Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Cell Therapy Based on Osteoblasts Derived from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Study Protocol for a Single-Center, Open-Label, Phase I Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Aims of This Study
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Characteristics and Preparation of the hUC-Os (CF-M801)
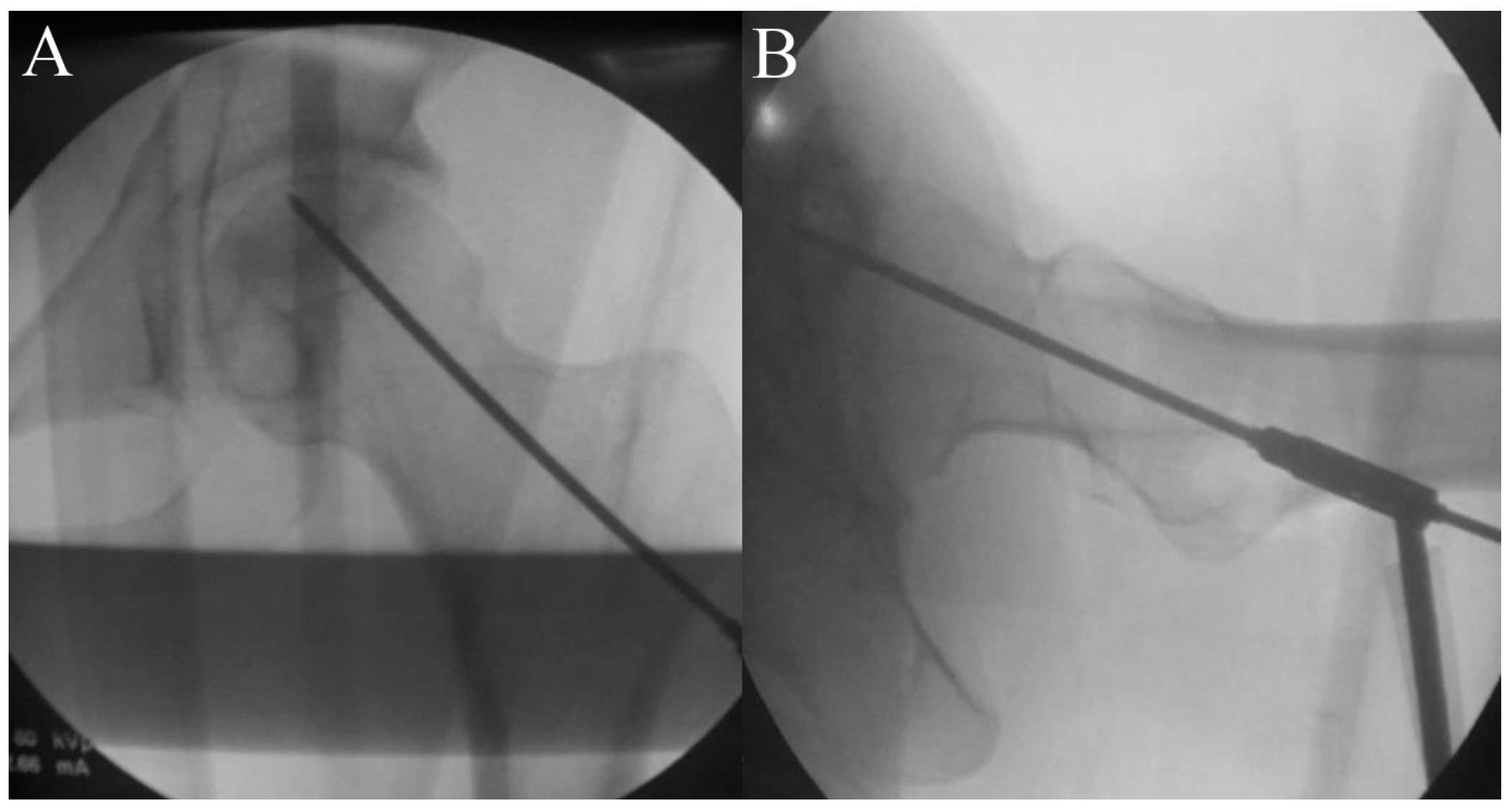
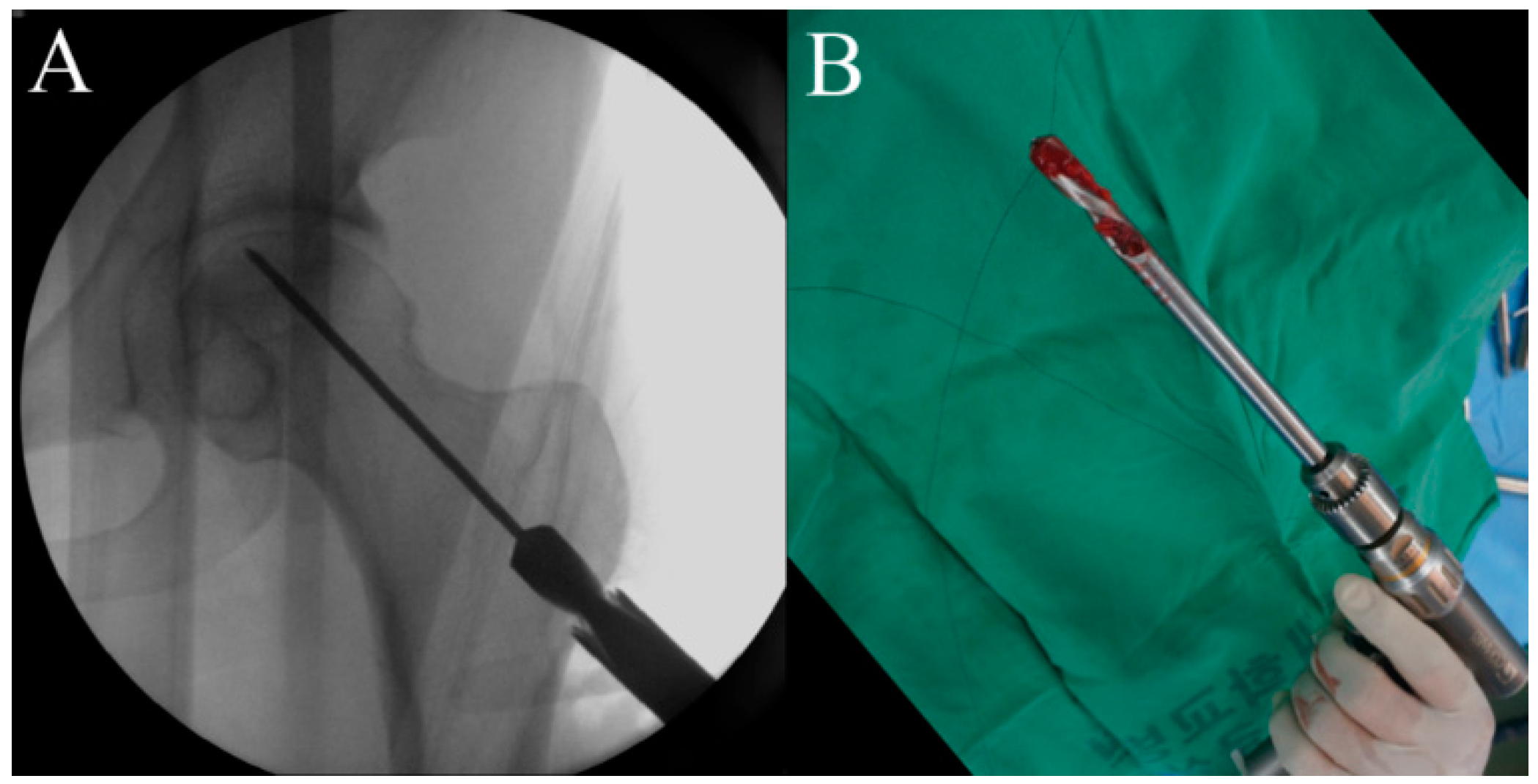
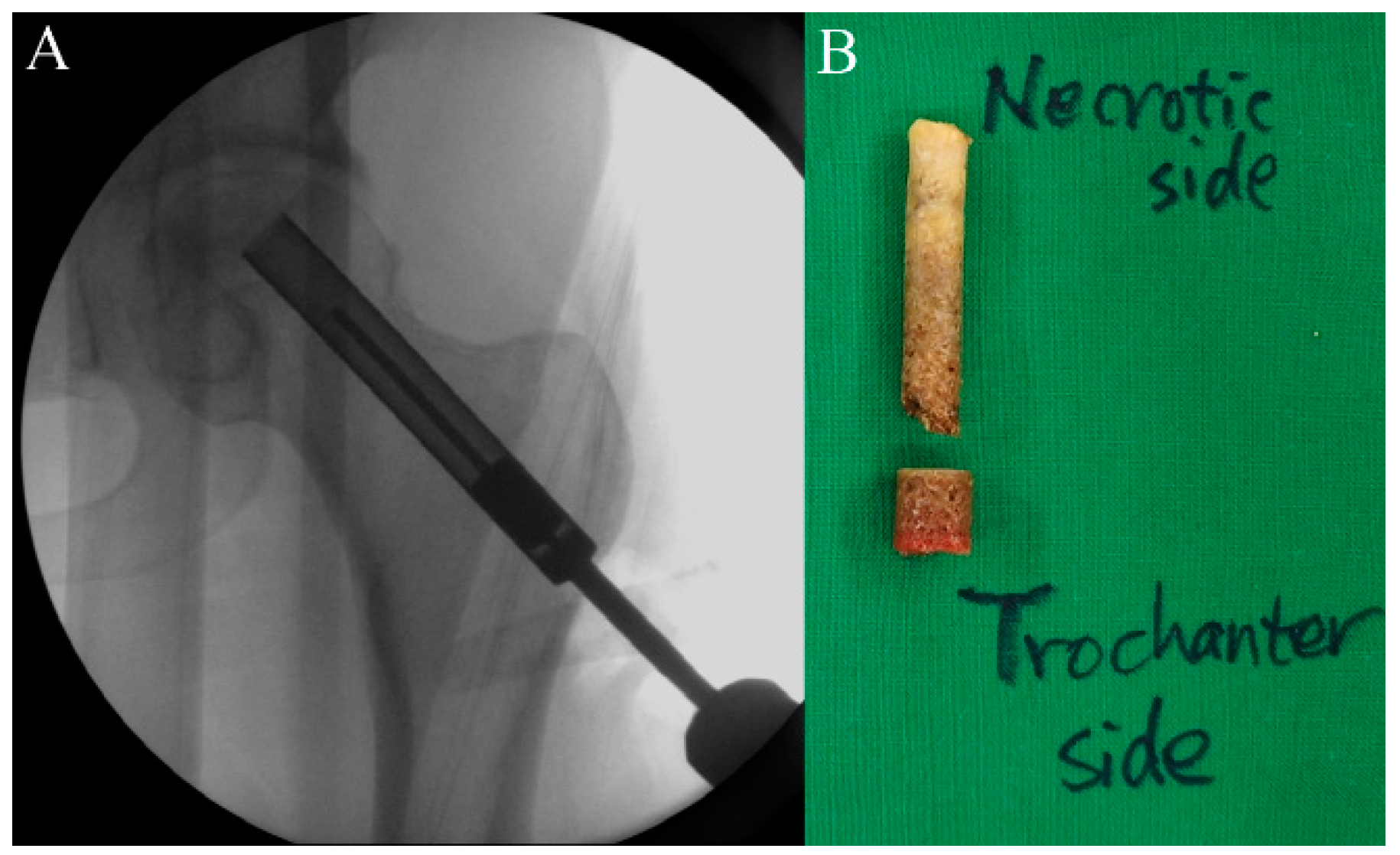
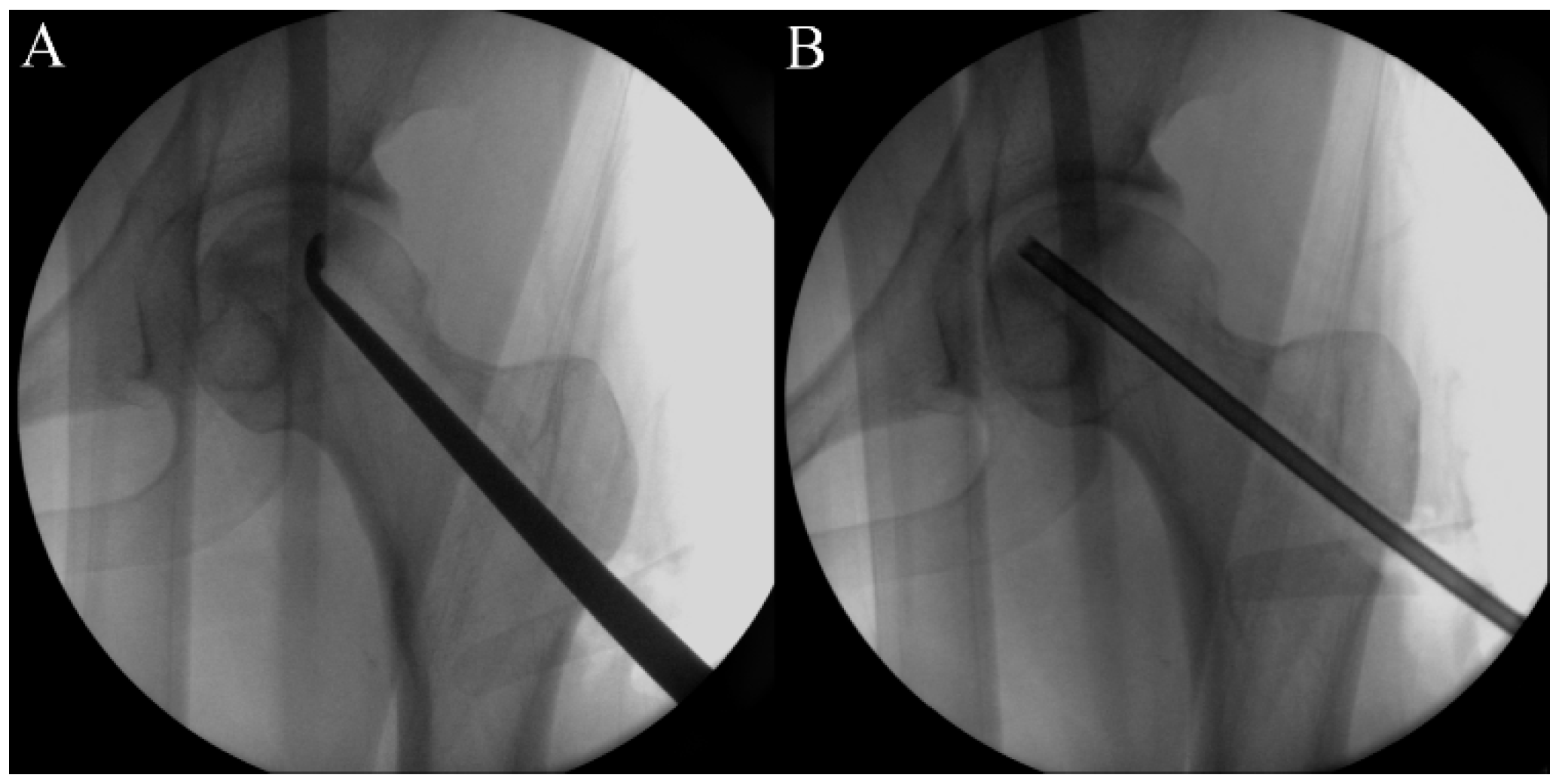
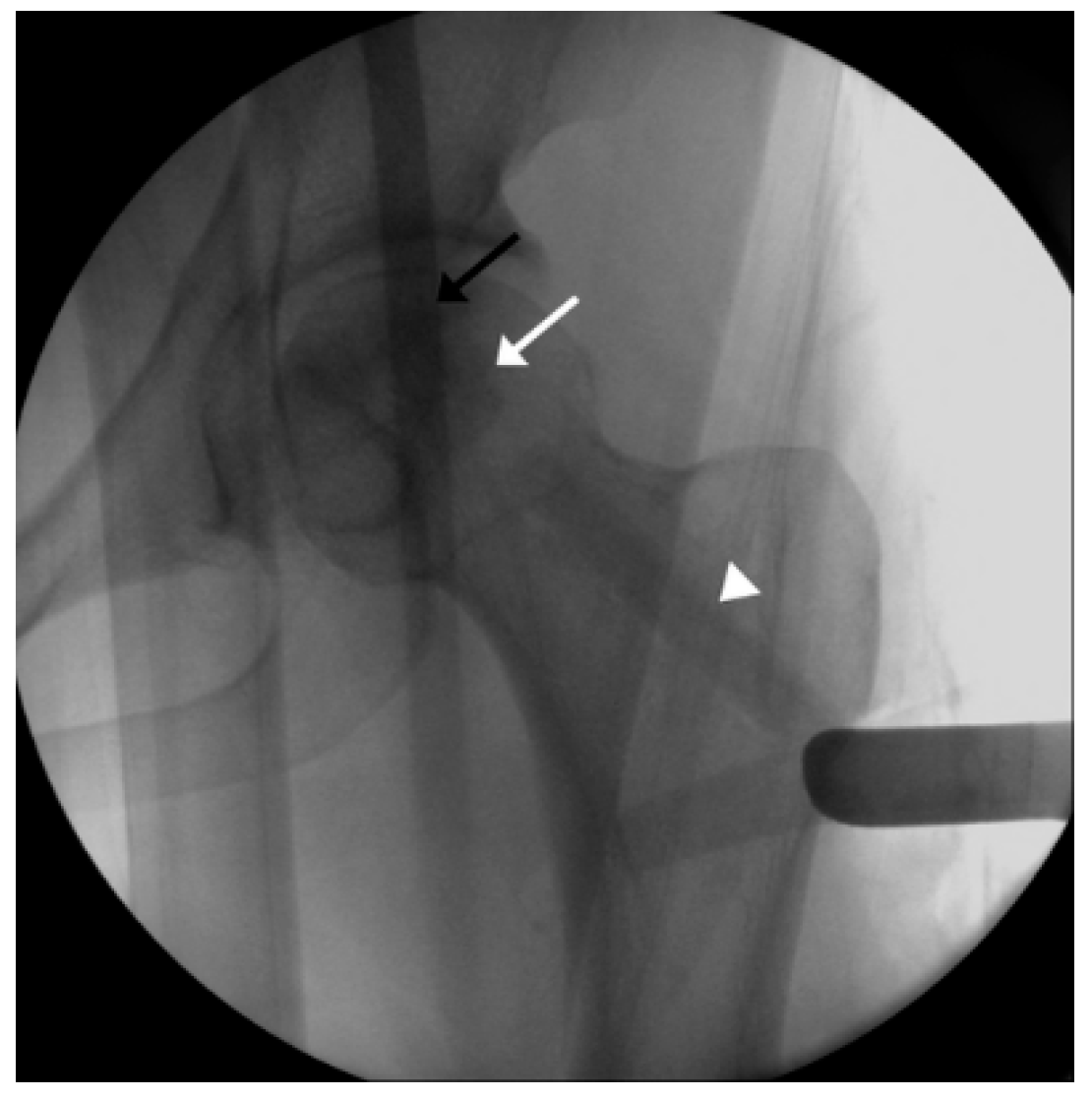
2.5. Procedure
2.6. Timeline and Study Protocol
2.7. Safety Assessment
2.7.1. Adverse Event
2.7.2. Laboratory Tests
- (1)
- Blood test: red blood cell (RBC) count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelet count, white blood cell (WBC) count, WBC differential count (neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, eosinophil, and basophil), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- (2)
- Blood chemistry test: total protein, albumin, total bilirubin, AST, ALT, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, glucose, alkaline phosphatase, total cholesterol, triglyceride, uric acid, C-reactive protein, panel reactive antibody (PRA), virus infection test (HIV antigen/antibody, hepatitis B surface antibody, anti-hepatitis C virus antibody, venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL).
- (3)
- Urinalysis: protein (albumin), glucose, ketones, WBC, RBC.
2.7.3. Vital Signs
2.7.4. Physical Examination
2.7.5. ECG Test
2.8. Clinical Assessment
2.8.1. Pain VAS Assessment [20]
2.8.2. HHS Assessment [21]
2.8.3. WOMAC Score Assessment [22]
2.9. Radiologic Assessment
2.9.1. Measuring Changes in Necrotic Lesion Size
2.9.2. ARCO Classification [23]
2.9.3. JIC Classification [26]
2.10. Data Collection, Management, and Analysis
2.10.1. Data Collection and Management
2.10.2. Data Analysis
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ARCO | Association research circulation osseous |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BMSC | Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell |
| CD | Cluster of differentiation |
| DLT | Dose-limiting toxicity |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| HA | Hydroxyapatite |
| HHS | Harris hip score |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| hUC-O | Human umbilical cord-derived osteoblast |
| hUCMSC | Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell |
| IRB | Institutional review board |
| JIC | Japanese investigation committee |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| MTD | Maximal tolerated dose |
| NCI-CTC | National Cancer Institute—Common Toxicity Criteria |
| ONFH | Osteonecrosis of the femoral head |
| PRA | Panel reactive antibody |
| RBC | Red blood cell |
| TCP | Tri-calcium phosphate |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| THA | Total hip arthroplasty |
| VAS | Visual analog scale |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| WOMAC | Western Ontario & McMaster Universities |
References
- Mont, M.A.; Zywiel, M.G.; Marker, D.R.; McGrath, M.S.; Delanois, R.E. The natural history of untreated asymptomatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic literature review. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2010, 92, 2165–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.N.; Racine, J.; Jones, L.C.; Aaron, R.K. Pathophysiology and risk factors for osteonecrosis. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2015, 8, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, L. Management of Severe Bone Defects in Femoral Revision following Total Hip Arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis 2024, 36, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopetz, J.J.; Losina, E.; Bliss, R.L.; Wright, J.; Baron, J.A.; Katz, J.N. Risk factors for revision of primary total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2012, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Baek, S.J. Outcomes of Hybrid Total Hip Arthroplasty for Subchondral Insufficiency Fracture of the Femoral Head. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2024, 16, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, T.P.; Jauregui, J.J.; Elmallah, R.K.; Lavernia, C.J.; Mont, M.A.; Nace, J. A current review of core decompression in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2015, 8, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronic, O.; Weiss, O.; Shoman, H.; Kriechling, P.; Khanduja, V. What are the outcomes of core decompression without augmentation in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head? Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, K.H.; Kim, R.; Ko, G.H.; Song, H.R.; Jeong, S.T.; Cho, S.H. Preventing collapse in early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A randomised clinical trial of core decompression. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1995, 77, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mont, M.A.; Carbone, J.J.; Fairbank, A.C. Core decompression versus nonoperative management for osteonecrosis of the hip. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 324, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Nuñez, J.H.; Sallent, A.; Gargallo-Margarit, A.; Gallardo-Calero, I.; Barro, V. Core Decompression Combined with Implantation of Autologous Bone Marrow Concentrate with Tricalcium Phosphate Does Not Prevent Radiographic Progression in Early Stage Osteonecrosis of the Hip. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Wu, W. Comparison of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and core decompression in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5024–5030. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaee, R.M.; Saberi, S.; Parvizi, J.; Mortazavi, S.M.; Farzan, M. Combining Concentrated Autologous Bone Marrow Stem Cells Injection with Core Decompression Improves Outcome for Patients with Early-Stage Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Comparative Study. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Xia, B.; Yu, N.; He, B.; Shen, Y.; Xiao, L.; Tong, P. The effects of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell arterial perfusion on vascular repair and angiogenesis in osteonecrosis of the femoral head in dogs. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.X.; Wang, L. Adenovirus-Mediated Expression of BMP-2 and BFGF in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with Demineralized Bone Matrix For Repair of Femoral Head Osteonecrosis in Beagle Dogs. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 43, 1648–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernigou, P.; Dubory, A.; Homma, Y.; Guissou, I.; Flouzat Lachaniette, C.H.; Chevallier, N.; Rouard, H. Cell therapy versus simultaneous contralateral decompression in symptomatic corticosteroid osteonecrosis: A thirty year follow-up prospective randomized study of one hundred and twenty five adult patients. Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piuzzi, N.S.; Chahla, J.; Jiandong, H.; Chughtai, M.; LaPrade, R.F.; Mont, M.A.; Muschler, G.F.; Pascual-Garrido, C. Analysis of Cell Therapies Used in Clinical Trials for the Treatment of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 2612–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, H.P.; Nguyen, X.H.; Do, P.T.X.; Dang, V.D.; Dam, P.T.M.; Bui, H.T.H.; Trinh, M.Q.; Vu, D.M.; et al. Differential Wound Healing Capacity of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Originated From Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue and Umbilical Cord Under Serum- and Xeno-Free Condition. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.J.; Ryu, H.H.; Park, S.S.; Koyama, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Woo, H.M.; Kim, W.H.; Kweon, O.K. Comparing the osteogenic potential of canine mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissues, bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, and Wharton’s jelly for treating bone defects. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 13, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Zhou, O.; Liu, J.; Zou, W.; Zhang, L.; Tian, D.; Dai, J.; Luo, Z.; Liu, E.; Fu, Z.; et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Alleviate Lung Injury in Rat Model of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia by Affecting Cell Survival and Angiogenesis. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63 (Suppl. S11), S240–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.H. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: Treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1969, 51, 737–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, N.; Buchanan, W.W.; Goldsmith, C.H.; Campbell, J.; Stitt, L.W. Validation study of WOMAC: A health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.H.; Mont, M.A.; Koo, K.H.; Chen, C.H.; Cheng, E.Y.; Cui, Q.; Drescher, W.; Gangji, V.; Goodman, S.B.; Ha, Y.C.; et al. The 2019 Revised Version of Association Research Circulation Osseous Staging System of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.C.; Jung, W.H.; Kim, J.R.; Seong, N.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Koo, K.H. Prediction of collapse in femoral head osteonecrosis: A modified Kerboul method with use of magnetic resonance images. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2006, 88 (Suppl. S3), 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.T.; Jo, W.L.; Cui, Q.; Mont, M.A.; Koo, K.H.; Cheng, E.Y.; Goodman, S.B.; Ha, Y.C.; Hernigou, P.; Jones, L.C.; et al. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: An Updated Review of ARCO on Pathogenesis, Staging and Treatment. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, N.; Atsumi, T.; Ohzono, K.; Kubo, T.; Hotokebuchi, T.; Takaoka, K. The 2001 revised criteria for diagnosis, classification, and staging of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J. Orthop. Sci. Off. J. Jpn. Orthop. Assoc. 2002, 7, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Li, N.; Xu, R. New perspective of skeletal stem cells. Biomater. Transl. 2022, 3, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, S.; Kover, K.; Luca, F. Thioredoxin Interacting Protein Expressed in Osteoblasts Mediates the Anti-Proliferative Effects of High Glucose and Modulates the Expression of Osteocalcin. J. Bone Metab. 2024, 31, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenschwander, B.; Branson, M.; Gsponer, T. Critical aspects of the Bayesian approach to phase I cancer trials. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 2420–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 5.0. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf (accessed on 9 August 2021).
- Hernigou, P.; Poignard, A.; Manicom, O.; Mathieu, G.; Rouard, H. The use of percutaneous autologous bone marrow transplantation in nonunion and avascular necrosis of bone. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2005, 87, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.H.; Dussault, R.G.; Kaplan, P.A.; Ahn, I.O.; Kim, R.; Devine, M.J.; Cui, Q.; Cho, S.H.; Wang, G.J. Fatty marrow conversion of the proximal femoral metaphysis in osteonecrotic hips. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1999, 361, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.N.; Yang, C.J.; Kim, J.E.; Du, Z.W.; Ren, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, H.Y.; Kim, K.O.; Noh, K.C. Enhanced Tendon-to-Bone Healing of Chronic Rotator Cuff Tears by Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate in a Rabbit Model. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 10, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piuzzi, N.S.; Chahla, J.; Schrock, J.B.; LaPrade, R.F.; Pascual-Garrido, C.; Mont, M.A.; Muschler, G.F. Evidence for the Use of Cell-Based Therapy for the Treatment of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 1698–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Cui, D.; Wang, B.; Tian, F.; Guo, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Yu, X. Treatment of early stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head with autologous implantation of bone marrow-derived and cultured mesenchymal stem cells. Bone 2012, 50, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, M.J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.G.; Zhang, R.; Ma, J.X.; Wang, D.C.; Ma, X.L. Exosomes derived from Wharton’s jelly of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce osteocyte apoptosis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via the miR-21-PTEN-AKT signalling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Qu, Z.; Yin, X.; Shang, C.; Ao, Q.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y. Efficacy of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A three-year follow-up study. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 4209–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tourneau, C.; Lee, J.J.; Siu, L.L. Dose escalation methods in phase I cancer clinical trials. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohan, P.; Treacy, O.; Griffin, M.D.; Ritter, T.; Ryan, A.E. Anti-Donor Immune Responses Elicited by Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles: Are We Still Learning? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hematopoietic | Mesenchymal | Osteoblast | Angiogenesis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markers | CD31 | CD45 | CD73 | CD105 | RUNX2 | COL1A | ANGPT-1 |
| Expression | ≤5% | ≤5% | ≥50% | ≥50% | ≥5 copies | ≥3000 pg/mL | ≥2000 pg/mL |
| Period | Screening | Treatment (g) | Follow-Up 1 | Follow-Up 2 | Study Completion /Dropout (i) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 (i) |
| Week | Within-3 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 12 |
| Visit window (days) | - | Within-3 | ±3 | ±7 | +7 |
| Written consent form (a) | X | ||||
| Demographic information | X | ||||
| Body weight and height measurement | X | ||||
| Review medical/operation history | X | X (h) | |||
| Review medication history | X | X (h) | |||
| Vital signs (b) | X | X (h) | X | X | X |
| Physical examination | X | X (h) | X | X | X |
| Clinical laboratory tests (c) | X (C−1), C−2) | X | X | X (C−1) | |
| ECG test | X | X | X | X | |
| Pregnancy test (d) | X | X | |||
| Radiographic examination | X (e) | X | X | X | |
| MRI examination | X | X | |||
| ARCO classification | X | X | |||
| JIC classification | X | X | |||
| Review inclusion/exclusion criteria | X | X | |||
| Patient selection | X | ||||
| Group allocation | X | ||||
| Core decompression | X | ||||
| hUC-Os administration | X | ||||
| Pain VAS assessment | X (h) | X | |||
| HHS assessment | X (h) | X | |||
| WOMAC assessment | X (h) | X | |||
| Adverse events assessment | X (f) | X | X | X | |
| Check concomitant drug use | X | X | X | X |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, S.-H.; Shim, B.-J.; Won, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Park, H.S.; Kim, S.-Y. Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Cell Therapy Based on Osteoblasts Derived from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Study Protocol for a Single-Center, Open-Label, Phase I Clinical Trial. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101366
Baek S-H, Shim B-J, Won H, Lee S, Lee YK, Park HS, Kim S-Y. Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Cell Therapy Based on Osteoblasts Derived from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Study Protocol for a Single-Center, Open-Label, Phase I Clinical Trial. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101366
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Seung-Hoon, Bum-Jin Shim, Heejae Won, Sunray Lee, Yeon Kyung Lee, Hyun Sook Park, and Shin-Yoon Kim. 2024. "Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Cell Therapy Based on Osteoblasts Derived from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Study Protocol for a Single-Center, Open-Label, Phase I Clinical Trial" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101366
APA StyleBaek, S.-H., Shim, B.-J., Won, H., Lee, S., Lee, Y. K., Park, H. S., & Kim, S.-Y. (2024). Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Cell Therapy Based on Osteoblasts Derived from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Study Protocol for a Single-Center, Open-Label, Phase I Clinical Trial. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101366






