inflammatory processes in the etiology of depression and provide new insights into the development of novel therapeutic strategies for this debilitating condition [45]. Bupleurum contains a variety of flavonoids, which have a good effect on improving neuroinflammation and achieving an antidepressant effect [46,47,48].
2.3. Neuroendocrine Factors
The HPA axis represents a cardinal neuroendocrine stress response system that maintains homeostasis by adapting the organism to fluctuating demands. Stress and acute challenges have long been recognized as potential risk factors for depression, which frequently co-occur with depressive episodes. Depressive symptoms may therefore be modulated by aberrations in the HPA axis in response to stress [49,50]. It has been shown that Saikosaponin D, one of the active components of Bupleurum, can mediate the depressive effect on CUMS model mice by enhancing the function of the HPA axis [51].
2.4. Monoamine Hypothesis
During the mid-20th century, it was observed that reserpine, an antihypertensive medication, elicited major depressive disorder symptoms and decreased levels of monoamine neurotransmitters. This finding sheds light on reduced levels of serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), and dopamine (DA) as potential factors in the etiology of major depressive disorder [52,53]. It has been found that eight active ingredients derived from Bupleurum can increase 5-HT levels and show significant antidepressant effects [54].
The monoamine hypothesis of depression continues to have proponents and detractors. While monoamine neurotransmitters likely play some role, depression is a heterogeneous and complex disorder. A more comprehensive understanding of the neurobiology of depression will require consideration of the interactions between monoamines and other neurotransmitter systems, neuroendocrine factors, circadian rhythms, and neuroplasticity [55].
2.5. Gut Microbiology
The precise environmental mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of depressive disorder remain elusive. The gut microbiome is an increasingly recognized environmental factor that shapes the brain through the microbiota–gut–brain axis. Recent studies suggested that imbalanced gut microbiota may contribute to depression through host metabolism [56]. By restoring the relative abundance of intestinal flora and regulating the metabolic disorder of endogenous markers, the low polarity fraction of Bupleurum radix proved to be a potential treatment for depressive symptoms [57].
The pretreatment of mice with Komagataella pastoris prevented stress- and inflammation-induced depression-like behaviors in mice. It possesses the properties of a newly proposed probiotic with antidepressant-like effects and is a promising therapeutic strategy for depression [58]. Moreover, depression is linked to reduced gut microbiota diversity. Transplanting fecal microbiota from depressed patients into microbiota-depleted rats induces depression-like symptoms and changes in tryptophan metabolism [59].
These findings suggest that the gut microbiome may play a vital role in depression (Figure 2). More research is needed to understand the mechanisms and develop novel treatments targeting the gut microbiome.
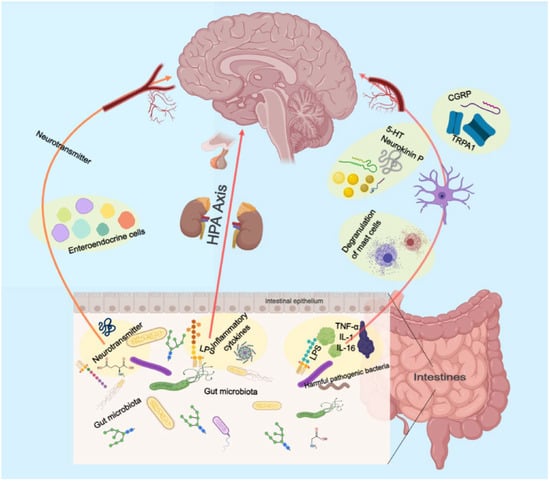
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the role of the intestinal flora in gut–brain axis.
3. Multiple Pharmacological Effects of Bupleurum
Phytochemical analysis of Bupleurum has revealed that it contains a variety of compounds, including saponins, polysaccharides, flavonoids, volatile oils, and others. These compounds have demonstrated significant pharmacological activities, such as antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor, improved glycolipid metabolism, and neuroprotective effects. Recent studies have highlighted the therapeutic potential of specific compounds found in Bupleurum. For example, Chai Hu aqueous extract had a mild but definite antipyretic effect on LPS-induced fever in rats by directly inhibiting the production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) by monocytes [60]. Another study showed that Saikosaponin A (SSA) had therapeutic potential in the treatment of oxidative liver injury through multiscale interactome-level analysis combined with experiments [61]. SSA also inhibited human bladder cancer T24 both in vitro and in vivo [62], while SSA extract had anticancer effects by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in 5637 cells [63]. Saikosaponin D (SSD) could attenuate cancer cachexia by directly inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) expression [64] as well as attenuate peripheral neuropathy in diabetic rats by regulating the Aquaporin 1 (AQP1)/Ras homolog family member A (RhoA)/Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) signaling pathway [65]. There is another report that Saikosaponins were able to ameliorate hyperlipidemia in rats by enhancing hepatic lipid and cholesterol metabolism [48]. Saikosaponin and Plumbagin had synergistic neuroprotective effects on corticosterone-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by regulating metabolic disorders and neuroinflammation [66].
In summary, bupleurum showed therapeutic potential for a wide range of health conditions through their antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects. Unlike other natural medicines, Bupleurum is rich in a large number of saikosaponins. As a class of triterpene saponins, saikosaponins have been reported to have therapeutic potential in improving neuroplasticity [67,68,69]. However, the depressive effects of bupleurum have not been well summarized. In the following paragraph, we concluded that the major compounds isolated from bupleurum and the representative formula contain bupleurum with antidepressive effects (Figure 3) (Table 1).
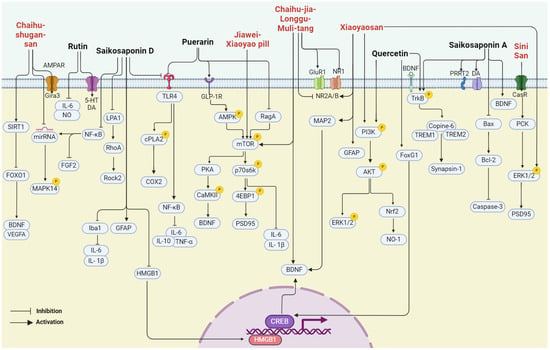
Figure 3.
The multiple cellular targets of pharmacological components and related formulations of bupleurum with antidepressive effects.

Table 1.
The overview of underlying mechanisms of potential compounds and present prescriptions from Chai Hu with antidepressive effects.
4. Pharmacological Components from Bupleurum with Antidepressive Effects
4.1. Rutin
Rutin, a common dietary flavonoid, is extensively ingested through plant-based foods and beverages, serving as a traditional and folk medicine across the globe. It is postulated that rutin possesses various pharmacological properties, encompassing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-adipogenic, neuroprotective, and hormonal therapeutic activities [97]. Studies have shown that rutin can effectively reduce the immobility time of depression-like rats in the forced swimming test and tail suspension test, showing an antidepressant effect. The antidepressant properties of rutin are attributed to elevated concentrations of NE, 5-HT, and DA in the cortical and hippocampal regions [70]. A recent investigation revealed that rutin reversed the decrease in sucrose preference in depression-like mice in the sucrose preference test. And its administration safeguarded against the loss of hippocampal neurons induced by chronic unpredictable stress, consequently yielding an antidepressant effect [71]. Additional research has suggested that the pretreatment of mice with the serotonin synthesis inhibitor PCPA effectively attenuated the decrease in immobility time induced by rutin. And the pretreatment of mice with AMPT, an inhibitor of tyrosine hydroxylase, significantly abolished the antidepressant-like effect of rutin in the tail suspension test. Rutin may manifest its antidepressant-like influences by augmenting the availability of serotonin and norepinephrine within the synaptic cleft [72]. The indoleaminergic pathway has been implicated in rutin’s preventive impact on alcohol-induced cognitive impairment and depression-like behavior in rat models [73].
4.2. Puerarin
Puerarin, a naturally occurring antioxidant, possesses considerable health-promoting properties. Its diverse range of biological activities encompasses antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-neoplastic properties, as well as immune system enhancement and the protection of cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and neuronal cells [98]. Recent studies have indicated that puerarin treatment improved sucrose preference and depression-like behavior in HFD/CUMS-induced rats by inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated intestinal mucus barrier dysfunction and neuroinflammation damage through the TLR4/cytosolic phospholipases A2 (cPLA2)/cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) pathway [74]. Furthermore, puerarin exhibits antidepressant-like effects in HFD diabetic mice. It can increase the number of hippocampal neurons in HFD mice, inhibit neuronal apoptosis, and protect hippocampal neuroplasticity. Puerarin can enhance the expression of GLP-1R in the hippocampus of HFD mice, and then activate AMPK, CREB, and BDNF/TrkB signaling, thereby improving neuroplasticity [76]. Recent experimental findings suggest that puerarin can alleviate depression-like behavior in mice stimulated by LPS by inhibiting the Ras-related GTP-binding protein A (RagA), and it significantly reduced the expression of phosphorylated mTOR and phosphorylated p70S6K induced by LPS stimulation [77].
4.3. Quercetin
Quercetin is a naturally occurring flavonoid and ubiquitously present in various sources such as tea, coffee, apples, and onions. A plethora of research has demonstrated its multifaceted biological activities, including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging properties [99]. The long-term administration of quercetin has been shown to significantly ameliorate CUMS-induced weight loss and depression-like behaviors in mice. Quercetin significantly reversed the protein levels of FoxG1, p-CREB, and BDNF in the hippocampus of mice compared with the CUMS-induced group [78]. Furthermore, Quercetin upregulated hippocampal Nrf2 and inhibited iNOS in CUMS-depressed mice, and it significantly reversed the decreased sucrose preference on the SPT [81]. Quercetin reduced the immobility time in the forced swimming test and tail suspension test in mice, which might be related to its ability to regulate the BDNF-related imbalance of Copine 6 and other synaptic-plasticity-related protein expressions in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. These results suggested that quercetin could improve LPS-induced depression-like behavior in rats [79]. In addition, Wang et al. showed that quercetin treatment significantly reduced the immobility time of TST and FST increases, significantly increased the protein expression level of BDNF in hippocampus and heart tissues of female mice, and increased the phosphorylation level of its downstream targets TrkB, AKT, and ERK1/2. The data suggested that quercetin exerts its antidepressant effect at least in part through BDNF and its downstream PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK intracellular signaling pathways [80].
4.4. Saikosaponin A
SSA is a triterpenoid saponin derived from Saikosaponin, exhibiting a broad spectrum of pharmacological properties [100]. Its antidepressant effects have been extensively documented. SSA has been shown to not only ameliorate depression-like behavior following cerebral ischemia through the cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB)/BDNF pathway and inhibit apoptosis of hippocampal neurons [35], but also alleviate perimenopausal depression-like symptoms. SSA could restore CUMS-induced hyperactivity of the HPA axis and pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as the downregulation of BDNF. SSA increased the expression of p-TrkB levels compared with model mice and promoted neuroplasticity in the hippocampus [82]. Furthermore, SSA may exert its antidepressant influence by upregulating the expression of proline-rich transmembrane protein 2 (PRRT2) and augmenting DA levels in the hippocampus. According to iTRAQ screening results, proteins, including PRRT2, SART1, CaMKII, DENND4B, DOHH, FMN1, TMEM160, REM2, SNX18, PTER, LIMD2, and GIMAP8, were downregulated during the CUMS procedure, while chronic treatment with SA (50 mg/kg daily) significantly counteracted this change [83].
4.5. Saikosaponin D
SSD is a biologically active triterpene saponin with anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidant, and liver fibrosis inhibitory properties [101]. Research findings indicate that SSD exerts antidepressant effects by enhancing HPA axis function and promoting neurogenesis in the hippocampus [51]. In CUMS model rats, SSD mitigated the depression-like behavior by negatively regulating nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), downregulating microRNA-155, and upregulating fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) [84]. Additionally, its antidepressant effect has been linked to the regulation of Homer1-mGluR5 and mTOR signaling [102]. Further experimental results demonstrate that SSD alleviates depression-like behaviors and inhibits neuronal apoptosis by modulating the endogenous lysophosphatidic acid (LPA1)/RhoA/ROCK2 pathway in the LPS model, compared with the LPS group. SSD also significantly inhibited the activation of the MAPK/NfκB-p65 signaling [85]. Moreover, SSD attenuated LPS-induced depressive behaviors by inhibiting microglial activation and neuroinflammation, inhibited HMGB1 nuclear translocation, and decreased the protein levels of TLR4, p-inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B-α (p-IκB-α), and NF-κB [86]. As for chronic mild stress (CMS), SSD has the potential to alleviate sexual behavior and neurological dysfunction, restore glial pathology, and suppress neuroinflammation and oxidative stress [68].
5. Representative Prescription
TCM, rooted in a rich history of thousands of years, offers a variety of herbal prescriptions and therapies for treating depressive disorders. There was a high occurrence of Chai Hu as an important Chinese herb in these antidepressant formulations. Some notable TCM prescriptions for depression include the following:
Chaihu-shugan-san (CSS) is a formulation comprising seven herb medicines, namely Chai Hu (Bupleurum chinense DC.), Xiang Fu (Cyperus rotundus L.), Zhi Qiao (Citrus aurantium L.), Chen Pi (Citrus reticulata Blanco), Chuan Xiong (Ligusticum striatum DC.), Bai Shao (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.), and Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch). It is a prescription commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine. The research indicates that CSS can play an antidepressant role by changing intestinal flora and related metabolites, for example, by upregulating hyocholic acid (HCA), 7-ketodeoxycholic acid (7-ketoDCA), BDNF, and TrkB and downregulating farnesoid X receptor (Fxr) [87]. In addition, in another study, CSS promoted rat hippocampal synapse formation and MAPK14 mRNA and Gria3, and downregulated miR-503, miR-532, miR212, miR-125a, miR-182, and miR-124. Its effects are similar to but do not exceed fluoxetine [42]. CSS in the treatment of major depressive disease (MDD) also needs to have exact efficacy and safety guarantees. A study was conducted to screen whether CSS can induce angiogenesis and neurogenesis in the mouse hippocampus, increase SIRT1, reduce the expression of forkhead Box O1 (FOXO1), and upregulate vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and BDNF, with the same result in brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMVECs) [88]. Deng et al. used CSS to evaluate its effect on cancer-related depression (CRD) in a large hospital in Beijing, and the results showed that CSS could effectively improve the anxiety and depression state of CRD patients [103].
Xiaoyao San (XYS) is one of the most famous prescriptions with a history of thousands of years. XYS is primarily used to treat liver stagnation and spleen deficiency syndrome. XYS is composed of Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.), Dang Gui (Angelica sinensis Diels.), Fu Lin (Poria cocos Wolf.), Bai Shao (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.), Bai Zhu (Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.), and Chai Hu (Bupleurum chinense DC.). Clinical studies have shown that XYS can effectively improve the depression-like performance of patients, and after treatment, creatinine, taurine, 2-oxoglutarate in urine, and xanthine acid were significantly increased, whereas citrate, lactic acid, alanine, and dimethylamine were decreased [104]. The most recent study conducted by Jiao performed computational modeling on mice and concluded that XYS increases the expression of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and ERK1/2, while it decreases acyl-coA synthetase long chain family member 4 (ACSL4), COX-2, total iron, ferrous content, and phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 (PEBP1). The opposite is true for p-ERK1/2 and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule1 (Iba1) [90]. Their team also claimed that XYS reduced the levels of glutamate and serum corticosterone (CORT) in the hippocampus and enhanced microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2B (NR2B), phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K), and p-AKT, revealing that XYS may play an antidepressant role through NR2B and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways [91]. Another study showed that XYS improved depression-like behavior in rats by altering the gut flora. Specifically, at the phylum level, it modulates the abundance of different flora, and at the genus level, it decreases the abundance of Prevotellaceae_Ga6A1 group, Prevotellaceae_UCG-001, and Desulfovibrio. The difference is that the abundance of Ruminococcus has been improved [92]. The results of XYS studied by senior researchers have shown that XYS can reverse the downregulation of BDNF caused by CUMS and promote the generation of Nestin-positive neurons and doublecortin-positive cells [89]. Wang et al. evaluated the efficacy of the XYS formulation in the treatment of post-stroke depression (PSD) in a clinical study involving 80 patients in Wuhan city. It is proved that it can effectively improve the degree of depression, neurological function, and activities of daily living in patients with mild PSD, improve the synthesis and release of neurotrophic factors, and has significant clinical efficacy and good safety evaluation [105].
The Jiawei-Xiaoyao pill (JWX) was recorded in the ancient Chinese official pharmacopoeia 900 years ago. JWX is composed of eight herbs: Chai Hu (Bupleurum chinense DC.), Dang Gui (Angelica sinensis Diels.), Bai Zhu (Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.), Fu Ling (Poria cocos Wolf.), Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.), Mu Dan Pi (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.), Zhi Zi (Gardenia jasminoides Ellis.), and Bo He (Mentha haplocalyx Briq.). Zhang et al. discovered that a single administration of JWX, within the prescribed dosage range, elicited rapid and sustained antidepressant effects in both normal mice and those with chronic depression. Furthermore, JWX swiftly enhanced neuroplasticity signaling and proteins such as mTOR, CaMKII, ERK, and BDNF in the hippocampus while also improving BDNF expression in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in mice models of depression induced by corticosterone exposure. They verified that activation of CaMKII is essential for stimulating the mTOR-BDNF signaling [93]. Wu et al. in a JWX control study involving 64 patients showed that JWX could improve the clinical symptoms and signs of patients with depression, improve the sleep quality of patients, and improve the quality of life of patients [106].
Sini San (SNS), another traditional Chinese herbal formula, is composed of four herbs: Chai Hu (Bupleurum chinense DC.), Bai Shao (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.), Zhi shi (Citrus aurantium L), and Gan cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.). SNS has antidepressant effects and improves synaptic plasticity through the calcium-sensitive receptor (CaSR)-protein kinase C (PKC)-ERK signaling pathway in rats. This study found that SNS treatment significantly upregulated the expression of CaSR, PKC, and p-ERK1/2 in the hippocampus and PFC of adult-stressed rats. This paper also reported that CaSR abnormalities are involved in the pathogenesis of depression [96]. In a clinical study of 100 patients with postpartum depression, Wang et al. found that SNS could improve the clinical symptoms of patients and relieve anxiety and depression, interpersonal communication skills, and quality of life [107].
Chaihu-jia-longgu-muli tang (CLM) is a classic Chinese herbal medicine used in the treatment of depression. CLM is composed of 11 Chinese herbs, including Chai Hu (Bupleurum chinense DC.), Long Gu (longgu), Huang Qin (Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi.), Sheng Jiang (Zingiber officinale Rose), Ren Shen (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey), Gui Zhi (Cinnamomum cassia Presl), Fu Ling (Poria cocos Wolf.), Ban Xia (Pineilia ternata Breit.), Da Huang (Rheum palmatum L.), Mu Li (Ostrea gigas Thunberg.), and Da Zao (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.). The researchers found that CLM produced immediate and lasting antidepressant activity by enhancing hippocampal BDNF expression, in which components of the Xiaochuhu decoction played a major role [94]. In addition, CLM induced rapid antidepressive-like effects in OB mice, which may be due to the reversal of abnormal expression of AMPA and NMDA receptors in the PFC and the related Akt-mTOR signaling [95]. In a clinical observation involving 121 patients, Tang et al. found that CLM had a certain clinical efficacy in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension complicated with depression, which could improve depression and reduce inflammatory response while reducing blood pressure [108].
6. Summary and Perspective
Bupleurum, a traditional herbal medicine, is widely used in Asian countries to treat ailments. With advancements in modern pharmacology, analytical chemistry, and other disciplines, researchers have identified many compounds in Bupleurum, including volatile oils, triterpenoid saponins, flavonoids, lignans, fatty acids, and sterols. Among these, triterpene saponins, flavonoids, and volatile oils exhibit various pharmacological activities and are considered the main active ingredients of Bupleurum [109]. Several compounds, such as saikosaponin A, quercetin, and rutin, possess antidepressant properties. These active ingredients are effective in treating depression by regulating neurotransmitters (e.g., 5-HT, DA), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and their intracellular signaling pathways. They also protect neurons through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities and regulate the expression of related proteins.
At present, there are still many limitations in the study of the antidepressant effect of bupleurum. The current literature reports are mostly based on animal or cell models, and the relationship between the target and the molecular mechanism needs to be further studied. Many radix bupleurum formulas, such as CSS, XYS, and SNS, are frequently used in clinical applications in China and Japan, but the specific active ingredients of radix bupleurum are still in the experimental stage. There is a lack of randomized double-blind testing of TCM compounds, and stronger evidence-based medicine is needed to prove the clinical role of bupleurum.
In addition, concerns about bupleurum toxicity are commonly reported, and it is believed that the long-term use of bupleurum can cause abnormal liver function [110,111]. It has been described that high doses (>19 g) of bupleurum increase the risk of liver failure in patients with hepatitis B [112]. This is much higher than the dose used in clinical practice and Chinese pharmacopoeia prescribes a daily dose of 3 to 10 g. In 2016, the Chinese Association of Chinese Medicine issued the clinical diagnosis and treatment guidelines for TCM-related liver injury to standardize the use of traditional Chinese herbs [113]. The use of bupleurum in regular medical institutions, in accordance with the guidance of the pharmacopoeia, is deemed safe.
As a natural product, Bupleurum contains a rich variety of pharmacological components and antidepressant active ingredients. Several compounds mentioned in this paper, such as saikosaponin A in Bupleurum, are about 0.35–0.63%. The content of saikosaponin C was about 0.15–0.27%, and the content of saikosaponin D was about 0.35–0.9%. The content of puerarin in Bupleurum was 0.04–0.145 mg/g [16,114], the content of rutin was 1.533–19.88 mg/g, and the content of quercetin was 0.059–0.927 mg/g [115]. And they provide a new avenue for scientific research: investigating whether two or more antidepressant active ingredients can produce a synergistic effect. For example, our previous study found that the co-administration of geniposide and shanzhiside methyl ester was able to increase hippocampal PACAP production, thereby synergizing to produce rapid antidepressant effects [116]. In this article, we only discussed the mechanism of action of single antidepressant active constituents of Bupleurum. The potential for synergistic antidepressant effects among compounds isolated from Bupleurum warrants further investigation in future studies. The prevalence of depression is rising yearly. Given the depth of fundamental research on depression, the translation of scientific findings into practice and the strengthening of clinical research and treatment of this condition should be actively promoted.
This article primarily introduces Bupleurum and its chemical constituents, focusing on recent advancements regarding its antidepressant active ingredients and the potential antidepressant mechanisms of relevant TCM prescriptions. It provides a theoretical foundation and clinical application for the treatment of depression using TCM (Figure 4).
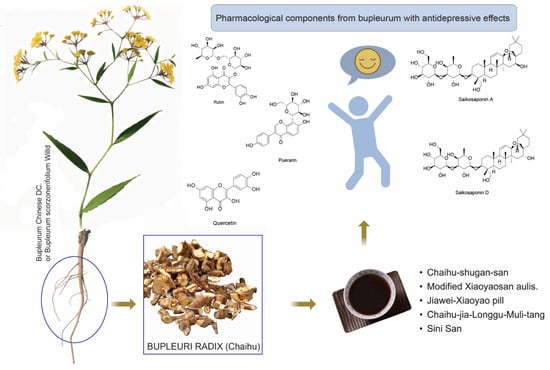
Figure 4.
Graphical abstract of Chai Hu.
Author Contributions
S.R.: Methodology, Validation, Investigation; R.P.: Visualization, Writing—Original Draft Preparation; Q.G. and J.C.: Visualization; Z.W.: Visualization, Funding, Resources, Writing—Original Draft Preparation; G.C.: Project Administration, Supervision, Conceptualization. All data were generated in-house, and no paper mill was used. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work, ensuring integrity and accuracy. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2022YFE0201000), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 82174002 and 82204652), Guangzhou Science and Technology Planning Project (Grant No. 202206010109), Guangzhou Science and Technology Planning Project (Grant No. 202201011429), GuangDong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2021A1515110571) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2021M691258).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Abbreviations
7-ketodeoxycholic acid: 7-ketoDCA; acyl-coA synthetase long chain family member 4: ACSL4; Aquaporin 1: AQP1; brain microvascular endothelial cells: BMVECs; brain-derived neurotrophic factor: BDNF; calcium-sensitive receptor: CaSR; cAMP-response element binding protein: CREB; Chaihu-shugan-san: CSS; chronic mild stress: CMS; chronic unpredictable mild stress: CUMS; cognitive behavioral therapy: CBT; corticosterone: CORT; cyclooxygenase-2: COX-2; cytosolic phospholipases A2: cPLA2; dopamine: DA; electroconvulsive therapy: ECT; endogenous lysophosphatidic acid: LPA1; extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2: ERK1/2; farnesoid X receptor: Fxr; fibroblast growth factor 2: FGF2; Forkhead Box O1: FOXO1; genome-wide association study: GWAS; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: GLP-1R; high-fat diet: HFD; hyocholic acid: HCA; hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal: HPA; Interleukin-6: IL-6; interpersonal psychotherapy: IPT; ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule1: Iba1; Kynurenine: Kyn; lipopolysaccharide: LPS; major depressive disease: MDD; mammalian target of rapamycin: mTOR; microtubule-associated protein 2: MAP2; modified Xiaoyao San: MXYS; Nerve Growth Factor-Inducible protein A: NFGI-A; Nod-like receptor protein 2: NLPR2; norepinephrine: NE; nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2: NFE2L2; Nuclear factor-kappa B: NF-κB; nucleus accumbens: Nac; p70 ribosomal S6 kinase: p70S6K; phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1: PEBP1; phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase: PI3K; p-inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B-α: p-IκB-α; prefrontal cortex: PFC; proline-rich transmembrane protein 2: PRRT2; protein kinase B: AKT; protein kinase C: PKC; Ras homolog family member A: RhoA; Ras-related GTP-binding protein A: RagA; repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: rTMS; Rho-associated protein kinase: ROCK; Saikosaponin A: SSA; Saikosaponin D: SSD; serotonin: 5-HT; signal transducer and activator of transcription 3: STAT3; Sini San: SNS; toll-like receptor 4: TLR4; traditional Chinese medicine: TCM; triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1/2: TREM1/2; Tropomyosin receptor kinase B: TrkB; tumor necrosis factor alpha: TNF-α; vagus nerve stimulation: VNS; vascular endothelial growth factor A: VEGFA; Xiaoyao San: XYS.
References
- Jin, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhao, L.; Fan, J.; Li, B. Mechanisms of Panax ginseng action as an antidepressant. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12696. [Google Scholar]
- König, H.; König, H.H.; Konnopka, A. The excess costs of depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2020, 29, e30. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.-L.; Qian, Y.; Jin, X.-H.; Yu, H.-R.; Wu, H.; Du, L.; Chen, H.-L.; Shi, Y.-Q. Suicide rates among people with serious mental illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.J.; Tian, J.S.; Gao, X.X.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Qin, X.M. Research on the Pathological Mechanism and Drug Treatment Mechanism of Depression. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mago, R.; Tripathi, N.; Andrade, C. Cardiovascular adverse effects of newer antidepressants. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2014, 14, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, S.R.; Kostis, W.J.; Celano, C.M.; Januzzi, J.L.; Ruskin, J.N.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Huffman, J.C. Meta-analysis of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor-associated QTc prolongation. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, e441–e449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Pae, C.U. How much to worry about the FDA warning in the use of citalopram? Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2013, 13, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindelegger, C.J.; Papageorgiou, K.; Grohmann, R.; Engel, R.; Greil, W.; Konstantinidis, A.; Agelink, M.W.; Bleich, S.; Ruether, E.; Toto, S.; et al. Cardiovascular adverse reactions during antidepressant treatment: A drug surveillance report of German-speaking countries between 1993 and 2010. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 18, pyu080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, A.H.; Brunoni, A.R.; Santos, I.S.; Nunes, M.A.; Dantas, E.M.; Carvalho de Figueiredo, R.; Pereira, A.C.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Mill, J.G.; Andreao, R.V.; et al. Effects of depression, anxiety, comorbidity, and antidepressants on resting-state heart rate and its variability: An ELSA-Brasil cohort baseline study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.; Vos, R.; Tack, J. The influence of citalopram on interdigestive gastrointestinal motility in man. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, P.; Cipriani, A.; Hotopf, M.; Barbui, C. Side-effect profile of fluoxetine in comparison with other SSRIs, tricyclic and newer antidepressants: A meta-analysis of clinical trial data. Pharmacopsychiatry 2005, 38, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, M.I.; Carvajal, A.; Andrade, R.J.; Velasco, A. Antidepressant-induced hepatotoxicity. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2003, 2, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voican, C.S.; Corruble, E.; Naveau, S.; Perlemuter, G. Antidepressant-induced liver injury: A review for clinicians. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartlehner, G.; Hansen, R.A.; Morgan, L.C.; Thaler, K.; Lux, L.; Van Noord, M.; Mager, U.; Thieda, P.; Gaynes, B.N.; Wilkins, T.; et al. Comparative benefits and harms of second-generation antidepressants for treating major depressive disorder: An updated meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Mandher, A.; Khalid, A.; Hamed, A.; Maryam Al, B.; Wedad Al, Z. Prevalence of antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction among psychiatric outpatients attending a tertiary care hospital. Neurosci. J. 2020, 25, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, M. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor-Induced Sexual Dysfunction: Current Management Perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, O.D.; Thase, M.E.; Pillinger, T. Treatment resistance in psychiatry: State of the art and new directions. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugi, G.; Pacchiarotti, I.; Mainardi, C.; Verdolini, N.; Menculini, G.; Barbuti, M.; Angst, J.; Azorin, J.-M.; Bowden, C.L.; Mosolov, S.; et al. Patterns of response to antidepressants in major depressive disorder: Drug resistance or worsening of depression are associated with a bipolar diathesis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yao, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Ketamine and its metabolites: Potential as novel treatments for depression. Neuropharmacology 2023, 222, 109305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, B.; Fong, J.; Galvez, V.; Shelker, W.; Loo, C.K. Side-effects associated with ketamine use in depression: A systematic review. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.B.; Fedgchin, M.; Daly, E.J.; De Boer, P.; Cooper, K.; Lim, P.; Pinter, C.; Murrough, J.W.; Sanacora, G.; Shelton, R.C.; et al. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Frequency Study of Intravenous Ketamine in Patients with Treatment-Resistant Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, M. Research Progress on Classical Traditional Chinese Medicine Jieyu Pills in the Treatment of Depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 3023–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Guo, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Wei, J.; Xiao, P. A comprehensive review on traditional and modern research of the genus Bupleurum (Bupleurum L., Apiaceae) in recent 10 years. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, P. Phytochemical investigation of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. (Umbelliferae) and their chemotaxonomic significance. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2023, 107, 104615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H.; Xin, C.; Wang, B.; Yu, M.; Wei, J. Traditional use, germplasm identification, phytochemistry, pharmacology of Bupleuri Radix: A review. Med. Plant Biol. 2023, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, X.; Kang, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Jing, W.; Wei, F.; Ma, S. Systematic Characterization and Identification of Saikosaponins in Extracts from Bupleurum marginatum var. stenophyllum Using UPLC-PDA-Q/TOF-MS. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 747987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, P.B.; Martínez, M.A.; Sen, A.S.; Gómez, A.S.; Matellano, L.F.; Contreras, S.S.; Lanza, A.D. In vivo and in vitro antiinflammatory activity of saikosaponins. Life Sci. 1998, 63, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Bao, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Chang, X.; Yang, G.; Meng, X. Anti-Inflammation Effects and Potential Mechanism of Saikosaponins by Regulating Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism and Arachidonic Acid Metabolism. Inflammation 2016, 39, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Woo, H.D.; Jeon, H.K.; Chung, H.W. Effect of Bupleuri Radix extracts on the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil in HepG2 hepatoma cells and normal human lymphocytes. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 103, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris-Usman, M.; John-Africa, L.; Akuodor, G.; Ugwu, T.; Osunkwo, U. Antinociceptive and antipyretic properties of the pharmaceutical herbal preparation, Radix bupleuri in rats. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 659–663. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, Y.; Nishiyama, Y.; Shimokata, K.; Takeyama, H.; Kunii, A. Active component of HVJ (sendai virus) for interferon on induction in mice. Nature 1978, 274, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.J.; Yue, S.Q.; Zhang, L.Y.; Dou, K.F. Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effect of a polysaccharide from Bei Chaihu (Bupleurum chinense DC). Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Yue, X.L.; Cheng, X.Q.; Hou, W.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Chen, D.F. Beneficial effect of Bupleurum polysaccharides on autoimmune disease induced by Campylobacter jejuni in BALB/c mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Sun, G.; Dai, W.; Zhao, T.; et al. Antidepressant Active Components of Bupleurum chinense DC-Paeonia lactiflora Pall Herb Pair: Pharmacological Mechanisms. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1024693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.R.; Mi, L.F.; Zhang, Z.L.; Hu, M.Z.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.B.; Zheng, S. Saikosaponin A improved depression-like behavior and inhibited hippocampal neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemia through p-CREB/BDNF pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 403, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shergis, J.L.; Di, Y.M.; Zhang, A.L.; Lu, C.; Guo, X.; Fang, Z.; Xue, C.C.; Li, Y. Managing Depression with Bupleurum chinense Herbal Formula: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2020, 26, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-F.; Lu, W.-T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.-D.; Wu, C.-Y.; Zhou, H.-F. Proprietary Medicines Containing Bupleurum chinense DC. (Chaihu) for Depression: Network Meta-Analysis and Network Pharmacology Prediction. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 773537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeland, M.; Zunszain, P.A.; Pariante, C.M. Molecular mechanisms in the regulation of adult neurogenesis during stress. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.B.; Duman, R. Neuroplasticity in cognitive and psychological mechanisms of depression: An integrative model. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molendijk, M.L.; Spinhoven, P.; Polak, M.; Bus, B.A.; Penninx, B.W.; Elzinga, B.M. Serum BDNF concentrations as peripheral manifestations of depression: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analyses on 179 associations (N = 9484). Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. BDNF signaling in context: From synaptic regulation to psychiatric disorders. Cell 2022, 185, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, N.-N.; Wu, Z.-Z.; Fan, D.-H.; Cao, M.-Q. Chaihu-Shugan-San exerts an antidepressive effect by downregulating miR-124 and releasing inhibition of the MAPK14 and Gria3 signaling pathways. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 837–845. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Feng, Y.B.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Song, Q.; Yu, S.Y. Interleukin-6: Its role and mechanisms in rescuing depression-like behaviors in rat models of depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 82, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, J.; Lu, M.; Hu, G. Kynurenine regulates NLRP2 inflammasome in astrocytes and its implications in depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodes, G.E.; Kana, V.; Menard, C.; Merad, M.; Russo, S.J. Neuroimmune mechanisms of depression. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, F.; Xing, Z.; Chen, J.; Peng, C.; Li, D. Beneficial effects of natural flavonoids on neuroinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1006434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Nie, K.; Wang, H.; Su, H.; Wang, Z.; Lu, F.; Huang, W.; Dong, H. Antidepressant Potential of Quercetin and Its Glycoside Derivatives: A Comprehensive Review and Update. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 865376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, N.; Li, F.; Ge, J.; Wang, D.; Sun, R.; Liu, R. Saikosaponins ameliorate hyperlipidemia in rats by enhancing hepatic lipid and cholesterol metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 305, 116110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.; Newport, D.J.; Mletzko, T.; Miller, A.H.; Nemeroff, C.B. The link between childhood trauma and depression: Insights from HPA axis studies in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, Z.; Grossman, A.; Kelestimur, F. Investigation of the Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis: A contemporary synthesis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 22, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zeng, M.J.; Fang, F.; Li, M.; Qin, T.T.; Ye, L.Y.; Li, H.W.; Qu, R.; Ma, S.P. Saikosaponin D relieves unpredictable chronic mild stress induced depressive-like behavior in rats: Involvement of HPA axis and hippocampal neurogenesis. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 3385–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, D.S.; Kuczenski, R.; Mandell, A.J. Theoretical implications of drug-induced adaptive regulation for a biogenic amine hypothesis of affective disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 1974, 9, 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Spellman, T.; Liston, C. Toward Circuit Mechanisms of Pathophysiology in Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Li, H.M.; Bing, Y.F.; Zheng, Y.; Li, W.L.; Zou, X.; Qu, Z.Y. Bupleurum scorzonerifolium: Systematic research through pharmacodynamics and serum pharmacochemistry on screening antidepressant Q-markers for quality control. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 225, 115202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boku, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Toda, H.; Hishimoto, A. Neural basis of major depressive disorder: Beyond monoamine hypothesis. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; Du, X.; et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, X.; Meng, M.; Xue, H.; Qin, X. Multi-omics reveals the mechanisms of antidepressant-like effects of the low polarity fraction of Bupleuri radix. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 256, 112806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmann, P.T.; Casaril, A.M.; Pesarico, A.P.; Caballero, P.S.; Smaniotto, T.A.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Moreira, A.N.; Conceicao, F.R.; Sousa, F.S.S.; Collares, T.; et al. Komagataella pastoris KM71H modulates neuroimmune and oxidative stress parameters in animal models of depression: A proposal for a new probiotic with antidepressant-like effect. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 171, 105740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; O’Brien, C.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.; Moloney, G.; et al. Transferring the blues: Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Wei, J.; Qi, Y. Bupleurum chinense exerts a mild antipyretic effect on LPS-induced pyrexia rats involving inhibition of peripheral TNF-alpha production. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 310, 116375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, S.B.; Song, Y.R.; Bae, S.J.; Lee, W.Y.; Kim, Y.W. Integrative approach to uncover antioxidant properties of Bupleuri Radix and its active compounds: Multiscale interactome-level analysis with experimental validation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 199, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Wu, W.W.; Yu, C.L.; Wang, P.; Wen, X.Q.; Chen, B.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; et al. Saikosaponin A Inhibits Growth of Human Bladder Carcinoma T24 and 5637 Cells Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Kim, A.; Lee, H.; Baek, S.J.; Kim, N.S.; Park, M.; Yi, J.M.; Cha, S. Systematic transcriptome analysis reveals molecular mechanisms and indications of bupleuri radix. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1010520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Xia, L.Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Guo, C.; Xu, W.H. Saikosaponin D alleviates cancer cachexia by directly inhibiting STAT3. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. Saikosaponin d (SSD) alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy by regulating the AQP1/RhoA/ROCK signaling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hou, R.; Qin, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Tian, J.; Gao, X.; Du, G.; Zhou, Y. Synergistic neuroprotective effect of saikosaponin A and albiflorin on corticosterone-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via regulation of metabolic disorders and neuroinflammation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 8801–8813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhao, G.; Shuang, R.; Wang, H.; Zeng, N. Saikosaponin a activates tet1/dll3/notch1 signalling and promotes hippocampal neurogenesis to improve depression-like behavior in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Qi, T.; Huang, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Ding, J.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Saikosaponin D Rescues Deficits in Sexual Behavior and Ameliorates Neurological Dysfunction in Mice Exposed to Chronic Mild Stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 625074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Nie, K.; Jiang, X.; Su, H.; Tang, Y.; Lu, F.; Dong, H.; et al. The therapeutic effects of saikosaponins on depression through the modulation of neuroplasticity: From molecular mechanisms to potential clinical applications. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 201, 107090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foudah, A.I.; Alqarni, M.H.; Alam, A.; Devi, S.; Salkini, M.A.; Alam, P. Rutin Improves Anxiety and Reserpine-Induced Depression in Rats. Molecules 2022, 27, 7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, A.; Mehta, V.; Udayabanu, M. Rutin alleviates chronic unpredictable stress-induced behavioral alterations and hippocampal damage in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 656, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, D.G.; Bettio, L.E.; Cunha, M.P.; Santos, A.R.; Pizzolatti, M.G.; Brighente, I.M.; Rodrigues, A.L. Antidepressant-like effect of rutin isolated from the ethanolic extract from Schinus molle L. in mice: Evidence for the involvement of the serotonergic and noradrenergic systems. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 587, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebokaiwe, A.P.; Obasi, D.O.; Obeten, U.; Onyemuche, T. Rutin co-treatment prevented cognitive impairment/depression-like behavior and decreased IDO activation following 35 days of ethanol administration in male Wistar rats. Alcohol 2023, 106, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.N.; Yan, M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Sai, C.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, L. Puerarin Alleviates Depression-Like Behavior Induced by High-Fat Diet Combined with Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress via Repairing TLR4-Induced Inflammatory Damages and Phospholipid Metabolism Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 767333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, W.; Ding, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H. Puerarin ameliorates depression-like behaviors of with chronic unpredictable mild stress mice by remodeling their gut microbiota. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 290, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liao, Y.; Shu, L. Puerarin alleviates depressive-like behaviors in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice via modulating hippocampal GLP-1R/BDNF/TrkB signaling. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 26, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Ngo, F.Y.; Luo, D.; Song, Y.; Lao, L.; Rong, J. Botanical Drug Puerarin Ameliorates Liposaccharide-Induced Depressive Behaviors in Mice via Inhibiting RagA/mTOR/p70S6K Pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 7716201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.X.; Zhang, R.Y.; Rui, W.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Feng, X. Quercetin alleviates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors by promoting adult hippocampal neurogenesis via FoxG1/CREB/ BDNF signaling pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 406, 113245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Li, H.R.; Chen, X.X.; Gao, X.R.; Huang, L.L.; Du, A.Q.; Jiang, C.; Li, H.; Ge, J.F. Quercetin Alleviates LPS-Induced Depression-Like Behavior in Rats via Regulating BDNF-Related Imbalance of Copine 6 and TREM1/2 in the Hippocampus and PFC. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Lei, C.; Lei, X.; Zhu, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, R. Quercetin exerts antidepressant and cardioprotective effects in estrogen receptor alpha-deficient female mice via BDNF-AKT/ERK1/2 signaling. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 206, 105795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Gong, M.; Li, B. Quercetin reverses chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior in vivo by involving nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2. Brain Res. 2021, 1772, 147661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Q.; Chen, S.J.; Liang, W.N.; Wang, M.; Li, C.F.; Wang, S.S.; Dong, S.Q.; Yi, L.T.; Li, C.D. Saikosaponin A attenuates perimenopausal depression-like symptoms by chronic unpredictable mild stress. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 662, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, F.; Gao, J.; Guan, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Qin, Z.; Tang, K.; Liu, S. Proteomics-based screening of the target proteins associated with antidepressant-like effect and mechanism of Saikosaponin A. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, B.; Huang, S.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Saikosaponin d downregulates microRNA-155 and upregulates FGF2 to improve depression-like behaviors in rats induced by unpredictable chronic mild stress by negatively regulating NF-kappaB. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 157, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Su, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; Deng, X.; Ma, S. Modulation of LPA1 receptor-mediated neuronal apoptosis by Saikosaponin-d: A target involved in depression. Neuropharmacology 2019, 155, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Pan, Y.W.; Wang, S.Q.; Li, X.Z.; Huang, F.; Ma, S.P. Saikosaponin-d attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviors via inhibiting microglia activation and neuroinflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yuan, D.; Renaud, S.J.; Zhou, T.; Yang, F.; Liou, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, L.; Guo, Y. Chaihu-shugan-san alleviates depression-like behavior in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable stress by altering the gut microbiota and levels of the bile acids hyocholic acid and 7-ketoDCA. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1040591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, Y.; Shi, W.; Ren, Y.; Xiao, K.; Chen, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, J. SIRT1/FOXO1 Axis-Mediated Hippocampal Angiogenesis is Involved in the Antidepressant Effect of Chaihu Shugan San. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2022, 16, 2783–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Huang, P.; Dong, Z.; Gao, T.; Huang, S.; Zhou, C.; Lai, Y.; Deng, G.; Liu, B.; Wen, G.; et al. Modified Xiaoyaosan (MXYS) Exerts Anti-Depressive Effects by Rectifying the Brain Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent fMRI Signals and Improving Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, H.; Yang, H.; Yan, Z.; Chen, J.; Xu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Z.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Traditional Chinese Formula Xiaoyaosan Alleviates Depressive-Like Behavior in CUMS Mice by Regulating PEBP1-GPX4-Mediated Ferroptosis in the Hippocampus. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021, 17, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.M.; Liu, C.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ma, Q.Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.M.; Li, X.J.; Chen, J.X. Xiaoyaosan Alleviates Hippocampal Glutamate-Induced Toxicity in the CUMS Rats via NR2B and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 586788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.Z.; Liang, Y.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Hao, W.Z.; Li, X.J.; Wu, M.S.; Deng, L.J.; Li, Y.M.; Chen, J.X. Xiaoyaosan improves depressive-like behavior in rats with chronic immobilization stress through modulation of the gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ying, Y.; Liu, R.; Lin, J.; Li, C.; Chen, G. Jiawei-Xiaoyao pill elicits a rapid antidepressant effect, dependent on activating CaMKII/mTOR/BDNF signaling pathway in the hippocampus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Zou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Sheng, L.; Xue, W.; Tang, J.; Wu, H.; et al. Immediate and persistent antidepressant-like effects of Chaihu-jia-Longgu-Muli-tang are associated with instantly up-regulated BDNF in the hippocampus of mice. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zou, Z.; Shen, Q.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Tang, J.; Xue, W.; Tao, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, D.; et al. Involvement of NMDA-AKT-mTOR Signaling in Rapid Antidepressant-Like Activity of Chaihu-jia-Longgu-Muli-tang on Olfactory Bulbectomized Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Cao, K.; Cui, S.; Cui, Y.; Mo, H.; Wen, W.; Dong, Z.; Lin, H.; Bai, S.; Yang, L.; et al. SiNiSan ameliorates depression-like behavior in rats by enhancing synaptic plasticity via the CaSR-PKC-ERK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, L.S. A review on plant-based rutin extraction methods and its pharmacological activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Bu, T.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, F.; Zou, L. Pharmacological Activity, Pharmacokinetics, and Clinical Research Progress of Puerarin. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Ye, H.; Kamaraj, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Pavek, P. A review on pharmacological activities and synergistic effect of quercetin with small molecule agents. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grichnik, K.P.; D’Amico, T.A. Acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome after pulmonary resection. Semin. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2004, 8, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Wei, W.; Yin, C.; Tang, F. Effects of saikosaponin-d on CYP3A4 in HepaRG cell and protein-ligand docking study. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Y.; Chen, J.B.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhou, X.M.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Y.M.; Ma, Q.Y.; Xue, Z.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Li, X.J.; et al. Saikosaponin D exerts antidepressant effect by regulating Homer1-mGluR5 and mTOR signaling in a rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, D. Clinical study of Chaihu Shugan Powder in the treatment of cancer-related depression. Int. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 44, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.S.; Peng, G.J.; Gao, X.X.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Xing, J.; Qin, X.M.; Du, G.H. Dynamic analysis of the endogenous metabolites in depressed patients treated with TCM formula Xiaoyaosan using urinary (1)H NMR-based metabolomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaixin, W.; Xueping, S.; Tao, L.; Congbing, W. Clinical study on Danzhi Xiaoyaosan combined with five phases music therapy in the treatment of mild post-stroke depression patients. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Min, W.; Feng, L. Effect of TCM Fumigation Combined with Jiawei Xiaoyao Pill on Insomnia and Quality of Life in Patients with Depression. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 46, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijin, W.; Jing, F.; Yanping, C. Clinical Study on the Treatment of Postpartum Depression with Frigid Extremities Powder Combined with Peach Kernel. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 44, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan-li, T.; Ji-ming, W.; Ting-yi, Z.; Cui, Y.; Jin-ping, F. Efficacy and Safety of Modified Chaihu Jia Longgu Muli Tang in Treating Mild to Moderate Essential Hypertension Syndrome. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2020, 26, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Wang, W.; You, L.; Ni, J. Radix Bupleuri: A Review of Traditional Uses, Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7597596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, F.; Sumino, M.; Fujii, Y.; Akiba, T.; Satoh, T. Pharmacology and Toxicology of Bupleurum Root-Containing Kampo Medicines in Clinical Use. Human. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, D.C.H.; Ng, P.S.L.; Tan, S.H.; Lim, A.T.; Toh, D.S.L.; Chan, S.Y.; Cheong, H.H. Drug-induced liver injury associated with Complementary and Alternative Medicine: A review of adverse event reports in an Asian community from 2009 to 2014. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Wang, J.-D.; Chen, P.-C. Risk of Liver Injury Associated with Chinese Herbal Products Containing Radix bupleuri in 639,779 Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Academic Department of the Chinese Association for Science and Technology. Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Herb-Induced Liver Injury; Academic Department of the Chinese Association for Science and Technology: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Suying, D.; Lingjun, D.; Wang, A.; Xin, Y.; Zhijie, Z.; Yilin, T. HPLC fingerprint and active component analysis of Bupleurum from different regions. J. Beijing Agric. Univ. 2021, 36, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jianran, H.; Ping, L.; Hongmei, Z.; Hongyan, L. In vitro anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of total flavonoids from Bupleurum. Chin. J. Food Addit. 2023, 34, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Yau, S.y.; Zhou, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.T.; Zhu, B.; Wu, H.; Chen, G. Synergistic effects of two naturally occurring iridoids in eliciting a rapid antidepressant action by up-regulating hippocampal PACAP signalling. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 4078–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).