Glucose-Lowering Drugs and Primary Prevention of Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Primary Care Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Incidence of CKD in the T2DM Cohort
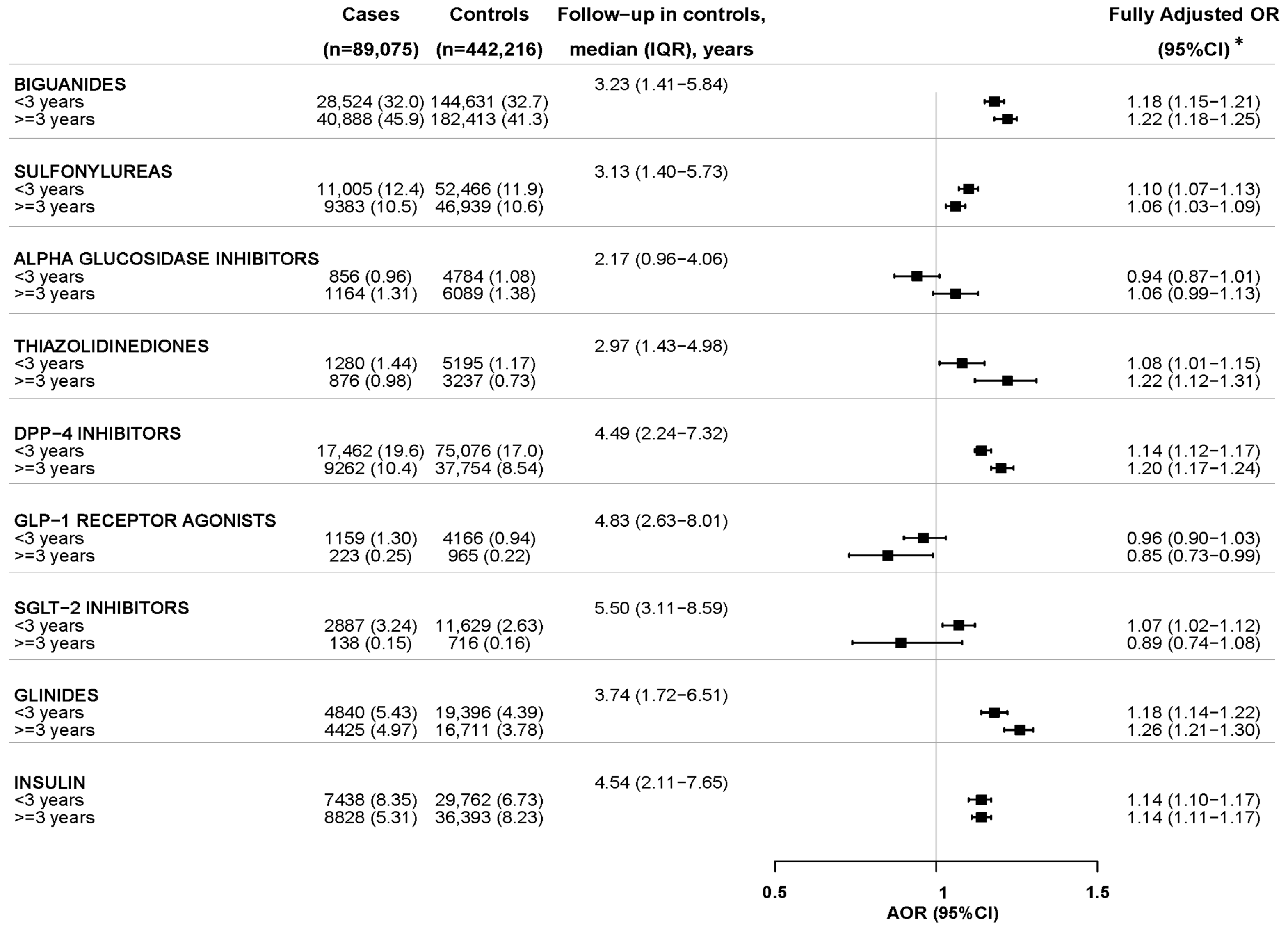
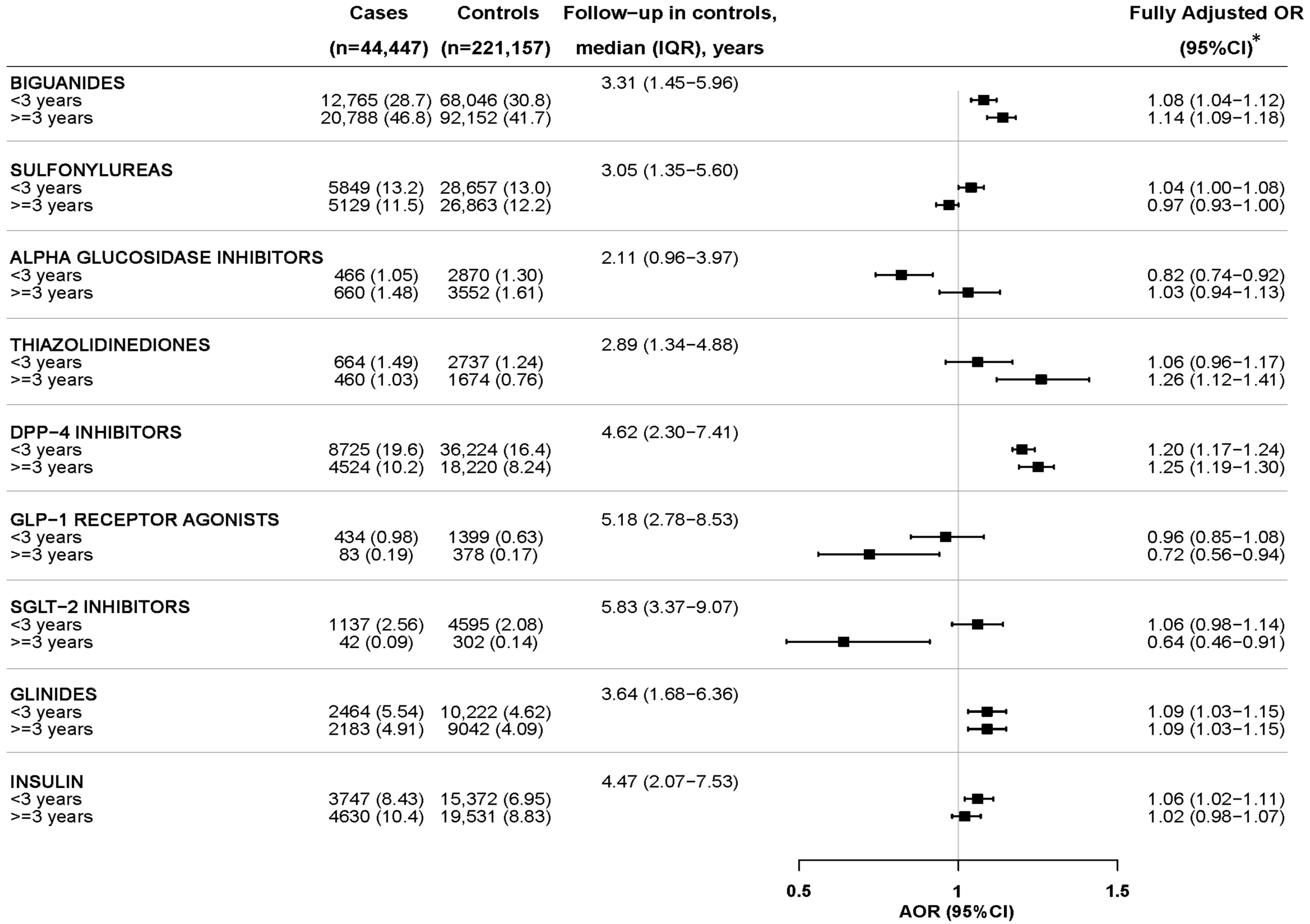
2.2. Nested Case–Control Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Patients and Methods
4.1. Source of Information
4.2. Design and Study Population
4.3. Case Definition
4.4. Follow-Up
4.5. Nested Case–Control Study
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEMPS | Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (Spanish Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices) |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| AOR | adjusted odds ratio |
| BIFAP | Base de datos para la Investigación Farmacoepidemiológica en el Ámbito Público |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CKD-EPI | chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration |
| CKI | chronic kidney insufficiency |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| GLD | glucose-lowering drug |
| GLP-1 RA | glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| KDIGO | kidney disease improving global outcomes |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PAD | peripheral artery disease |
| SGLT-2i | Sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors |
| TIA | transient ischemic attack |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
References
- Jager, K.J.; Kovesdy, C.; Langham, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Jha, V.; Zoccali, C. A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1803–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz A; Asociación Información Enfermedades Renales Genéticas (AIRG-E); European Kidney Patients’ Federation (EKPF); Federación Nacional de Asociaciones para la Lucha Contra las Enfermedades del Riñón (ALCER); Fundación Renal Íñigo Álvarez de Toledo (FRIAT); Red de Investigación Renal (REDINREN); Resultados en Salud 2040 (RICORS2040); Sociedad Española de Nefrología (SENEFRO) Council; Sociedad Española de Trasplante (SET) Council; Organización Nacional de Trasplantes (ONT). RICORS2040: The need for collaborative research in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J. 2021, 15, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.-W.; et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ERA-EDTA Council; ERACODA Working Group. Chronic kidney disease is a key risk factor for severe COVID-19: A call to action by the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gomez, M.V.; Bartsch, L.-A.; Castillo-Rodriguez, E.; Fernandez-Prado, R.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Gracia-Iguacel, C.; Ortiz, A. Clarifying the concept of chronic kidney disease for non-nephrologists. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; De Francisco, A.L.; De Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J.; et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Ruiz-Hurtado, G.; Miranda, B.; Ortiz, A.A. Use of chronic kidney disease blind spot to prevent cardiorenal outcomes. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.; Wanner, C.; Council, T.E.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Cozzolino, M.; Fliser, D.; Gambaro, G.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Rychlık, I.; Sarafidis, P.; et al. Chronic kidney disease as cardiovascular risk factor in routine clinical practice: A position statement by the Council of the European Renal Association. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Ortiz, A.; Lucia, A.; Miranda, B.; Alvarez-Llamas, G.; Barderas, M.G.; Volpe, M.; Ruiz-Hurtado, G.; Pitt, B. Prevention of cardiorenal damage: Importance of albuminuria. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Fernandez, B.; Sarafidis, P.; Soler, M.J.; Ortiz, A. EMPA-KIDNEY: Expanding the range of kidney protection by SGLT2 inhibitors. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astley, M.E.; Boenink, R.; ElHafeez, S.A.; Trujillo-Alemán, S.; Arribas, F.; Åsberg, A.; Beckerman, P.; Bell, S.; Bouzas-Caamaño, M.E.; Farnés, J.C.; et al. The ERA Registry Annual Report 2020: A summary. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1330–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosenzon, O.; Raz, I.; Wiviott, S.D.; Schechter, M.; Goodrich, E.L.; Yanuv, I.; Rozenberg, A.; Murphy, S.A.; Zelniker, T.A.; Langkilde, A.M.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Prevention of Kidney Disease Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Post Hoc Analyses From the DECLARE-TIMI 58 Trial. Diabetes Care. 2022, 45, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gragnano, F.; De Sio, V.; Calabrò, P. FLOW trial stopped early due to evidence of renal protection with semaglutide. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2024, 10, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, C.; Carriazo, S.; Soler, M.J.; Ortiz, A.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B. Tirzepatide and prevention of chronic kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 16, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Perkovic, V.; Wheeler, D.C.; Hantel, S.; George, J.T.; von Eynatten, M.; Koitka-Weber, A.; Wanner, C.; EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes across KDIGO Risk Categories: Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multinational Trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuen, B.L.; Ohkuma, T.; Neal, B.; Matthews, D.R.; de Zeeuw, D.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Fulcher, G.; Blais, J.; Li, M.Q.; Jardine, M.J.; et al. Relative and Absolute Risk Reductions in Cardiovascular and Kidney Outcomes with Canagliflozin across KDIGO Risk Categories: Findings from the CANVAS Program. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 23–34.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciá-Martínez, M.; Gil, M.; Huerta, C.; Martín-Merino, E.; Álvarez, A.; Bryant, V.; Montero, D.; BIFAP Team. Base de Datos para la Investigación Farmacoepidemiológica en Atención Primaria (BIFAP): A data resource for pharmacoepidemiology in Spain. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2020, 29, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Sattar, N.; Pavo, I.; Haupt, A.; Duffin, K.L.; Yang, Z.; Wiese, R.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; I Cherney, D.Z. Effects of tirzepatide versus insulin glargine on kidney outcomes in type 2 diabetes in the SURPASS-4 trial: Post-hoc analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L.S.; Eggers, P.W.; Star, R.A.; Kimmel, P.L. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivielso, J.M.; Balafa, O.; Ekart, R.; Ferro, C.J.; Mallamaci, F.; Mark, P.B.; Rossignol, P.; Sarafidis, P.; Del Vecchio, L.; Ortiz, A. Hyperkalemia in Chronic Kidney Disease in the New Era of Kidney Protection Therapies. Drugs 2021, 81, 1467–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafidis, P.; Ortiz, A.; Ferro, C.J.; Halimi, J.-M.; Kreutz, R.; Mallamaci, F.; Mancia, G.; Wanner, C.; ‘Hypertension and the Kidney’ working group of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and the ‘European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine’ (EURECA-m) working group of the European Renal Association—European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA). Sodium–glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for patients with diabetic and nondiabetic chronic kidney disease: A new era has already begun. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafidis, P.; Ferro, C.J.; Morales, E.; Ortiz, A.; Malyszko, J.; Hojs, R.; Khazim, K.; Ekart, R.; Valdivielso, J.; Fouque, D.; et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists for nephroprotection and cardioprotection in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. A consensus statement by the EURECA-m and the DIABESITY working groups of the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Von Eynatten, M.; Mattheus, M.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Zinman, B.; et al. Empagliflozin and Progression of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazner, M.H. SGLT2 Inhibition in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction—A Win against a Formidable Foe. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1522–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes management in chronic kidney disease: A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górriz, J.L.; Soler, M.J.; Navarro-González, J.F.; García-Carro, C.; Puchades, M.J.; D’marco, L.; Castelao, A.M.; Fernández-Fernández, B.; Ortiz, A.; Górriz-Zambrano, C.; et al. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Call of Attention to Nephrologists. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, K.; Taneda, S.; Yokota, I.; Okada, K.; Kurihara, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Iwamoto, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Ishigaki, Y.; Manda, N.; et al. The renoprotective effect of once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonist dulaglutide on progression of nephropathy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease (JDDM67). J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Wakabayashi, M.; Bhalla, A.; Chopra, N.; Miyashita, H.; Mikami, T.; Ueyama, H.; Fujisaki, T.; Saigusa, Y.; Yamaji, T.; et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with SGLT-2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med 2023. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossing, P.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Bakris, G.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Gislum, M.; Gough, S.C.L.; Idorn, T.; Lawson, J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; E Mann, J.F.; et al. The rationale, design and baseline data of FLOW, a kidney outcomes trial with once-weekly semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, G.; Huerta, C.; Gardarsdottir, H.; Logie, J.; González-González, R.; Abbing-Karahagopian, V.; Miret, M.; Schneider, C.; Souverein, P.C.; Webb, D.; et al. Hip/femur fractures associated with the use of benzodiazepines (anxiolytics, hypnotics and related drugs): A methodological approach to assess consistencies across databases from the PROTECT-EU project. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2016, 25 (Suppl. S1), 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernán, M.A. The hazards of hazard ratios. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanders, W.D.; Louv, W.C. The exposure odds ratio in nested case-control studies with competing risks. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 124, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; et al. 3. Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes and Associated Comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. S1), S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cases (%) | Person-Years | Incidence Rate (per 10 000 p-y) (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 89,075 (100) | 2,746,449.0 | 324.3 (322.2–326.5) |
| Overall, >40 years | 88,124 (98.9) | 2,635,660.2 | 334.4 (332.2–336.6) |
| Sex: Males Females | 45,059 (50.6) 44,016 (49.4) | 1,466,109 1,280,340 | 307.3 (304.5–310.2) 343.8 (340.6–347.0) |
| Obesity: No Yes | 36,079 (40.5) 52,996 (59.5) | 1,220,921 1,525,528 | 295.5 (292.5–298.6) 347.4 (344.4–350.4) |
| Dyslipidemia: No Yes | 38,238 (42.9) 50,837 (57.1) | 1,278,445 1,468,004 | 299.1 (296.1–302.1) 346.3 (343.3–349.3) |
| Hypertension: No Yes | 21,489 (24.1) 67,586 (75.9) | 1,069,286 1,677,163 | 201.0 (198.3–203.7) 403.0 (400.0–406.0) |
| AMI: No Yes | 83,145 (93.3) 5930 (6.66) | 2,616,625 1,298,241 | 317.8 (315.6–319.9) 456.8 (445.2–468.6) |
| Heart failure: No Yes | 82,320 (92.4) 6755 (7.58) | 2,656,553 89,895.8 | 309.9 (307.8–312.0) 751.4 (733.6–769.6) |
| Stroke: No Yes | 83,265 (93.5) 5450 (6.52) | 2,630,715 115,734.2 | 317.9 (315.7–320.0) 470.9 (458.5–483.6) |
| TIA: No Yes | 86,587 (97.2) 2488 (2.79) | 2,692,669 53,779.9 | 321.6 (319.4–323.7) 462.6 (444.6–481.2) |
| PAD: No Yes | 83,420 (93.7) 5655 (6.35) | 2,638,262 108,187.5 | 316.2 (314.1–318.3) 522.7 (509.2–536.5) |
| Cases (n = 89,075) | Controls (n = 442,216) | Age and Sex-Adjusted OR (95%CI) a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 44,016 (49.4) | 218,238 (49.4) | Matched |
| Age at index date, in years, median (IQR) | 72 (64–79) | 72 (64–79) | Matched |
| Follow-up to index date, years, median (IQR) | 3.42 (1.57–6.10) | 3.26 (1.47–5.87) | 1.02 (1.02–1.02) |
| Alcohol abuse, n (%) | 19,530 (21.9) | 98,870 (22.4) | 0.97 (0.96–0.99) |
| BMI, n (%): <30 kg/m2/not recorded ≥30 kg/m2 (obesity) | 31,993 (35.9) 57,082 (64.1) | 186,814 (42.2) 255,402 (57.8) | Reference 1.32 (1.29–1.33) |
| Smoking, n (%): Non-smokers Ex-smokers Current smokers Not recorded | 26,523 (29.8) 4359 (4.89) 25,784 (29.0) 32,409 (36.4) | 147,870 (33.4) 29,406 (6.65) 104,678 (23.7) 160,262 (36.2) | Reference 0.85 (0.82–0.88) 1.40 (1.38–1.43) 1.12 (1.10–1.14) |
| Isolated records of eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 prior to index date, n (%) >1 record | 16,160 (18.1) 3178 (3.57) | 49,280 (11.1) 7050 (1.59) | 1.82 (1.78–1.85) |
| Isolated records of positive albuminuria/proteinuria prior to index date, n (%) >1 record | 13,996 (15.7) 3564 (4.0) | 50,763 (11.5) 7360 (1.66) | 1.45 (1.42–1.48) |
| CKD stage, n (%): G1–G2 G3a G3b G4 G5 Not available b | 36,358 (40.8) 37,732 (42.4) 5763 (6.47) 777 (0.87) 175 (0.20) 8270 (9.28) | - | - |
| Comorbidities at index date, n (%): c Hypertension Dyslipidemia Atrial fibrillation Ischemic heart diseases Heart failure Gout (record or ULD use) Hyperuricemia (non-gout) Stroke PAD Hyperparathyroidism Osteoporosis Hematuria d Hyperkalemia d | 73,151 (82.1) 70,861 (79.6) 16,718 (18.8) 14,917 (16.8) 14,379 (16.1) 8263 (9.28) 41,010 (46.0) 13,226 (14.9) 9309 (10.5) 1050 (1.18) 11,950 (13.4) 8661 (9.72) 2988 (3.35) | 328,205 (74.2) 328,464 (74.3) 66,095 (15.0) 57,795 (13.1) 47,708 (10.8) 26,681 (6.03) 131,817 (29.8) 58,634 (13.3) 33,989 (7.69) 3265 (0.74) 61,233 (13.9) 34,470 (7.79) 6960 (1.57) | 1.65 (1.62–1.68) 1.36 (1.33–1.38) 1.34 (1.31–1.36) 1.35 (1.32–1.38) 1.64 (1.61–1.68) 2.38 (2.32–2.45) 2.30 (2.26–2.34) 1.15 (1.12–1.17) 1.42 (1.38–1.45) 1.61 (1.50–1.72) 0.96 (0.94–0.98) 1.28 (1.25–1.31) 2.18 (2.08–2.27) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Miguel, A.; Fernández-Fernández, B.; Ortiz, A.; Gil, M.; Rodríguez-Martín, S.; Ruiz-Hurtado, G.; Fernández-Antón, E.; Ruilope, L.M.; de Abajo, F.J. Glucose-Lowering Drugs and Primary Prevention of Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Primary Care Study. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101299
Rodríguez-Miguel A, Fernández-Fernández B, Ortiz A, Gil M, Rodríguez-Martín S, Ruiz-Hurtado G, Fernández-Antón E, Ruilope LM, de Abajo FJ. Glucose-Lowering Drugs and Primary Prevention of Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Primary Care Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101299
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Miguel, Antonio, Beatriz Fernández-Fernández, Alberto Ortiz, Miguel Gil, Sara Rodríguez-Martín, Gema Ruiz-Hurtado, Encarnación Fernández-Antón, Luis M. Ruilope, and Francisco J. de Abajo. 2024. "Glucose-Lowering Drugs and Primary Prevention of Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Primary Care Study" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101299
APA StyleRodríguez-Miguel, A., Fernández-Fernández, B., Ortiz, A., Gil, M., Rodríguez-Martín, S., Ruiz-Hurtado, G., Fernández-Antón, E., Ruilope, L. M., & de Abajo, F. J. (2024). Glucose-Lowering Drugs and Primary Prevention of Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Primary Care Study. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101299








