A Dataset for Constructing the Network Pharmacology of Overactive Bladder and Its Application to Reveal the Potential Therapeutic Targets of Rhynchophylline
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Creation of the OAB Disease Target Dataset
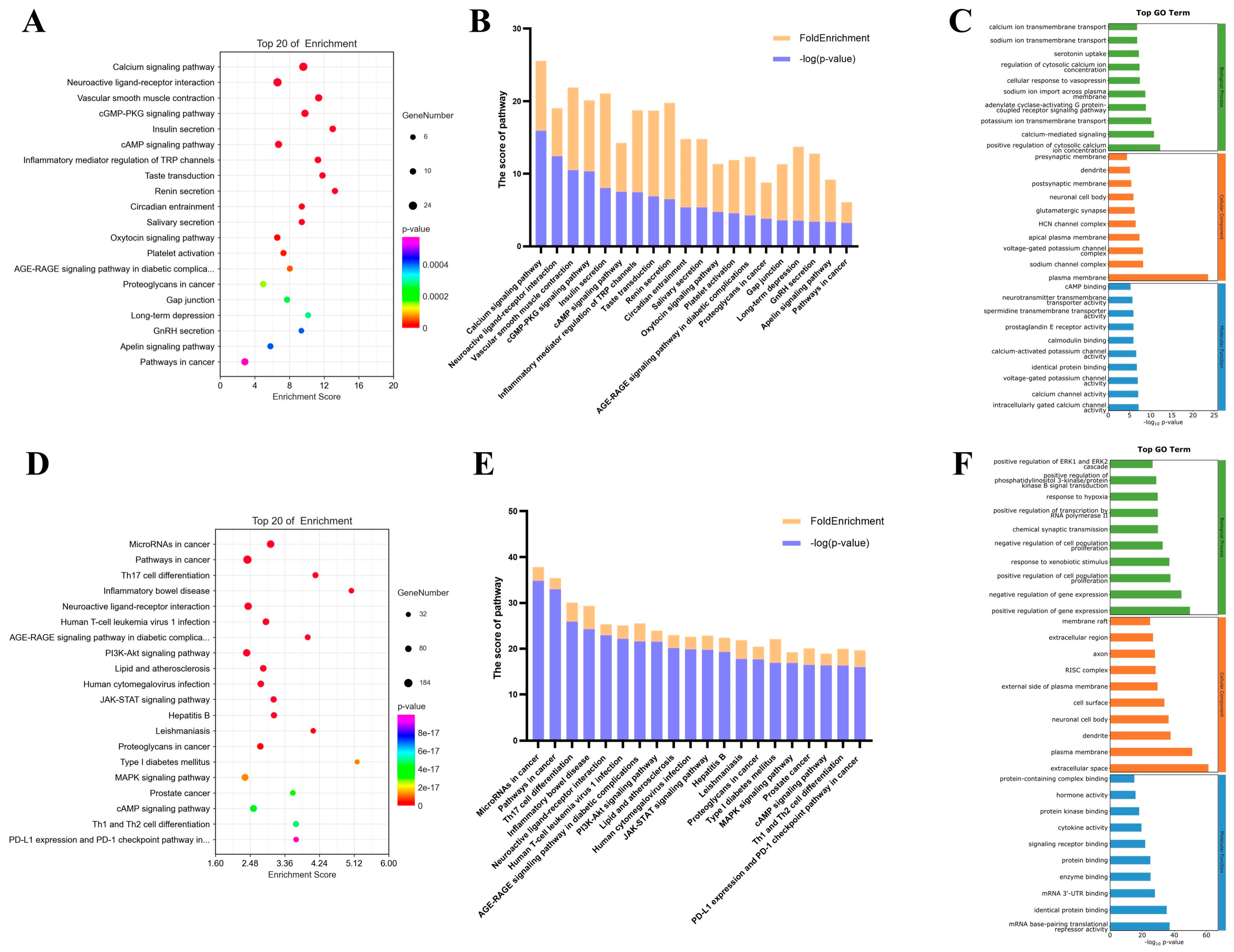
2.2. KEGG and GO Enrichment Results
2.3. Predicted Toxicity of Rhynchophylline
2.4. Rhynchophylline Targets and Intersecting Targets
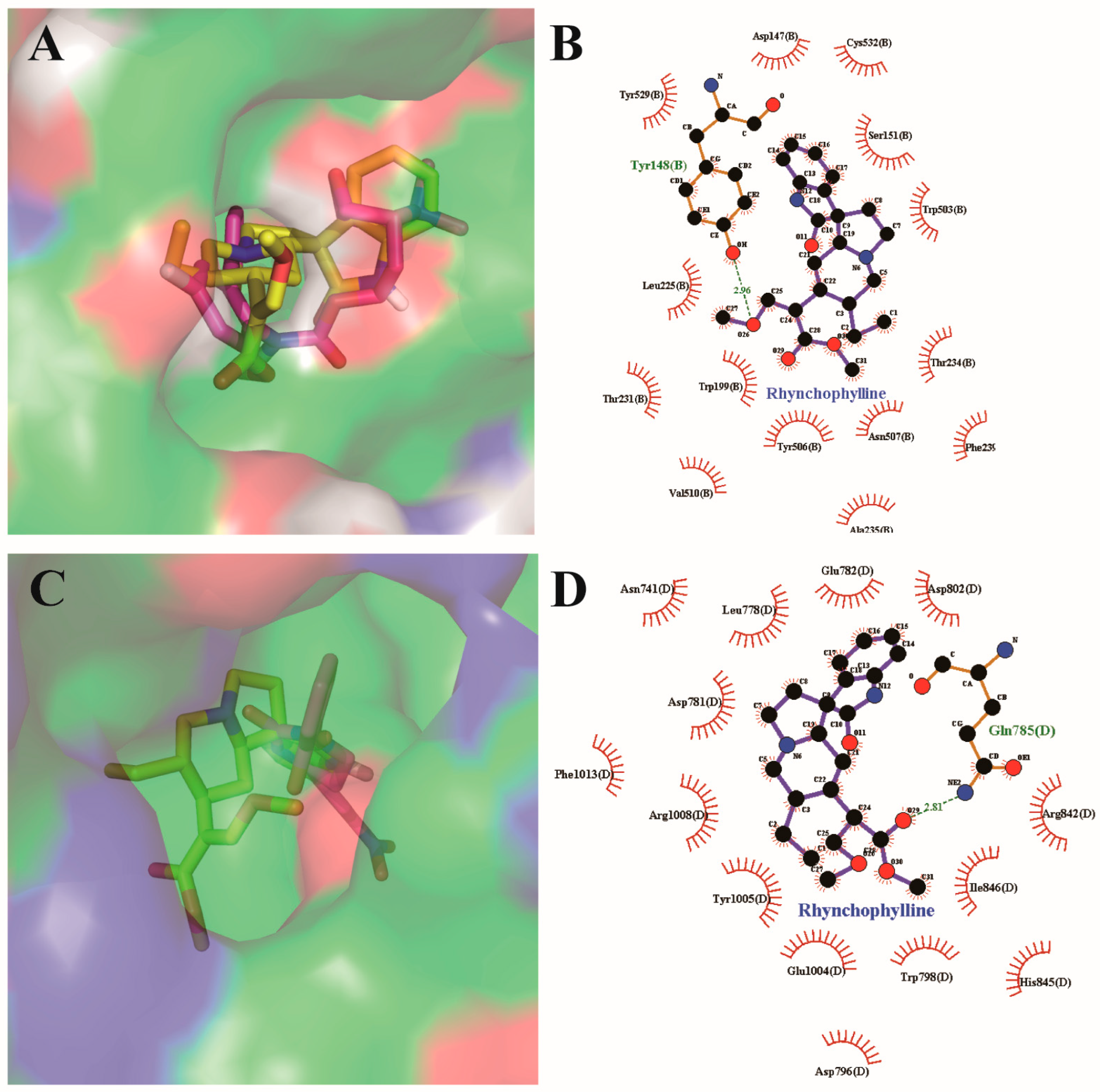
2.5. Resutls for Molecular Docking Analysis
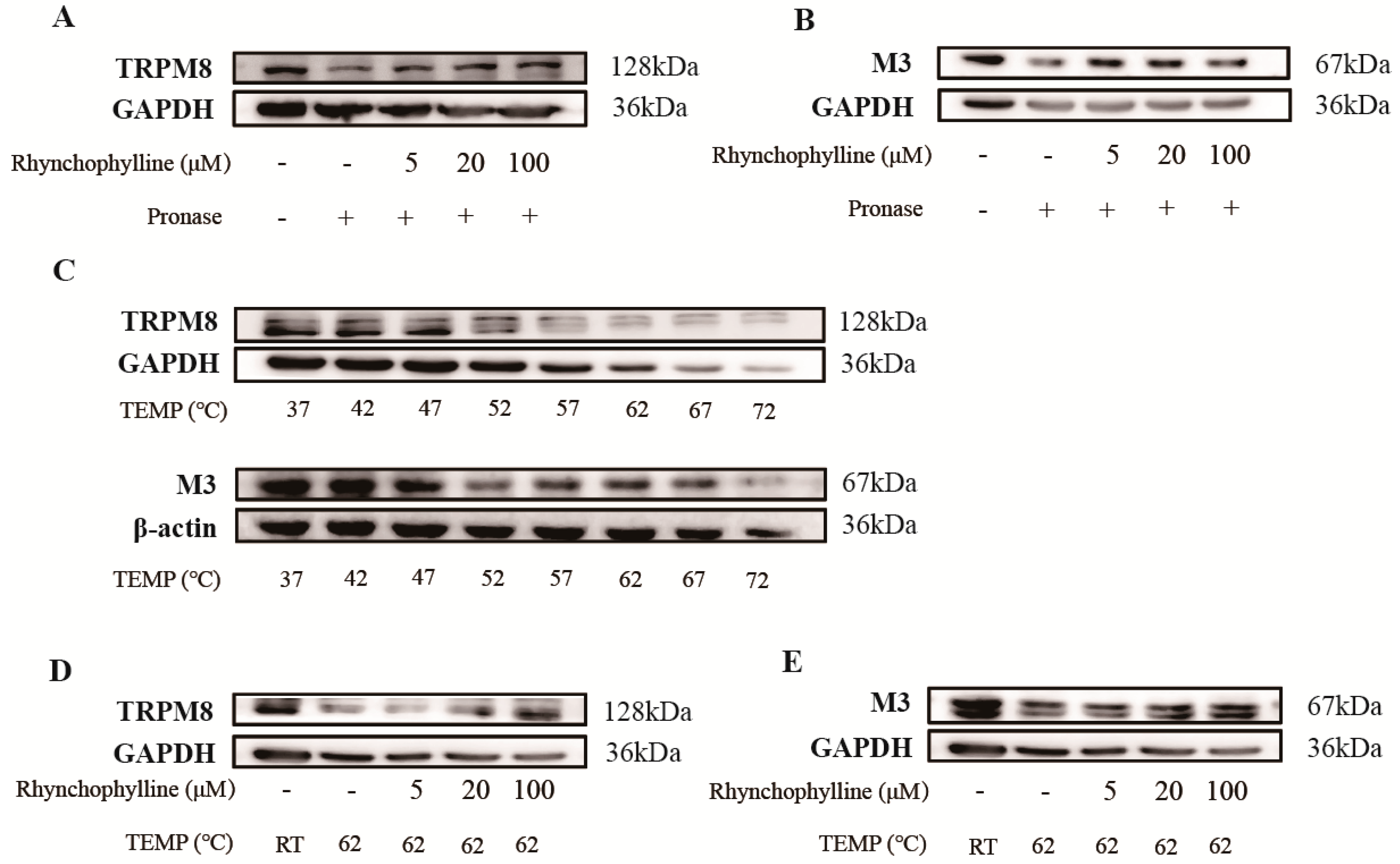
2.6. Verification of the Binding of Rhy to CHRM3 and TRPM8
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of Potential Targets of OAB
4.2. Prediction of Toxicity of Rhynchophylline
4.3. Collection and Screening of Rhynchophylline’s Targets
4.4. Acquisition of Disease and Drug Intersection Targets
4.5. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.6. Chemicals
4.7. Animals
4.8. Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stabilization Assay (DARTS)
4.9. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
4.10. Western Blotting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nambiar, A.K.; Arlandis, S.; Bø, K.; Cobussen-Boekhorst, H.; Costantini, E.; de Heide, M.; Farag, F.; Groen, J.; Karavitakis, M.; Lapitan, M.C.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Female Non-neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Part 1: Diagnostics, Overactive Bladder, Stress Urinary Incontinence, and Mixed Urinary Incontinence. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, W.; Van Rooyen, J.; Cundiff, G.; Abrams, P.; Herzog, A.; Corey, R.; Hunt, T.; Wein, A. Prevalence and burden of overactive bladder in the United States. World J. Urol. 2003, 20, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-S.; Yoo, T.K.; Liao, L.; Wang, J.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Liu, S.-P.; Chu, R.; Sumarsono, B. Prevalence of overactive bladder in China, Taiwan and South Korea: Results from a cross-sectional, population-based study. Low Urin. Tract Symptoms 2019, 11, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.J.; Gomelsky, A.; Souter, L.; Vasavada, S.P. Diagnosis and Treatment of Overactive Bladder (Non-Neurogenic) in Adults: AUA/SUFU Guideline Amendment 2019. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Ito, Y.; Nishijima, S.; Kadekawa, K.; Sugaya, K. Basic and clinical aspects of antimuscarinic agents used to treat overactive bladder. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 189, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, A.A.; Tailor, V.; Fernando, R.; Khullar, V.; Digesu, G.A. Posterior tibial nerve stimulation for overactive bladder-techniques and efficacy. Int. Urogynecology J. 2020, 31, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviana, A.; Jellison, F.; Kim, J.-H. Sacral neuromodulation for refractory overactive bladder, interstitial cystitis, and painful bladder syndrome. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 25, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.; Ellsworth, P. Emerging therapies for overactive bladder: Preclinical, phase I and phase II studies. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2024, 33, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-M.; Fu, D.-W.; Zang, L.-E.; Si, S.-B.; Song, B. Effects of Rhynchophylline on relaxation and contraction of the bladder detrusor in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Chou, D.; Bian, X.; Li, R.; Wang, M.; Zheng, C. Rhynchophylline ameliorates cerebral ischemia by improving the synaptic plasticity in a middle cerebral artery occlusion induced stroke model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 940, 175390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Ikarashi, Y. Ikarashi, Properties, Pharmacology, and Pharmacokinetics of Active Indole and Oxindole Alkaloids in Uncaria Hook. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 688670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Nie, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Cheng, J. Rhynchophylline Regulates Calcium Homeostasis by Antagonizing Ryanodine Receptor 2 Phosphorylation to Improve Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 882198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, J.; Lv, P.; Ge, H. Rhynchophylline attenuates migraine in trigeminal nucleus caudalis in nitroglycerin-induced rat model by inhibiting MAPK/NF-кB signaling. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 461, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, E.L.; Forner, S.; Bento, A.F.; Leite, D.F.P.; Dias, M.A.; Leal, P.C.; Koepp, J.; Calixto, J.B. TRPA1 receptor modulation attenuates bladder overactivity induced by spinal cord injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2011, 300, F1223–F1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokumacioglu, E.; Demiray, O.; Dokumacioglu, A.; Sahin, A.; Sen, T.M.; Cankaya, S. Measuring urinary 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine and malondialdehyde levels in women with overactive bladder. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2018, 59, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.-F.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Kuo, H.-C. Discriminating Different Bladder and Bladder Outlet Dysfunctions by Urinary Biomarkers in Women with Frequency-Urgency Syndrome. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luptak, J.; Kocmalova, M.; Franova, S.; Sutovsky, J.; Grendar, M.; Svihra, J.; Kliment, J.; Dusenka, R.; Sutovska, M. Involvement of calcium regulating ion channels in contractility of human isolated urinary bladder. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2018, 37, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zheng, J.-H.; Li, S. TCM network pharmacology: A new trend towards combining computational, experimental and clinical approaches. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, X.; Bai, H.; Ning, K. Network Pharmacology Databases for Traditional Chinese Medicine: Review and Assessment. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 1.30.1–1.30.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Kemmler, E.; Dunkel, M.; Preissner, R. ProTox 3.0: A webserver for the prediction of toxicity of chemicals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W513–W520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Lai, L.; Pei, J.; Li, H. PharmMapper 2017 update: A web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W356–W360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, M.J.; Roth, B.L.; Armbruster, B.N.; Ernsberger, P.; Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Relating protein pharmacology by ligand chemistry. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y.; Bai, L.; Tian, S.; Ma, Y.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Xue, M.; Zhou, X. Daidzein is the in vivo active compound of Puerariae Lobatae Radix water extract for muscarinic receptor-3 inhibition against overactive bladder. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 924251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xie, Y.; Xu, L.; Ye, F.; Xu, X.; Yang, W.; Yang, F.; Guo, J. Structures of a mammalian TRPM8 in closed state. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.-L.; Gulbahce, N.; Loscalzo, J. Network medicine: A network-based approach to human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Lin, M.; Chen, Y.; Jin, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y. Applications of Network Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1646905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogales, C.; Mamdouh, Z.M.; List, M.; Kiel, C.; Casas, A.I.; Schmidt, H.H. Network pharmacology: Curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J.-R.; Cai, Y.; Mitra, J.; Zhang, Z.D. HEDD: Human Enhancer Disease Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D113–D120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Knight, J.C. Knight, Priority index: Database of genetic targets in immune-mediated disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1358–D1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, X.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Zhu, F.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Y. Therapeutic target database update 2022: Facilitating drug discovery with enriched comparative data of targeted agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1398–D1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; I Furlong, L. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB, an Integrated Resource of Pharmacogenomic Knowledge. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.A.; Hamosh, A. What’s in a name? Issues to consider when naming Mendelian disorders. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1573–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleuren, W.W.; Alkema, W. Application of text mining in the biomedical domain. Methods 2015, 74, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.; Olorisade, B.K.; McGuinness, L.A.; Thomas, J.; Higgins, J.P.T. Data extraction methods for systematic review (semi)automation: A living review protocol. F1000Res 2020, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, D.; Zhang, C. Combined mining: Discovering informative knowledge in complex data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern 2011, 41, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sacchi, L.; Holmes, J.H. Progress in Biomedical Knowledge Discovery: A 25-year Retrospective. Yearb. Med. Inform. 2016, 25 (Suppl. S1), S117–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naulaerts, S.; Meysman, P.; Bittremieux, W.; Vu, T.N.; Berghe, W.V.; Goethals, B.; Laukens, K. A primer to frequent itemset mining for bioinformatics. Brief. Bioinform. 2015, 16, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siadaty, M.S.; Harrison, J.H., Jr. Multi-database mining. Clin. Lab Med. 2008, 28, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.Y.; Pazmino, S.; Qian, H.; Bergh, B.; SchreiweisStructured, B. Data Retrieval and Analysis of HL7 v2 Messages with Elasticsearch. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2024, 310, 1464–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Boyer, M.-P.; Dufour, P.; Belleau, F.; Ongaro-Carcy, R.; Plessis, C.; Périn, O.; Droit, A. Use of Elasticsearch-based business intelligence tools for integration and visualization of biological data. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24(6), bbad348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.R.; Moya, J.A.; Schwickerath, U. Anomaly Detection for the Centralised Elasticsearch Service at CERN. Front. Big Data 2021, 4, 718879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaroyan, A.; Sil, P.; Martin, O.C.; Samal, A. Leveraging developmental landscapes for model selection in Boolean gene regulatory networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24(3), bbad160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, E. Mathematical model of the cell signaling pathway based on the extended Boolean network model with a stochastic process. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomingdale, P.; Nguyen, V.A.; Niu, J.; Mager, D.E. Boolean network modeling in systems pharmacology. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2018, 45, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemedan, A.A.; Niarakis, A.; Schneider, R.; Ostaszewski, M. Boolean modelling as a logic-based dynamic approach in systems medicine. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 3161–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, N.; Twik, M.; Nativ, N.; Stelzer, G.; Bahir, I.; Stein, T.I.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. MalaCards: A Comprehensive Automatically-Mined Database of Human Diseases. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 47, 1.24.1–1.24.19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, N.; Twik, M.; Plaschkes, I.; Nudel, R.; Stein, T.I.; Levitt, J.; Gershoni, M.; Morrey, C.P.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. MalaCards: An amalgamated human disease compendium with diverse clinical and genetic annotation and structured search. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D877–D887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’mara-Eves, A.; Thomas, J.; McNaught, J.; Miwa, M.; Ananiadou, S. Using text mining for study identification in systematic reviews: A systematic review of current approaches. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xiang, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Qian, Q.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Chen, P.; et al. Changes in the expression and function of the PDE5 pathway in the obstructed urinary bladder. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 13181–13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, P.; Andersson, K. Muscarinic receptor antagonists for overactive bladder. BJU Int. 2007, 100, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.S. Muscarinic receptors in the bladder: From basic research to therapeutics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147 (Suppl. S2), S80–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinner, N.; Susset, J.; Gittelman, M.; Arguinzoniz, M.; Rekeda, L.; Haab, F. Efficacy, tolerability and safety of darifenacin, an M(3) selective receptor antagonist: An investigation of warning time in patients with OAB. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2006, 60, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinner, N.; Susset, J.; Arguinzoniz, M.; Rekeda, L.; Haab, F. Darifenacin: A muscarinic M3-selective receptor antagonist for the treatment of overactive bladder. Expert Opin. Pharmacother 2007, 8, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Gratzke, C.; Hedlund, P. The role of the transient receptor potential (TRP) superfamily of cation-selective channels in the management of the overactive bladder. BJU Int. 2010, 106, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Jin, M.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Im, Y.J.; Jung, H.J.; Han, S.W. Function of the Cold Receptor (TRPM8) Associated with Voiding Dysfunction in Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Rats. Int. Neurourol. J. 2012, 16, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, O.; Fujimori, Y.; Aizawa, N.; Hayashi, T.; Matsuzawa, A.; Kobayashi, J.-I.; Hirasawa, H.; Mutai, Y.; Tanada, F.; Igawa, Y. Efficacy of the combination of KPR-5714, a novel transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) antagonist, and β(3)-adrenoceptor agonist or anticholinergic agent on bladder dysfunction in rats with bladder overactivity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 899, 173995. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Malemud, C.J. Malemud, Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase: A Regulator of Cell Growth, Inflammation, Chondrocyte and Bone Cell Receptor-Mediated Gene Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Tian, H. Development of ERK1/2 inhibitors as a therapeutic strategy for tumour with MAPK upstream target mutations. J. Drug Target. 2020, 28, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulombe, P.; Meloche, S. Atypical mitogen-activated protein kinases: Structure, regulation and functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.C.; Vilela, M.; Juarez, J.E.; Blenis, J.; Danuser, G. ERK reinforces actin polymerization to power persistent edge protrusion during motility. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, H.; Gupta, M.; Vedula, S.R.K.; Lim, C.T.; Ladoux, B.; Sokabe, M. Quantifying Tensile Force and ERK Phosphorylation on Actin Stress Fibers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1487, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Mossa, A.H.; Flores, M.V.; Cammisotto, P.G.; Campeau, L. Succinate, increased in metabolic syndrome, activates GPR91 receptor signaling in urothelial cells. Cell Signal. 2017, 37, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, Ł.; Kulik-Rechberger, B.; Wróbel, A.; Rechberger, T. Overactive bladder--a new insight into the pathogenesis of its idiopathic form. Ginekol. Pol. 2012, 83, 844–848. [Google Scholar]
- Squire, J. Special Issue: The Actin—Myosin Interaction in Muscle: Background and Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guhathakurta, P.; Prochniewicz, E.; Thomas, D.D. Actin-Myosin Interaction: Structure, Function and Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Tie, Y.; Tong, X.; Cheng, M.; Wu, Y.; Xu, P.; Xue, M.; Xu, L.; Zhou, X. Multi-omics approaches revealed the therapeutic mechanisms of Suo-Quan-Wan for treating overactive bladder in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Seftel, A.; DiSanto, M.E. Blebbistain, a myosin II inhibitor, as a novel strategy to regulate detrusor contractility in a rat model of partial bladder outlet obstruction. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R. AlphaFold2 and its applications in the fields of biology and medicine. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tie, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Qiang, Y.; Cai’Li, G.; Xu, P.; Xue, M.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, X. A Dataset for Constructing the Network Pharmacology of Overactive Bladder and Its Application to Reveal the Potential Therapeutic Targets of Rhynchophylline. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101253
Tie Y, Liu J, Wu Y, Qiang Y, Cai’Li G, Xu P, Xue M, Xu L, Li X, Zhou X. A Dataset for Constructing the Network Pharmacology of Overactive Bladder and Its Application to Reveal the Potential Therapeutic Targets of Rhynchophylline. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101253
Chicago/Turabian StyleTie, Yan, Jihan Liu, Yushan Wu, Yining Qiang, Ge’Er Cai’Li, Pingxiang Xu, Ming Xue, Liping Xu, Xiaorong Li, and Xuelin Zhou. 2024. "A Dataset for Constructing the Network Pharmacology of Overactive Bladder and Its Application to Reveal the Potential Therapeutic Targets of Rhynchophylline" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101253
APA StyleTie, Y., Liu, J., Wu, Y., Qiang, Y., Cai’Li, G., Xu, P., Xue, M., Xu, L., Li, X., & Zhou, X. (2024). A Dataset for Constructing the Network Pharmacology of Overactive Bladder and Its Application to Reveal the Potential Therapeutic Targets of Rhynchophylline. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101253





