3-Methoxy-Phencyclidine Induced Psychotic Disorder: A Literature Review and an 18F-FDG PET/CT Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Emerging Phenomenon of NPS
1.2. About 3-Methoxy-Phencyclidine
1.2.1. General Pharmacology
1.2.2. Intoxication and Clinical Manifestations
1.2.3. The Effects of Other PCP-Derivatives and Novel Dissociative Compounds
1.3. Limitations and ‘Unmet Needs’
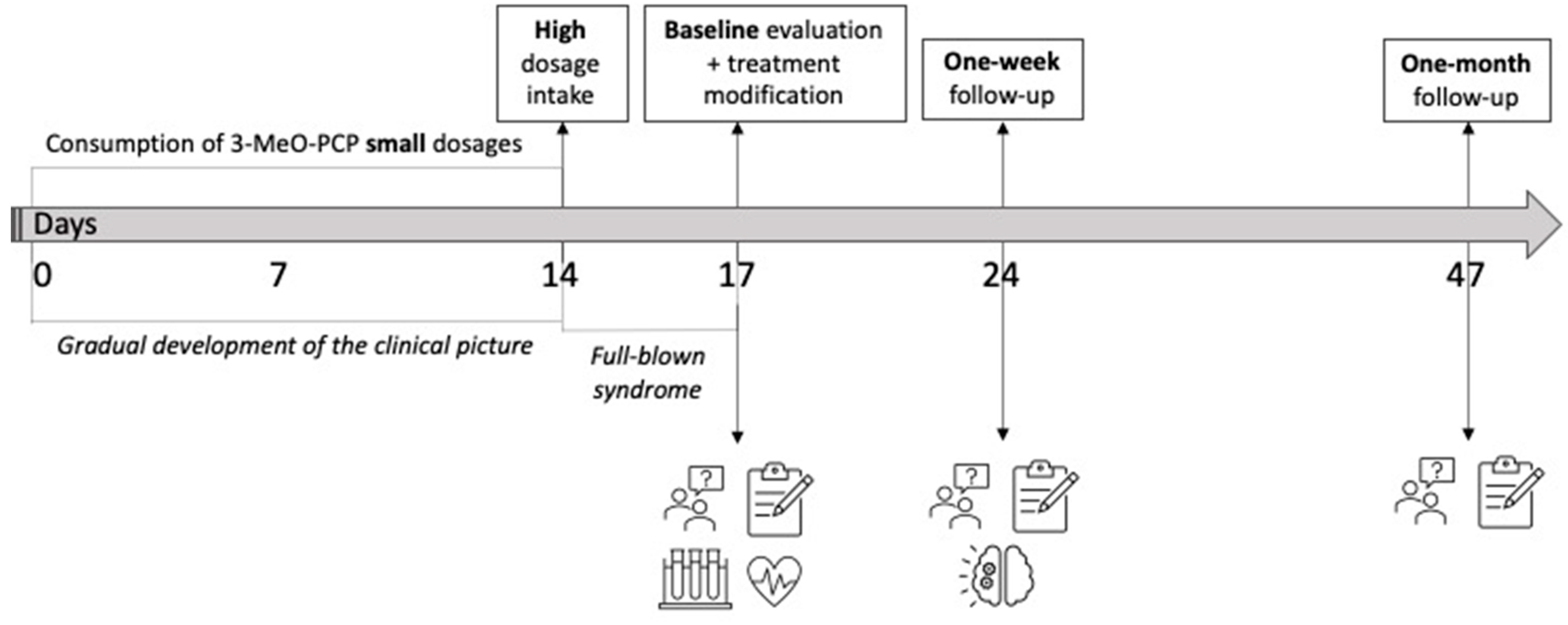
2. Case History
2.1. Methods
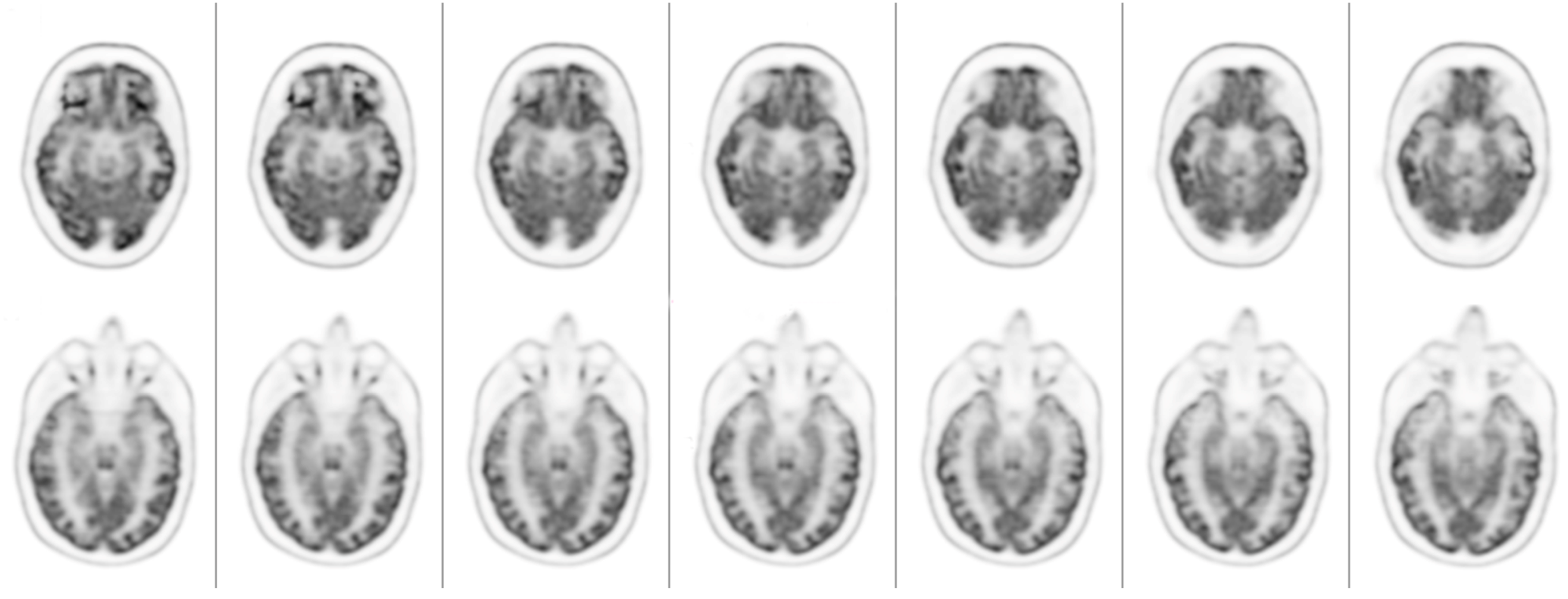
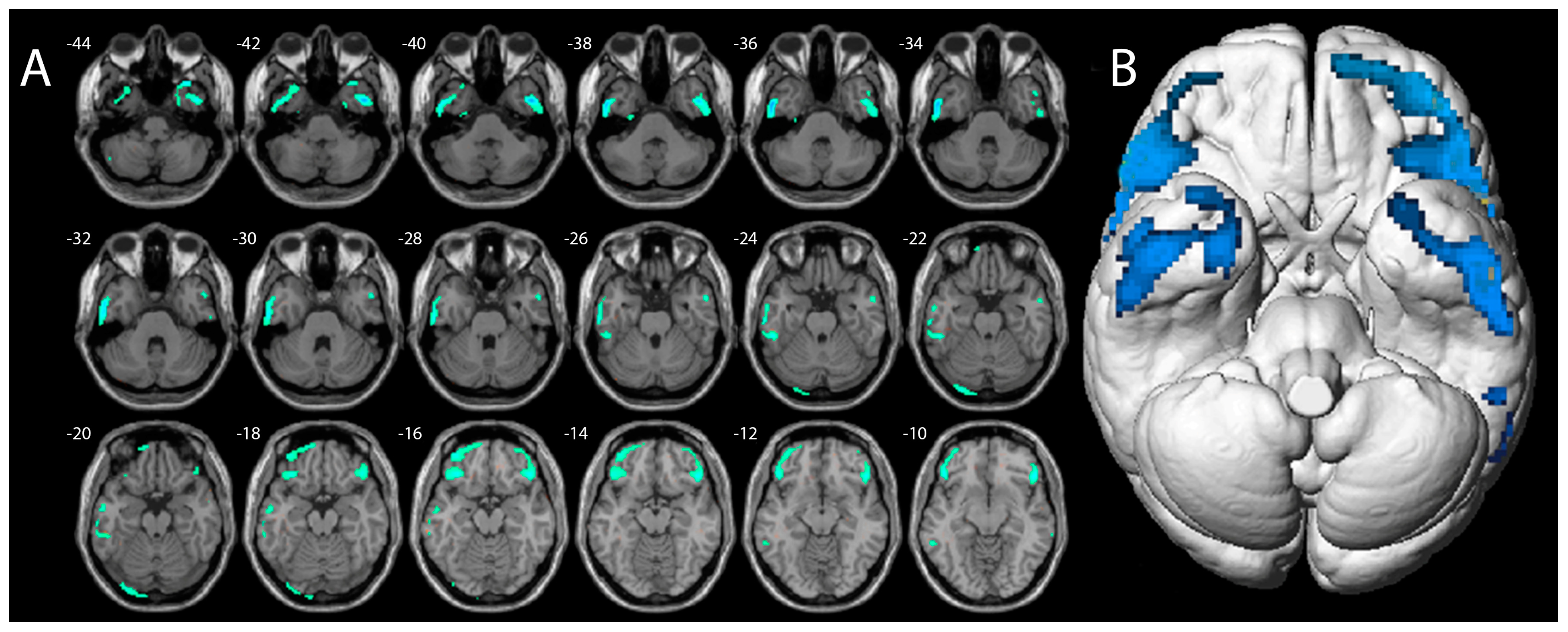
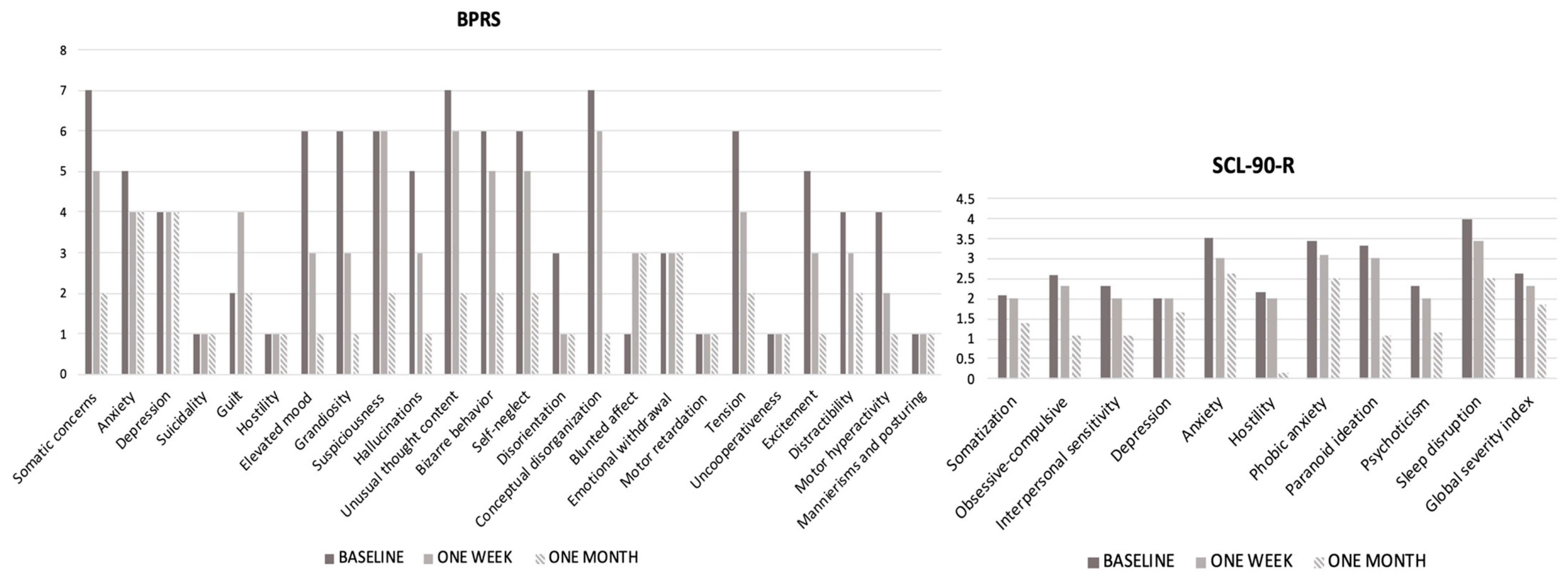
2.2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Substance-Induced Psychosis: A Diagnostic Challenge
3.2. NPS-Induced Psychosis: Focus on 3-MeO-PCP
3.3. The Effects of 3-MeO-PCP on Cognitive Functioning and Brain Metabolism
3.4. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. UNODC, World Drug Report, 2013; United Nations Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. UNODC, World Drug Report 2023; United Nations Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, R.; Le Daré, B.; Grandin, L.; Couette, A.; Ferron, P.-J.; Morel, I.; Gicquel, T. New psychoactive substance cocktail in an intensive care intoxication case elucidated by molecular networking. Clin. Toxicol. 2022, 60, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Faro, A.F.; Berardinelli, D.; Cassano, T.; Dendramis, G.; Montanari, E.; Montana, A.; Berretta, P.; Zaami, S.; Busardò, F.P.; Huestis, M.A. New Psychoactive Substances Intoxications and Fatalities during the COVID-19 Epidemic. Biology 2023, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. European Drug Report 2023: Trends and Developments. 2023. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/european-drug-report/2023_en (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Presidenza Consiglio dei Ministri, Dipartimento Politiche Antidroga. Relazione annuale al Parlamento sul Fenomeno Delle Tossicodipendenze in Italia Anno 2023 (Dati 2022). Available online: https://www.politicheantidroga.gov.it (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Shafi, A.; Berry, A.J.; Sumnall, H.; Wood, D.M.; Tracy, D.K. New psychoactive substances: A review and updates. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 10, 2045125320967197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertol, E.; Pascali, J.; Palumbo, D.; Catalani, V.; Di Milia, M.G.; Fioravanti, A.; Mari, F.; Vaiano, F. 3-MeO-PCP intoxication in two young men: First in vivo detection in Italy. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 274, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.L.; da Costa, M.J.C.S.P.; Tarelho, S.; Sousa, L.; Russo, F.; Franco, J.M. Intoxication by 3-MeO-PCP and O-desmethyltramadol: An unusual NPS mix. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2022, 136, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holborn, T.; Schifano, F.; Deluca, P. No prescription? No problem: A qualitative study investigating self-medication with novel psychoactive substances (NPS). Int. J. Drug Policy 2023, 118, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, D.K.; Wood, D.M.; Baumeister, D. Novel psychoactive substances: Types, mechanisms of action, and effects. BMJ. 2017, 356, i6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, R.; Le Daré, B.; Le Bouëdec, D.; Kernalléguen, A.; Ferron, P.-J.; Morel, I.; Gicquel, T. Arylcyclohexylamine Derivatives: Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacodynamic, Clinical and Forensic Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javitt, D.C.; Zukin, S.R.; Heresco-Levy, U.; Umbricht, D. Has an angel shown the way? Etiological and therapeutic implications of the PCP/NMDA model of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2012, 38, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouri, A.; Noda, Y.; Enomoto, T.; Nabeshima, T. Phencyclidine animal models of schizophrenia: Approaches from abnormality of glutamatergic neurotransmission and neurodevelopment. Neurochem. Int. 2007, 51, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, H.; Wallach, J. From PCP to MXE: A comprehensive review of the non-medical use of dissociative drugs. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 614–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palamar, J.J.; Le, A.; Cleland, C.M.; Keyes, K.M. Trends in drug use among nightclub and festival attendees in New York City, 2017–2022. Int. J. Drug Policy 2023, 115, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, M.A.B.; Lövgren, H.; Kronstrand, R.; Green, H.; Bergström, M.A. Retrospective identification of new psychoactive substances in patient samples submitted for clinical drug analysis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 131, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, M.L.S.; Trujillo, K.A. Use and abuse of dissociative and psychedelic drugs in adolescence. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 203, 173129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendau, A.; Viohl, L.; Petzold, M.B.; Helbig, J.; Reiche, S.; Marek, R.; Romanello, A.; Moon, D.U.; Gross, R.E.; Masah, D.J.; et al. No party, no drugs? Use of stimulants, dissociative drugs, and GHB/GBL during the early COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Drug Policy 2022, 102, 103582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geneste, P.; Kamenka, J.M.; Ung, S.N.; Herrmann, P.; Goudal, R.; Trouiller, G. Conformational determination of phencyclidine derivatives in view of structure-activity correlation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 14–301. [Google Scholar]
- EMCDDA–Europol 2012 Annual Report on the Implementation of Council Decision 2005/387/JHA (New Drugs in Europe, 2012). Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/implementation-reports/2012_en (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Expert Committee on Drug Dependence. Critical Review Report: 3-Methoxyphencyclidine 3-MeO-PCP; World Health Organization: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wallach, J.; Brandt, S.D. Phencyclidine-based new psychoactive substances. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2018, 252, 261–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, B.L.; Gibbons, S.; Arunotayanun, W.; Huang, X.P.; Setola, V.; Treble, R.; Iversen, L. The ketamine analogue methoxetamine and 3- and 4-methoxy analogues of phencyclidine are high affinity and selective ligands for the glutamate NMDA receptor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, C.S.; Hudson, S.; Treble, R.; Hamnett, H.J. The First Fatal Intoxication with 3-MeO-PCP in the UK and a Review of the Literature. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2022, 46, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, S.; Allard, P.M.; Morel, I.; Gicquel, T. Application of a molecular networking approach for clinical and forensic toxicology exemplified in three cases involving 3-MeO-PCP, doxylamine, and chlormequat. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.; Lindstedt, D.; Roman, M.; Thelander, G.; Nielsen, E.I.; Lennborn, U.; Sandler, H.; Rubertsson, S.; Ahlner, J.; Kronstrand, R.; et al. A non-fatal intoxication and seven deaths involving the dissociative drug 3-MeO-PCP. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 275, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Tang, J.; Ma, M.; Wu, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Fletcher, P.C.; Hao, W. Frontal white matter abnormalities following chronic ketamine use: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain 2010, 133 Pt 7, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckberg, M.; Beck, O.; Helander, A. Phencyclidine analog use in Sweden—Intoxication cases involving 3-MeO-PCP and 4-MeO-PCP from the STRIDA project. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berar, A.; Allain, J.S.; Allard, S.; Lefevre, C.; Baert, A.; Morel, I.; Bouvet, R.; Gicquel, T. Intoxication with 3-MeO-PCP alone: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2019, 98, e18295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zidkova, M.; Hlozek, T.; Balik, M.; Kopecky, O.; Tesinsky, P.; Svanda, J.; Balikova, M.A. Two Cases of Non-fatal Intoxication with a Novel Street Hallucinogen: 3-Methoxy-Phencyclidine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 41, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Frison, G.; Zancanaro, F.; Frasson, S.; Quadretti, L.; Agnati, M.; Vlassich, F.; Gagliardi, G.; Salerno, T.M.G.; Donato, P.; Mondello, L. Analytical Characterization of 3-MeO-PCP and 3-MMC in Seized Products and Biosamples: The Role of LC-HRAM-Orbitrap-MS and Solid Deposition GC-FTIR. Front Chem. 2021, 8, 618339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameline, A.; Garnier, D.; Gheddar, L.; Richeval, C.; Gaulier, J.-M.; Raul, J.-S.; Kintz, P. Identification and analytical characterization of seven NPS, by combination of 1H NMR spectroscopy, GC-MS and UPLC-MS/MS®, to resolve a complex toxicological fatal case. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 298, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameline, A.; Greney, H.; Monassier, L.; Raul, J.S.; Kintz, P. Metabolites to parent 3-MeO-PCP ratio in human urine collected in two fatal cases. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbouche, N.; Kintz, P.; Zagdoun, C.; Gheddar, L.; Raul, J.S.; Ameline, A. Determination of 3-MeO-PCP in human blood and urine in a fatal intoxication case, with a specific focus on metabolites identification. Forensic Sci. Res. 2021, 6, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakota, E.; Arndt, C.; Romoser, A.A.; Wilson, S.K. Fatal Intoxication Involving 3-MeO-PCP: A Case Report and Validated Method. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.N.; Smith, M.P. A Case of Unusual Drug Screening Results. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, L.A.A.; Olyslager, E.J.H.; Duijst, W.L.J.M. The risk of emerging new psychoactive substances: The first fatal 3-MeO-PCP intoxication in The Netherlands. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2019, 65, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomila, I.; Leciñena, M.Á.; Elorza, M.Á.; Pastor, Y.; Sahuquillo, L.; Servera, M.; Puiguriguer, J.; Barcelo, B. Detectability of Dissociative Psychoactive Substances in Urine by Five Commercial Phencyclidine Immunoassays. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossenbacher, F.; Cazaubon, Y.; Feliu, C.; Ameline, A.; Kintz, P.; Passouant, O.; Mourvillier, B.; Djerada, Z. About 5 cases with 3 Meo-PCP including 2 deaths and 3 non-fatal cases seen in France in 2018. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2019, 31, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, A.; Beck, O.; Bäckberg, M. Intoxications by the dissociative new psychoactive substances diphenidine and methoxphenidine. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintz, P.; Ameline, A.; Walch, A.; Farrugia, A.; Raul, J.S. Murdered while under the influence of 3-MeO-PCP. Int. J. Legal Med. 2019, 133, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotulski, A.J.; Papsun, D.M.; Friscia, M.; Swartz, J.L.; Holsey, B.D.; Logan, B.K. Fatality Following Ingestion of Tetrahydrofuranylfentanyl, U-49900 and Methoxy-Phencyclidine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, e27–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leciñena, M.A.; Moreno, E.; Sahuquillo, L.; Ferrando, J.P.; Yates, C.; Gomila, I.; Elorza, M.A.; Martin, B.B. Analytically confirmed use of 3-methoxy-phencyclidine (3-MeO-PCP) in acute non-fatal polysubstance poisonings in Ibiza. In Proceedings of the 39th international Congress of the European Association of Poisons Centres and Clinical Toxicologists (EAPCCT), Naples, Italy, 21–24 May 2019; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell-Mata, C.; Thomas, B.; Peterson, B.; Couper, F. Two Fatal Intoxications Involving 3-Methoxyphencyclidine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 41, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.; Tuddenham, L. Novel psychoactive substance intoxication resulting in attempted murder. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2014, 25, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, S.; Lisbon, D.; Lin, T.; Gerona, R. Beyond Ketamine and Phencyclidine: Analytically Confirmed Use of Multiple Novel Arylcyclohexylamines. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2017, 49, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bersselaar, L.R.; van der Hoeven, J.G.; de Jong, B. Feeling death, being alive: 4-methylethcathinone/pentedrone addiction and 3-methoxyphencyclidine intoxication. Addict. Disord. Their Treatment 2021, 20, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsolini, L.; Chiappini, S.; Papanti, D.; De Berardis, D.; Corkery, J.M.; Schifano, F. The Bridge between Classical and “Synthetic”/Chemical Psychoses: Towards a Clinical, Psychopathological, and Therapeutic Perspective. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schifano, F.; Napoletano, F.; Chiappini, S.; Guirguis, A.; Corkery, J.M.; Bonaccorso, S.; Ricciardi, A.; Scherbaum, N.; Vento, A. New/emerging psychoactive substances and associated psychopathological consequences. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, A.; Cantù, F.; Crisanti, C.; Cereda, G.; Oldani, L.; Brambilla, P. Substance-Induced Psychoses: An Updated Literature Review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 694863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moccia, L.; Tofani, A.; Mazza, M.; Covino, M.; Martinotti, G.; Schifano, F.; Janiri, L.; Di Nicola, M. Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Impairment in Methoxetamine-Induced Psychosis: An 18F-FDG PET/CT Case Study. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2019, 51, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morosini, P.L.; Casacchia, M. Traduzione italiana della Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale, versione 4.0 ampliata (BPRS 4.0). Riv. Di Riabil. Psichiatr. E Psicosoc. 1995, III, 199–228. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, W. (Ed.) ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology; US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare Public Health Service Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 1976.
- Prunas, A.; Sarno, I.; Preti, E.; Madeddu, F.; Perugini, M. Psychometric properties of the Italian version of the SCL-90-R: A study on a large community sample. Eur. Psychiatry 2012, 27, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J. Digit Symbol Substitution Test: The Case for Sensitivity Over Specificity in Neuropsychological Testing. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 38, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombaugh, T.N. Trail Making Test A and B: Normative data stratified by age and education. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2004, 19, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E.; Sherman, E.M.S.; Spreen, O. A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms, and Commentary; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 14, pp. 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, A.B.; Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Simonsick, E.; Cawthon, P.M.; Harris, T.B. The Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) Study-Ground-Breaking Science for 25 Years and Counting. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 2024–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezak, M.D. Neuropsychological Assessment, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Foderaro, G.; Isella, V.; Mazzone, A.; Biglia, E.; Di Gangi, M.; Pasotti, F.; Sansotera, F.; Grobberio, M.; Raimondi, V.; Mapelli, C.; et al. Brand new norms for a good old test: Northern Italy normative study of MiniMental State Examination. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucht, S.; Kane, J.M.; Kissling, W.; Hamann, J.; Etschel, E.; Engel, R. Clinical implications of Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale scores. Br. J. Psychiatry 2005, 187, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucht, S.; Kane, J.M.; Etschel, E.; Kissling, W.; Hamann, J.; Engel, R.R. Linking the PANSS, BPRS, and CGI: Clinical implications. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gicas, K.M.; Parmar, P.K.; Fabiano, G.F.; Mashhadi, F. Substance-induced psychosis and cognitive functioning: A systematic review. Psychiatry Res. 2022, 308, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Classification of Diseases Eleventh Revision (ICD-11); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Martinotti, G.; De Risio, L.; Vannini, C.; Schifano, F.; Pettorruso, M.; Di Giannantonio, M. Substance-related exogenous psychosis: A postmodern syndrome. CNS Spectr. 2021, 26, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, D.; Lowman, K.L.; Nargiso, J.; McKowen, J.; Watt, L.; Yule, A.M. Substance-induced Psychosis in Youth. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 29, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.; Szigeti, A.; Kearney, A.; Clarke, M. Clinical characteristics of primary psychotic disorders with concurrent substance abuse and substance-induced psychotic disorders: A systematic review. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 197, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Koob, G.F.; McLellan, A.T.; Longo, D.L. Neurobiologic advances from the brain disease model of addiction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murnane, K.S.; Edinoff, A.N.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.D. Updated Perspectives on the Neurobiology of Substance Use Disorders Using Neuroimaging. Subst. Abuse Rehabil. 2023, 14, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terbeck, S.; Akkus, F.; Chesterman, L.P.; Hasler, G. The role of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in the pathogenesis of mood disorders and addiction: Combining preclinical evidence with human Positron Emission Tomography (PET) studies. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, C.G.; De Feyter, H.M.; Averill, L.A.; Jiang, L.; Averill, C.L.; Chowdhury, G.M.I.; Purohit, P.; de Graaf, R.A.; Esterlis, I.; Juchem, C.; et al. The effects of ketamine on prefrontal glutamate neurotransmission in healthy and depressed subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodo, E. The role of the hippocampo-prefrontal cortex system in phencyclidine-induced psychosis: A model for schizophrenia. J. Physiol. Paris 2013, 107, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, M.J.; Mead, R.N.; Galizio, M. Effects of N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists ketamine, methoxetamine, and phencyclidine on the odor span test of working memory in rats. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 26, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, S.; Pugliese, A.; Christensen, M.C.; Rosso, G.; Di Nicola, M.; Simonsen, K.; Ren, H. Effectiveness of Vortioxetine in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder in Real-World Clinical Practice in Italy: Results from the RELIEVE Study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Liu, K.; Qu, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; et al. Reduced Gray Matter Volume in Orbitofrontal Cortex Across Schizophrenia, Major Depressive Disorder, and Bipolar Disorder: A Comparative Imaging Study. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 919272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, K.E.; Carmody, D.P. Symbol Digit and the Quantitative EEG. J. Neurother. 2012, 16, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinàs-Reglà, J.; Vilalta-Franch, J.; López-Pousa, S.; Calvó-Perxas, L.; Torrents Rodas, D.; Garre-Olmo, J. The Trail Making Test. Assessment 2017, 24, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, M.; Bartolucci, G.; Marcelli, I.; Simonetti, A.; Camardese, G.; Di Nicola, M.; Sani, G. Reduction in Cognitive Symptoms Following Intranasal Esketamine Administration in Patients with Chronic Treatment-resistant Depression: A 12-Week Case Series. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2023, 29, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbey, A.K.; Colom, R.; Solomon, J.; Krueger, F.; Forbes, C.; Grafman, J. An integrative architecture for general intelligence and executive function revealed by lesion mapping. Brain 2012, 135 Pt 4, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, B.A.; Weyandt, L.L.; Hall, L.E.; Oster, D.R.; Gudmundsdottir, B.G.; Kuhar, B.G. Physiological substrates of executive functioning: A systematic review of the literature. Atten. Defic Hyperact. Disord. 2018, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horacek, J.; Dockery, C.; Kopecek, M.; Spaniel, F.; Novak, T.; Tislerova, B.; Klirova, M.; Palenicek, T.; Höschl, C. Regional brain metabolism as the predictor of performance on the Trail Making Test in schizophrenia. A 18FDG PET covariation study. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2006, 27, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, L.M.; Cochran, S.M.; Morris, B.J.; Pratt, J.A.; Reynolds, G.P. Chronic phencyclidine administration induces schizophrenia-like changes in N-acetylaspartate and N-acetylaspartylglutamate in rat brain. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 73, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-López, L.; Stamatakis, E.A.; Fernández-Serrano, M.J.; Gómez-Río, M.; Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Pérez-García, M.; Verdejo-García, A. Neural correlates of hot and cold executive functions in polysubstance addiction: Association between neuropsychological performance and resting brain metabolism as measured by positron emission tomography. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 203, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bralet, M.C.; Mitelman, S.A.; Goodman, C.R.; Lincoln, S.; Hazlett, E.A.; Buchsbaum, M.S. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography scans in patients with alcohol use disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 46, 994–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moujaes, F.; Preller, K.H.; Ji, J.L.; Murray, J.D.; Berkovitch, L.; Vollenweider, F.X.; Anticevic, A. Toward Mapping Neurobehavioral Heterogeneity of Psychedelic Neurobiology in Humans. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 93, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardo, T.; Batchelor, J.; Berry, J.; Francis, H.; Jafar, D.; Borchard, T. Cognitive Remediation as an Adjunct Treatment for Substance Use Disorders: A Systematic Review. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2022, 32, 161–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, A.; Barlati, S.; Ceraso, A.; Ariu, C.; Deste, G.; Wykes, T. Effectiveness, Core Elements, and Moderators of Response of Cognitive Remediation for Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.; Rainey-Smith, S.R.; Bird, S.; Bomke, J.; Bourgeat, P.; Brown, B.M.; Burnham, S.C.; Bush, A.I.; Chadunow, C.; Collins, S.; et al. Fifteen Years of the Australian Imaging, Biomarkers and Lifestyle (AIBL) Study: Progress and Observations from 2,359 Older Adults Spanning the Spectrum from Cognitive Normality to Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2021, 5, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrosky, F.; Decety, J.; Lozano, A.; Lujan, A.; Perez, M.; Munguia, A.; Castañeda, D.; Diaz, K.; Lara, R.; Sacristan, E.; et al. Can psychopathy be prevented? Clinical, neuroimaging, and genetic data: An exploratory study. Child Neuropsychol. 2023, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmer, A.T.; Mason, G.F.; Fucito, L.M.; O’Malley, S.S.; Cosgrove, K.P. How Imaging Glutamate, γ-Aminobutyric Acid, and Dopamine Can Inform the Clinical Treatment of Alcohol Dependence and Withdrawal. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 2268–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Country | Number of Cases | Gender, Age (Years) | Biological Samples | Other Substances/Drugs | Outcome | 3-MeO-PCP Concentration (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allard et al., 2019 [26] | France | 1 | M, 17 | Whole blood, Urine | No | Nonfatal | Not quantified |
| Ameline et al., 2019 [33] | France | 2 | M, 41 | Femoral blood, Urine | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 498, Urine: 16,700 |
| F, 39 | Femoral blood, Urine, Bile | Yes | Fatal | Blood:63, Urine: 94, Bile: 64 | |||
| Ameline et al., 2019 [34] | France | 1 | M, 41 | Femoral blood, Urine | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 498, Urine: 16,700 |
| Arbouche et al., 2021 [35] | France | 1 | M, 44 | Femoral blood, Urine | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 3525, Urine: 7384 |
| Backberg et al., 2015 [29] | Sweden | 59 (recorded from STRIDA Project) | M and F, 14–55 | Serum, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Serum range: 1–242 Urine range: 2–52,759 |
| Bakota et al., 2016 [36] | USA | 1 | M, 29 | Femoral blood, Heart blood | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 139 |
| Berar et al., 2019 [30] | France | 1 | M, 17 | Whole blood, Urine | No | Nonfatal | Blood: 71, Urine: 701 |
| Bertol et al., 2017 [8] | Italy | 2 | M, 19 | Whole blood, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Blood: 350, Urine: 6109 |
| M, 21 | Whole blood, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Blood: 180, Urine: 3003 | |||
| Chang et al., 2017 [37] | USA | 1 | M, 27 | Urine | No | Nonfatal | Not quantified |
| Copeland et al., 2022 [25] | UK | 1 | M, 33 | Femoral blood, Urine | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 48 Urine: 196 |
| de Jong et al., 2019 [38] | The Netherlands | 1 | M, 30 | Serum, Femoral blood | Yes | Fatal | Serum: 123, Femoral blood: 152 |
| Frison et al., 2021 [32] | Italy | 2 | - | Serum, Whole blood, Urine | No | Nonfatal | Not quantified |
| Gomila et al., 2019 [39] | Spain | 2 | F, 32 | Serum, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Serum: 47, Urine: 9645 |
| M, 24 | Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Urine: 561 | |||
| Grossenbacher et al., 2019 [40] | France | 5 | M, 36 | Blood, Urine | No | Nonfatal | Not quantified |
| M, 32 | Urine | No | Nonfatal | Not quantified | |||
| - | Urine | No | Nonfatal | Not quantified | |||
| M, 41 | Femoral blood, Urine | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 498, Urine: 16,700 | |||
| F, 39 | Femoral blood, Urine | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 63, Urine: 94 | |||
| Kintz et al., 2019 [42] | France | 1 | F, 39 | Femoral blood, Urine, Bile, Hair | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 63, Urine: 94, Bile: 64 |
| Helander et al., 2015 [41] | Sweden | 4 (recorded from STRIDA Project) | M and F, 27–48 | Serum, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Not quantified |
| Johansson et al., 2017 [27] | Sweden | 8 | M, 27 | Femoral blood | No | Fatal | 380 |
| M, 21 | Femoral blood | Yes | Fatal | 180 | |||
| M, 27 | Femoral blood | Yes | Fatal | 230 | |||
| M, 29 | Femoral blood | Yes | Fatal | 120 | |||
| M, 32 | Femoral blood | Yes | Fatal | 60 | |||
| M, 27 | Femoral blood | Yes | Fatal | 50 | |||
| F, 20 | Femoral blood | Yes | Fatal | 80 | |||
| M, 19 | Whole blood | No | Nonfatal | 140 | |||
| Krotulski et al., 2018 [43] | USA | 1 | M, 31 | Peripheral blood, Urine | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 1, Urine: 32 |
| Leciñena et al., 2019 [44] | Spain | 2 | F, 32 | Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Not quantified |
| M, 24 | Serum, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Serum: 47 | |||
| Mitchell-Mata et al., 2017 [45] | USA | 2 | M, 21 | Peripheral blood | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 3200 |
| M, 58 | Central blood, Urine | Yes | Fatal | Blood: 630 | |||
| Pelletier et al., 2021 [3] | France | 1 | M, 37 | Peripheral blood, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Urine: 1,100,000 |
| Stevenson et al., 2014 [46] | UK | 1 | M, 20 | - | Yes | Nonfatal | - |
| Thornton et al., 2017 [47] | USA | 1 | M, 27 | Whole blood, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Serum: 167 |
| van den Bersselaar et al., 2021 [48] | The Netherlands | 1 | M, 40 | - | No | Nonfatal | - |
| Zidkova et al., 2017 [31] | Czech Republic | 2 | M, 37 | Whole blood, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Serum: 49 |
| M, 40 | Whole blood, Urine | Yes | Nonfatal | Serum: 66 |
| Baseline | One Week | One Month | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSST a | 29 | 31 | 42 |
| TMT-A b | 30 | 26 | 23 |
| TMT-B b | 120 | 118 | 81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pepe, M.; Di Nicola, M.; Cocciolillo, F.; Chiappini, S.; Martinotti, G.; Calcagni, M.L.; Sani, G. 3-Methoxy-Phencyclidine Induced Psychotic Disorder: A Literature Review and an 18F-FDG PET/CT Case Report. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040452
Pepe M, Di Nicola M, Cocciolillo F, Chiappini S, Martinotti G, Calcagni ML, Sani G. 3-Methoxy-Phencyclidine Induced Psychotic Disorder: A Literature Review and an 18F-FDG PET/CT Case Report. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040452
Chicago/Turabian StylePepe, Maria, Marco Di Nicola, Fabrizio Cocciolillo, Stefania Chiappini, Giovanni Martinotti, Maria Lucia Calcagni, and Gabriele Sani. 2024. "3-Methoxy-Phencyclidine Induced Psychotic Disorder: A Literature Review and an 18F-FDG PET/CT Case Report" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040452
APA StylePepe, M., Di Nicola, M., Cocciolillo, F., Chiappini, S., Martinotti, G., Calcagni, M. L., & Sani, G. (2024). 3-Methoxy-Phencyclidine Induced Psychotic Disorder: A Literature Review and an 18F-FDG PET/CT Case Report. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040452








