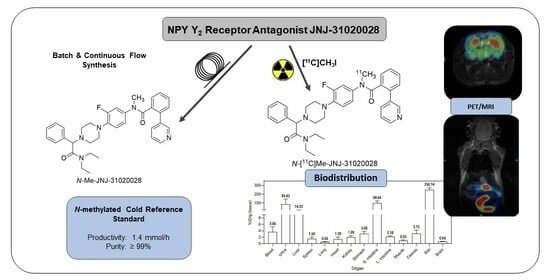
Improved Chemical and Radiochemical Synthesis of Neuropeptide Y Y2 Receptor Antagonist N-Methyl-JNJ-31020028 and Preclinical Positron Emission Tomography Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
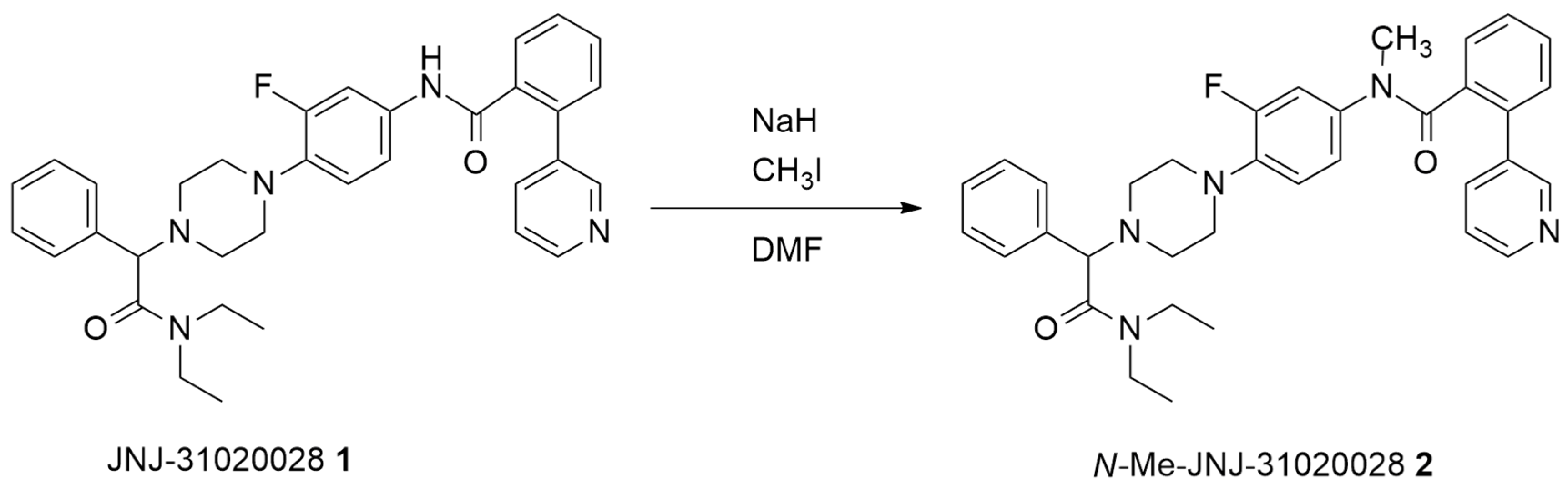
2.1. Batch Synthesis
2.2. Continuous Flow Synthesis
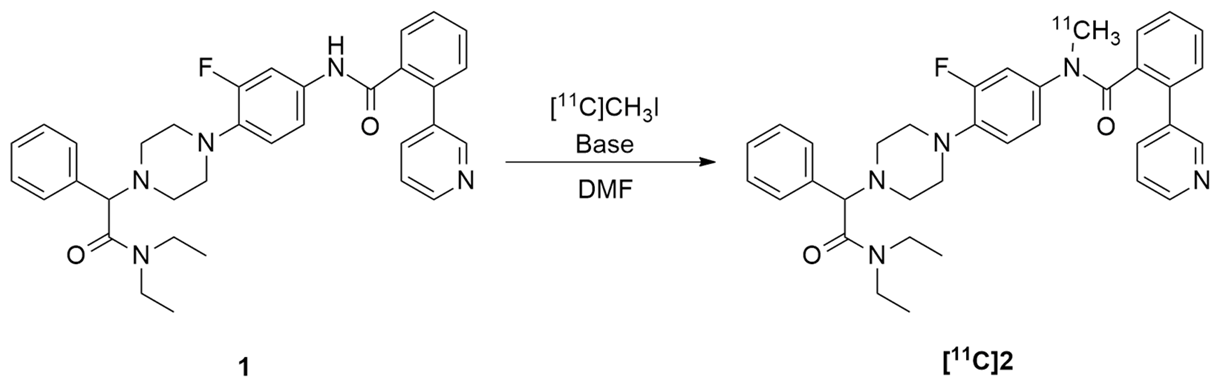
2.3. Radiochemistry
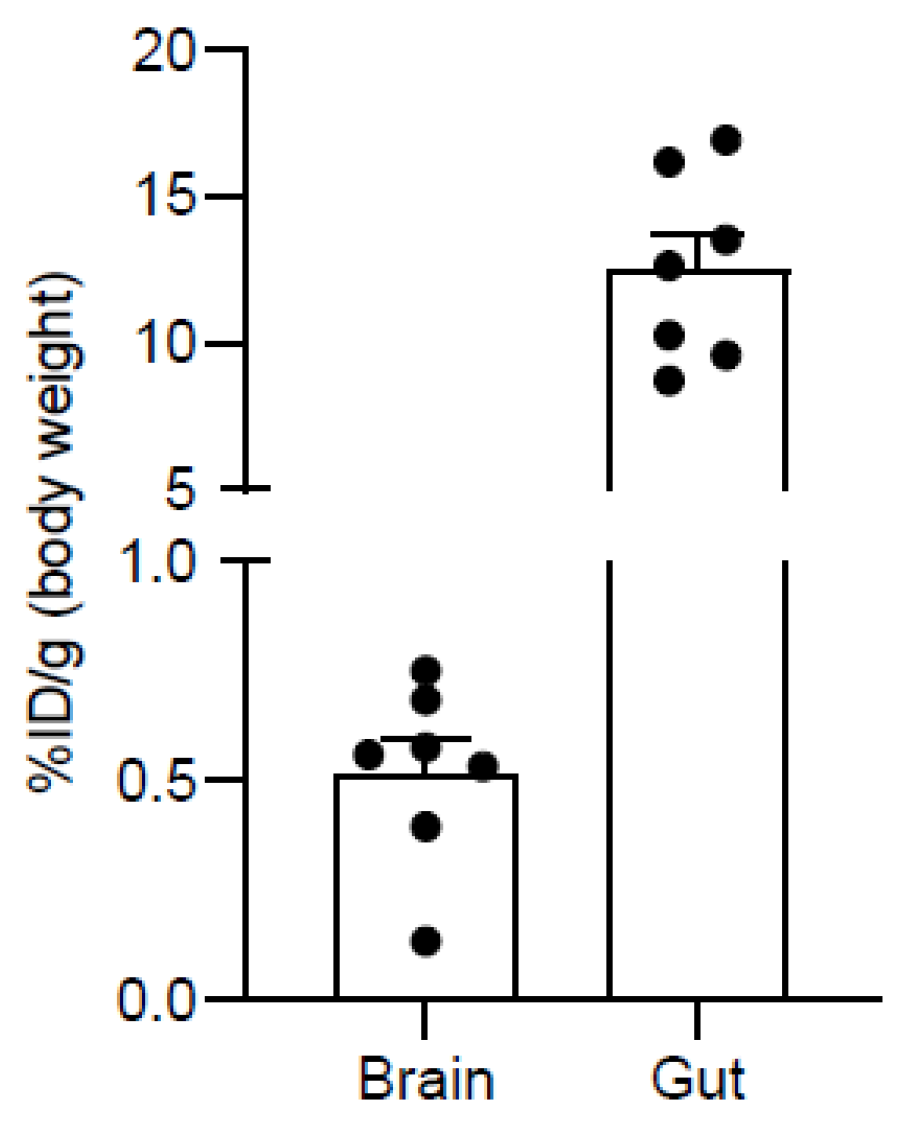
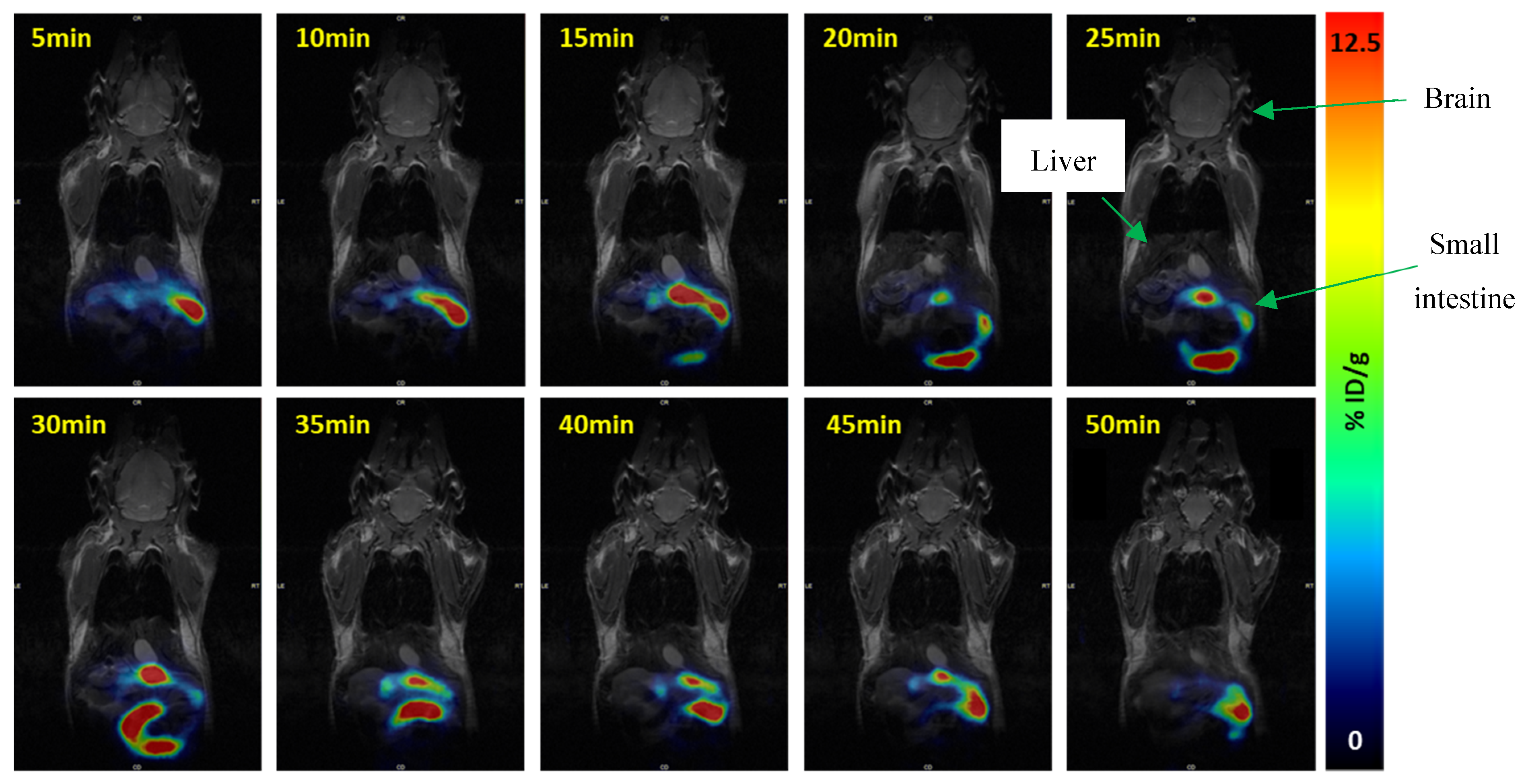
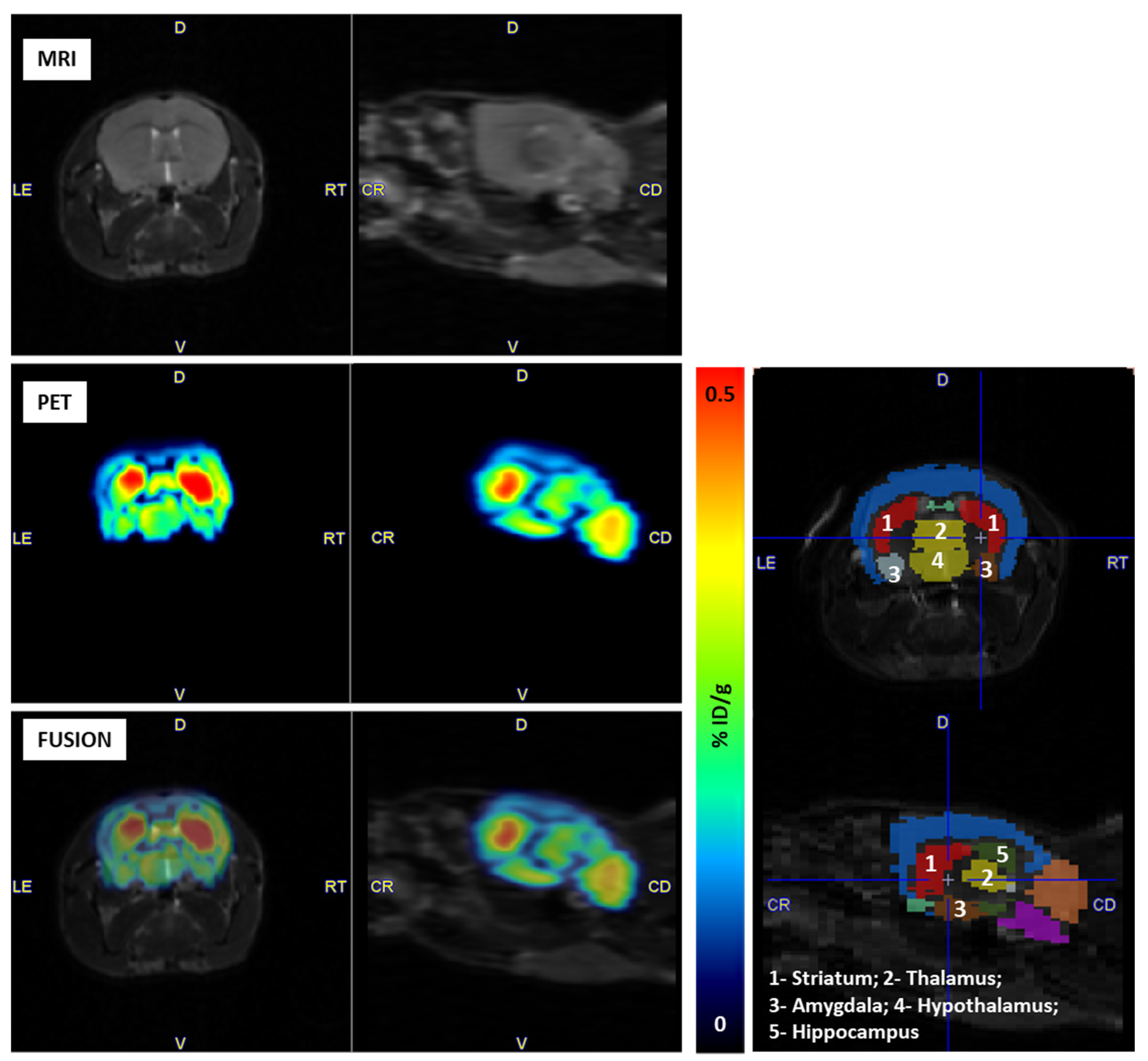
2.4. PET Imaging
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Synthesis of N-Me-JNJ-31020028
3.4. Radiochemistry
3.5. Pre-Clinical Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tatemoto, K.; Carlsquist, M.; Mutt, V. Neuropeptide Y—A novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature 1982, 296, 659–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, K. Neuropeptide Y: Complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 5485–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienast, C.; Gunga, H.C.; Steinach, M. Neuropeptide Y—Its role in human performance and extreme environments. REACH-Rev. Hum. Space Explor. 2019, 14–15, 100032. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, M.C.; Beck-Sickinger, A.; Cox, H.; Doods, H.N.; Herzog, H.; Larhammar, D.; Quirion, R.; Schwartz, T.; Westfall, T. XVI. International Union of Pharmacology Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Neuropeptide Y, Peptide YY, and Pancreatic Polypeptide Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998, 50, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, S.L.; Balasubramaniam, A. Neuropeptide Y Y2 receptor in health and disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soscia, S.J.; Harrington, M.E. Neuropeptide Y does not reset the circadian clock in NPY Y2−/− mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 373, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsell, A.; Rimondini, R.; Heilig, M. Blockade of central neuropeptide Y (NPY) Y2 receptors reduces ethanol self-administration in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 332, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redrobe, J.P.; Dumont, Y.; Herzog, H.; Quirion, R. Characterization of Neuropeptide Y, Y2 Receptor Knockout Mice in Two Animal Models of Learning and Memory Processing. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2004, 22, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelsbrunner, M.E.; Painsipp, E.; Herzog, H.; Holzer, P. Evidence from knockout mice for distinct implications of neuro-peptide-Y Y2 and Y4 receptors in the circadian control of locomotion, exploration, water and food intake. Neuropeptides 2009, 43, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.J.; Widdowson, P.S.; Doods, H.N.; Williams, G. Regulation of Neuropeptide Y Release by Neuropeptide Y Receptor Ligands and Calcium Channel Antagonists in Hypothalamic Slices. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterdahl, M.; Audrain, H.; Landau, A.M.; Smith, D.F.; Bonaventure, P.; Shoblock, J.R.; Carruthers, N.; Swanson, D.; Bender, D. PET Brain Imaging of Neuropeptide Y2 Receptors Using N-11C-Methyl-JNJ-31020028 in Pigs. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoblock, J.R.; Welty, N.; Nepomuceno, D.; Lord, B.; Aluisio, L.; Fraser, I.; Motley, S.T.; Sutton, S.W.; Morton, K.; Galici, R.; et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of JNJ-31020028 (N-(4-{4-[2-(diethylamino)-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl]piperazin1-yl}-3-fluorophenyl)-2-pyridin-3-ylbenzamide), a selective brain penetrant small molecule antagonist of the neuropeptide Y Y2 receptor. Psychopharmacology 2010, 208, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luurtsema, G.; Pichler, V.; Bongarzone, S.; Seimbille, Y.; Elsinga, P.; Gee, A.; Vercouillie, J. EANM guideline for harmonisation on molar activity or specific activity of radiopharmaceuticals: Impact on safety and imaging quality. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2021, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutschack, M.B.; Pieber, B.; Gilmore, K.; Seeberger, P.H. The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Flow Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 11796–11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensch, C.; Jackson, A.; Lindner, S.; Salvamoser, R.; Samper, V.; Riese, S.; Bartenstein, P.; Wängler, C.; Wängler, B. Microfluidics: A Groundbreaking Technology for PET Tracer Production? Molecules 2013, 18, 7930–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascali, G.; Watts, P.; Salvadori, P.A. Microfluidics in radiopharmaceutical chemistry. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2013, 40, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-W.; Lin, W.-Y.; Liu, K.; Masterman-Smith, M.; Kwang-Fu Shen, C. Microfluidics for positron emission tomography probe development. Mol. Imaging 2010, 9, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-Y.; Watts, P.; Chin, F.T.; Hong, J.; Musachio, J.L.; Briard, E.; Pike, V.W. Syntheses of 11C- and 18F-labeled carboxylic esters within a hydrodynamically-driven micro-reactor. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungersboeck, J.; Philippe, C.; Haeusler, D.; Mitterhauser, M.; Lanzenberger, R.; Dudczak, R.; Wadsak, W. Optimization of [11C]DASB-synthesis: Vessel-based and flow-through microreactor methods. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 2615–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, H.; Kimura, H.; Nakaya, Y.; Tomatsu, K.; Arimitsu, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Ozeki, E.; Kuge, Y.; Saji, H. Application of Microreactor to the Preparation of C-11-Labeled Compounds via O-[11C]Methylation with [11C]CH3I: Rapid Synthesis of [11C]Raclopride. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallapura, H.; Tanguy, L.; Långström, B.; Meunier, L.L.; Halldin, C.; Nag, S. Production of [11C]Carbon Labelled Flumazenil and L-Deprenyl Using the iMiDEV™ Automated Microfluidic Radiosynthesizer. Molecules 2022, 27, 8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.; Ulin, J.; Dahlstrøm, K.; Jensen, M. Synthesis of [11C]iodomethane by iodination of [11C]methane. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1997, 48, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, J.M.; Krohn, K.A.; Clark, J.C. Production of [11C]CH3I by single pass reaction of [11C]CH4 with I2. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1997, 24, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Pharmacopoeia 11th Edition, 0125 (04/2023).
- ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guidelines, Specifications: Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for New Drug Substances and New Drug Products: Chemical Substances, Q6A. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, Geneva, Switzerland, 9–10 November 1999.
- European Pharmacopoeia 11th Edition, 5.4 (04/2022).
- Goumain, M.; Voisin, T.; Lorinet, A.-M.; Laburthe, M. Identification and distribution of mRNA encoding the Y1, Y2, Y4, and Y5 receptors for peptides of the PP-fold family in the rat intestine and colon. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 247, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, T.; Rouyer-Fessard, C.; Laburthe, M. Peptide YY/Neuropeptide Y Receptors in Small Intestine Characterization, Signal Transduction, and Expression during Cell Differentiation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 611, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, P.; Reichmann, F.; Farzi, A. Neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide in the gut-brain axis. Neuropeptides 2012, 46, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.M.; Herzog, H. Regional distribution of Y-receptor subtype mRNAs in rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 1431–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriver, D.F.; Drezdzon, M.A. The Manipulation of Air-Sensitive Compounds; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, P.; Crespo, P.; Marques, R.F.; Kajetanowicz, M.; Korcyl, G.; Lopes, L.; Michel, J.; Palka, M.; Traxler, M.; Fonte, P. Experimental sub-millimeter resolution with a small-animal RPC-PET prototype. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record (NSS/MIC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 27 October–3 November 2012; pp. 3760–3764. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, P.; Blanco, A.; Couceiro, M.; Ferreira, N.C.; Lopes, L.; Martins, P.; Ferreira Marques, R.; Fonte, P. Resistive plate chambers in positron emission tomography. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2013, 128, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboghazleh, R.; Boyajian, S.D.; Atiyat, A.; Udwan, M.; Al-Helalat, M.; Al-Rashaideh, R. Rodent brain extraction and dissection: A comprehensive approach. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spijker, S. Dissection of Rodent Brain Regions. In Neuroproteomics; Li, K.W., Ed.; Humana: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 57, pp. 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- DiCarlo, L.M.; Vied, C.; Nowakowski, R.S. The stability of the transcriptome during the estrous cycle in four regions of the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 3360–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Meng, F.; Smerin, S.E.; Xing, G.; Zhang, L.; Su, D.M.; Benedek, D.; Ursano, R.; Su, Y.A.; Li, H. Biomarkers in an Animal Model for Revealing Neural, Hematologic, and Behavioral Correlates of PTSD. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 68, 3361. [Google Scholar]
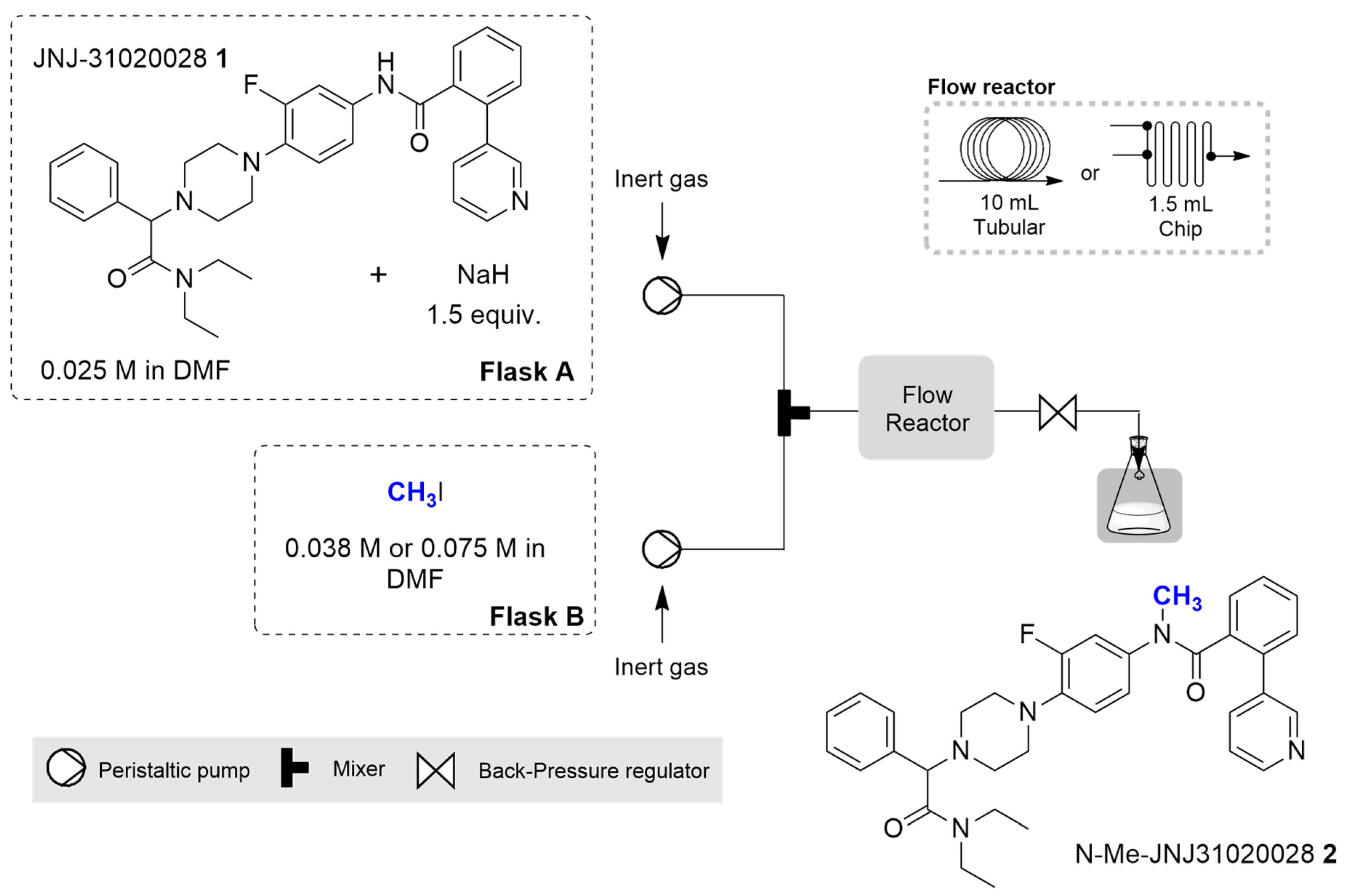


| Entry | Stoichiometry (Equiv. of CH3I) | Temperature (°C) | Residence Time (min) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Conversion (%) (b),(c) | Yield (%) (b),(c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | 25 | 25 | 0.4 | 82 ± 3.8 | 64 ± 7.2 |
| 2 | 1.5 | 25 | 10 | 1.0 | 99 ± 0.6 | 87 ± 3.5 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 25 | 5 | 2.0 | 99 ± 1.0 | 90 ± 1.5 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 25 | 3 | 3.3 | 99 ± 1.5 | 88 ± 2.5 |
| 5 | 1.5 | 40 | 5 | 2.0 | 97 ± 2.0 | 92 ± 1.5 |
| 6 | 3.0 | 25 | 5 | 2.0 | 98 ± 2.0 | 81 ± 3.2 |
| 7 | 3.0 | 40 | 5 | 2.0 | 98 ± 1.5 | 77 ± 7.6 |
| Entry | Stoichiometry (Equiv. of CH3I) | Temperature (°C) | Residence Time (min) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Conversion (%) (b),(c) | Yield (%) (b),(c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | 25 | 5 | 0.3 | 66 ± 2.1 | 60 ± 4.9 |
| 2 | 1.5 | 40 | 5 | 0.3 | 94 ± 2.0 | 88 ± 0.6 |
| 3 | 3.0 | 40 | 5 | 0.3 | 95 ± 1.0 | 89 ± 1.5 |
| 4 | CH3I (gas) | 40 | 5 | 0.3 | 98 ± 3.2 | 67 ± 5.3 |
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Base | Temperature (°C) | Stirring | Reaction Time (min) | [11C]2 (%) (a),(b) | RCY (d.c) (%) (b),(c) |
| 1 (d) | NaH (0.02 mg/mL) | 50 | Yes | 3 | 90.4 ± 0.65 | 41.8 ± 1.06 |
| 2 | NaH (0.02 mg/mL) | 50 | Yes | 3 | 85.4 ± 5.69 | 39.9 ± 0.68 |
| 3 | NaH (0.02 mg/mL) | 50 | No | 3 | 81.1 ± 7.77 | 37.4 ± 1.22 |
| 4 | NaH (0.02 mg/mL) | 50 | Yes | 5 | 78.4 ± 14.95 | 34.4 ± 5.06 |
| 5 | NaOH (5M) | 50 | No | 5 | 91.2 ± 3.04 | 38.3 ± 4.37 |
| 6 | NaOH (5M) | 50 | Yes | 5 | 68.7 ± 11.77 | 26.4 ± 3.66 |
| 7 | NaOH (5M) | 75 | No | 5 | 88.5 ± 6.30 | 41.0 ± 4.8 |
| 8 | NaOH (5M) | 75 | Yes | 5 | 80.3 ± 8.27 | 33.0 ± 7.83 |
| 9 (e) | NaOH (5M) | rt | No | 5 | 98.7 ± 1.14 | 31.3 ± 1.07 (f) |
| Tests | Specifications | N-[11C]-Me-JNJ31020028-1 | N-[11C]-Me-JNJ31020028-2 | N-[11C]-Me-JNJ31020028-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, colourless solution | Comply | Comply | Comply |
| pH after dilution | 4.5–8.5 | 6.4 | 6.4 | 6.5 |
| Chemical purity | ||||
| N-Me-JNJ31020028 | ≥95% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Radiochemical purity | ||||
| N-[11C]-Me-JNJ31020028 | ≥95% | 99.2% | 99.9% | 99.4% |
| Radionuclidic purity | ||||
| Radionuclidic identification − Energy photons ϒ | The only gamma photons have energy of 0.511 MeV. A sum peak of 1.022 MeV may be observed | Comply | Comply | Comply |
| Half-life | 19.9 to 20.9 min | 20.1 | 20.2 | 20.2 |
| Residual Solvents | ||||
| Ethanol | ≤2500 mg/10 mL (a) | 491.2 | 900.8 | 504.2 |
| Acetonitrile | ≤4 mg/10 mL | 2.9 | 2.0 | 0.8 |
| Biological Tests | ||||
| Sterility (b) | No evidence of microbial growth should be found | Comply | Comply | Comply |
| Bacterial endotoxins | ≤175 IU/10 mL | Comply | Comply | Comply |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fonseca, I.C.F.; Pais, M.L.; Rodrigues, F.M.S.; Sereno, J.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Cavadas, C.; Pereira, M.M.; Abrunhosa, A.J. Improved Chemical and Radiochemical Synthesis of Neuropeptide Y Y2 Receptor Antagonist N-Methyl-JNJ-31020028 and Preclinical Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040474
Fonseca ICF, Pais ML, Rodrigues FMS, Sereno J, Castelo-Branco M, Cavadas C, Pereira MM, Abrunhosa AJ. Improved Chemical and Radiochemical Synthesis of Neuropeptide Y Y2 Receptor Antagonist N-Methyl-JNJ-31020028 and Preclinical Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040474
Chicago/Turabian StyleFonseca, Inês C. F., Mariana Lapo Pais, Fábio M. S. Rodrigues, José Sereno, Miguel Castelo-Branco, Cláudia Cavadas, Mariette M. Pereira, and Antero J. Abrunhosa. 2024. "Improved Chemical and Radiochemical Synthesis of Neuropeptide Y Y2 Receptor Antagonist N-Methyl-JNJ-31020028 and Preclinical Positron Emission Tomography Studies" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040474
APA StyleFonseca, I. C. F., Pais, M. L., Rodrigues, F. M. S., Sereno, J., Castelo-Branco, M., Cavadas, C., Pereira, M. M., & Abrunhosa, A. J. (2024). Improved Chemical and Radiochemical Synthesis of Neuropeptide Y Y2 Receptor Antagonist N-Methyl-JNJ-31020028 and Preclinical Positron Emission Tomography Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040474